Simultaneous Determination of Albendazole and Its Three Metabolites in Pig and Poultry Muscle by Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standards and Reagents
2.2. Equipment
2.3. Standard Solutions
2.4. Blank Samples and Sample Preparation
2.5. UPLC-FLD Analysis
2.6. Method Validation
2.6.1. Sensitivity
2.6.2. Linearity
2.6.3. Recovery and Precision
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Chromatographic Conditions
3.1.1. Selection of a Chromatographic Column
3.1.2. Optimization of the Mobile Phase
3.1.3. Optimization of Column Temperature and Flow Rate
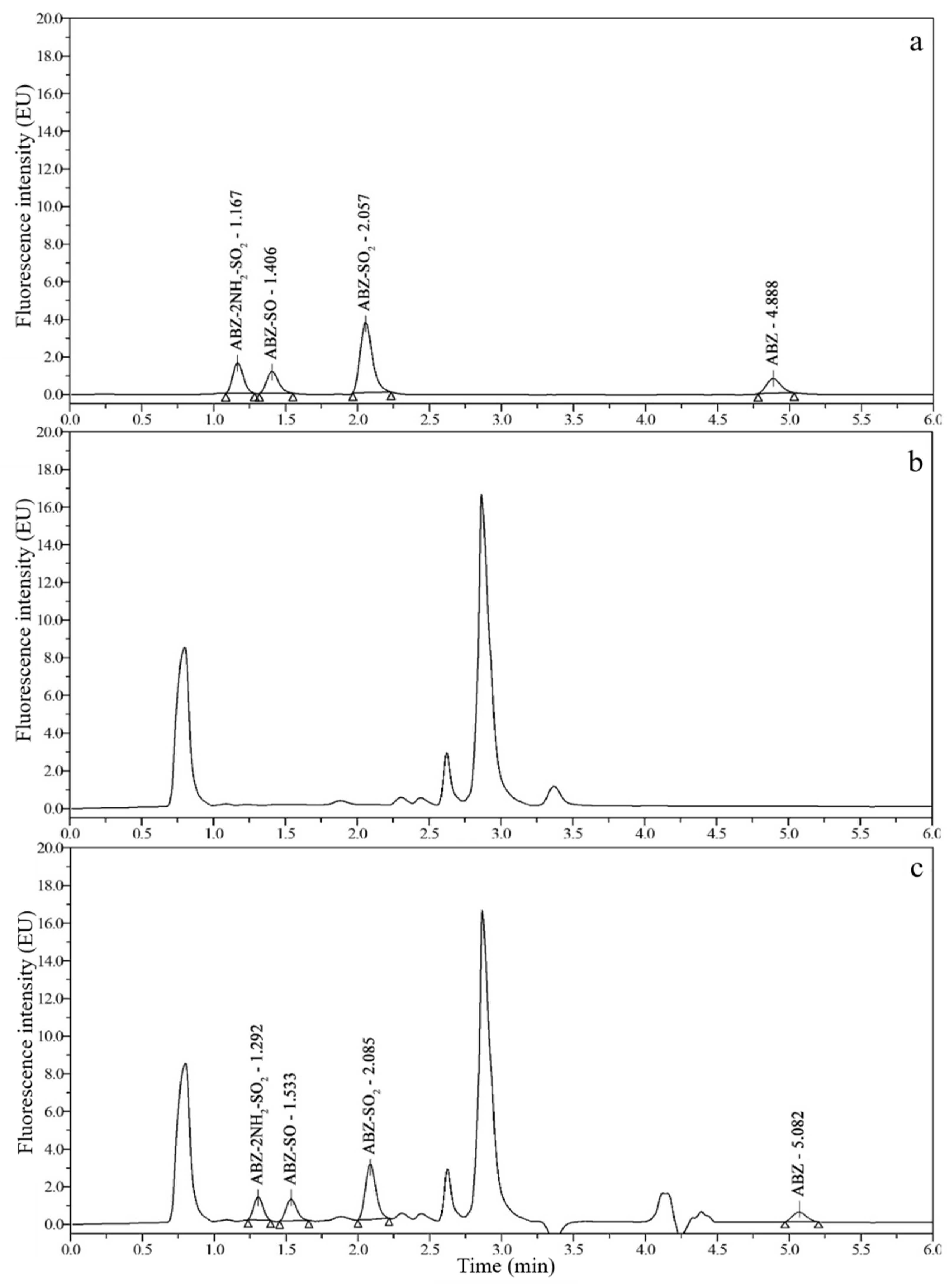
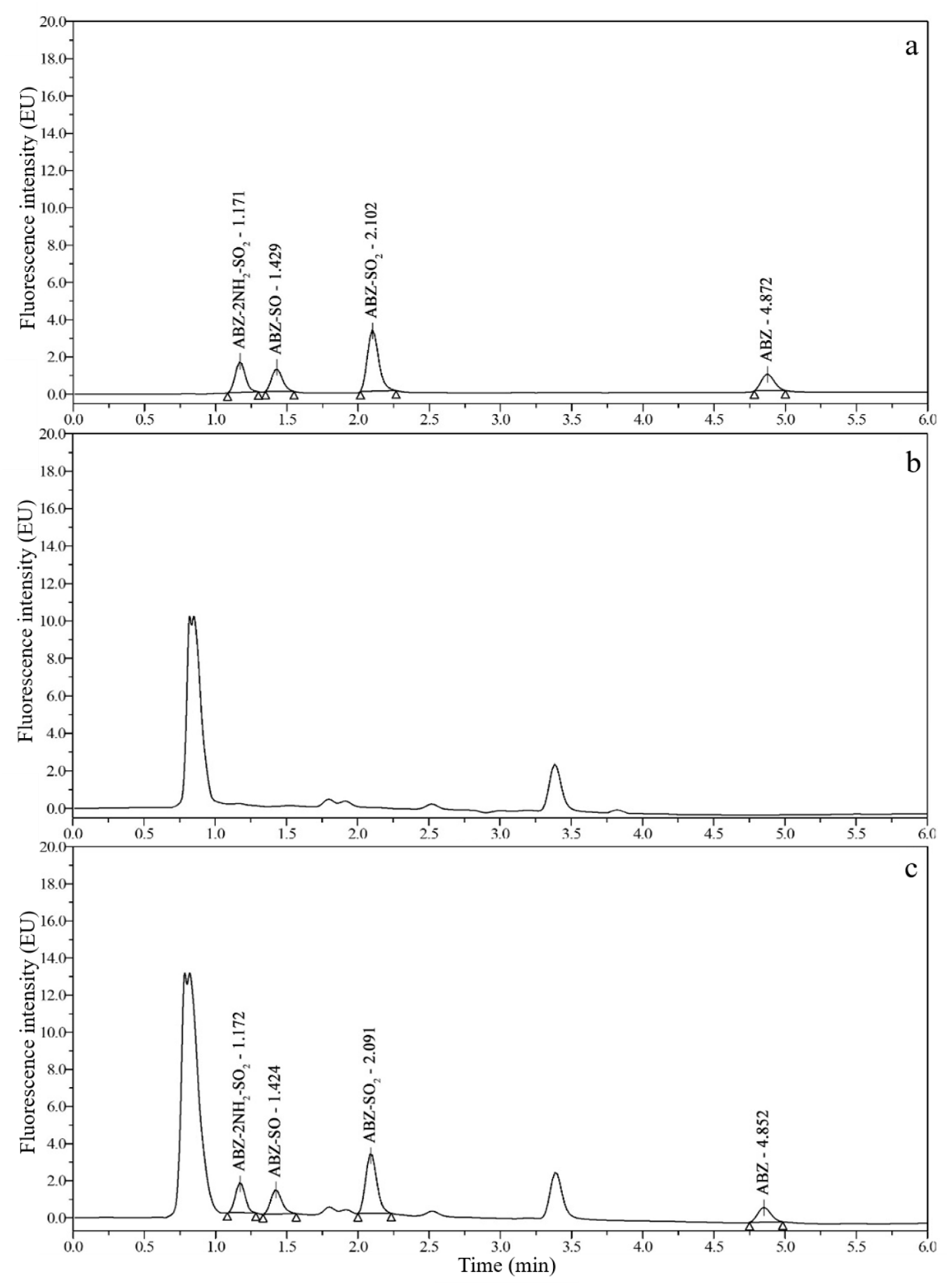
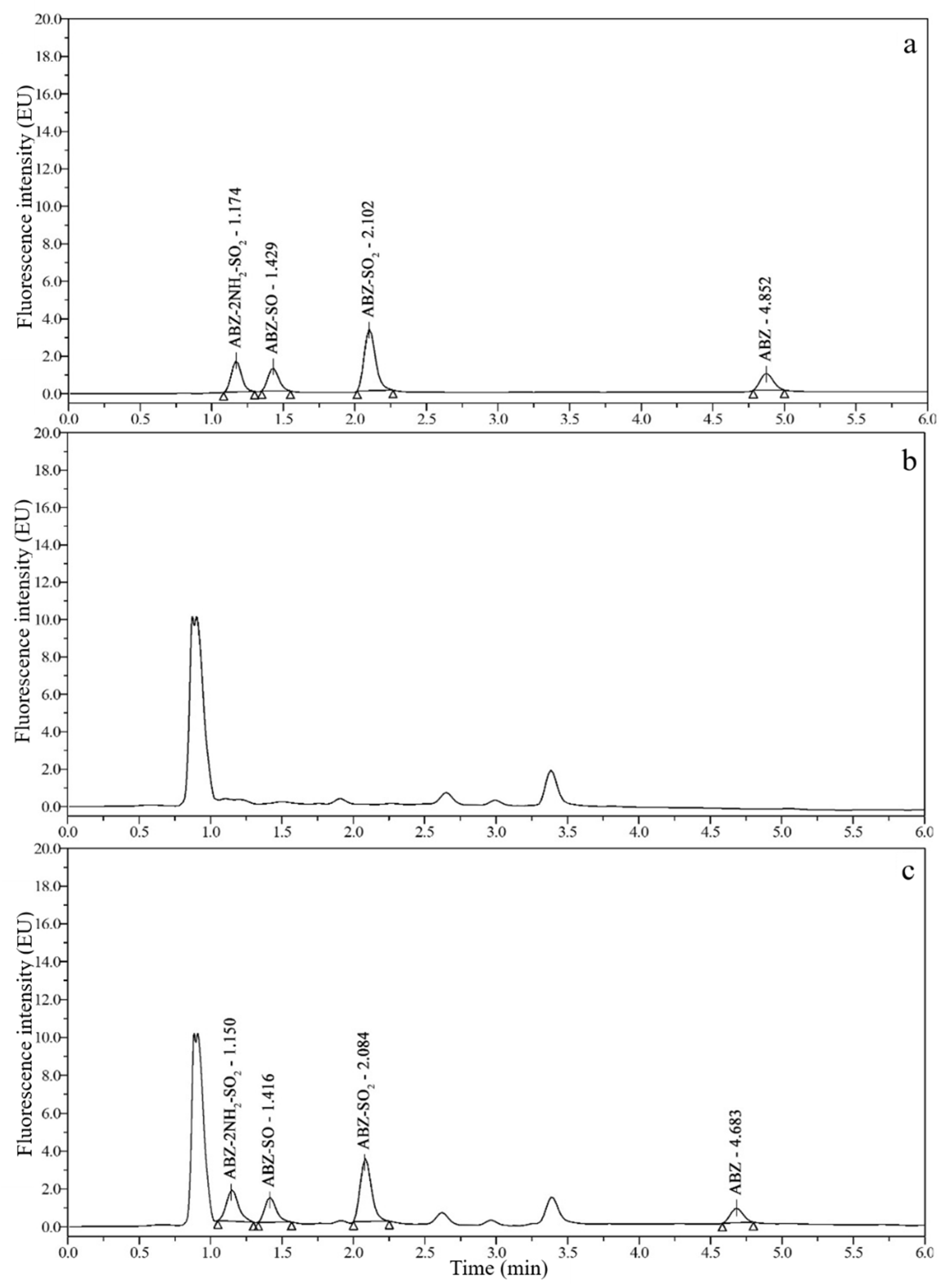
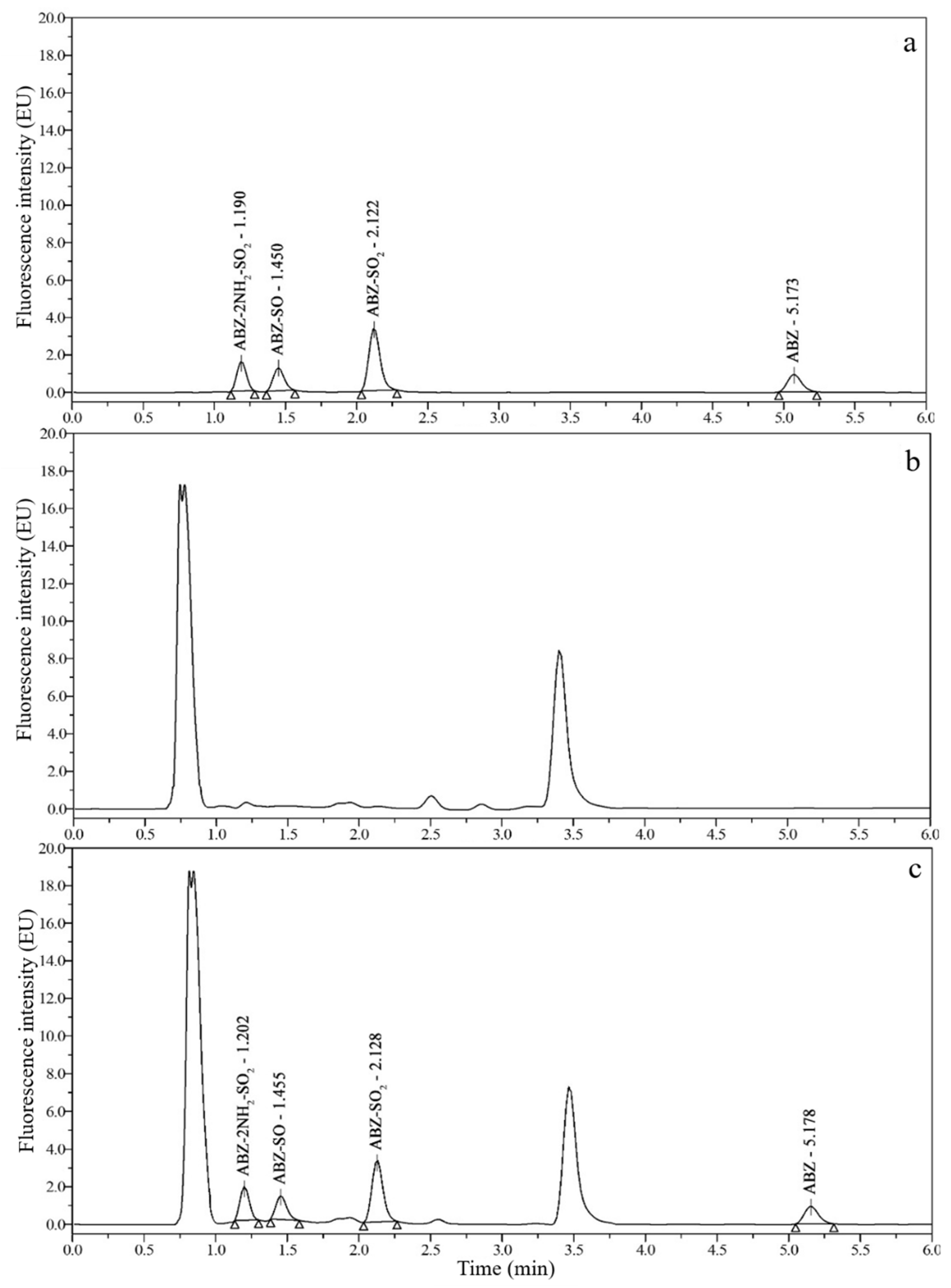
3.2. Chromatograms and Determination of Detection Wavelengths
3.3. Optimization of Sample Preparation
3.4. Method Comparison
3.5. Validation Results of the Method
3.5.1. Sensitivity
3.5.2. Linearity
3.5.3. Recovery and Precision
3.6. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romero, T.; Althaus, R.; Moya, V.J.; Beltrán, M.C.; Reybroeck, W.; Molina, M.P. Albendazole residues in goat’s milk: Interferences in microbial inhibitor tests used to detect antibiotics in milk. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Permana, A.D.; Tekko, I.A.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. New HPLC–MS method for rapid and simultaneous quantification of doxycycline, diethylcarbamazine and albendazole metabolites in rat plasma and organs after concomitant oral administration. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 170, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, P. Loss of the central rachis and synaptonemal complexes during meiotic prophase in female Ascaris lumbricoides var. suum after exposure to albendazole. J. Helminthol. 2021, 95, E32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bistoletti, M.; Alvarez, L.; Lanusse, C.; Moreno, L. Disposition kinetics of albendazole and metabolites in laying hens. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 36, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piloiu, C.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Albendazole-induced liver injury. Am. J. Ther. 2021, 28, e335–e340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, G.; Patring, J.; Ullerås, E.; Oskarsson, A. Developmental toxicity of albendazole and its three main metabolites in zebrafish embryos. Reprod. Toxicol. 2011, 32, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassaing, C.; Berger, M.; Heckeroth, A.; Ilg, T.; Jaeger, M.; Kern, C.; Schmid, K.; Uphoff, M. Highly water-soluble prodrugs of anthelmintic benzimidazole carbamates: Synthesis, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 31650-2019; National Food Safety Standard. Maximum Residue Limits for Veterinary Drugs in Foods; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Afairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- The European Medicines Agency. Commission Regulation (EU) No. 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on Pharmacologically Active Substances and their Classification Regarding Maximum Residue Limits in Foodstuffs of Animal Origin; The European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Romvfiri, Z.; Kemény, S.; Pokol, G.; Fekete, J. A new approach for development of rugged sample preparation of metabolites of albendazole in cow milk. Microchim. Acta 1999, 130, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permana, A.D.; Wahyudin, E.; Ismail; Amir, M.N.; Raihan, M.; Anjani, Q.K.; Utomo, E.; Layadi, P.; Donnelly, R.F. New and sensitive HPLC-UV method for concomitant quantification of a combination of antifilariasis drugs in rat plasma and organs after simultaneous oral administration. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletouris, D.J.; Botsoglou, N.A.; Psomas, I.E.; Mantis, A.I. Determination of the marker residue of albendazole in cheese by ion-pair liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, M.; Dadfarnia, S.; Haji Shabani, A.M. Simultaneous extraction and determination of albendazole and triclabendazole by a novel syringe to syringe dispersive liquid phase microextraction-solidified floating organic drop combined with high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 932, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, B.; Rummel, N.; Reimschuessel, R. Determination of albendazole and its major metabolites in the muscle tissues of Atlantic salmon, tilapia, and rainbow trout by high performance liquid chromatography with fluorometric detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3254–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletouris, D.J.; Botsoglou, N.A.; Psomas, I.E.; Mantis, A.I. Determination of the marker residue of albendazole in milk using ion-pair liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 345, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, N.; Chung, I.; Shaikh, B. Determination of albendazole, fenbendazole, and their metabolites in mouse plasma by high performance liquid chromatography using fluorescence and ultraviolet detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2011, 34, 2211–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Dong, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Ai, X. Development of a liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method with modified QuEChERS extraction for the quantification of mebendazole and its metabolites, albendazole and its metabolites, and levamisole in edible tissues of aquatic animals. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msagati, T.A.M.; Nindi, M.M. Comparative study of sample preparation methods; supported liquid membrane and solid phase extraction in the determination of benzimidazole anthelmintics in biological matrices by liquid chromatography–electrospray–mass spectrometry. Talanta 2006, 69, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jedziniak, P.; Szprengier-Juszkiewicz, T.; Olejnik, M. Determination of benzimidazoles and levamisole residues in milk by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry: Screening method development and validation. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8165–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsella, B.; Lehotay, S.J.; Mastovska, K.; Lightfield, A.R.; Furey, A.; Danaher, M. New method for the analysis of flukicide and other anthelmintic residues in bovine milk and liver using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 637, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojnicz, A.; Cabaleiro-Ocampo, T.; Román-Martínez, M.; Ochoa-Mazarro, D.; Abad-Santos, F.; Ruiz-Nuño, A. A simple assay for the simultaneous determination of human plasma albendazole and albendazole sulfoxide levels by high performance liquid chromatography in tandem mass spectrometry with solid-phase extraction. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 426, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The European Communities. Commission decision 2002/657/EC of 12 august 2002 implementing council directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off. J. Eur. Union 2002, 221, 8–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, B.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Shou, X.; Wen, L.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, H.; Ruan, J.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution study of liposomal albendazole in naturally Echinococcus granulosus infected sheep by a validated UPLC-Q-TOF-MS method. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1141, 122016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, N.; Shaikh, B. Determination of albendazole and its metabolites in the muscle tissue of hybrid striped and largemouth bass using liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batzias, G.C.; Delis, G.A. Reversed-phase liquid chromatographic method with fluorescence detection for the simultaneous determination of albendazole sulphoxide, albendazole sulphone and albendazole 2-aminosulphone in sheep plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 805, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichapong, J.; Santaladchaiyakit, Y.; Burakham, R.; Kanchanamayoon, W.; Srijaranai, S. Determination of benzimidazole anthelmintics using HPLC after vortex-assisted mixed anionic–cationic surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction with solidification of floating organic droplet procedure. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 37, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
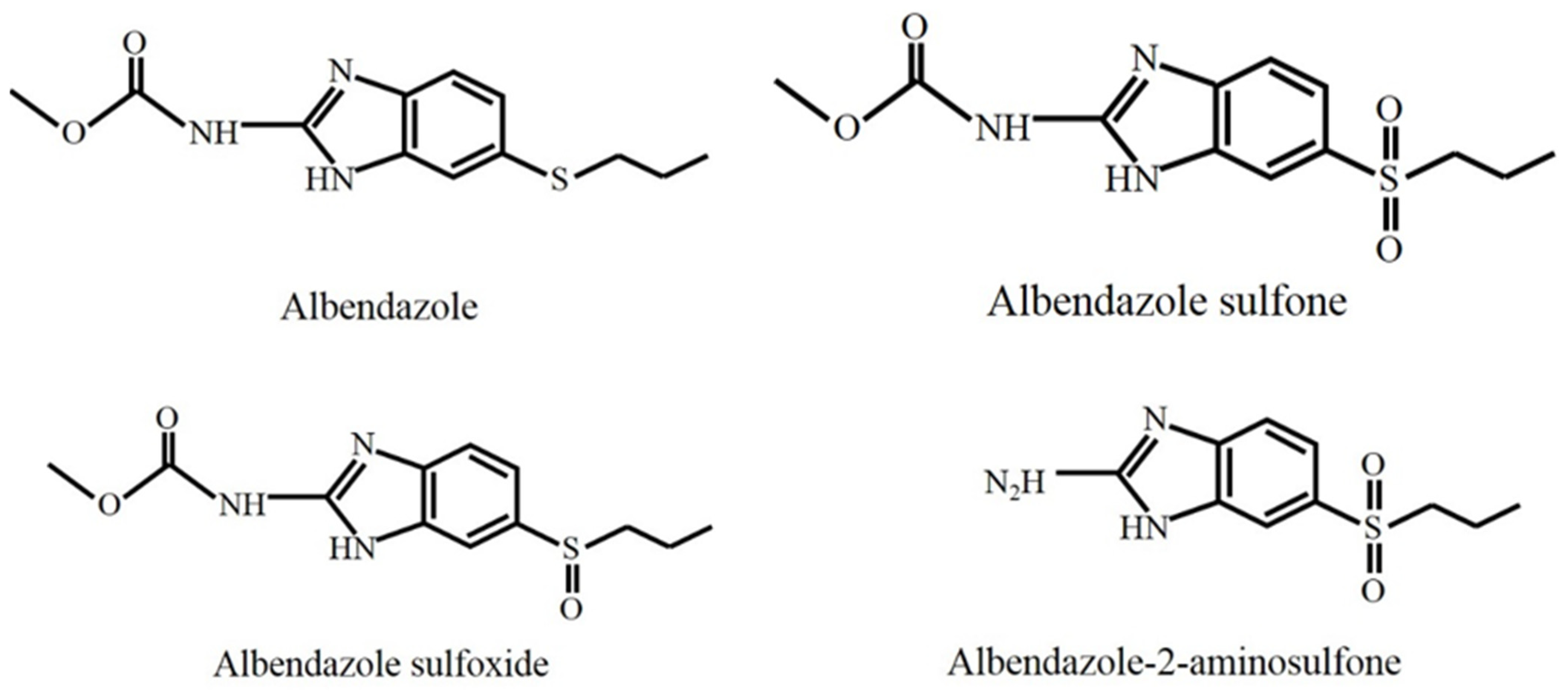
| Analyte | Animal Matrix | LOD (μg/kg) | LOQ (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABZ | Pig muscle | 2.8 | 10.0 |
| Chicken muscle | 3.2 | 10.7 | |
| Duck muscle | 3.1 | 10.0 | |
| Goose muscle | 3.6 | 10.9 | |
| ABZ-SO2 | Pig muscle | 0.4 | 1.5 |
| Chicken muscle | 0.3 | 1.0 | |
| Duck muscle | 0.2 | 1.0 | |
| Goose muscle | 0.2 | 1.0 | |
| ABZ-SO | Pig muscle | 3.8 | 9.7 |
| Chicken muscle | 3.0 | 8.3 | |
| Duck muscle | 2.4 | 8.0 | |
| Goose muscle | 2.5 | 8.5 | |
| ABZ-2NH2-SO2 | Pig muscle | 0.9 | 3.0 |
| Chicken muscle | 0.6 | 1.8 | |
| Duck muscle | 0.5 | 1.5 | |
| Goose muscle | 0.5 | 1.9 |
| Analyte | Linearity Range (μg/L) | Linear Regression Equation | Determination Coefficient (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABZ | 10.0–400.0 | y = 1355.7x + 11,560 | 0.9995 |
| ABZ-SO2 | 1.0–400.0 | y = 32,757x + 61,988 | 0.9994 |
| ABZ-SO | 8.0–400.0 | y = 2498.1x + 14,519 | 0.9991 |
| ABZ-2NH2-SO2 | 1.5–400.0 | y = 13,573x + 32,379 | 0.9995 |
| Analyte | Adding Level (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Intraday RSD (%) | Interday RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABZ | 10.0 | 80.37 ± 1.87 | 2.33 | 4.67 | 5.77 |
| 50.0 | 85.55 ± 2.28 | 2.67 | 3.42 | 6.20 | |
| 100.0 α | 89.67 ± 2.12 | 2.36 | 3.17 | 5.74 | |
| 200.0 | 92.07 ± 0.97 | 1.05 | 2.54 | 3.56 | |
| ABZ-SO2 | 1.5 | 91.69 ± 3.42 | 3.73 | 4.53 | 3.54 |
| 50.0 | 93.54 ± 3.27 | 3.49 | 2.97 | 4.35 | |
| 100.0 α | 95.44 ± 2.14 | 2.24 | 2.15 | 3.87 | |
| 200.0 | 97.08 ± 2.02 | 2.08 | 3.37 | 4.84 | |
| ABZ-SO | 9.7 | 84.65 ± 2.97 | 3.51 | 4.34 | 4.77 |
| 50.0 | 91.79 ± 1.73 | 1.89 | 3.04 | 5.03 | |
| 100.0 α | 92.49 ± 3.43 | 3.70 | 3.17 | 3.64 | |
| 200.0 | 97.93 ± 2.73 | 2.79 | 2.70 | 2.93 | |
| ABZ-2NH2-SO2 | 3.0 | 84.56 ± 3.93 | 4.65 | 4.71 | 5.03 |
| 50.0 | 90.48 ± 2.16 | 2.39 | 2.52 | 6.29 | |
| 100.0 α | 96.58 ± 1.36 | 1.41 | 3.77 | 4.79 | |
| 200.0 | 97.18 ± 2.23 | 2.30 | 3.10 | 4.35 |
| Analyte | Adding Level (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Intraday RSD (%) | Interday RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABZ | 10.7 | 88.77 ± 1.89 | 2.13 | 2.18 | 2.63 |
| 50.0 | 89.61 ± 2.73 | 3.05 | 3.24 | 3.81 | |
| 100.0 α | 94.77 ± 1.15 | 1.22 | 2.85 | 3.47 | |
| 200.0 | 98.39 ± 1.50 | 1.53 | 2.88 | 2.23 | |
| ABZ-SO2 | 1.0 | 83.13 ± 3.94 | 4.74 | 5.11 | 4.91 |
| 50.0 | 89.36 ± 1.60 | 1.79 | 2.84 | 2.10 | |
| 100.0 α | 94.01 ± 3.38 | 3.60 | 3.62 | 3.14 | |
| 200.0 | 97.12 ± 2.76 | 2.84 | 2.89 | 2.85 | |
| ABZ-SO | 8.3 | 88.08 ± 3.38 | 3.84 | 4.10 | 4.77 |
| 50.0 | 89.65 ± 3.13 | 3.49 | 3.72 | 4.11 | |
| 100.0 α | 94.39 ± 2.73 | 2.90 | 3.00 | 3.27 | |
| 200.0 | 94.66 ± 2.68 | 2.83 | 2.88 | 3.04 | |
| ABZ-2NH2-SO2 | 1.8 | 83.53 ± 2.68 | 3.20 | 3.57 | 3.98 |
| 50.0 | 88.88 ± 3.35 | 3.77 | 4.25 | 4.65 | |
| 100.0 α | 94.07 ± 1.28 | 1.36 | 2.08 | 2.95 | |
| 200.0 | 95.34 ± 1.79 | 1.87 | 2.77 | 3.36 |
| Analyte | Adding Level (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Intraday RSD (%) | Interday RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABZ | 10.0 | 89.00 ± 2.19 | 2.46 | 3.00 | 3.38 |
| 50.0 | 91.50 ± 2.91 | 3.18 | 3.64 | 3.49 | |
| 100.0 α | 89.60 ± 1.64 | 1.83 | 2.37 | 2.79 | |
| 200.0 | 97.51 ± 1.87 | 1.92 | 2.34 | 2.69 | |
| ABZ-SO2 | 1.0 | 88.14 ± 4.33 | 4.91 | 4.64 | 5.10 |
| 50.0 | 90.58 ± 3.23 | 3.57 | 4.03 | 4.45 | |
| 100.0 α | 93.44 ± 2.11 | 2.26 | 2.62 | 2.97 | |
| 200.0 | 95.55 ± 2.00 | 2.09 | 2.71 | 2.84 | |
| ABZ-SO | 8.0 | 87.37 ± 2.99 | 3.43 | 3.58 | 4.02 |
| 50.0 | 93.77 ± 2.78 | 2.96 | 3.12 | 2.97 | |
| 100.0 α | 91.05 ± 3.36 | 3.69 | 3.88 | 4.38 | |
| 200.0 | 96.20 ± 2.68 | 2.79 | 2.90 | 3.39 | |
| ABZ-2NH2-SO2 | 1.5 | 90.84 ± 3.60 | 3.96 | 3.98 | 3.95 |
| 50.0 | 90.21 ± 2.13 | 2.36 | 2.66 | 3.04 | |
| 100.0 α | 95.74 ± 1.35 | 1.41 | 2.04 | 2.90 | |
| 200.0 | 96.09 ± 2.20 | 2.29 | 2.27 | 2.50 |
| Analyte | Adding Level (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Intraday RSD (%) | Interday RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABZ | 10.9 | 84.09 ± 3.96 | 4.71 | 4.85 | 5.36 |
| 50.0 | 88.72 ± 2.21 | 2.49 | 2.35 | 2.47 | |
| 100.0 α | 90.36 ± 2.09 | 2.32 | 2.40 | 3.92 | |
| 200.0 | 95.09 ± 3.62 | 3.81 | 4.27 | 4.71 | |
| ABZ-SO2 | 1.0 | 89.11 ± 1.59 | 1.79 | 1.33 | 3.80 |
| 50.0 | 93.84 ± 2.17 | 2.31 | 2.34 | 2.56 | |
| 100.0 α | 95.19 ± 2.63 | 2.76 | 2.62 | 2.92 | |
| 200.0 | 97.68 ± 1.51 | 1.55 | 1.67 | 3.50 | |
| ABZ-SO | 8.5 | 87.98 ± 3.32 | 3.78 | 3.89 | 4.07 |
| 50.0 | 88.37 ± 1.13 | 1.28 | 1.68 | 3.40 | |
| 100.0 α | 92.49 ± 2.63 | 2.85 | 3.76 | 3.42 | |
| 200.0 | 97.03 ± 2.15 | 2.21 | 2.11 | 2.72 | |
| ABZ-2NH2-SO2 | 1.9 | 91.83 ± 3.24 | 3.53 | 3.56 | 3.63 |
| 50.0 | 92.03 ± 2.70 | 2.94 | 2.91 | 3.06 | |
| 100.0 α | 94.26 ± 2.30 | 2.44 | 2.77 | 3.11 | |
| 200.0 | 97.25 ± 0.81 | 0.84 | 2.47 | 3.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Diao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Xie, K.; Chen, L.; Xue, C.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T. Simultaneous Determination of Albendazole and Its Three Metabolites in Pig and Poultry Muscle by Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection. Foods 2021, 10, 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102350
He Z, Diao Z, Guo Y, Xie K, Chen L, Xue C, Lu Y, Chen J, Zhang T. Simultaneous Determination of Albendazole and Its Three Metabolites in Pig and Poultry Muscle by Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection. Foods. 2021; 10(10):2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102350
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zhaoyuan, Zhixiang Diao, Yawen Guo, Kaizhou Xie, Lan Chen, Chun Xue, Yang Lu, Jinyuan Chen, and Tao Zhang. 2021. "Simultaneous Determination of Albendazole and Its Three Metabolites in Pig and Poultry Muscle by Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection" Foods 10, no. 10: 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102350
APA StyleHe, Z., Diao, Z., Guo, Y., Xie, K., Chen, L., Xue, C., Lu, Y., Chen, J., & Zhang, T. (2021). Simultaneous Determination of Albendazole and Its Three Metabolites in Pig and Poultry Muscle by Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection. Foods, 10(10), 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102350






