Comparison of Morphological and Physicochemical Properties of a Floury Rice Variety upon Pre-Harvest Sprouting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rice Material and Experimental Design
2.2. Starch Isolation
2.3. Color Measurement
2.4. Granule Size Analysis
2.5. Damaged Starch Quantification
2.6. Total Amylose and Protein Content
2.7. Starch Pasting Properties
2.8. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.10. Amylopectin Branch Chain Length Distribution
2.11. X-ray Diffraction and Crystallinity Analysis
2.12. Fourier Transform Infrared Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Color Measurement
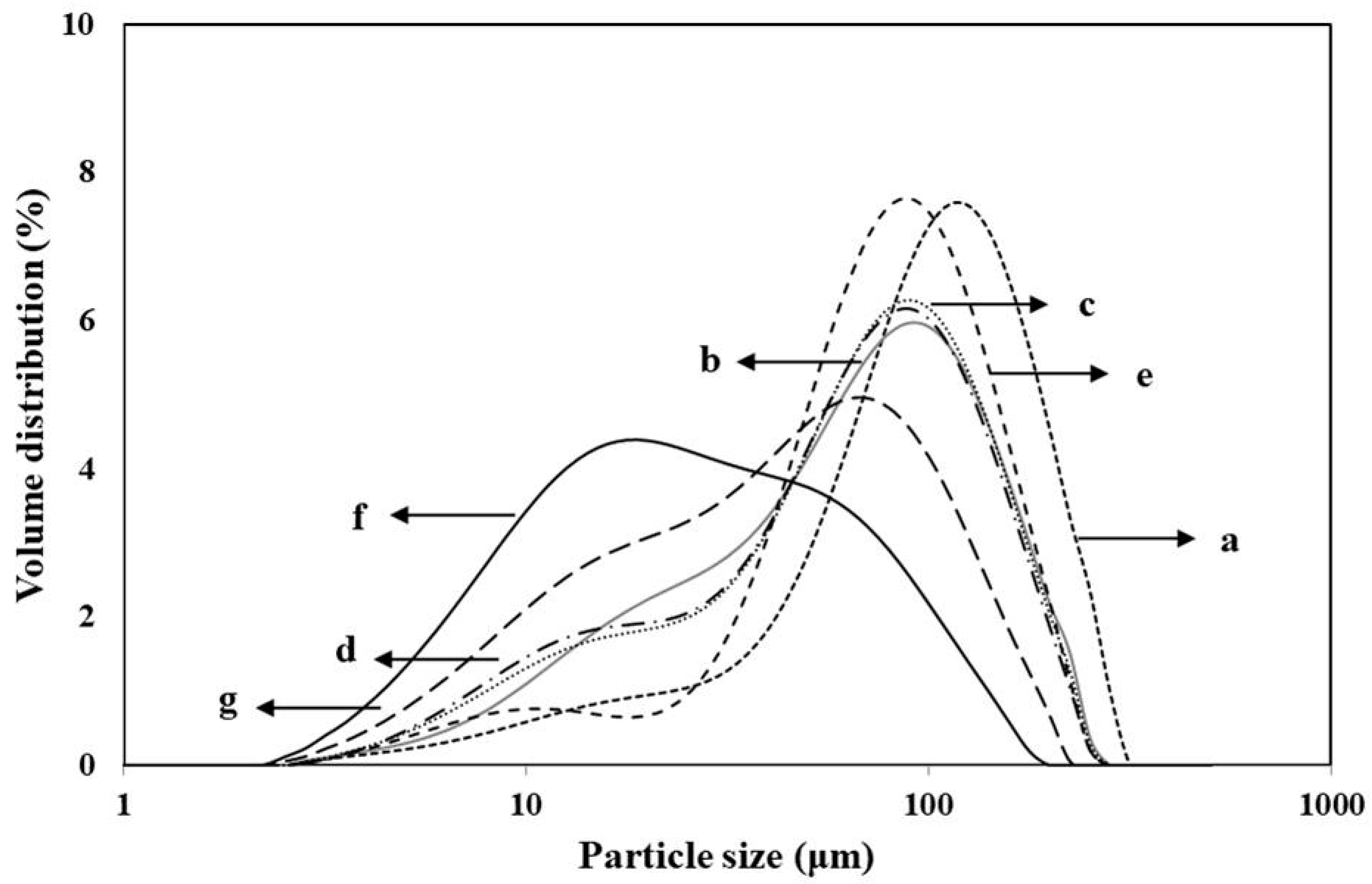
3.2. Granule Size Distribution
3.3. Damaged Starch Quantification
3.4. Total Amylose and Protein Content
3.5. Pasting Properties
3.6. Thermal Properties
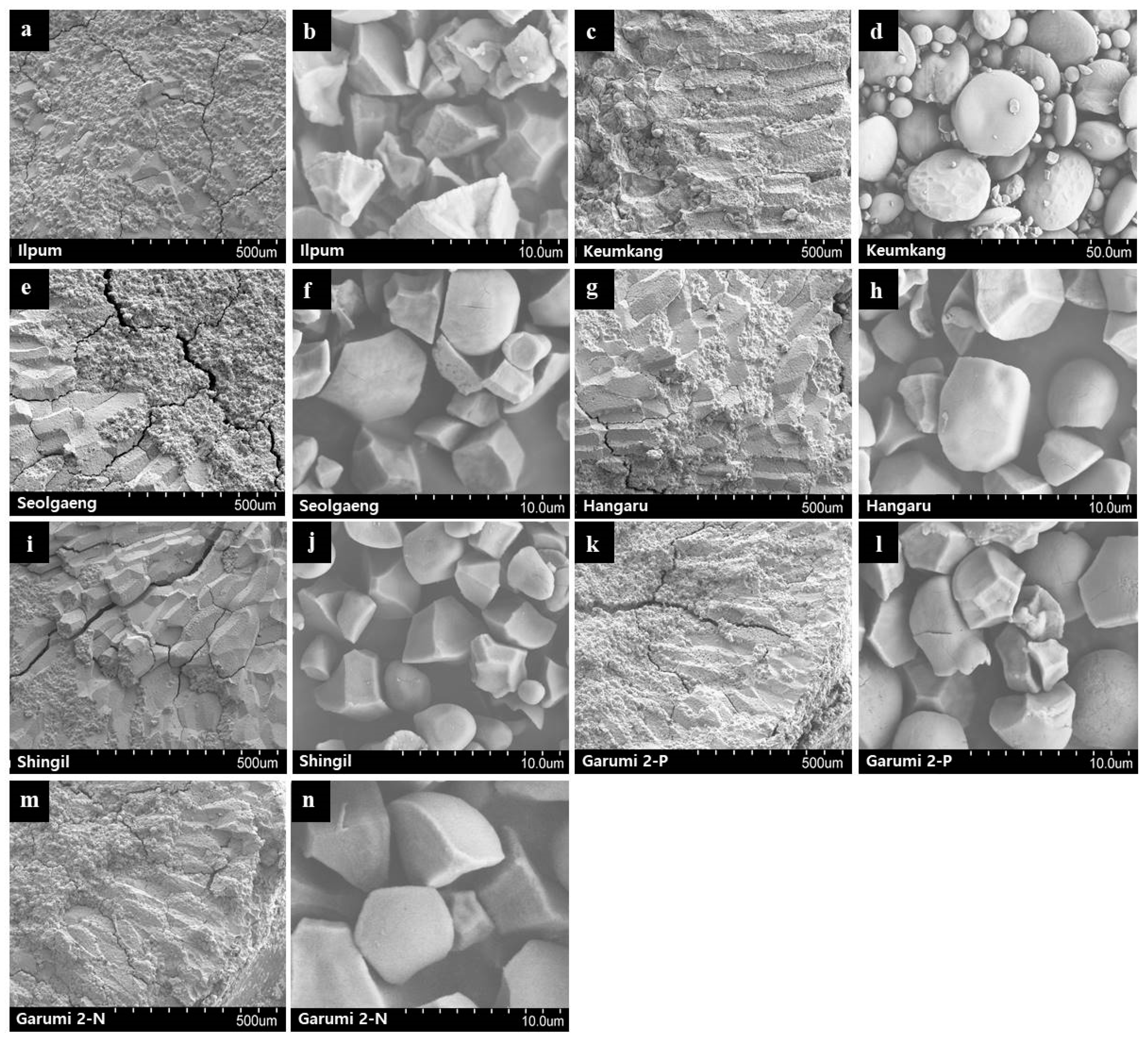
3.7. Morphological Studies by SEM
3.8. Amylopectin Branch Chain Length Distribution
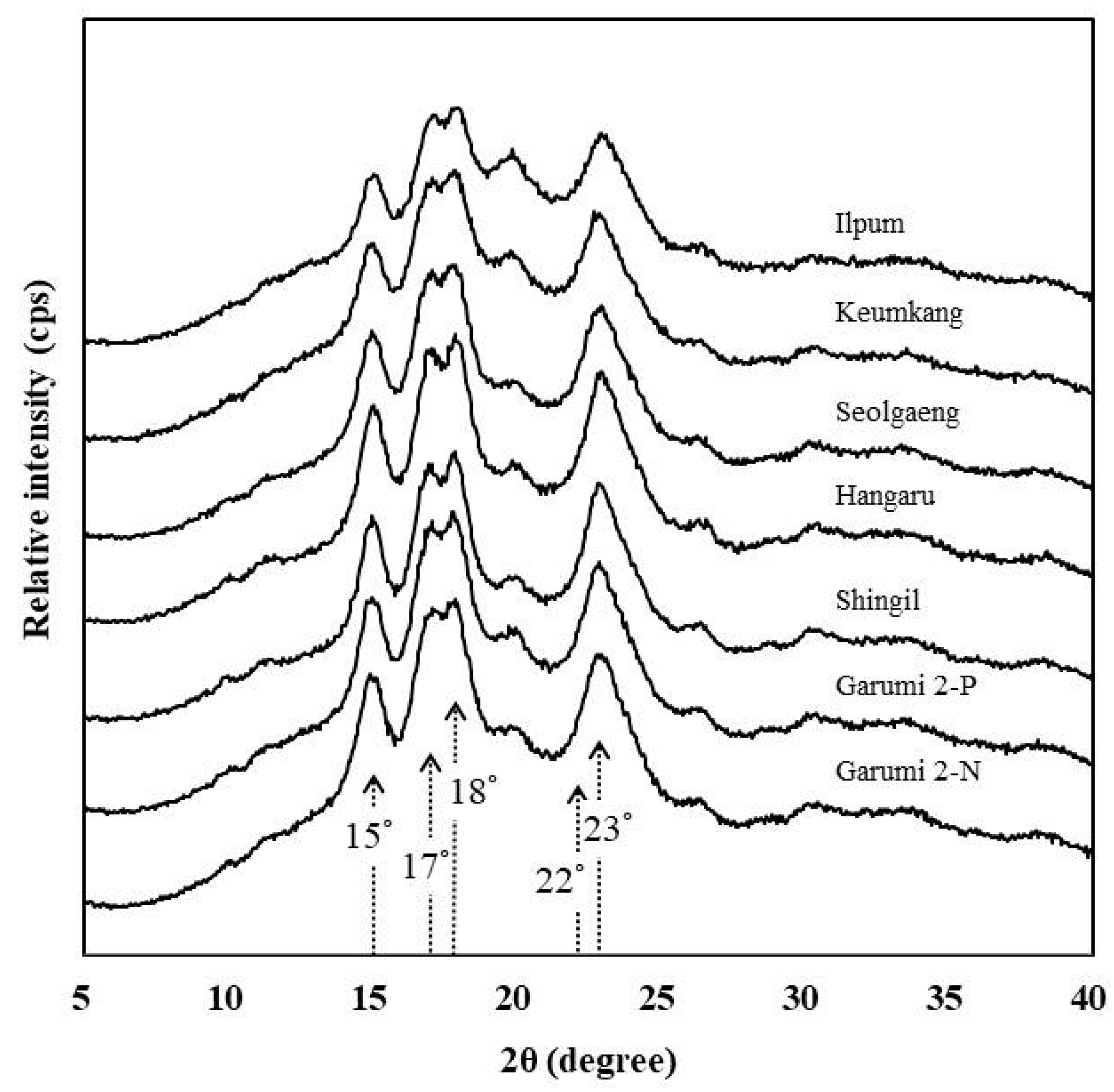
3.9. X-ray Diffraction and Crystallinity
3.10. FT-IR Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- KOSTAT. The 2019 Results of Grain Consumption Survey. Available online: http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/kor_nw/1/4/8/index.board (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Choi, S.Y.; Shin, M.S. Properties of rice flours prepared from domestic high amylose rices. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 41, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.; Park, H.; Choi, H.; Cho, D.; Lee, K.H.; Han, S. Physicochemical properties of rice flour of different cultivars using wet and dry milling processes. Korean J. Crop Sci. 2017, 62, 184–192. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, P.Y.; Yeh, A.I. Effect of soaking on wet-milling of rice. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 35, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeung, J.U. Don’t Soak ‘Garumi 2 Rice’ in Water. Available online: http://www.korea.kr/news/pressReleaseView.do?newsId=156347637&call_from=naver_news (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Hong, H.C.; Moon, H.P.; Choi, H.C.; Hwang, H.G.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, H.Y.; Yea, J.D.; Shin, Y.S.; Kang, K.H.; Choi, Y.H.; et al. A Lodging Tolerant, opaque rice cultivar ‘Seolgaeng’. Korean J. Breed. Sci. 2011, 43, 532–537. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, J.E.; Yoon, M.R.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Ko, S.h.; Tai, T.H.; Won, Y.J. Morphological and starch characteristics of the Japonica rice mutant variety Seolgaeng for dry-milled flour. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, Y.J.; Ahn, E.K.; Jeong, E.G.; Chang, J.K.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, K.H.; Hyun, U.J.; Cho, Y.C.; Oh, S.K.; Yoon, M.R.; et al. An Opaque endosperm rice cultivar, ‘Hangaru’, suitable for exclusive dry-milling rice flour production. Korean J. Breed. Sci. 2020, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.C.; Ahn, S.N.; Hong, H.C.; Kim, Y.K.; Hwang, H.G.; Kim, T.Y. New mutants of specialty rice induced from Ilpumbyeo, a high-quality rice cultivar, by MNU (N-methyl-N-nitrosourea) treatment on fertilized egg cells. Korean J. Breed. 2006, 38, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.E.; No, J.H.; Shin, M.S. Physicochemical properties of resistant starch prepared from Shingil rice starch. Korean J. Food Cookery Sci. 2018, 34, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, H.; Matsusaka, H.; Kumamaru, T. Use of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea treatment of fertilized egg cells for saturation mutagenesis of rice. Breed. Sci. 2010, 60, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoshikawa, K. Morphogenesis of endosperm tissue in rice. JARQ 1973, 7, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ryoo, N.; Yu, C.; Park, C.S.; Baik, M.Y.; Park, I.M.; Cho, M.H.; Bhoo, S.H.; An, G.; Hahn, T.R.; Jeon, J.S. Knockout of a starch synthase gene OsSSIIIa/Flo5 causes white-core floury endosperm in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rural Development Administration. The Information of Waxy Rice Cultivars. Available online: http://www.nongsaro.go.kr (accessed on 30 March 2019).
- Yamamoto, A.; Shirakawa, K. Annealing of long-term stored rice grains improves gelatinization properties. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochan, A.; Bieganowski, A.; Ryzak, M.; Dobrowolski, R.; Bartmiński, P. Comparison of soil texture determined by two dispersion units of Mastersizer 2000. Int. Agrophys. 2012, 26, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.J.; Atwell, W.A. Starches; Eagan Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1999; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.J. Rice quality grading system using automated image analysis. Korean J. Crop. Sci. 2004, 49, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Donovan, J.W.; Lorenz, K.; Kulp, K. Differential scanning calorimetry of heat-moisture. Cereal Chem. 1983, 60, 381–387. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; Shao, K.; Gu, M.; Liu, Q. Toward underlying reasons for rice starches having low viscosity and high amylose: Physiochemical and structural characteristics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lee, L.F.; McPherson, A.E.; Wong, K.S.; Radosavljevic, M.; Kasemsuwan, T. Effects of amylopectin branch chain length and amylose content on the gelatinization and pasting properties of starch. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Effects of modification sequence on structures and properties of hydroxypropylated and crosslinked waxy maize starch. Starch/Stärke 2000, 52, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Shin, J.H.; Ahn, D.J.; Kim, S.J. Changes in amylopectin structure and pasting properties of starch as affected by different transplanting dates in rice. Korean J. Crop. Sci. 2016, 61, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sevenou, O.; Hill, S.E.; Farhat, I.A.; Mitchell, J.R. Organisation of the external region of the starch granule as determined by infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2002, 31, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S. Quality Characteristics of Sponge Cakes Prepared from Rice Flours with Different Amylose Contents. Ph.D. Thesis, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, O.J.; Jung, H.N.; Shim, K.H. Physicochemical Properties of Powdered, Soft and Hard Type Rice Flour by Different Milling Methods. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2015, 22, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallick, J.V.; Kelly, V.J. Gelatinization and pasting characteristics of rice varieties as related to cooking behaviour. Cereal Chem. 1992, 36, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Cagampang, G.B.; Perez, C.M.; Juliano, B.O. A gel consistency test for eating quality of rice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1973, 24, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, A.D.; Stevens, D.J. Starch damage. Adv. Cereal Sci. Technol. 1985, 7, 321–349. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, F.; Luh, B.S. Rice snack foods. In Rice; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1991; pp. 644–668. [Google Scholar]
- Juliano, B.O.; Perez, C.M.; Alyoshin, E.P.; Romanov, V.B.; Bean, M.M.; Nishita, K.D.; Blakeney, A.B.; Welsh, L.A.; Delgado, L.L.; El Bayâ, A.W.; et al. Cooperative test on amylography of milled-rice flour for pasting viscosity and starch gelatinization temperature. Starch/Stärke 1985, 37, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Nakazato, T.; Kosegawa, T. Cooking quality of rice flour. Nippon Shokuhin Kogyo Gakkaishi 1971, 18, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.S.; Oh, M.S. Effect of Cooking with Pressure cooker and particle size of rice flour on quality characteristics of Packsulgi. Korean J. Food Cookery Sci. 1992, 8, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Zeleznak, K.J.; Hoseney, R.C. The role of water in the retrogradation of wheat starch gels and bread crumb. Cereal Chem. 1986, 63, 407–411. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, M.R.; Lee, J.S.; Kwak, J.; Ko, S.; Lee, J.H.; Chun, J.B.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, W.H. Comparative analysis on quality and bread-making properties by particle size of dry-milled rice flours of rice varieties. Korean J. Int. Agric. 2016, 28, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Kang, K.J.; Kim, S.K. Relationship between hot water solubles of rice and texture of cooked rice. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 1991, 23, 498–502. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.I.; Kim, K.; Shin, J.C.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, M.H.; Oh, Y.J. Effects of ripening temperature on quality appearance and chemical quality characteristics of rice grain. RDA J. Agric. Sci. 1996, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Juliano, B.O. In Processing of the Workshop on Chemical Aspects of Rice Quality; IRRI: Los Banos, Philippines, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, B.D.; Stermer, R.A. Rice; Houston, D.F., Ed.; The American Association of Cereal Chemists, Inc.: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, M.R. Comparative study of the physicochemical properties of rice endosperm components expressing sugary-2 mutant in different genetic backgrounds. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2009, 52, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Oh, S.G.; Lee, D.H.; Baik, H.W.; Chung, H.J. Effect of germination on the structures and physicochemical properties of starches from brown rice, oat, sorghum, and millet. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Chen, H.; Yang, N.; Wang, J.; Duan, X.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Effect of germination time on physicochemical properties of brown rice flour and starch from different rice cultivars. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 58, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Qian, Z.; Wei, H.; Guo, B.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, H.; Huo, Z. The effects of field pre-harvest sprouting on the morphological structure and physicochemical properties of rice (Oryza sativa L.) starch. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayabe, S.; Kasai, M.; Ohishi, K.; Hatae, K. Textural properties and structures of starches from indica and japonica rice with similar amylose content. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2009, 15, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, G. Physicochemical properties of vitreous and floury endosperm flours in maize. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.Y.; Mok, C.K.; Lee, C.H. Comparison of differential scanning calorimetry with enzymatic method for the determination of gelatinization degree of corn starch. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 1993, 25, 400–403. [Google Scholar]
- Hanashiro, I.; Abe, J.I.; Hizukuri, S. A periodic distribution of the chain length of amylopectin as revealed by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 283, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Shin, J.; Kim, S.; Kwon, T.; Kim, J. Influence of different transplanting dates on amylopectin branch-chain-length and pasting properties of rice flour varieties. Korean J. Crop. Sci. 2018, 63, 210–218. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.I. Study on Physicochemical Characteristics and Assessment of Specialty Rice Cultivar ‘Seonong17, Keunnunjami’. Ph.D. Thesis, Kyungbook University, Daegu, Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Imberty, A.; Buléon, A.; Tran, V.; Péerez, S. Recent advances in knowledge of starch structure. Starch/Stärke 1991, 43, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, B.; Huang, Q.; Lu, H. Research progress of determination crystallinity of starch granular by X-ray diffraction. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2010, 1, 432–435. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Choi, S.J.; Shin, S.I.; Sohn, M.R.; Lee, C.J.; Kim, Y.; Cho, W.I.; Moon, T.W. Resistant glutarate starch from adlay: Preparation and properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, J.F.; Koniarova, D.; Reis, R.L. Thermal properties of thermoplastic starch/synthetic polymer blends with potential biomedical applicability. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variety | Amylose Content (%) | Protein Content (%) | Damaged Starch (%) | Color Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | ΔE | ||||
| Ilpum | 19.5 ± 1.06 b | 7.8 ± 0.12 c | 8.1 ± 0.37 b | 94.61 ± 0.04 e | −0.76 ± 0.01 g | 6.50 ± 0.01 b | 8.00 ± 0.02 b |
| Keumkang ** | 22.3 ± 1.55 a | 12.5 ± 0.45 a | 9.5 ± 0.37 a | 92.75 ± 0.16 f | 0.61 ± 0.03 a | 8.48 ± 0.17 a | 10.48 ± 0.21 a |
| Seolgaeng | 17.3 ± 0.08 b | 7.7 ± 0.53 cd | 5.2 ± 0.16 d | 95.94 ± 0.02 c | −0.17 ± 0.01 f | 4.48 ± 0.02 c | 5.70 ± 0.01 c |
| Hangaru | 17.6 ± 0.69 b | 8.0 ± 0.16 bc | 5.7 ± 0.16 c | 95.94 ± 0.14 c | 0.06 ± 0.01 d | 3.79 ± 0.02 e | 5.02 ± 0.01 d |
| Shingil | 22.2 ± 1.55 a | 8.2 ± 0.24 b | 5.1 ± 0.24 d | 95.40 ± 0.18 d | 0.00 ± 0.02 e | 4.14 ± 0.11 d | 5.48 ± 0.16 c |
| Garumi 2-P | 18.8 ± 0.16 b | 7.3 ± 0.37 de | 5.0 ± 0.08 d | 97.39 ± 0.17 a | 0.28 ± 0.01 b | 1.66 ± 0.06 g | 2.87 ± 0.04 f |
| Garumi 2-N | 19.4 ± 0.91 b | 7.0 ± 0.16 e | 4.4 ± 0.00 e | 96.65 ± 0.25 b | 0.18 ± 0.01 c | 2.82 ± 0.05 f | 3.98 ± 0.06 e |
| Variety | Pasting Time (min) | Pasting Temp (°C) | Viscosity (cP) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV | HPV | CPV | BD | SB | |||
| Ilpum | 2.9 ± 0.03 e | 72.6 ± 0.40 e | 2765 ± 35.12 b | 2190 ± 17.21 a | 3274 ± 28.58 a | 575 ± 25.35 d | 508 ± 17.52 c |
| Keumkang * | 4.4 ± 0.07 b | 90.3 ± 0.73 b | 1167 ± 33.73 d | 898 ± 22.84 e | 1768 ± 45.70 e | 269 ± 11.78 e | 601 ± 20.61 b |
| Seolgaeng | 4.0 ± 0.03 c | 84.9 ± 0.38 c | 2374 ± 12.66 c | 1534 ± 41.04 c | 2652 ± 44.84 c | 840 ± 30.27 b | 277 ± 41.71 e |
| Hangaru | 3.9 ± 0.00 c | 84.6 ± 0.05 c | 2430 ± 41.35 c | 1664 ± 74.37 b | 2832 ± 72.69 b | 766 ± 35.95 c | 402 ± 31.38 d |
| Shingil | 4.8 ± 0.06 a | 94.3 ± 0.82 a | 646 ± 19.34 e | 548 ± 15.77 f | 1318 ± 36.74 f | 98 ± 11.90 f | 671 ± 25.49 a |
| Garumi 2-P | 3.1 ± 0.03 d | 74.6 ± 0.40 d | 3091 ± 46.48 a | 1692 ± 30.92 b | 2896 ± 45.96 b | 1398 ± 19.19 a | −195 ± 2.49 f |
| Garumi 2-N | 3.0 ± 0.06 de | 73.6 ± 0.67 de | 2723 ± 74.68 b | 1387 ± 17.05 d | 2528 ± 36.46 d | 1336 ± 58.79 a | −195 ± 39.42 f |
| Variety | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔT (Tc-To) | ΔH (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ilpum | 63.98 ± 0.33 bc | 69.49 ± 0.10 b | 74.56 ± 0.20 b | 10.58 ± 0.34 b | 8.11 ± 0.71 ns |
| Keumkang * | 62.10 ± 1.02 d | 65.16 ± 0.38 d | 69.46 ± 0.79 e | 7.35 ± 1.79 c | 6.36 ± 0.72 |
| Seolgaeng | 63.07 ± 0.29 cd | 68.07 ± 0.30 c | 72.74 ± 0.22 c | 9.67 ± 0.34 b | 8.06 ± 2.30 |
| Hangaru | 63.79 ± 0.07 bc | 68.53 ± 0.21 c | 73.40 ± 0.37 c | 9.61 ± 0.39 b | 9.41 ± 1.50 |
| Shingil | 58.56 ± 0.43 e | 64.08 ± 0.42 e | 71.45 ± 0.79 d | 12.89 ± 0.36 a | 7.20 ± 2.45 |
| Garumi 2-P | 64.80 ± 0.15 a | 70.90 ± 0.19 a | 75.95 ± 0.12 a | 11.15 ± 0.19 b | 8.65 ± 0.75 |
| Garumi 2-N | 65.09 ± 0.14 ab | 70.68 ± 0.07 a | 75.25 ± 0.21 ab | 10.16 ± 0.12 b | 7.50 ± 0.39 |
| Variety | Distribution (%) | Relative Crystallinity (%) | 1047 cm−1/1022 cm−1 IR Ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP 6–12 | DP 13–24 | DP 25–36 | DP > 37 | |||
| Ilpum | 50.78 ± 0.02 b | 31.32 ± 0.02 b | 3.80 ± 0.02 b | 0.49 ± 0.01 b | 25.0 ± 0.41 e | 1.03 ± 0.00 f |
| Keumkang * | 42.80 ± 0.76 d | 47.38 ± 0.82 a | 8.17 ± 0.15 a | 0.69 ± 0.01 a | 35.0 ± 0.37 a | 1.02 ± 0.00 f |
| Seolgaeng | 50.99 ± 0.06 b | 31.53 ± 0.08 b | 3.63 ± 0.05 c | 0.45 ± 0.01 c | 35.7 ± 0.57 a | 1.12 ± 0.00 d |
| Hangaru | 50.90 ± 0.15 b | 31.62 ± 0.09 b | 3.61 ± 0.08 c | 0.45 ± 0.00 bc | 30.7 ± 0.33 d | 1.07 ± 0.00 e |
| Shingil | 55.32 ± 0.16 a | 30.46 ± 0.12 c | 3.15 ± 0.04 d | 0.25 ± 0.03 e | 33.5 ± 0.16 b | 1.27 ± 0.01 a |
| Garumi 2-P | 48.02 ± 0.96 c | 27.23 ± 0.50 e | 3.27 ± 0.02 d | 0.47 ± 0.02 bc | 31.9 ± 0.12 c | 1.22 ± 0.01 c |
| Garumi 2-N | 51.88 ± 0.58 b | 28.08 ± 0.23 d | 2.68 ± 0.05 e | 0.38 ± 0.00 d | 32.8 ± 0.16 b | 1.25 ± 0.01 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, C.-M.; Shin, J.-H.; Kwon, J.-B.; Kim, J.-S.; Won, J.-G.; Kim, J.-S. Comparison of Morphological and Physicochemical Properties of a Floury Rice Variety upon Pre-Harvest Sprouting. Foods 2021, 10, 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040746
Han C-M, Shin J-H, Kwon J-B, Kim J-S, Won J-G, Kim J-S. Comparison of Morphological and Physicochemical Properties of a Floury Rice Variety upon Pre-Harvest Sprouting. Foods. 2021; 10(4):746. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040746
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Chae-Min, Jong-Hee Shin, Jung-Bae Kwon, Jong-Soo Kim, Jong-Gun Won, and Jong-Sang Kim. 2021. "Comparison of Morphological and Physicochemical Properties of a Floury Rice Variety upon Pre-Harvest Sprouting" Foods 10, no. 4: 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040746
APA StyleHan, C.-M., Shin, J.-H., Kwon, J.-B., Kim, J.-S., Won, J.-G., & Kim, J.-S. (2021). Comparison of Morphological and Physicochemical Properties of a Floury Rice Variety upon Pre-Harvest Sprouting. Foods, 10(4), 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040746






