Anti-Proliferative and Anti-Migration Activity of Arene–Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Azole Therapeutic Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
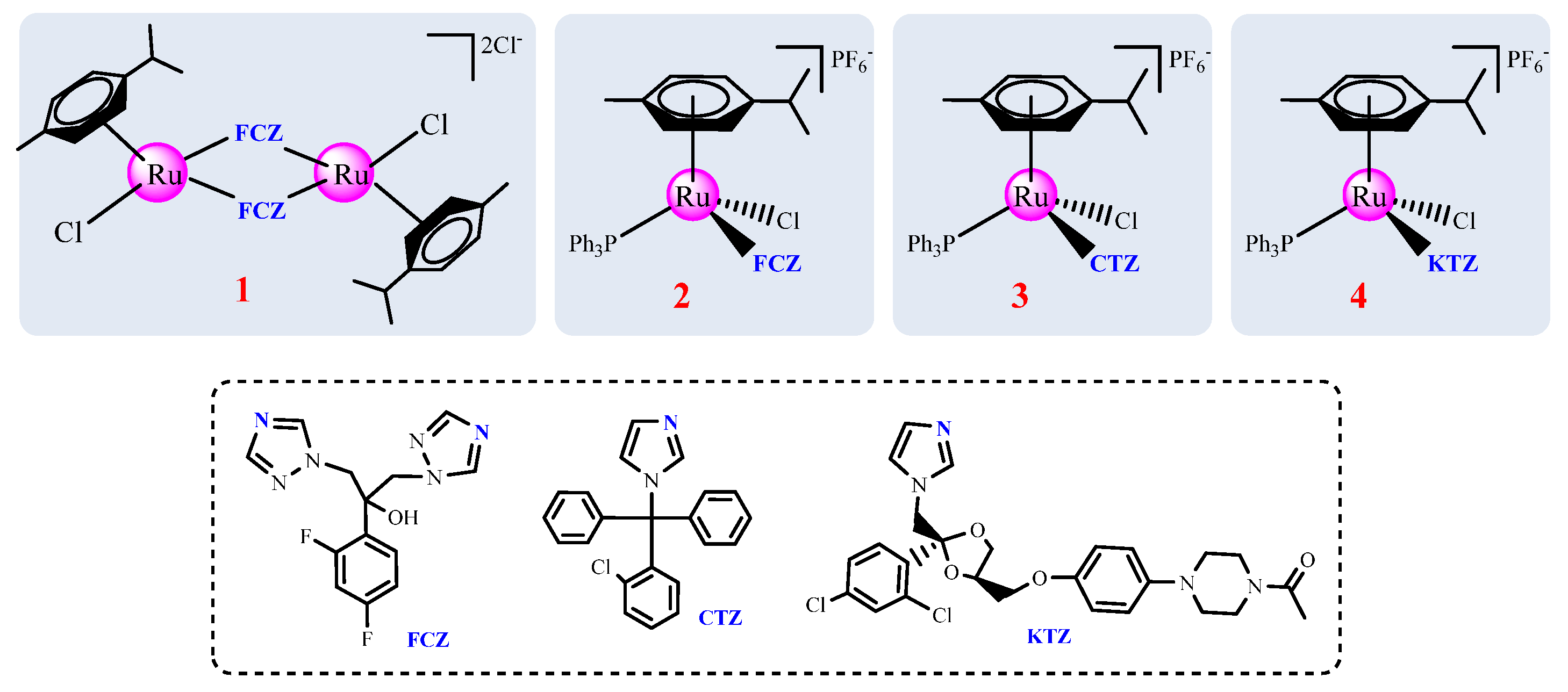
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Interaction Studies with Macro-Biological Targets: Blood Human Serum Albumin and DNA
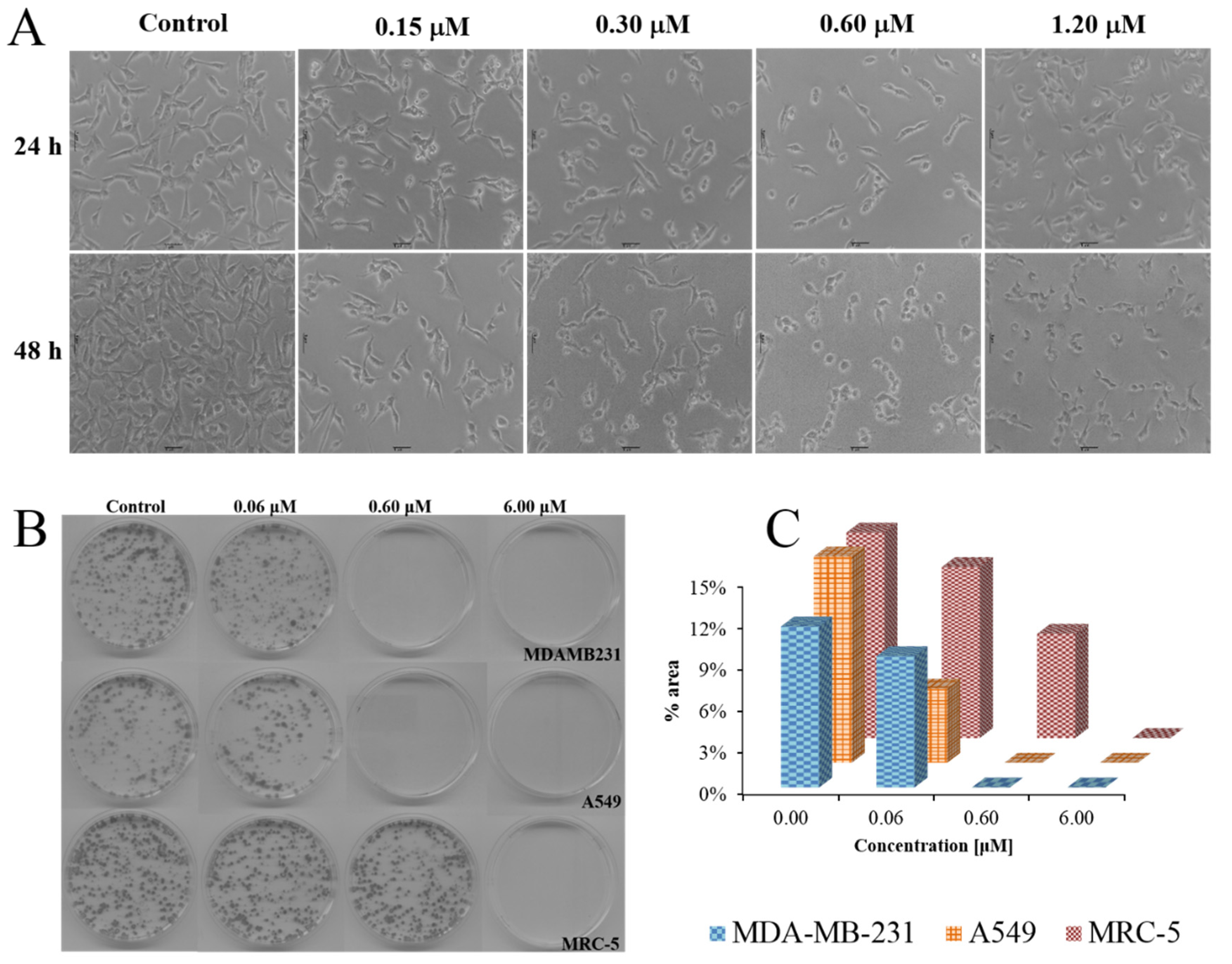
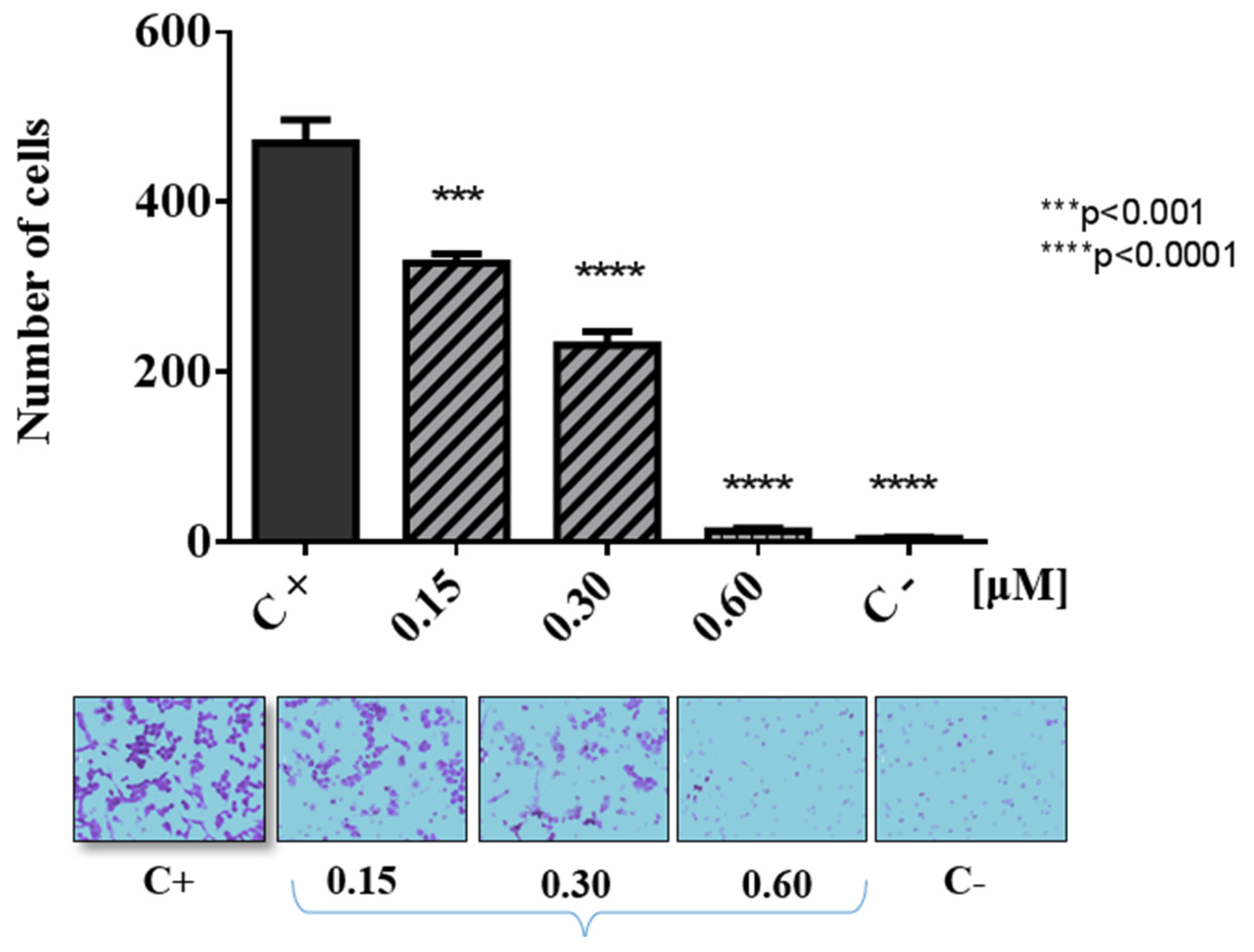
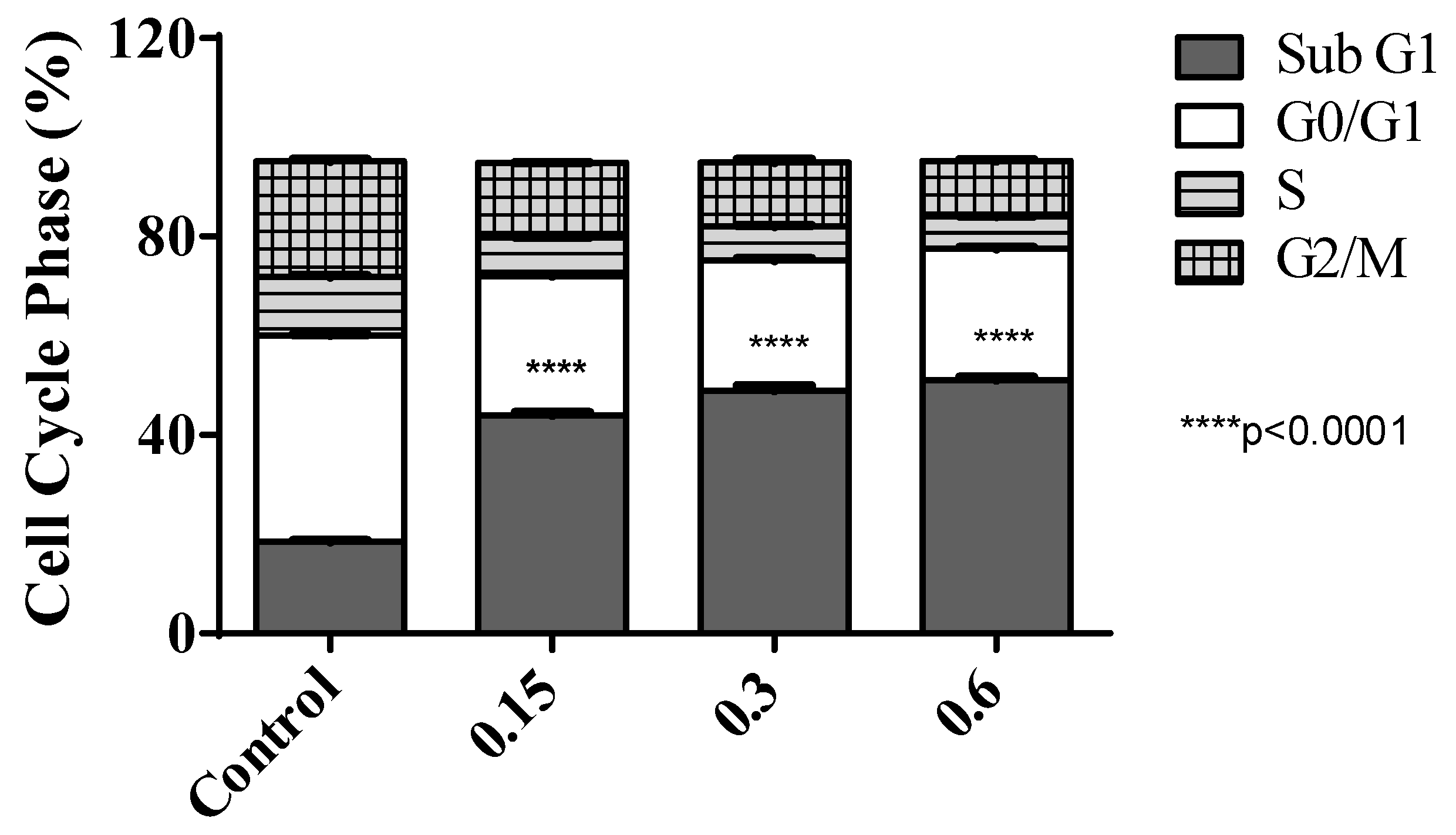
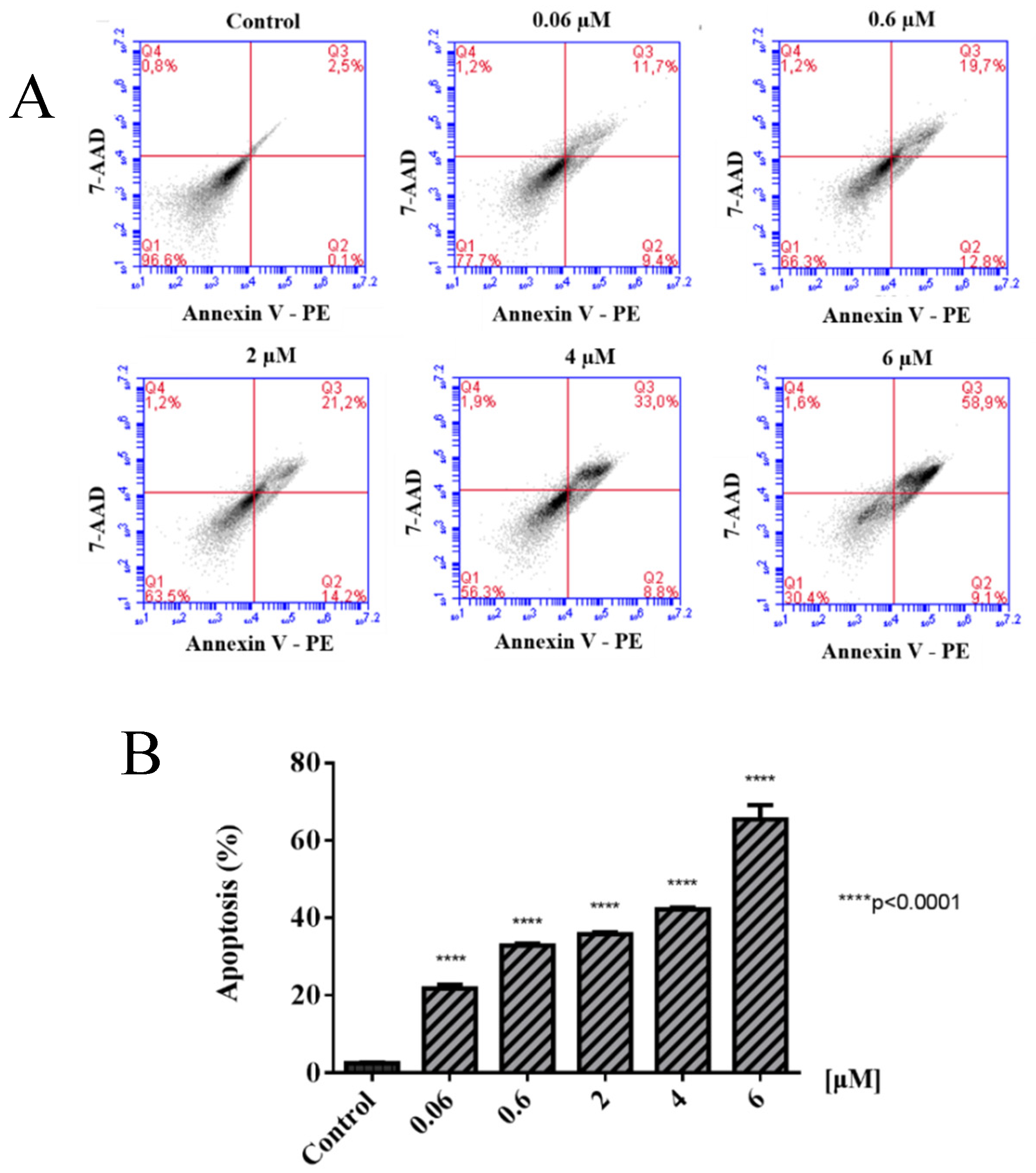
2.2. Biological Evaluations against Tumor Cell Lines
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Biomolecules Interaction
3.2. Biological Evaluations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Cancer Report 2014; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; ISBN 9283204298.
- Steeg, P.S. Targeting metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, N.P. Multi-platinum anti-cancer agents. Substitution-inert compounds for tumor selectivity and new targets. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8773–8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamo, A.; Sava, G. Ruthenium anticancer compounds: Myths and realities of the emerging metal-based drugs. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 7817–7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Menches, S.M.; Gerner, C.; Berger, W.; Hartinger, C.G.; Keppler, B.K. Structure–activity relationships for ruthenium and osmium anticancer agents—Towards clinical development. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 909–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Tang, Z.; Li, P. Development of arene ruthenium antitumor complexes. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Gupta, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, E.; Ji, L.; Chao, H.; Chen, Z.S. The development of anticancer ruthenium(II) complexes: From single molecule compounds to nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 5771–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Li, Y.; Li, P. Design of Ru-arene Complexes for Antitumor Drugs. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babak, M.B.; Ang, W.H. Metallo-Drugs: Development and Action of Anticancer Agents; Sigel, A., Sigel, H., Freisinger, E., Sigel, R.K.O., Eds.; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Volume 18, Chapter 6; p. 161. [Google Scholar]
- Merlino, A. Interactions between proteins and Ru compounds of medicinal interest: A structural perspective. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 26, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; van Beijnum, J.R.; Casini, A.; Nazarov, A.A.; Wagnieres, G.; van den Bergh, H.; Dyson, P.J.; Griffioen, A.W. Organometallic Ruthenium(II) Arene Compounds with Antiangiogenic Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3895–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, N.; Maksimoska, J.; Bregman, H.; Williams, D.S.; Webster, R.D.; Xue, F.; Meggers, E. Ruthenium half-sandwich complexes as protein kinase inhibitors: Derivatization of the pyridocarbazole pharmacophore ligand. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, J.; Görls, H.; Häfner, N.; Ferraro, G.; Dürst, M.; Runnebaum, I.B.; Weigand, W.; Merlino, A. Unusual mode of protein binding by a cytotoxic π-arene ruthenium(II) piano-stool compound containing an O,S-chelating ligand. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 12283–12287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurzwernhart, A.; Kandioller, W.; Bartel, C.; Bächler, S.; Trondl, R.; Mühlgassner, G.; Jakupec, M.A.; Arion, V.B.; Marko, D.; Keppler, B.K.; et al. Targeting the DNA-topoisomerase complex in a double-strike approach with a topoisomerase inhibiting moiety and covalent DNA binder. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4839–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.; Carreon, T.; Iniguez, E.; Anzellotti, A.; Sanchez, A.; Tyan, M.; Sattler, A.; Herrera, L.; Maldonado, R.A.; Sánchez-Delgado, R. Searching for new chemotherapies for tropical diseases: Ruthenium-clotrimazole complexes display high in vitro activity against Leishmania major and Trypanosoma cruzi and low toxicity toward normal mammalian cells. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3867–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colina-Vegas, L.; Lucena Dutra, J.; Villarreal, W.; Neto, J.H.; Cominetti, M.R.; Pavan, F.; Navarro, M.; Batista, A.A. Ru(II)/clotrimazole/diphenylphosphine/bipyridine complexes: Interaction with DNA, BSA and biological potential against tumor cell lines and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 162, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Escajeda, E.; Martínez, A.; Varela-Ramirez, A.; Sánchez-Delgado, R.A.; Aguilera, R.J. Analysis of the cytotoxic effects of ruthenium–ketoconazole and ruthenium–clotrimazole complexes on cancer cells. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2013, 29, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.H. Imidazole Antifungal Drugs Inhibit the Cell Proliferation and Invasion of Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colina-Vegas, L.; Coutinho, T.; Correa, R.S.; de Souza, W.; Rodrigues, J.C.F.; Batista, A.A.; Navarro, M. Antiparasitic activity and ultrastructural alterations provoked by organoruthenium complexes against Leishmania amazonensis. New J. Chem. under review.
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-38-746312-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Ruthenium (II) complexes interact with human serum albumin and induce apoptosis of tumor cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2015, 163, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.; Subramanian, S. Thermodynamics of protein association reactions: Forces contributing to stability. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Peng, S.; Zhu, F.; Lei, X.; Xiao, Q.; Su, W.; Liu, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L. Multispectroscopic investigation of the interaction between two ruthenium(II) arene complexes of curcumin analogs and human serum albumin. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 169, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colina-Vegas, L.; Luna-Dulcey, L.; Plutín, A.M.; Castellano, E.E.; Cominetti, M.R.; Batista, A.A. Half sandwich Ru(II)-acylthiourea complexes: DNA/HSA-binding, anti-migration and cell death in a human breast tumor cell line. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 12865–12875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, G.R.; Chaires, J.B. Characterization of DNA structures by circular dichroism. Curr. Protoc. Nucleic Acid Chem. 2003, 11, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.J.; Duan, Z.M.; Hao, Q.; Zheng, S.Z.; Wang, K.Z. Molecular Light Switches for Calf Thymus DNA Based on Three Ru(II) Bipyridyl Complexes with Variations of Heteroatoms. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 16577–16585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.B.; Liu, D.D.; Lin, Y.; Hu, W.; Mao, Z.W.; Le, X.Y. Water-soluble DNA minor groove binders as potential chemotherapeutic agents: Synthesis, characterization, DNA binding and cleavage, antioxidation, cytotoxicity and HSA interactions. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 8721–8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabnis, R.W. Handbook of Biological Dyes and Stains: Synthesis and Industrial Applications, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-47-040753-0. [Google Scholar]
- Fornander, L.H.; Wu, L.; Billeter, M.; Lincoln, P.; Nordeń, B. Minor-Groove binding drugs: Where is the second Hoechst 33258 molecule? J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 5820–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pages, B.J.; Ang, D.L.; Wrightb, E.P.; Aldrich-Wright, A.R. Metal complex interactions with DNA. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 3505–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, M.; Castro, W.; Higuera-Padilla, A.R.; Sierraalta, A.; Abad, M.J.; Taylor, P.; Sánchez-Delgado, R.A. Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of trans-platinum(II) complexes with chloroquine. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2011, 105, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frik, M.; Martínez, A.; Elie, B.T.; Gonzalo, O.; de Mingo, D.R.; Sanau, M.; Sanchez-Delgado, R.A.; Sadhukha, T.; Prabha, S.; Ramos, J.W.; et al. In vitro and in vivo Evaluation of water-soluble iminophosphorane ruthenium(II) compounds. A potential chemotherapeutic agent for triple negative breast cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 9995–10012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.R.; Kumar, A.; Paitandi, R.P.; Singh, R.S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Verma, S.P.; Dasb, P.; Pandey, P.S. Heteroleptic arene Ru(II) dipyrrinato complexes: DNA, protein binding and anti-cancer activity against the ACHN cancer cell line. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 7163–7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, M.P.; Gray, S.G.; Hoffmann, A.C.; Hilger, R.A.; Thomale, J.; O’Flaherty, J.D.; Fennell, D.A.; Richard, D.; O’Leary, J.J.; O’Byrne, K.J. Generation and characterization of cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cell lines displaying a stem-like signature. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicek, A.; Turel, I.; Kanduser, M.; Miklavcic, D. Combined therapy of the antimetastatic compound NAMI-A and electroporation on B16F1 tumour cells in vitro. Bioelectrochemistry 2007, 71, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.C. Cell Migration. In Developmental Methods and Protocols, 1st ed.; Guan, J.L., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 15–22. ISBN 978-1-59-259860-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Zheng, W.; Chen, T. Ruthenium Polypyridyl Complex Inhibits Growth and Metastasis of Breast Cancer Cells by Suppressing FAK signaling with Enhancement of TRAIL-induced Apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Halicka, H.D.; Traganos, F.; Tanaka, T.; Kurose, A.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Cytometric assessment of DNA damage in relation to cell cycle phase and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 2005, 38, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutte, B.; Nuydens, R.; Geerts, H.; Ramaekers, F. Annexin V binding assay as a tool to measure apoptosis in differentiated neuronal cells. J. Neurosci. Methods 1998, 86, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass-Marmor, L.; Morgenstern, H.; Beitner, R. Calmodulin antagonists decrease glucose 6-bisphosphate, fructose 6-bisphosphate, ATP and viability of melanoma cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 313, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.A.; Huang, T.N.; Matheson, T.W.; Smith, A.K. (η6-Hexamethylbenzene) ruthenium Complexes. Inorg. Synth. 1982, 21, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, E.; Simpson, S.J. Synthesis and characterization of [(η6-cymene)Ru(L)X2] compounds: Single crystal X-ray structure of [(η6-cymene)Ru(P{OPh}3)Cl2] at 203 K. Polyhedron 2004, 23, 2695–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | T (K) | Ksv (104) | Kb (105) | n | ΔG | ΔH | ΔS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 295 | 1.32 ± 0.06 | 2.35 ± 0.04 | 1.30 | −30.35 | 15.73 | 156.12 |
| 310 | 1.24 ± 0.10 | 1.72 ± 0.02 | 1.25 | −31.10 | |||
| 3 | 295 | 1.93 ± 0.08 | 5.35 ± 0.70 | 1.25 | −32.40 | 38.90 | 241.32 |
| 310 | 1.83 ± 0.03 | 2.50 ± 0.20 | 1.25 | −32.04 | |||
| 4 | 295 | 2.71 ± 0.04 | 7.90 ± 0.14 | 1.35 | −34.30 | 17.70 | 172.90 |
| 310 | 2.45 ± 0.03 | 5.57 ± 0.22 | 1.30 | 34.10 |
| T (K) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ksv (104) | 298 310 | 56.71 ± 0.49 32.04 ± 0.14 | 39.12 ± 0.01 24.42 ± 2.57 | 11.99 ± 0.38 9.71 ± 0.81 | 2.76 ± 0.29 2.30 ± 0.41 |
| Compound | A549 | DU-145 | MDA-MB-231 | MRC-5 | L929 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 2 | 2.94 ± 0.73 | 3.90 ± 0.85 | 2.35 ± 0.42 | 2.02 ± 0.10 | 2.00 ± 0.16 |
| 3 | 0.61 ± 0.07 | 5.13 ± 0.98 | 0.63 ± 0.03 | 1.16 ± 0.01 | 1.15 ± 0.03 |
| 4 | 0.64 ± 0.04 | 4.45 ± 0.75 | 0.62 ± 0.02 | 1.09 ± 0.06 | 1.80 ± 0.13 |
| Fluconazole | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| Clotrimazole | 14.47 ± 0.95 | 15.82 ± 0.23 | 10.11 ± 2.43 | 12.70 ± 0.65 | 9.74 ± 2.05 |
| Ketoconazole | 41.85 ± 2.54 | 47.54 ± 2.53 | 10.26 ± 1.04 | 37.50 ± 2.25 | 16.35 ± 0.47 |
| Cisplatin | 14.42 ± 1.45 | 2.33 ± 0.40 | 2.44 ± 0.20 | 23.90 ± 0.70 | 16.53 ± 2.38 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colina-Vegas, L.; Oliveira, K.M.; Cunha, B.N.; Cominetti, M.R.; Navarro, M.; Azevedo Batista, A. Anti-Proliferative and Anti-Migration Activity of Arene–Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Azole Therapeutic Agents. Inorganics 2018, 6, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6040132
Colina-Vegas L, Oliveira KM, Cunha BN, Cominetti MR, Navarro M, Azevedo Batista A. Anti-Proliferative and Anti-Migration Activity of Arene–Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Azole Therapeutic Agents. Inorganics. 2018; 6(4):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6040132
Chicago/Turabian StyleColina-Vegas, Legna, Katia M. Oliveira, Beatriz N. Cunha, Marcia Regina Cominetti, Maribel Navarro, and Alzir Azevedo Batista. 2018. "Anti-Proliferative and Anti-Migration Activity of Arene–Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Azole Therapeutic Agents" Inorganics 6, no. 4: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6040132
APA StyleColina-Vegas, L., Oliveira, K. M., Cunha, B. N., Cominetti, M. R., Navarro, M., & Azevedo Batista, A. (2018). Anti-Proliferative and Anti-Migration Activity of Arene–Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Azole Therapeutic Agents. Inorganics, 6(4), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6040132