Effect of Eggplant Powder on the Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Reduced-Fat Pork Sausages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Eggplant Powder
2.3. Preparation of Pork Sausages
2.4. Proximate Composition of the Pork Sausages
2.5. Water- and Oil-Binding Properties
2.6. Colour Measurements
2.7. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Relaxation Measurements
2.8. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.9. Sensory Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Composition of Pork Sausages
3.2. Water- and Oil-Binding Properties
3.3. Colour Measurements
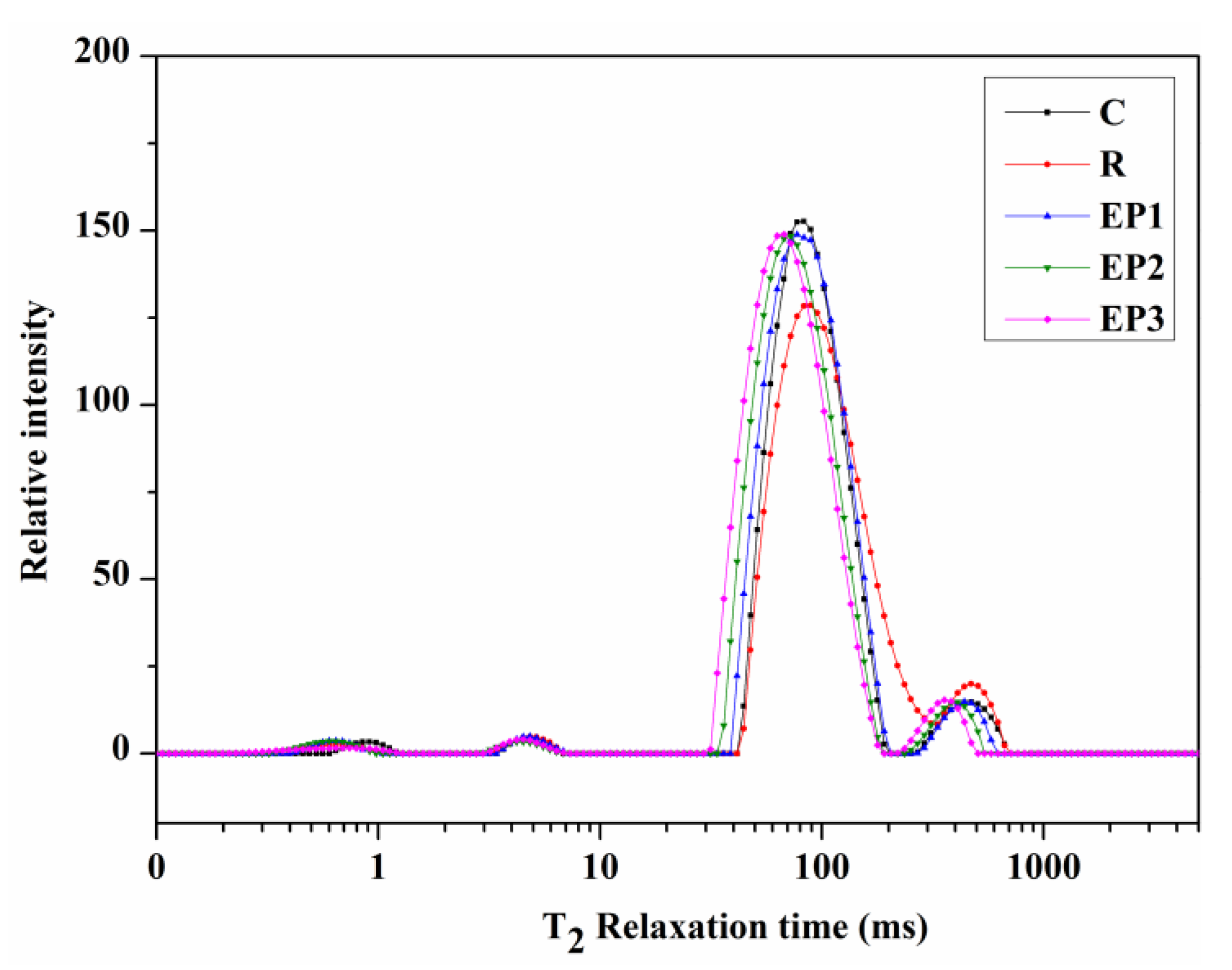
3.4. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) Transverse (T2) Analysis
3.5. Texture Profile Analysis
3.6. Sensory Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Camila, D.S.P.; Guilherme, D.F.F.; Honório, A.R.; Mokarze, L.; Vidal, V.A.; Ribeiro, A.P.B.; Cunha, R.L.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Functional emulsion gels as pork back fat replacers in Bologna sausage. Food Struct. 2019, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Herrero, A.; Pintado, T.; Solas, M.T.; Ruiz-Capillas, C. Influence of emulsified olive oil stabilizing system used for pork backfat replacement in frankfurters. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2068–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Choi, J.H.; Han, D.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.A.; Lee, E.S.; Jeong, J.Y.; Paik, H.D.; Kim, C.J. Effects of rice bran fiber on quality of low-fat tteokgalbi. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 17, 959–964. [Google Scholar]
- O’Shea, N.; Arendt, E.K.; Gallagher, E. Dietary fibre and phytochemical characteristics of fruit and vegetable by-products and their recent applications as novel ingredients in food products. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2012, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.B.; Han, M.Y.; Kang, Z.L.; Wang, K.; Bai, Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Effects of the sugarcane dietary fiber and pre-emulsified sesame oil on low-fat meat batter physicochemical property, texture, and microstructure. Meat Sci. 2016, 113, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Y.; Lu, X.J.; Hu, Y.Y.; Qiao, C.L.; Wu, T.; Zhou, G.H.; Zhang, W.G. Effects of regenerated cellulose on oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by sodium caseinate. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintado, T.; Cofrades, S. Quality characteristics of healthy dry fermented sausages formulated with a mixture of olive and chia oil structured in oleogel or emulsion gel as animal fat replacer. Foods 2020, 9, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz-Turp, G.; Serdaroglu, M. Effect of replacing beef fat with hazelnut oil on quality characteristics of sucuk—A Turkish fermented sausage. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Choi, J.H.; Han, D.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.A.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, J.W.; Chung, H.J.; Kim, C.J. Optimization of replacing pork back fat with grape seed oil and rice bran fiber for reduced-fat meat emulsion systems. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandre, M.; Astiasarán, I.; Ansorena, D.; Barbut, S. Using canola oil hydrogels and organogels to reduce saturated animal fat in meat batters. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerma, H.R.; Specht, J.E. Soybeans: Improvement, Production, and Uses, 3rd ed.; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2004; pp. 621–677. [Google Scholar]
- Schmiele, M.; Nucci Mascarenhas, M.C.C.; Silva Barretto, A.C.D.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Dietary fiber as fat substitute in emulsified and cooked meat model system. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Park, K.S.; Kim, H.W.; Hwang, K.E.; Song, D.H.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Paik, H.D.; Kim, C.J. Quality characteristics of reduced-fat frankfurters with pork fat replaced by sunflower seed oils and dietary fiber extracted from makgeolli lees. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.B.; Zhang, W.G.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.F.; Xing, L.J.; Han, M.Y.; Kang, Z.L.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Improved gel functionality of myofibrillar proteins incorporation with sugarcane dietary fiber. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.J.; Kim, H.W.; Hwang, K.E.; Song, D.H.; Ham, Y.K.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Choi, Y.S. Effects of dietary fiber extracted from pumpkin (cucurbita maxima duch.) on the physico-chemical and sensory characteristics of reduced-fat frankfurters. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2016, 36, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henning, S.S.C.; Tshalibe, P.; Hoffman, L.C. Physico-chemical properties of reduced-fat beef species sausage with pork back fat replaced by pineapple dietary fibres and water. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerón-Guevara, M.I.; Rangel-Vargas, E.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Bermúdez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Sánchez-Ortega, I.; Santos, E.M. Reduction of salt and fat in frankfurter sausages by addition of agaricus bisporus and pleurotus ostreatus flour. Foods 2020, 9, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelm, L.; Mielby, L.A.; Gregersen, S.; Eggers, N.; Bertram, H.C. Partial substitution of fat with rye bran fibre in frankfurter sausages—bridging technological and sensory attributes through inclusion of collagenous protein. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 101, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Choi, J.H.; Han, D.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.A.; Kim, H.W.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, C.J. Effects of rice bran fiber on heat-induced gel prepared with pork salt-soluble meat proteins in model system. Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, W.N.; Keeton, J.T. Evaluation of low-fat sausage containing desinewed lamb and konjac gel. Meat Sci. 2004, 68, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi, M.A.; Kechaou, A.; Makni, I.; Attia, H. Influence of carrageenan addition on turkey meat sausages properties. J. Food Eng. 2009, 93, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulu, H. Effects of carrageenam and guar gum on the cooking and textual properties of low fat meatballs. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.B.; Lin, K.W. Influences of xylooligosaccharides on the quality of Chinese-style meatball (kung-wan). Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibis, M.; Schuh, V.; Weiss, J. Effects of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) as fat replacers on the microstructure and sensory characteristics of fried beef patties. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.W.; Baird, P.; Davis, R.H., Jr.; Ferreri, S.; Mary, K.; Koraym, A.; Waters, V.; Williams, C. Health benefits of dietary fiber. Nutr. Rev. 2009, 67, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, D.J.A.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Augustine, M.; Faulkner, D.A.; Wong, J.M.W.; Russell, D.S.; Azadeh, E.; Parker, T.L.; Edward, V. Effects of a dietary portfolio of cholesterol-lowering foods vs lovastatin on serum lipids and C-reactive protein. JAMA 2003, 290, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Ren, X.P.; Bao, Y.J.; Li, S.; Peng, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhou, G.H. Emulsification of oil-in-water emulsions with eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). J. Colloid Inter. Sci. 2020, 563, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 17th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemistry: Rockville, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez-Colmenero, F.; Cofrades, S.; Lopez-Lopez, I.; Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Pintado, T.; Solas, M.T. Technological and sensory characteristics of reduced/low-fat, low-salt frankfurters as affected by the addition of konjac and seaweed. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.; Librelotto, J.; Cofrades, S.; Sánchez-Muniz, F.J.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F. Composition and physicochemical characteristics of restructured beef steaks containing walnuts as affected by cooking method. Meat Sci. 2007, 77, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.Y.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Liu, T.X.; Kong, J.; Long, Z.; Zhao, M. Sodium caseinate/carboxymethylcellulose interactions at oil–water interface: Relationship to emulsion stability. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1822–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustunol, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Means, W.J.; Decker, E.A. Forces involved in mixed pork myofibrillar protein and calcium alginate gels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Kumar, S.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, J.S. Coloration of colloidal polymer particles through selective extraction of Mie backscattering for cation-responsible colorimetric sensors. J. Colloid Inter. Sci. 2020, 560, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concellón, A.; Anón, M.C.; Chaves, A.R. Characterization and changes in polyphenol oxidase from eggplant fruit (Solanum melongena L.) during storage at low temperature. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Choi, J.H.; Han, D.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, M.A.; Chung, H.J.; Kim, C.J. Effects of Laminaria japonica on the physico-chemical and sensory characteristics of reduced-fat pork patties. Meat Sci. 2012, 91, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, M.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; He, L.; Zeng, X. Effects of replacing fat with Perilla seed on the characteristics of meatballs. Meat Sci. 2019, 161, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.B.; Jiang, X.P.; Zhou, H.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, G.H. Insight into the mechanism of physicochemical influence by three polysaccharides on myofibrillar protein gelation. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 229, 115449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.B.; Han, M.Y.; Bai, Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Xing, L.J.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Insight into the mechanism of myofibrillar protein gel improved by insoluble dietary fiber. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 74, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, S.M.; Grossi, A.; Christensen, M.; Orlien, V.; Søltoft-Jensen, J.; Straadt, I.K.; Thybo, A.K.; Bertram, H.C. Water properties and structure of pork sausages as affected by high-pressure processing and addition of carrot fibre. Meat Sci. 2011, 87, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Kim, H.W.; Hwang, K.E.; Song, D.H.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, M.A.; Chung, H.J.; Kim, C.J. Physicochemical properties and sensory characteristics of reduced-fat frankfurters with pork back fat replaced by dietary fiber extracted from makgeolli lees. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetriades, K.; Coupland, J.N.; McClements, D.J. Physical properties of whey protein stabilized emulsions as related to pH and NaCl. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turhan, S.; Sagir, I.; Ustun, N.S. Utilization of hazelnut pellicle in low-fat beef burgers. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, D.S.D.; Cobas, A.C.; Nascimento, B.S.D.; Monteiro, M.J.; Pintado, M.M.E. Development of a low fat fresh pork sausage based on chitosan with health claims: Impact on the quality, functionality and shelf-life. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Chin, K.B.; Kim, Y.D. Rheological properties of the mixture and heat-induced gel prepared from pork salt soluble protein in combined with water soluble chitooligosaccharide and chitosan. Koren J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 36, 594–597. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.Y.; Bertram, H.C.S. Designing healthier comminuted meat products: Effect of dietary fibers on water distribution and texture of a fat-reduced meat model system. Meat Sci. 2017, 133, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehlet, U.; Pagter, M.; Aaslyng, M.D.; Raben, A. Meatballs with 3% and 6% dietary fibre from rye bran or pea fibre—Effects on sensory quality and subjective appetite sensations. Meat Sci. 2017, 125, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ingredient | Treatment (g/100 g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | R | EP1 | EP2 | EP3 | |
| Pork leg muscle | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Pork fat | 30 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Ice water | 20 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 |
| Soybean oil | 0 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| EP | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Salt | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Sodium caseinate | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Sodium tripolyphosphate | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| White pepper | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Sugar | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Treatment | Cholesterol (mg/100 g) | Moisture (%) | Fat (%) | Protein (%) | Ash (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 71.90 ± 1.12 a | 56.35 ± 0.55 c | 29.44 ± 0.68 a | 12.10 ± 0.13 | 1.86 ± 0.09 |
| R | 55.25 ± 1.65 b | 58.80 ± 0.50 b | 25.28 ± 0.78 b | 11.73 ± 0.14 | 1.89 ± 0.05 |
| EP1 | 55.05 ± 1.85 b | 59.20 ± 0.30 b | 25.02 ± 0.34 b | 11.96 ± 0.12 | 1.91 ± 0.15 |
| EP2 | 56.05 ± 1.15 b | 61.00 ± 0.50 a | 24.86 ± 0.74 b | 12.18 ± 0.12 | 1.94 ± 0.12 |
| EP3 | 54.75 ± 1.55 b | 60.61 ± 0.25 a | 24.56 ± 0.11 b | 12.16 ± 0.18 | 1.92 ± 0.08 |
| F Value | 24.94 ** | 15.47 ** | 11.79 ** | 1.29 | 0.09 |
| Treatment | TR (%) | WR (%) | OR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 2.52 ± 0.26 c | 2.22 ± 0.32 c | 0.29 ± 0.06 b |
| R | 8.63 ± 0.36 a | 6.38 ± 0.29 a | 2.25 ± 0.65 a |
| EP1 | 5.64 ± 0.09 b | 4.77 ± 0.31 b | 0.87 ± 0.22 b |
| EP2 | 3.21 ± 0.26 c | 2.86 ± 0.16 c | 0.35 ± 0.10 b |
| EP3 | 2.72 ± 0.21 c | 2.52 ± 0.26 c | 0.20 ± 0.05 b |
| F Value | 66.68 ** | 41.76 ** | 7.52 * |
| Treatment | L* | a* | b* |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 75.58 ± 0.43 c | 5.49 ± 0.25 a | 10.70 ± 0.21 d |
| R | 80.24 ± 0.06 a | 3.52 ± 0.05 b | 10.92 ± 0.16 d |
| EP1 | 77.13 ± 0.57 b | 2.94 ± 0.38 c | 12.32 ± 0.16 c |
| EP2 | 76.27 ± 0.32 b,c | 2.23 ± 0.12 d | 15.57 ± 0.16 b |
| EP3 | 75.72 ± 0.30 c | 2.25 ± 0.06 d | 16.20 ± 0.39 a |
| F Value | 32.18 ** | 52.03 ** | 80.50 ** |
| Treatment | T2a | T2b | T21 | T22 | P2a | P2b | P21 | P22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 0.81 ± 0.06 | 4.61 ± 0.29 | 85.92 ± 2.08 b | 462.30 ± 39.31 b | 0.89 ± 0.02 a | 1.85 ± 0.14 | 91.05 ± 0.65 b | 5.98 ± 0.57 b |
| R | 0.76 ± 0.07 | 4.86 ± 0.40 | 89.07 ± 0.00 a | 568.48 ± 38.03 a | 0.63 ± 0.06 b | 1.83 ± 0.21 | 87.67 ± 0.59 c | 8.94 ± 0.43 a |
| EP1 | 0.75 ± 0.09 | 4.84 ± 0.34 | 83.10 ± 0.00 b | 450.30 ± 14.90 b | 0.64 ± 0.03 b | 1.74 ± 0.05 | 91.24 ± 0.15 b | 5.57 ± 0.18 b |
| EP2 | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 4.55 ± 0.31 | 72.33 ± 0.00 c | 410.23 ± 0.00 b,c | 0.69 ± 0.03 b | 1.59 ± 0.26 | 92.95 ± 0.14 a | 4.61 ± 0.24 c |
| EP3 | 0.79 ± 0.08 | 4.68 ± 0.53 | 67.48 ± 0.00 d | 365.64 ± 12.10 c | 0.68 ± 0.06 b | 1.71 ± 0.30 | 93.54 ± 0.28 a | 4.35 ± 0.35 c |
| F Value | 0.36 | 0.14 | 33.14 ** | 17.02 ** | 8.42 * | 1.07 | 71.79 ** | 44.73 ** |
| Treatment | Hardness | Springiness | Cohesiveness | Adhesiveness | Chewiness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 2177.39 ± 100.88 b,c | 0.70 ± 0.01 | 0.68 ± 0.00 | 1470.24 ± 78.98 a,b | 978.36 ± 10.04 b,c |
| R | 1998.12 ± 129.90 c | 0.67 ± 0.03 | 0.63 ± 0.02 | 1269.82 ± 113.40 b | 888.67 ± 62.98 c |
| EP1 | 2492.21 ± 104.70 a,b | 0.68 ± 0.00 | 0.67 ± 0.00 | 1677.04 ± 65.48 a,b | 1130.33 ± 44.13 a,b |
| EP2 | 2734.66 ± 141.18 a | 0.66 ± 0.06 | 0.64 ± 0.00 | 1751.48 ± 89.06 a,b | 1231.26 ± 27.67 a |
| EP3 | 2891.68 ± 167.30 a | 0.67 ± 0.03 | 0.65 ± 0.05 | 1885.74 ± 264.73 a | 1256.62 ± 97.53 a |
| F Value | 24.26 ** | 0.60 | 1.78 | 8.67 * | 23.56 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Z. Effect of Eggplant Powder on the Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Reduced-Fat Pork Sausages. Foods 2021, 10, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040743
Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Peng Z. Effect of Eggplant Powder on the Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Reduced-Fat Pork Sausages. Foods. 2021; 10(4):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040743
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yuxia, Yawei Zhang, and Zengqi Peng. 2021. "Effect of Eggplant Powder on the Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Reduced-Fat Pork Sausages" Foods 10, no. 4: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040743
APA StyleZhu, Y., Zhang, Y., & Peng, Z. (2021). Effect of Eggplant Powder on the Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Reduced-Fat Pork Sausages. Foods, 10(4), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040743





