Abstract
Using nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery to cancer, in response to its weakly acidic environment, represents a promising approach toward increasing the effectiveness and reducing the adverse effects of cancer therapy. Hence, the aim of this study is to construct novel mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSN)-based acidification-responsive drug delivery systems for targeted cancer therapy. Herein, the surface of MSN is covalently functionalized with Ir(III)-based complex through a pH-cleavable hydrazone-based linker and characterized by nitrogen sorption, SEM, FTIR, EDS, TGA, DSC, DLS, and zeta potential measurements. Enhanced release of Ir(III)-complexes is evidenced by UV/VIS spectroscopy at the weakly acidic environments (pH 5 and pH 6) in comparison to the release at physiological conditions. The in vitro toxicity of the prepared materials is tested on healthy MRC-5 cells while their potential for the efficient treatment of glioblastoma multiforme is demonstrated on the U251 cell line.
1. Introduction
Typical problem that occurs in cancer chemotherapy is that it targets all rapidly dividing cells, i.e., healthy cells as well as cancer cells. As a possible solution, research advances are being made toward developing cancer-targeting therapeutics that may be capable of delivering therapeutic cargo specifically to cancer tissues and in response to the specific environment of cancer [1]. These advanced therapeutics for targeted cancer treatment and imaging are seen as a promising approach toward increasing treatment selectivity and for enhancing its efficiency [2]. The application of nanoparticles for stimuli-responsive drug delivery is one of the most favored strategies [3]. Namely, due to the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect that is observed in cancer tissues [4], nanoparticles exhibit an innate ability for accumulation in cancer tissues. Furthermore, their structure may enable preservation of the therapeutic cargo and prevent its premature release before reaching the target site, where it may be delivered in a controlled manner [5]. One of the possible approaches for achieving targeted cancer therapy is through devising nanotherapeutics for delivering cargo drugs in response to a weakly acidic cancer microenvironment [6,7]. Therapy with cancer-targeting nanoparticles could effect in reducing side effects [8], minimizing multidrug resistance [9], and increased intracellular drug concentration [10]. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN), owing to their customizable features, represent a nanomaterial with promising potential for designing advanced cancer-targeting nanotherapeutics for effective controlled drug and gene delivery applications [11,12,13]. Thus, for construction of therapeutics that are sensitive to the acidic conditions, pH-sensitive bonds, coatings and gatekeepers can be employed on MSN-based nanotherapeutics, that can be cleaved under the influence of acidification and enable therapeutic effects [14]. Studies on the in vivo toxicity and biodistribution of MSN-based materials evidence their high biocompatibility and capabilities for preferential accumulation in tumor tissues [15]. Their biodistribution profiles can be affected by the shape [16] as well as the size and functionalization of the particles [17].
Different types of drug delivery systems have been developed recently, including ionically crosslinked gels [18], Janus nanofibrous membranes [19], mesoporous silica [20], and other inorganic nanoparticles [21]. In the past decade, iridium-based complexes have been extensively studied for possible applications in cancer treatment [22]. Organoiridium(III) complexes with the half sandwich structure are particularly attractive due to their excellent anticancer potency [23,24,25,26]. However, their poor water-solubility typically limits the possibilities for their use in cancer treatment [27]. Recent advances have shown the applicability of different types of nanoparticles for the delivery of iridium(III)-based therapeutics for cancer treatment [28,29,30]. On the other hand, only one report was published very recently on the incorporation of Ir(III) within MSN for application in cancer therapy [31]. Hence, as the goal for our study, we aimed to construct a novel pH-responsive platform based on MSN for the controlled delivery of Ir(III) complexes. Firstly, two different pH-responsive hydrazone ligands were grafted to the surface of MSN nanoparticles, containing (2-thienylmethyl)hydrazine hydrochloride (H1) or (5,6-dimethylthieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)hydrazine (H2), as recently reported in our study [32]. In continuation of this work, Ir(III) prodrug was coordinated to these ligands upon exposing the prepared materials to (pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)iridium(III) chloride dimer ([Ir]2). We further investigated the release kinetics of Ir(III) complexes from the MSN-based materials, while cytotoxic effects of the constructed nanotherapeutics were investigated in vitro on healthy MRC-5 cells and U251 glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells.
2. Results and Discussion
The synthesis and functionalization of MSN are represented in Figure 1. Full characterization of the starting MSN material and the functionalized analogues MSN-H1 and MSN-H2 is published in our previous study [32]. Namely, H1 and H2 are bound to the surface of MSN through an acidification-cleavable hydrazone linkage (marked in yellow squares). In this study, commercially available (pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)iridium(III) chloride dimer, [Ir]2, complex is reacted with H1-MSN and H2-MSN and the characteristics of the novel iridium(III)-complex functionalized MSN-H1 and MSN-H2 are reported in terms of its acidification-responsive release of iridium(III)-complexes and activity against healthy and cancer cells.
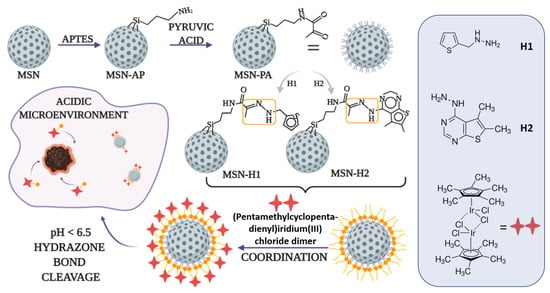
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of functionalization of MSN with ligands (H1 and H2), and coordination of the (pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)iridium(III) chloride dimer.
As can be seen on the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of MSN-H1[Ir], and MSN-H[Ir] (Figure 2), the diameter of the majority of nanoparticles is in the range of 280–360 nm, with predominantly spherical morphology. The presence of the Ir(III) complex was verified by FTIR spectroscopy (Figure 3a and Figure S1). The appearance of bands at 695 cm−1 and 730 cm−1, and in the region 1500–1400 cm−1, could be associated with the presence of the Ir-based complex and its binding to H1 and H2 ligands.

Figure 2.
SEM images of (a) MSN-H1[Ir] and (b) MSN-H2[Ir].
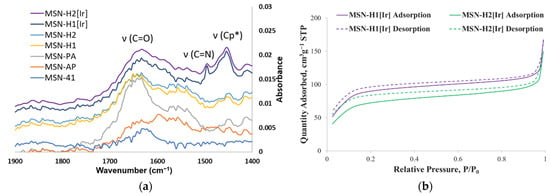
Figure 3.
(a) FTIR spectra of MSN-H1[Ir] and MSN-H2[Ir] (Cp* = pentamethylcyclopentadienyl), along with the spectra of previously reported precursor materials (MSN, MSN-AP, MSN-PA, MSN-H1, MSN-H2) [32] and (b) Nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms of MSN-H1[Ir] and MSN-H2[Ir].
Nitrogen adsorption experiments revealed type II isotherms for both samples after functionalization with Ir(III) complex, which are characteristic for microporous materials (Figure 3b). The determined Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) specific surface areas were 315 and 262 cm3/g for MSN-H1[Ir] and MSN-H2[Ir], respectively. The results of thermogravimetric analyses and the weight losses in the range from 150 °C to 750 °C gave the amounts of organic functional groups present on MSN-H1[Ir] and MSN-H2[Ir], in the amounts of 12.0% and 13.0%, respectively. EDS measurements revealed that MSN-H1[Ir] and MSN-H2[Ir] materials contain iridium in the amounts of 12.93 wt.%, and 12.07 wt.%, respectively. This result agrees with higher zeta potential of MSN-H1[Ir] in comparison to MSN-H2[Ir], as MSN-H1 material evidently contains more positively charged [Ir] species. The hydrodynamic diameter and zeta potential of the prepared materials are shown in Table 1. The stability of prepared particles was investigated in water and culture medium, as well as upon incubation in medium without stirring (Figure 4). Interestingly, the hydrodynamic diameter of MSN-H2[Ir] gets significantly larger than MSN-H1[Ir] when measured in cell medium. Possibly, a higher amount of [Ir] on the MSN-H1 material protects from further aggregation in the conditions of cell medium.

Table 1.
Hydrodynamic radius and zeta potential of prepared nanomaterials *.
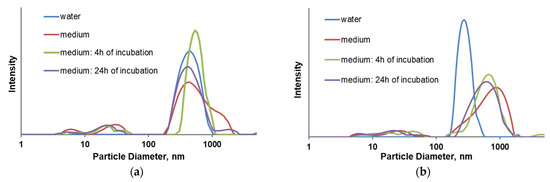
Figure 4.
Particle size distribution of (a) MSN-H1[Ir] and (b) MSN-H2[Ir] in water and culture medium.
The responsiveness of the formed hydrazone bond was investigated by monitoring UV/VIS absorption spectra of supernatants obtained after centrifugation of the materials’ suspensions of different pH values at different time points. The release profiles are presented in Figure 5, where Figure 5a displays the normalized release kinetics of the Ir(III) complexes, as measured by the absorbances at 344 nm for 48 h, at different pH values. Evidently, upon enhancing acidity of the suspension, the release of [Ir] species increases substantially. In comparison to the highest release at pH 5, the maximum of the released % observed after 48 h for both materials lowered to approximately 60% in the case of pH 6 and to 30% in the case of pH 7.4. Figure 5b shows UV/VIS spectra of the supernatants after 48 h stirring at different pH values, which evidences the differences in the concentration of the released Ir(III) complexes.
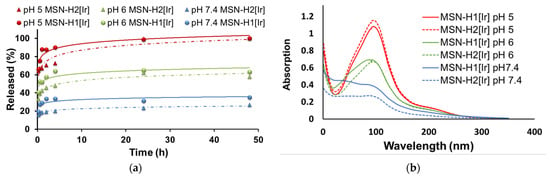
Figure 5.
(a) Release profiles of Ir(III) complex from MSN-H1[Ir] (●) and MSN-H2[Ir] (▲) in PBS buffers with pH 5.0 (red), pH 6.0 (green) and pH 7.4 (blue) for 48 h; (b)—UV/VIS spectra of supernatants after 48 h of stirring at different pH values.
In vitro cell viability experiments were performed against human glioblastoma U251 cell line. The nanoparticles were first stirred in buffers (acetate pH 5.0 or PBS buffer pH 7.4) for 24 h. Afterward, the samples were diluted in the culture medium to prepare solutions for treating the cells for 48 h. The half-maximal inhibitory mass concentration (MC50) was calculated as a mass concentration (µg/mL) of the Ir-based MSNs needed to inhibit the cell viability by 50% (Table 2). The half-maximal inhibitory molar concentration (IC50) was calculated upon taking into account the amounts of loaded [Ir]2 complex on the materials and expressing the results in the micromolar (μM) concentration of the loaded [Ir]2 complex on the materials needed to inhibit the cell viability by 50% (Table 3).

Table 2.
MC50 (IC50) values of the U251 and MRC-5 cells treated for 48 h after pre-incubation of materials in corresponding buffers for 24 h.

Table 3.
MC50 (IC50) values of the U251 and MRC-5 cells treated for 48 h after dispersing/dissolving materials in DMSO.
The viability measurements reveal that all materials exhibit high biocompatibility toward healthy cells (MRC-5), while their toxicity against tumor cells (U251) increases particularly in the case of materials containing coordinated Ir(III) complex (Figures S2–S7). In the case of MSN-H2[Ir], the MC50 value significantly decreases upon preincubation of the material at pH 5, which evidences the positive influence of the enhanced drug delivery from the material on its toxicity against glioblastoma cells.
To compare the effects of different Ir(III)-containing materials, the results are compared by taking into account the amount of starting [Ir]2 complex (with IC50 expressed in μM) that was loaded on the materials, as shown in in Figure 6. Evidently, IC50 values are very similar when comparing the values of materials [Ir]2 and MSN-H1[Ir] dispersed directly in medium. The IC50 value of MSN-H2[Ir] is higher, possibly due to the fact that the hydrodynamic diameter of MSN-H2[Ir] in the medium is significantly larger, as discussed above, which might inhibit its endocytosis. Nevertheless, the same figure also reveals that if the materials were exposed to buffers for 24 h prior to testing their activity, their toxicity against glioblastoma increases by an order of magnitude. In particular, the IC50 values of MSN-H2[Ir] are very low, around 10 μM, which classifies the material among the highly toxic agents with possible applicability in cancer treatment. Furthermore, the IC50 values for this material decreases from 13.3 to 9.3 μM in the case of pretreatment at pH 7.4 and pH 5, respectively, which evidences the potential of MSN-H2[Ir] material for enhanced cancer treatment in response to the weakly acidic tumor tissue microenvironment.
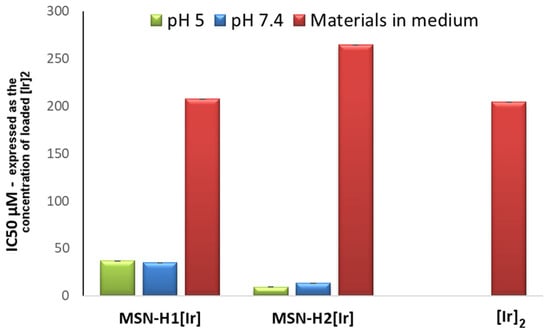
Figure 6.
Comparison of the IC50 by taking into account the amounts of loaded [Ir]2 complex on the materials and expressing the results in the micromolar (μM) concentration of the loaded [Ir]2 complex on the materials needed to inhibit the cell viability by 50%.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis and Functionalization of MSN
The preparation methodology to obtain MSN and functionalized MSN containing the pH-responsive ligands was presented in our previous work [32]. In brief, we synthesized MSN using the sol-gel surfactant-templated method. After removing the surfactant, the surface of MSN was grafted with aminopropyl groups, which were further modified with pyruvic acid through NHS/EDC-catalyzed coupling and finally through hydrazone formation with hydrazine-based ligands H1 and H2.
3.2. Functionalization with Ir(III) Complex
Equal amounts (200 mg) of MSN-H1, and MSN-H2 were separately dried under vacuum for 4 h at 100 °C. After cooling to room temperature, anhydrous toluene (30 mL) and (pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)iridium(III) chloride dimer ([Ir]2, 0.09 mmol Sigma-Aldrich, Burlington, MA, USA) were added under an inert atmosphere using the standard Schlenk technique. The reaction was continued at 60 °C overnight. Afterwards, materials denoted as MSN-H1[Ir], and MSN-H2[Ir] were collected via filtration, washed 3 times with toluene and subsequently dried under vacuum.
3.3. Characterization
The morphology of nanoparticles was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) on a Tescan Vega3 Phenom (Tescan, Brno, the Czech Republic). The samples were prepared by placing them on a conductive carbon adhesive tape and sputtered with gold to increase conductivity. The surface areas of materials were characterized by nitrogen sorption analyses on an Autosorb iQ/ASiQwin (Quantachrome Instruments, Anton Paar, QuantaTec Inc., Boynton Beach, FL, USA). Thermogravimetric analyses (TGA) were performed on a Netzsch STA 449 F5 Jupiter® (Netzsch Holding, Selb, Germany) under a nitrogen stream with a heating rate of 10 °C/min. FTIR (Fourier transform infrared) spectra were recorded using IR spectrometer Bruker Vertex 70 (Bruker, Massachusetts, USA). The particle size distribution of the synthesized nanoparticles was examined by dynamic light scattering (DLS) on a Particle size analyzer—Litesizer 500 (Anton Paar, Graz, Austria). Particles dispersed in water (0.1 mg/mL) were analyzed immediately, while experiments in DMEM containing 10% FSB were conducted after 4 h and 24 h of incubation, as well. The zeta potential of particles was measured by electrophoretic light scattering (ELS) on Zetasizer Ultra (Malvern Panalytical, Kassel, Germany). Energy-dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) experiments were conducted on Tabletop Scanning Electron Microscope Hitachi TM3030.
3.4. Drug Release Measurements
MSN-H1[Ir] and MSN-H2[Ir] were separately dispersed in PBS solution (1 mg/mL) with different pH values (7.4, 6.0, and 5.0) and stirred at room temperature. At predefined time intervals, suspensions were centrifuged, and supernatants were analyzed using a UV/VIS spectrophotometer DSH-L6/L6S (Dshing Instrument Co., Zhuhai, China). Samples were then immediately re-dispersed in the supernatant and stirring was resumed until the next time point.
3.5. Cell Viability Experiments
The cell lines used in the study were: U-251 MG (ECACC 09063001, human glioblastoma astrocytoma) and MRC-5 (ATCC CCL 171, normal fetal lung fibroblasts). The cells were grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) with 4.5 % of glucose, supplemented with 10% of fetal calf serum (FTS, Sigma) and antibiotics and antimycotics solution (Sigma). Cell line was cultured in flasks (Costar, 25 cm2) at 37 °C in the atmosphere of 100% humidity and 5% of CO2 (Heraeus). Exponentially growing viable cells were used throughout the assays.
The tested materials (MSN, MSN-H1, MSN-H2, MSN-H1[Ir], MSN-H2[Ir], and [Ir]2) were used at seven different concentrations to determine the half maximal inhibitory mass concentration (MC50) of all materials, as well as the half maximal inhibitory molar concentration (IC50), normalized to the concentration of Ir(III) complex, after 48 h of the treatment. The substances were added in volume of 10 μL/well. The stock solutions of the tested materials were prepared by either dispersing the materials directly in DMEM by sonication, while DMEM solutions of [Ir]2 were prepared by dilutions from DMSO stock solution. The MSN-based materials were also tested in conditions after preincubation in PBS (pH 7.4) or acetate buffer (pH 5.0). The stock solutions of prepared materials were stirred for 24 h and further tested by dilution of stock solutions in a completed medium against glioblastoma U251 and MRC-5 cell lines and incubated for 48 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Subsequently, MTT assays were performed according to the literature [33]. Inhibition of growth was expressed as a percent of a control and cytotoxicity was calculated according to the formula: (1 − Atest/Acontrol) × 100.
The substance potency was expressed as the MC50 and IC50 (50% inhibitory mass and molar concentration, respectively).
4. Conclusions
Novel mesoporous silica nanoparticles are synthesized and characterized for the pH-responsive delivery of surface-functionalized Ir(III) complexes. The materials demonstrated the capabilities for enhanced release of the surface-functionalized iridium(III)-complexes upon exposure to a weakly acidic environment in comparison to the physiological pH. All materials showed low toxicity against healthy MRC-5 cells. The materials containing Ir(III) exhibited enhanced toxicity against glioblastoma multiforme cells. When the materials were exposed to buffers for 24 h prior to testing their activity, their toxicity against glioblastoma increased by an order of magnitude in comparison to their direct dispersion and testing from the cell media. The results of this study reveal the promising potential of the prepared materials for targeted cancer treatment in response to a weakly acidic environment.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/inorganics10120250/s1, Figure S1. Full FTIR spectra of the prepared materials, Figure S2. Cytotoxicity of MSN-H1[Ir] against U251 and MRC-5 cells, Figure S3. Cytotoxicity of MSN-H2[Ir] against U251 and MRC-5 cells, Figure S4. Cytotoxicity of (Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)iridium(III) chloride dimer ([Ir]2), with stock solution prepared in DMSO, against U251 and MRC-5 cells, Figure S5. Cytotoxicity of MSN against U251 and MRC-5 cells, Figure S6. Cytotoxicity of MSN-H1 against U251 and MRC-5 cells, Figure S7. Cytotoxicity of MSN-H2 against U251 and MRC-5 cells.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.Ž.K. and G.N.K.; methodology, N.Ž.K., N.I. and G.N.K., validation, N.Ž.K. and N.I.; formal analysis, N.I.; investigation, N.Ž.K. and N.I.; resources, N.Ž.K. and G.N.K.; data curation N.Ž.K. and G.N.K.; writing—original draft preparation, N.Ž.K.; writing—review and editing, G.N.K.; visualization, N.Ž.K. and G.N.K.; supervision, N.Ž.K. and G.N.K.; project administration, N.Ž.K. and G.N.K.; funding acquisition, N.Ž.K. and G.N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors (G.N.K. and N.I.) acknowledge financial support from the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) [grant number: 57393212]. This Research was supported by the Science Fund of the Republic of Serbia, PROMIS, #6060755, PRECAST (N.Ž.K) and has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement 952259 (NANOFACTS).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This article is a revised and expanded version of a paper entitled “Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery to Glioblastoma Multiforme”, which was presented at the 22nd IEEE International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO 2022), Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 4–8 July 2022. The study is expanded from the published study [34], with permission from IEEE in the following manner: Figure 2B, Figure 3, Figure 4, Table 1, Table 2, adjusted Table 3 are reused. Portions of the text are adapted and expanded.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shi, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, T.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mei, L. Inorganic nano-carriers based smart drug delivery systems for tumor therapy. Smart Mater. Med. 2020, 1, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, S.; Mahanta, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Maiti, P. Controlled drug delivery vehicles for cancer treatment and their performance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Meel, R.; Sulheim, E.; Shi, Y.; Kiessling, F.; Mulder, W.J.M.; Lammers, T. Smart cancer nanomedicine. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greish, K. Enhanced permeability and retention of macromolecular drugs in solid tumors: A royal gate for targeted anticancer nanomedicines. J. Drug Target. 2007, 15, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Theranostic Antitumoral Nanomedicines. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saroj, S.; Rajput, S.J. Composite smart mesoporous silica nanoparticles as promising therapeutic and diagnostic candidates: Recent trends and applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, N.Ž.; Durand, J.-O. Targeted Treatment of Cancer with Nanotherapeutics Based on Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. ChemPlusChem 2015, 80, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, T.; Lu, X. Controlled release of silyl ether camptothecin from thiol-ene click chemistry-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yao, H.; Shi, J. Core-shell hierarchical mesostructured silica nanoparticles for gene/chemo-synergetic stepwise therapy of multidrug-resistant cancer. Biomaterials 2017, 133, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Luo, H.; Zeng, M.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, X. Intracellular pH-Triggered, Targeted Drug Delivery to Cancer Cells by Multifunctional Envelope-Type Mesoporous Silica Nanocontainers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2015, 7, 17399–17407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živojević, K.; Mladenović, M.; Djisalov, M.; Mundzic, M.; Ruiz-Hernandez, E.; Gadjanski, I.; Knežević, N.Ž. Advanced mesoporous silica nanocarriers in cancer theranostics and gene editing applications. J. Control. Release 2021, 337, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, N.Ž.; Kaluđerović, G.N. Silicon-based nanotheranostics. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 12821–12829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Shi, S.; Goel, S.; Shen, X.; Xie, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Qin, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Recent advancements in mesoporous silica nanoparticles towards therapeutic applications for cancer. Acta Biomater. 2019, 89, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Yang, K.; Liu, F.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S. Diverse gatekeepers for mesoporous silica nanoparticle based drug delivery systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6024–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Li, Z.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Biocompatibility, Biodistribution, and Drug-Delivery Efficiency of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy in Animals. Small 2010, 6, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.; Lu, M.-M.; Zhao, Y.-W.; Zhang, F.; Tan, Y.-F.; Zheng, X.; Pan, Y.; Xiao, X.-A.; Wang, Z.; Dong, W.-F.; et al. The shape effect of magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles on endocytosis, biocompatibility and biodistribution. Acta Biomater. 2017, 49, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.; Shi, J. In vivo Biodistribution and Urinary Excretion of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Effects of Particle Size and PEGylation. Small 2011, 7, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.-F.; Tang, R.; Wong, W.-T. Ionically Crosslinked Complex Gels Loaded with Oleic Acid-Containing Vesicles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guan, X.; Qiu, X.; Gao, T.; Yu, W.; Zhang, M.; Song, L.; Liu, D.; Dong, J.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Bioactive composite Janus nanofibrous membranes loading Ciprofloxacin and Astaxanthin for enhanced healing of full-thickness skin defect wounds. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 610, 155290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargazi, S.; Laraib, U.; Barani, M.; Rahdar, A.; Fatima, I.; Bilal, M.; Pandey, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Kyzas, G.Z. Recent trends in mesoporous silica nanoparticles of rode-like morphology for cancer theranostics: A review. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1261, 132922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Feng, J.; Wen, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhu, R. MgFe-LDH Nanoparticles: A Promising Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Replacement for Self-Renewal and Pluripotency Maintenance in Cultured Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, L.K.; Sazanovich, I.V.; Baggaley, E.; Bonneau, M.; Guerchais, V.; Williams, J.A.G.; Weinstein, J.A.; Bryant, H.E. Metal Complexes for Two-Photon Photodynamic Therapy: A Cyclometallated Iridium Complex Induces Two-Photon Photosensitization of Cancer Cells under Near-IR Light. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, L.; Tian, Z.; Gong, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Ge, X.; Liu, Z. Novel and Versatile Imine-N-Heterocyclic Carbene Half-Sandwich Iridium(III) Complexes as Lysosome-Targeted Anticancer Agents. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 11087–11098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, G.; Ranđelović, I.; Maksimović-Ivanić, D.; Mijatović, S.; Bulatović, M.Z.; Miljković, D.; Korb, M.; Lang, H.; Steinborn, D.; Kaluđerović, G.N. Anticancer Potential of (Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)chloridoiridium(III) Complexes Bearing κP and κP,κS-Coordinated Ph2PCH2CH2CH2S(O)xPh (x = 0–2) Ligands. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, G.; Steinborn, D.; Kaluđerović, G. Biological Potential of Halfsandwich Ruthenium(II) and Iridium(III) Complexes. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. (Former. Curr. Med. Chem. Agents) 2016, 16, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, G.; Mijatović, S.; Ranđelović, I.; Bulatović, M.; Miljković, D.; Maksimović-Ivanić, D.; Korb, M.; Lang, H.; Steinborn, D.; Kaluđerović, G.N. Biological activity of neutral and cationic iridium(III) complexes with κP and κP,κS coordinated Ph2PCH2S(O)xPh (x = 0–2) ligands. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 69, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, A.C.; Rodríguez-Fanjul, V.; Habtemariam, A.; Pizarro, A.M. Structurally Strained Half-Sandwich Iridium(III) Complexes As Highly Potent Anticancer Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 4005–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xie, Y.; Cong, F. Reduction- and pH-Sensitive Hyaluronan Nanoparticles for Delivery of Iridium(III) Anticancer Drugs. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2102–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J.H.; Tan, C.P.; He, L.; Zhang, W.; Ji, L.N.; Mao, Z.W. Delivery of Phosphorescent Anticancer Iridium(III) Complexes by Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Targeted Combined Photothermal-Chemotherapy and Thermal/Photoacoustic/Lifetime Imaging. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Huang, G.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Liang, H. Versatile delivery systems for non-platinum metal-based anticancer therapeutic agents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 441, 213975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevão, B.M.; Vilela, R.R.C.; Geremias, I.P.; Zanoni, K.P.S.; de Camargo, A.S.S.; Zucolotto, V. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles incorporated with Ir(III) complexes: From photophysics to photodynamic therapy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 40, 103052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenović, M.; Morgan, I.; Ilić, N.; Saoud, M.; Pergal, M.V.; Kaluđerović, G.N.; Knežević, N.Ž. pH-Responsive Release of Ruthenium Metallotherapeutics from Mesoporous Silica-Based Nanocarriers. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knežević, N.Ž.; Ilić, N.; Kaluđerović, G.N. Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery to Glioblastoma Multiforme. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Nanotechnology (NANO), Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 4–8 July 2022; pp. 321–324. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).