Effectiveness of Gutting Blue Whiting (Micromesistius poutassou, Risso, 1827), in Spanish Supermarkets as an Anisakidosis Safety Measure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample and Data Collection
2.2. Larvae Quantification and Identification
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baird, F.J.; Gasser, R.B.; Jabbar, A.; Lopata, A.L. Foodborne Anisakiasis and Allergy. Mol. Cell Probes 2014, 28, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Pierce, G.J.; Pascual, S.; González-Muñoz, M.; Mattiucci, S.; Mladineo, I.; Cipriani, P.; Bušelić, I.; Strachan, N.J.C. Assessing the Risk of an Emerging Zoonosis of Worldwide Concern: Anisakiasis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiucci, S.; Cipriani, P.; Webb, S.C.; Paoletti, M.; Marcer, F.; Bellisario, B.; Gibson, D.I.; Nascetti, G. Genetic and Morphological Approaches Distinguish the Three Sibling Species of the Anisakis Simplex Species Complex, with a Species Designation as Anisakis Berlandi n. Sp. for A. Simplex Sp. C (Nematoda: Anisakidae). J. Parasitol. 2014, 100, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.W.; Wootten, R. Anisakis and Anisakiasis. In Advances in Parasitology; Lumsden, W.H.R., Muller, R., Baker, J.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1978; Volume 16, pp. 93–163. [Google Scholar]
- Aibinu, I.E.; Smooker, P.M.; Lopata, A.L. Anisakis Nematodes in Fish and Shellfish- from Infection to Allergies. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, K.; Mehrdana, F. Effects of Anisakid Nematodes Anisakis Simplex (s.l.), Pseudoterranova Decipiens (s.l.) and Contracaecum Osculatum (s.l.) on Fish and Consumer Health. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2016, 4, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Amores, Y.; Clavijo-Frutos, E.; Salas-Casanova, C.; Alcain-Martínez, G. Direct Parasitologial Diagnosis of Infection with Hysterothylacium Aduncum in a Patient with Epigastralgia. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2015, 107, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kassai, T.; Cordero del Campillo, M.; Euzeby, J.; Gaafar, S.; Hiepe, T.; Himonas, C.A. Standardized Nomenclature of Animal Parasitic Diseases (SNOAPAD). Vet. Parasitol. 1988, 29, 299–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, S.; Butcher, A.R. First Report of Human Anisakidosis in Australia. Med. J. Aust. 2011, 194, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, K.; Nagasawa, K.; Ishikura, H.; Nakagawa, A.; Sato, N.; Kikuchi, K.; Ishikura, H. Female Worm Hysterothylacium Aduncum Excreted from Human: A Case Report. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Female-worm-Hysterothylacium-aduncum-excreted-from-Yagi-Nagasawa/2e4919615c9f5c11af1672f0843ec5344a7266db (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Audicana, M.T.; Kennedy, M.W. Anisakis Simplex: From Obscure Infectious Worm to Inducer of Immune Hypersensitivity. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 360–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audicana, L.; Audicana, M.T.; de Corres, L.F.; Kennedy, M.W. Cooking and Freezing May Not Protect against Allergenic Reactions to Ingested Anisakis Simplex Antigens in Humans. Vet. Record. 1997, 140, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiucci, S.; Fazii, P.; De Rosa, A.; Paoletti, M.; Megna, A.S.; Glielmo, A.; De Angelis, M.; Costa, A.; Meucci, C.; Calvaruso, V.; et al. Anisakiasis and Gastroallergic Reactions Associated with Anisakis Pegreffii Infection, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuizen, N.E. Anisakis—Immunology of a Foodborne Parasitosis. Parasite Immunol. 2016, 38, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraballo, L.; Coronado, S. Parasite Allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuya, S.; Hamano, H.; Izumi, S. Mackerel-Induced Urticaria and Anisakis. Lancet 1990, 335, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, F.; de las Heras, C.; Solas, M.T.; Tejada, M. Effect of the Mechanical Separation of Muscles on the Retention and Viability of Anisakis Larvae during the Production of Surimi. Ecol. Apl. 2013, 12, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Olivares, F.; González-Muñoz, M.; Carballeda-Sangiao, N.; Rodríguez-Mahillo, A.; Careche, M.; de Las Heras, C.; Navas, A.; Tejada, M. Removal of Anisakis Simplex Allergens from Infected Fish during the Washing Step of Surimi Production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2626–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godínez-González, C.; Roca-Geronès, X.; Cancino-Faure, B.; Montoliu, I.; Fisa, R. Quantitative SYBR Green QPCR Technique for the Detection of the Nematode Parasite Anisakis in Commercial Fish-Derived Food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 261, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, A.R.; Kiani, B.; Afshari, A.; Moghaddas, E.; Williams, M.; Shamsi, S. World-Wide Prevalence of Anisakis Larvae in Fish and Its Relationship to Human Allergic Anisakiasis: A Systematic Review. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3585–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.-Y.; Darwin Murrell, K.; Lymbery, A.J. Fish-Borne Parasitic Zoonoses: Status and Issues. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1233–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Evaluates Parasites in Fish. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/press/news/biohaz100414 (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Puente, P.; Anadón, A.M.; Rodero, M.; Romarís, F.; Ubeira, F.M.; Cuéllar, C. Anisakis Simplex: The High Prevalence in Madrid (Spain) and Its Relation with Fish Consumption. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 118, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uña-Gorospe, M.; Herrera-Mozo, I.; Canals, M.L.; Martí-Amengual, G.; Sanz-Gallen, P. Occupational Disease Due to Anisakis Simplex in Fish Handlers. Int. Marit. Health 2018, 69, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Aznar, F.J.; Montero, F.E.; Raga, J.A. Endoparasites of the Blue Whiting, Micromesistius Poutassou from North-West Spain. J. Helminthol. 2005, 79, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henríquez Santana, A.; Villafruela Cives, M. Anisakis: Pasado, presente y futuro. Med. Clin. 2009, 132, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Peñas, D.; Ramírez Ortiz, L.M.; del Rosal Palomeque, R.; López Rubio, F.; Fernández-Crehuet Navajas, R.; Miño Fugarolas, G. Anisakiasis en España: Una enfermedad creciente. Revisión. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 23, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roca-Geronès, X.; Montoliu, I.; Godínez-González, C.; Fisa, R.; Shamsi, S. Morphological and Genetic Characterization of Hysterothylacium Ward & Magath, 1917 (Nematoda: Raphidascarididae) Larvae in Horse Mackerel, Blue Whiting and Anchovy from Spanish Atlantic and Mediterranean Waters. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca-Geronès, X.; Segovia, M.; Godínez-González, C.; Fisa, R.; Montoliu, I. Anisakis and Hysterothylacium Species in Mediterranean and North-East Atlantic Fishes Commonly Consumed in Spain: Epidemiological, Molecular and Morphometric Discriminant Analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 325, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villafruela Cives, M.; Henríquez Santana, A. Anisakiasis. Rev. Española Enferm. Dig. 2010, 102, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pointin, F.; Payne, M.R. A Resolution to the Blue Whiting (Micromesistius Poutassou) Population Paradox? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, K.D.; Lotz, J.M.; Shostak, A.W. Parasitology Meets Ecology on Its Own Terms: Margolis et al. Revisited. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Fernández, D.; Rubio-Calvo, D.; Adroher, F.J.; Benítez, R. Molecular Epidemiology of Anisakis Spp. in Blue Whiting Micromesistius Poutassou in Eastern Waters of Spain, Western Mediterranean Sea. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 282, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podolska, M.; Pawlikowski, B.; Nadolna-Ałtyn, K.; Pawlak, J.; Komar-Szymczak, K.; Szostakowska, B. How Effective Is Freezing at Killing Anisakis Simplex, Pseudoterranova Krabbei, and P. Decipiens Larvae? An Experimental Evaluation of Time-Temperature Conditions. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Pierce, G.J.; Strachan, N.J.C.; Pascual, S.; González-Muñoz, M.; Levsen, A. Human Health, Legislative and Socioeconomic Issues Caused by the Fish-Borne Zoonotic Parasite Anisakis: Challenges in Risk Assessment. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsdottir, G.; Nesvadba, P.; Natale, C.D.; Careche, M.; Tryggvadottir, S.V.; Schubring, R.; Kroeger, M.; Heia, K.; Esaiassen, M.; Macagnano, A.; et al. Multisensor for Fish Quality Determination. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, S.; Suthar, J. A Revised Method of Examining Fish for Infection with Zoonotic Nematode Larvae. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 227, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercado, R.; Torres, P.; Muñoz, V.; Apt, W. Human Infection by Pseudoterranova Decipiens (Nematoda, Anisakidae) in Chile: Report of Seven Cases. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 2001, 96, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berland, B. Nematodes from Some Norwegian Marine Fishes. Sarsia 1961, 2, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, L.M. Keys to the Nematode Parasites of Vertebrates. Supplementary Volume|Parasites & Vectors|Full Text. Available online: https://parasitesandvectors.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1756-3305-3-9 (accessed on 17 November 2020).
- Moravec, F. Parasitic Nematodes of Freshwater Fishes of Europe; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; ISBN 978-0-7923-2172-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, F.B.; Luque, J.L. An Integrated Phylogenetic Analysis on Ascaridoid Nematodes (Anisakidae, Raphidascarididae), Including Further Description and Intraspecific Variations of Raphidascaris (Sprentascaris) Lanfrediae in Freshwater Fishes from Brazil. Parasitol. Int. 2017, 66, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debenedetti, Á.L.; Madrid, E.; Trelis, M.; Codes, F.J.; Gil-Gómez, F.; Sáez-Durán, S.; Fuentes, M.V. Prevalence and Risk of Anisakid Larvae in Fresh Fish Frequently Consumed in Spain: An Overview. Fishes 2019, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre Molina, R.; Pérez Aparicio, J.; Hernández Bienes, M.; Jurado Pérez, R.; Martínez Ruso, A.; Morales Franco, E. Anisakiasis in fresh fish sold in the north of Córdoba. Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 2000, 74, 517–526. [Google Scholar]
- Madrid, E.; Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Fuentes, M.V. Risk Analysis of Human Anisakidosis through the Consumption of the Blue Whiting, Micromesistius Poutassou, Sold at Spanish Supermarkets. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A.; Martín-Sánchez, J.; Reyes-Muelas, E.; Adroher, F.J. Larval Anisakids Parasitizing the Blue Whiting, Micromesistius Poutassou, from Motril Bay in the Mediterranean Region of Southern Spain. J. Helminthol. 2000, 74, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Sánchez, J.; Artacho-Reinoso, M.E.; Díaz-Gavilán, M.; Valero-López, A. Structure of Anisakis Simplex s.l. Populations in a Region Sympatric for A. Pegreffii and A. Simplex s.s. Absence of Reproductive Isolation between Both Species. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2005, 141, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horbowy, J.; Podolska, M.; Nadolna-Ałtyn, K. Increasing Occurrence of Anisakid Nematodes in the Liver of Cod (Gadus Morhua) from the Baltic Sea: Does Infection Affect the Condition and Mortality of Fish? Fish. Res. 2016, 179, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Kania, P.W.; Mehrdana, F.; Marana, M.H.; Buchmann, K. Contracaecum Osculatum and Other Anisakid Nematodes in Grey Seals and Cod in the Baltic Sea: Molecular and Ecological Links. J. Helminthol. 2018, 92, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørndrup, S.; Buchmann, K. Carbohydrate Localization on Gyrodactylus Salaris and G. derjavini and Corresponding Carbohydrate Binding Capacity of Their Hosts Salmo Salar and S. trutta. J. Helminthol. 2005, 79, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, S.; Steller, E.; Chen, Y. New and Known Zoonotic Nematode Larvae within Selected Fish Species from Queensland Waters in Australia. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 272, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llarena-Reino, M.; González, Á.F.; Vello, C.; Outeiriño, L.; Pascual, S. The Accuracy of Visual Inspection for Preventing Risk of Anisakis Spp. Infection in Unprocessed Fish. Food Control 2012, 23, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llarena-Reino, M.; Piñeiro, C.; Antonio, J.; Outeriño, L.; Vello, C.; González, Á.F.; Pascual, S. Optimization of the Pepsin Digestion Method for Anisakids Inspection in the Fishing Industry. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 191, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abollo, E.; Gestal, C.; Pascual, S. Anisakis Infestation in Marine Fish and Cephalopods from Galician Waters: An Updated Perspective. Parasitol. Res. 2001, 87, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strømnes, E.; Andersen, K. “Spring Rise” of Whaleworm (Anisakis Simplex; Nematoda, Ascaridoidea) Third-Stage Larvae in Some Fish Species from Norwegian Waters. Parasitol. Res. 2000, 86, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootten, R.; Waddell, I.F. Studies on the Biology of Larval Nematodes from the Musculature of Cod and Whiting in Scottish Waters. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1977, 37, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A.; Terrados, S.; Díaz, V.; Reguera, V.; Lozano, J. Determination of IgE in the Serum of Patients with Allergic Reactions to Four Species of Fish-Parasite Anisakids. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2003, 13, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Mattiucci, S.; Cipriani, P.; Levsen, A.; Paoletti, M.; Nascetti, G. Molecular Epidemiology of Anisakis and Anisakiasis: An Ecological and Evolutionary Road Map. Adv. Parasitol. 2018, 99, 93–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipriani, P.; Acerra, V.; Bellisario, B.; Sbaraglia, G.L.; Cheleschi, R.; Nascetti, G.; Mattiucci, S. Larval Migration of the Zoonotic Parasite Anisakis Pegreffii (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in European Anchovy, Engraulis Encrasicolus: Implications to Seafood Safety. Food Control 2016, 59, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, H. Nematode Larvae in Fish on the German Market 20 Years of Consumer Related Research. Archiv. Lebensmittelhygiene 2008, 59, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, G.; Meloni, M.; Merella, P.; Sardu, F.; Madeddu, S.; Marrosu, R.; Petza, F.; Salati, F. Prevalence of Anisakis Spp. and Hysterothylacium Spp. Larvae in Teleosts and Cephalopods Sampled from Waters off Sardinia. J. Food Prot. 2011, 74, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomba, M.; Cipriani, P.; Giulietti, L.; Levsen, A.; Nascetti, G.; Mattiucci, S. Differences in Gene Expression Profiles of Seven Target Proteins in Third-Stage Larvae of Anisakis Simplex (Sensu Stricto) by Sites of Infection in Blue Whiting (Micromesistius Poutassou). Genes 2020, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łopieńska-Biernat, E.; Stryiński, R.; Polak, I.; Pawlikowski, B.; Pawlak, J.; Podolska, M. Effect of Freezing on the Metabolic Status of L3 Larvae of Anisakis Simplex ss. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 82, 104312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łopieńska-Biernat, E.; Stryiński, R.; Dmitryjuk, M.; Wasilewska, B. Infective Larvae of Anisakis Simplex (Nematoda) Accumulate Trehalose and Glycogen in Response to Starvation and Temperature Stress. Biol. Open 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, P.; Palomba, M.; Giulietti, L.; Bao, M.; Mattiucci, S.; Levsen, A. Anisakis Simplex (s.s.) Larvae (Nematoda: Anisakidae) Hidden in the Mantle of European Flying Squid Todarodes Sagittatus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in NE Atlantic Ocean: Food Safety Implications. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 339, 109021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.F.; Gracia, J.; Miniño, I.; Romón, J.; Larsson, C.; Maroto, J.; Regueira, M.; Pascual, S. Approach to Reduce the Zoonotic Parasite Load in Fish Stocks: When Science Meets Technology. Fish. Res. 2018, 202, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
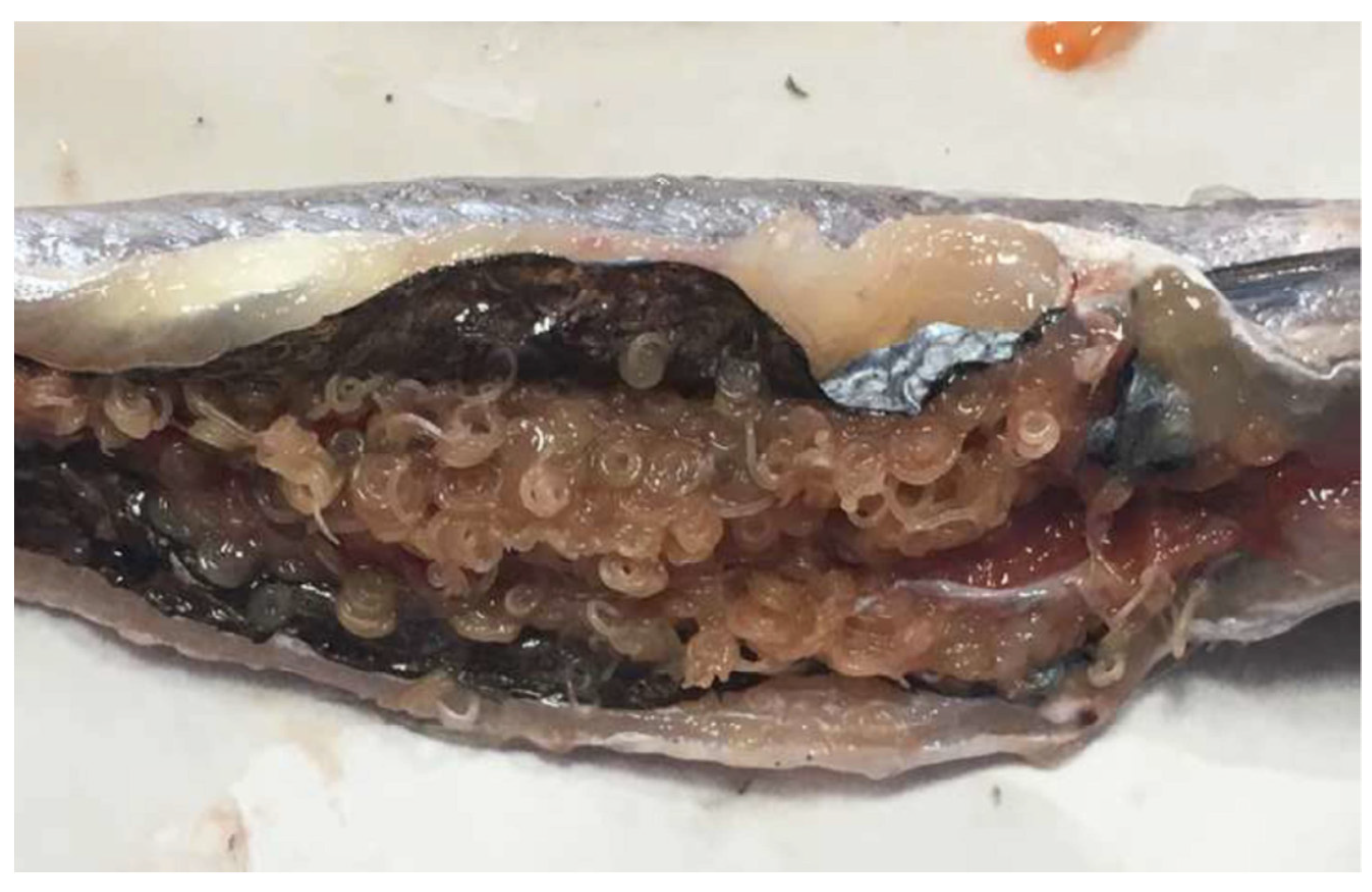
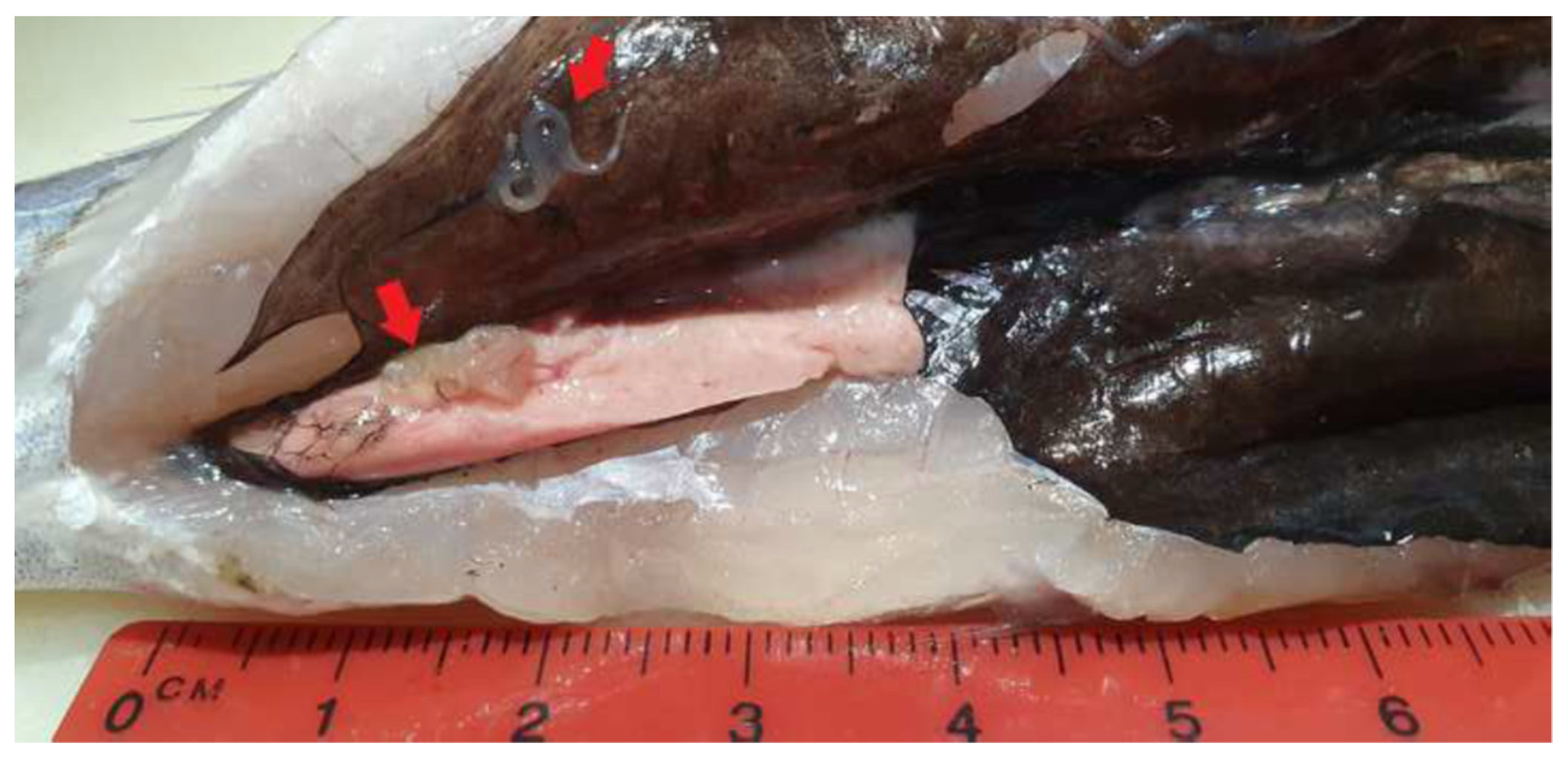
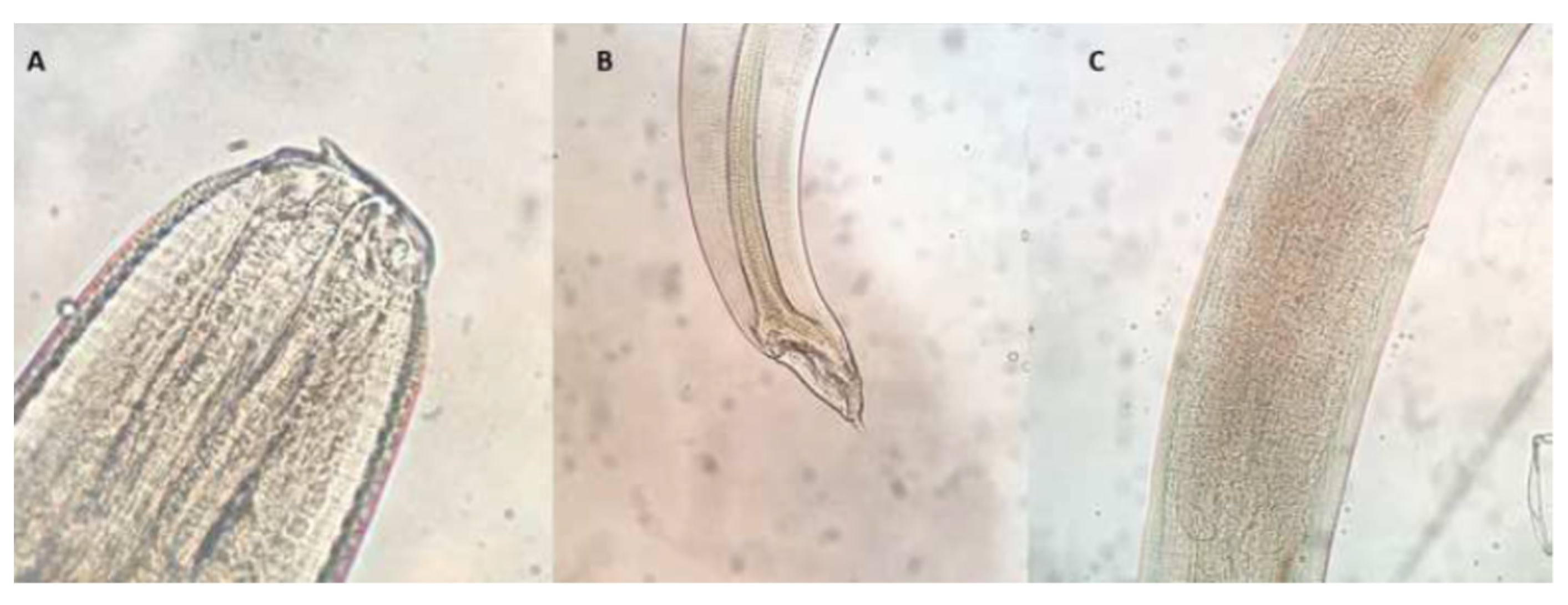
| Prevalence of Ascaridoid Larvae in Muscle | Total Prevalence of Ascaridoid Larvae | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Categories and Subgroups | Number of Fish Examined | Mean Length of Fish Examined ±SD (cm) | Weigh of fish Examined ±SD (g) | Mean Abundance in Fishes without Massive Infection (IC 95%) | Prevalence (%) | χ2 (p-Value) | Mean Abundance in Fishes without Massive Infection (IC 95%) | Prevalence (%) | χ2 (p-Value) | |
| Ungutted fish | <24 h since purchase | 119 | 20.9 ± 2.1 | 54.3 ± 13.4 | 0.1 (0.0, 0.2) | 21 | 5.9 (<0.05) * | 1 (0.7, 1.3) | 52.9 | 3.1 (ns) |
| 24 h since purchase | 81 | 22.3 ± 2.6 | 64.9 ± 21.6 | 0.2 (0.0, 0.4) | 40.7 | 1.7 (0.6, 2.8) | 65.4 | |||
| Gutted fish | <24 h since purchase | 103 | 21.6 ± 2.3 | 46.3 ± 12.8 | 0.9 (0.3, 1.4) | 18.4 | 1.5 (ns) | 1 (0.4, 1.6) | 23.3 | 1.1 (ns) |
| 24 h since purchase | 17 | 23.2 ± 2.5 | 56.7 ± 24.0 | 1.5 (−1.3, 4.4) | 35.3 | 2.2 (−1.3, 5.8) | 35.3 | |||
| Overall | 320 | 21.5 ± 2.1 | 48.9 ± 17.3 | 0.1 (0.1, 0.2) | 25.9 | 0.3 (0.2, 0.4) | 45.6 | |||
| Standard Length (cm) (Mean ± SD) | p- Value | Weight (g) (Mean ± SD) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infected fish | 22.5 ± 2.7 | <0.05 * | 65.2 ± 20.3 | <0.05 * |
| Non-infected fish | 20.3 ± 1.0 | 49.5 ± 7.4 | ||
| Massive infection | 24.7 ± 1.8 | <0.05 * | 80.7 ± 16.0 | <0.05 * |
| No massive infection | 20.5 ± 1.7 | 51.2 ± 11.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahuir-Baraja, A.E.; Llobat, L.; Garijo, M.M. Effectiveness of Gutting Blue Whiting (Micromesistius poutassou, Risso, 1827), in Spanish Supermarkets as an Anisakidosis Safety Measure. Foods 2021, 10, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040862
Ahuir-Baraja AE, Llobat L, Garijo MM. Effectiveness of Gutting Blue Whiting (Micromesistius poutassou, Risso, 1827), in Spanish Supermarkets as an Anisakidosis Safety Measure. Foods. 2021; 10(4):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040862
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhuir-Baraja, Ana Elena, Lola Llobat, and Maria Magdalena Garijo. 2021. "Effectiveness of Gutting Blue Whiting (Micromesistius poutassou, Risso, 1827), in Spanish Supermarkets as an Anisakidosis Safety Measure" Foods 10, no. 4: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040862
APA StyleAhuir-Baraja, A. E., Llobat, L., & Garijo, M. M. (2021). Effectiveness of Gutting Blue Whiting (Micromesistius poutassou, Risso, 1827), in Spanish Supermarkets as an Anisakidosis Safety Measure. Foods, 10(4), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040862








