Development and Validation of an Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method to Determine Maduramicin in Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) and Evaluate Food Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Experimental Animals and Sample Pre-Preparation
2.3. Standard Solutions
2.4. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.4.1. Chromatography
2.4.2. Mass Spectrometry (MS)
2.5. Sample Preparation
2.6. Validation of The Method
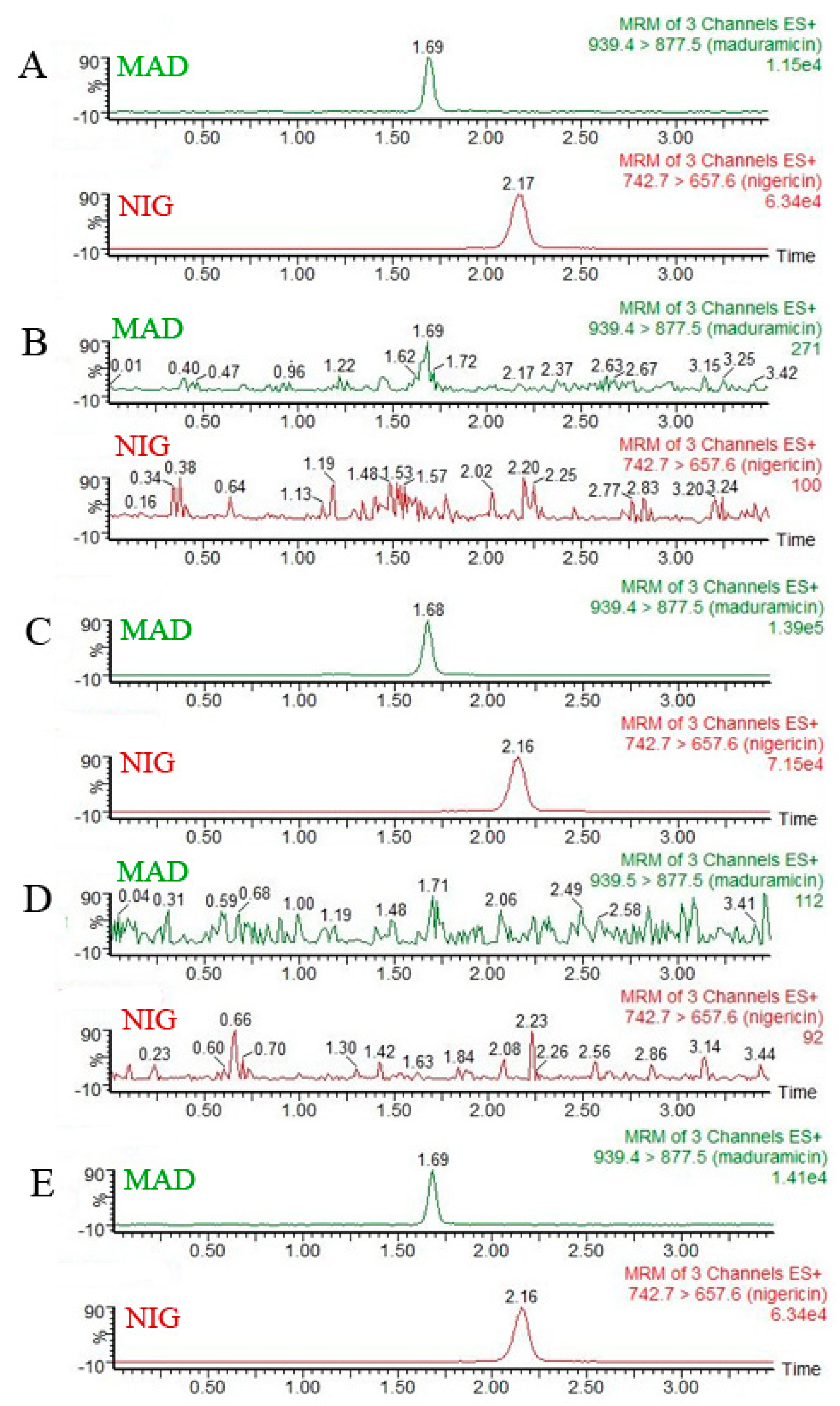
2.6.1. Selectivity Investigation
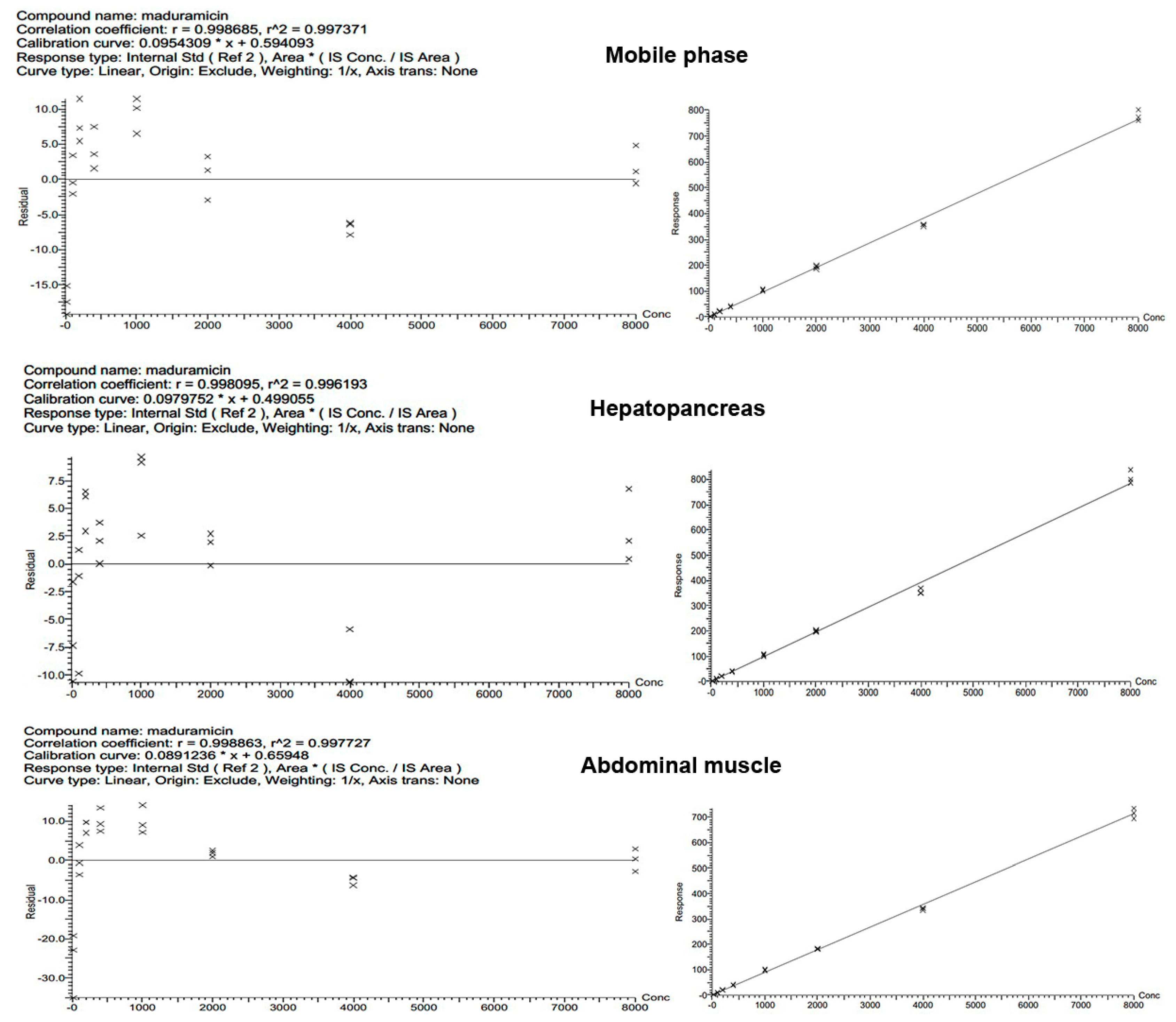
2.6.2. Linearity Range and Matrix Effects (ME)
2.6.3. Recovery and Precision
2.6.4. Limits of Detection (LOD) and Quantification (LOQ)
2.6.5. Sample Stability
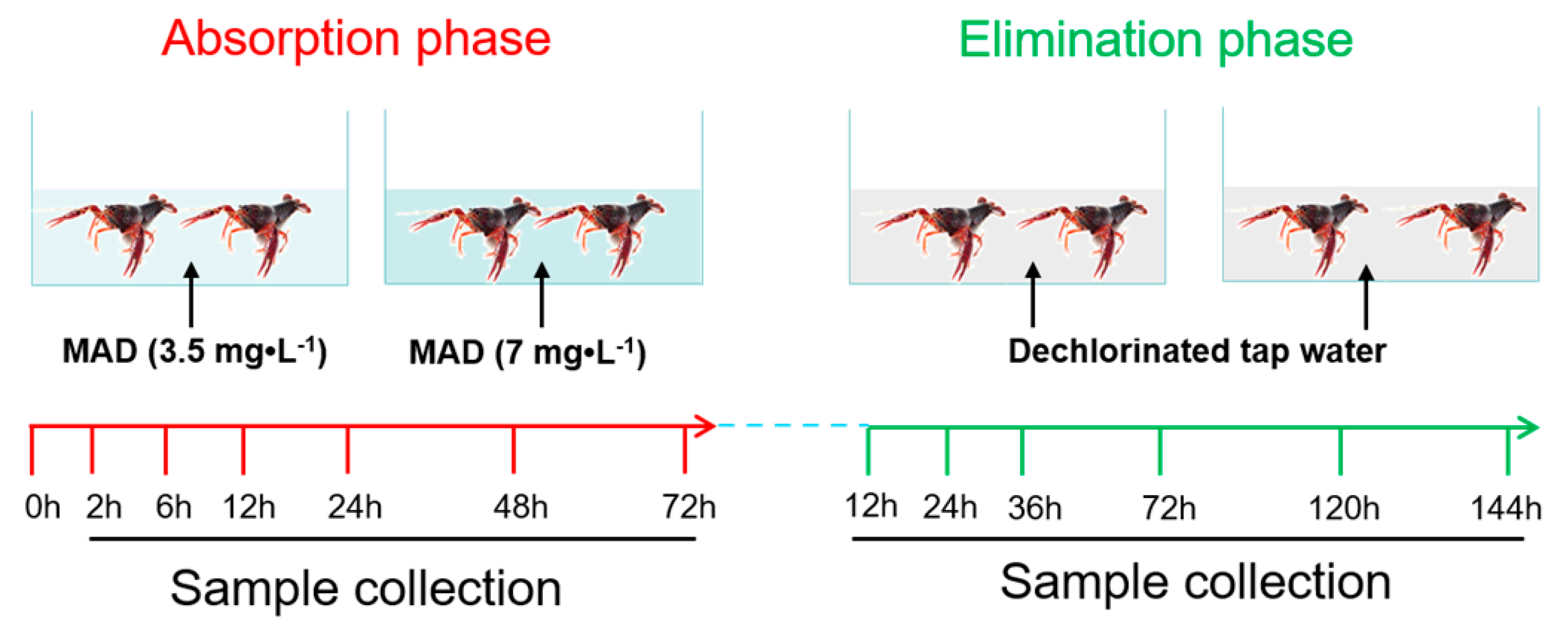
2.7. Applications in Crayfish Samples Exposed to MAD
2.8. Maximum Residue Limits (MRLs) and Withdrawal Time (WT)
2.9. Data Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chromatographic Separation and Mass Spectrometric Optimization
3.2. Specificity and Sensitivity
3.3. Linearity and Matrix Effects (ME)
3.4. Accuracy and Precision
3.5. Sample Stability
3.6. Absorption and Elimination of MAD in Crayfish Hepatopancreas and Muscle Tissues
3.7. Maxiumum Residue Limits and Withdrawal Times of MAD in Crayfish
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noack, S.; Chapman, H.D.; Selzer, P.M. Anticoccidial drugs of the livestock industry. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2009–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Barmaz, D.; Cabrera, M.L.; Pavlostathis, S.G.; Huang, C.H. Detection and quantification of ionophore antibiotics in runoff, soil and poultry litter. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1312, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, J.; Carlson, K.H. Occurrence of beta-lactam and polyether ionophore antibiotics in lagoon water and animal manure. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; McGrath, J.M.; Sapkota, A. Quantification of ionophores in aged poultry litter using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2012, 47, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, M.; Krogh, K.A.; Björklund, E.; Halling-Sørensen, B.; Brandt, A. Environmental risk assessment of ionophores. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, L.L.; Demetrio, P.M.; Capparelli, A.L.; Marino, D.J.G. Behavior of ionophore antibiotics in aquatic environments in Argentina: The distribution on different scales in water courses and the role of wetlands in depuration. Environ. Int. 2019, 133 Pt A, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, P.; Borrull, F.; Marce, R.M.; Pocurull, E. Determination of polyether ionophores in urban sewage sludge by pressurised liquid extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Study of different clean-up strategies. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1285, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, S.A.; Björklund, E. Occurrence of Ionophores in the Danish Environment. Antibiotics 2014, 3, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yopasa-Arenas, A.; Fostier, A.H. Exposure of Brazilian soil and groundwater to pollution by coccidiostats and antimicrobial agents used as growth promoters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J.; Wang, W.X.; Lv, Y.J.; Mao, Z.G.; Chen, C.; Wu, Q.L. Tissue concentrations, trophic transfer and human risks of antibiotics in freshwater food web in Lake Taihu, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Carlson, K. Occurrence of ionophore antibiotics in water and sediments of a mixed-landscape watershed. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2549–2560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dorne, J.L.; Fernandez-Cruz, M.L.; Bertelsen, U.; Renshaw, D.W.; Peltonen, K.; Anadon, A.; Feil, A.; Sanders, P.; Wester, P.; Fink-Gremmels, J. Risk assessment of coccidostatics during feed cross-contamination: Animal and human health aspects. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 270, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimshoni, J.A.; Britzi, M.; Pozzi, P.S.; Edery, N.; Berkowitz, A.; Bouznach, A.; Cuneah, O.; Soback, S.; Bellaiche, M.; Younis, A.; et al. Acute maduramicin toxicosis in pregnant gilts. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Peng, L.; Ruan, X.; Chen, X.; Ji, H.; Ma, J.; Ni, H.; Jiang, S.; Guo, D. Transcriptome profile analysis reveals cardiotoxicity of maduramicin in primary chicken myocardial cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, L.; Ruan, X.; Ji, H.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, X.; Teng, P.; Guo, D.; Jiang, S. Maduramicin induces apoptosis in chicken myocardial cells via intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 50, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Bhalla, A.; Varma, S.; Jain, S.; Singh, S. Toxicity of maduramicin. Emerg. Med. J. 2005, 22, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, U.; Mouzin, E.; Dickey, R.; Moolenaar, R.; Sass, N.; Mascola, L. Haff disease: From the Baltic Sea to the U.S. shore. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.H. Global incidence of rhabdomyolysis after cooked seafood consumption (Haff disease). Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.Y. The emergence and epidemiology of Haff disease in China. Toxins 2016, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, L.L.; Bies, C. Haff disease: Rhabdomyolysis after eating buffalo fish. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 15, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Ni, J.; Huang, J.A.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, J. Clinical features of Haff disease and myositis after the consumption of boiled brackish water crayfish: A retrospective study of 96 cases at a single centre. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2018, 13, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Peng, L.; Gong, N.; Xue, C.; Wang, W.; Jiang, J. A retrospective analysis of crayfish-related rhabdomyolysis (Haff disease). Emerg. Med. Int. 2019, 2019, 4209745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, G.; Yu, X.; Mao, H.; Xing, C.; Liu, J. Haff disease after eating crayfish in east China. Intern. Med. 2012, 51, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bai, L.; Xu, M.J.; Li, W.W.; Han, H.H.; Liu, J.K.; Fu, P.; Xu, L.Z.; Ouyang, Y.Y.; You, X.Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Retrospective case analysis of crayfish-transmitted Haff disease in China during 2016–2017. Food Control 2019, 104, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Li, X.Y.; Lu, S.S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Lu, X.C.; Lu, K. The emergence, epidemiology, and etiology of Haff disease. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 769–778. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, B.J.; Xie, G.X.; Zhen, S.Q.; Zhou, Y.J.; Shao, B.; Zhang, J.; Ji, H.; Wu, Y.N. Outbreak of Haff Disease caused by consumption of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii), Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China. Food Control 2016, 59, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilderman, P.A.E.L.; Moonen, E.J.C.; Maas, L.M.; Welle, I.; Kleinjans, J.C.S. Use of crayfish in biomonitoring studies of environmental pollution of the river Meuse. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 1999, 44, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kazakova, J.; Fernandez-Torres, R.; Ramos-Payan, M.; Bello-Lopez, M.A. Multiresidue determination of 21 pharmaceuticals in crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) using enzymatic microwave-assisted liquid extraction and ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2018, 160, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigosky, S.R.; Alvarez-Hernandez, X.; Glass, J. Lead, cadmium, and aluminum accumulation in the red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii G. collected from roadside drainage ditches in Louisiana. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1991, 20, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkacikova, S.; Kozarova, I.; Mate, D. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry determination of maduramycin residues in the tissues of broiler chickens. Food Addit. Contam. A 2010, 27, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasz, S.; Debreczeni, L.; Rikker, T.; Eke, Z. Development and validation of a liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric method for determination of eleven coccidiostats in milk. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.C.; Su, J.J.; Cheng, C. Development of online sampling and matrix reduction technique coupled liquid chromatography/ion trap mass spectrometry for determination maduramicin in chicken meat. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, J.J.; Wallace, J.S.; Aga, D.S. Method development for the analysis of ionophore antimicrobials in dairy manure to assess removal within a membrane-based treatment system. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasenaki, M.E.; Thomaidis, N.S. Multi-residue methodology for the determination of 16 coccidiostats in animal tissues and eggs by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography—Tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Xing, G.; Deng, R.; Hu, X.; Zhang, G. Competitive electrochemical immunosensor for maduramicin detection by multiple signal amplification strategy via hemin@Fe-MIL-88NH2/AuPt. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Peng, L.; Gao, X.; Ji, H.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, S. Effects of maduramicin on adult zebrafish (Danio rerio): Acute toxicity, tissue damage and oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Song, G.; Ai, L.F.; Li, J.C. Determination of six polyether antibiotic residues in foods of animal origin by solid phase extraction combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1017–1018, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, S.; Busetto, M.; Vitelli, M.; Colzani, L.; Clerici, L.; Dellavedova, P. Online solid-phase extraction LC-MS/MS: A rapid and valid method for the determination of perfluorinated compounds at sub ng.L-1 level in natural water. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 3780825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Xian, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Bai, W.; Zeng, X. Analysis of heterocyclic aromatic amine profiles in Chinese traditional bacon and sausage based on ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-Orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS). Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Spiked Concentration (μg·kg-1) | Mean Recovery (%) | Inter-RSD (%) | Intra-RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatopancreas | 20 | 83.8 | 8.0 | 8.1 |
| 200 | 89.1 | 2.4 | 3.7 | |
| 1000 | 90.5 | 2.0 | 2.9 | |
| 4000 | 87.5 | 2.2 | 4.5 | |
| Abdominal muscle | 20 | 82.2 | 3.7 | 5.0 |
| 200 | 108.0 | 1.4 | 1.9 | |
| 1000 | 106.7 | 2.0 | 2.7 | |
| 4000 | 101.3 | 3.1 | 3.2 |
| Treatment Time (h) | MAD in Muscle (μg·kg−1) | MAD in Hepatopancreas (μg·kg−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | Low | High | ||
| Absorption phase | 2 | 35.22 ± 10.71 | 47.13 ± 11.89 | 87.65 ± 30.52 | 110.96 ± 73.00 |
| 6 | 40.41 ± 5.31 | 58.13 ± 10.26 | 107.73 ± 31.92 | 207.89 ± 48.36 | |
| 12 | 56.13 ± 22.85 | 65.25 ± 10.58 | 185.99 ± 50.17 | 362.86 ± 72.63 | |
| 24 | 49.47 ± 6.77 | 62.49 ± 9.71 | 280.89 ± 101.45 | 541.56 ± 158.18 | |
| 48 | 69.75 ± 23.44 | 115.45 ± 18.09 | 369.10 ± 101.09 | 672.21 ± 134.29 | |
| 72 | 75.63 ± 7.32 | 105.12 ± 37.01 | 364.90 ± 49.31 | 689.55 ± 162.84 | |
| Elimination phase | 12 | 42.24 ± 19.48 | 51.80 ± 17.85 | 150.90 ± 59.66 | 224.04 ± 80.48 |
| 24 | 33.57 ± 17.27 | 47.83 ± 11.32 | 135.20 ± 44.72 | 245.01 ± 146.22 | |
| 36 | 29.31 ± 9.66 | 46.58 ± 10.14 | 73.17 ± 24.25 | 152.05 ± 51.54 | |
| 72 | ND | 20.80 ± 0.54 | 30.12 ± 8.40 | 68.29 ± 32.94 | |
| 120 | ND | ND | 28.89 ± 5.33 | 31.91 ± 7.39 | |
| 144 | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Group | Sample | MRLs (μg·kg−1) | WT (°C·d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low MAD (3.5 mg·L−1) | Hepatopancreas | 600 | 4.6 |
| Abdominal muscle | 200 | -- | |
| High MAD (7 mg·L−1) | Hepatopancreas | 600 | 25.8 |
| Abdominal muscle | 200 | -- |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Teng, P.; Peng, L.; Ji, H.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, D.; Jiang, S. Development and Validation of an Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method to Determine Maduramicin in Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) and Evaluate Food Safety. Foods 2021, 10, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020301
Gao X, Teng P, Peng L, Ji H, Qiu Y, Liu X, Guo D, Jiang S. Development and Validation of an Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method to Determine Maduramicin in Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) and Evaluate Food Safety. Foods. 2021; 10(2):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020301
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xiuge, Pei Teng, Lin Peng, Hui Ji, Yawei Qiu, Xiaoxiao Liu, Dawei Guo, and Shanxiang Jiang. 2021. "Development and Validation of an Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method to Determine Maduramicin in Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) and Evaluate Food Safety" Foods 10, no. 2: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020301
APA StyleGao, X., Teng, P., Peng, L., Ji, H., Qiu, Y., Liu, X., Guo, D., & Jiang, S. (2021). Development and Validation of an Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method to Determine Maduramicin in Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) and Evaluate Food Safety. Foods, 10(2), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020301








