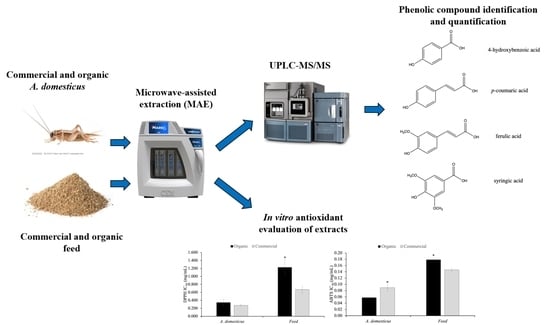
Targeted Phenolic Characterization and Antioxidant Bioactivity of Extracts from Edible Acheta domesticus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Cricket and Feed Extracts
2.3. Total Phenolic Content of Extracts
2.4. Phenolic Composition by UPLC/MS-MS
2.5. Antioxidant Activity
2.5.1. DPPH (2,2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl Radical Cation) Radical-Scavenging Activity
2.5.2. ABTS (2,2′-Azino-Bis 3-Ethylbenzothiazoline-6-Sulphonic Acid) Radical Scavenging Activity
2.6. Protein Content
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Extraction Yields
3.2. Total Phenolic Content of Extracts
3.3. Phenolic Composition of Extracts Using LC-MS
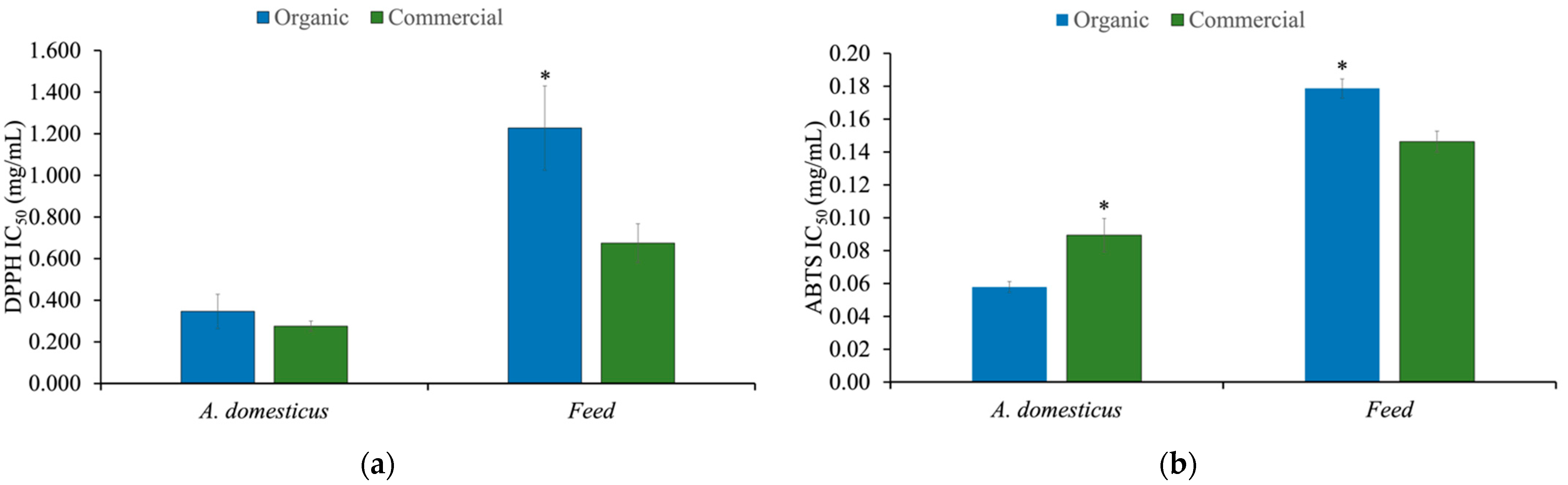
3.4. Antioxidant Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Payne, C.; Megido, R.C.; Dobermann, D.; Frédéric, F.; Shockley, M.; Sogari, G. Insects as Food in the Global North—The Evolution of the Entomophagy Movement. In Edible Insects in the Food Sector; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sosa, D.A.T.; Fogliano, V. Potential of insect-derived ingredients for food applications. In Insect Physiology and Ecology; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; pp. 215–231. [Google Scholar]
- Van Huis, A. Potential of insects as food and feed in assuring food security. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, N.; van Huis, A. Consuming insects: Are there health benefits? J. Insects Food Feed. 2017, 3, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, L.; Lakemond, C.M.M.; Sagis, L.M.C.; Eisner-Schadler, V.; van Huis, A.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S. Extraction and characterisation of protein fractions from five insect species. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3341–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halloran, A.; Roos, N.; Eilenberg, J.; Cerutti, A.; Bruun, S. Life cycle assessment of edible insects for food protein: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagaki, B.J.; Defoliart, G.R. Comparison of diets for mass-rearing Acheta domesticus (Orthoptera: Gryllidae) as a novelty food, and comparison of food conversion efficiency with values reported for livestock. J. Econ. Entomol. 1991, 84, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpold, B.A.; Schlüter, O.K. Potential and challenges of insects as an innovative source for food and feed production. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poma, G.; Cuykx, M.; Amato, E.; Calaprice, C.; Focant, J.F.; Covaci, A. Evaluation of hazardous chemicals in edible insects and insect-based food intended for human consumption. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 100, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonincx, D.G.; van Itterbeeck, J.; Heetkamp, M.J.; van den Brand, H.; van Loon, J.J.; van Huis, A. An exploration on greenhouse gas and ammonia production by insect species suitable for animal or human consumption. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva Lucas, A.J.; de Oliveira, L.M.; da Rocha, M.; Prentice, C. Edible insects: An alternative of nutritional, functional and bioactive compounds. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 126022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada-Luna, G.; San Martin-Gonzalez, F.; Mauer, L.; Liceaga, A.M. Cricket (Acheta domesticus) Protein Hydrolysates Impact on the Physicochemical, Structural and Sensory properties of Tortillas and Tortilla chips. J. Insects Food Feed. 2021, 7, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Hierro, J.N.; Gutiérrez-Docio, A.; Otero, P.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Characterization, antioxidant activity, and inhibitory effect on pancreatic lipase of extracts from the edible insects Acheta domesticus and Tenebrio molitor. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignat, I.; Volf, I.; Popa, V.I. A critical review of methods for characterisation of polyphenolic compounds in fruits and vegetables. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carocho, M.; CFR Ferreira, I. The role of phenolic compounds in the fight against cancer—A review. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. (Former. Curr. Med. Chem. -Anti-Cancer Agents) 2013, 13, 1236–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Carlo, G.; Mascolo, N.; Izzo, A.A.; Capasso, F. Flavonoids: Old and new aspects of a class of natural therapeutic drugs. Life Sci. 1999, 65, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, F.; Khameneh, B.; Iranshahi, M.; Iranshahy, M. Antibacterial activity of flavonoids and their structure-activity relationship: An update review. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 13–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomes, A.; Fernandes, E.; Lima, J.L.; Mira, L.; Corvo, M.L. Molecular mechanisms of anti-inflammatory activity mediated by flavonoids. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1586–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nino, M.; Reddivari, L.; Osorio, C.; Kaplan, I.; Liceaga, A. Insects as a source of phenolic compounds and potential health benefits. J. Insects Food Feed. in press. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt, F.; Proksch, P.; Fiedler, K. Flavonoid sequestration by the common blue butterfly Polyommatus icarus: Quantitative intraspecific variation in relation to larval hostplant, sex and body size. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2001, 29, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, C.; Ono, H.; Meng, Y.; Shimada, T.; Daimon, T. Flavonoids from the cocoon of Rondotia menciana. Phytochemistry 2013, 94, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, J.; Yu, L.; Zhang, C.; Bi, J.; Zhu, F.; Qu, M.; Yang, Q. Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of Holotrichia parallela Motschulsky extracts. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Cuadrado-Silva, C.; Pozo-Bayón, M.; Osorio, C. Targeted metabolomic analysis of polyphenols with antioxidant activity in sour guava (Psidium friedrichsthalianum Nied.) fruit. Molecules 2017, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddivari, L.; Hale, A.L.; Miller, J.C. Determination of phenolic content, composition and their contribution to antioxidant activity in specialty potato selections. Am. J. Potato Res. 2007, 84, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketnawa, S.; Liceaga, A.M. Effect of microwave treatments on antioxidant activity and antigenicity of fish frame protein hydrolysates. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.-J.; Kim, S.-R.; Lee, K.-S.; Park, S.; Kang, S.C. Antioxidant activity of various solvent extracts from Allomyrina dichotoma (Arthropoda: Insecta) larvae. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2010, 99, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musundire, R.; Zvidzai, C.; Chidewe, C. Bio-Active Compounds Composition in Edible Stinkbugs Consumed in South-Eastern Districts of Zimbabwe. Int. J. Biol. 2014, 6, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musundire, R.; Zvidzai, C.; Chidewe, C.; Ngadze, R.; Macheka, L.; Manditsera, F.; Mubaiwa, J.; Masheka, A. Nutritional and bioactive compounds composition of Eulepida mashona, an edible beetle in Zimbabwe. J. Insects Food Feed. 2016, 2, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musundire, R.; Zvidzai, C.; Chidewe, C.; Samende, B.; Manditsera, F. Nutrient and anti-nutrient composition of Henicus whellani (Orthoptera: Stenopelmatidae), an edible ground cricket, in south-eastern Zimbabwe. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2014, 34, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everette, J.D.; Bryant, Q.M.; Green, A.M.; Abbey, Y.A.; Wangila, G.W.; Walker, R.B. Thorough study of reactivity of various compound classes toward the Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8139–8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magalhães, L.M.; Santos, F.; Segundo, M.A.; Reis, S.; Lima, J.L. Rapid microplate high-throughput methodology for assessment of Folin-Ciocalteu reducing capacity. Talanta 2010, 83, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghardt, F.; Fiedlert, K.; Proksch, P. Uptake of flavonoids from Vicia villosa (Fabaceae) by the lycaenid butterfly, Polyommatus icarus (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1997, 25, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesen, B.; Krug, E.; Fiedler, K.; Wray, V.; Proksch, P. Sequestration of host-plant-derived flavonoids by lycaenid butterfly Polyommatus icarus. J. Chem. Ecol. 1994, 20, 2523–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schittko, U.; Burghardt, F.; Fiedler, K.; Wray, V.; Proksch, P. Sequestration and distribution of flavonoids in the common blue butterfly Polyommatus icarus reared on Trifolium repens. Phytochemistry 1999, 51, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuder, M.; Wray, V.; Fiedler, K.; Proksch, P. Sequestration and metabolism of host-plant flavonoids by the lycaenid butterfly Polyommatus bellargus. J. Chem. Ecol. 1997, 23, 1361–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreres, F.; Valentão, P.; Pereira, J.A.; Bento, A.; Noites, A.; Seabra, R.M.; Andrade, P.B. HPLC-DAD-MS/MS-ESI screening of phenolic compounds in Pieris brassicae L. reared on Brassica rapa var. rapa L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreres, F.; Fernandes, F.; Pereira, D.M.; Pereira, J.A.; Valentao, P.; Andrade, P.B. Phenolics metabolism in insects: Pieris brassicae—Brassica oleracea var. costata ecological duo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9035–9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheynier, V. Phenolic compounds: From plants to foods. Phytochem. Rev. 2012, 11, 153–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifie, I.; Marshall, L.J. Food processing and its impact on phenolic constituents in food. Cogent Food Agric. 2018, 4, 1507782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Measurement of antioxidant activity. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 757–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, B.D.; Kerrihard, A.L.; Amarowicz, R.; Pegg, R.B. Phenol-based antioxidants and the in vitro methods used for their assessment. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2012, 11, 148–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.; Lapsley, K.; Jeong, W.-S.; Lachance, P.A.; Ho, C.-T.; Rosen, R.T. Antioxidative phenolic compounds isolated from almond skins (Prunus amygdalus Batsch). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2459–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, D.I.; Saraiva, J.M.A.; Vicente, A.A.; Moldão-Martins, M. Methods for determining bioavailability and bioaccessibility of bioactive compounds and nutrients. In Innovative Thermal and Non-Thermal Processing, Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 23–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, I.C.; Martins, N.; Barros, L. Phenolic compounds and its bioavailability: In vitro bioactive compounds or health promoters? In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 82, pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
| Extracts | Organic Acheta | Commercial Acheta | OrganicFeed | Commercial Feed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC (g GAE/100 g extract) | 2.1 ± 0.05 a | 1.9 ± 0.04 b | 1.2 ± 0.08 x | 1.5 ± 0.08 y |
| Crude protein (g/100 g) | 45.13 | 43.88 | 9.88 | 13.94 |
| Yield (%) | 7.9 ± 0.27 | 8.4 ± 0.12 | 6.5 ± 0.02 | 7.8 ± 0.19 |
| Target Compound | RT (min) | Molecular Weight | MRM Transition | Phenolic Compounds (ng/10 mg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Acheta | Commercial Acheta | Organic Feed | Commercial Feed | ||||
| Phenolic Acids | |||||||
| Quinic acid | 0.34 | 192 | 191 > 85 | 1.6 ± 0.9 a | 4.0 ± 2.2 a | 6.5 ± 0.9 x | 6.0 ± 1.5 x |
| Gallic acid | 0.64 | 170 | 169 > 125 | 1.4 ± 0.1 a | 0.5 ± 0.2 b | 6.3 ± 0.7 x | 9.2 ± 0.9 y |
| 4-hydroxybenzoic acid | 1.28 | 138 | 137 > 93 | 29.4 ± 3.3 a | 20.6 ± 2.9 a | 79.9 ± 4.6 x | 70.3 ± 3.9 x |
| Chlorogenic Acid | 1.53 | 354 | 353 > 191 | 3.1 ± 0.7 a | 1.5 ± 0.7 a | 11.8 ± 1.3 x | 104.0 ± 13.2 y |
| Caffeic acid | 1.69 | 180 | 179 > 135 | 1.8 ± 0.3 a | 0.8 ± 0.1 b | 16.7 ± 1.6 x | 35.8 ± 4.5 y |
| Syringic acid | 1.98 | 198 | 197 > 167 | 13.8 ± 3.5 a | 4.7 ± 1.0 b | 127.3 ± 14.6 x | 132.8 ± 15.3 x |
| p-coumaric acid | 2.5 | 164 | 163 > 119 | 7.0 ± 1.3 a | 5.8 ± 0.7 b | 115.0 ± 9.1 x | 126.5 ± 15.7 x |
| Ferulic acid | 3.08 | 194 | 193 > 134 | 9.9 ± 1.2 a | 12.9 ± 1.6 a | 95.0 ± 5.4 x | 144.2 ± 9.1 y |
| Sinapic acid | 3.24 | 224 | 223 > 208 | 3.0 ± 0.2 a | 1.8 ± 0.2 b | 33.1 ± 3.7 x | 20.6 ± 2.3 y |
| 2-hydroxybenzoic acid | 3.59 | 138 | 137 > 65 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | n.d | 20.0 ± 1.5 x | 12.8 ± 1.0 y |
| Flavonoids | |||||||
| Quercetin-3-glucoside | 3.41 | 464 | 463 > 300 | n.d | n.d | 7.2 ± 0.8 x | 88.8 ± 4.7 y |
| Quercetin-3-rutinoside | 3.48 | 610 | 609 > 300 | n.d | n.d | 1.5 ± 0.1 x | 2.3 ± 0.2 y |
| Kaempferol-3-glucoside | 3.71 | 448 | 447 > 284 | n.d | n.d | 6.8 ± 0.8 x | 8.2 ± 0.5 x |
| Daidzein | 3.73 | 254 | 253 > 91 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | n.d | 7.4 ± 0.1 x | 5.6 ± 0.2 y |
| Quercetin | 4.28 | 302 | 301 > 151 | 1.3 ± 0.6 | n.d | 6.3 ± 0.6 x | 14.9 ± 0.9 y |
| Naringenin | 4.54 | 272 | 271 > 151 | 1.0 ± 0.1 a | 0.7 ± 0.1 b | 2.6 ± 0.2 x | 3.1 ± 0.3 x |
| Apigenin | 4.57 | 270 | 269 > 117 | 3.0 ± 0.2 a | 1.9 ± 0.0 b | 26.4 ± 2.4 x | 13.4 ± 0.4 y |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nino, M.C.; Reddivari, L.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Liceaga, A.M. Targeted Phenolic Characterization and Antioxidant Bioactivity of Extracts from Edible Acheta domesticus. Foods 2021, 10, 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102295
Nino MC, Reddivari L, Ferruzzi MG, Liceaga AM. Targeted Phenolic Characterization and Antioxidant Bioactivity of Extracts from Edible Acheta domesticus. Foods. 2021; 10(10):2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102295
Chicago/Turabian StyleNino, Maria Catalina, Lavanya Reddivari, Mario G. Ferruzzi, and Andrea M. Liceaga. 2021. "Targeted Phenolic Characterization and Antioxidant Bioactivity of Extracts from Edible Acheta domesticus" Foods 10, no. 10: 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102295
APA StyleNino, M. C., Reddivari, L., Ferruzzi, M. G., & Liceaga, A. M. (2021). Targeted Phenolic Characterization and Antioxidant Bioactivity of Extracts from Edible Acheta domesticus. Foods, 10(10), 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102295