Fluorolytic Sol–Gel Synthesis of Nanometal Fluorides: Accessing New Materials for Optical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nanometal Fluoride Particles and Their Application as Optical Materials
- Binary fluorides (MgF2, CaF2), e.g., for antireflective coatings;
- Complex fluorides (MgxAlFy), fluorperovskites (MIMIIF3) for antireflective coatings and hosts for rare earth metal (relevant for luminescent materials);
- Hosts for up and down conversion (CaF2, SrF2, BaF2, complex lanthanide fluorides);
- Other applications—composites, dental materials, wood protection, etc.
2.1. Binary Fluorides for Antireflective Coatings
2.1.1. Magnesium Fluoride
2.1.2. Calcium Fluoride
2.2. Complex Fluorides for Antireflective Coatings
Magnesium Fluoro Aluminates—MgxAlFy and [K1−xNax]MgF3
2.3. Up and Down Conversion Materials
CaF2, SrF2 and BaF2 as Hosts for Rare Earth Metals
OR’ = Lactate; OR’’ = Acetate, x = 0…0.1
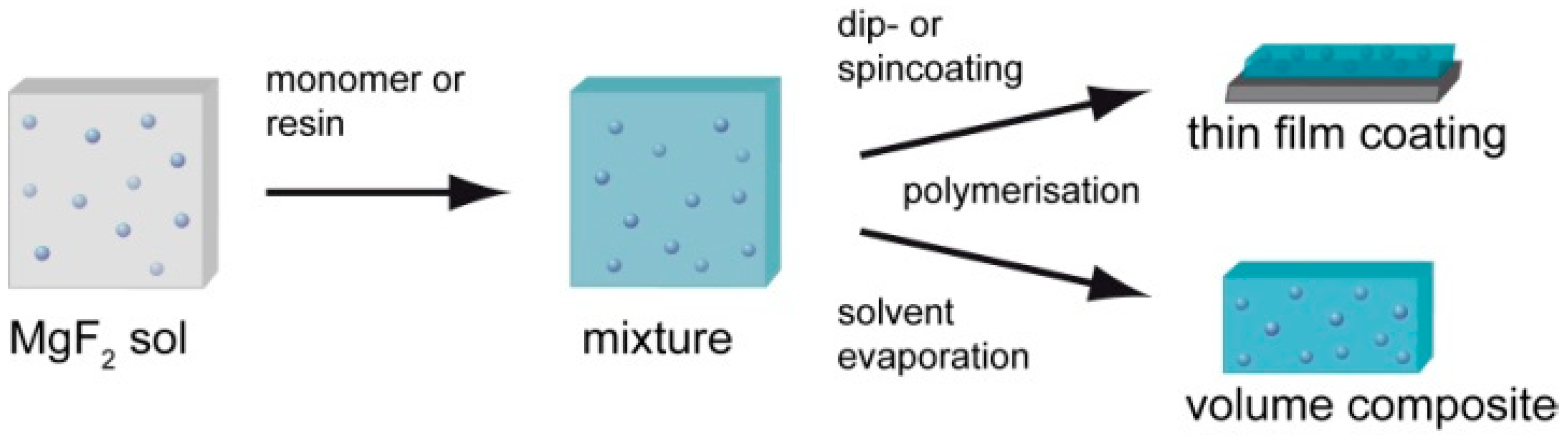
2.4. Composites
3. Summary and Outlook
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kemnitz, E.; Gross, U.; Rüdiger, S.; Shekar, C.S. Amorphous Metal Fluorides with Extraordinary High Surface Areas. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 4251–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetzov, S.V.; Osiko, V.V.; Tkatchenko, E.A.; Fedorov, P.P. Inorganic nanofluorides and related nanocomposites. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2006, 75, 1065–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, P.P.; Luginina, A.A.; Kuznetsov, S.V.; Osiko, V.V. Nanofluorides. J. Fluorine Chem. 2011, 132, 1012–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, P.P.; Kuznetsov, S.V.; Osiko, V.V. Photonic. In Electronic Properties of Fluoride Materials; Tressaud, A., Poeppelmeier, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 7–31. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Sun, L.-D.; Zhang, Y.W.; Yan, C.-H. Synthesis and assembly of rare earth nanostructures directed by the principle of coordination chemistry in solution-based process. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 1038–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lin, J. Rare earth fluoride nano-/microcrystals: Synthesis, surface modification and application. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6831–6847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüdiger, S.; Gross, U.; Kemnitz, E. Non-aqueous sol–gel synthesis of nano-structured metal fluorides. J. Fluorine Chem. 2007, 128, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüdiger, S.; Kemnitz, E. The fluorolytic sol–gel route to metal fluorides—A versatile process opening a variety of application fields. Dalton Trans. 2008, 9, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemnitz, E.; Rüdiger, S. Alain Tressaud. In Functionalized Inorganic Fluorides; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 69–97. [Google Scholar]
- Kemnitz, E.; Wuttke, S.; Coman, S.M. Tailor-Made MgF2-Based Catalysts by Sol–Gel Synthesis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 2011, 4773–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemnitz, E. Nanoscale metal fluorides: A new class of heterogeneous catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 786–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemnitz, E.; Noack, J. The non-aqueous fluorolytic sol–gel synthesis of nanoscaled metal fluorides. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 19411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemnitz, E. Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology; Klein, L., Aparicio, M., Jitianu, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kemnitz, E.; Coman, S. New Materials for Catalytic Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 133–187. [Google Scholar]
- Krahl, T.; Kemnitz, E. Aluminium fluoride—The strongest solid Lewis acid: Structure and reactivity. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 773–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucier, B.E.G.; Johnston, K.E.; Arnold, D.C.; Lemyre, J.-L.; Beaupre, A.; Blanchette, M.; Ritcey, A.M.; Schurko, R.W. Comprehensive Solid-State Characterization of Rare Earth Fluoride Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccache, R.; Yu, Q.; Capobianco, J.A. The Fluoride Host: Nucleation, Growth, and Upconversion of Lanthanide-Doped Nanoparticles. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2015, 3, 482–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Han, S.; Huang, W.; Lin, X. Enhancing solar cell efficiency: The search for luminescent materials as spectral converters. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 42, 173–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basiev, T.T.; Doroshenko, M.E.; Fedorov, P.P.; Konyushkin, V.A.; Kuznetsov, S.V.; Osiko, V.V.; Akchurin, M.S. Efficient laser based on CaF2–SrF2–YbF3 nanoceramics. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aballea, P.; Suganuma, A.; Druon, F.; Hostalrich, J.; Georges, P.; Gredin, P.; Mortier, M. Laser performance of diode-pumped Yb:CaF2 optical ceramics synthesized using an energy-efficient process. Optica 2015, 2, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.W.; Han, H.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhong, J.X. White emission by frequency up-conversion in Yb3+-Ho3+-Tm3+ triply doped hexagonal NaYF4 nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. 2009, 133, 18995–18999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Ramos, J.; Yanes, A.C.; Santana-Alonso, A.; del-Castillo, J. Highly efficient up-conversion and bright white light in RE co-doped KYF4 nanocrystals in sol–gel silica matrix. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 555, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Deng, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, X. Tuning upconversion through energy migration in core-shell nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukka, T.; Rantanen, T.; Kuningas, K. Photon upconversion in homogeneous fluorescence-based bioanalytical assays. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1130, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Gu, Z.J.; Zhou, L.J.; Yin, W.Y.; Liu, X.X.; Yan, L.; Jin, S.; Ren, W.L.; Xing, G.M.; Li, S.J. Mn2+ Dopant-Controlled Synthesis of NaYF4:Yb/Er Upconversion Nanoparticles for in vivo Imaging and Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Feng, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, F. Upconversion nanoparticles dramatically promote plant growth without toxicity. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Liu, J.; Padmanabhan, P.; Yeow, E.; Xing, B. Recent advance of biological molecular imaging based on lanthanide-doped upconversion-luminescent nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, A.; Koch, J.; Troyanov, S.I.; Kemnitz, E. Aluminum Alkoxide Fluorides Involved in the Sol–Gel Synthesis of Nanoscopic AlF3. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 5299–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astruc, A.; Cochon, C.; Dessources, S.; Célérier, S.; Brunet, S. High specific surface area metal fluorides as catalysts for the fluorination of 2-chloropyridine by HF. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 453, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, S.; Tada, M.; Kimura, T. Preparation and characterization of MgF2 thin film by a trifluoroacetic acid method. Thin Solid Films 1997, 304, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemnitz, E.; Scholz, G.; Rüdiger, S. Sol-Gel-Synthesis of Nano-Scaled Metal Fluorides—Mechanism and Properties. In Functionalized Inorganic Fluorides: Synthesis, Characterization and Properties of Nanostructured Solids; Tressaud, A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, M.J. Handbook of Optical Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, G.; Kemnitz, E. Sol-Gel Synthesis of Metal Fluorides: Reactivity and Mechanism. In Modern Synthesis Processes and Reactivity of Fluorinated Compounds; Groult, H., Leroux, F., Tressaud, A., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 609–650. [Google Scholar]
- Ishizawa, H.; Niisaka, S.; Murata, T.; Tanaka, A. Preparation of MgF2-SiO2 thin films with a low refractive index by a solgel process. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, C200-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, D.; Pendse, S.; Sakthivel, S.; Ramasamy, E.; Joshi, S.V. High performance broad band antireflective coatings using a facile synthesis of ink-bottle mesoporous MgF2 nanoparticles for solar applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 159, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, J.; Scheurell, K.; Kemnitz, E.; Garcia-Juan, P.; Rau, H.; Lacroix, M.; Eicher, J.; Lintner, B.; Sontheimer, T.; Hofmann, T.; et al. MgF2 antireflective coatings by sol–gel processing: Film preparation and thermal densification. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 18535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurell, K.; Noack, J.; König, R.; Hegmann, J.; Jahn, R.; Hofmann, T.; Löbmann, P.; Lintner, B.; Garcia-Juan, P.; Eicher, J.; Kemnitz, E. Optimisation of a sol–gel synthesis route for the preparation of MgF2 particles for a large scale coating process. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 19501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurell, K.; Kemnitz, E.; Garcia-Juan, P.; Eicher, J.; Lintner, B.; Hegmann, J.; Jahn, R.; Hofmann, T.; Löbmann, P. Porous MgF2 antireflective λ/4 films prepared by sol–gel processing: Comparison of synthesis approaches. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 76, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogush, G.H.; Zukovsky, C.F. Uniform silica particle precipitation: An aggregative growth model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1992, 142, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahl, T.; Broßke, D.; Scheurell, K.; Lintner, B.; Kemnitz, E. Novel aspects in the chemistry of the non-aqueous fluorolytic sol–gel synthesis of nanoscaled homodisperse MgF2 sols for antireflective coatings. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, F.; Scheurell, K.; Scholz, G.; Kemnitz, E. Effects of Chloride Additives on Mechanical Stability and Environmental Durability of Porous MgF2 Thin Films. In Nanostructured Thin Films IX; Lakhtakia, A., Mackay, T.G., Suzuki, M., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9929, p. 992914. [Google Scholar]
- Löbmann, P. Antireflective coatings by sol–gel processing: Commercial products and future perspectives. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 83, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malitson, I.H. A redetermination of some optical properties of calcium fluoride. Appl. Opt. 1963, 2, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, C.; Fendrych, F.; Recker, K.; Triska, A.; Wallrafen, F. Influence of crystallisation conditions on the microtexture of the directionally solidified eutectic of the MgF2–CaF2 system. Cryst. Res. Technol. 1990, 25, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilvi, T.; Arstila, K.; Leskelä, M.; Ritala, M. Novel ALD Process for Depositing CaF2 Thin Films. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 3387–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmer, A.; Scheurell, K.; Kemnitz, E. Formation of nanoscopic CaF2 via a fluorolytic sol–gel process for antireflective coatings. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmer, A.; Kemnitz, E. Characterization of nanoscopic calcium fluoride films. In Nanostructured Thin Films IX; Lakhtakia, A., Mackay, T.G., Suzuki, M., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9929, p. 99290F. [Google Scholar]
- Schütz, F.; Bäthge, M.; Scheurell, K.; Scholz, G.; Feist, M.; Kemnitz, E. Development of complex magnesium fluoro aluminates via the fluorolytic sol–gel synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, F.; Lange, L.; Scheurell, K.; Scholz, G.; Kemnitz, E. Synthesis and Characterization of Perovskite-Type [K1−xNax]MgF3 Mixed Phases via the Fluorolytic Sol–Gel Synthesis. Crystals 2018, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, U.; Jacinto, C.; Silva, W.F.; Guedes, I.; Benayas, A.; Maestro, L.M.; Elias, M.A.; Bovero, E.; van Veggel, F.C.J.M.; Sole, J.A.G.; et al. Sub-Tissue Thermal Sensing Based on Neodymium-Doped LaF3 Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.H.; Setlur, A.A.; Lauerhaas, J.M.; Dai, J.Y.; Seelig, E.W.; Chang, R.P.H. A nanotube-based field-emission flat panel display. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 2912–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Alonso, A.; Mendez-Ramos, J.; Yanes, A.C.; del-Castillo, J.; Rodriguez, V.D. Up-conversion in sol–gel derived nano-glass–ceramics comprising NaYF4 nano-crystals doped with Yb3+, Ho3+ and Tm3+. Opt. Mater. 2010, 32, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalav, A.; Richards, B.S.; Trupke, T.; Kramer, K.W.; Gudel, H.U. Application of NaYF4:Er3+ up-converting phosphors for enhanced near-infrared silicon solar cell response. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 013505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, C.; Roming, M.; Trampert, K. Polyol-Mediated Synthesis of Nanoscale CaF2 and CaF2:Ce,Tb. Small 2006, 2, 1248–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Miao, W.R.; Li, Y.X.; Yao, H.C.; Li, Z.J. Water-soluble Ln3+-doped calcium fluoride nanocrystals: Controlled synthesis and luminescence properties. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 1794–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Gu, M.; Huang, S.M.; Jin, X.J.; Liu, X.L.; Liu, B.; Ni, C. Luminescence behavior of Tb3+ ions in transparent glass and glass-ceramics containing CaF2 nanocrystals. J. Lumin. 2009, 129, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, B.; Krahl, T.; Rurack, K.; Kemnitz, E. Nanoscale CaF2 doped with Eu3+ and Tb3+ through fluorolytic sol–gel synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 8607–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, B.; Haida, P.; Fink, F.; Krahl, T.; Gawlitza, K.; Rurack, K.; Scholz, G.; Kemnitz, E. Novel and easy access to highly luminescent Eu and Tb doped ultra-small CaF2, SrF2 and BaF2 nanoparticles—Structure and luminescence. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 2925–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, B.; Haida, P.; Krahl, T.; Scholz, G.; Kemnitz, E. Core–shell metal fluoride nanoparticles via fluorolytic sol–gel synthesis—A fast and efficient construction kit. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 5444–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmer, A.; Scheurell, K.; Scholz, G.; Kemnitz, E. Sol–Gel-Synthesis of Nanoscopic Complex Metal Fluorides. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, J.; Schmidt, L.; Gläsel, H.-J.; Bauer, M.; Kemnitz, E. Inorganic–organic nanocomposites based on sol–gel derived magnesium Fluoride. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4774–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, J.; Fritz, C.; Flügel, C.; Hemmann, F.; Gläsel, H.-J.; Kahle, O.; Dreyer, C.; Bauer, M.; Kemnitz, E. Metal fluoride-based transparent nanocomposites with low refractive indices. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 5706–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

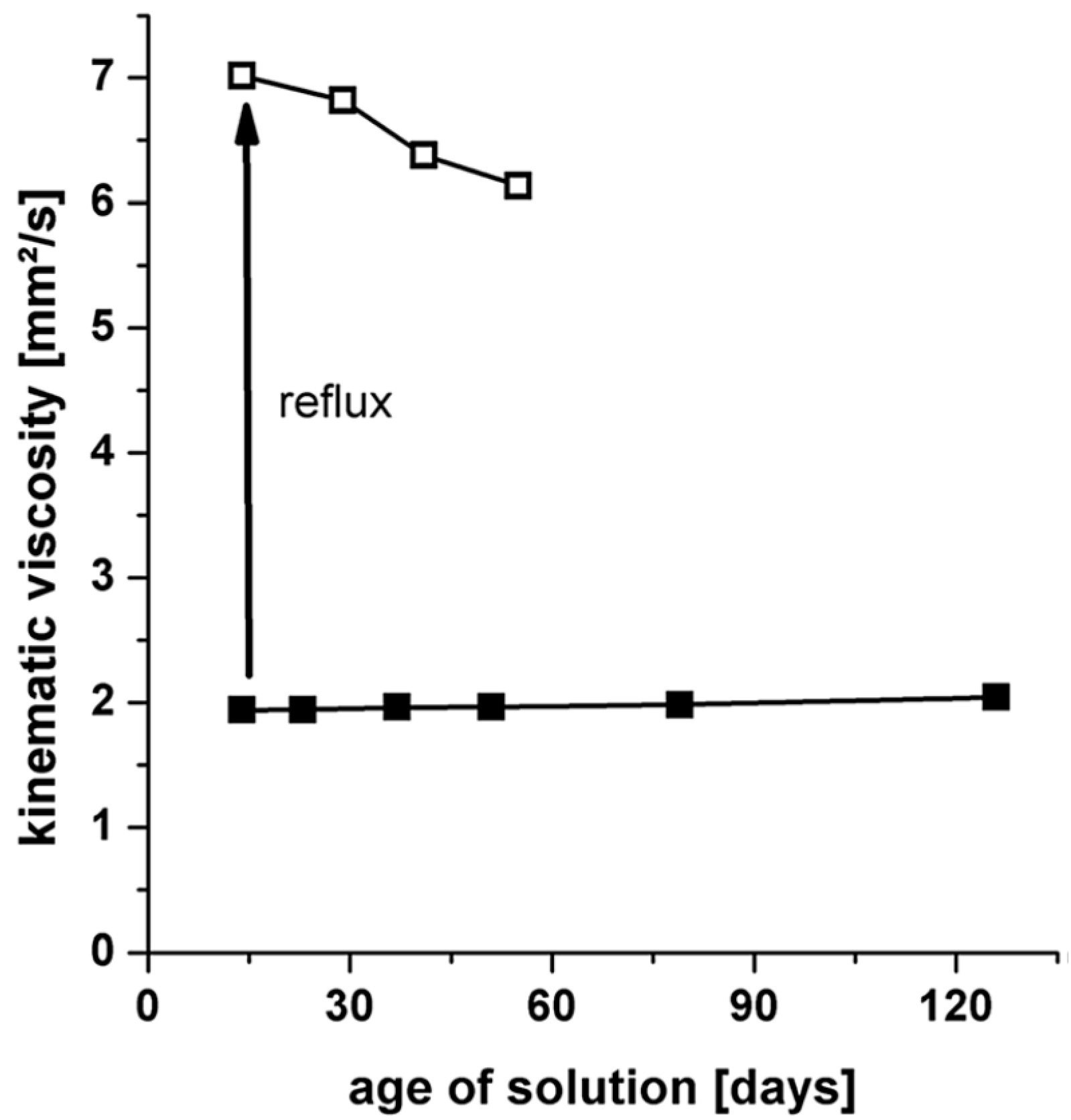
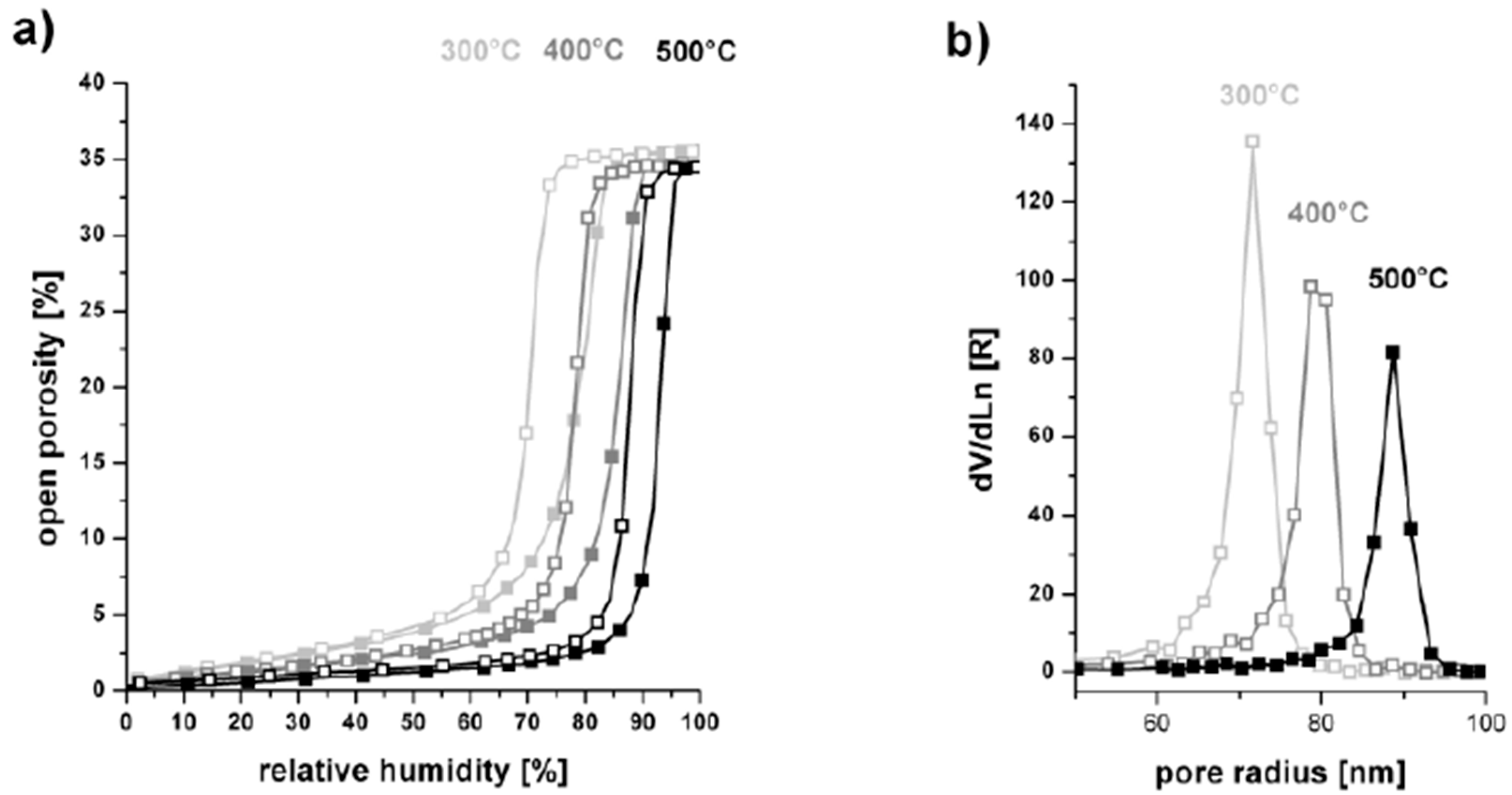
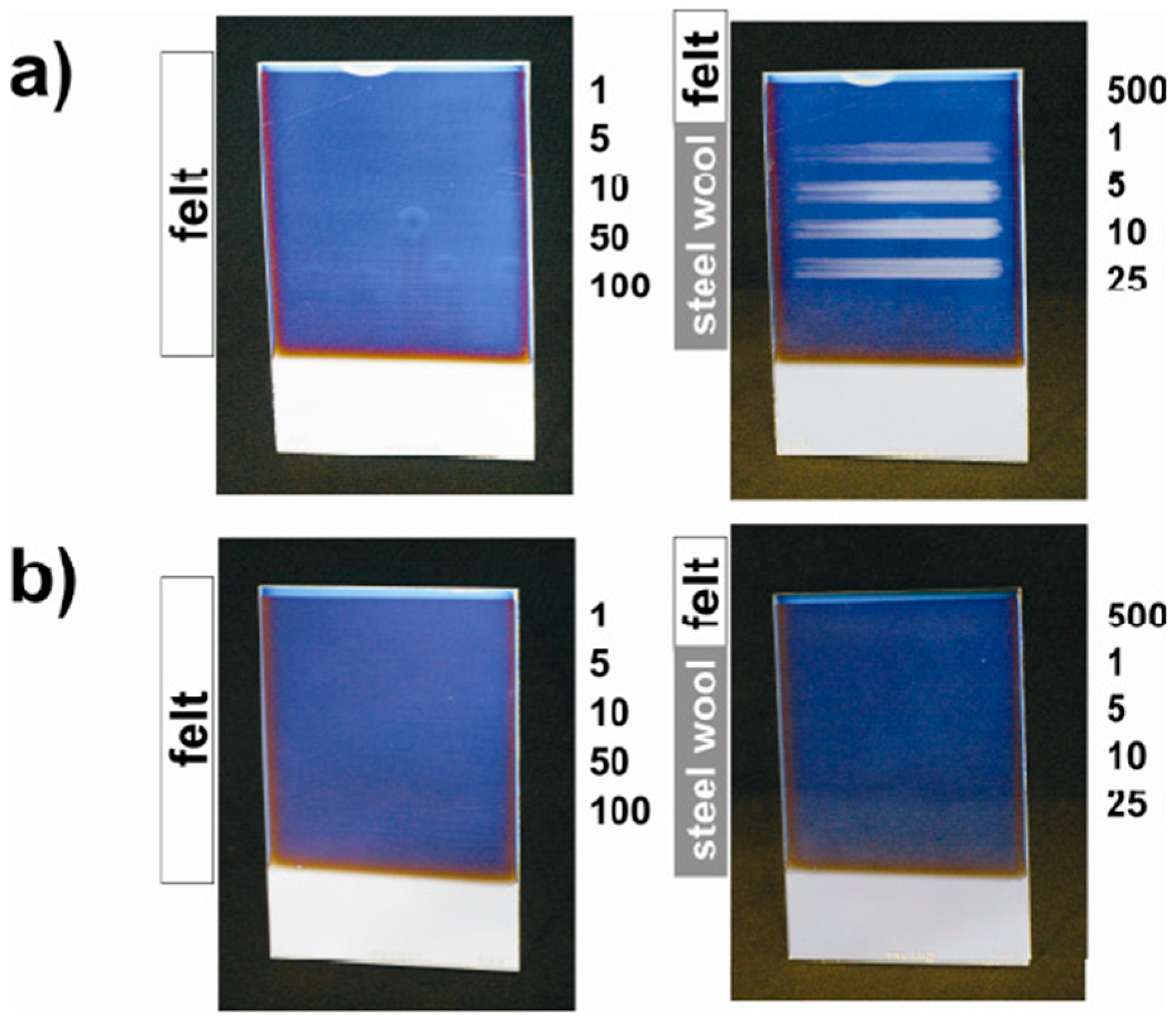

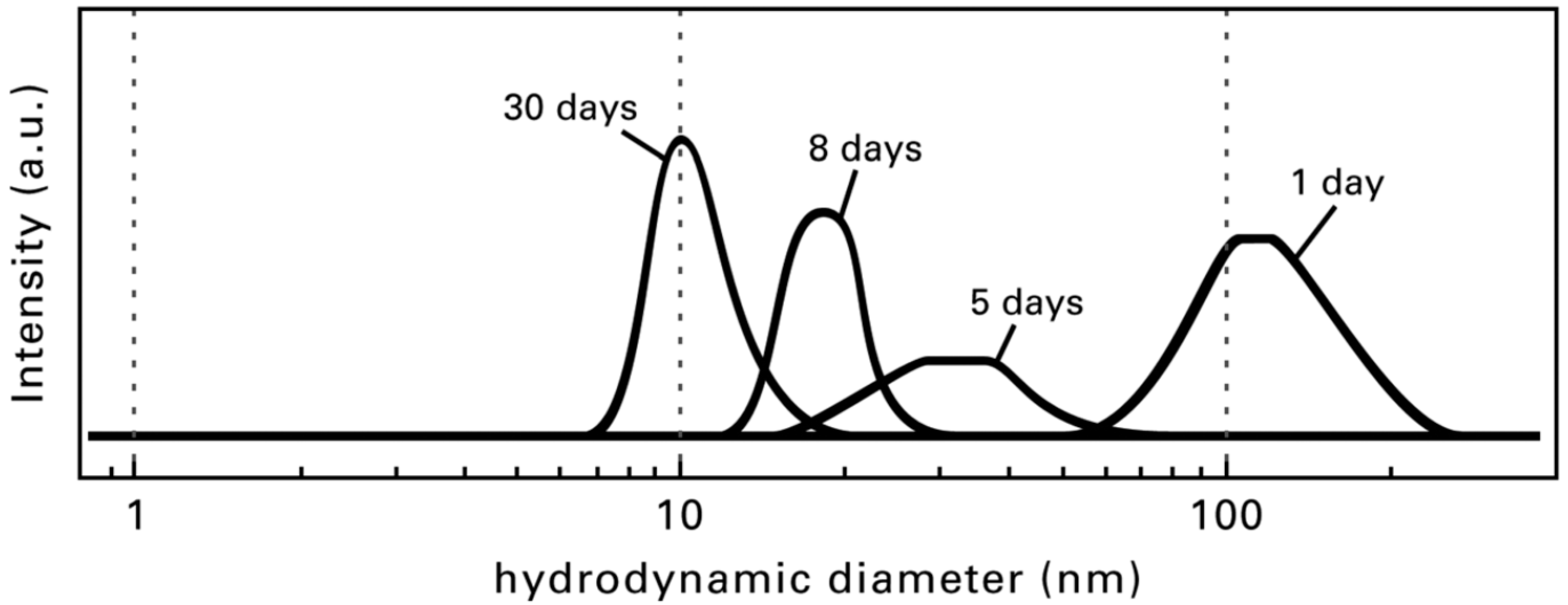
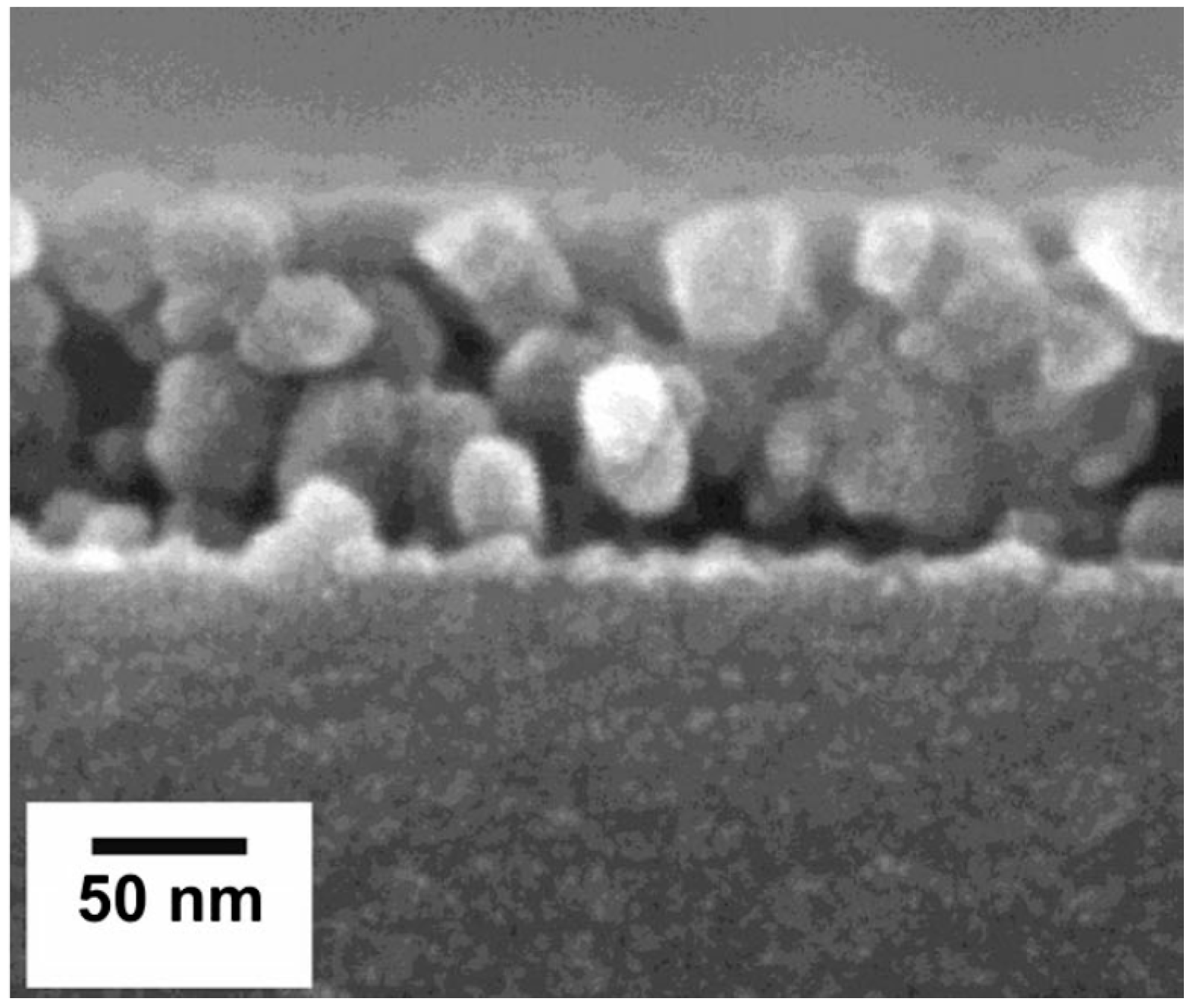
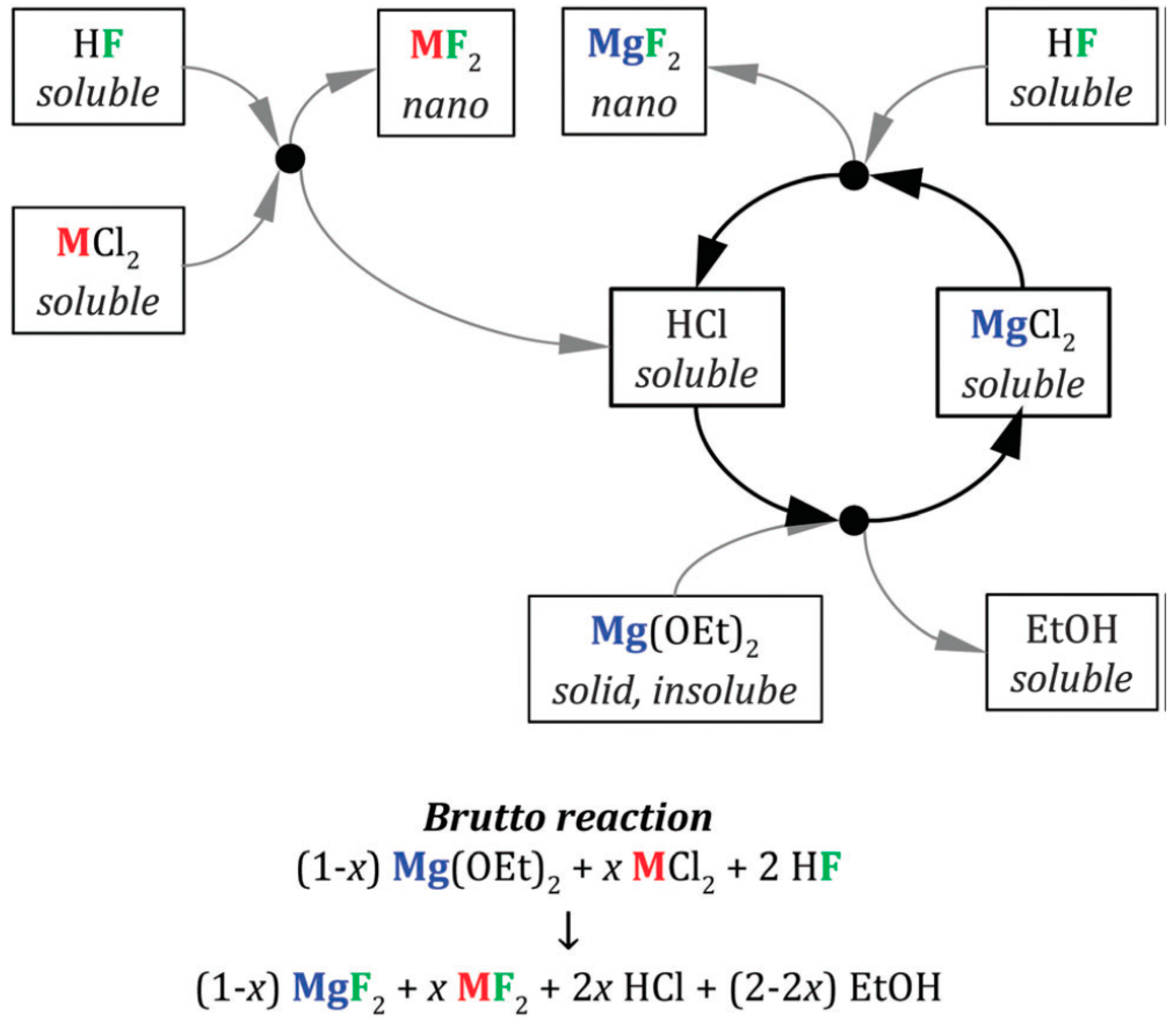
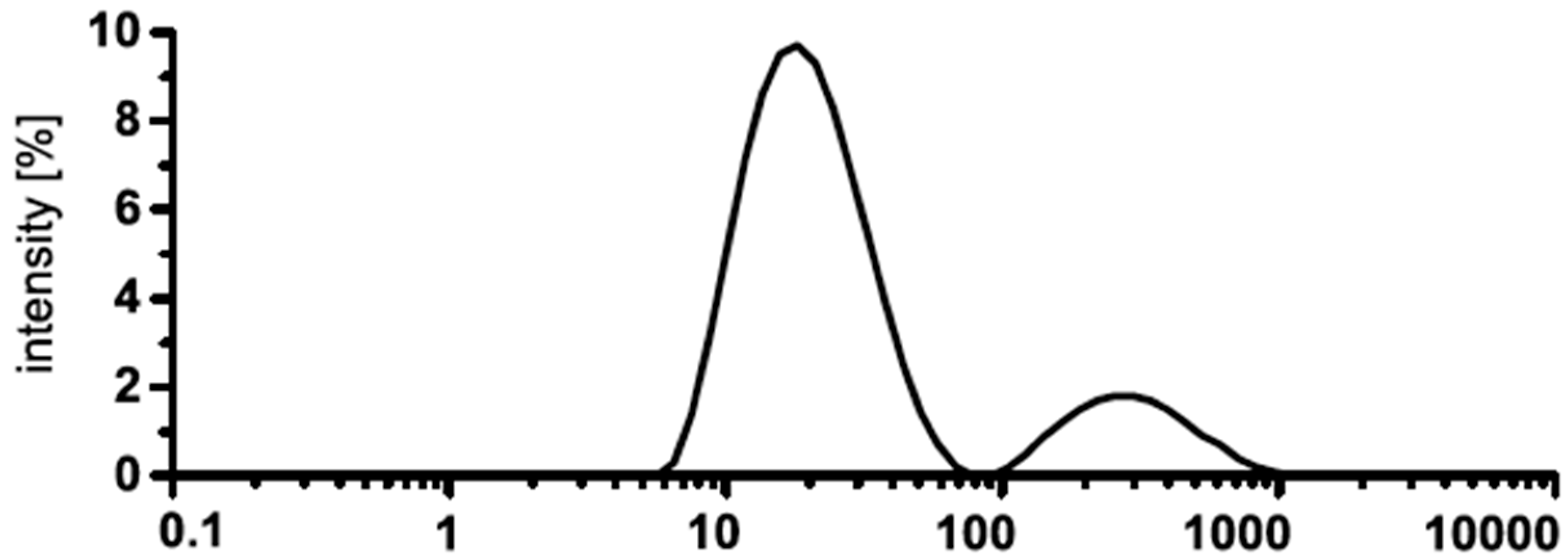
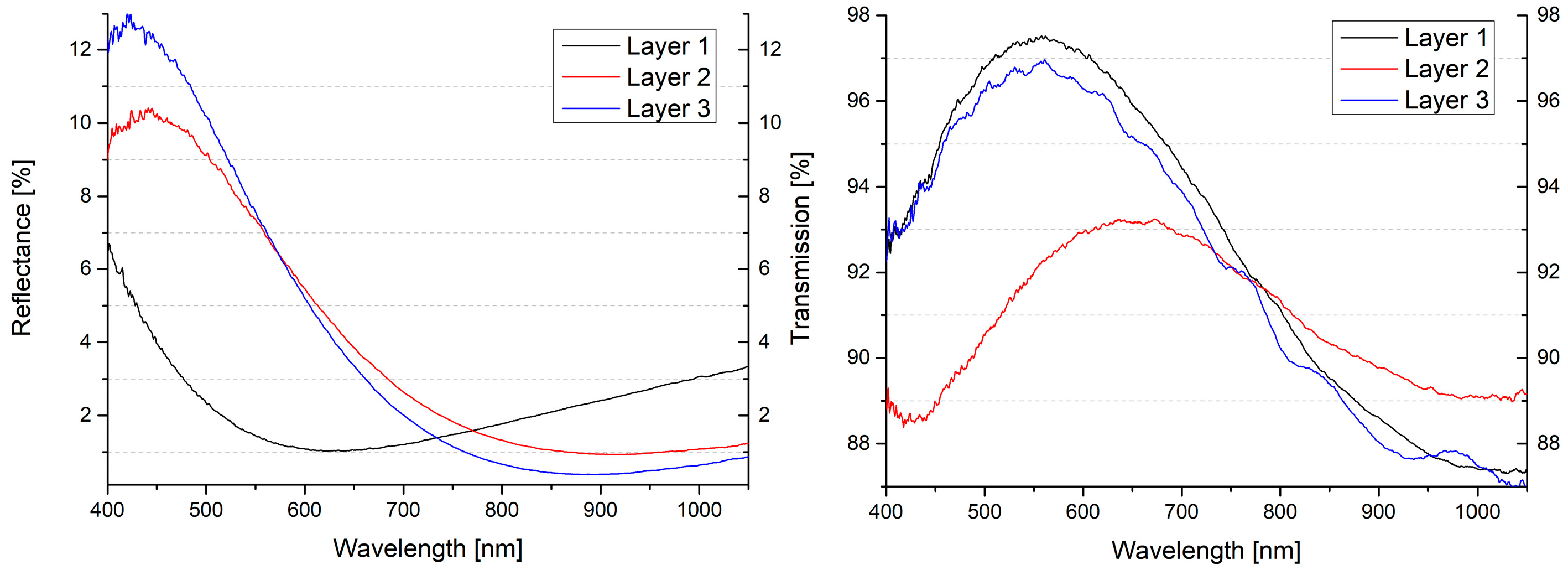
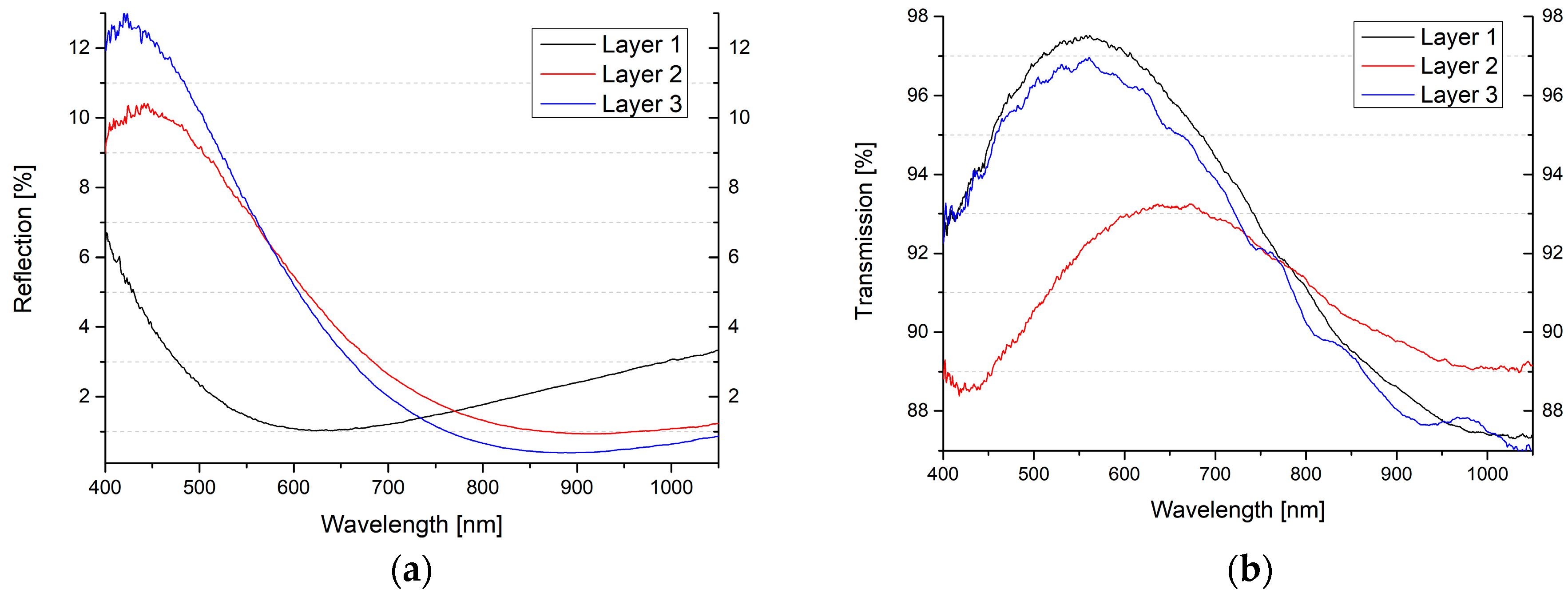
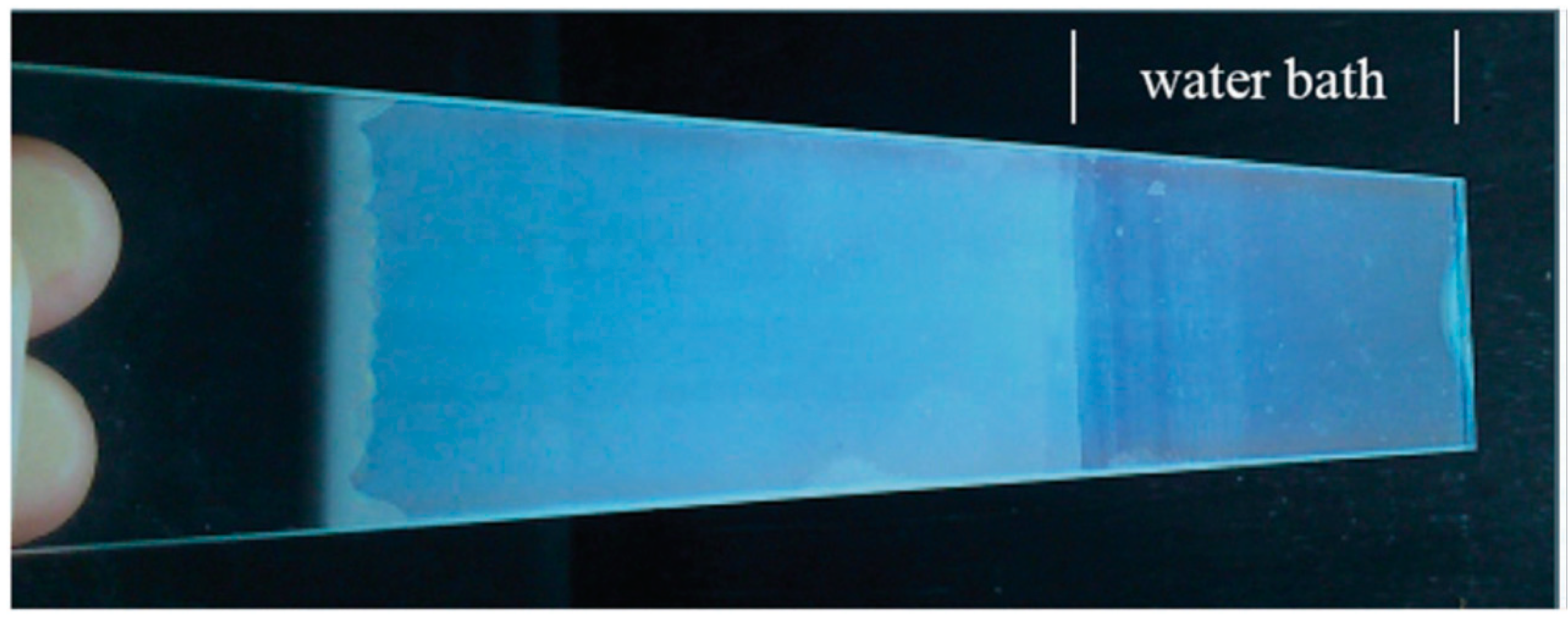
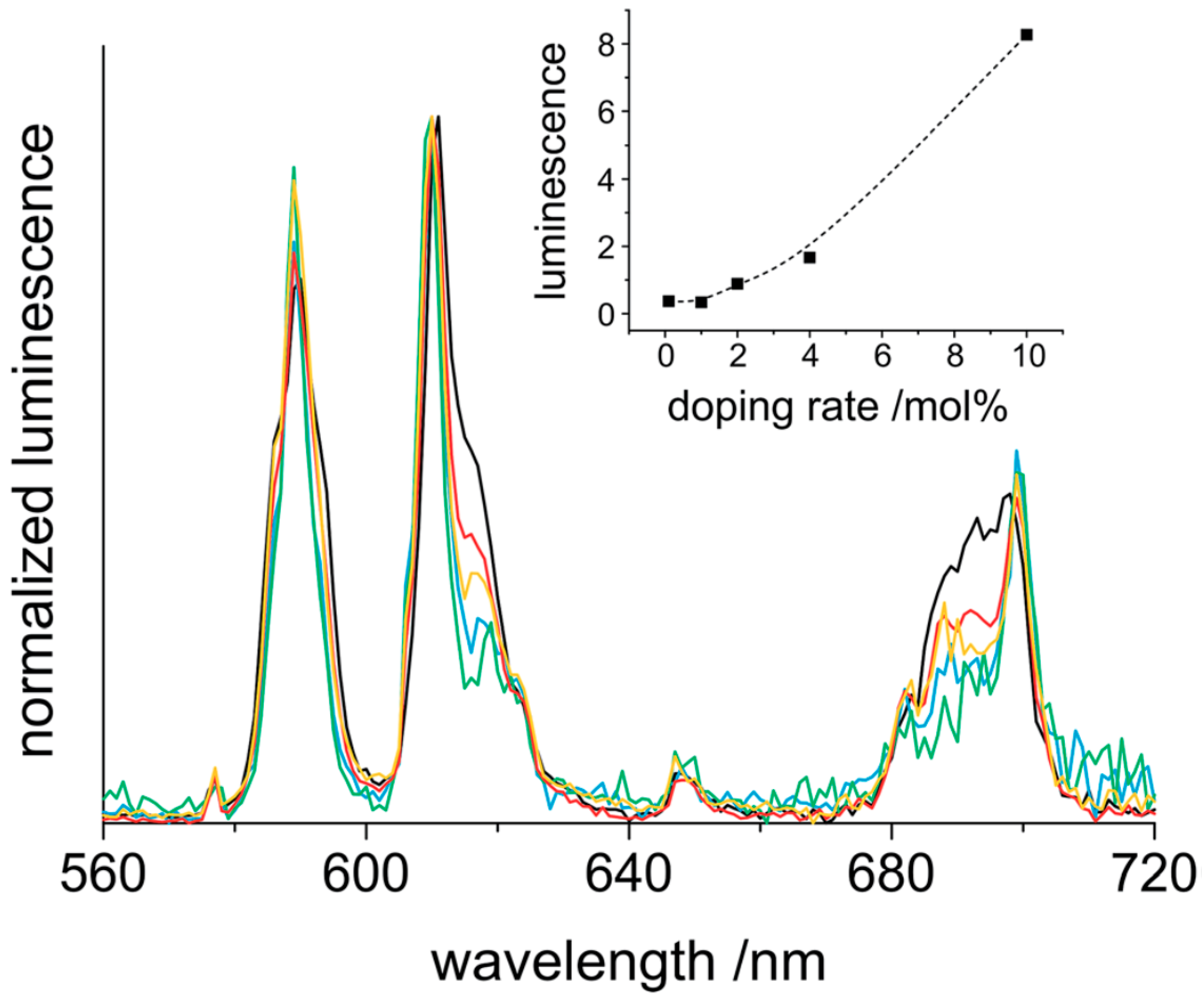
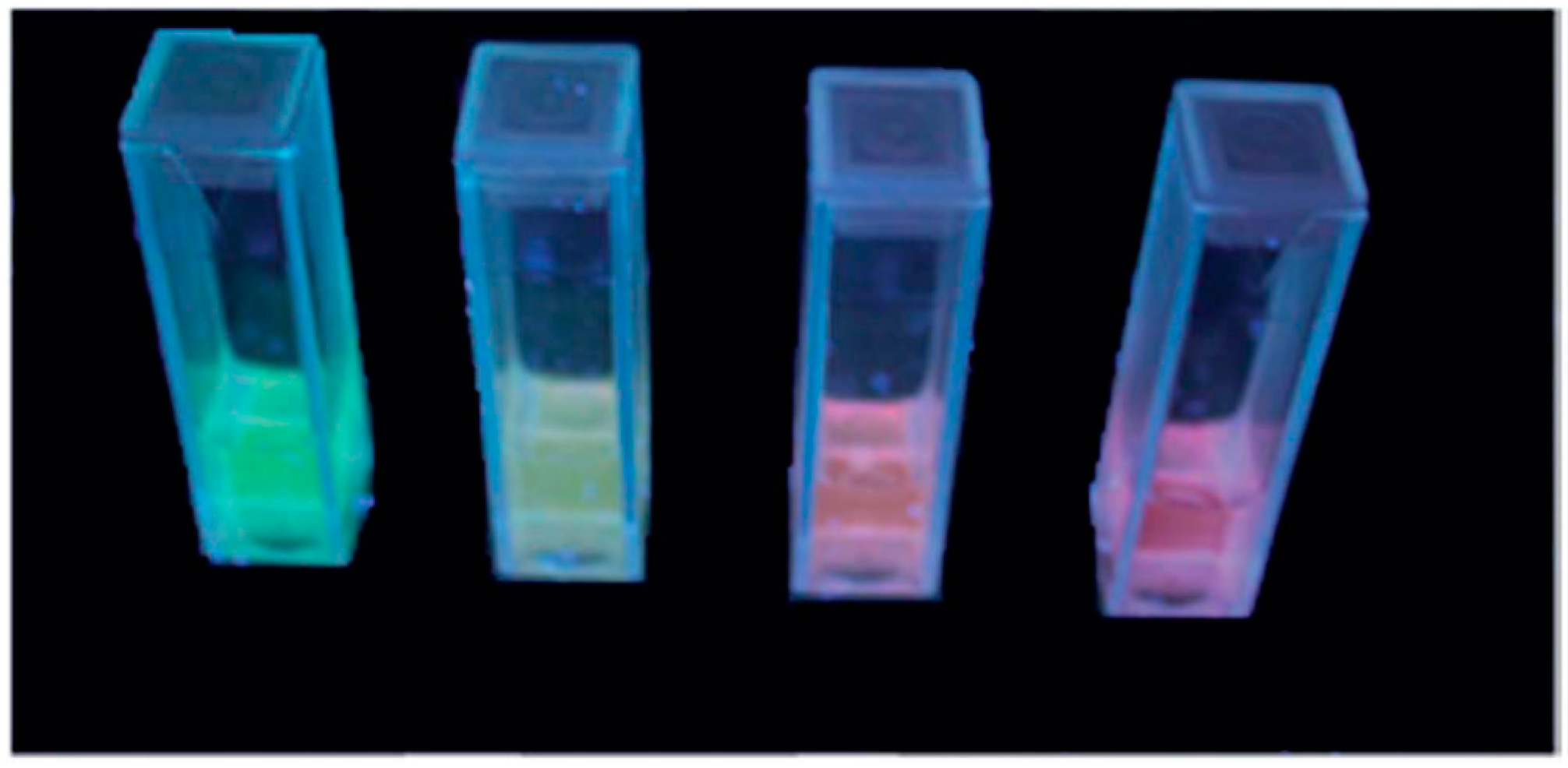
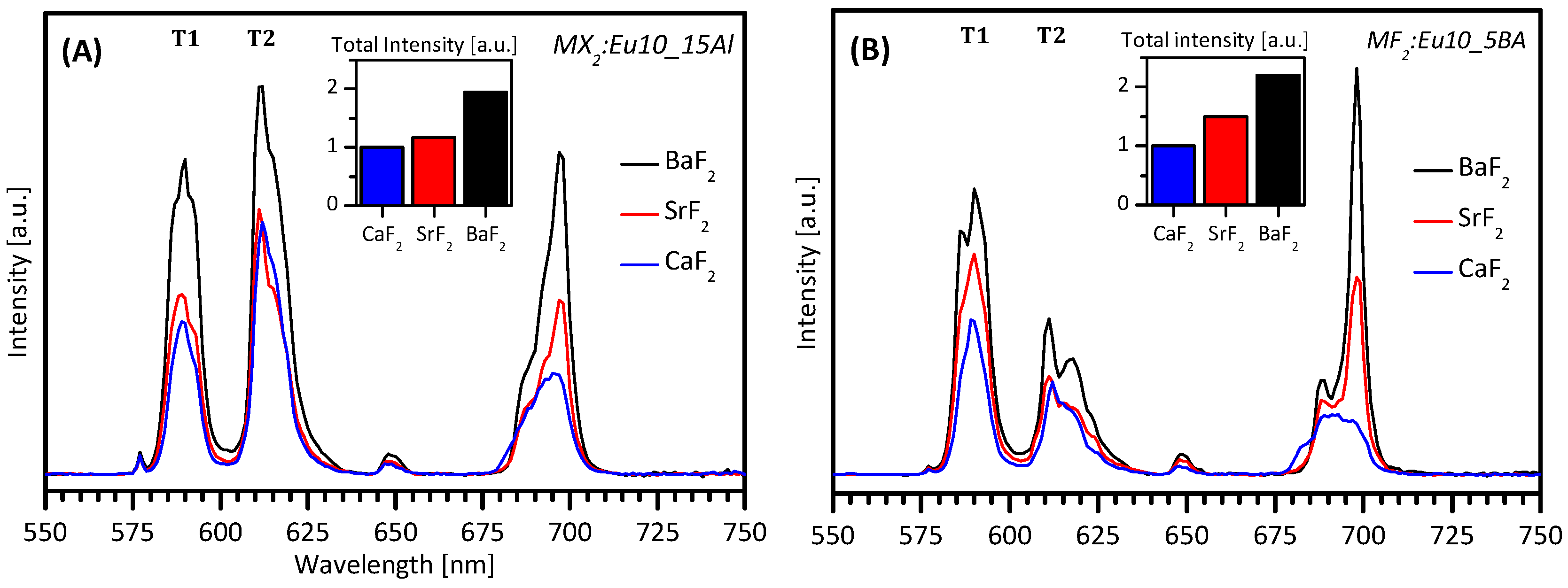
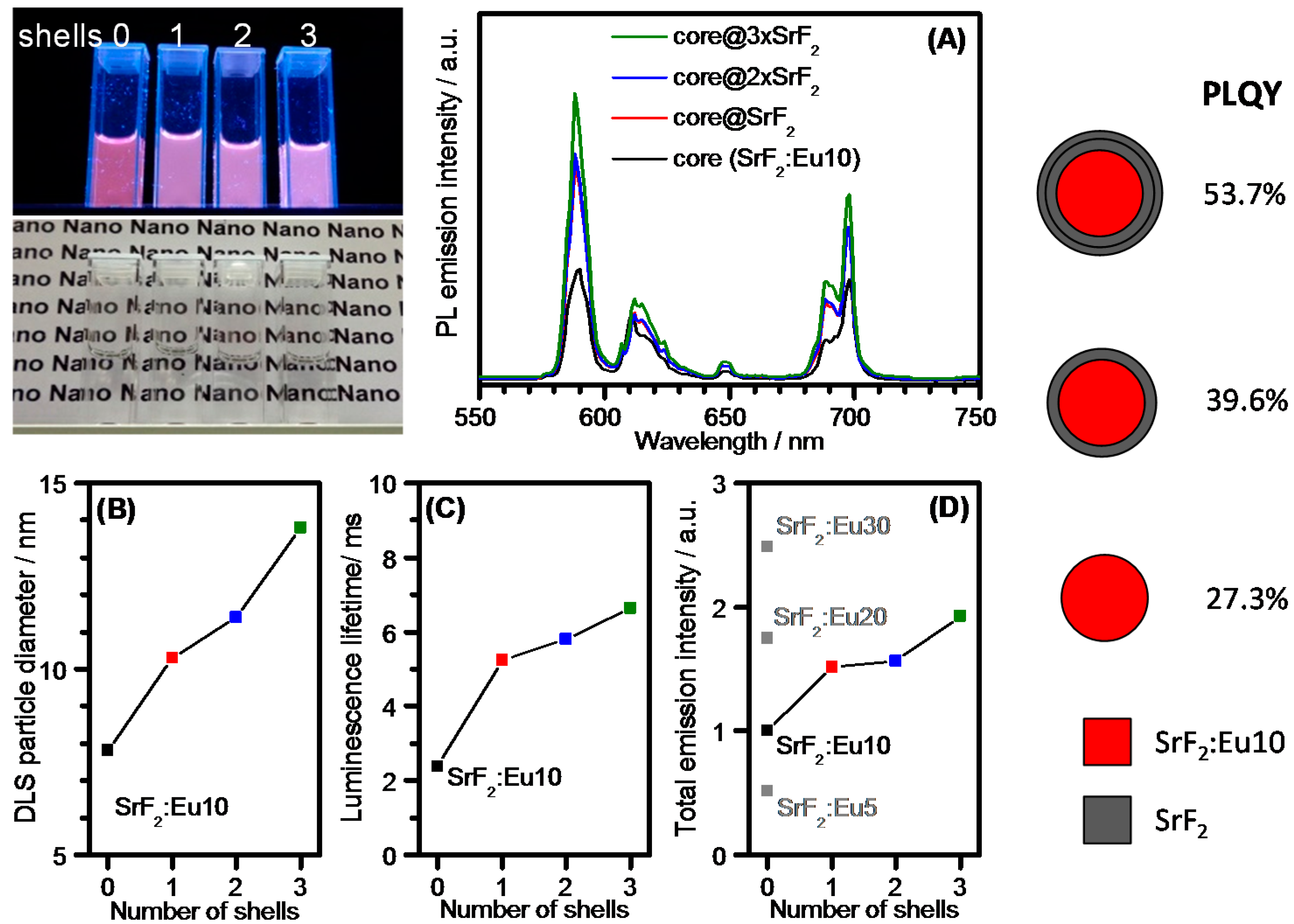
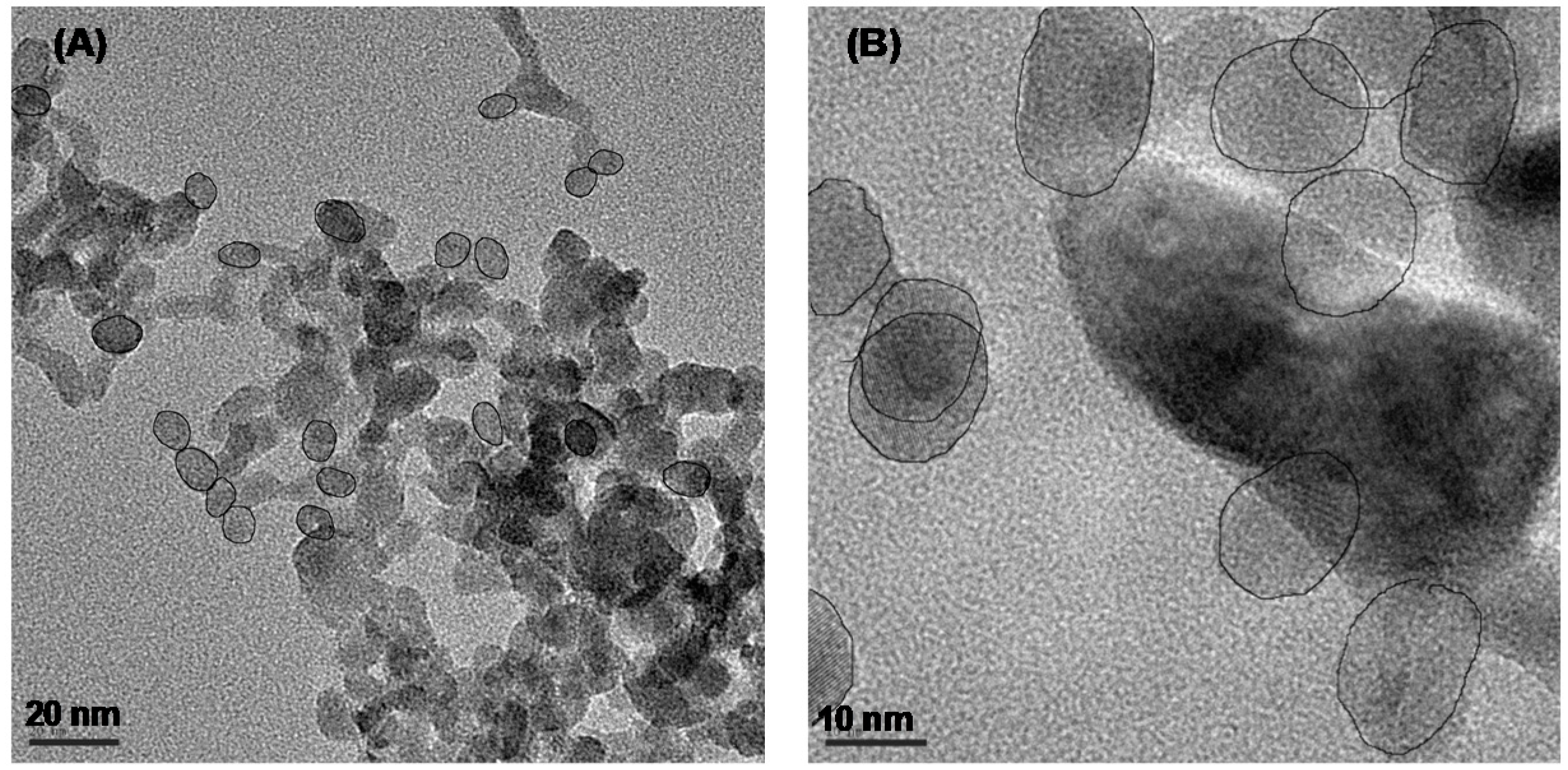

| Formula | Structure | FP (°C) | Opt. Range | n | Solubility (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgF2 | Rutile | 1256 | 120 nm–8 µm | 1.38 | 0.13 |
| CaF2 | Cubic | 1423 | 130 nm–8 µm | 1.40 | 0.016 |
| SrF2 | Cubic | 1477 | 130 nm–11 µm | 1.44 | 0.11 |
| BaF2 | Cubic | 1368 | 150 nm–12 µm | 1.48 | 1.60 |
| SiO2 | Trigonal | 1713 | 150 nm–4 µm 50 µm–1000 µm | 1.54 | 0.01 Quartz 0.12 am. SiO2 |
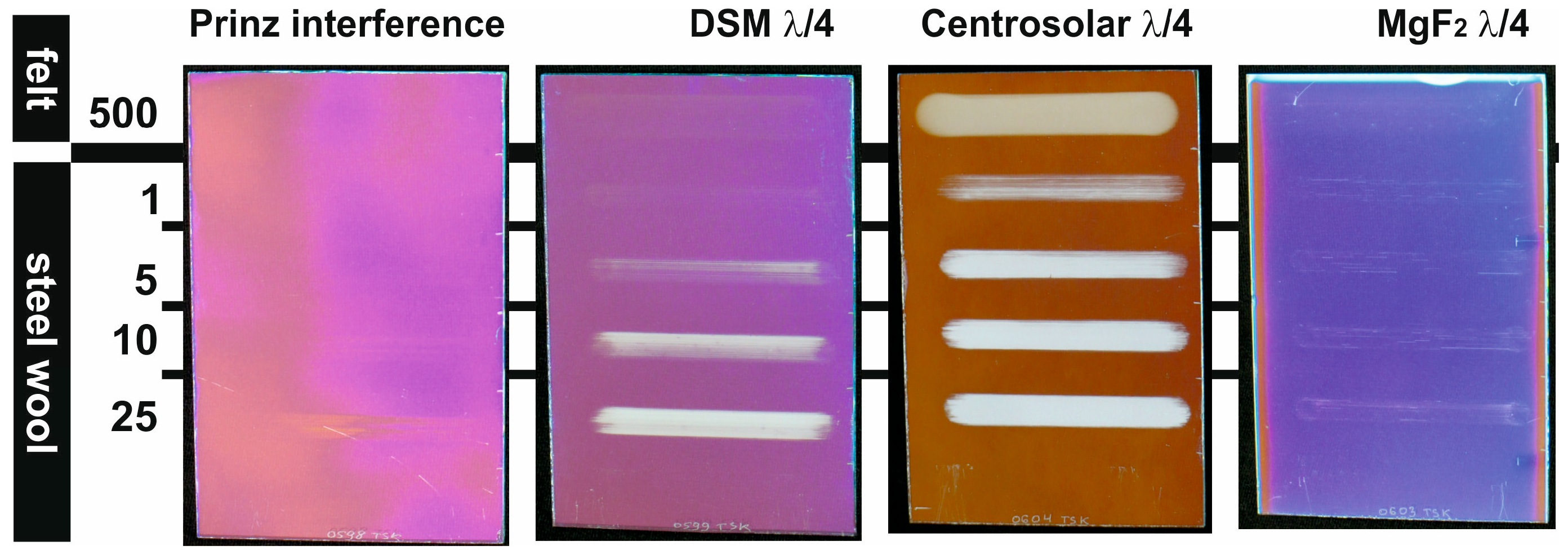
| Film System | Film Thickness (nm) | Open Porosity (%) | Max. Pore Radius (nm) | Peak Transmittance (%) | at λ (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prinz interference | 297 | <6 | n.a. | 98.6 | 515 |
| DSM λ/4 | 113 | 33.2 | (19) | 97.5 | 545 |
| Centrosolar λ/4 | 105 | 50.2 | 5.9 | 99.7 | 515 |
| MgF2 λ/4 | 115 | 27.3 | 8.7 | 98.5 | 540 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scheurell, K.; Kemnitz, E. Fluorolytic Sol–Gel Synthesis of Nanometal Fluorides: Accessing New Materials for Optical Applications. Inorganics 2018, 6, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6040128
Scheurell K, Kemnitz E. Fluorolytic Sol–Gel Synthesis of Nanometal Fluorides: Accessing New Materials for Optical Applications. Inorganics. 2018; 6(4):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6040128
Chicago/Turabian StyleScheurell, Kerstin, and Erhard Kemnitz. 2018. "Fluorolytic Sol–Gel Synthesis of Nanometal Fluorides: Accessing New Materials for Optical Applications" Inorganics 6, no. 4: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6040128
APA StyleScheurell, K., & Kemnitz, E. (2018). Fluorolytic Sol–Gel Synthesis of Nanometal Fluorides: Accessing New Materials for Optical Applications. Inorganics, 6(4), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6040128





