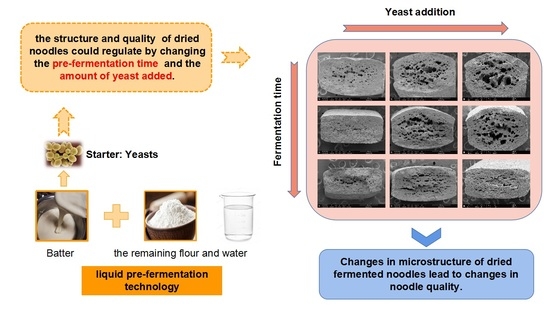
Regulation of Structure and Quality of Dried Noodles by Liquid Pre-Fermentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dried Noodles Preparation
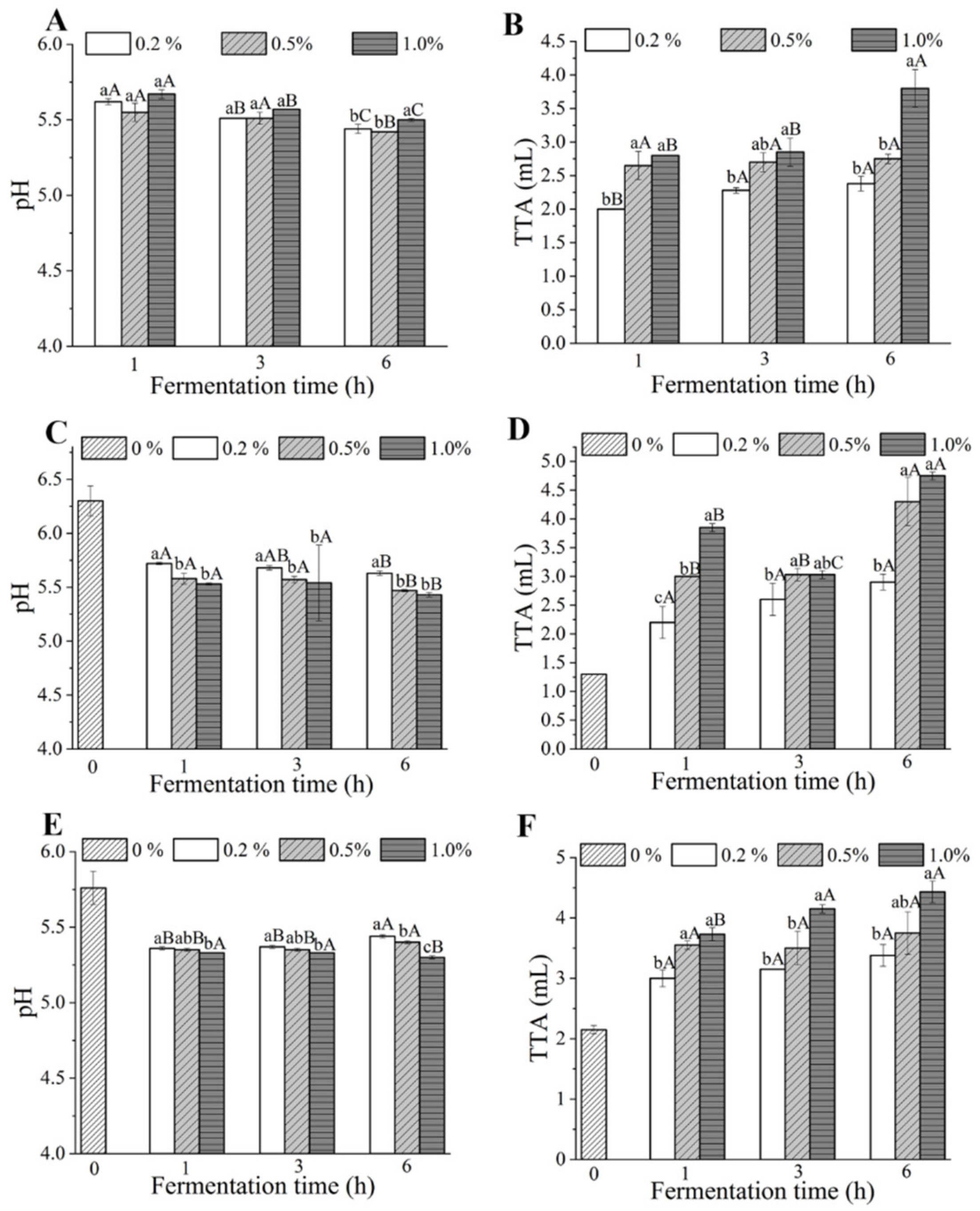
2.3. pH and Total Titratable Acidity (TTA)
2.4. Dough Sheet Color
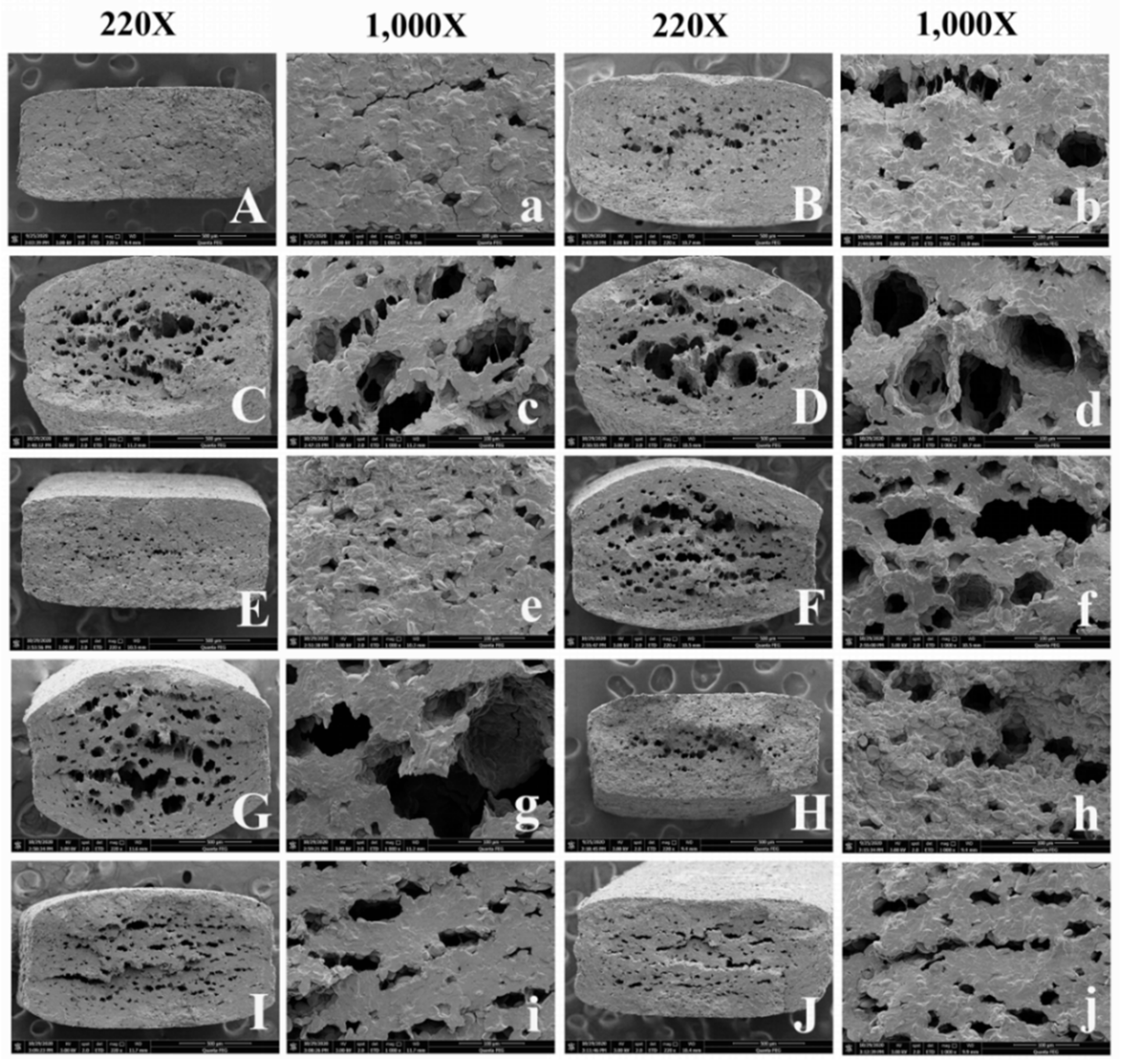
2.5. Microstructure
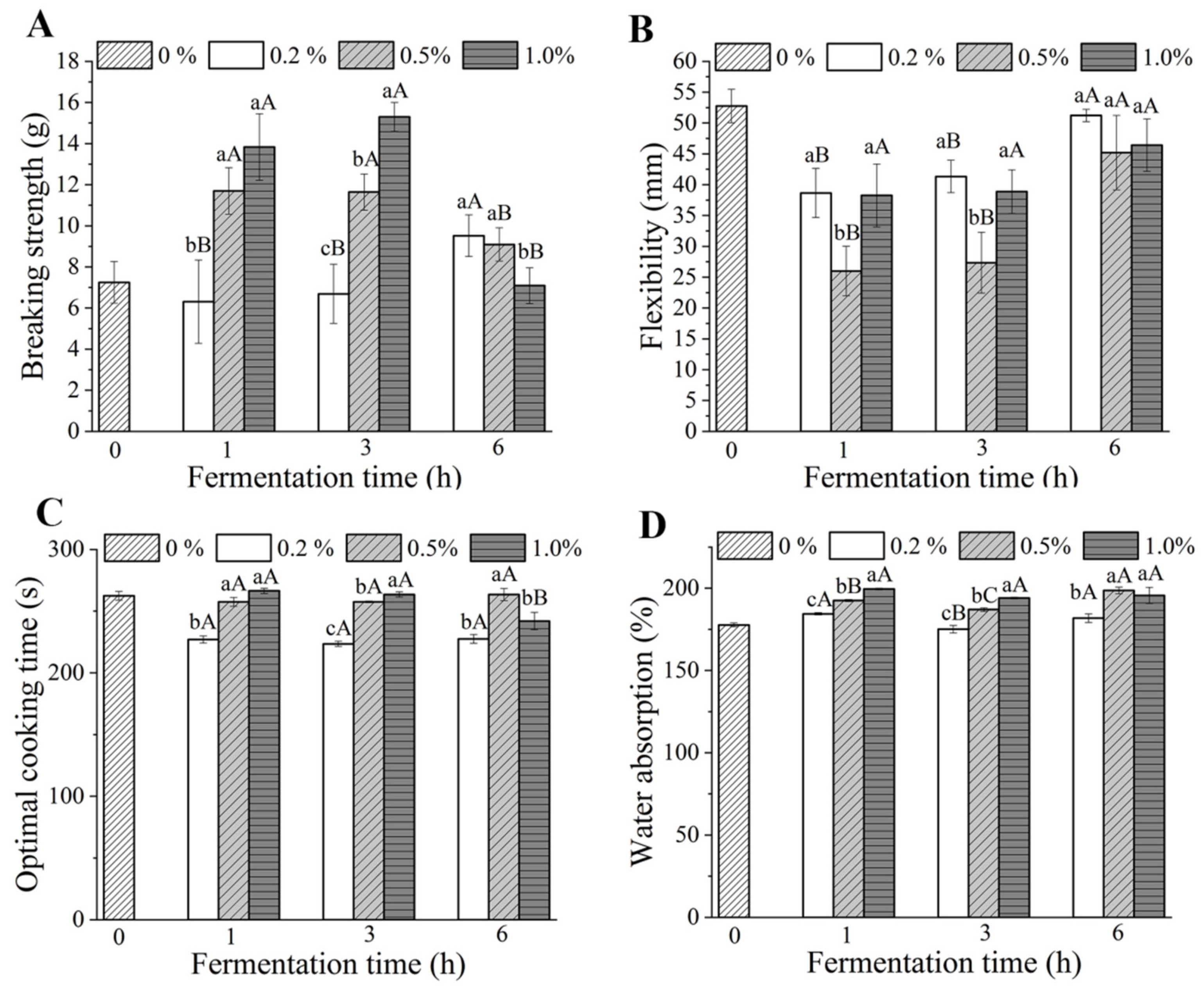
2.6. Mechanical Properties
2.7. Cooking Properties
2.8. Texture Properties
2.9. Volatile Compounds in Dried Noodles
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. pH and TTA
3.2. Dough Sheet Color
3.3. Microstructure
3.4. Mechanical Properties
3.5. Cooking Properties
3.6. Textural Properties
3.7. Volatile Compounds in Dried Fermented Noodles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, B.X. Asian noodles: History, classification, raw materials and processing. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 888–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.S.; Yadav, R.B.; Kumari, M.; Khatkar, B.S. Studies on suitability of wheat flour blends with sweet potato, colocasia and water chestnut flours for noodle making. LWT 2014, 57, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, K.-X.; Guo, X.-N.; Brijs, K.; Zhou, H.-M. Natural Additives in Wheat-Based Pasta and Noodle Products: Opportunities for Enhanced Nutritional and Functional Properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-R.; Guo, X.-N.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, K.-X. Effect of sodium bicarbonate on quality of machine-made Kongxin noodles. LWT 2020, 138, 110670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Liu, C.; Song, M.; Zheng, X. Effect of characteristics of different wheat flours on the quality of fermented hollow noodles. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4927–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestra, F.; Pinnavaia, G.G.; Romani, S. Evaluation of the Effects of Different Fermentation Methods on Dough Characteristics. J. Texture Stud. 2015, 46, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Bi, Y.; Zhao, R.; Nie, Y.; Yuan, W. Dynamics of microbial community and changes of metabolites during production of type I sourdough steamed bread made by retarded sponge-dough method. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poutanen, K.; Flander, L.; Katina, K. Sourdough and cereal fermentation in a nutritional perspective. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, E.K.; Ryan, L.A.; Bello, F.D. Impact of sourdough on the texture of bread. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montemurro, M.; Coda, R.; Rizzello, C. Recent Advances in the Use of Sourdough Biotechnology in Pasta Making. Foods 2019, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fois, S.; Campus, M.; Piu, P.P.; Siliani, S.; Sanna, M.; Roggio, T.; Catzeddu, P. Fresh Pasta Manufactured with Fermented Whole Wheat Semolina: Physicochemical, Sensorial and Nutritional Properties. Foods 2019, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fois, S.; Piu, P.P.; Sanna, M.; Roggio, T.; Catzeddu, P. Starch digestibility and properties of fresh pasta made with semolina-based liquid sourdough. LWT 2018, 89, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, A.V.; Bello, F.D.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K. Impact of sourdough on buckwheat flour, batter and bread: Biochemical, rheological and textural insights. J. Cereal Sci. 2011, 54, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Matsumura, Y.; Shimizu, M. Emulsifying and Surface Properties of Wheat Gluten under Acidic Conditions. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabric, D.; Ben-Aissa, F.; Le-Bail, A.; Monteau, J.; Ćurić, D. Impact of process conditions on the structure of pre-fermented frozen dough. J. Food Eng. 2011, 105, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayati, S.-V.; Hamdami, N.; Le-Bail, A. Frozen Sangak dough and bread properties: Impact of pre-fermentation and freezing rate. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 20, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dysvik, A.; Liland, K.H.; Myhrer, K.S.; Westereng, B.; Rukke, E.-O.; de Rouck, G.; Wicklund, T. Pre-fermentation with lactic acid bacteria in sour beer production. J. Inst. Brew. 2019, 125, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Bail, A.; Nicolitch, C.; Vuillod, C. Fermented Frozen Dough: Impact of Pre-fermentation Time and of Freezing Rate for a Pre-fermented Frozen Dough on Final Volume of the Bread. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2008, 3, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassenmeier, K.; Schieberle, P. Potent aromatic compounds in the crumb of wheat bread (French-type)? Influence of pre-ferments and studies on the formation of key odorants during dough processing. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 1995, 201, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemist, 10th ed.; AACC Inc.: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Schlichting, L.; Pozniak, C.; Singh, A. Pigment loss from semolina to dough: Rapid measurement and relationship with pasta colour. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 57, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikaeo, K.; Laothongsan, P.; Lerdluksamee, C. Effects of gums on physical properties, microstructure and starch digestibility of dried-natural fermented rice noodles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.M.; Cho, J.H.; Koh, B.K. Processing properties of Korean rice varieties in relation to rice noodle quality. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Bian, K.; Guan, E.; Zheng, X. Effect of heat-moisture treatment of germinated wheat on the quality of Chinese white salted noodles. Cereal Chem. J. 2018, 96, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Q.; Guo, S.; Zhang, S. Effects of flour free lipids on textural and cooking qualities of Chinese noodles. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhu, H.; Rayas-Duarte, P. Spontaneous sourdough processing of Chinese Northern-style steamed breads and their volatile compounds. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loponen, J.; Mikola, M.; Katina, K.; Sontag-Strohm, T.; Salovaara, H. Degradation of HMW Glutenins During Wheat Sourdough Fermentations. Cereal Chem. J. 2004, 81, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitmann, M.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E. Impact of Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolites produced during fermentation on bread quality parameters: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 58, 1152–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pronk, J.T.; Steensma, H.Y.; Dijken, J.V. Pyruvate metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 2010, 12, 1607–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regev-Rudzki, N.; Karniely, S.; Ben-Haim, N.N.; Pines, O. Yeast Aconitase in Two Locations and Two Metabolic Pathways: Seeing Small Amounts Is Believing. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 4163–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rezaei, M.N.; Aslankoohi, E.; Verstrepen, K.J.; Courtin, C.M. Contribution of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and the glyoxylate shunt in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to succinic acid production during dough fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 204, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Hong, B.H.; Baik, B.-K. Protein Quality of Wheat Desirable for Making Fresh White Salted Noodles and Its Influences on Processing and Texture of Noodles. Cereal Chem. J. 2003, 80, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowell, F.E.; Maghirang, E.B.; Xie, F.; Lookhart, G.L.; Pierce, R.O.; Seabourn, B.W.; Bean, S.R.; Wilson, J.D.; Chung, O.K. Predicting Wheat Quality Characteristics and Functionality Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Cereal Chem. J. 2006, 83, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, S.L., Jr.; Herberts, R.A.; Hollatz, C.; Miletti, L.C.; Stambuk, B.U. Maltose and Maltotriose Active Transport and Fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiaes. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2007, 65, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Yao, D.-D.; Sun, K.; Zhu, M.-R. Effects of Different Processing Conditions on the Mechanical Properties of Dry Noodles. J. Texture Stud. 2014, 45, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fei, M.; Shi, C.; Tian, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Z.; Dong, H. Effect of particle size and addition level of wheat bran on quality of dry white Chinese noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2011, 53, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia, N.; Khatkar, B. Effect of Processing Variables on the Oil Uptake, Textural Properties and Cooking Quality of Instant Fried Noodles. J. Food Qual. 2013, 36, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Xiao, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, G. Spontaneous fermentation tunes the physicochemical properties of sweet potato starch by modifying the structure of starch molecules. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 213, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Li, X.; Zhu, R.; Ma, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, X. Effect of natural fermentation on the structure and physicochemical properties of wheat starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pétel, C.; Onno, B.; Prost, C. Sourdough volatile compounds and their contribution to bread: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zheng, X.; Ai, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, R.; Bian, K. Analysis of volatile aroma components from Mantou fermented by different starters. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starowicz, M.; Zieliński, H. How Maillard Reaction Influences Sensorial Properties (Color, Flavor and Texture) of Food Products? Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Fermentation Time (h) | Yeast Addition (%) | L * | a * | b * | ∆E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 86.84 ± 0.84 | 0.27 ± 0.06 | 21.16 ± 0.30 | ― |
| 1 | 0.2 | 88.27 ± 0.21 c,A | 0.30 ± 0.00 a,B | 22.00 ± 0.10 a,A | 1.66 ± 0.17 c,A,B |
| 0.5 | 93.17 ± 0.25 b,B | 0.27 ± 0.06 a,B | 21.10 ± 0.17 b,A | 6.33 ± 0.25 b,B | |
| 1.0 | 94.47 ± 0.12 a,A | 0.20 ± 0.00 b,C | 20.77 ± 0.12 c,A | 7.64 ± 0.12 a,A | |
| 3 | 0.2 | 89.03 ± 0.15 c,A | 0.20 ± 0.00 b,B | 22.13 ± 0.06 a,A | 2.40 ± 0.14 c,A |
| 0.5 | 93.00 ± 0.10 b,B | 0.33 ± 0.06 a,A,B | 20.73 ± 0.06 c,B | 6.18 ± 0.10 b,B | |
| 1.0 | 93.43 ± 0.15 a,B | 0.27 ± 0.06 a,b,B | 21.07 ± 0.12 b,A | 6.59 ± 0.15 a,B | |
| 6 | 0.2 | 87.80 ± 1.37 b,A | 0.47 ± 0.12 a,A | 21.00 ± 0.36 a,B | 1.42 ± 0.68 c,B |
| 0.5 | 93.60 ± 0.10 a,A | 0.40 ± 0.00 a,A | 21.10 ± 0.10 a,A | 6.76 ± 0.10 a,A | |
| 1.0 | 92.33 ± 0.06 a,C | 0.40 ± 0.00 a,A | 20.93 ± 0.29 a,A | 5.50 ± 0.07 b,C |
| Alcohols | Aldehydes | Esters | Carbonic Acids | Aromatics | Olefins | Furans | Others | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h–0.0% | Types | 1 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Relative content (%) | 1.07 | 13.40 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.83 | 73.61 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1 h–0.2% | Types | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Relative content (%) | 0.00 | 14.77 | 9.23 | 0.00 | 7.29 | 68.70 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1 h–0.5% | Types | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Relative content (%) | 0.00 | 9.32 | 11.51 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 78.68 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1 h–1.0% | Types | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 1 |
| Relative content (%) | 0.00 | 9.24 | 26.17 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 58.00 | 0.00 | 4.01 | |
| 3 h–0.2% | Types | 2 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 1 | 0 |
| Relative content (%) | 3.10 | 5.91 | 16.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 63.37 | 7.66 | 0.00 | |
| 3 h–0.5% | Types | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 1 | 0 |
| Relative content (%) | 0.00 | 6.05 | 12.69 | 0.00 | 3.70 | 66.72 | 9.24 | 0.00 | |
| 3 h–1.0% | Types | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 14 | 1 | 0 |
| Relative content (%) | 0.00 | 4.68 | 6.50 | 0.00 | 4.51 | 70.74 | 5.30 | 0.00 | |
| 6 h–0.2% | Types | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 0 |
| Relative content (%) | 0.00 | 12.12 | 4.02 | 2.73 | 3.44 | 54.17 | 9.91 | 0.00 | |
| 6 h–0.5% | Types | 0 | 3 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 11 | 1 | 0 |
| Relative content (%) | 0.00 | 5.36 | 47.75 | 3.83 | 0.00 | 39.71 | 2.28 | 0.00 | |
| 6 h–1.0% | Types | 1 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 0 |
| Relative content (%) | 0.50 | 3.48 | 55.87 | 0.42 | 2.37 | 29.59 | 4.68 | 0.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, X.; Liu, C.; Zheng, X. Regulation of Structure and Quality of Dried Noodles by Liquid Pre-Fermentation. Foods 2021, 10, 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102408
Xiong X, Liu C, Zheng X. Regulation of Structure and Quality of Dried Noodles by Liquid Pre-Fermentation. Foods. 2021; 10(10):2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102408
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Xiaoqing, Chong Liu, and Xueling Zheng. 2021. "Regulation of Structure and Quality of Dried Noodles by Liquid Pre-Fermentation" Foods 10, no. 10: 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102408
APA StyleXiong, X., Liu, C., & Zheng, X. (2021). Regulation of Structure and Quality of Dried Noodles by Liquid Pre-Fermentation. Foods, 10(10), 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102408