Effect of Moisture Distribution Changes Induced by Different Cooking Temperature on Cooking Quality and Texture Properties of Noodles Made from Whole Tartary Buckwheat
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Determination of Optimum Cooking Time
2.3. Color of the Tartary Buckwheat Noodles
2.4. Cooking Qualities of the Tartary Buckwheat Noodles
2.5. Texture Profiles of Tartary Buckwheat Noodles
2.6. Total Flavonoid Content (TFC) and Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.7. In Vitro Starch Digestibility
2.8. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR)
2.9. Microscopic Morphology
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
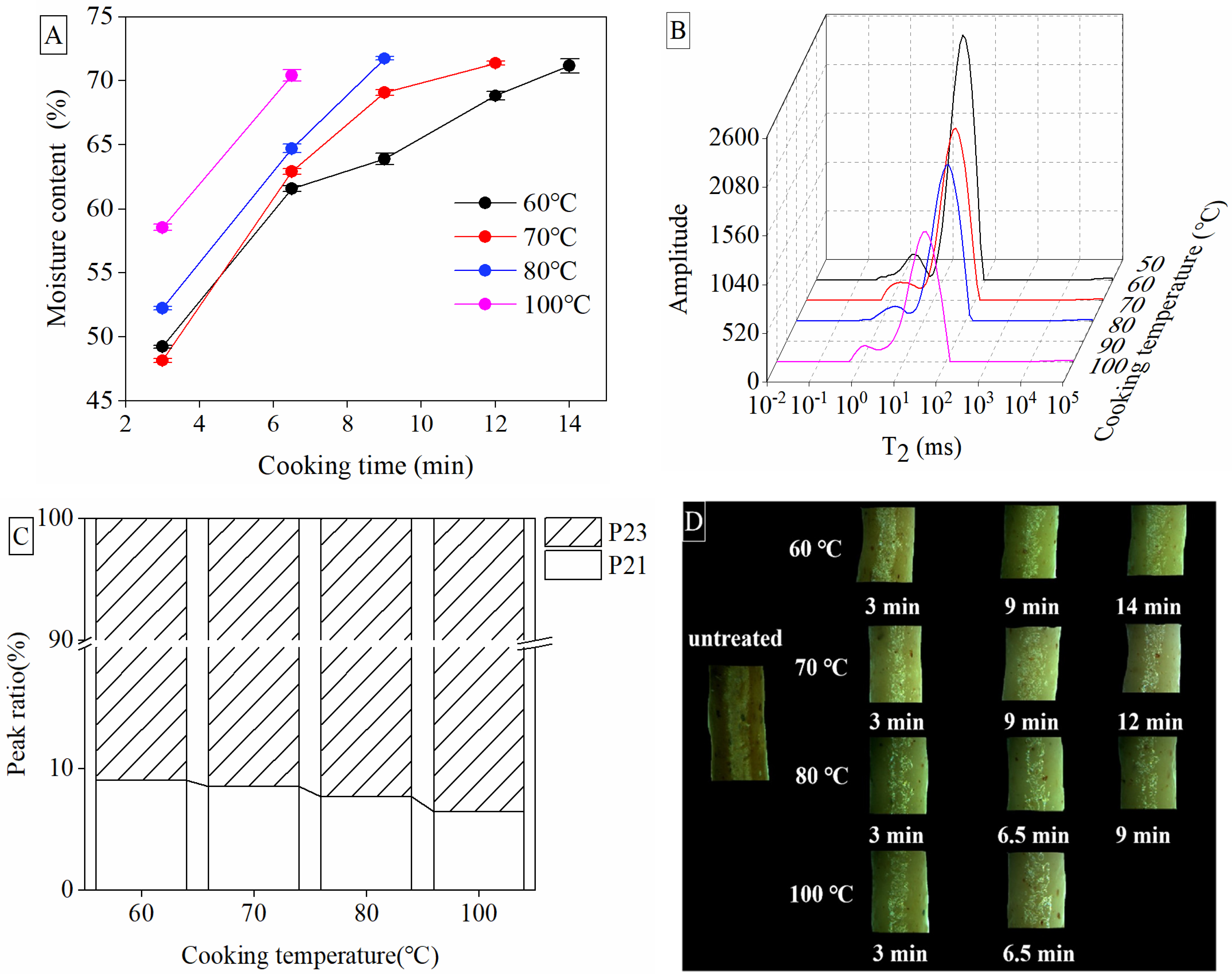
3.1. Optimum Time at Different Cooking Temperatures
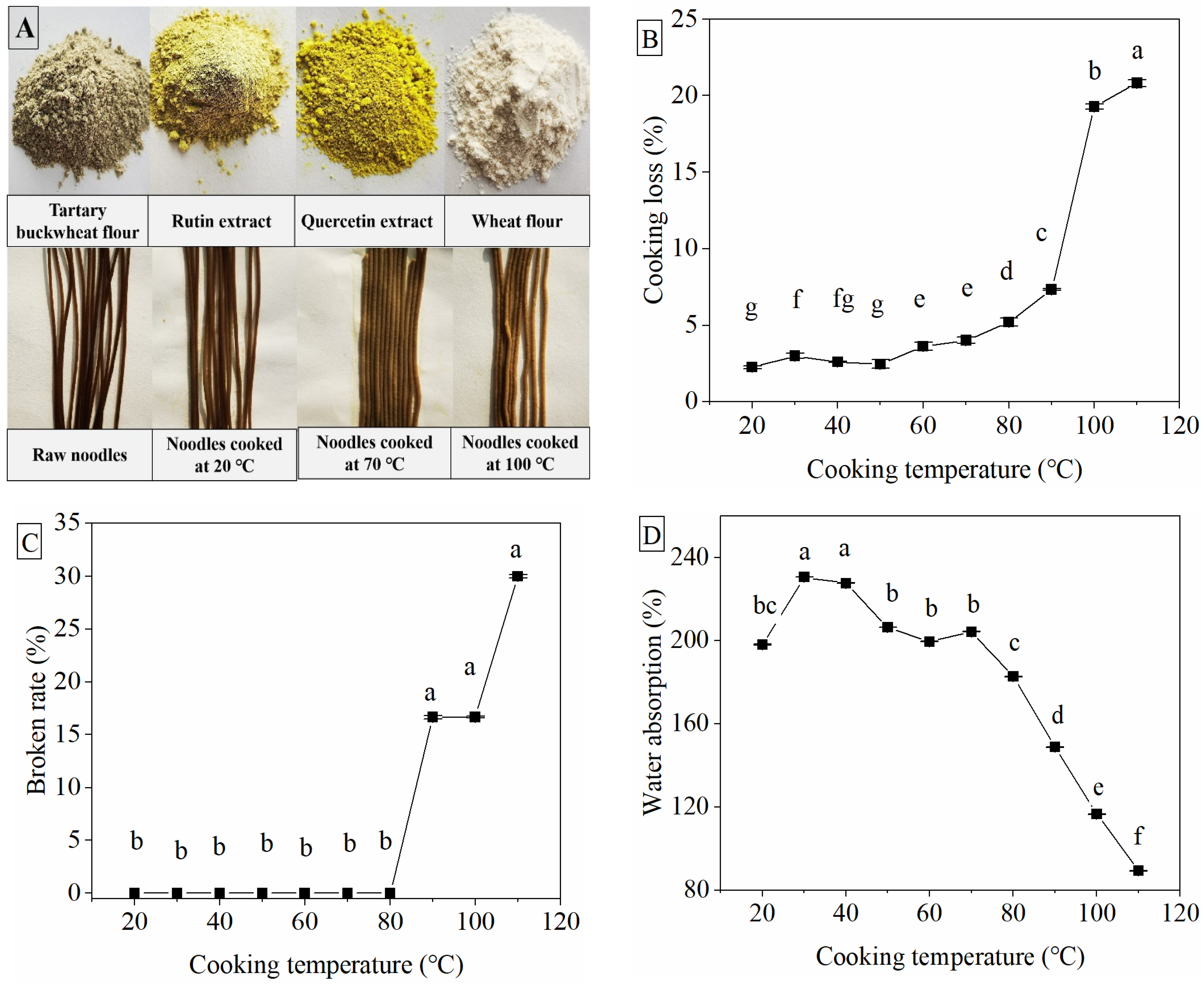
3.2. Effect of Cooking Temperature on Color and Cooking Qualities
3.3. Changes in Texture Profile Analysis of Noodles
3.4. Moisture Content and Water Distribution of Noodles during Cooking
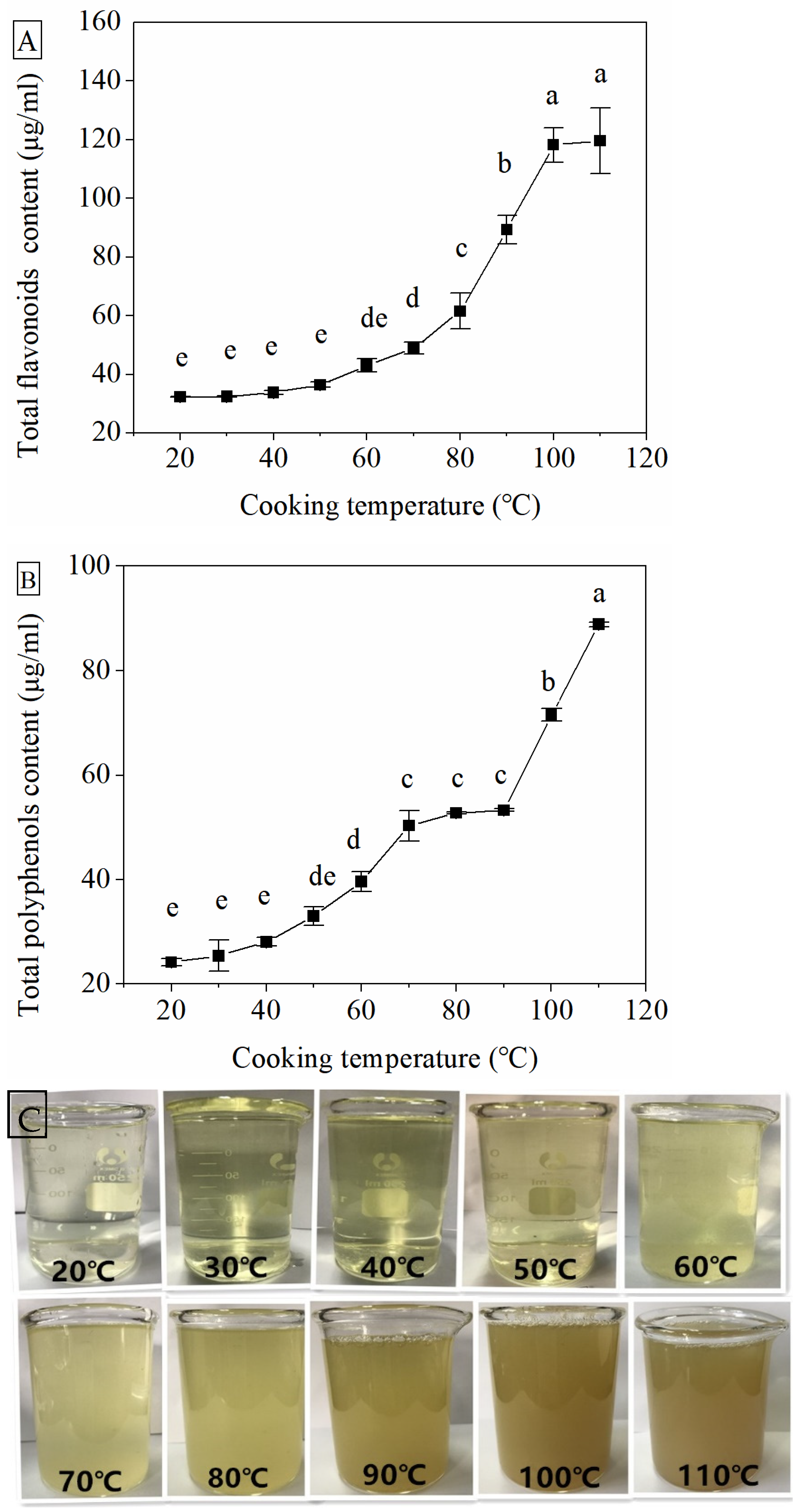
3.5. Effect of Cooking Temperature on Functional Properties
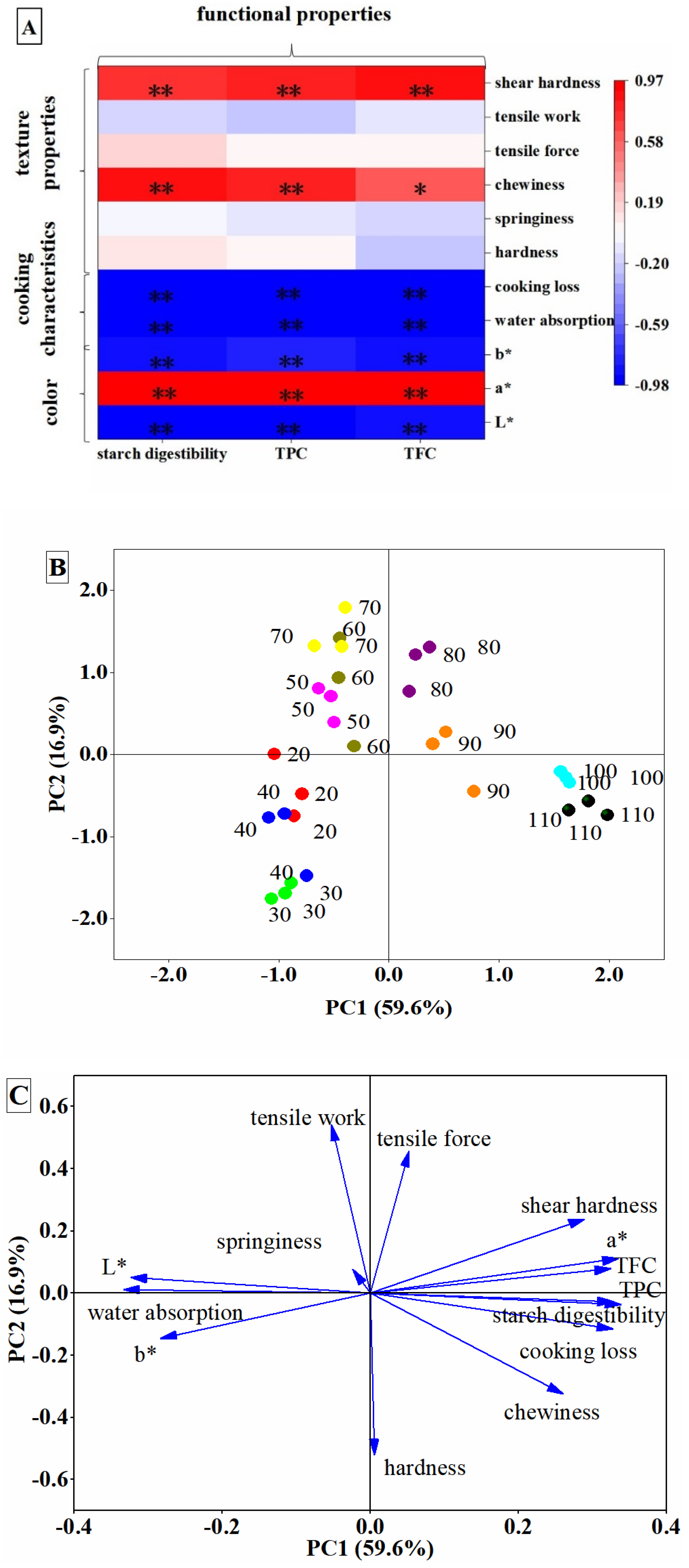
3.6. Association of Cooking Temperature with Noodle Qualities and Functional Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Ma, M.; Zhu, K.X.; Guo, X.N.; Zhou, H.M. Delineating the physico-chemical, structural, and water characteristic changes during the deterioration of fresh noodles understanding the deterioration mechanisms of fresh noodles. Food Chem. 2017, 216, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xing, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.; Wei, Y.M. Effect of mixing time on the structural characteristics of noodle dough under vacuum. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, S.; Petocz, P.; Duve, E.; Abbott, K.; Cassettari, T.; Blumfield, M.; Fayet-Moore, F. The effect of replacing refined grains with whole grains on cardiovascular risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials with GRADE clinical recommendation. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 120, 1859–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, I.; Ibrugger, S.; Bache, J.; Thomassen, M.T.; Contaldo, F.; Pasanisi, F.; Kristensen, M. Effects on satiation, satiety and food intake of wholegrain and refined grain pasta. Appetite 2016, 107, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Diet Collaborators. Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet 2019, 393, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.N.; Wei, X.M.; Zhu, K.X. The impact of protein cross-linking induced by alkali on the quality of buckwheat noodles. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Bastida, J.A.; Piskuła, M.; Zieliński, H. Recent advances in development of gluten-free buckwheat products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 44, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Duan, W.; Zhou, S.M.; Qian, H.F.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X.G. Effects of extrusion conditions on the extrusion responses and the quality of brown rice pasta. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouasla, A.; Wojtowicz, A.; Zidoune, M.N.; Olech, M.; Nowak, R.; Mitrus, M.; Oniszczuk, A. Gluten-free precooked rice-yellow pea pasta: Effect of extrusion-cooking conditions on phenolic acids composition, selected properties and microstructure. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, C1070–C1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, A.; Pagani, M.A. What can play the role of gluten in gluten free pasta? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.S.; Choi, E.J.; Kim, C.H.; Sung, J.M.; Kim, Y.B.; Seo, D.H.; Choi, H.W.; Choi, Y.S.; Kum, J.S.; Park, J.D. Contribution of flavonoids to the antioxidant properties of common and tartary buckwheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 68, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Liu, Y.P.; Yue, Y.F.; Qin, Y.C.; Li, Z.G. Dietary tartary buckwheat intake attenuates insulin resistance and improves lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Yu, C.; Fu, M.X.; Wu, D.; Gao, C.C.; Feng, X.; Cheng, W.W.; Shen, X.C.; Tang, X.Z. Extruded whole buckwheat noodles: Effects of processing variables on the degree of starch gelatinization, changes of nutritional components, cooking characteristics and in vitro starch digestibility. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6362–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, M.A.; González, R.J.; Wagner, J.; Torres, R.; Lobo, M.O.; Samman, N.C. Effect of extrusion conditions on physicochemical and sensorial properties of corn-broad beans (Vicia faba) spaghetti type pasta. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgila, D.; Baraka, S.; Khatkarb, B.S. Optimization of textural properties of noodles with soluble fiber, dough mixing time and different water levels. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 69, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, R.; Gao, J.; Ananingsih, V.K.; Ranawana, V.; Henry, C.J.; Zhou, W. Green tea catechins reduced the glycaemic potential of bread: An in vitro digestibility study. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.S.; Pan, Y.; Xie, Q.T.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H.Q. Evaluation studies on effects of pectin with different concentrations on the pasting, rheological and digestibility properties of corn starch. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, X.N.; Zhu, K.X. Effects of frozen storage on the quality characteristics of frozen cooked noodles. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.J.; Li, W.H.; Hu, Y.Y.; Zhou, X.J.; Ji, M.Y.; Yu, D.D.; Fujita, K.; Tatsumi, E.; Luan, G.Z. Comparison of pregelatinization methods on physicochemical, functional and structural properties of tartary buckwheat flour and noodle quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 80, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, A.L.; Morrison, P.D.; Hughes, J.G.; Marriott, P.J.; Small, D.M. Quality and antioxidant properties of instant noodles enhanced with common buckwheat flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 57, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.T.; Gao, X.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, K.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S. Effects of semidry flour milling on the quality attributes of rice flour and rice noodles China. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 62, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.B.; Li, M.; Chen, S.Q.; Hui, Y.; Tang, A.X.; Wei, Y.M. Effects of flour dynamic viscosity on the quality properties of buckwheat noodles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Nishijima, N.; Oda, Y.; Handa, A.; Majumder, K.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y. Utilization of egg white solids to improve the texture and cooking quality of cooked and frozen pasta. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 109031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, V.; Surasani, R. Quinoa protein isolate supplemented pasta: Nutritional, physical, textural and morphological characterization. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 135, 110045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.X.; Sun, X.Y.; Wu, D.; Meng, L.H.; Feng, X.; Cheng, W.W.; Gao, C.C.; Yang, Y.L.; Shen, X.C.; Tang, X.Z. Effect of partial substitution of buckwheat on cooking characteristics, nutritional composition, and in vitro starch digestibility of extruded gluten-free rice noodles. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 126, 109332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.J.; Guo, X.D.; Liu, H.; Xu, B.N.; Wang, M. Cooking, textural, sensorial, and antioxidant properties of common and tartary buckwheat noodles. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparre, N.; Betoret, B.E.; Rosell, C.M. Quality indicators and heat damage of dried and cooked gluten free spaghetti. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2019, 74, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milde, L.B.; Chigal, P.S.; Olivera, J.E.; González, K.G. Incorporation of xanthan gum to gluten-free pasta with cassava starch Physical, textural and sensory attributes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 131, 109674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Luo, L.J.; Zhu, K.X.; Guo, X.N.; Peng, W.; Zhou, H.M. Effect of vacuum mixing on the quality characteristics of fresh noodles. J. Food Eng. 2012, 110, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.I.; Horigane, A.K.; Nakajima, H.; Yoshida, M.; Negasawa, A. T2 map, moisture distribution, and texture of boiled Japanese noodles prepared from different types of flour. Cereal Chem. 2004, 81, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, M.C.; Perez, G.T.; Leon, A.E. Structure and quality of pasta enriched with functional ingredients. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30780–30792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangpring, Y.; Fukuoka, M.; Ratanasumawong, S. The effect of sodium chloride on microstructure, water migration, and texture of rice noodle. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oniszczuk, A.; Kasprzak, K.; Wojtowicz, A.; Oniszczuk, T.; Olech, M. The Impact of processing parameters on the content of phenolic compounds in new gluten-free Precooked buckwheat pasta. Molecules 2019, 24, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sytar, O. Phenolic acids in the inflorescences of different varieties of buckwheat and their antioxidant activity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2015, 27, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, J.C.; Chen, H.J.; Lu, S.; Chiang, W. Effects of cooking, retro gradation and drying on starch digestibility instant rice making. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 65, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cooking Temperature/°C | Optimal Cooking Time/min | Color | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | ΔE | ||
| 20 | 57.00 | 62.37 ± 0.61 a | 0.16 ± 0.06 f | 14.49 ± 0.58 a | 64.03 ± 0.85 a |
| 30 | 41.00 | 60.95 ± 0.28 a,b | −0.14 ± 0.05 g | 13.94 ± 1.05 a,b | 62.52 ± 1.09 a,b,c |
| 40 | 27.50 | 61.46 ± 0.91 a | 0.10 ± 0.05 f | 14.32 ± 1.18 a,b | 63.11 ± 1.49 a,b |
| 50 | 18.00 | 59.70 ± 0.18 b,c | 0.37 ± 0.08 e | 12.38 ± 1.02 b | 60.97 ± 1.08 c,d |
| 60 | 14.00 | 61.04 ± 1.00 a,b | 0.36 ± 0.06 e | 12.36 ± 1.43 b | 62.28 ± 1.75 b,c |
| 70 | 12.00 | 61.34 ± 0.75 a | 0.53 ± 0.19 d | 12.65 ± 1.27 a,b | 62.63 ± 1.48 a,b |
| 80 | 9.00 | 58.94 ± 1.12 c | 0.74 ± 0.03 c | 9.99 ± 0.85 c | 59.79 ± 1.41 d,e |
| 90 | 7.50 | 58.35 ± 0.36 c | 0.91 ± 0.06 b | 10.37 ± 1.39 c | 59.27 ± 1.44 e |
| 100 | 6.50 | 55.04 ± 0.59 d | 1.39 ± 0.10 a | 10.31 ± 1.07 c | 56.01 ± 1.23 f |
| 110 | 5.50 | 55.75 ± 1.08 d | 1.40 ± 0.05 a | 9.71 ± 0.22 c | 56.60 ± 1.09 f |
| Cooking Temperature/°C | TPA | Tensile Properties | Shear Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness /N | Springiness /% | Chewiness /N | Tensile Force/N | Tensile Work/N*s | Shear Hardness/N | |
| 20 | 65.45 ± 4.19 a,b | 89.55 ± 2.09 a | 29.12 ± 2.27 c,d | 0.10 ± 0.00 b,c | 4.53 ± 0.72 d | 2.55± 0.17 f |
| 30 | 66.95 ± 1.42 a | 88.24 ± 0.58 a | 28.93 ± 0.44 c,d | 0.07 ± 0.01 f | 1.96 ± 0.29 f | 2.32 ± 0.28 f |
| 40 | 60.55 ± 7.32 a,b,c | 86.44 ± 5.36 a | 27.94 ± 4.25 c,d | 0.07 ± 0.00 e,f | 2.81 ±0.21 e,f | 2.64 ± 0.05 f |
| 50 | 60.41 ± 0.91 a,b,c | 84.41 ± 2.34 a | 26.49 ± 1.41 d,e | 0.09 ± 0.01 b,c | 7.30 ± 0.47 a | 3.63 ± 0.15 d,e |
| 60 | 46.07 ± 5.33 d | 89.83 ± 0.78 a | 26.64 ± 2.00 d,e | 0.08 ± 0.00 b,c,d | 4.45 ±1.18 d | 4.61 ± 0.24 b |
| 70 | 43.58 ± 1.83 d | 88.16 ± 0.72 a | 23.51 ± 0.51 e | 0.09 ± 0.01 b,c | 6.19 ± 0.44 b | 3.51 ± 0.03 e |
| 80 | 55.16 ± 2.63 c | 91.46 ± 1.45 a | 29.38 ± 0.90 c,d | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 5.54 ±0.06 b,c | 4.22 ± 0.20 c |
| 90 | 58.67 ± 5.85 b,c | 90.90 ± 1.94 a | 31.18 ± 2.18 b,c | 0.08 ± 0.01 c,d,e | 4.95 ± 0.35 c,d | 3.94 ± 0.04 c,d |
| 100 | 59.50 ± 0.78 b,c | 87.44 ± 0.32 a | 35.30 ± 1.24 a | 0.10 ± 0.01 b | 3.50 ±0.48 e | 4.64 ± 0.22 b |
| 110 | 60.14 ± 0.64 a,b,c | 84.99 ± 1.84 a | 33.81 ± 1.97 a,b | 0.07 ± 0.00 d,e,f | 2.90 ± 0.05 e,f | 5.38 ± 0.26 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Qiu, J. Effect of Moisture Distribution Changes Induced by Different Cooking Temperature on Cooking Quality and Texture Properties of Noodles Made from Whole Tartary Buckwheat. Foods 2021, 10, 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112543
Zou S, Wang L, Wang A, Zhang Q, Li Z, Qiu J. Effect of Moisture Distribution Changes Induced by Different Cooking Temperature on Cooking Quality and Texture Properties of Noodles Made from Whole Tartary Buckwheat. Foods. 2021; 10(11):2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112543
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Shuping, Lijuan Wang, Aili Wang, Qian Zhang, Zaigui Li, and Ju Qiu. 2021. "Effect of Moisture Distribution Changes Induced by Different Cooking Temperature on Cooking Quality and Texture Properties of Noodles Made from Whole Tartary Buckwheat" Foods 10, no. 11: 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112543
APA StyleZou, S., Wang, L., Wang, A., Zhang, Q., Li, Z., & Qiu, J. (2021). Effect of Moisture Distribution Changes Induced by Different Cooking Temperature on Cooking Quality and Texture Properties of Noodles Made from Whole Tartary Buckwheat. Foods, 10(11), 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112543





