Fermentation of Lupin Protein Hydrolysates—Effects on Their Functional Properties, Sensory Profile and the Allergenic Potential of the Major Lupin Allergen Lup an 1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Chemicals
2.1.1. Lupin Seeds
2.1.2. Enzymes
2.1.3. Strain Selection
2.1.4. Nutrient Media
2.2. Preparation of Lupin Protein Isolate
2.3. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of LPI
2.4. Fermentation of Hydrolysed LPI
2.5. Chemical Composition
2.6. Molecular Weight Distribution
2.7. Determination of Lup an 1 with Specific Monoclonal Antibodies
2.8. Technofunctional Properties
2.8.1. Protein Solubility
2.8.2. Foaming Properties
2.8.3. Emulsifying Capacity
2.9. Sensory Analysis of Fermented Hydrolysates
2.9.1. Panelists
2.9.2. Descriptive Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Properties
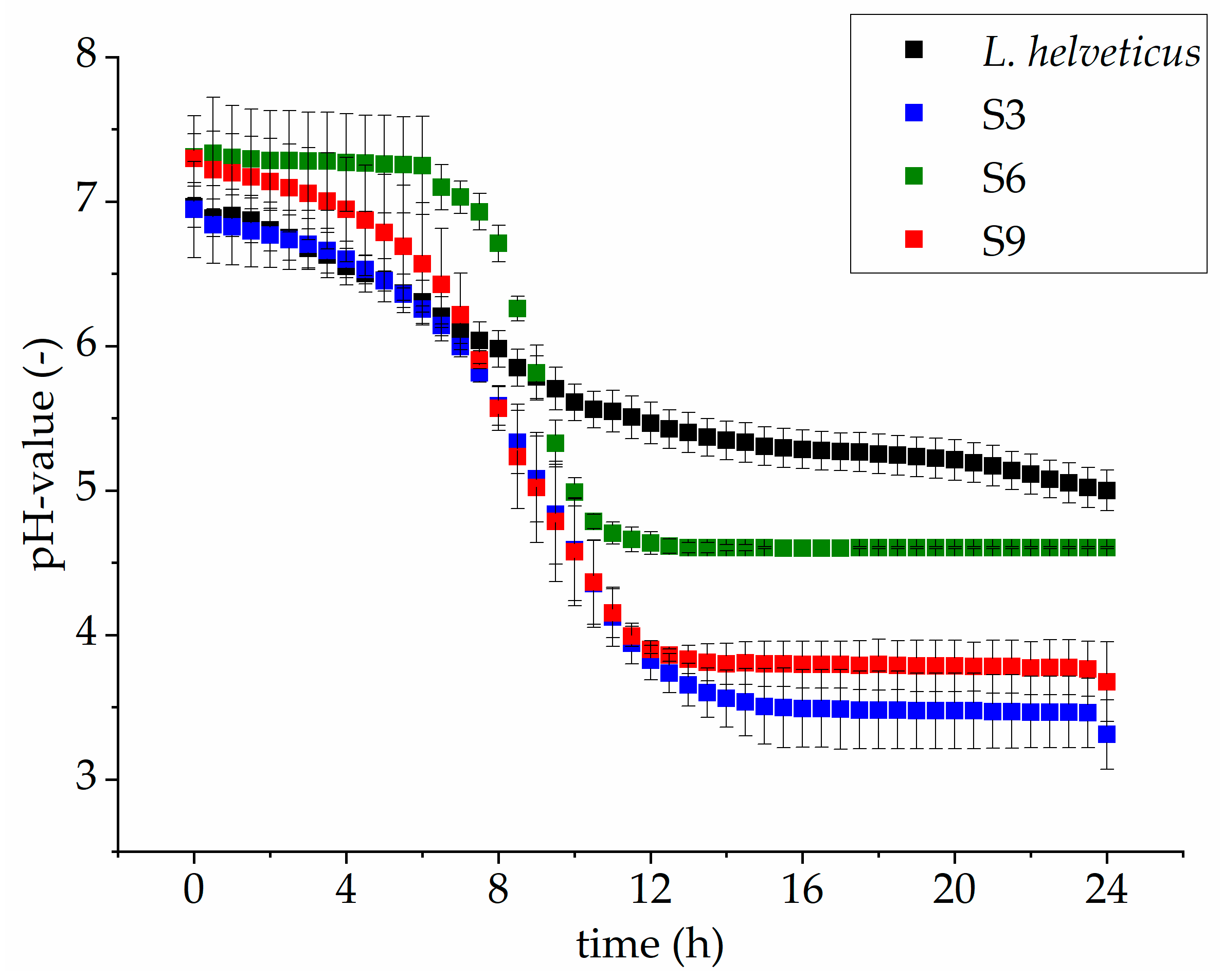
3.2. Comparison of Microbial Growth on Lupin Protein Isolate Solutions
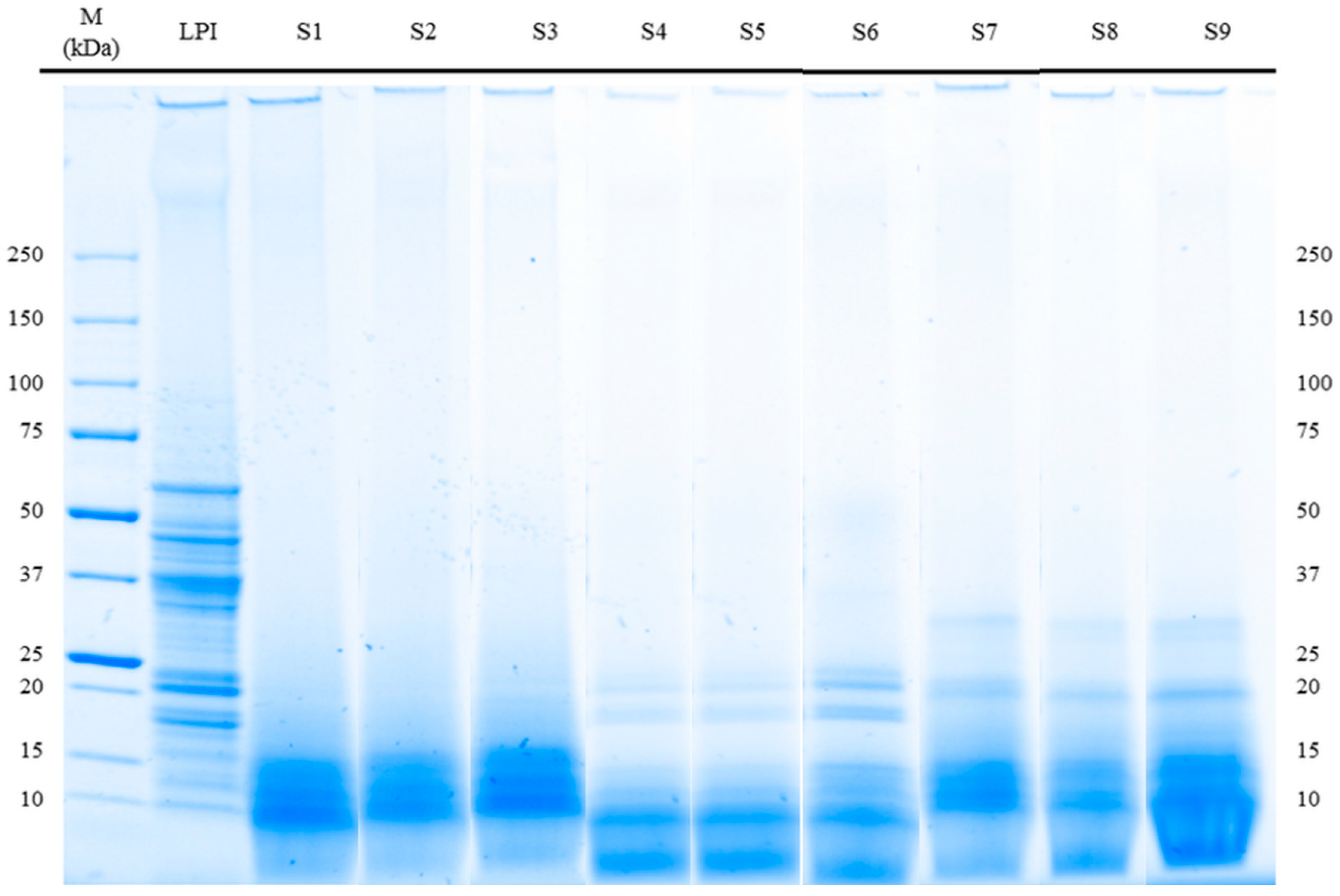
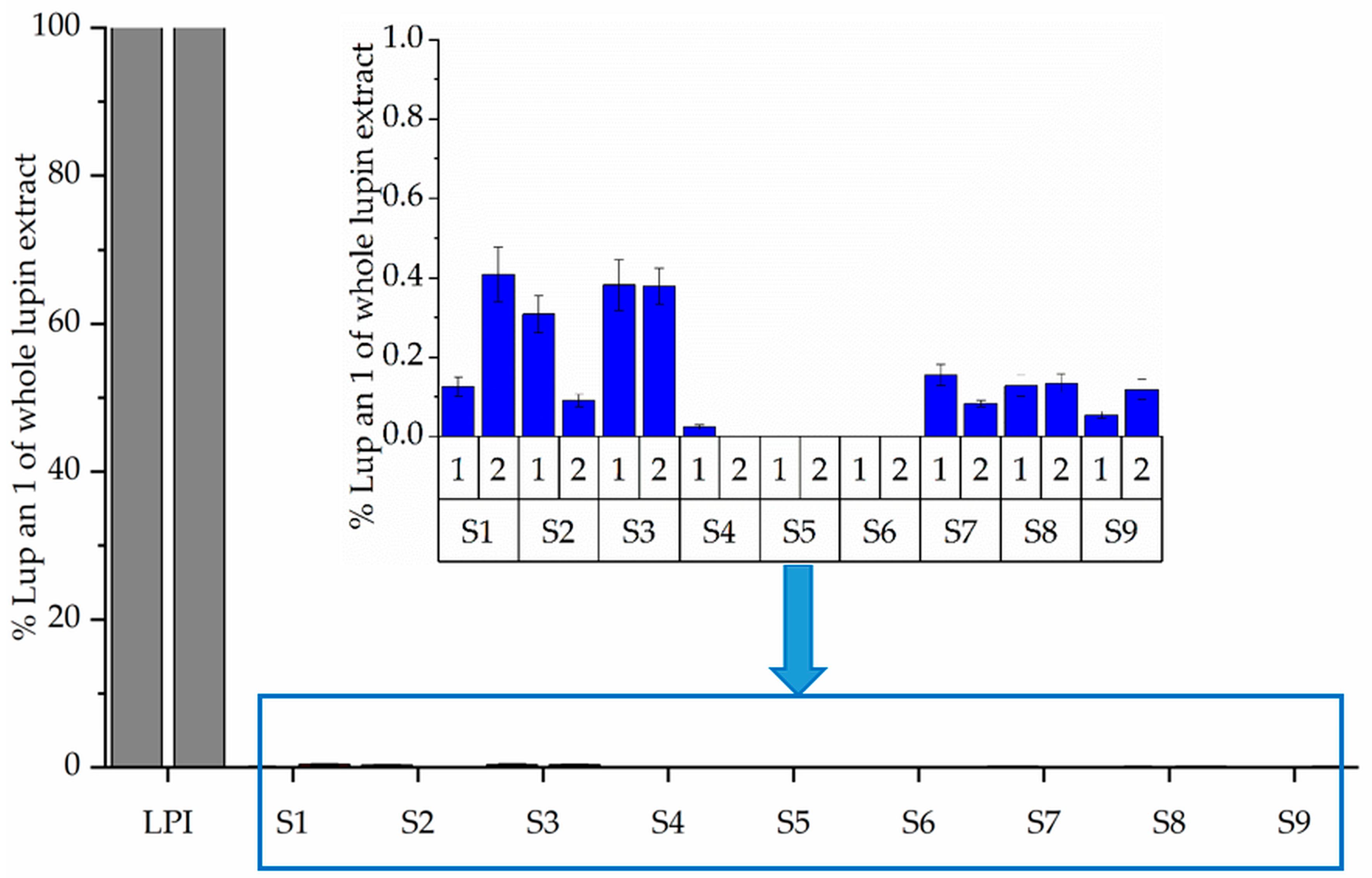
3.3. Molecular Weight Distribution (SDS-PAGE) and Immunoreactivity
3.4. Technofunctional Properties
3.4.1. Protein Solubility
3.4.2. Foaming Properties
3.4.3. Emulsifying Capacity
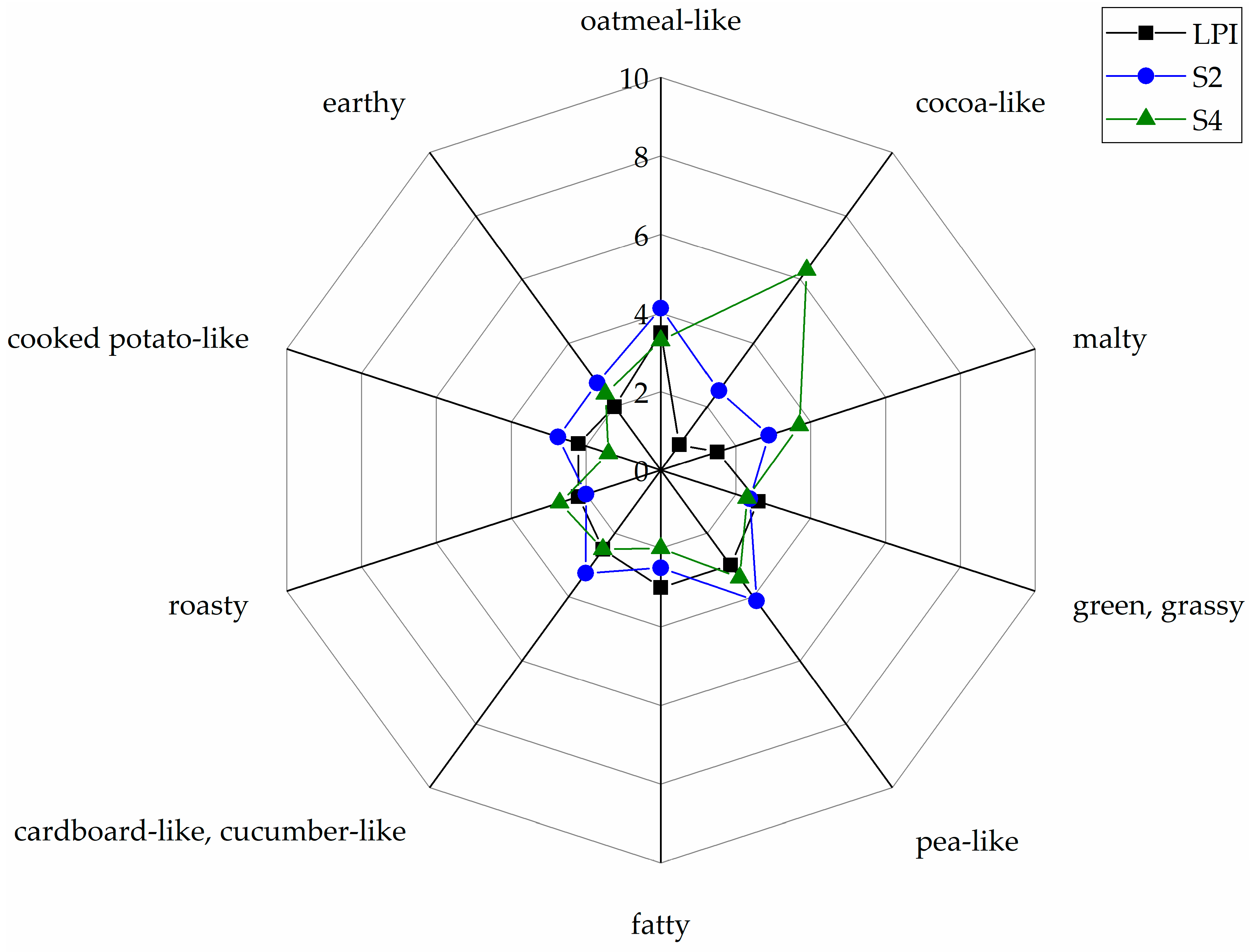
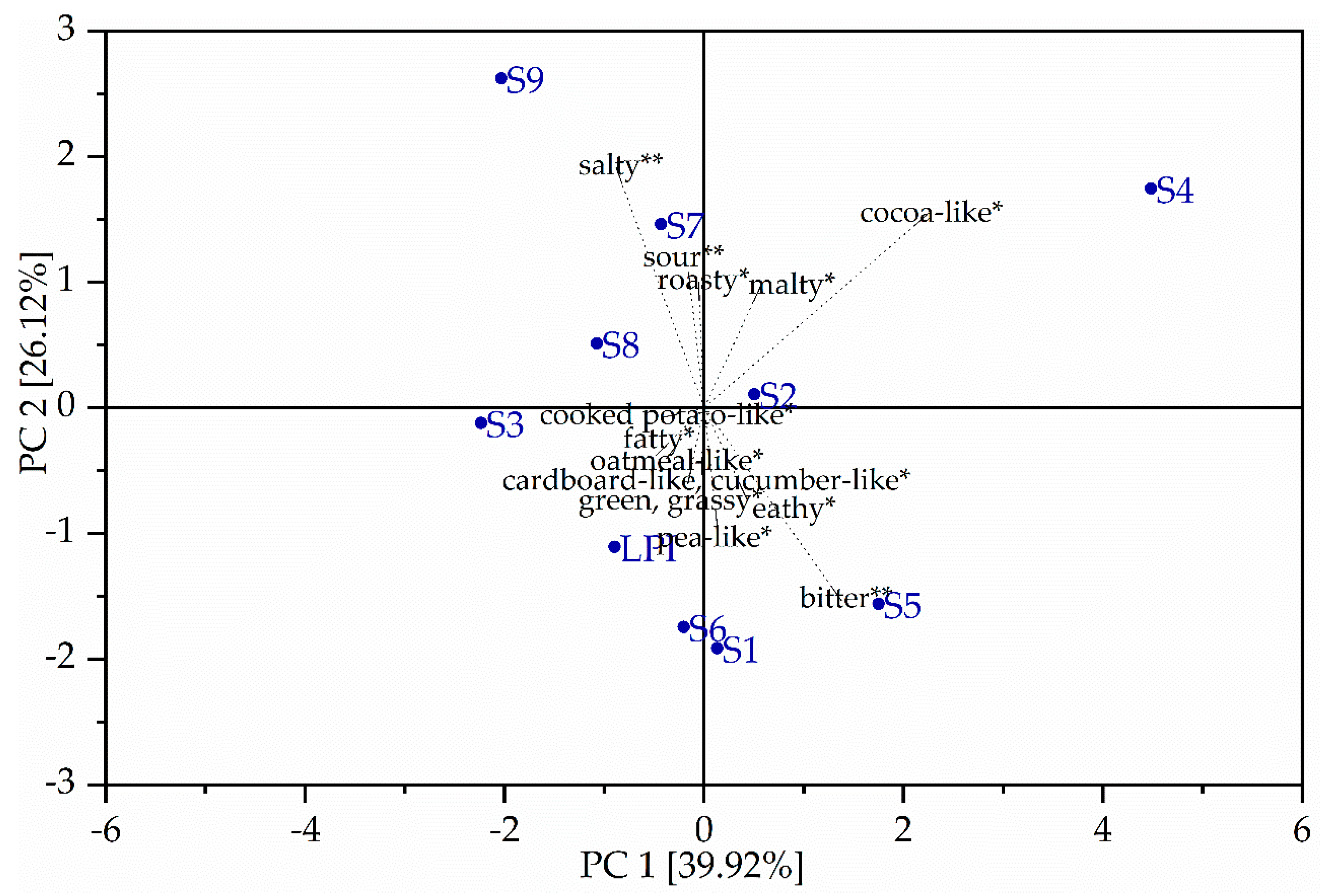
3.5. Sensory Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Word Population Prospects—The 2019 Revision; Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2020.
- Eshel, G.; Shepon, A.; Makov, T.; Milo, R. Land, irrigation water, greenhouse gas, and reactive nitrogen burdens of meat, eggs, and dairy production in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11996–12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bähr, M.; Fechner, A.; Hasenkopf, K.; Mittermaier, S.; Jahreis, G. Chemical composition of dehulled seeds of selected lupin cultivars in comparison to pea and soya bean. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, S.; Oviedo, J.P.; Pickardt, C.; Eisner, P. Influence of different organic solvents on the functional and sensory properties of lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) proteins. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purschke, B.; Meinlschmidt, P.; Horn, C.; Rieder, O.; Jäger, H. Improvement of techno-functional properties of edible insect protein from migratory locust by enzymatic hydrolysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinlschmidt, P.; Sussmann, D.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Eisner, P. Enzymatic treatment of soy protein isolates: Effects on the potential allergenicity, technofunctionality, and sensory properties. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 4, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel, K.; Sontheimer, K.; Hickisch, A.; Wani, A.A.; Eisner, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. Enzymatic hydrolysis of lupin protein isolates—Changes in the molecular weight distribution, technofunctional characteristics and sensory attributes. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2747–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, N.; Mohammadzadeh Milani, J.; Biparva, P. Functional and conformational properties of proteolytic enzyme-modified potato protein isolate. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klost, M.; Drusch, S. Functionalisation of pea protein by tryptic hydrolysis—Characterisation of interfacial and functional properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 86, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, K.; Sontheimer, K.; Eisner, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. Effect of enzyme-assisted hydrolysis on protein pattern, technofunctional, and sensory properties of lupin protein isolates using enzyme combinations. Food Sci. Nutri 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Tan, Y.; Chang, S.; Li, J.; Maleki, S.; Puppala, N. Peanut allergen reduction and functional property improvement by means of enzymatic hydrolysis and transglutaminase crosslinking. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lqari, H.; Pedroche, J.; Girón-Calle, J.; Vioque, J.; Millán, F. Production of Lupinus angustifolius protein hydrolysates with improved functional properties. Grasas y Aceites 2005, 56, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, S.; Wittig, M.; Zelena, K.; Krings, U.; Bez, J.; Eisner, P.; Berger, R.G. Lactic fermentation to improve the aroma of protein extracts of sweet lupin (Lupinus angustifolius). Food Chem. 2011, 128, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, S.; Zelena, K.; Krings, U.; Bez, J.; Eisner, P.; Berger, R.G. Improvement of the Aroma of Pea (Pisum sativum) Protein Extracts by Lactic Acid Fermentation. Food Biotechnol. 2012, 26, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, K.; Leidigkeit, A.; Eisner, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. Technofunctional and Sensory Properties of Fermented Lupin Protein Isolates. Foods 2019, 8, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosse, J.; Huet, J.-C.; Baudet, J. Relationships between nitrogen, amino acids and storage proteins in Lupinus albus seeds. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 2453–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morr, C.V.; German, B.; Kinsella, J.E.; Regenstein, J.M.; Vanburen, J.P.; Kilara, A.; Lewis, B.A.; Mangino, M.E. A Collaborative Study to Develop a Standardized Food Protein Solubility Procedure. J. Food Sci. 1985, 50, 1715–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, L.G.; Haque, Z.; Kinsella, J.E. A Method for the Measurement of Foam Formation and Stability. J. Food Sci. 1987, 52, 1074–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Johnson, L.A. Functional properties of hydrothermally cooked soy protein products. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goggin, D.E.; Mir, G.; Smith, W.B.; Stuckey, M.; Smith, P.A.C. Proteomic analysis of lupin seed proteins to identify conglutin beta as an allergen, Lup an 1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6370–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sormus de Castro Pinto, S.E.; Neves, V.A.; Machado de Medeiros, B.M. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Sweet Lupin, Chickpea, and Lentil 11S Globulins Decreases their Antigenic Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Bu, G.; Chen, F. The influence of composite enzymatic hydrolysis on the antigenicity of β-conglycinin in soy protein hydrolysates. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasera, R.; Singh, A.B.; Lavasa, S.; Prasad, K.N.; Arora, N. Enzymatic hydrolysis: A method in alleviating legume allergenicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 76, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinlschmidt, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Eisner, P. Soy protein hydrolysates fermentation: Effect of debittering and degradation of major soy allergens. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Arteaga, V.; Apestegui, M.; Muranyi, I.; Eisner, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on molecular weight distribution, techno-functional properties and sensory perception of pea protein isolates. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 65, 102449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muranyi, I.S.; Otto, C.; Pickardt, C.; Osen, R.; Koehler, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. Influence of the Isolation Method on the Technofunctional Properties of Protein Isolates from Lupinus angustifolius L. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, C2656–C2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelsang-O’Dwyer, M.; Bez, J.; Petersen, I.; Joehnke, M.; Detzel, A.; Busch, M.; Krueger, M.; Ispiryan, L.; O’Mahony, J.; Arendt, E.; et al. Techno-Functional, Nutritional and Environmental Performance of Protein Isolates from Blue Lupin and White Lupin. Foods 2020, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klupsaite, D.; Juodeikiene, G.; Zadeike, D.; Bartkiene, E.; Maknickiene, Z.; Liutkute, G. The influence of lactic acid fermentation on functional properties of narrow-leaved lupine protein as functional additive for higher value wheat bread. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumura, K.; Saito, T.; Tsuge, K.; Ashida, H.; Kugimiya, W.; Inouye, K. Functional properties of soy protein hydrolysates obtained by selective proteolysis. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 38, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Adawy, T.A.; Rahma, E.H.; El-Bedawey, A.A.; Gafar, A.F. Nutritional potential and functional properties of sweet and bitter lupin seed protein isolates. Food Chem. 2001, 74, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Enzyme | Type | Biological Source | Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Papain | cysteine endopeptidase | Papaya (Carica sp.) latex | AppliChem GmbH (Darmstadt, Germany) |
| Alcalase 2.4 L FG | serine endopeptidase | Bacillus licheniformis | Novozymes A/S (Bagsvaerd, Denmark) |
| Pepsin | aspartic endopeptidase | Porcine (Sus domesticus) gastric mucosa | Merck KGaA(Darmstadt, Germany) |
| System | E/S (%) 1 | Temperature (°C) | pH Value (-) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Papain | 0.2 | 80 | 7.0 | |
| S1 | Lactobacillus sakei ssp. carnosus | |||
| S2 | Lactobacillus amylolyticus | |||
| S3 | Lactobacillus helveticus | |||
| Alcalase 2.4 L | 0.5 | 50 | 8.0 | |
| S4 | Lactobacillus sakei ssp. carnosus | |||
| S5 | Lactobacillus amylolyticus | |||
| S6 | Lactobacillus helveticus | |||
| Pepsin | 0.5 | 50 | 2.0 | |
| S7 | Lactobacillus sakei ssp. carnosus | |||
| S8 | Lactobacillus amylolyticus | |||
| S9 | Lactobacillus helveticus | |||
| Samples | Dry Matter (%) | Protein Content (%) | Ash Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPI | 95.4 ± 0.0 | 89.6 ± 0.0 | 4.2 ± 0.12 |
| Papain | |||
| S1 | 93.8 ± 0.0 * | 74.7 ± 2.5 | 6.7 ± 0.9 |
| S2 | 93.6 ± 0.2 * | 78.7 ± 2.0 | 5.4 ± 0.6 |
| S3 | 93.1 ± 0.0 * | 66.8 ± 0.0 * | 6.5 ± 1.1 |
| Alcalase 2.4 L | |||
| S4 | 92.8 ± 0.2 * | 74.8 ± 0.6 * | 6.2 ± 0.9 * |
| S5 | 93.5 ± 0.3 * | 75.6 ± 1.3 * | 5.3 ± 0.4 |
| S6 | 93.0 ± 0.2 * | 77.2 ± 5.6 | 7.4 ± 0.1 * |
| Pepsin | |||
| S7 | 94.0 ± 0.0 * | 73.1 ± 5.9 | 7.1 ± 0.4 |
| S8 | 93.9 ± 0.1 * | 78.0 ± 1.5 | 6.3 ± 0.6 |
| S9 | 93.7 ± 0.2 * | 72.2 ± 4.5 | 8.8 ± 0.7 * |
| Samples | CFU/mL | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 24 h | ΔECFU/mL | |
| Papain | |||
| S1 | 2.25 × 107 ± 2.12 × 106 | 4.86 × 108 ± 7.85 × 107 | 4.63 × 108 ± 8.06 × 107 |
| S2 | 1.03 × 107 ± 1.20 × 106 | 1.03 × 109 ± 1.41 × 107 | 1.02 × 109 ± 1.29 × 107 |
| S3 | 6.45 × 106 ± 1.30 × 106 | 2.10 × 108 ± 5.21 × 107 | 2.03 × 108 ± 5.09 × 107 |
| Alcalase 2.4 L | |||
| S4 | 1.26 × 107 ± 1.91 × 106 | 1.30 × 109 ± 7.21 × 108 | 1.29 × 109 ± 7.23 × 108 |
| S5 | 1.36 × 107 ± 1.41 × 106 | 1.23 × 109 ± 3.56 × 108 | 1.21 × 109 ± 3.54 × 108 |
| S6 | 8.45 × 106 ± 1.53 × 106 | 3.62 × 108 ± 1.63 × 108 | 3.54 × 108 ± 1.61 × 108 |
| Pepsin | |||
| S7 | 7.01 × 106 ± 1.34 × 105 | 1.97 × 108 ± 1.91 × 107 | 1.89 × 108 ± 1.90 × 107 |
| S8 | 1.14 × 107 ± 2.88 × 106 | 1.34 × 109 ± 2.62 × 108 | 1.32 × 109 ± 2.59 × 108 |
| S9 | 1.06 × 107 ± 2.12 × 106 | 1.12 × 108 ± 6.48 × 107 | 1.02 × 108 ± 6.70 × 107 |
| Samples | pH-Values | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 24 h | |
| Papain | ||
| S1 | 7.1 ± 0.1 | 4.6 ± 0.1 |
| S2 | 7.1 ± 0.0 | 4.9 ± 0.1 |
| S3 | 6.9 ± 0.3 | 3.3 ± 0.2 |
| Alcalase 2.4 L | ||
| S4 | 7.1 ± 0.0 | 5.1 ± 0.0 |
| S5 | 7.0 ± 0.1 | 4.8 ± 0.1 |
| S6 | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 4.9 ± 0.4 |
| Pepsin | ||
| S7 | 7.0 ± 0.0 | 4.9 ± 0.1 |
| S8 | 7.1 ± 0.0 | 4.9 ± 0.0 |
| S9 | 7.3 ± 0.2 | 3.7 ± 0.3 |
| Samples | Protein Solubility | Foaming Activity | Foam Stability | Emulsifying Capacity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 4.0 | pH 7.0 | pH 4.0 | pH 7.0 | pH 4.0 | pH 7.0 | pH 4.0 | pH 7.0 | |
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | |
| LPI | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 63.6 ± 3.0 | 828 ± 3 | 1613 ± 11 | 92 ± 1 | 89 ± 0 | 410 ± 7 | 666 ± 0 |
| Papain | ||||||||
| S1 | 24.8 ± 3.2 * | 53.3 ± 7.7 | 2118 ± 47 * | 2544 ± 39 * | 0 ± 0 * | 1 ± 0 * | 350 ± 21 | 393 ± 15 * |
| S2 | 19.7 ± 2.4 * | 45.2 ± 10.7 | 1819 ± 38 * | 2606 ± 53 * | 0 ± 0 * | 38 ± 8 * | 340 ± 0 * | 432 ± 65 * |
| S3 | 36.7 ± 3.0 * | 66.6 ± 6.9 | 2395 ± 45 * | 2505 ± 54 * | 0 ± 0 * | 29 ± 6 * | 415 ± 28 | 432 ± 9 * |
| Alcalase 2.4 L | ||||||||
| S4 | 23.4 ± 4.6 * | 60.4 ± 9.3 | 2458 ± 58 * | 2466 ± 54 * | 0 ± 0 * | 96 ± 3 | 358 ± 32 | 246 ± 28 * |
| S5 | 25.6 ± 8.8 * | 55.0 ± 7.9 | 2766 ± 54 * | 2676 ± 56 * | 0 ± 0 * | 96 ± 2 * | 258 ± 18 | 283 ± 30 * |
| S6 | 27.3 ± 1.7 * | 46.0 ± 3.8 * | 2789 ± 28 * | 2721 ± 91 | 0 ± 0 * | 0 ± 0 * | 429 ± 8 * | 323 ± 3 * |
| Pepsin | ||||||||
| S7 | 25.7 ± 5.0 * | 57.5 ± 12.2 | 1819 ± 51 * | 3338 ± 71 * | 0 ± 0 * | 41 ± 1 * | 400 ± 35 | 477 ± 16 * |
| S8 | 24.0 ± 2.1 * | 56.8 ± 6.3 | 1993 ± 46 * | 3481 ± 39 * | 0 ± 0 * | 90 ± 4 | 400 ± 7 * | 439 ± 5 * |
| S9 | 25.6 ± 2.7 * | 55.7 ± 11.9 | 2001 ± 40 * | 3443 ± 51 * | 0 ± 0 * | 7 ± 1 * | 405 ± 0 | 417 ± 6 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schlegel, K.; Lidzba, N.; Ueberham, E.; Eisner, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. Fermentation of Lupin Protein Hydrolysates—Effects on Their Functional Properties, Sensory Profile and the Allergenic Potential of the Major Lupin Allergen Lup an 1. Foods 2021, 10, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020281
Schlegel K, Lidzba N, Ueberham E, Eisner P, Schweiggert-Weisz U. Fermentation of Lupin Protein Hydrolysates—Effects on Their Functional Properties, Sensory Profile and the Allergenic Potential of the Major Lupin Allergen Lup an 1. Foods. 2021; 10(2):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020281
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchlegel, Katharina, Norbert Lidzba, Elke Ueberham, Peter Eisner, and Ute Schweiggert-Weisz. 2021. "Fermentation of Lupin Protein Hydrolysates—Effects on Their Functional Properties, Sensory Profile and the Allergenic Potential of the Major Lupin Allergen Lup an 1" Foods 10, no. 2: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020281
APA StyleSchlegel, K., Lidzba, N., Ueberham, E., Eisner, P., & Schweiggert-Weisz, U. (2021). Fermentation of Lupin Protein Hydrolysates—Effects on Their Functional Properties, Sensory Profile and the Allergenic Potential of the Major Lupin Allergen Lup an 1. Foods, 10(2), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020281







