A Novel Process for the Recovery of Betalains from Unsold Red Beets by Low-Temperature Enzyme-Assisted Extraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Red Beet
2.2. Enzymes and Chemicals
2.3. Red Beet Analysis
2.3.1. Chemico-Physical Parameters
2.3.2. Total Sugar Content
2.3.3. Cell Wall Polysaccharide Composition
2.4. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Betalains
2.5. Determination of Betalain Content
2.6. Color Measurements
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemico-Physical Properties of Red Beets and Optimization of the Extraction Conditions
3.2. Influence of Different Enzyme Mix Dosages, Processing Times, and Temperatures on Betalain Extraction
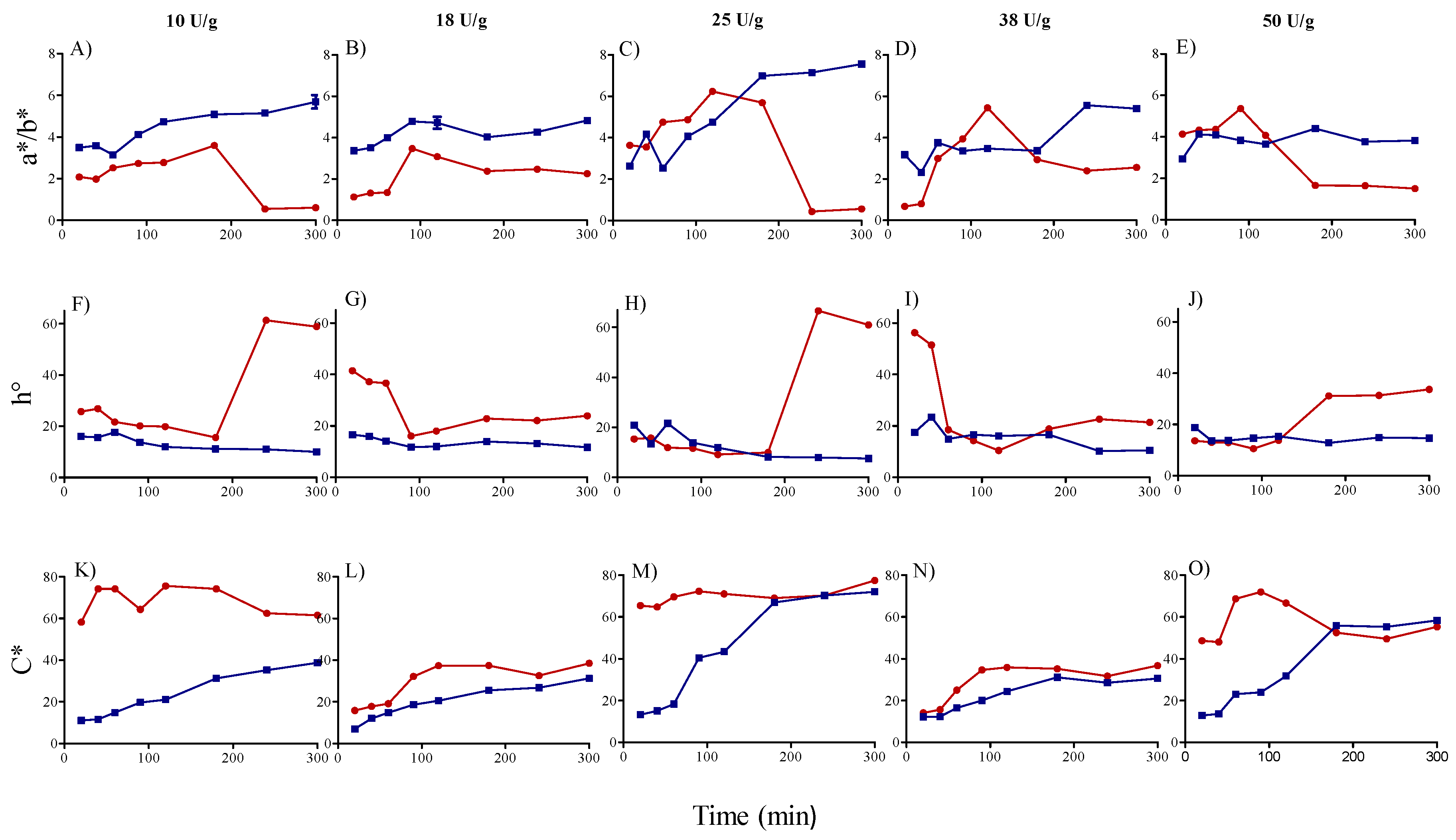
3.3. Color Characterization of Betalain Extracts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cerreti, M.; Liburdi, K.; Del Franco, F.; Esti, M. Heat and light stability of natural yellow colourants in model beverage systems. Food Addit. Contam. 2020, 37, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, R.; Luna-Vital, D.A.; Margulis, D.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Natural pigments: Stabilization methods of anthocyanins for food applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F 2017, 16, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, P.; Kaur, C.; Rudra, S.G.; Varghese, E. Enzyme-assisted extraction of carotenoid-rich extract from red capsicum (Capsicum annuum). Agric. Res. 2016, 5, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, A. Food Colors Market by Type (Natural, Synthetic, Nature-Identical), Application (Beverages, Processed Food, Bakery & Confectionery Products, Oils & Fats, Dairy Products, Meat, Poultry, Seafood), Form, Solubility, and Region-Global Forecast to 2023. 2018. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/food-colors-market-36725323.html (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Lombardelli, C.; Liburdi, K.; Benucci, I.; Esti, M. Tailored and synergistic enzyme-assisted extraction of carotenoid-containing chromoplasts from tomatoes. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 121, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdson, G.T.; Tang, P.; Giusti, M.M. Natural colorants: Food colorants from natural sources. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. T 2017, 8, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Santiago, E.; Yahia, E.M. Identification and quantification of betalains from the fruits of 10 Mexican prickly pear cultivars by high-performance liquid chromatography and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5758–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esatbeyoglu, T.; Wagner, A.E.; Schini-Kerth, V.B.; Rimbach, G. Betanin—A food colorant with biological activity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, E.A.; Sadiq, Z.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M. Bioavailability of betalains. In Betalains: Biomolecular Aspects; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 165–183. [Google Scholar]
- Gandía-Herrero, F.; García-Carmona, F. Biosynthesis of betalains: Yellow and violet plant pigments. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellar, M.R.; Obon, J.M.; Fernandez-Lopez, J.A. The isolation and properties of a concentrated red-purple betacyanin food colourant from Opuntia stricta fruits. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz, C.; Cancino, B.; Robert, P. Red betalains from Opuntia spp.: Natural colorants with potential applications in foods. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 60, 291–299. [Google Scholar]
- Ciriminna, R.; Fidalgo, A.; Danzì, C.; Timpanaro, G.; Ilharco, L.M.; Pagliaro, M. Betanin: A bioeconomy insight into a valued betacyanin. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2860–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeredo, H.M. Betalains: Properties, sources, applications, and stability–a review. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2009, 44, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Vargas, F.; Jimenez, A.R.; Paredes-Lopez, O. Natural pigments: Carotenoids, anthocyanins, and betalains -characteristics, biosynthesis, processing, and stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 173–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fincan, M.; DeVito, F.; Dejmek, P. Pulsed electric field treatment for solid–liquid extraction of red beetroot pigment. J. Food Eng. 2004, 64, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowbhagya, H.B.; Chitra, V.N. Enzyme-assisted extraction of flavorings and colorants from plant materials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, M.; Heidari, O.; Mohammadi Nafchi, A.R. Optimization of lycopene extraction from tomato waste with the integration of ultrasonic-enzymatic processes by response surface methodology. J. Ind. Eng. Int. 2015, 1, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Naderi, N.; Stintzing, F.C.; Ghazali, H.M.; Manap, Y.A.; Jazayeri, S.D. Betalain extraction from Hylocereus polyrhizus for natural food coloring purposes. J. Prof. Assoc. Cactus Dev. 2010, 12, 143–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ververis, C.; Georghiou, K.; Danielidis, D.; Hatzinikolaou, D.G.; Santas, P.; Santas, R.; Corleti, V. Cellulose, hemicelluloses, lignin and ash content of some organic materials and their suitability for use as paper pulp supplements. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desseva, I.; Stoyanova, M.; Petkova, N.; Mihaylova, D. Red Beetroot Juice Phytochemicals Bioaccessibility: An In Vitro Approach. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2020, 70, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, M.R.A.; Okina, V.S.; Pimentel, T.C.; Prudencio, S.H. Physicochemical stability, antioxidant activity, and acceptance of beet and orange mixed juice during refrigerated storage. Beverages 2017, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyn, J.W.; Van Keulen, H.A.; Ferguson, J.H.A. Rapid method for the simultaneous determination of glucose and fructose using anthrone reagent. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1968, 19, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, R.B. Diurnal changes in the sugar and organic anion concentrations in red beet leaves. Ann. Bot. 1972, 36, 475–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wruss, J.; Waldenberger, G.; Huemer, S.; Uygun, P.; Lanzerstorfer, P.; Müller, U.; Weghuber, J. Compositional characteristics of commercial beetroot products and beetroot juice prepared from seven beetroot varieties grown in Upper Austria. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 42, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Santiago, V.; Cavia, M.M.; Alonso-Torre, S.R.; Carrillo, C. Relationship between color and betalain content in different thermally treated beetroot products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3305–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onofri, A. Enhancing Excel capability to perform statistical analyses in agriculture applied research. In Computational Statistics and Data Analysis–Statistical Software Newsletters; International Association for Statistical Computing: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Montes-Lora, S.; Rodríguez-Pulido, F.J.; Cejudo-Bastante, M.J.; Heredia, F.J. Implications of the red beet ripening on the colour and betalain composition relationships. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2018, 73, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemiński, K.; Romanowska, I.; Kowalska, M. Enzymatic pretreatment of lignocellulosic wastes to improve biogas production. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnuolo, M.; Crecchio, C.; Pizzigallo, M.D.; Ruggiero, P. Fractionation of sugar beet pulp into pectin, cellulose, and arabinose by arabinases combined with ultrafiltration. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1999, 64, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M. Recovery of high added-value components from food wastes: Conventional, emerging technologies and commercialized applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Poddar, K.; Sarkar, D.; Kumari, N.; Padhan, B.; Sarkar, A. Fruit waste management by pigment production and utilization of residual as bioadsorbent. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamwonglumlert, L.; Devahastin, S.; Chiewchan, N. Natural colorants: Pigment stability and extraction yield enhancement via utilization of appropriate pretreatment and extraction methods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3243–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlíková, L.; Miková, K.; Kyzlink, V. Heat stability of betacyanins. Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch. 1983, 177, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, N.; Puértolas, E.; Condón, S.; Raso, J.; Alvarez, I. Enhancement of the extraction of betanine from red beetroot by pulsed electric fields. J. Food Eng. 2009, 90, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çinar, I. Effects of cellulase and pectinase concentrations on the colour yield of enzyme extracted plant carotenoids. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranveer, R.C.; Patil, S.N.; Sahoo, A.K. Effect of different parameters on enzyme-assisted extraction of lycopene from tomato processing waste. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dosage (U/g) | Color Parameter | Betalain Content (45 °C) | Betalain Content (25 °C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | a*/b* | −0.0968 | 0.8077 |
| h° | 0.3760 | −0.8050 | |
| C* | −0.0235 | 0.9505 | |
| 18 | a*/b* | 0.7539 | 0.6181 |
| h° | −0.8694 | −0.6557 | |
| C* | 0.9364 | 0.9612 | |
| 25 | a*/b* | 0.6607 | 0.9478 |
| h° | −0.1613 | −0.8823 | |
| C* | 0.6392 | 0.9802 | |
| 38 | a*/b* | 0.7576 | 0.8928 |
| h° | −0.8286 | −0.8043 | |
| C* | 0.873 | 0.9112 | |
| 50 | a*/b* | −0.4401 | 0.4122 |
| h° | 0.4852 | −0.4480 | |
| C* | −0.0059 | 0.9026 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lombardelli, C.; Benucci, I.; Mazzocchi, C.; Esti, M. A Novel Process for the Recovery of Betalains from Unsold Red Beets by Low-Temperature Enzyme-Assisted Extraction. Foods 2021, 10, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020236
Lombardelli C, Benucci I, Mazzocchi C, Esti M. A Novel Process for the Recovery of Betalains from Unsold Red Beets by Low-Temperature Enzyme-Assisted Extraction. Foods. 2021; 10(2):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020236
Chicago/Turabian StyleLombardelli, Claudio, Ilaria Benucci, Caterina Mazzocchi, and Marco Esti. 2021. "A Novel Process for the Recovery of Betalains from Unsold Red Beets by Low-Temperature Enzyme-Assisted Extraction" Foods 10, no. 2: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020236
APA StyleLombardelli, C., Benucci, I., Mazzocchi, C., & Esti, M. (2021). A Novel Process for the Recovery of Betalains from Unsold Red Beets by Low-Temperature Enzyme-Assisted Extraction. Foods, 10(2), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020236







