Effect of Eggplant Powder on the Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Reduced-Fat Pork Sausages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Eggplant Powder
2.3. Preparation of Pork Sausages
2.4. Proximate Composition of the Pork Sausages
2.5. Water- and Oil-Binding Properties
2.6. Colour Measurements
2.7. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Relaxation Measurements
2.8. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.9. Sensory Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Composition of Pork Sausages
3.2. Water- and Oil-Binding Properties
3.3. Colour Measurements
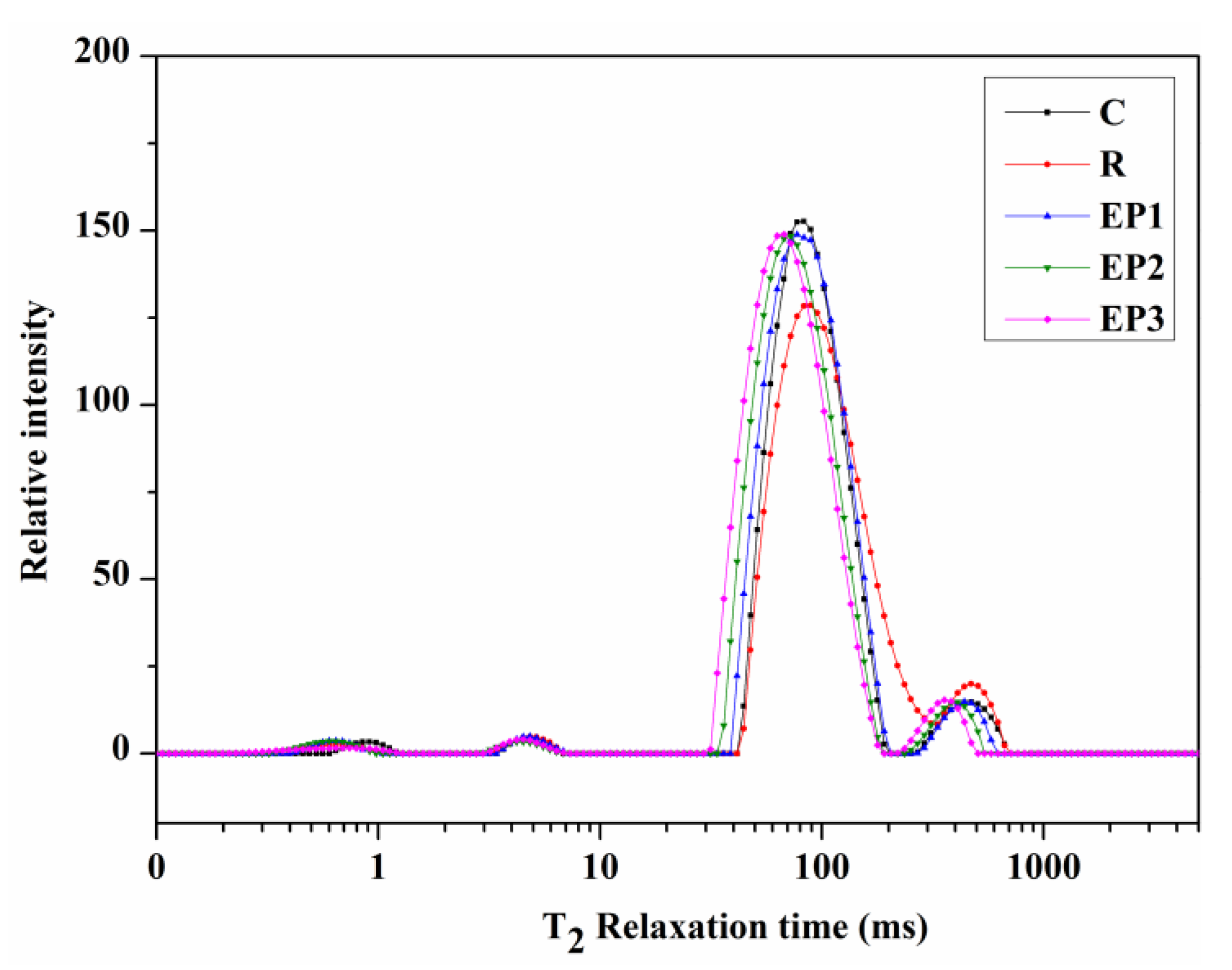
3.4. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) Transverse (T2) Analysis
3.5. Texture Profile Analysis
3.6. Sensory Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Camila, D.S.P.; Guilherme, D.F.F.; Honório, A.R.; Mokarze, L.; Vidal, V.A.; Ribeiro, A.P.B.; Cunha, R.L.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Functional emulsion gels as pork back fat replacers in Bologna sausage. Food Struct. 2019, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Herrero, A.; Pintado, T.; Solas, M.T.; Ruiz-Capillas, C. Influence of emulsified olive oil stabilizing system used for pork backfat replacement in frankfurters. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2068–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Choi, J.H.; Han, D.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.A.; Lee, E.S.; Jeong, J.Y.; Paik, H.D.; Kim, C.J. Effects of rice bran fiber on quality of low-fat tteokgalbi. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 17, 959–964. [Google Scholar]
- O’Shea, N.; Arendt, E.K.; Gallagher, E. Dietary fibre and phytochemical characteristics of fruit and vegetable by-products and their recent applications as novel ingredients in food products. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2012, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.B.; Han, M.Y.; Kang, Z.L.; Wang, K.; Bai, Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Effects of the sugarcane dietary fiber and pre-emulsified sesame oil on low-fat meat batter physicochemical property, texture, and microstructure. Meat Sci. 2016, 113, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Y.; Lu, X.J.; Hu, Y.Y.; Qiao, C.L.; Wu, T.; Zhou, G.H.; Zhang, W.G. Effects of regenerated cellulose on oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by sodium caseinate. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintado, T.; Cofrades, S. Quality characteristics of healthy dry fermented sausages formulated with a mixture of olive and chia oil structured in oleogel or emulsion gel as animal fat replacer. Foods 2020, 9, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz-Turp, G.; Serdaroglu, M. Effect of replacing beef fat with hazelnut oil on quality characteristics of sucuk—A Turkish fermented sausage. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Choi, J.H.; Han, D.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.A.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, J.W.; Chung, H.J.; Kim, C.J. Optimization of replacing pork back fat with grape seed oil and rice bran fiber for reduced-fat meat emulsion systems. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandre, M.; Astiasarán, I.; Ansorena, D.; Barbut, S. Using canola oil hydrogels and organogels to reduce saturated animal fat in meat batters. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerma, H.R.; Specht, J.E. Soybeans: Improvement, Production, and Uses, 3rd ed.; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2004; pp. 621–677. [Google Scholar]
- Schmiele, M.; Nucci Mascarenhas, M.C.C.; Silva Barretto, A.C.D.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Dietary fiber as fat substitute in emulsified and cooked meat model system. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Park, K.S.; Kim, H.W.; Hwang, K.E.; Song, D.H.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Paik, H.D.; Kim, C.J. Quality characteristics of reduced-fat frankfurters with pork fat replaced by sunflower seed oils and dietary fiber extracted from makgeolli lees. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.B.; Zhang, W.G.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.F.; Xing, L.J.; Han, M.Y.; Kang, Z.L.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Improved gel functionality of myofibrillar proteins incorporation with sugarcane dietary fiber. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.J.; Kim, H.W.; Hwang, K.E.; Song, D.H.; Ham, Y.K.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Choi, Y.S. Effects of dietary fiber extracted from pumpkin (cucurbita maxima duch.) on the physico-chemical and sensory characteristics of reduced-fat frankfurters. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2016, 36, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henning, S.S.C.; Tshalibe, P.; Hoffman, L.C. Physico-chemical properties of reduced-fat beef species sausage with pork back fat replaced by pineapple dietary fibres and water. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerón-Guevara, M.I.; Rangel-Vargas, E.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Bermúdez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Sánchez-Ortega, I.; Santos, E.M. Reduction of salt and fat in frankfurter sausages by addition of agaricus bisporus and pleurotus ostreatus flour. Foods 2020, 9, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelm, L.; Mielby, L.A.; Gregersen, S.; Eggers, N.; Bertram, H.C. Partial substitution of fat with rye bran fibre in frankfurter sausages—bridging technological and sensory attributes through inclusion of collagenous protein. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 101, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Choi, J.H.; Han, D.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.A.; Kim, H.W.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, C.J. Effects of rice bran fiber on heat-induced gel prepared with pork salt-soluble meat proteins in model system. Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, W.N.; Keeton, J.T. Evaluation of low-fat sausage containing desinewed lamb and konjac gel. Meat Sci. 2004, 68, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi, M.A.; Kechaou, A.; Makni, I.; Attia, H. Influence of carrageenan addition on turkey meat sausages properties. J. Food Eng. 2009, 93, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulu, H. Effects of carrageenam and guar gum on the cooking and textual properties of low fat meatballs. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.B.; Lin, K.W. Influences of xylooligosaccharides on the quality of Chinese-style meatball (kung-wan). Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibis, M.; Schuh, V.; Weiss, J. Effects of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) as fat replacers on the microstructure and sensory characteristics of fried beef patties. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.W.; Baird, P.; Davis, R.H., Jr.; Ferreri, S.; Mary, K.; Koraym, A.; Waters, V.; Williams, C. Health benefits of dietary fiber. Nutr. Rev. 2009, 67, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, D.J.A.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Augustine, M.; Faulkner, D.A.; Wong, J.M.W.; Russell, D.S.; Azadeh, E.; Parker, T.L.; Edward, V. Effects of a dietary portfolio of cholesterol-lowering foods vs lovastatin on serum lipids and C-reactive protein. JAMA 2003, 290, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Ren, X.P.; Bao, Y.J.; Li, S.; Peng, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhou, G.H. Emulsification of oil-in-water emulsions with eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). J. Colloid Inter. Sci. 2020, 563, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 17th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemistry: Rockville, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez-Colmenero, F.; Cofrades, S.; Lopez-Lopez, I.; Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Pintado, T.; Solas, M.T. Technological and sensory characteristics of reduced/low-fat, low-salt frankfurters as affected by the addition of konjac and seaweed. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.; Librelotto, J.; Cofrades, S.; Sánchez-Muniz, F.J.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F. Composition and physicochemical characteristics of restructured beef steaks containing walnuts as affected by cooking method. Meat Sci. 2007, 77, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.Y.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Liu, T.X.; Kong, J.; Long, Z.; Zhao, M. Sodium caseinate/carboxymethylcellulose interactions at oil–water interface: Relationship to emulsion stability. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1822–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustunol, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Means, W.J.; Decker, E.A. Forces involved in mixed pork myofibrillar protein and calcium alginate gels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Kumar, S.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, J.S. Coloration of colloidal polymer particles through selective extraction of Mie backscattering for cation-responsible colorimetric sensors. J. Colloid Inter. Sci. 2020, 560, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concellón, A.; Anón, M.C.; Chaves, A.R. Characterization and changes in polyphenol oxidase from eggplant fruit (Solanum melongena L.) during storage at low temperature. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Choi, J.H.; Han, D.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, M.A.; Chung, H.J.; Kim, C.J. Effects of Laminaria japonica on the physico-chemical and sensory characteristics of reduced-fat pork patties. Meat Sci. 2012, 91, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, M.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; He, L.; Zeng, X. Effects of replacing fat with Perilla seed on the characteristics of meatballs. Meat Sci. 2019, 161, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.B.; Jiang, X.P.; Zhou, H.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, G.H. Insight into the mechanism of physicochemical influence by three polysaccharides on myofibrillar protein gelation. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 229, 115449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.B.; Han, M.Y.; Bai, Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Xing, L.J.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Insight into the mechanism of myofibrillar protein gel improved by insoluble dietary fiber. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 74, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, S.M.; Grossi, A.; Christensen, M.; Orlien, V.; Søltoft-Jensen, J.; Straadt, I.K.; Thybo, A.K.; Bertram, H.C. Water properties and structure of pork sausages as affected by high-pressure processing and addition of carrot fibre. Meat Sci. 2011, 87, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Kim, H.W.; Hwang, K.E.; Song, D.H.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, M.A.; Chung, H.J.; Kim, C.J. Physicochemical properties and sensory characteristics of reduced-fat frankfurters with pork back fat replaced by dietary fiber extracted from makgeolli lees. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetriades, K.; Coupland, J.N.; McClements, D.J. Physical properties of whey protein stabilized emulsions as related to pH and NaCl. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turhan, S.; Sagir, I.; Ustun, N.S. Utilization of hazelnut pellicle in low-fat beef burgers. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, D.S.D.; Cobas, A.C.; Nascimento, B.S.D.; Monteiro, M.J.; Pintado, M.M.E. Development of a low fat fresh pork sausage based on chitosan with health claims: Impact on the quality, functionality and shelf-life. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Chin, K.B.; Kim, Y.D. Rheological properties of the mixture and heat-induced gel prepared from pork salt soluble protein in combined with water soluble chitooligosaccharide and chitosan. Koren J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 36, 594–597. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.Y.; Bertram, H.C.S. Designing healthier comminuted meat products: Effect of dietary fibers on water distribution and texture of a fat-reduced meat model system. Meat Sci. 2017, 133, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehlet, U.; Pagter, M.; Aaslyng, M.D.; Raben, A. Meatballs with 3% and 6% dietary fibre from rye bran or pea fibre—Effects on sensory quality and subjective appetite sensations. Meat Sci. 2017, 125, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ingredient | Treatment (g/100 g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | R | EP1 | EP2 | EP3 | |
| Pork leg muscle | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Pork fat | 30 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Ice water | 20 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 |
| Soybean oil | 0 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| EP | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Salt | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Sodium caseinate | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Sodium tripolyphosphate | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| White pepper | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Sugar | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Treatment | Cholesterol (mg/100 g) | Moisture (%) | Fat (%) | Protein (%) | Ash (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 71.90 ± 1.12 a | 56.35 ± 0.55 c | 29.44 ± 0.68 a | 12.10 ± 0.13 | 1.86 ± 0.09 |
| R | 55.25 ± 1.65 b | 58.80 ± 0.50 b | 25.28 ± 0.78 b | 11.73 ± 0.14 | 1.89 ± 0.05 |
| EP1 | 55.05 ± 1.85 b | 59.20 ± 0.30 b | 25.02 ± 0.34 b | 11.96 ± 0.12 | 1.91 ± 0.15 |
| EP2 | 56.05 ± 1.15 b | 61.00 ± 0.50 a | 24.86 ± 0.74 b | 12.18 ± 0.12 | 1.94 ± 0.12 |
| EP3 | 54.75 ± 1.55 b | 60.61 ± 0.25 a | 24.56 ± 0.11 b | 12.16 ± 0.18 | 1.92 ± 0.08 |
| F Value | 24.94 ** | 15.47 ** | 11.79 ** | 1.29 | 0.09 |
| Treatment | TR (%) | WR (%) | OR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 2.52 ± 0.26 c | 2.22 ± 0.32 c | 0.29 ± 0.06 b |
| R | 8.63 ± 0.36 a | 6.38 ± 0.29 a | 2.25 ± 0.65 a |
| EP1 | 5.64 ± 0.09 b | 4.77 ± 0.31 b | 0.87 ± 0.22 b |
| EP2 | 3.21 ± 0.26 c | 2.86 ± 0.16 c | 0.35 ± 0.10 b |
| EP3 | 2.72 ± 0.21 c | 2.52 ± 0.26 c | 0.20 ± 0.05 b |
| F Value | 66.68 ** | 41.76 ** | 7.52 * |
| Treatment | L* | a* | b* |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 75.58 ± 0.43 c | 5.49 ± 0.25 a | 10.70 ± 0.21 d |
| R | 80.24 ± 0.06 a | 3.52 ± 0.05 b | 10.92 ± 0.16 d |
| EP1 | 77.13 ± 0.57 b | 2.94 ± 0.38 c | 12.32 ± 0.16 c |
| EP2 | 76.27 ± 0.32 b,c | 2.23 ± 0.12 d | 15.57 ± 0.16 b |
| EP3 | 75.72 ± 0.30 c | 2.25 ± 0.06 d | 16.20 ± 0.39 a |
| F Value | 32.18 ** | 52.03 ** | 80.50 ** |
| Treatment | T2a | T2b | T21 | T22 | P2a | P2b | P21 | P22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 0.81 ± 0.06 | 4.61 ± 0.29 | 85.92 ± 2.08 b | 462.30 ± 39.31 b | 0.89 ± 0.02 a | 1.85 ± 0.14 | 91.05 ± 0.65 b | 5.98 ± 0.57 b |
| R | 0.76 ± 0.07 | 4.86 ± 0.40 | 89.07 ± 0.00 a | 568.48 ± 38.03 a | 0.63 ± 0.06 b | 1.83 ± 0.21 | 87.67 ± 0.59 c | 8.94 ± 0.43 a |
| EP1 | 0.75 ± 0.09 | 4.84 ± 0.34 | 83.10 ± 0.00 b | 450.30 ± 14.90 b | 0.64 ± 0.03 b | 1.74 ± 0.05 | 91.24 ± 0.15 b | 5.57 ± 0.18 b |
| EP2 | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 4.55 ± 0.31 | 72.33 ± 0.00 c | 410.23 ± 0.00 b,c | 0.69 ± 0.03 b | 1.59 ± 0.26 | 92.95 ± 0.14 a | 4.61 ± 0.24 c |
| EP3 | 0.79 ± 0.08 | 4.68 ± 0.53 | 67.48 ± 0.00 d | 365.64 ± 12.10 c | 0.68 ± 0.06 b | 1.71 ± 0.30 | 93.54 ± 0.28 a | 4.35 ± 0.35 c |
| F Value | 0.36 | 0.14 | 33.14 ** | 17.02 ** | 8.42 * | 1.07 | 71.79 ** | 44.73 ** |
| Treatment | Hardness | Springiness | Cohesiveness | Adhesiveness | Chewiness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 2177.39 ± 100.88 b,c | 0.70 ± 0.01 | 0.68 ± 0.00 | 1470.24 ± 78.98 a,b | 978.36 ± 10.04 b,c |
| R | 1998.12 ± 129.90 c | 0.67 ± 0.03 | 0.63 ± 0.02 | 1269.82 ± 113.40 b | 888.67 ± 62.98 c |
| EP1 | 2492.21 ± 104.70 a,b | 0.68 ± 0.00 | 0.67 ± 0.00 | 1677.04 ± 65.48 a,b | 1130.33 ± 44.13 a,b |
| EP2 | 2734.66 ± 141.18 a | 0.66 ± 0.06 | 0.64 ± 0.00 | 1751.48 ± 89.06 a,b | 1231.26 ± 27.67 a |
| EP3 | 2891.68 ± 167.30 a | 0.67 ± 0.03 | 0.65 ± 0.05 | 1885.74 ± 264.73 a | 1256.62 ± 97.53 a |
| F Value | 24.26 ** | 0.60 | 1.78 | 8.67 * | 23.56 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Z. Effect of Eggplant Powder on the Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Reduced-Fat Pork Sausages. Foods 2021, 10, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040743
Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Peng Z. Effect of Eggplant Powder on the Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Reduced-Fat Pork Sausages. Foods. 2021; 10(4):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040743
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yuxia, Yawei Zhang, and Zengqi Peng. 2021. "Effect of Eggplant Powder on the Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Reduced-Fat Pork Sausages" Foods 10, no. 4: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040743
APA StyleZhu, Y., Zhang, Y., & Peng, Z. (2021). Effect of Eggplant Powder on the Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Reduced-Fat Pork Sausages. Foods, 10(4), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040743





