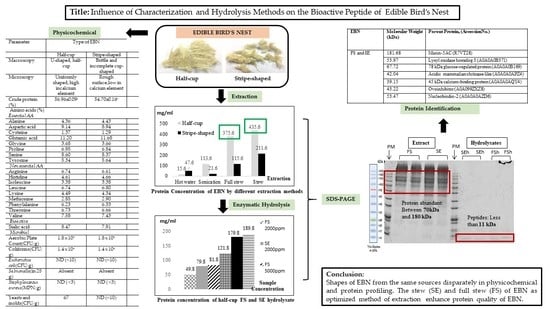
Characterization and Extraction Influence Protein Profiling of Edible Bird’s Nest
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Edible Bird’s Nest (EBN)
2.2. Characterization
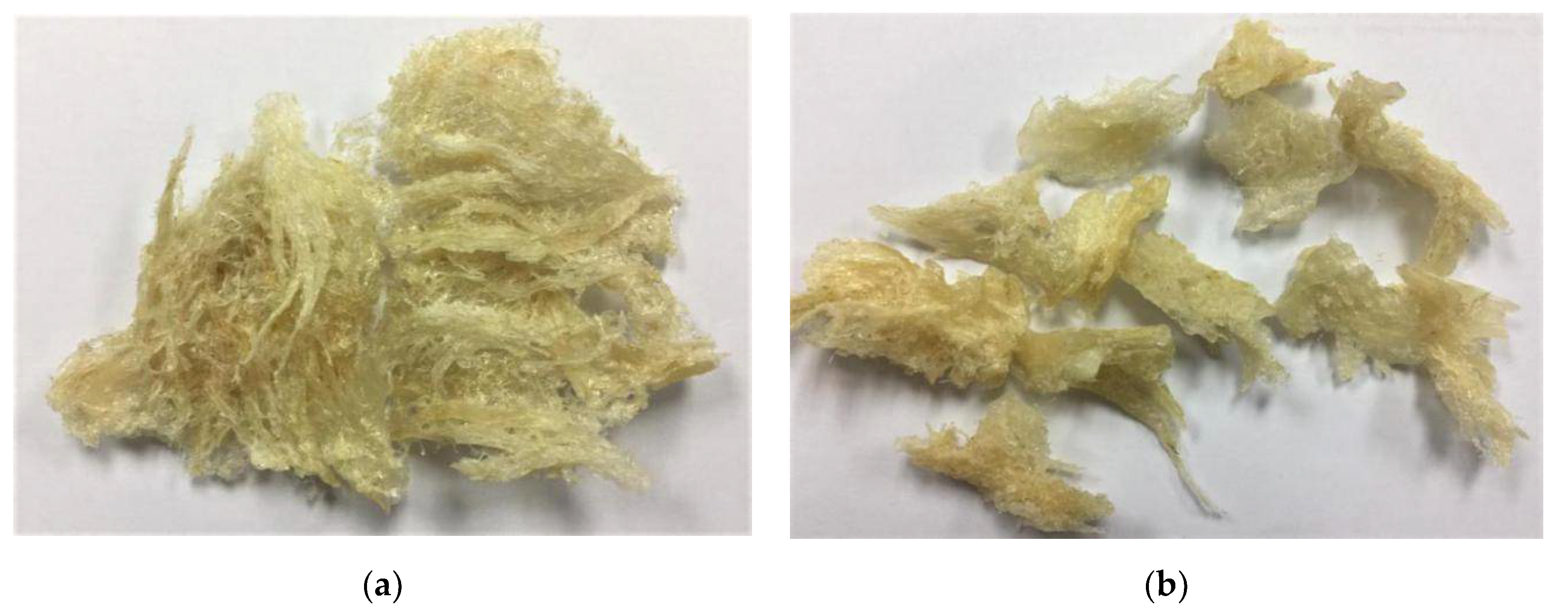
2.2.1. Physicochemical Analysis (Physical, Morphology, Elemental Composition, and Microbial Content)
2.2.2. Chemical Analysis (Crude Protein and Amino Acid)
2.3. EBN Extraction
2.3.1. Stew and Full Stew Extraction
2.3.2. Sonication
2.3.3. Hot Water
2.4. Determination of Sialic Acid by HPLC
2.5. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of EBN
2.6. Estimation of Soluble Protein
2.7. Protein Separation and Molecular Weight Determination Using SDS-PAGE
2.8. Protein Identification by LC-MS/MS Q-TOF
2.8.1. EBN Protein Digestion
2.8.2. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Coupled Quadrupole-Time of Flight (LC-MS/MS Q-TOF) Analysis
2.8.3. Data Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
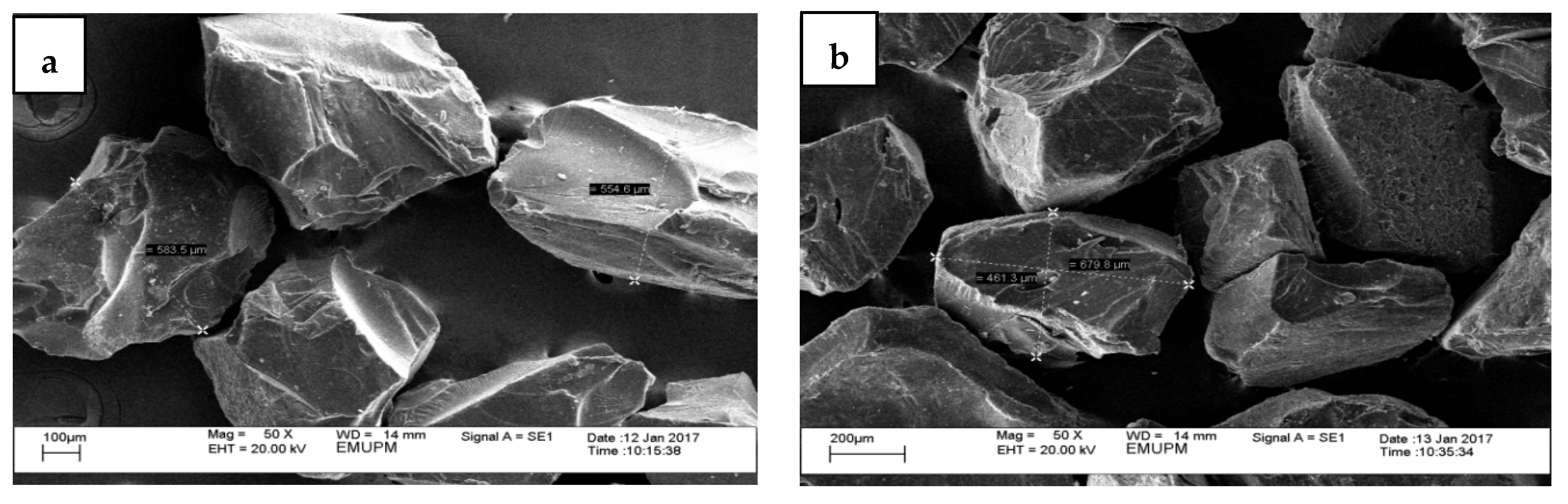
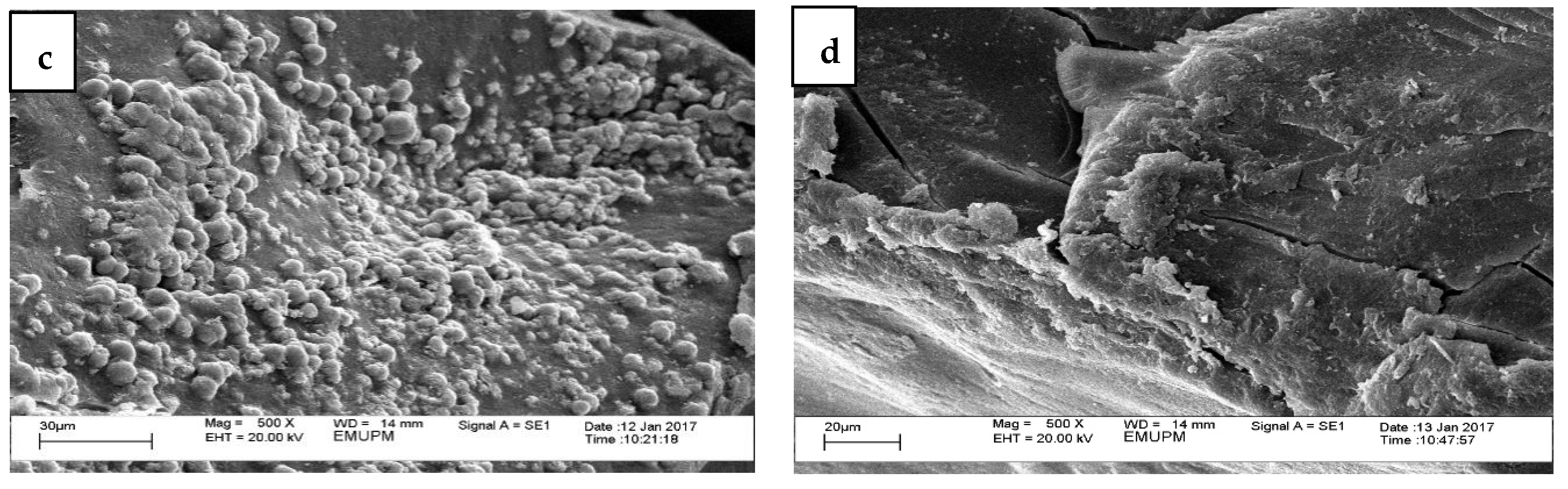
3.1. Physicochemical Analysis (Physical, Morphology, Elemental Composition, and Microbial Content)
3.2. Chemical Analysis (Crude Protein and Amino Acid)
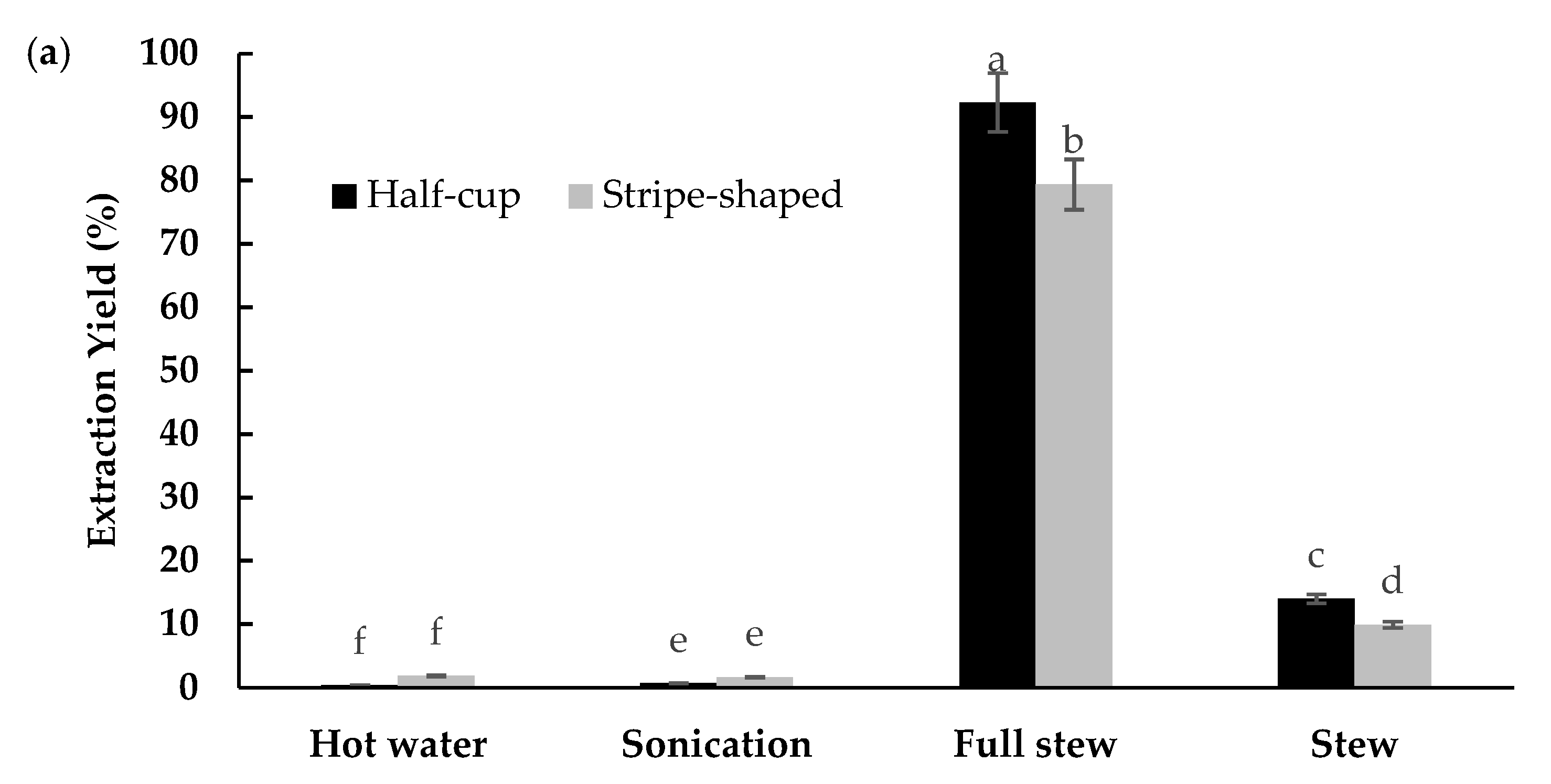
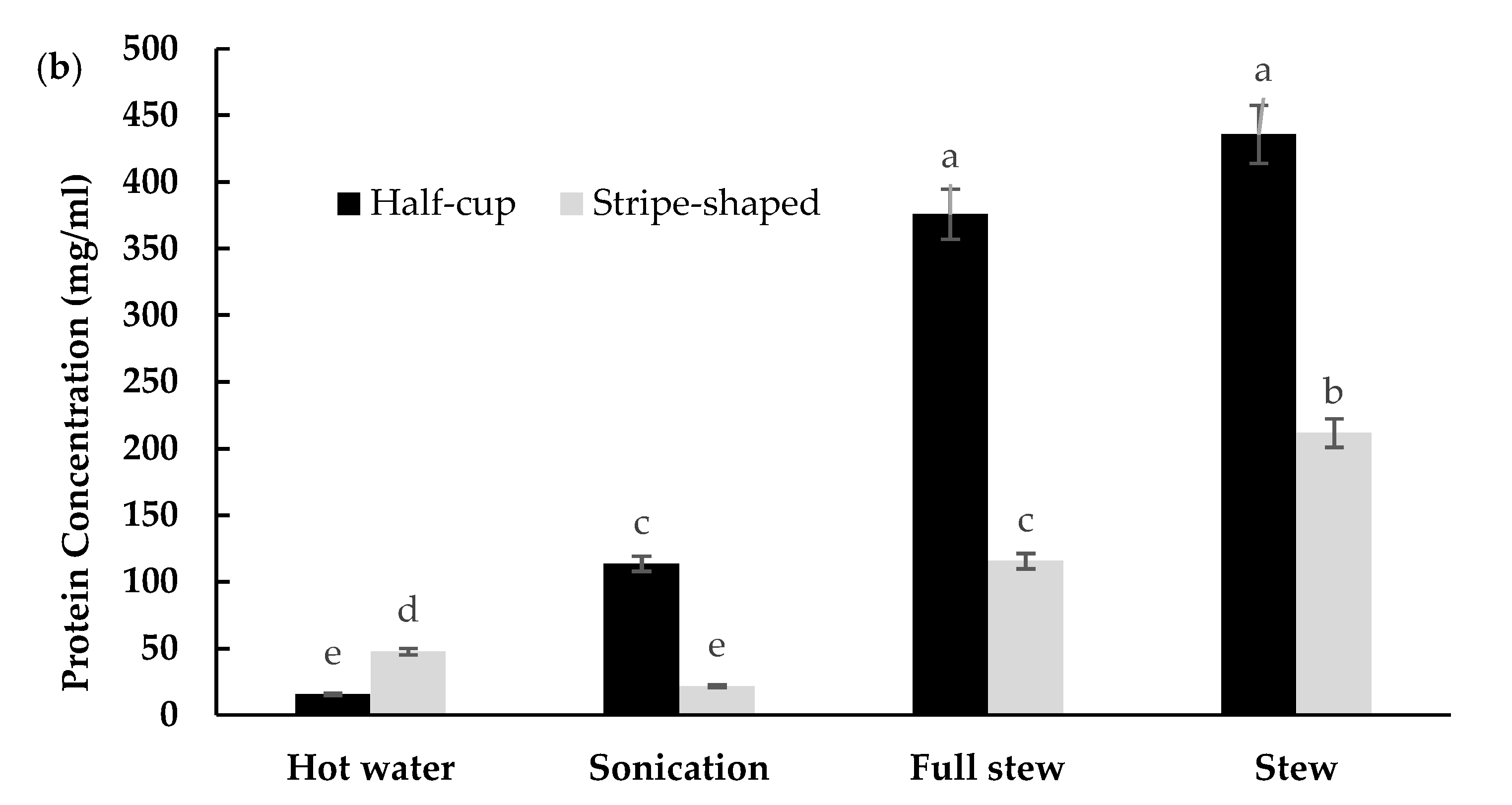
3.3. EBN Extracts and Soluble Protein Concentration
3.4. Sialic Acid Content of EBN Extracts
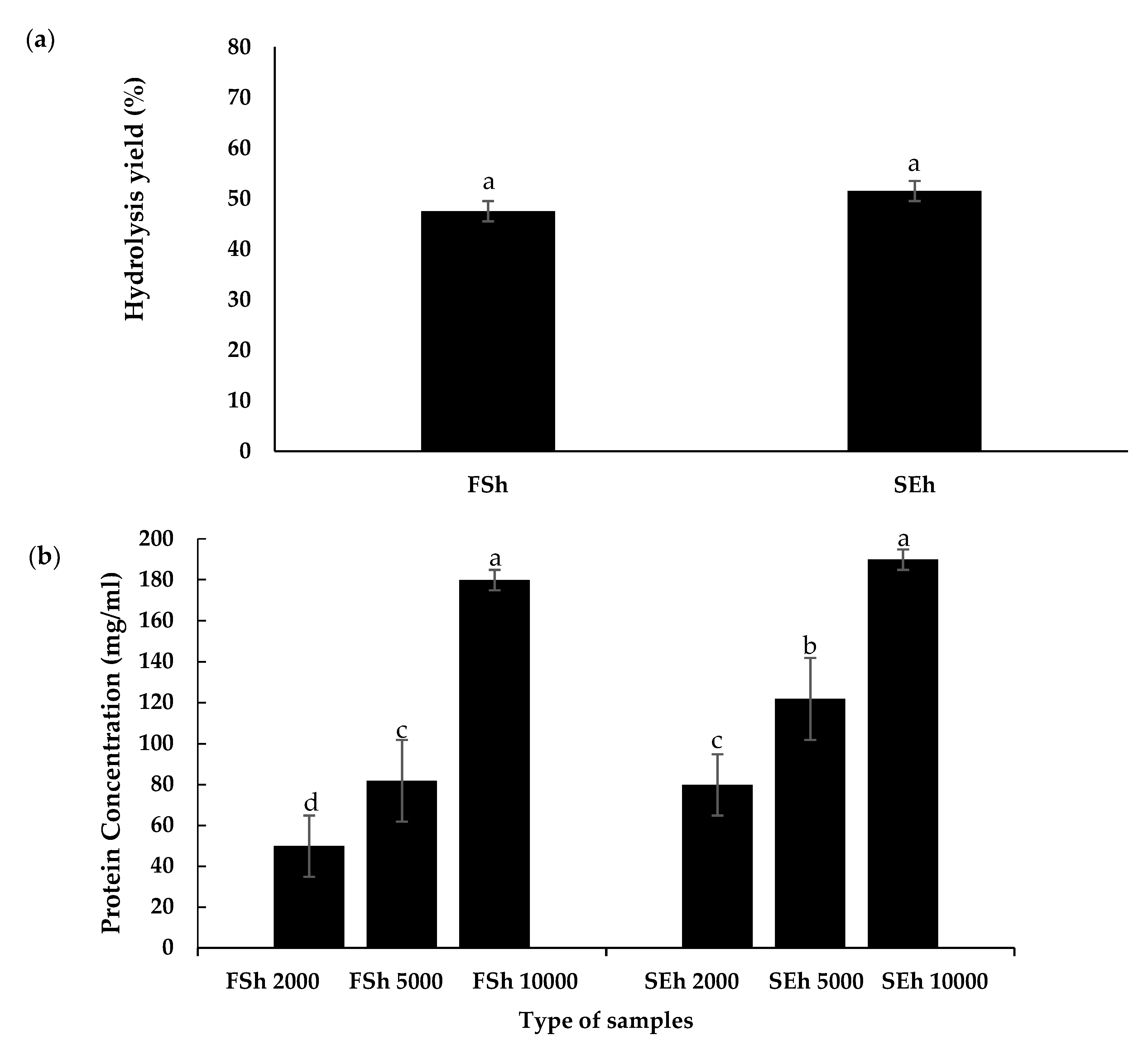
3.5. Soluble Protein Concentration of EBN Hydrolysates
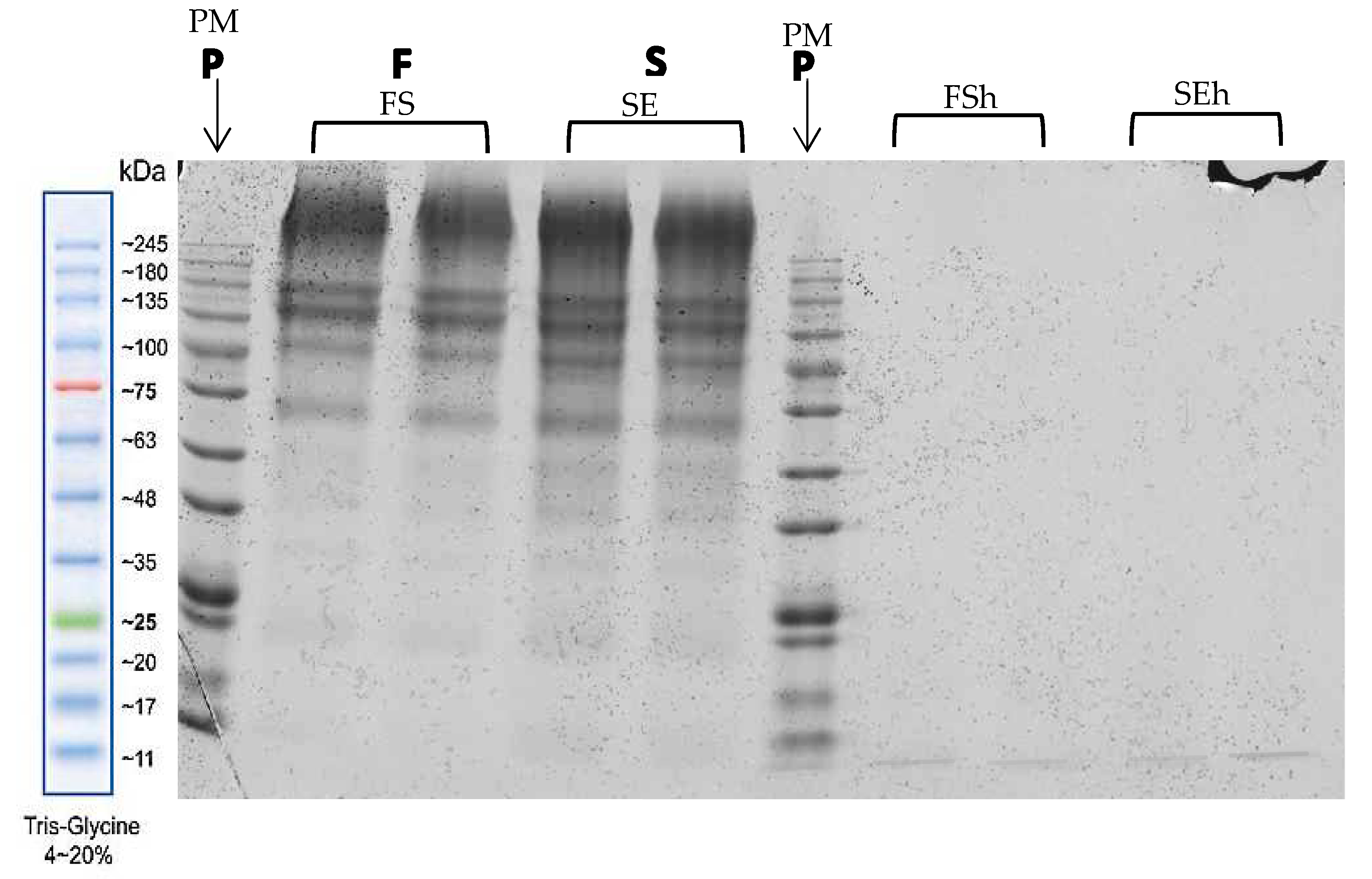
3.6. Molecular Weight Distribution of Protein in Extracts and Hydrolysates of EBNs
3.7. Protein and Peptide Profile of EBN
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamaruddin, R.; Engku Ismail, C.E.M.; Ahmad, S.A. Key Factors for the Sustainable Production of Swiftlet Birds’ Nest Industry in Malaysia: A Case Study in Northern Peninsular Malaysia. Supply Chain Manag. 2019, 8, 724–733. [Google Scholar]
- Halimi, N.M.; Kasim, Z.M.; Babji, A.S. Nutritional composition and solubility of edible bird nest (Aerodramus fuchiphagus). In Proceedings of the THE 2014 UKM FST POSTGRADUATE COLLOQUIUM: Proceedings of the Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Faculty of Science and Technology 2014 Postgraduate Colloquium, Selangor, Malaysia, 9–11 April 2014; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1614, pp. 476–481. [Google Scholar]
- Ghassem, M.; Arihara, K.; Mohammadi, S.; Sani, N.A.; Babji, A.S. Identification of two novel antioxidant peptides from edible bird’s nest (Aerodramus fuciphagus) protein hydrolysates. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2046–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, N.; Yusop, S.M.; Babji, A.S.; Lim, S.J.; Sarbini, S.R.; Yan, T.H. Edible Bird’s Nest: Physicochemical Properties, Production, and Application of Bioactive Extracts and Glycopeptides. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 37, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Liu, D. Sketch of the edible bird’s nest and its important bioactivities. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurfatin, M.H.; Etty Syarmila, I.K.; Nur‘Aliah, D.; Zalifah, M.K.; Babji, A.S.; Ayob, M.K. Effect of Enzymatic Hydrolysis on Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity in Swiftlet Saliva. Int. Food Res. 2016, 23, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, P.; Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yin, J.; Zhou, G.; Guo, S. Exogenous supplement of N-acetylneuraminic acid improves macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaq, O.; Rameli, M.A.P.; Edward, M.J.; Hanafi, N.M.; Aziz, S.A.; Abu Hassim, H.; Noor, M.H.M.; Ahmad, H. The effects of dietary edible bird nest supplementation on learning and memory functions of multigenerational mice. Brain Behav. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsukawa, N.; Matsumoto, M.; Bukawa, W.; Chiji, H.; Nakayama, K.; Hara, H.; Tsukahara, T. Improvement of Bone Strength and Dermal Thickness Due to Dietary Edible Bird’s Nest Extract in Ovariectomized Rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yew, M.Y.; Koh, R.Y.; Chye, S.M.; Othman, I.; Ng, K.Y. Edible bird’s nest ameliorates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yida, Z.; Imam, M.U.; Ismail, M.; Hou, Z.; Abdullah, M.A.; Ideris, A.; Ismail, N. Edible Bird’s Nest attenuates high fat diet-induced oxidative stress and inflammation via regulation of hepatic antioxidant and inflammatory genes. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, L.S.; Zukefli, S.N. A comprehensive review of edible bird nests and swiftlet farming. J. Integr. Med. 2016, 14, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zeng, H.; Huang, Z.; Xu, H.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B. Effect of Maternal Administration of Edible Bird’s Nest on the Learning and Memory Abilities of Suckling Offspring in Mice. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 7697261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Khan, A.; Etty Syarmila, I.K.; Nurfatin, M.H.; Farahniza, Z.; Engku Hanisah, E.U.; Norhasidah, S.; Masitah, E.H.; Masturah, A.K.; Nurul’Ain, M.; Maaruf, A.G.; et al. Antioxidative properties of ready-to-drink products incorporated with enzymatically hydrolysed edible bird nest. In Proceedings of the Edible Bird Nest Industry Conference, Marriot Hotel Putrajaya, Putrajaya, Malaysia, 25–26 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Standards Malaysia. Edible-birdnest (EBN)—Specification. In Malaysian Standard MS 2334:2011; Food Safety and Quality Division; Ministry of Health Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hun, L.T.; Wani, W.A.; Tan, E.T.T.; Adnan, N.A.; Ling, Y.L.; Abdul Aziz, R. Investigations into the physicochemical, biochemical, and antibacterial properties of edible bird’s nest. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 228–247. [Google Scholar]
- Shinners, T.C.; Tewari, J.P. Diversity in crystal production by some bird’s nest fungi (Nidulariaceae) in culture. Can. J. Chem. 1997, 75, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.F.; Lim, P.K.C.; Mak, J.W.; Ooi, S.S.; Chen, D.K.F. Molecular characterization of culturable bacteria in raw and commercial edible bird nests (EBNs). Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 25, 966–974. [Google Scholar]
- Wan Syahidah, H.; Normah, M.; Albert, T. Protein content and amino acid composition of farmed edible bird’s nests in Malaysia. MJVR 2014, 5, 342–346. [Google Scholar]
- Najafian, L.; Babji, A. A review of fish-derived antioxidant and antimicrobial peptides: Their production, assessment, and applications. Peptides 2012, 33, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, M.U.; Ismail, M.; Ooi, D.J.; Azmi, N.H.; Sarega, N.; Chan, K.W.; Bhanger, M.I. Are bioactive-rich fractions functionally richer? Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2015, 36, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Z.C.; Chan, G.K.; Wu, L.; Lam, H.H.; Yao, P.; Dong, T.T.; Tsim, K.W. A comprehensive proteomics study on edible bird’s nest using new monoclonal antibody approach and application in quality control. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 66, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration/Bacteriological Analytical Manual (FDA/BAM). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/laboratory-methods-food/bacteriological-analytical-manual-bam (accessed on 23–27 August 2021).
- AOAC. Method 991.14. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 17th ed; AOAC: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1995; pp. 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz, W. Methods 930.15, 942.05, 920.39, 954.01, 991.43, 50.1.14, 9.1.09. In Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mæhre, H.; Dalheim, L.; Edvinsen, G.; Elvevoll, E.; Jensen, I.-J. Protein Determination—Method Matters. Foods 2018, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, M.; Abdullah, A.; Mustapha, W.A.W. Antioxidant capacity and amino acid profiles of egg tofu. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2013, 10, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careena, S.; Sani, D.; Tan, S.N.; Lim, C.W.; Hassan, S.; Norhafizah, M.; Kirby, B.; Ideris, A.; Stanslas, J.; Bin Basri, H. Effect of Edible Bird’s Nest Extract on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Impairment of Learning and Memory in Wistar Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Rosni, S.; Fisal, A.; Azwan, A.; Chye, F.Y.; Matanjun, P. Crude proteins, total soluble proteins, total phenolic contents and SDS-PAGE profile of fifteen varieties of seaweed from Semporna, Sabah, Malaysia. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 22, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.-Q.; Gilar, M.; Lee, P.J.; Bouvier, E.S.P.; Gebler, J.C. Enzyme-Friendly, Mass Spectrometry-Compatible Surfactant for In-Solution Enzymatic Digestion of Proteins. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6023–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Food Safety. Food Safe. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/newsroom/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Kew, P.E.; Wong, S.F.; Lim, P.K.; Mak, J.W. Structural analysis of raw and commercial farm edible bird nests. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 31, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deveaux, A.; Pham, I.; West, S.G.; André, E.; Lantoine-Adam, F.; Bunouf, P.; Sadi, S.; Hermier, D.; Mathé, V.; Fouillet, H.; et al. L-Arginine Supplementation Alleviates Postprandial Endothelial Dysfunction When Baseline Fasting Plasma Arginine Concentration Is Low: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Healthy Overweight Adults with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, R.; Costa, F.G.P.; Givisiez, P.E.N.; Goulart, C.C.; Dos Santos, R.A.; De Lima, M.R. Glutamic acid supplementation on low protein diets for laying hens. Acta Sci. Anim. Sci. 2015, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukefli, S.N.; Chua, L.S.; Rahmat, Z. Protein Extraction and Identification by Gel Electrophoresis and Mass Spectrometry from Edible bird’s Nest Samples. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 10, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norhayati, M.K.; Azman, O.; Wan Nazaimoon, W.M. Preliminary study of the nutritional content of Malaysian edible bird’s nest. Malays. J. Nutr. 2010, 16, 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Khushairay, E.S.I.; Ayub, M.K.; Babji, A.S. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis of pancreatin and alcalase enzyme on some properties of edible bird’s nest hydrolysate. In Proceedings of the THE 2014 UKM FST POSTGRADUATE COLLOQUIUM: Proceedings of the Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Faculty of Science and Technology 2014 Postgraduate Colloquium, Selangor, Malaysia, 9–11 April 2014; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1614, pp. 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Utomo, B.; Rosyidi, D.; Radiati, L.; Puspaningsih, N.; Proborini, W. Protein Characterization of Extracted Water from Three Kinds of Edible Bird Nest Using SDS-PAGE CBB Staining and SDSPAGE Glycoprotein Staining and LC-MS/MS Analyses. IOSR J. Agric. Veter-Sci. 2014, 7, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.-F.; Chan, G.K.-L.; Zhang, M.-L.; Yao, P.; Lin, H.-Q.; Dong, T.T.-X.; Li, G.; Lai, X.-P.; Tsim, K.W.-K. Characterization of edible bird’s nest by peptide fingerprinting with principal component analysis. Food Qual. Saf. 2017, 1, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Martin, T.A.; Sanders, A.J.; Jiang, A.; Sun, P.; Jiang, W.G. Location, function and role of stromal cell-derived factors and possible implications in cancer (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 47, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, K.; Szilágyi, T. New Approach for Untangling the Role of Uncommon Calcium-Binding Proteins in the Central Nervous System. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravussin, A.; Youm, Y.-H.; Sander, J.; Ryu, S.; Nguyen, K.; Varela, L.; Shulman, G.I.; Sidorov, S.; Horvath, T.L.; Schultze, J.L.; et al. Loss of Nucleobindin-2 Causes Insulin Resistance in Obesity without Impacting Satiety or Adiposity. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Słowińska, M.; Liszewska, E.; Nynca, J.; Bukowska, J.; Hejmej, A.; Bilińska, B.; Szubstarski, J.; Kozłowski, K.; Jankowski, J.; Ciereszko, A.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of an Ovoinhibitor, a Multidomain Kazal-Like Inhibitor from Turkey (Meleagris gallopavo) Seminal Plasma1. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 91, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Edible Bird Nest | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Half-Cup | Stripe-Shaped | |||
| Macroscopic | |||||
| Measurement | n = 10 | Range | Mean ± SD | Range | Mean ± SD |
| Height | cm | 3.0–5.1 | 4.08 ± 0.72 a | 1.0–1.5 | 1.28 ± 0.15 b |
| Length | cm | 5.5–9.0 | 7.06 ± 1.33 a | 2.5–4.0 | 3.26 ± 0.48 b |
| Weight | g | 5.0–5.5 | 5.19 ± 0.18 a | 2.0–2.5 | 2.26 ± 0.18 b |
| Element | n = 3 | Microscopic Weight | |||
| Carbon | % | 4.78 ± 11.72 b | 28.49 ± 22.26 a | ||
| Oxygen | % | 5.61 ± 13.75 b | 27.13 ± 21.30 a | ||
| Magnesium | % | ND | 0.22 ± 0.53 | ||
| Calcium | % | 72.94 ± 43.58 a | 44.16 ± 43.31 b | ||
| Unit | Microbial Content | ||||
| Aerobic Plate Count | CFU/g | 1.8 × 108 | 1.8 × 108 | ||
| Coliforms | CFU/g | 1.4 × 104 | 1.4 × 104 | ||
| Escherichia coli | CFU/g | ND (<10) | ND (<10) | ||
| Salmonella | in 25 g | Absent | Absent | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus | MPN/g | ND (<3) | ND (<3) | ||
| Yeasts and molds | CFU/g | 67 | ND (<10) | ||
| Parameter | This Study | [2] | [19] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Half-Cup | Stripe-Shaped | |||||
| Location | Compound (%) | Terengganu | Pahang | Perak, Penang, Kedah | Sabah, Sarawak | |
| Crude protein | 56.96 ± 0.09 a | 54.70 ± 0.16 b | 58.55 ± 0.62 | 53.8 ± 0.18 | 52.8 ± 1.04 | |
| Arginine | 6.74 | 6.61 | 3.80 | 4.50 | 4.10 | |
| Essential amino acids (EAAs) | Histidine | 4.61 | 4.66 | 1.40 | 1.50 | 1.40 |
| Isoleucine | 3.38 | 3.38 | 3.40 | 0.60 | 0.50 | |
| Leucine | 6.74 | 6.80 | 5.30 | 2.70 | 2.50 | |
| Lysine | 4.49 | 4.34 | 5.40 | 1.30 | 1.10 | |
| Methionine | 2.85 | 2.90 | 2.20 | 0.70 | 0.70 | |
| Phenylalanine | 6.23 | 6.33 | 2.70 | 2.30 | 2.20 | |
| Threonine | 6.73 | 6.66 | 2.90 | 2.70 | 2.40 | |
| Valine | 7.58 | 7.43 | 3.30 | 1.60 | 1.40 | |
| Total EEA | 49.35 | 49.11 | 30.40 | 17.90 | 16.30 | |
| Alanine | 4.36 | 4.43 | 3.90 | 1.30 | 1.20 | |
| Non-essential amino acids (nEAAs) | Aspartic acid | 9.14 | 8.94 | 6.30 | 4.00 | 3.70 |
| Cysteine | 1.37 | 1.29 | 1.70 | 1.10 | 1.40 | |
| Glutamic acid | 11.20 | 11.68 | 9.60 | 3.00 | 2.60 | |
| Glycine | 3.68 | 3.66 | 2.50 | 1.50 | 1.60 | |
| Proline | 6.95 | 6.84 | 2.90 | 3.20 | 2.90 | |
| Serine | 8.60 | 8.37 | 2.40 | 4.30 | 4.00 | |
| Tyrosine | 5.34 | 5.64 | 2.90 | 2.70 | 2.60 | |
| Total nEAA | 50.64 | 50.85 | 32.20 | 21.10 | 20.00 | |
| Protein | MW (kDa) | Parent Protein, (Accession No.) a | Score b | Sample | Peptide Sequence c | Position d | mz−1 | Biological Function (Annotated in UniProt/SwissProt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Stew(FS) | Stew (SE) | ||||||||
| 1 | 67.72 | 78 kDa glucose- regulated protein(A0A0A0B169) | 204.84 | 39.01 | FS/SE | [K]. SQIFSTASDNQPTVTIK. [V] | 407–423 | 918.96 | Stress response |
| 2 | 53.97 | Lysyl oxidase homolog 3 (A0A0A0B371) | 538.63 | 538.63 | FS/SE | [R]. QLPVTEGIVEVR. [Y] | 97–108 | 670.38 | Stabilization of collagen fibrils, elasticity of mature elastin |
| FS/SE | [R]. IPGFKDSNVIETEQSHVEEVR. [L] | 66–86 | 604.05 | ||||||
| FS/SE | [R]. LRPVVSGAR. [R] | 87–95 | 318.87 | ||||||
| FS/SE | [K]. DSNVIETEQSHVEEVR. [L] | 71–86 | 935.94 | ||||||
| SE | RQLPVTEGIVEVR. [Y] | 96–108 | 499.29 | ||||||
| 3 | 181.68 | Mucin-5AC (R7VT28) | 668.96 | 326.51 | FS/SE | [K]. GVLLTGWR. [S] | 700–707 | 451.27 | Gel-forming glycoprotein of gastric and respiratory tract epithelia |
| FS/SE | [K]. TTSGVIEGTSAAFGNTWK. [T] | 598–615 | 913.95 | ||||||
| FS/SE | [K]. SPYEDFNIQIR. [R] | 115–125 | 691.34 | ||||||
| FS/SE | [R]. SQSVVGNVLEFANSWK. [V] | 1064–1079 | 882.95 | ||||||
| FS | [R]. GSVLLDGK. [L] | 152–159 | 394.72 | ||||||
| 4 | 42.04 | Acidic mammalian chitinase-like (A0A0A0APZ4 | 198.81 | 213.39 | FS/SE | [K]. LLVGFPTYGR. [N] | 243–252 | 561.82 | Chitin degradation, inflammatory response against pathogen |
| FS/SE | [K]. FSTMVSTPQNR. [Q] | 94–104 | 634.31 | ||||||
| FS/SE | [K]. YPLITTLK. [N] | 360–367 | 474.79 | ||||||
| 5 | 39.15 | 45 kDa calcium- binding protein (A0A0A0AQY4) | 119.81 | 147.78 | FS/SE | [K]. NNEELKIDEETQEVLDNLKDR. [W] | 153–173 | 636.82 | Exocytosis |
| FS/SE | [K]. LTLSEFISLPVGTVENQQAQDIDDDWVK. [D] | 223–250 | 1054.19 | ||||||
| FS/SE | [K]. TDEHFQEAVEENK. [M] | 101–113 | 525.9 | ||||||
| FS/SE | [K]. EMEEFEEDSEPR. [K] | 56–67 | 763.8 | ||||||
| FS/SE | [R]. AVDPDGDGHVSWDEYK. [I] | 118–133 | 895.39 | ||||||
| FS | [K]. QMIAVADENQNHHLELEEILK. [Y] | 291–311 | 619.31 | ||||||
| SE | [K]. IKNNEELKIDEETQEVLDNLK. [D] | 151–171 | 629.33 | ||||||
| 6 | 53.47 | Nucleobindin-2 (A0A0A0AZD6) | 38.59 | 73.77 | FS/SE | [K]. EVWEEADGLDPNEFDPK. [T] | 231–247 | 995.44 | Calcium homeostasis |
| FS/SE | [R]. LVTLEEFLR. [A] | 312–320 | 560.32 | ||||||
| FS/SE | [K]. AATSDLENYDK. [T] | 161–171 | 613.78 | ||||||
| FS | [K]. LHDVNNDGFLDEQELEALFTK. [E] | 252–272 | 816.39 | ||||||
| SE | [K]. VENPDTGLYYDEYLR. [Q] | 45–59 | 923.93 | ||||||
| SE | [K]. QFEHLNHQNPDTFEPK. [D] | 138–153 | 495.99 | ||||||
| SE | [K]. LQTADIEEIK. [S] | 75–84 | 580.31 | ||||||
| 7 | 43.22 | Ovoinhibitor (A0A099ZXZ8) | 46.77 | 41.4 | FS/SE | [R]. QLMACTMIYDPVCGTDGVTYASECTLCAHNLEHR. [T] | 344–377 | 998.43 | Anti-viral |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamad Nasir, N.N.; Mohamad Ibrahim, R.; Abu Bakar, M.Z.; Mahmud, R.; Ab Razak, N.A. Characterization and Extraction Influence Protein Profiling of Edible Bird’s Nest. Foods 2021, 10, 2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102248
Mohamad Nasir NN, Mohamad Ibrahim R, Abu Bakar MZ, Mahmud R, Ab Razak NA. Characterization and Extraction Influence Protein Profiling of Edible Bird’s Nest. Foods. 2021; 10(10):2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102248
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamad Nasir, Nurul Nadiah, Ramlah Mohamad Ibrahim, Md Zuki Abu Bakar, Rozi Mahmud, and Nor Asma Ab Razak. 2021. "Characterization and Extraction Influence Protein Profiling of Edible Bird’s Nest" Foods 10, no. 10: 2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102248
APA StyleMohamad Nasir, N. N., Mohamad Ibrahim, R., Abu Bakar, M. Z., Mahmud, R., & Ab Razak, N. A. (2021). Characterization and Extraction Influence Protein Profiling of Edible Bird’s Nest. Foods, 10(10), 2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102248