Role of Lactic Acid Bacteria Phospho-β-Glucosidases during the Fermentation of Cereal by-Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbial and Biochemical Characterization of Raw-BSG
2.2. Preparation of Finnish Brewers’ Spent Grain (FL-BSG)-Based Medium
2.3. Microorganisms and Growth Condition
2.4. Phenotypic Microarray Analysis
2.5. Determination of Organic Acids and Sugars
2.6. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) Analysis of Phenolic Compounds
2.7. RNA Isolation and Transcript Analysis by Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Microbial and Biochemical Characterization of Raw FL-BSG
3.2. Kinetics of Growth and Organic Acids Production during FL-BSG Fermentation
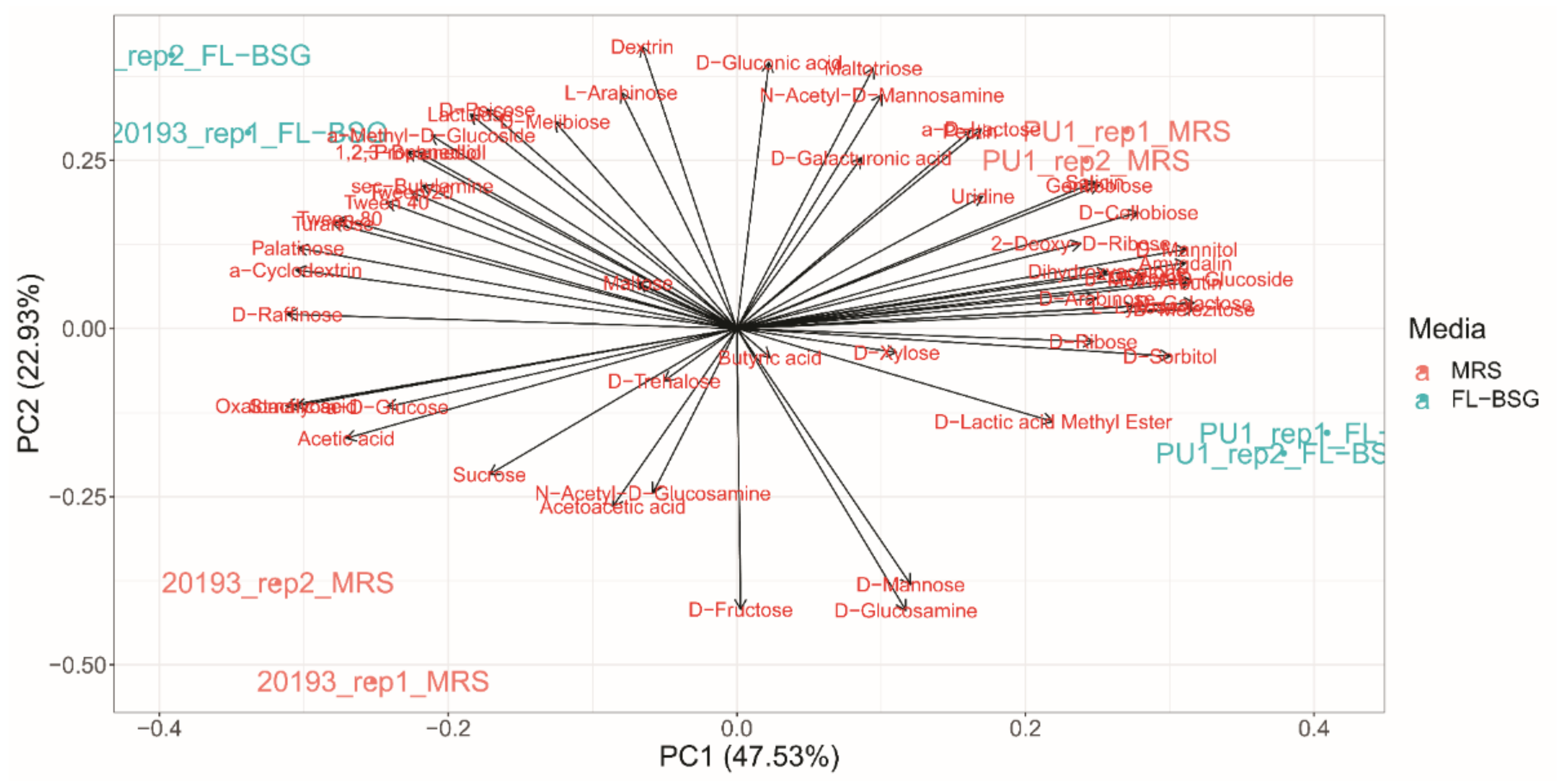
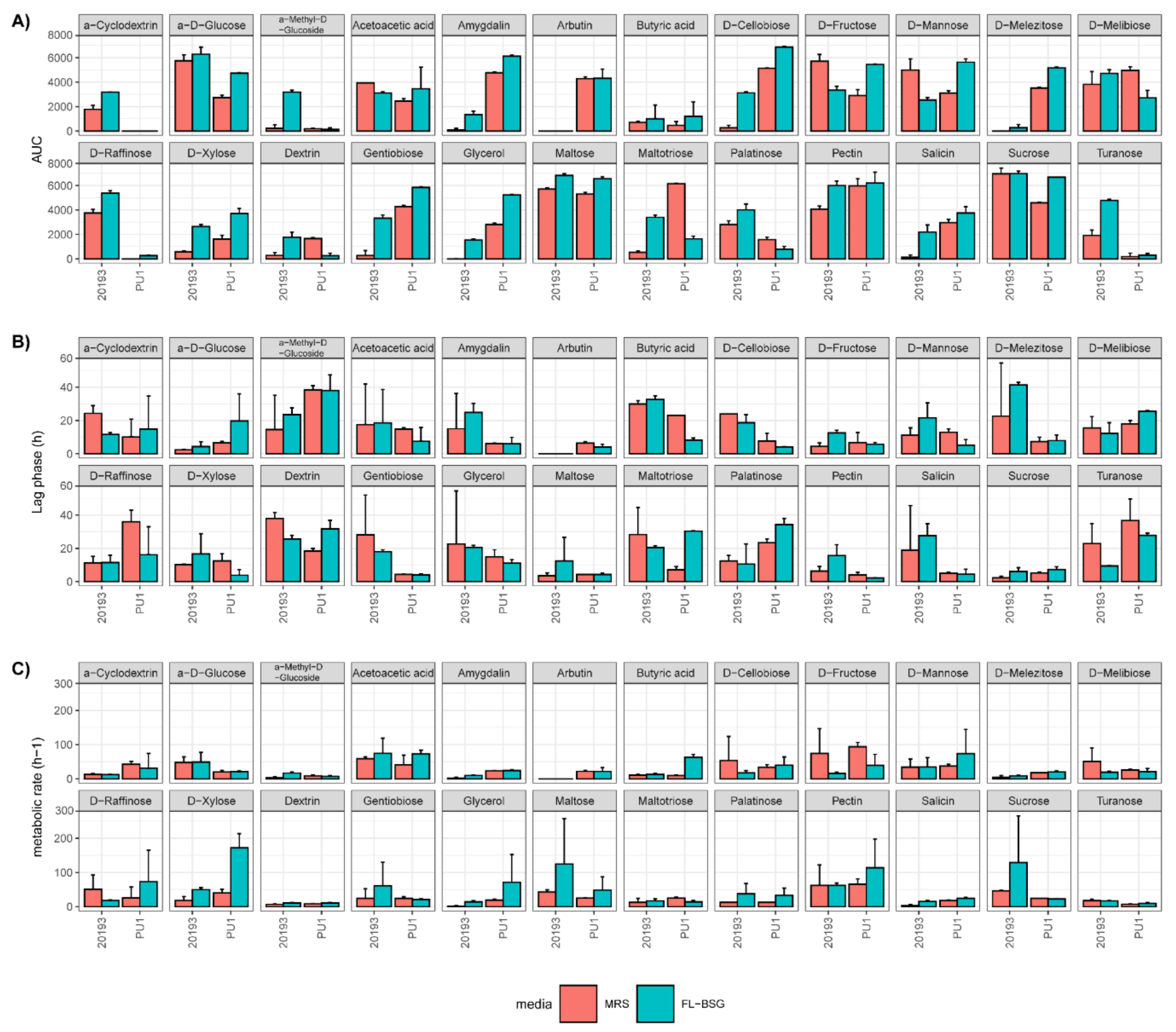
3.3. Phenotypic Profiles Adaptation to Brewers’ Spent Grain Ecosystem
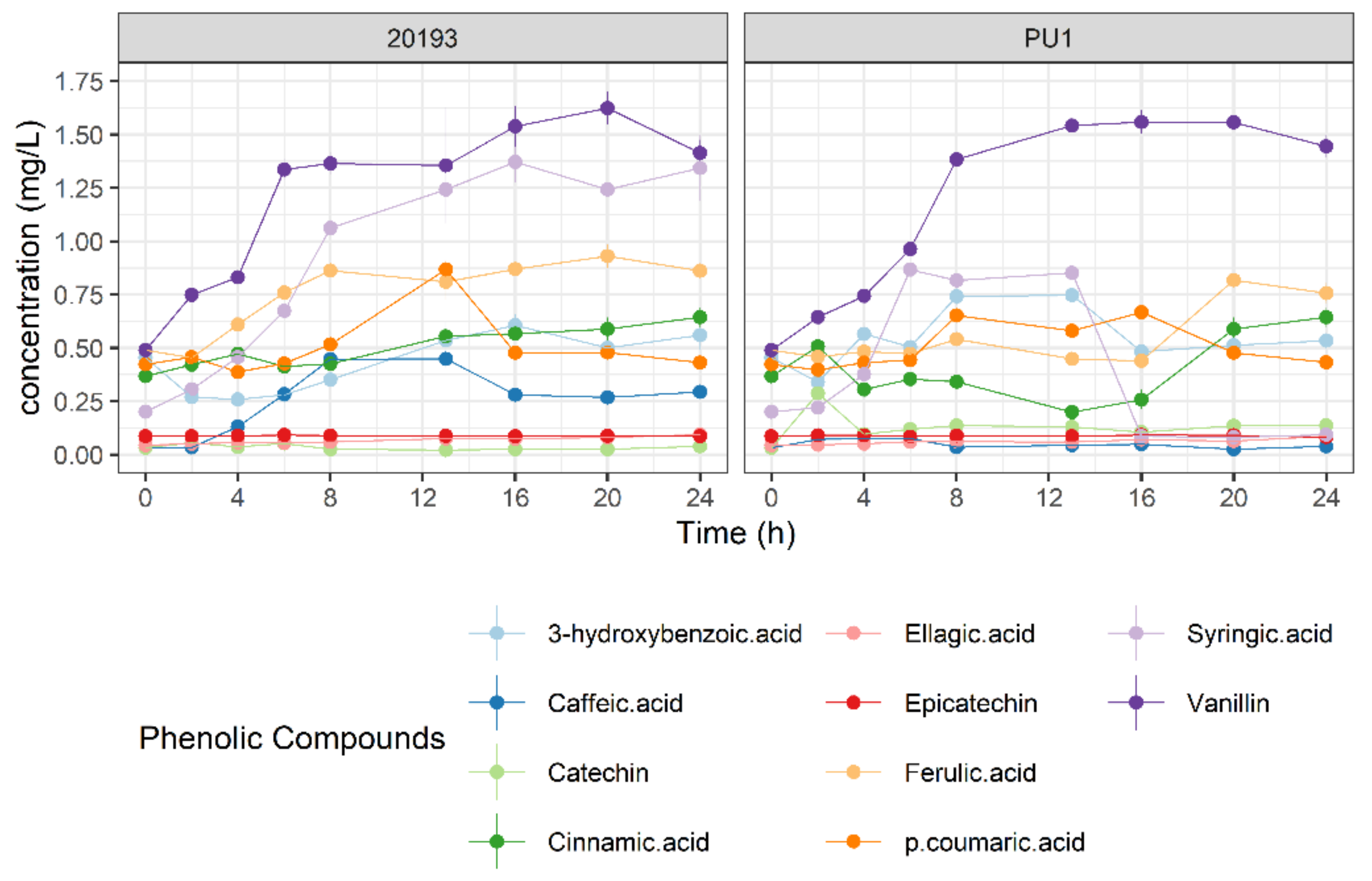
3.4. Phenolic Profile Changes during BSG Fermentation
3.5. Gene Expression Coding for Galactose, Sucrose and Starch and Glucuronate Interconversions Pathways under Brewers’ Spent Grain Conditions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salvetti, E.; O’Toole, P.W. The Genomic Basis of Lactobacilli as Health-Promoting Organisms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verni, M.; Rizzello, C.G.; Coda, R. Fermentation Biotechnology Applied to Cereal Industry By-Products: Nutritional and Functional Insights. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarova, K.; Slesarev, A.; Wolf, Y.; Sorokin, A.; Mirkin, B.; Koonin, E.; Pavlov, A.; Pavlova, N.; Karamychev, V.; Polouchine, N.; et al. Comparative Genomics of the Lactic Acid Bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15611–15616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filannino, P.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M. Metabolic and Functional Paths of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Plant Foods: Get out of the Labyrinth. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 49, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michlmayr, H.; Kneifel, W. β-Glucosidase Activities of Lactic Acid Bacteria: Mechanisms, Impact on Fermented Food and Human Health. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 352, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riou, C.; Salmon, J.M.; Vallier, M.J.; Günata, Z.; Barre, P. Purification, Characterization, and Substrate Specificity of a Novel Highly Glucose-Tolerant Beta-Glucosidase from Aspergillus Oryzae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3607–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.-H.; Jeon, H.-L.; Yang, S.-J.; Sim, M.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, N.-K.; Paik, H.-D. Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Traditional Korean Fermented Foods Based on β-Glucosidase Activity. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, K.; Li, H. GH1-Family 6-P-b-Glucosidases from Human Microbiome Lactic Acid Bacteria. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2013, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, P.W.; Lengeler, J.W.; Jacobson, G.R. Phosphoenolpyruvate:Carbohydrate Phosphotransferase Systems of Bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 57, 543–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I. Brewer’s Spent Grain: A Valuable Feedstock for Industrial Applications. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.M.; Steffen, E.J.; Arendt, E.K. Brewers’ Spent Grain: A Review with an Emphasis on Food and Health. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verni, M.; Pontonio, E.; Krona, A.; Jacob, S.; Pinto, D.; Rinaldi, F.; Verardo, V.; Díaz-de-Cerio, E.; Coda, R.; Rizzello, C.G. Bioprocessing of Brewers’ Spent Grain Enhances Its Antioxidant Activity: Characterization of Phenolic Compounds and Bioactive Peptides. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Bai, Y.; Jia, Y.; Shao, T. Ensiling as Pretreatment of Rice Straw: The Effect of Hemicellulase and Lactobacillus Plantarum on Hemicellulose Degradation and Cellulose Conversion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plessas, S.; Trantallidi, M.; Bekatorou, A.; Kanellaki, M.; Nigam, P.; Koutinas, A.A. Immobilization of Kefir and Lactobacillus Casei on Brewery Spent Grains for Use in Sourdough Wheat Bread Making. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sorvali, P.; Laitila, A.; Maina, N.H.; Coda, R.; Katina, K. Dextran Produced in Situ as a Tool to Improve the Quality of Wheat-Faba Bean Composite Bread. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahm, M.; Hasenbrink, G.; Ludwig, J. Grofit: Fitting Biological Growth Curves with R. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acin-Albiac, M.; Filannino, P.; Gobbetti, M.; Di Cagno, R. Microbial High Throughput Phenomics: The Potential of an Irreplaceable Omics. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2290–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehkala, M.; Shubin, M.; Connor, T.R.; Thomson, N.R. Novel R Pipeline for Analyzing Biolog Phenotypic Microarray Data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppa, G.; Conterno, L.; Gerbi, V. Determination of Organic Acids, Sugars, Diacetyl, and Acetoin in Cheese by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2722–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, C.G.; Nionelli, L.; Coda, R.; De Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M. Effect of Sourdough Fermentation on Stabilisation, and Chemical and Nutritional Characteristics of Wheat Germ. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlais, A.Z.A.; Da Ros, A.; Pasquale, F.; Vicentini, O.; Gobbetti, M.; Di Cagno, R. Biotechnological Re-Cycling of Apple by-Products: A Reservoir Model to Produce a Dietary Supplement Fortified with Biogenic Phenolic Compounds. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acin-Albiac, M.; Filannino, P.; Coda, R.; Rizzello, C.G.; Gobbetti, M.; Di Cagno, R. The Metabolism of Lignocellulose-Derived Substrates Drives the Adaptation of Lactic Acid Bacteria during Fermentation of Brewers´ Spent Grain: A Phenomics Evidence. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Applied Biosystems. Real-Time PCR Handbook; ThermoFisher Scientific: Waltham, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Derveaux, S.; Vandesompele, J.; Hellemans, J. How to Do Successful Gene Expression Analysis Using Real-Time PCR. Methods 2010, 50, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desroche, N.; Beltramo, C.; Guzzo, J. Determination of an Internal Control to Apply Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR to Study Stress Response in the Lactic Acid Bacterium Oenococcus Oeni. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 60, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mendiburu, F. Package ‘Agricolae’ 2020. Available online: ftp://mirror.csclub.uwaterloo.ca/CRAN/web/packages/agricolae/agricolae.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Jin, Q.; Liu, J.; Cassland, B.L.P.A.; Higgins, D.L. Detoxifying Pre-Treated Lignocellulose-Containing Materials 2018. U.S. Patent 20180273984, 17 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Côté, G.L.; Skory, C.D. Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of an Insoluble Glucan-Producing Glucansucrase from Leuconostoc Mesenteroides NRRL B-1118. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 2387–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olvera, C.; Centeno-Leija, S.; López-Munguía, A. Structural and Functional Features of Fructansucrases Present in Leuconostoc Mesenteroides ATCC 8293. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2007, 92, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Pitkänen, L.; Maina, N.H.; Coda, R.; Katina, K.; Tenkanen, M. Interactions between Fava Bean Protein and Dextrans Produced by Leuconostoc Pseudomesenteroides DSM 20193 and Weissella Cibaria Sj 1b. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, E.; Selvi, S.S.; Nikerel, E.; Teusink, B.; Toksoy Öner, E.; Çakır, T. A Genome-Scale Metabolic Network of the Aroma Bacterium Leuconostoc Mesenteroides Subsp. Cremoris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3153–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglin, R.C.; Meile, L.; Stevens, M.J.A. Clustering of Pan- and Core-Genome of Lactobacillus Provides Novel Evolutionary Insights for Differentiation. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duar, R.M.; Lin, X.B.; Zheng, J.; Martino, M.E.; Grenier, T.; Pérez-Muñoz, M.E.; Leulier, F.; Gänzle, M.; Walter, J. Lifestyles in Transition: Evolution and Natural History of the Genus Lactobacillus. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, S27–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleerebezem, M.; Boekhorst, J.; van Kranenburg, R.; Molenaar, D.; Kuipers, O.P.; Leer, R.; Tarchini, R.; Peters, S.A.; Sandbrink, H.M.; Fiers, M.W.E.J.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence of Lactobacillus Plantarum WCFS1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siezen, R.J.; Francke, C.; Renckens, B.; Boekhorst, J.; Wels, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; van Hijum, S.A.F.T. Complete Resequencing and Reannotation of the Lactobacillus Plantarum WCFS1 Genome. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, D.M.; Jacob, F.; Titze, J.; Arendt, E.K.; Zannini, E. Fibre, Protein and Mineral Fortification of Wheat Bread through Milled and Fermented Brewer’s Spent Grain Enrichment. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 235, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.A.; I’Anson, K.J.; Treimo, J.; Faulds, C.B.; Brocklehurst, T.F.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Waldron, K.W. Profiling Brewers’ Spent Grain for Composition and Microbial Ecology at the Site of Production. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.S.; Wang, Y.P.; Yang, F.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Screening a Lactobacillus Plantarum Strain for Good Adaption in Alfalfa Ensiling and Demonstrating Its Improvement of Alfalfa Silage Quality. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, J.M.; Barrangou, R.; Hachem, M.A.; Lahtinen, S.J.; Goh, Y.J.; Svensson, B.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Transcriptional Analysis of Prebiotic Uptake and Catabolism by Lactobacillus Acidophilus NCFM. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gänzle, M.G.; Follador, R. Metabolism of Oligosaccharides and Starch in Lactobacilli: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucar, R.A.; Pérez-Díaz, I.M.; Dean, L.L. Gentiobiose and Cellobiose Content in Fresh and Fermenting Cucumbers and Utilization of Such Disaccharides by Lactic Acid Bacteria in Fermented Cucumber Juice Medium. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktenioudaki, A.; Alvarez-Jubete, L.; Smyth, T.J.; Kilcawley, K.; Rai, D.K.; Gallagher, E. Application of Bioprocessing Techniques (Sourdough Fermentation and Technological Aids) for Brewer’s Spent Grain Breads. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filannino, P.; Di Cagno, R.; Crecchio, C.; De Virgilio, C.; De Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M. Transcriptional Reprogramming and Phenotypic Switching Associated with the Adaptation of Lactobacillus Plantarum C2 to Plant Niches. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rencoret, J.; Prinsen, P.; Gutiérrez, A.; Martinez, Á.T.; Del Rio, J.C. Isolation and Structural Characterization of the Milled Wood Lignin, Dioxane Lignin, and Cellulolytic Lignin Preparations from Brewer’S Spent Grain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roy, J.; Huss, B.; Creach, A.; Hawkins, S.; Neutelings, G. Glycosylation Is a Major Regulator of Phenylpropanoid Availability and Biological Activity in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dima, O.; Morreel, K.; Vanholme, B.; Kim, H.; Ralph, J.; Boerjana, W. Small Glycosylated Lignin Oligomers Are Stored in Arabidopsis Leaf Vacuoles. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, H.; Antonio, J.; María, J.; De, B.; López, F.; Felipe, D.; Gómez-cordovés, C.; Miguel, J.; Muñoz, R. Food Phenolics and Lactic Acid Bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 132, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamimura, N.; Goto, T.; Takahashi, K.; Kasai, D.; Otsuka, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Katayama, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Masai, E. A Bacterial Aromatic Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Critical for the Efficient Catabolism of Syringaldehyde. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, G.; Chen, W.; Guo, B. Metabolism of Fructooligosaccharides in Lactobacillus Plantarum ST-III via Differential Gene Transcription and Alteration of Cell Membrane Fluidity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7697–7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zúñiga, M.; Yebra, M.J.; Monedero, V. Complex Oligosaccharide Utilization Pathways in Lactobacillus. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2020, 40, 49–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buntin, N.; Hongpattarakere, T.; Ritari, J.; Douillard, F.P.; Paulin, L.; Boeren, S.; Shetty, S.A.; de Vos, W.M. An Inducible Operon Is Involved in Inulin Utilization in Lactobacillus Plantarum Strains, as Revealed by Comparative Proteogenomics and Metabolic Profiling. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoli, R.; Bosco, F.; Mizrahi, I.; Bayer, E.A.; Pessione, E. Towards Lactic Acid Bacteria-Based Biorefineries. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1216–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siezen, R.; Boekhorst, J.; Muscariello, L.; Molenaar, D.; Renckens, B.; Kleerebezem, M. Lactobacillus Plantarum Gene Clusters Encoding Putative Cell-Surface Protein Complexes for Carbohydrate Utilization Are Conserved in Specific Gram-Positive Bacteria. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
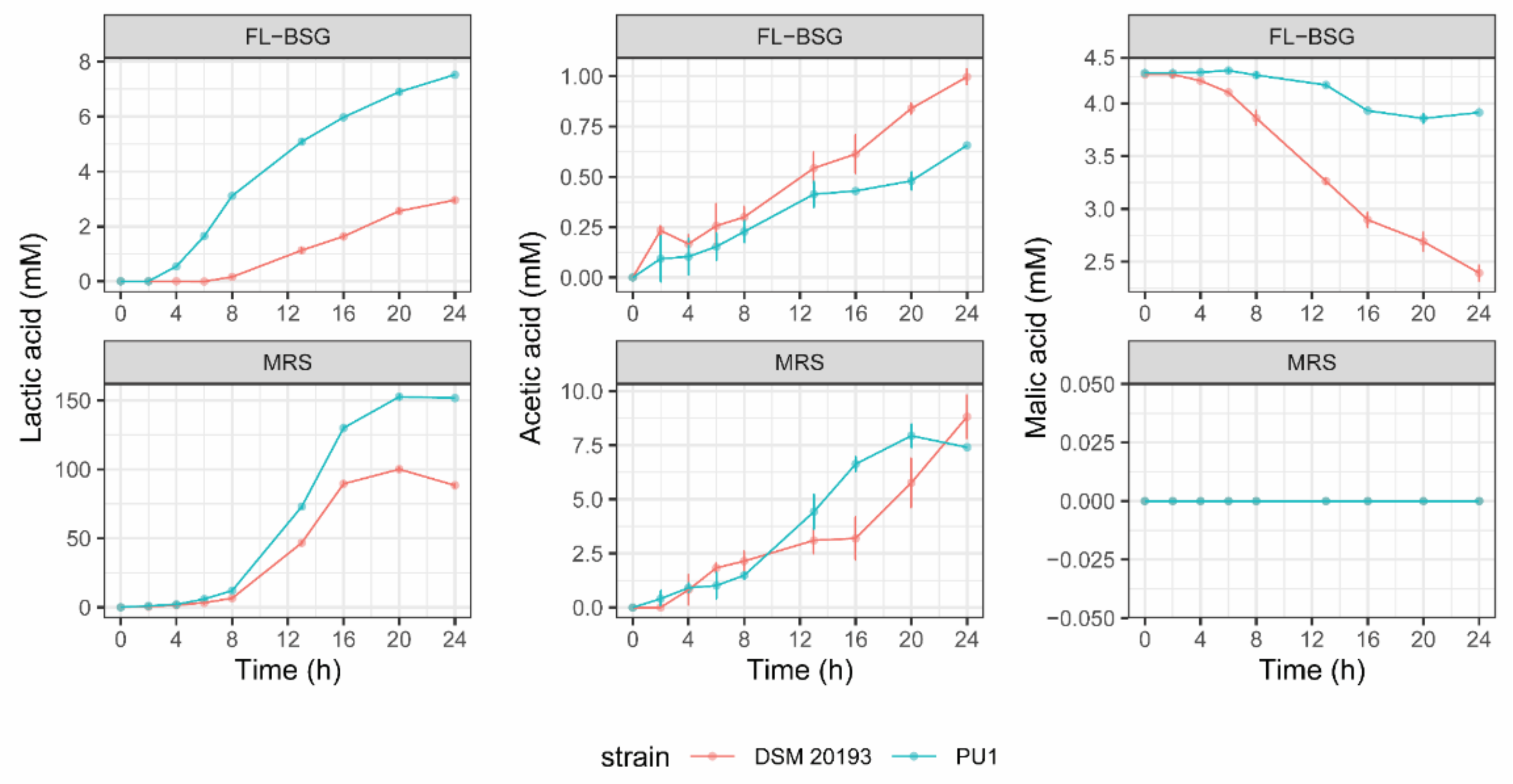
| Media a | Species/Strain | Growth b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | μmax | λ | ||
| FL-BSG | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum PU1 | 8.19 ± 0.03 C | 0.27 ± 0.02 C | 4.03 ± 0.17 C |
| Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides DSM 20193 | 8.10 ± 0.06 D | 0.40 ± 0.03 C | 3.30 ± 0.08 B | |
| MRS | L. plantarum PU1 | 9.73 ± 0.03 A | 0.53 ± 0.01 B | 2.38 ± 0.06 A |
| Leuc. pseudomesenteroides DSM 20193 | 9.53 ± 0.03 B | 0.62 ± 0.01 A | 1.47 ± 0.06 C | |
| Strain | Gene | Culture media | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactiplantibacillus plantarum PU1 | pbg4 | FL-BSG | 27.18 ± 2.17 |
| MRS | 1.00 ± 0.09 | ||
| pbg6 | FL-BSG | 70.76 ± 9.62 | |
| MRS | 1.01 ± 0.15 | ||
| scrB | FL-BSG | 64.47 ± 14.6 | |
| MRS | 1.41 ± 1.01 | ||
| Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides DSM 20193 | pbg-like | FL-BSG | 7.03 ± 2.68 |
| MRS | 1.00 ± 0.12 | ||
| INV | FL-BSG | 9.36 ± 3.36 | |
| MRS | 1.01 ± 0.18 | ||
| xylA | FL-BSG | 19.02 ± 3.9 | |
| MRS | 1.00 ± 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acin-Albiac, M.; Filannino, P.; Arora, K.; Da Ros, A.; Gobbetti, M.; Di Cagno, R. Role of Lactic Acid Bacteria Phospho-β-Glucosidases during the Fermentation of Cereal by-Products. Foods 2021, 10, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010097
Acin-Albiac M, Filannino P, Arora K, Da Ros A, Gobbetti M, Di Cagno R. Role of Lactic Acid Bacteria Phospho-β-Glucosidases during the Fermentation of Cereal by-Products. Foods. 2021; 10(1):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010097
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcin-Albiac, Marta, Pasquale Filannino, Kashika Arora, Alessio Da Ros, Marco Gobbetti, and Raffaella Di Cagno. 2021. "Role of Lactic Acid Bacteria Phospho-β-Glucosidases during the Fermentation of Cereal by-Products" Foods 10, no. 1: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010097
APA StyleAcin-Albiac, M., Filannino, P., Arora, K., Da Ros, A., Gobbetti, M., & Di Cagno, R. (2021). Role of Lactic Acid Bacteria Phospho-β-Glucosidases during the Fermentation of Cereal by-Products. Foods, 10(1), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010097






