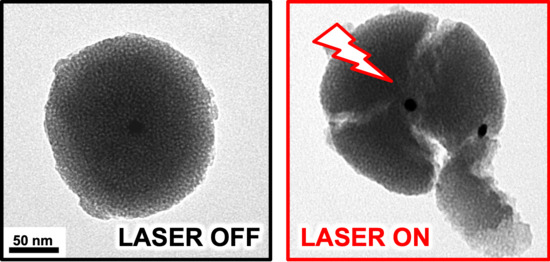
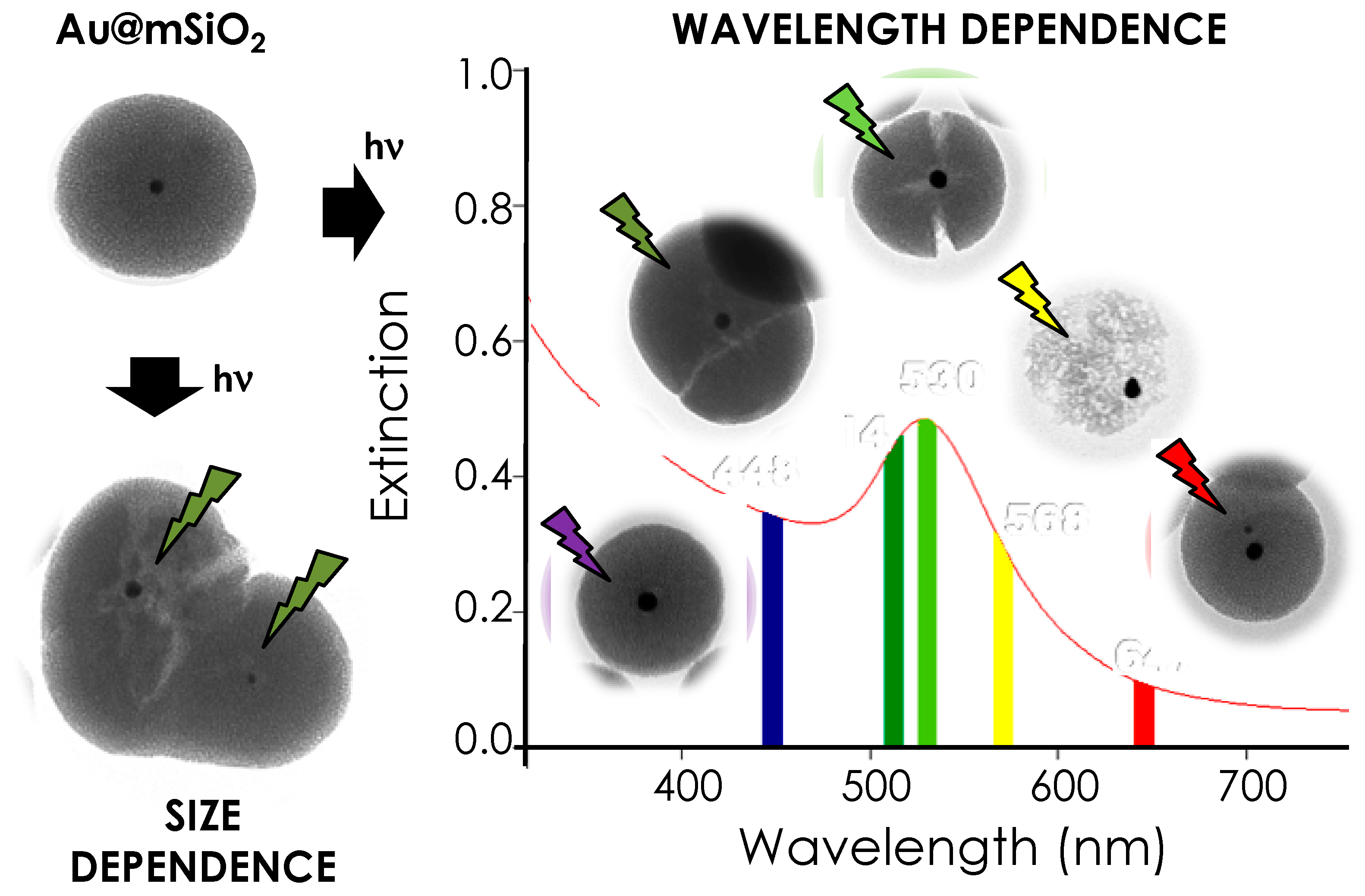
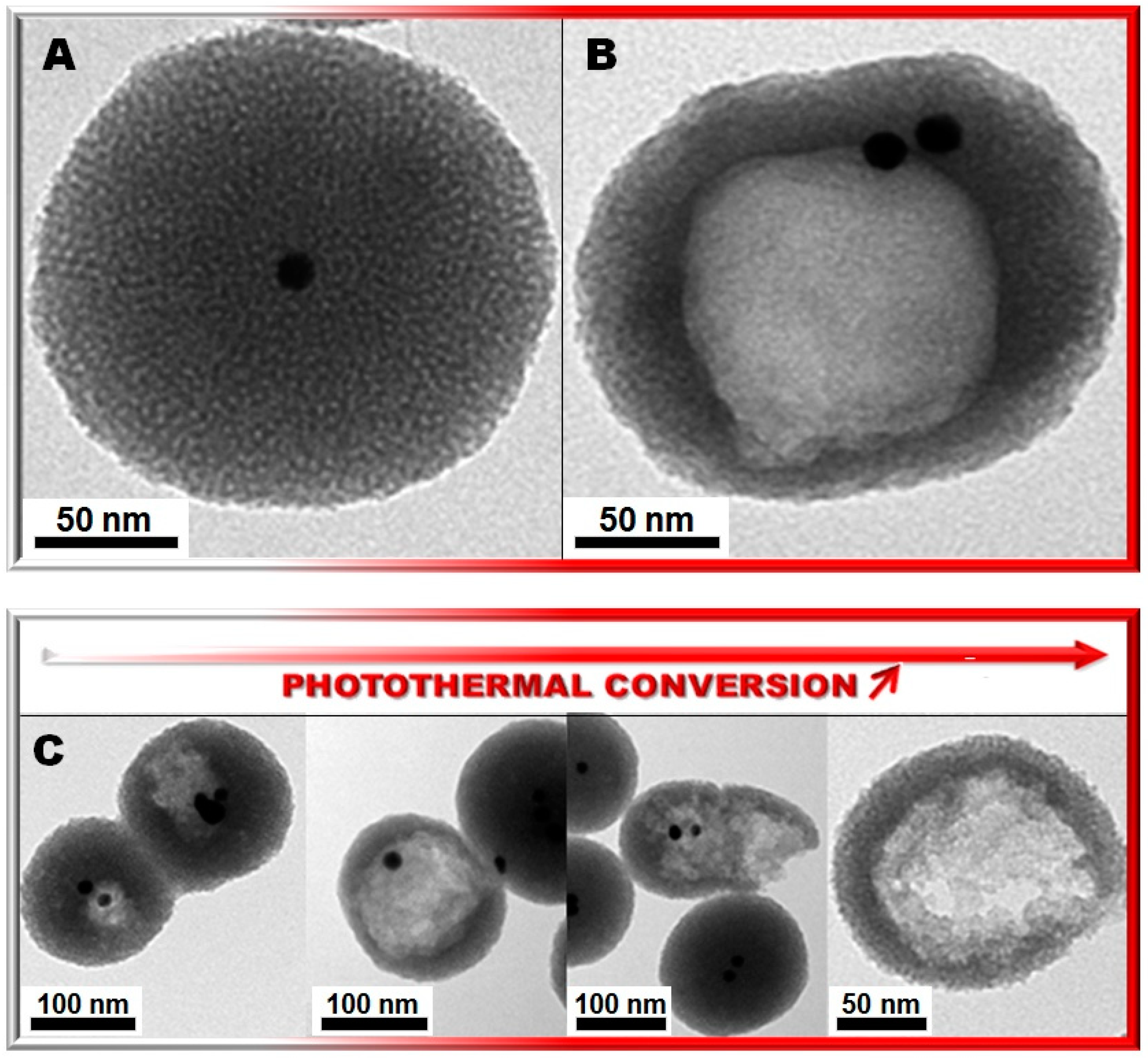
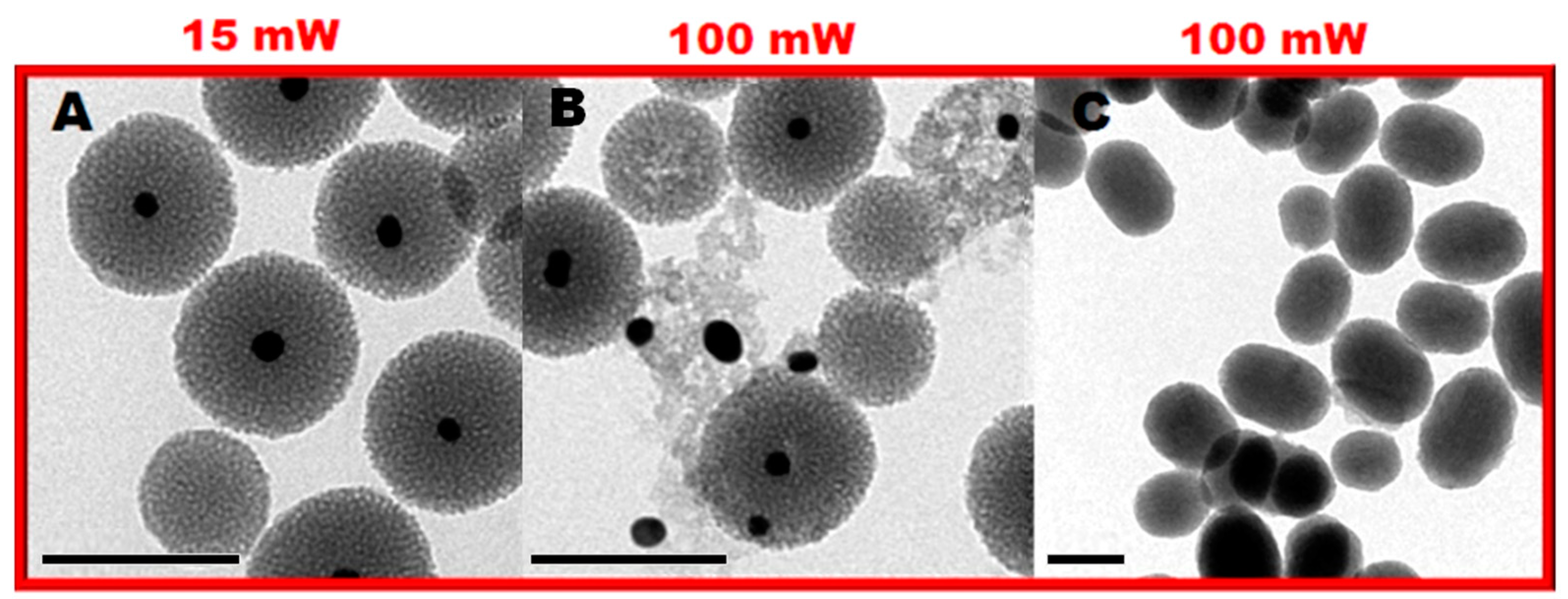
Photocracking Silica: Tuning the Plasmonic Photothermal Degradation of Mesoporous Silica Encapsulating Gold Nanoparticles for Cargo Release
Abstract
1. Introduction
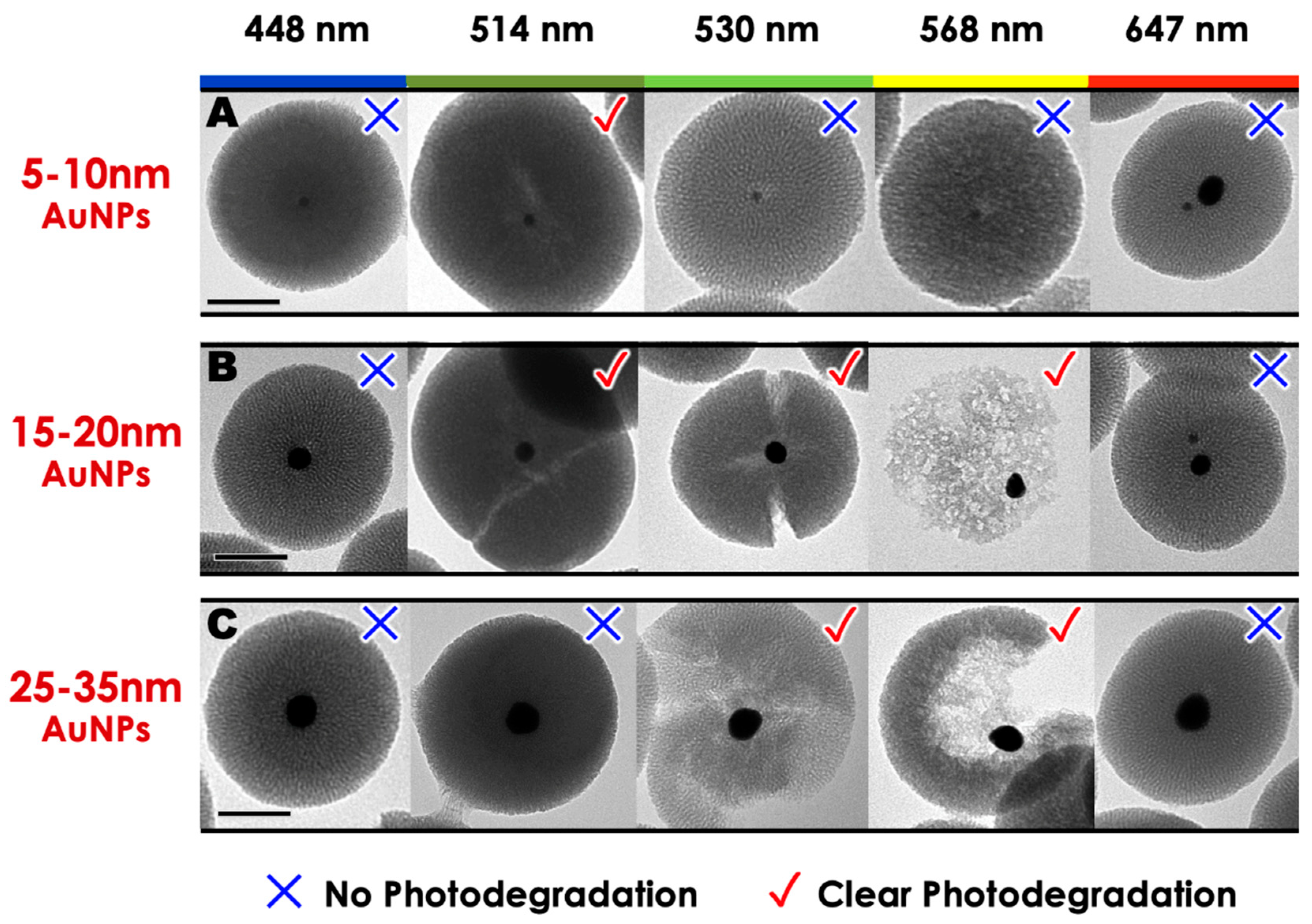
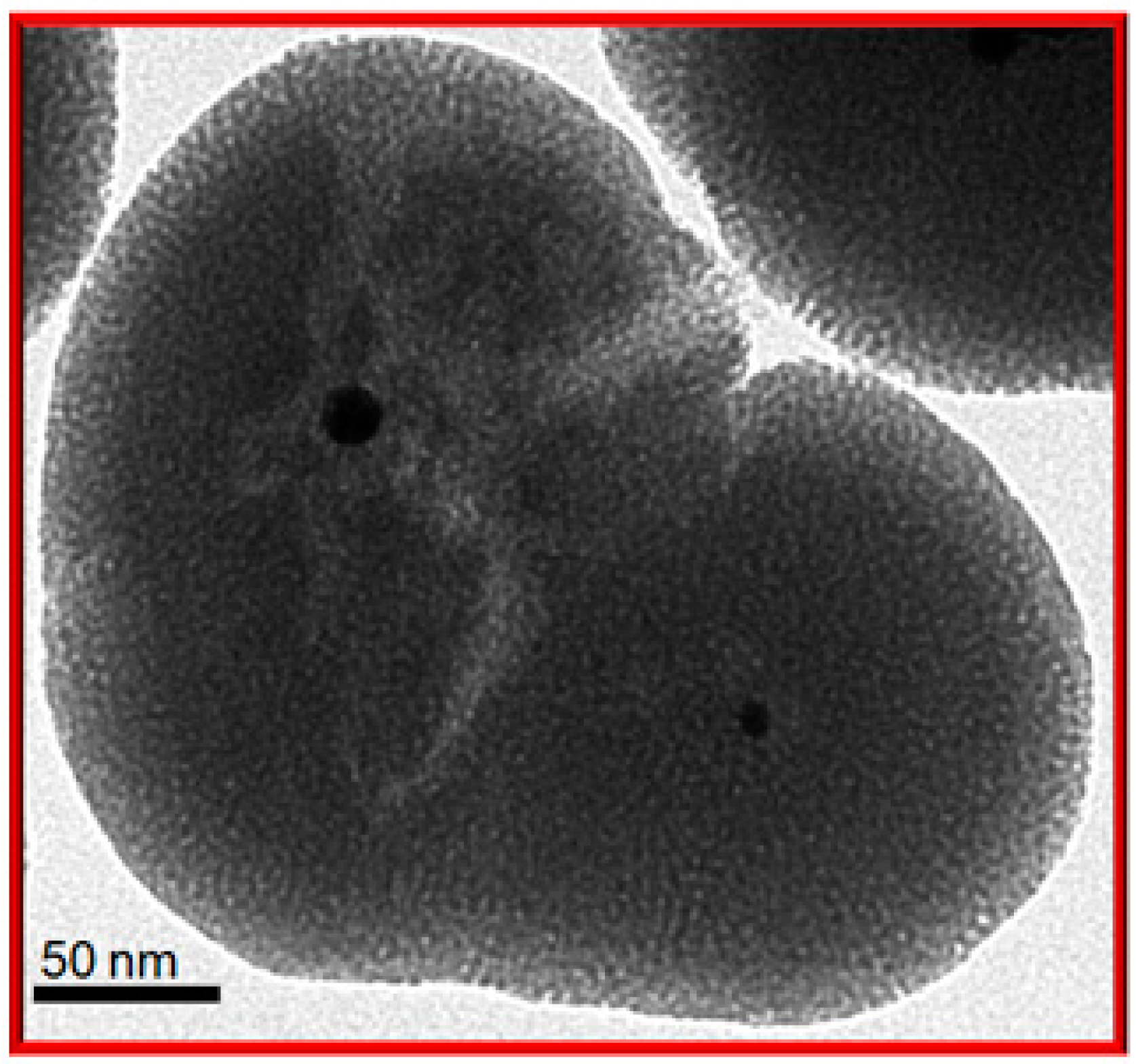
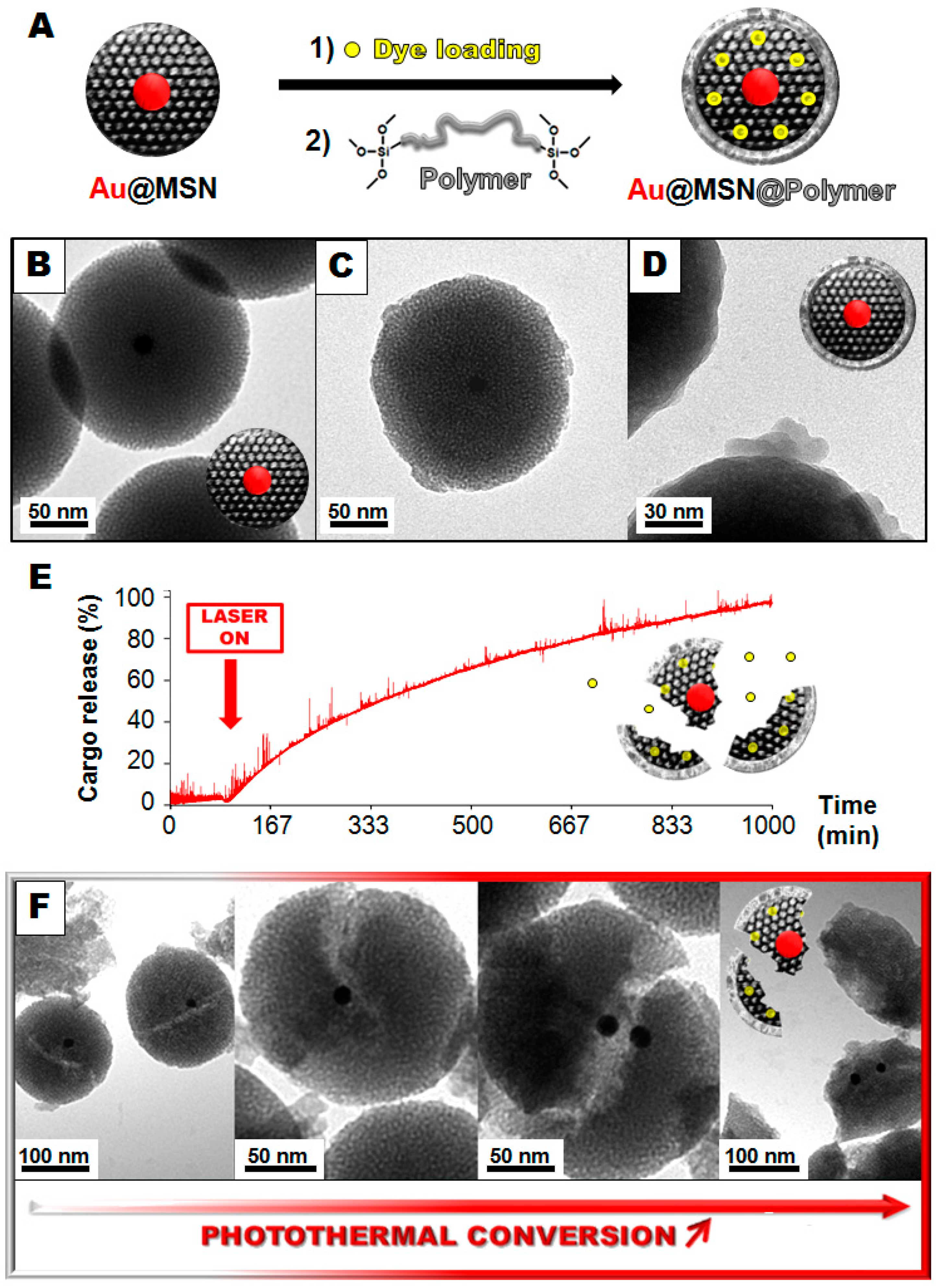
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, F.; Khashab, N.M. Degradability and clearance of silicon, organosilica, silsesquioxane, silica mixed oxide, and mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croissant, J.G.; Brinker, C.J. Biodegradable silica-based nanoparticles: Dissolution kinetics and selective bond cleavage. In The Enzymes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 43, pp. 181–214. [Google Scholar]
- Croissant, J.; Cattoën, X.; Wong Chi Man, M.; Gallud, A.; Raehm, L.; Trens, P.; Maynadier, M.; Durand, J.O. Biodegradable ethylene-bis(propyl)disulfide-based periodic mesoporous organosilica nanorods and nanospheres for efficient in-vitro drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6174–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Phua, S.Z.F.; Bindra, A.K.; Zhao, Y. Degradability and clearance of inorganic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Hitzky, E.; Ariga, K.; Lvov, Y.M. Bio-Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials: Strategies, Synthesis, Characterization and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Almalik, A.; Khashab, N.M. Mesoporous silica and organosilica nanoparticles: Physical chemistry, biosafety, delivery strategies, and biomedical applications. Adv. Health. Mater. 2018, 7, 1700831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croissant, J.G.; Cattoën, X.; Wong Chi Man, M.; Durand, J.O.; Khashab, N.M. Syntheses and applications of periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 20318–20334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croissant, J.; Cattoën, X.; Wong Chi Man, M.; Dieudonné, P.; Charnay, C.; Raehm, L.; Durand, J.O. One-pot construction of multipodal hybrid periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles with crystal-like architectures. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, S.M.; Hurley, K.R.; Datt, A.; Swindlehurst, G.; Haynes, C.L. Ultraporous mesostructured silica nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 3193–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, L.L.; Jiang, J.G.; Calin, N.; Lam, K.F.; Zhang, S.J.; Wu, H.H.; Wu, G.D.; Albela, B.; Bonneviot, L.; et al. Facile large-scale synthesis of monodisperse mesoporous silica nanospheres with tunable pore structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2427–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, M.; Cai, X.; Yao, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. “Manganese extraction” strategy enables tumor-sensitive biodegradability and theranostics of nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9881–9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Jia, G.; Liu, D.; Ge, K.; et al. Hybrid mesoporous silica-based drug carrier nanostructures with improved degradability by hydroxyapatite. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9614–9625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Julfakyan, K.; Lu, J.; Emwas, A.H.; Anjum, D.H.; Omar, H.; Tamanoi, F.; Zink, J.I.; Khashab, N.M. Biodegradable oxamide-phenylene-based mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles with unprecedented drug payloads for delivery in cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 14806–14811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggini, L.; Travaglini, L.; Cabrera, I.; Castro-Hartmann, P.; De Cola, L. Biodegradable peptide–silica nanodonuts. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 3697–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Mauriello-Jimenez, C.; Maynadier, M.; Cattoën, X.; Wong Chi Man, M.; Raehm, L.; Mongin, O.; Blanchard-Desce, M.; Garcia, M.; Gary-Bobo, M.; et al. Synthesis of disulfide-based biodegradable bridged silsesquioxane nanoparticles for two-photon imaging and therapy of cancer cells. Chem. Commum. 2015, 51, 12324–12327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Du, X.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Huang, H.; Liao, Q.; Shi, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M. One-pot synthesis of redox-triggered biodegradable hybrid nanocapsules with a disulfide-bridged silsesquioxane framework for promising drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4455–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, S.P.H.; Yazdimamaghani, M.; Ghandehari, H. Glutathione-sensitive hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2018, 282, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Kleitz, F.; Li, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, S.Z. Disulfide-bridged organosilica frameworks: Designed, synthesis, redox-triggered biodegradation, and nanobiomedical applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1707325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, H.; Croissant, J.G.; Alamoudi, K.; Alsaiari, S.; Alradwan, I.; Majrashi, M.A.; Anjum, D.H.; Martins, P.; Laamarti, R.; Eppinger, J.; et al. Biodegradable magnetic silica@iron oxide nanovectors with ultra-large mesopores for high protein loading, magnetothermal release, and delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 259, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohaku Mitchell, K.K.; Liberman, A.; Kummel, A.C.; Trogler, W.C. Iron(III)-doped, silica nanoshells: A biodegradable form of silica. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13997–14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.K.; Tseng, Y.J.; Liu, C.L.; Chou, S.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Tsang, S.E.; Chou, P.T. One-step synthesis of degradable T1-FeOOH functionalized hollow mesoporous silica nanocomposites from mesoporous silica spheres. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2676–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huo, M.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Iron-engineered mesoporous silica nanocatalyst with biodegradable and catalytic framework for tumor-specific therapy. Biomaterials 2018, 163, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Jiang, Y.B.; Dunphy, D.; Xiong, H.; Coker, E.; Chou, S.; Zhang, H.; Vanegas, J.M.; Croissant, J.G.; Cecchi, J.L.; et al. Ultra-thin enzymatic liquid membrane for CO2 separation and capture. Nat. Commum. 2018, 9, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, R.M.; Maier, W.F.; Verweij, H. Hydrophobic silica membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 158, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, F.; Cornelius, M.; Morell, J.; Fröba, M. Silica-based mesoporous organic–inorganic hybrid materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3216–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Qi, L.; Ma, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, O.; Cheng, H. Large-pore mesoporous silica spheres: Synthesis and application in HPLC. Colloids Surf. A 2003, 229, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, P.J.; Prewitt, C.T.; Gibbs, G.V. (Eds.) Silica: Physical Behavior, Geochemistry, and Materials Applications; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Margelefsky, E.L.; Zeidan, R.K.; Davis, M.E. Cooperative catalysis by silica-supported organic functional groups. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Zink, J.I.; Raehm, L.; Durand, J.O. Two-photon-excited silica and organosilica nanoparticles for spatiotemporal cancer treatment. Adv. Health. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauriello Jimenez, C.; Aggad, D.; Croissant, J.G.; Tresfield, K.; Laurencin, D.; Berthomieu, D.; Cubedo, N.; Rossel, M.; Alsaiari, S.; Anjum, D.H.; et al. Porous porphyrin-based organosilica nanoparticles for NIR two-photon photodynamic therapy and gene delivery in zebrafish. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 28, 1800235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Quan, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Niu, B.; Wu, B.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühle, B.; Saint-Cricq, P.; Zink, J.I. Externally controlled nanomachines on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for biomedical applications. ChemPhysChem 2016, 17, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, P.; Adolphi, N.L.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Y.S.; Butler, K.S.; Durfee, P.N.; Croissant, J.G.; Noureddine, A.; Coker, E.N.; Bearer, E.L.; et al. Establishing the effects of mesoporous silica nanoparticle properties on in vivo disnmposition using imaging-based pharmacokinetics. Nat. Commum. 2018, 9, 4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. In vivo bio-safety evaluations and diagnostic/therapeutic applications of chemically designed mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3144–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Beack, S.; Yoo, J.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, C.; Kwon, W.; Hahn, S.K.; Kim, C. In Vivo Photoacoustic Imaging of Livers Using Biodegradable Hyaluronic Acid-Conjugated Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Gao, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, X. Gold nanoparticles for in vitro diagnostics. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10575–10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Pilot, R.; Frasconi, M.; Marago, O.M.; Iati, M.A. Surface plasmon resonance in gold nanoparticles: A review. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 203002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraee, H.; Eatemadi, A.; Abbasi, E.; Fekri Aval, S.; Kouhi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. Application of gold nanoparticles in biomedical and drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Noble metals on the nanoscale: Optical and photothermal properties and some applications in imaging, sensing, biology, and medicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykman, L.; Khlebtsov, N. Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2256–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.E.; Anderton, C.R.; Thompson, L.B.; Maria, J.; Gray, S.K.; Rogers, J.A.; Nuzzo, R.G. Nanostructured plasmonic sensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 494–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Rycenga, M.; Skrabalak, S.E.; Wiley, B.; Xia, Y. Chemical synthesis of novel plasmonic nanoparticles. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2009, 60, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J.; Yee, S.S.; Gauglitz, G. Surface plasmon resonance sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 54, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.L.; Kim, J.; Lu, Y.; Lee, L.P. Optofluidic control using photothermal nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rycenga, M.; Wang, Z.; Gordon, E.; Cobley, C.M.; Schwartz, A.G.; Lo, C.S.; Xia, Y. Probing the photothermal effect of gold-based nanocages with surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9924–9927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, V.; Kumar, J.; Rejiya, C.S.; Vibin, M.; Shenoi, V.N.; Abraham, A. Selective photothermal efficiency of citrate capped gold nanoparticles for destruction of cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 2052–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.R.; Millstone, J.E.; Giljohann, D.A.; Seferos, D.S.; Young, K.L.; Mirkin, C.A. Plasmonically controlled nucleic acid dehybridization with gold nanoprisms. ChemPhysChem 2009, 10, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Murphy, A.B. Heat generation by optically and thermally interacting aggregates of gold nanoparticles under illumination. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 375702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiss, W.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Aveyard, J.; Fernig, D.G. Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV–Vis spectra. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Lee, K.S.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: Applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7238–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hleb, E.Y.; Lapotko, D.O. Photothermal properties of gold nanoparticles under exposure to high optical energies. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 355702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, Z.; Lu, W.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Q.; Tian, M.; Li, L.; Liang, D.; Li, C. Influence of anchoring ligands and particle size on the colloidal stability and in vivo biodistribution of polyethylene glycol-coated gold nanoparticles in tumor-xenografted mice. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paasonen, L.; Laaksonen, T.; Johans, C.; Yliperttula, M.; Kontturi, K.S.; Urtti, A. Gold nanoparticles enable selective light-induced contents release from liposomes. J. Control. Release 2007, 122, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelatos, A.S.; Radt, B.; Caruso, F. Light-responsive polyelectrolyte/gold nanoparticle microcapsules. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 3071–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Han, M.Y. Silica-coated metal nanoparticles. Chem. Asian J. 2010, 5, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, V.; Mikhailovsky, A.; Zasadzinski, J.A. Inside-out disruption of silica/gold core–shell nanoparticles by pulsed laser irradiation. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7528–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.; Zink, J.I. Nanovalve-controlled cargo release activated by plasmonic heating. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7628–7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, N.R.; Gearheart, L.; Murphy, C.J. Seeding growth for size control of 5–40 nm diameter gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 2001, 17, 6782–6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enustun, B.V.; Turkevich, J. Coagulation of colloidal gold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 3317–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, K.; Gailhanou, H.; Raison, L.; Panizza, P.; Ushiki, H.; Sellier, E.; Delville, J.P.; Delville, M.H. Smart control of monodisperse Stöber silica particles: Effect of reactant addition rate on growth process. Langmuir 2005, 21, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.; Marchettini, P.; Stuart, O.A.; Urano, M.; Sugarbaker, P. Thermal enhancement of new chemotherapeutic agents at moderate hyperthermia. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2003, 10, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Croissant, J.G.; Guardado-Alvarez, T.M. Photocracking Silica: Tuning the Plasmonic Photothermal Degradation of Mesoporous Silica Encapsulating Gold Nanoparticles for Cargo Release. Inorganics 2019, 7, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics7060072
Croissant JG, Guardado-Alvarez TM. Photocracking Silica: Tuning the Plasmonic Photothermal Degradation of Mesoporous Silica Encapsulating Gold Nanoparticles for Cargo Release. Inorganics. 2019; 7(6):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics7060072
Chicago/Turabian StyleCroissant, Jonas G., and Tania M. Guardado-Alvarez. 2019. "Photocracking Silica: Tuning the Plasmonic Photothermal Degradation of Mesoporous Silica Encapsulating Gold Nanoparticles for Cargo Release" Inorganics 7, no. 6: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics7060072
APA StyleCroissant, J. G., & Guardado-Alvarez, T. M. (2019). Photocracking Silica: Tuning the Plasmonic Photothermal Degradation of Mesoporous Silica Encapsulating Gold Nanoparticles for Cargo Release. Inorganics, 7(6), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics7060072