Abstract
This study presents the synthesis, characterization, and application of magnetic magnetite–zirconium dioxide (Fe3O4–ZrO2) nanoparticles as an efficient nanoadsorbent for fluoride removal from water. The nanoparticles were synthesized using a wet chemical co-precipitation method with Fe/Zr molar ratios of 1:1, 1:2, and 1:4, and characterized using Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). FTIR analysis confirmed the presence of Fe3O4 and ZrO2 functional groups, while XRD showed that increased Zr content led to a dominant amorphous phase. SEM and EDS analyses revealed quasi-spherical and elongated morphologies with uniform elemental distribution, maintaining the designed Fe/Zr ratios. Preliminary adsorption tests identified the Fe/Zr = 1:1 (M1) nanoadsorbent as the most effective due to its high surface homogeneity and optimal fluoride-binding characteristics. Adsorption experiments demonstrated that the material achieved a maximum fluoride adsorption capacity of 70.4 mg/g at pH 3, with the adsorption process best fitting the Temkin isotherm model (R2 = 0.987), suggesting strong adsorbate–adsorbent interactions. pH-dependent studies confirmed that adsorption efficiency decreased at higher pH values due to electrostatic repulsion and competition with hydroxyl ions. Competitive ion experiments revealed that common anions such as nitrate, chloride, and sulfate had negligible effects on fluoride adsorption, whereas bicarbonate, carbonate, and phosphate reduced removal efficiency due to their strong interactions with active adsorption sites. The Fe3O4–ZrO2 nanoadsorbent exhibited excellent magnetic properties, facilitating rapid and efficient separation using an external magnetic field, making it a promising candidate for practical water treatment applications.
1. Introduction
The contamination of drinking water with fluoride from both natural sources and human activities is a significant global concern [1]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the maximum permissible fluoride concentration in drinking water is 1.5 mg/L [2,3,4]. Excess fluoride intake can lead to dental and skeletal fluorosis, posing serious health risks [5,6]. Various methods have been employed to remove fluoride from water, including precipitation, ion exchange, and adsorption [7,8,9]. Among these, adsorption stands out as a highly effective approach, capable of reducing fluoride levels below 1 mg/L [10,11]. The use of nanosized adsorbents is particularly promising due to their high surface area, which enhances adsorption efficiency [12,13].
Metal oxides such as titanium dioxide (TiO2), aluminum oxide (Al2O3), and zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) have demonstrated excellent selectivity for anion removal in aqueous solutions [14,15,16]. Among them, zirconium-based materials have attracted significant attention due to their strong affinity for fluoride ions [17,18,19]. However, challenges remain in using nanomaterials for water treatment, particularly in conventional packed-bed reactors and stirred tank reactors, where their small size complicates solid–liquid separation [20].
Magnetic adsorbents offer a practical solution to these limitations, combining high adsorption efficiency with easy recovery using an external magnetic field [21]. Magnetite (Fe3O4) has been widely employed for removing contaminants such as heavy metals [22], nanoplastics [23], dyes [24], pharmaceuticals [25], and fluoride [26]. Among the various synthesis methods for magnetic iron oxides, co-precipitation is preferred for its simplicity, scalability, and ability to produce high-purity Fe3O4 nanoparticles. This method involves the simultaneous precipitation of Fe2+ and Fe3+ salts in an alkaline medium, typically under nitrogen or inert atmospheres to prevent oxidation [27]. Optimizing parameters such as pH, temperature, ionic strength, and reaction time significantly influences particle size, crystallinity, and magnetic properties [28]. Additionally, co-precipitation has been successfully used to synthesize Fe3O4 composites with other oxides (e.g., ZrO2, TiO2, SiO2), enhancing their stability and adsorption performance [29].
Magnetic zirconium–iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4@ZrO2) synthesized via co-precipitation have demonstrated promising adsorption capabilities for various contaminants. Studies have shown that Fe/Zr molar ratios influence surface area and adsorption capacity, with lower Fe/Zr ratios improving phosphate removal [30]. Similarly, Alam et al. [31] synthesized Fe3O4@mZrO2 nanoparticles doped with rare-earth elements, achieving enhanced arsenic adsorption. Recently, Riahi et al. [20] reported the modification of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with zirconium oxide for fluoride removal.
In this study, we present a simple and efficient method for fluoride removal using magnetic Fe3O4–ZrO2 nanoparticles. First, we synthesized and characterized the nanoparticles using the co-precipitation method. Then, we systematically investigated key factors affecting fluoride adsorption, including the Fe/Zr ratio, solution pH, contact time, initial fluoride concentration, and the presence of competing anions. Our results demonstrate that Fe3O4–ZrO2 nanoparticles exhibit a high fluoride adsorption capacity, fast kinetics, and strong selectivity in complex water matrices. Furthermore, the nanoparticles can be efficiently separated using a magnetic field, enabling their potential application in practical water treatment systems.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Magnetic Fe3O4–ZrO2 Adsorbents
2.1.1. FTIR Spectra Analysis
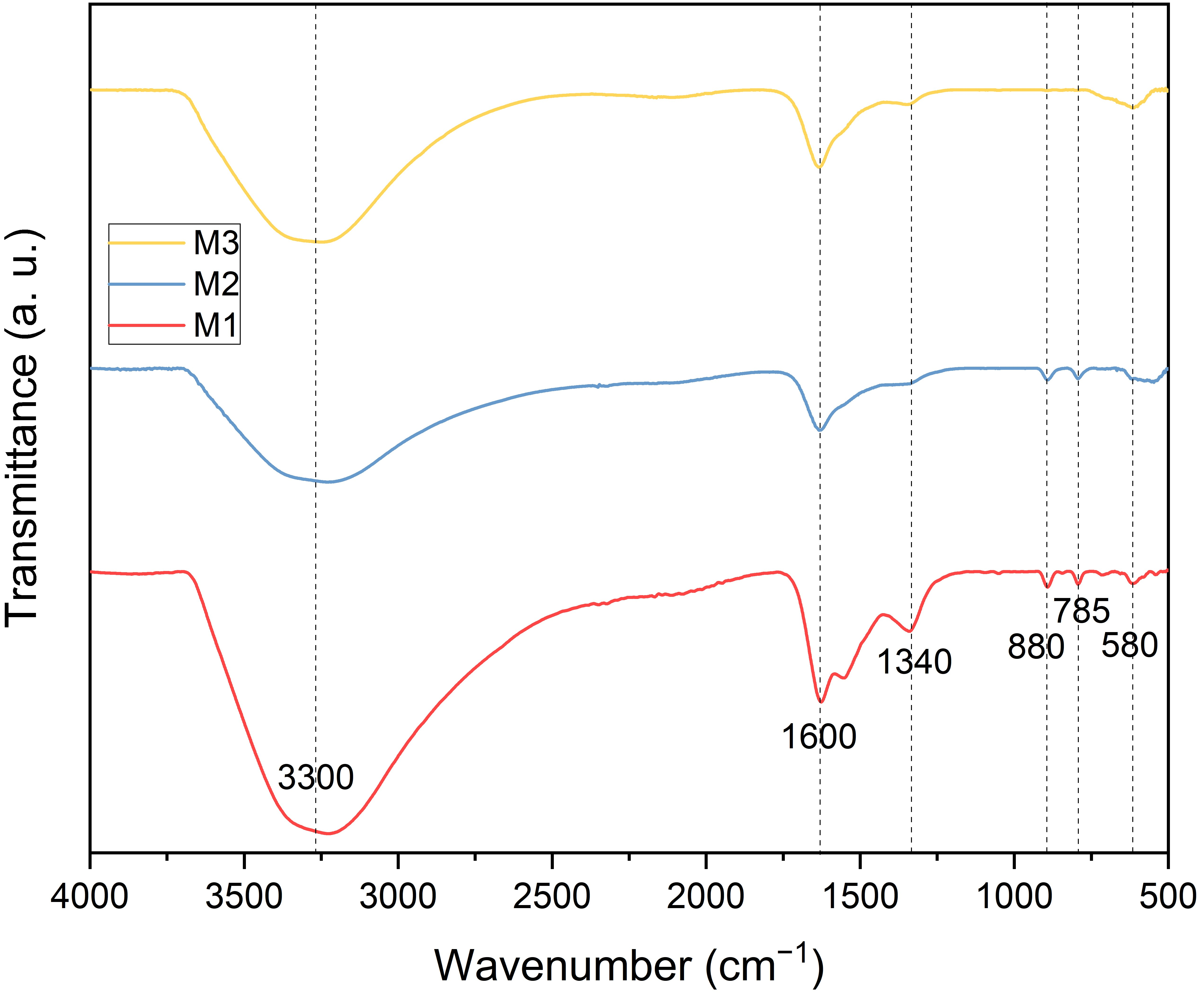
The FTIR spectra of the synthesized magnetic adsorbents are presented in Figure 1. All adsorbents exhibited similar absorption bands, though with varying intensities depending on the Fe/Zr ratios. The signal at 3300 cm−1 corresponds to the stretching vibration of hydroxyl (-OH) groups from surface-bound water [32], which appears with comparable intensity in all spectra. The band at 880 cm−1, associated with the bending vibrational mode of iron hydroxide [33], is present in the spectra of M1 and M2 but absent in M3. This absence is attributed to the stabilizing effect between the metal oxides, which promotes the crystalline phase of Fe3O4 as Zr content increases, thereby preventing the formation of iron hydroxide byproducts [34]. Similarly, the characteristic Fe3O4 fingerprint at 580 cm−1, corresponding to the stretching vibrational mode of Fe3O4 [35], intensifies with increasing Zr content. Peaks at 1340 cm−1 and 1600 cm−1 are associated with the stretching and bending vibrational modes of zirconium–oxygen and zirconium hydroxide (Zr–OH), respectively [36].
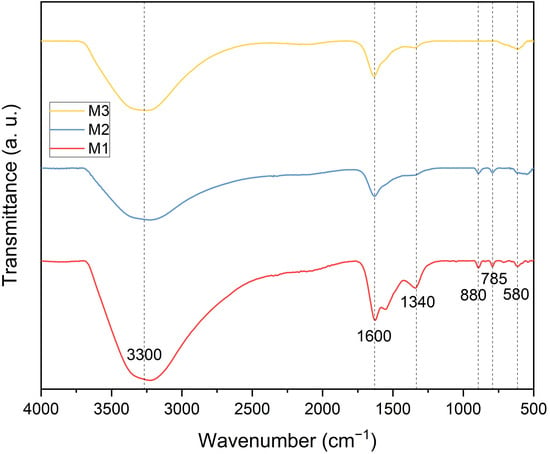
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of the Fe3O4–ZrO2 adsorbents: M1, M2, and M3. Dotted vertical lines indicate the peaks in the three spectra.
2.1.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
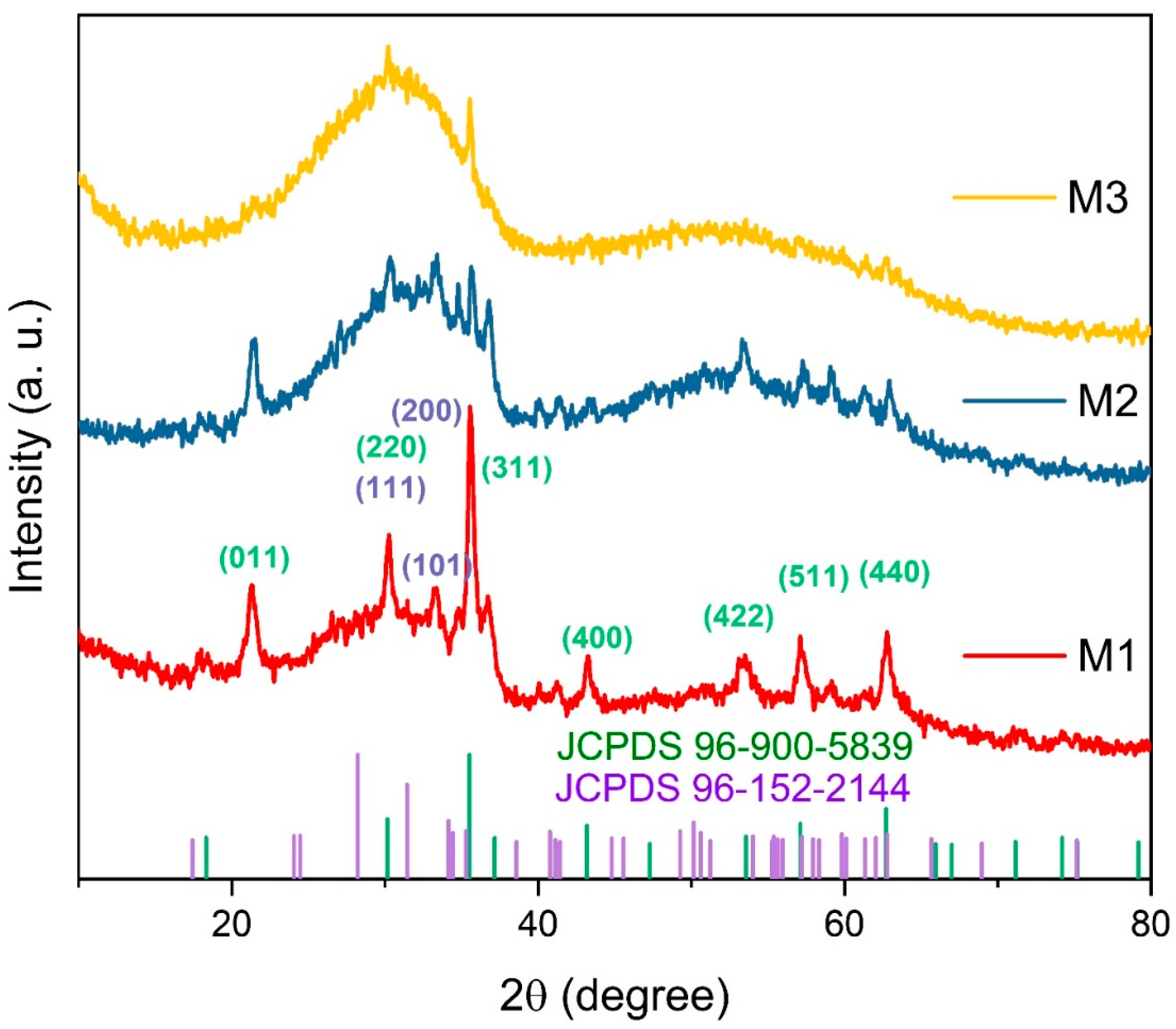
Figure 2 presents the XRD patterns of the magnetic adsorbents. The diffraction peaks observed for M1 at 2θ values of 30.2°, 33.3°, and 35.5° correspond to the (111), (101), and (200) planes of zirconium oxide, respectively (JCPDS 96-152-2144) [20,37,38]. Peaks at 30.2°, 35.5°, 43.2°, 53.4°, 57.2°, and 62.7° were assigned to the (220), (311), (400), (422), (511), and (440) planes of Fe3O4 (JCPDS 96-900-5839) [20,30,39,40]. A peak at 21.1° corresponds to iron hydroxide, with no impurity peaks detected, confirming the spinel structure of Fe3O4 [20].
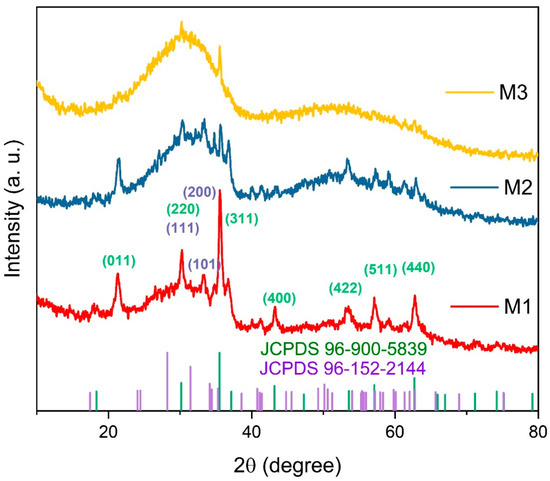
Figure 2.
Typical X-ray diffraction patterns of the magnetic adsorbents: M1, M2, and M3, and JCPDS cards for Fe3O4 (purple) and ZrO2 (green).
The XRD patterns reveal a progressive decrease in Fe3O4 diffraction peak intensity as ZrO2 content increases. With increasing zirconium oxide, the amorphous phase dominates in M2 and M3 due to the lack of calcination [41], with only the (200) and (111) peaks of ZrO2 remaining detectable. This phenomenon is attributed to the predominant amorphous phase of ZrO2, which suppresses the diffraction signals of the crystalline Fe3O4 phase. Additionally, increased dispersion of Fe3O4 within the ZrO2 matrix results in a dilution effect, further diminishing peak intensity [31]. These observations suggest that higher ZrO2 content induces structural distortions in Fe3O4, reducing its crystallinity and promoting a more homogeneous composite material [42].
2.1.3. Morphology and Elemental Composition (SEM and EDS)
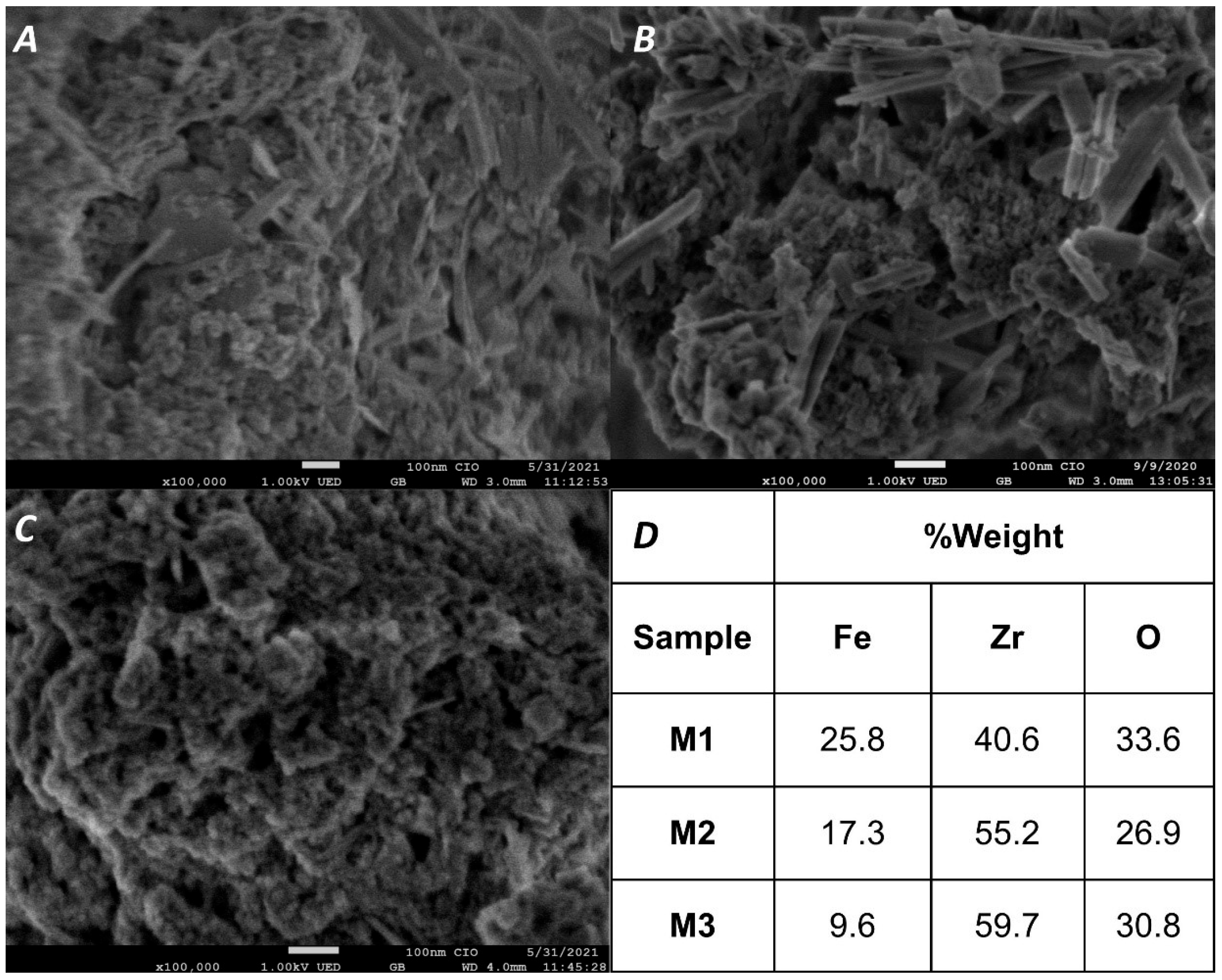
The morphology and elemental composition of M1, M2, and M3 were examined using SEM and EDS (Figure 3). The magnetic adsorbents consisted of elongated and quasi-spherical nanoparticles, structures previously reported in the literature [43]. As the zirconium oxide content increased, the proportion of elongated and quasi-spherical nanoparticles increased, while rectangular structures almost disappeared in M3. The decrease in elongated structures with increasing Zr content suggests that these initial structures were associated with iron oxides. The surface of the composites appeared relatively rough, composed of numerous aggregated nanoparticles, likely due to oxidation during SEM preparation.
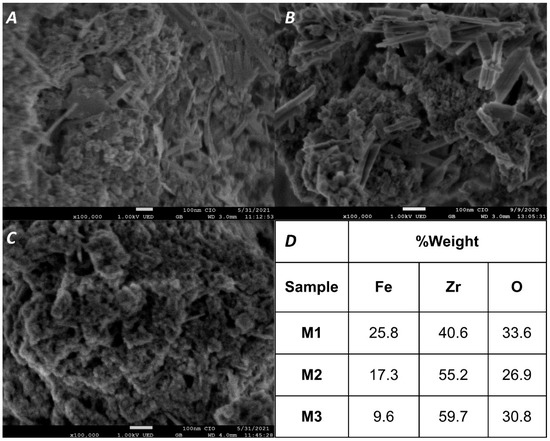
Figure 3.
SEM images of M1, M2, and M3 (panels (A), (B), and (C), respectively) and results of the elemental analysis with EDS (D).
EDS analysis (Figure 3D, Supplementary Information Figures S1–S3) confirmed the presence of Fe, Zr, and O in the synthesized material. The empirical formulas obtained—FeZrO4·5, Fe2Zr4O11, and FeZr4O11 for M1, M2, and M3, respectively—demonstrate that the Fe/Zr ratios used during synthesis were maintained in the final products, validating the proposed compositions.
2.2. Fluoride Adsorption Studies
2.2.1. Effect of pH on Fluoride Removal
Preliminary adsorption tests, where the adsorbents interacted with water samples for 24 h, showed that all three materials (M1, M2, and M3) captured nearly the same amount of fluoride: 99.0, 99.4, and 99.5%, respectively. Since zirconium was the most expensive reagent, we excluded M2 and M3 from further analysis, as their higher zirconia content did not provide a significant advantage in fluoride adsorption. Additionally, SEM images indicated that M1 exhibited the most uniform size distribution among the three materials; therefore, subsequent tests were conducted exclusively with the M1 adsorbent.
Fluoride adsorption onto the synthesized material occurs at the adsorbent’s surface, where ion exchange and electrostatic interactions take place. The adsorption capacity for F− ions is significantly influenced by pH, as it dictates the surface charge distribution of the material [44].
The relationship between pH and the surface zeta potential of Fe3O4–ZrO2 composites was studied by Zhang et al. [30]. The point of zero charge (PZC) values of the composites were in the pH range of 8–9. Superparamagnetic zirconia material had a PZC around pH 5.8 [45]. The PZC of Fe3O4 nanoparticles was about pH 7.38 [46]. According to these results, it is assumed that the M1 adsorbent had a similar value of PZC. When the solution pH is below this point, adsorbents have a positive charge. The positive surface charge promotes the electrostatic attraction of fluoride anions.
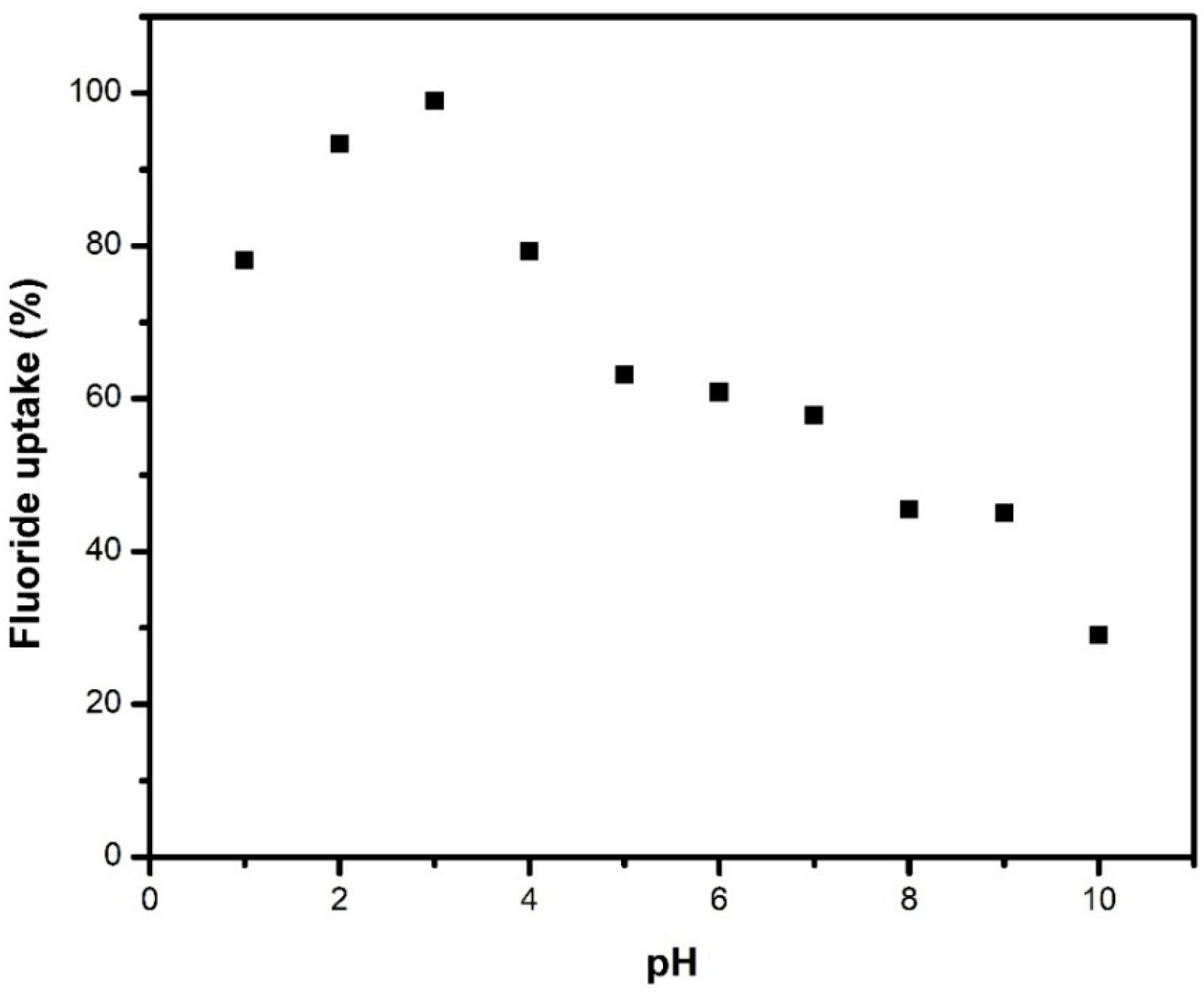
As illustrated in Figure 4, maximum adsorption was observed at pH 3, corresponding to a positively charged surface that facilitates efficient interaction with negatively charged fluoride ions. At higher pH levels, surface deprotonation results in a negatively charged surface, leading to electrostatic repulsion between the adsorbent and fluoride ions, as well as competition from hydroxyl ions for available adsorption sites. However, fluoride adsorption remained over 60% across a range of pH values from 1 to 7, indicating that the material retains its adsorptive properties under different conditions. Additionally, pH adjustment to acidic conditions is a simple and cost-effective strategy widely employed in water treatment processes, as it can be achieved using common acidifying agents such as sulfuric or hydrochloric acid without significantly increasing operational complexity [47]. Moreover, the natural fluoride contamination and industrial processes like metal smelting contribute vast amounts of untreated fluoridated wastewater [48,49]. Metallurgical wastewater often exhibits acidic pH due to the use of acids in various metal processing steps. Based on these considerations, a pH of 3 was selected for subsequent experiments.
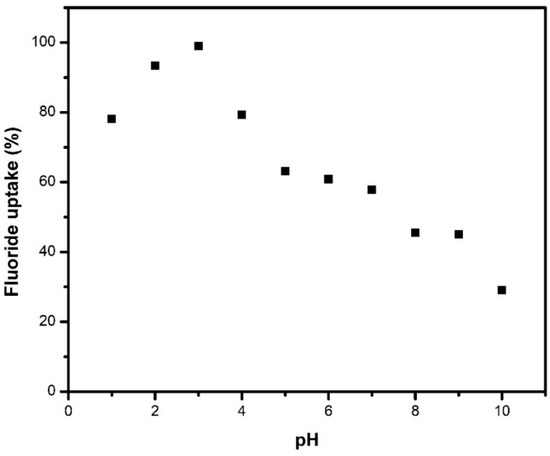
Figure 4.
Effect of pH on the removal of fluoride by M1 for an initial fluoride concentration of 50 mg/L, an adsorbent dose of 1 mg/mL at 25 °C, and a contact time of 24 h.
2.2.2. Kinetics Analysis
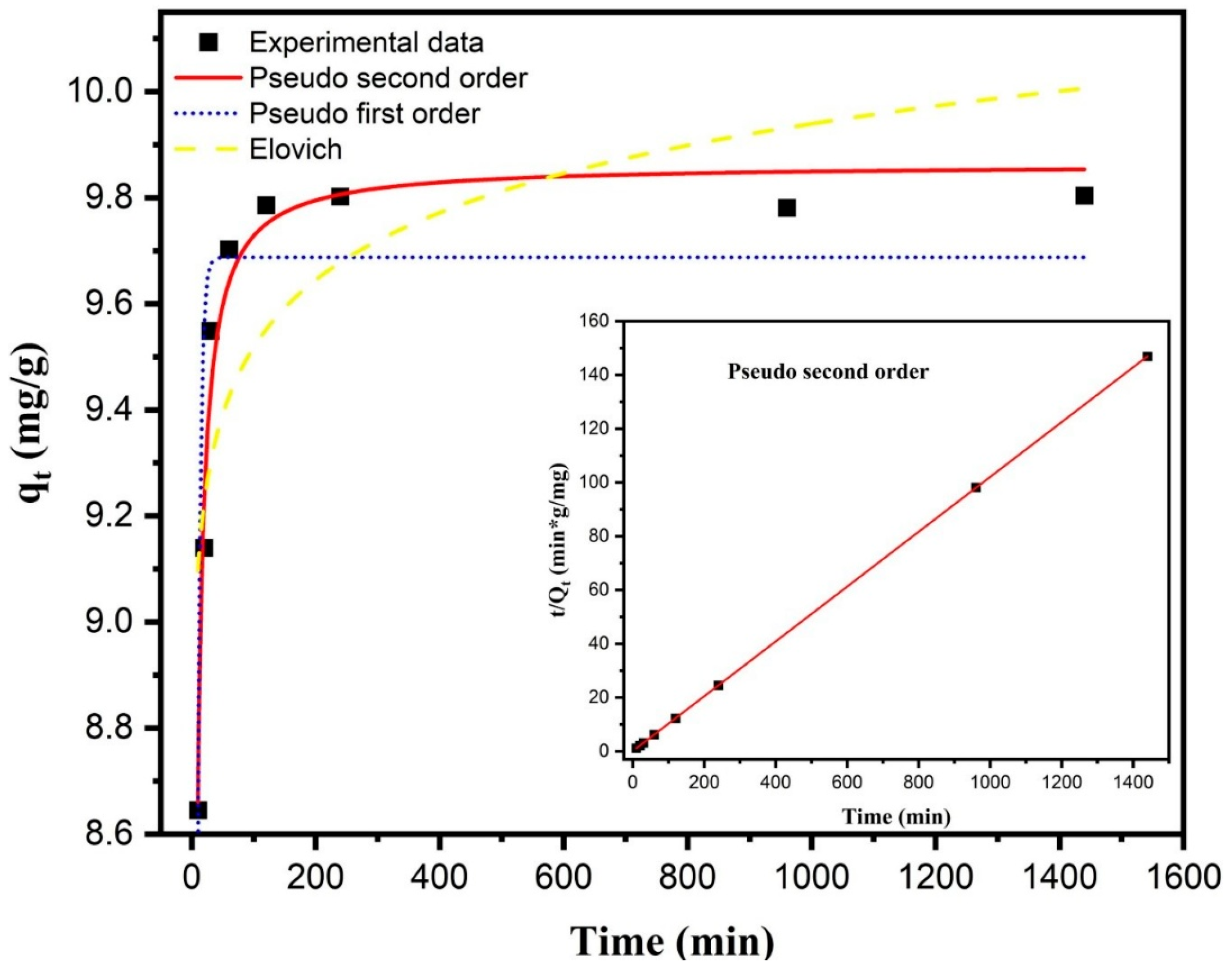
The adsorption kinetics of fluoride onto the M1 composite was evaluated using three kinetic models: pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order (both linear and nonlinear forms), and the Elovich model. Experiments were carried out using an initial fluoride concentration of 10 mg/L, with 50 mg of adsorbent dispersed in 50 mL of deionized water at pH 3 and ambient temperature. In these graphs, it can be observed that more than 90% of the fluoride adsorbed at equilibrium (qe, mg/g) occurred within the first 30 min from the start of the reaction. The results indicate that the equilibrium time (te) for fluoride adsorption from a 10.0 mg/L solution was approximately 2 h (Figure 5).
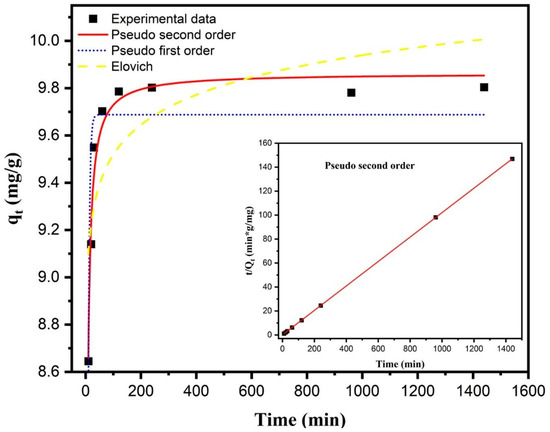
Figure 5.
Nonlinear kinetic fitting of fluoride adsorption onto composite M1 using pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, and Elovich models. The experiments were conducted with an initial fluoride concentration of 10 mg/L, 50 mg of adsorbent in 50 mL of fluoride solution, at pH 3 and room temperature.
The best fit to the experimental data was obtained using the nonlinear pseudo-second-order model [50], expressed as follows:
where qt (mg/g) is the amount of fluoride adsorbed at time t (min), qe (mg/g) is the adsorption capacity at equilibrium, and k2 (g·mg−1·min−1) is the pseudo-second-order rate constant. This model produced the highest correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.9724) and the lowest reduced chi-square value (0.00572) (Table 1). The estimated parameters were qe = 9.86 mg/g and k2 = 0.07307 g/(mg·min).
qt = (k2·qe2·t)/(1 + k2·qe·t)

Table 1.
Kinetic models, equations, and estimated parameters for fluoride adsorption onto composite M1.
In contrast, the pseudo-first-order model [51] is defined by the equation:
where qt (mg/g) is the amount of fluoride adsorbed at time t (min), qe (mg/g) is the adsorption capacity at equilibrium, and k1 (min−1) is the pseudo-first-order rate constant. This model exhibited a weaker correlation with the experimental data (R2 = 0.8063) (Table 1), indicating that it does not adequately describe the fluoride adsorption mechanism on M1.
qt = qe·(1 − e^(−k1·t))
Finally, the Elovich model [52] is given by the following:
where α (mg·g−1·min−1) is the initial adsorption rate, and β (g·mg−1) is related to surface coverage and activation energy. The Elovich model showed the poorest fit (R2 = 0.6095) (Table 1), confirming that the pseudo-second-order model best represents the kinetic behavior of fluoride adsorption on M1.
qt = (1/β)·ln(1 + α·β·t)
These results support a mechanism dominated by chemisorption, likely involving electron sharing or exchange between fluoride ions and active sites on the composite surface [53].
2.2.3. Adsorption Isotherm Analysis
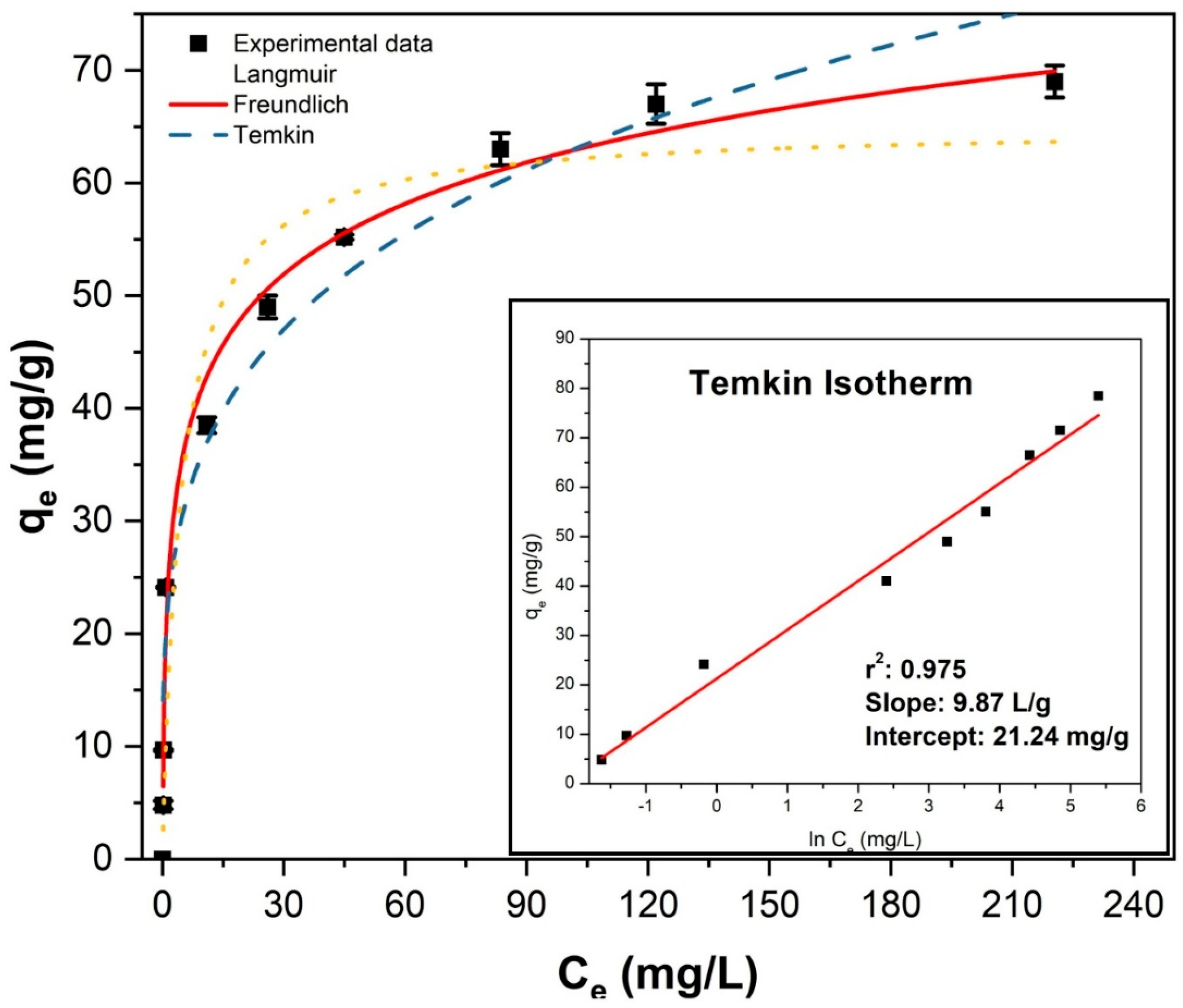
Experimental adsorption data and the best-fit linear equation are shown in Figure 6. Experiments were conducted with a rotating mixer at 40 rpm for 2 h, followed by magnetic separation of the adsorbents and measurement of fluoride concentrations using an ion-selective electrode. Tests were performed in duplicate.
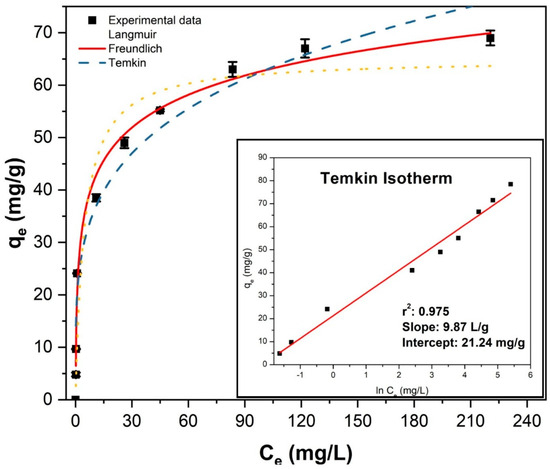
Figure 6.
Nonlinear fitting of adsorption isotherms for fluoride removal and the linear Temkin model fitting (inset).
The Freundlich, Langmuir, and Temkin isotherm models were applied to analyze fluoride adsorption equilibrium, with results compared in Table 2. The nonlinear model fitting and the inset in Figure 6 indicate that the Temkin model provided the best fit, as evidenced by superior regression coefficients (R2) and chi-square (χ2) values. The maximum adsorption capacity of Fe3O4–ZrO2 nanoparticles, determined from the Langmuir model, was 70.4 mg/g, closely matching the experimentally measured capacity of 69.1 mg/g.

Table 2.
Freundlich, Langmuir, and Temkin isotherms for the adsorption of fluoride ions onto the Fe3O4–ZrO2 composites.
Langmuir adsorption parameters were obtained using both linear and nonlinear equations, where KL (L/g) represents the Langmuir constant and Q0max (mg/g) signifies the maximum monolayer coverage capacity. The Freundlich model describes adsorption intensity (n) and the isotherm constant (KF). For the Temkin model, the adsorption parameters AT (8.60–10.42 L/g) and bT (251.1–274.4 J/mol) correspond to equilibrium binding and adsorption energy constants, respectively [54]. The positive B value (9.87) suggests an exothermic adsorption process [55].
The Gibbs free energy can also be calculated from the thermodynamic equilibrium constant, K0, which is defined as follows:
where as is the activity of the adsorbed fluoride ion, ae is the activity of the fluoride ion in the equilibrium solution, νs is the activity coefficient of the adsorbed fluoride, and νe is the activity coefficient of fluoride in the equilibrium solution. The above equation can be rewritten as follows:
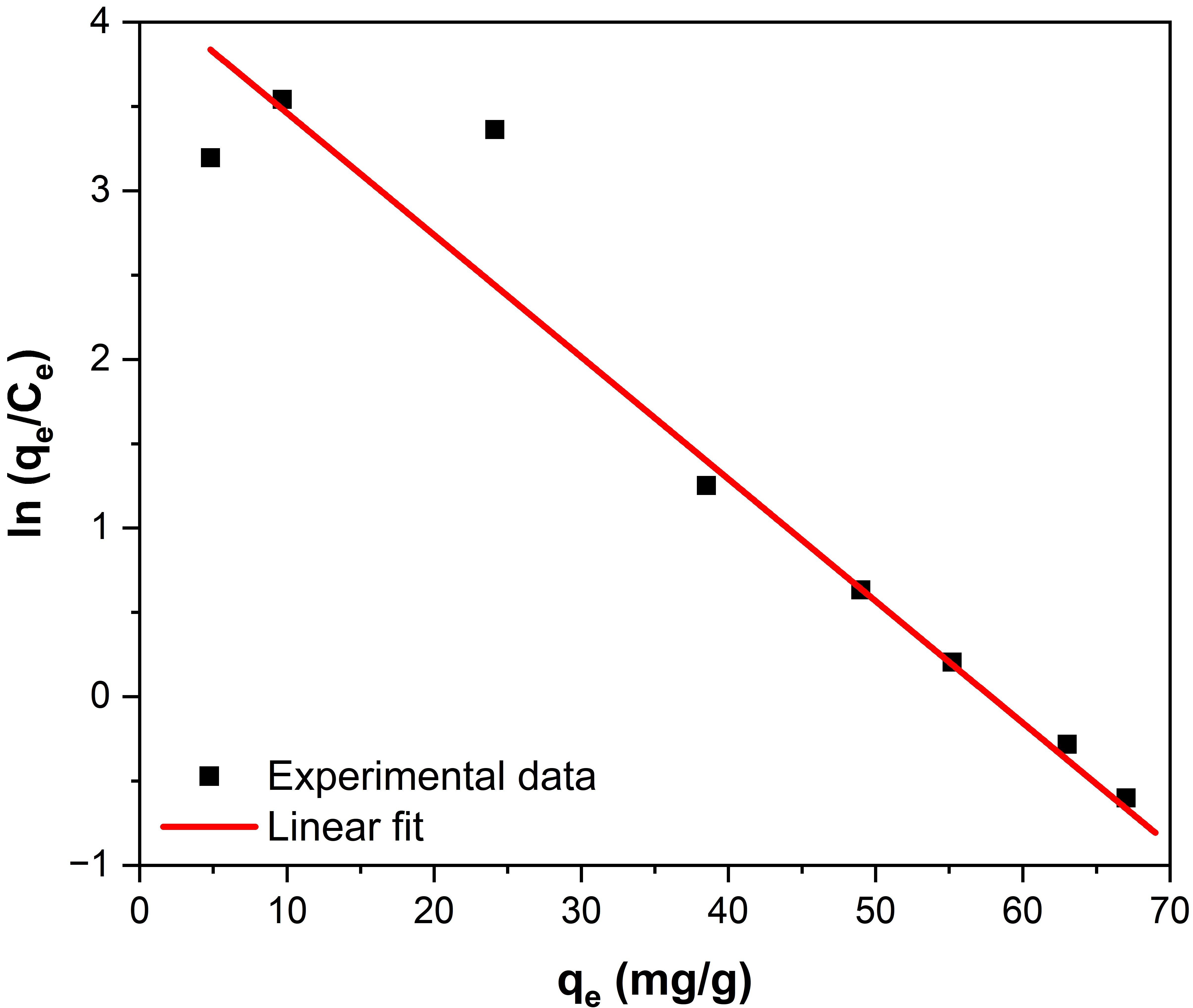
K0 can be obtained by plotting ln (qe/Ce) vs. qe (Figure 7) and extrapolating to zero [56]. Its intersection gives the values of K0. In this analysis, the value of K0 could be calculated from the data obtained from the adsorption isotherms at room temperature.
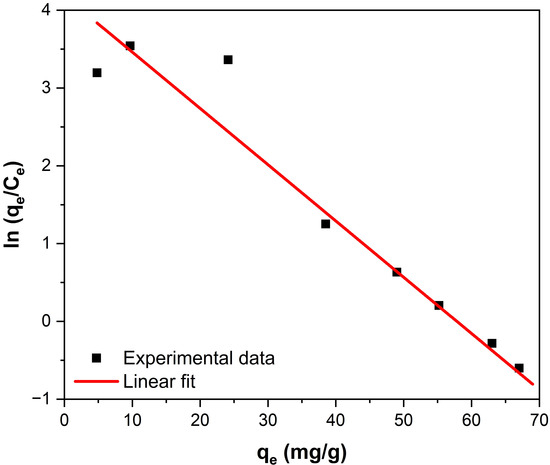
Figure 7.
Plot of ln(qe/Ce) vs. qe for fluoride adsorption on Fe3O4–ZrO2.
The standard Gibbs free energy changes of adsorption (ΔG0) can be calculated according to the following:
The obtained values are shown in Table 3. The standard Gibbs free energy change (ΔG0) in the F−–Fe3O4–ZrO2 system is −10.37 kJ/mol, indicating that the adsorption process is spontaneous.

Table 3.
Equilibrium constant K0 and Gibbs free energy of fluoride ion adsorption on Fe3O4–ZrO2 at room temperature and C0 = 5−300 mg/L.
The Dubinin–Radushkevich (D-R) equation was developed to account for the effect of the porous structure of an adsorbent [57]. It is expressed as follows:
The linear form of the Dubinin–Radushkevich equation is as follows:
where qe (mol/g) is the amount of fluoride adsorbed at equilibrium, Ce (mol/L) is the equilibrium fluoride concentration, qDR (mol/g) is the theoretical adsorption capacity, KDR (mol2/kJ2) is a constant related to the sorption energy, ε is the Polanyi potential, R is the universal gas constant (8.314 × 10−3 kJ/mol·K), and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
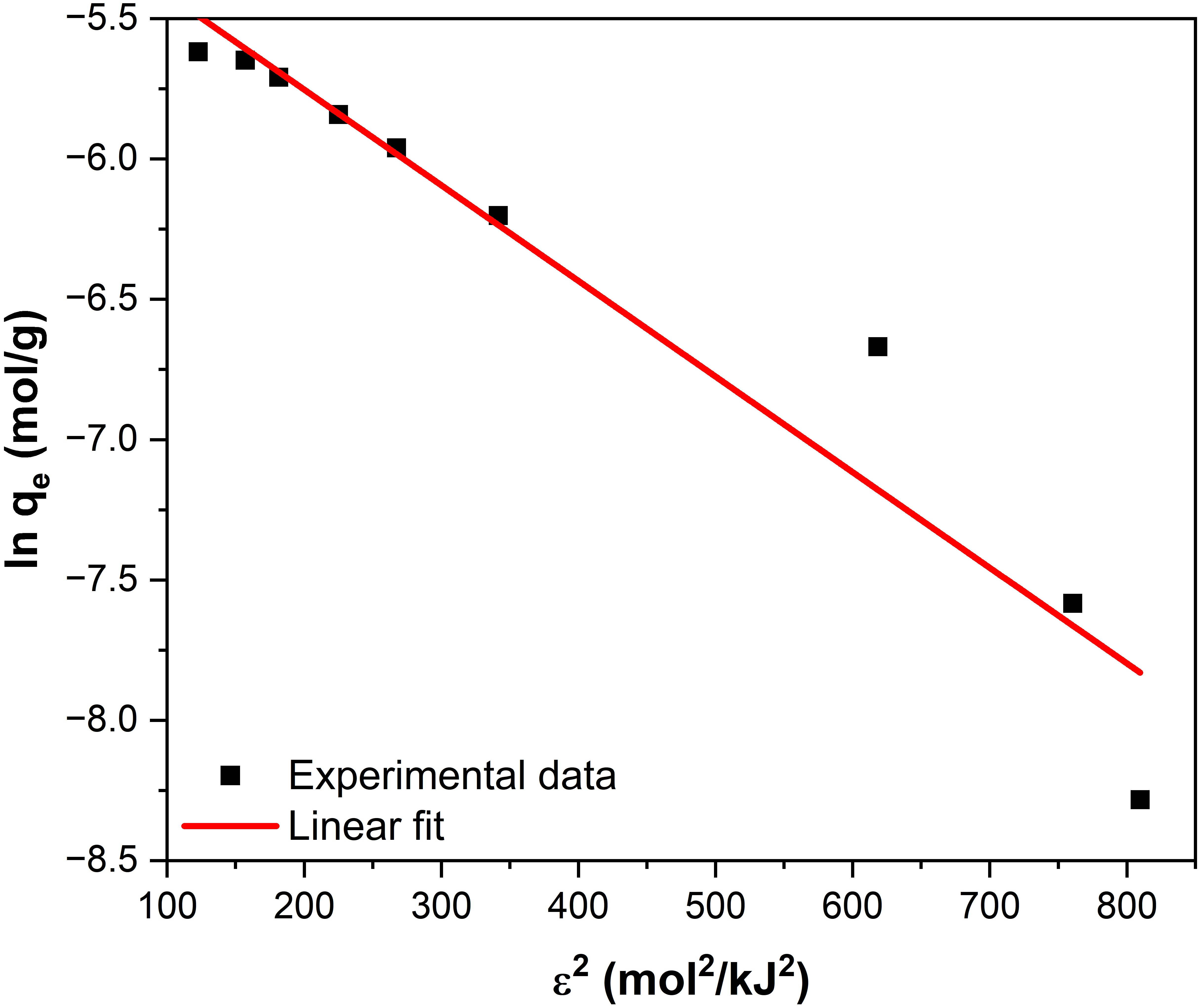
The parameters qDR and KDR in the above equation can be obtained as follows: a plot of ln qe versus R2T2 ln2 (1 + 1/Ce) has a slope of -KDR and an intercept of lnqDR (Figure 8).
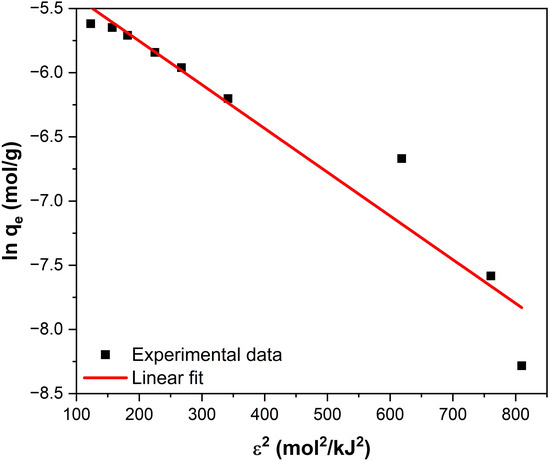
Figure 8.
Linear fitting of the D-R equation for fluoride adsorption on Fe3O4–ZrO2.
The mean free energy of adsorption EDR is important for distinguishing between physical and chemical adsorption processes. It is defined as the change in free energy when 1 mole of a solute is transferred to the surface of an adsorbent from infinity, i.e., from the solution [58], and it can be calculated using the following equation [59]:
The obtained EDR value was 12.11 kJ/mol (Table 4). The magnitude of EDR is used to estimate the type of adsorption mechanism:

Table 4.
Parameter values for fluoride adsorption on Fe3O4–ZrO2.
- (i)
- Physisorption if EDR < 8 kJ/mol;
- (ii)
- Ion exchange if EDR = 8.0–16.0 kJ/mol;
- (iii)
- Chemisorption if EDR > 16.0 kJ/mol [60].
2.2.4. Effects of Interfering Anions on Fluoride Adsorption
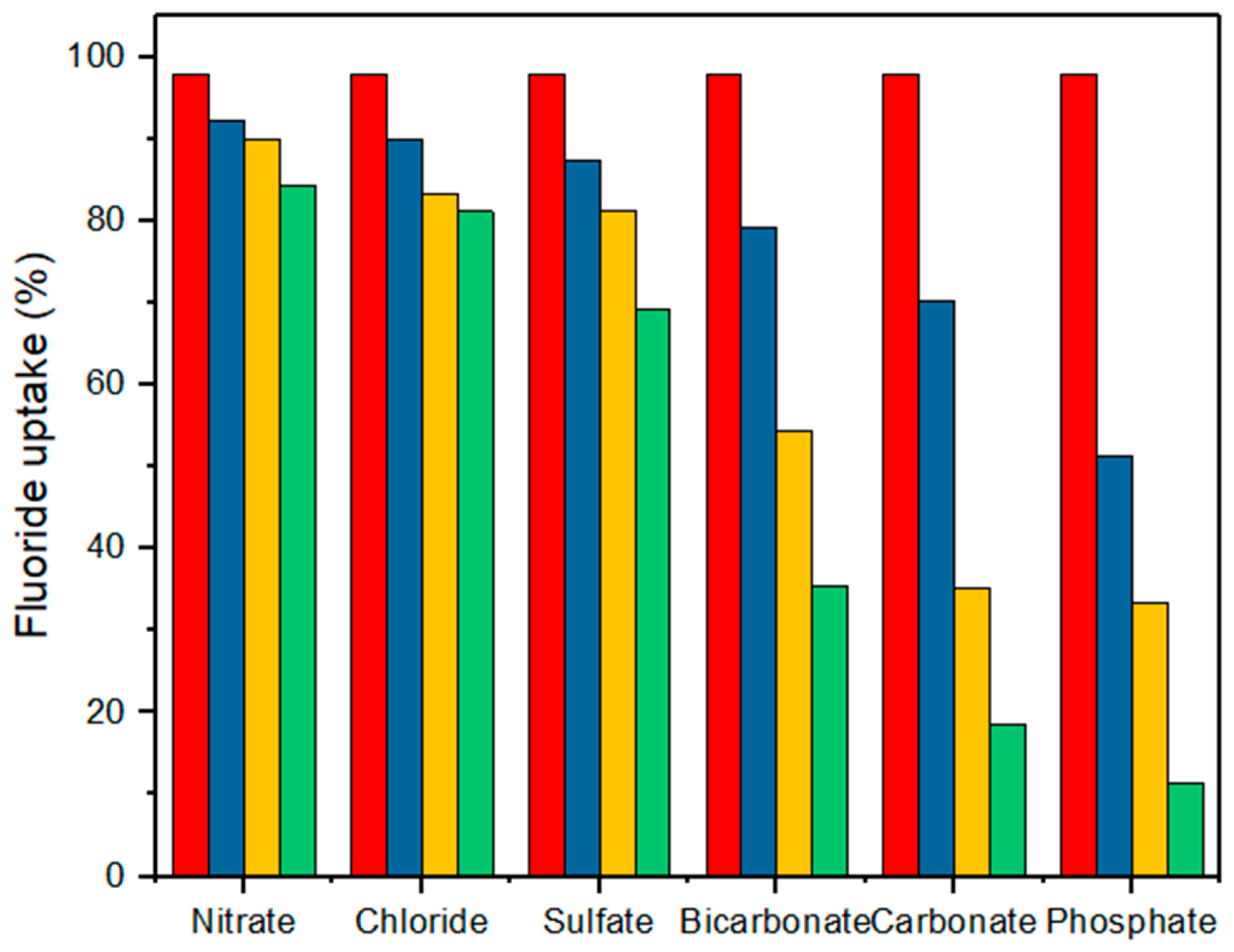
Adsorption selectivity is a crucial factor in fluoride removal efficiency, as competing ions in wastewater can affect adsorption performance. Interference tests were conducted using common anions found in drinking water: nitrate (NO3−), chloride (Cl−), sulfate (SO42−), bicarbonate (HCO3−), phosphate (PO43−), and carbonate (CO32−). The results (Figure 9) showed that nitrate, chloride, and sulfate had a minimal impact on fluoride adsorption, aligning with previous studies [17].
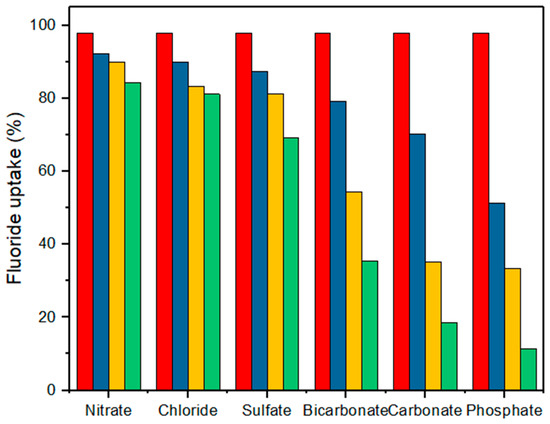
Figure 9.
Effects of different concentrations (0.1, 1, and 10 mM) of interfering ions on the adsorption capacity (the initial F− concentration was constant, i.e., 10 mg/L). Interfering ion concentrations of 0, 0.1, 1, and 10 mM correspond to the red, blue, yellow, and green bars, respectively.
However, bicarbonate and carbonate ions significantly reduced fluoride uptake by more than 50% at concentrations above 1 mM. This is attributed to the formation of a stable pentacyclic complex between carbonate ions and Zr4+, occupying active sites and competing with fluoride ions [61]. Phosphate ions also inhibited fluoride adsorption, primarily due to hydroxyl (-OH) groups formed during Na3PO4 hydrolysis, which increased the pH and intensified competition for active sites [30]. FTIR spectroscopy was used to confirm carbonate and phosphate ions’ adsorption on the surface of the M1 adsorbent (Figure S4).
These findings underscore the importance of understanding competing ion interactions to optimize fluoride removal using Fe3O4–ZrO2 composites.
2.2.5. Comparison of Fe3O4–ZrO2 with Other Fluoride Adsorbents
To evaluate the efficiency and practicality of Fe3O4–ZrO2 as a fluoride adsorbent, a comparative analysis with other materials reported in the literature was conducted. Table 5 summarizes key properties such as adsorption capacity, synthesis method, operational pH, contact time, and scalability. This comparison highlights the advantages of Fe3O4–ZrO2, particularly in terms of synthesis simplicity, scalability, and magnetic separation capabilities.

Table 5.
Comparison of fluoride adsorbents with different compositions and synthesis methods.
Several adsorbents in the literature exhibit higher fluoride adsorption capacities than our adsorbent. For instance, Zr(IV)-Polypirrole-Zr iodate (183.5 mg/g) [74] and CeO2-ZrO2 (175 mg/g) [73] surpass its performance. However, these materials require complex synthesis methods such as polymerization or solvothermal techniques, which involve long reaction times, high energy consumption, and expensive reagents. Additionally, these materials are not magnetic, making their separation from water difficult, requiring filtration or centrifugation.
Magnetic adsorbents like Fe3O4 offer the advantage of easy separation from water using an external magnetic field, enhancing their practicality. Among them, Fe3O4-activated carbon (146.2 mg/g) [64] and Fe3O4@MgO (98.4 mg/g) [62] have higher adsorption capacities, but their synthesis involves high-temperature treatments (650–700 °C), making them less energy-efficient and costly.
In contrast, our adsorbent demonstrates a high adsorption capacity (70.8 mg/g) over a broad pH range (optimum at 3), making it applicable to various water conditions. Furthermore, its simple and scalable co-precipitation synthesis eliminates the need for high temperatures or long reaction times, ensuring an energy-efficient and cost-effective alternative. Unlike other Fe3O4-based composites, our adsorbent requires no calcination, simplifying its fabrication while maintaining superior adsorption performance. Compared to Fe3O4-SiO2 (5.6 mg/g) [63] and Fe3O4-CaCO3 (17.95 mg/g) [65], Fe3O4–ZrO2 exhibits significantly enhanced fluoride removal efficiency, confirming its effectiveness as a viable and practical adsorbent.
For real-world water treatment applications, an adsorbent must combine efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ease of recovery. Our adsorbent successfully balances adsorption capacity, scalability, and magnetic separation, making it a highly promising candidate for fluoride removal.
The reusability of the M1 composite was evaluated over four consecutive fluoride adsorption–desorption cycles, as shown in the Supplementary Information. The adsorption capacity gradually decreased to approximately 25% (Table S1). This decline in performance may be attributed to irreversible fluoride binding at active sites or incomplete regeneration of adsorption sites. Despite the reduction, the material retained measurable adsorption capacity, indicating its potential for limited reuse in low-demand applications.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
Iron(II) chloride tetrahydrate (FeCl2·4H2O, 99%), iron(III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O, 98%), zirconium oxychloride octahydrate (ZrOCl2·8H2O, 99%), and sodium fluoride (NaF, 99%) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). Sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 97%) and hydrochloric acid (HCl, 37%) were supplied by Merck S.A. de C.V. (Naucalpan de Juárez, Estado de México, Mexico). All reagents were of analytical grade and used without further purification. Deionized water was used throughout the experiments.
3.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4–ZrO2 Nanoparticles
Fe3O4–ZrO2 nanoparticles were synthesized using a modified wet chemical co-precipitation method based on the previous literature [30]. Unlike the original approach, where iron sulfates were used, this synthesis employed iron chlorides (FeCl3 and FeCl2) due to their higher solubility in aqueous media, allowing for more homogeneous nucleation and facilitating a better dispersion of the zirconia phase. Briefly, a 200 mL aqueous solution containing 0.5 M FeCl3, 0.25 M FeCl2, and ZrOCl2 was prepared in stoichiometric proportions according to the Fe/Zr ratios of 1:1, 1:2, and 1:4, designated as M1, M2, and M3, respectively. A 6 M NaOH solution was slowly added under vigorous mechanical stirring at room temperature until the pH reached 11, ensuring the co-precipitation of Fe3O4 and hydrated zirconia. The resulting precipitates were aged at 90 °C for 18 h, a step that promotes phase interaction, enhances structural stability, and reduces lattice defects. The Fe3O4–ZrO2 composites were then magnetically separated using a neodymium magnet, thoroughly washed with distilled water until the supernatant was clear, and dried at 90 °C for 8 h. The adsorbents in this work were manually pulverized using a mortar and pestle. The final products were stored in a desiccator until further use.
3.2.1. Characterization
X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns were recorded using a Malvern Panalytical X-ray diffractometer (Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Model Empyrean, Worcestershire, UK) (resolution: 0.0525°) with monochromatized Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å). Morphological and elemental analyses were performed with a JEOL JSM-7800F (Tokyo, Japan) scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) module (X-Max 80, Oxford Instruments, Abingdon, UK). Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was conducted using a Perkin Elmer Frontier spectrophotometer (Waltham, MA, USA) in the range of 4000–500 cm−1.
3.2.2. Batch Adsorption Experiments
A standard fluoride stock solution (1000 mg/L F−) was prepared by dissolving sodium fluoride in deionized water and stored in the dark. Fluoride solutions with concentrations ranging from 5 to 300 mg/L were obtained by diluting the stock solution.
To determine the most effective adsorbent, 50 mg of each sample (M1, M2, and M3) was dispersed in 50 mL of a 50 mg/L fluoride solution and mixed at 40 rpm for 24 h at room temperature using an IKA Loopster Digital shaker rotator (IKA Works, Inc., Wilmington, NC, USA). Afterward, the adsorbents were separated using a magnet, and the remaining fluoride concentration in the supernatant was measured with an ion-selective electrode (HI 98402, Hanna Instruments, Padua, Italy).
The effect of pH on fluoride adsorption was evaluated following the same procedure, varying the pH from 1 to 10 while using only the M1 adsorbent.
To study the adsorption isotherm, 50 mg of the M1 adsorbent was added to 50 mL of fluoride solutions with initial concentrations ranging from 5 to 300 mg/L at pH 3. The suspensions were stirred for 2 h, after which the adsorption capacity at equilibrium (qe) was calculated using the equation:
where C0 and Ce are the initial and equilibrium fluoride concentrations (mg/L), respectively, V is the volume of the solution (mL), and m is the mass of the adsorbent (g).
To perform the kinetic analysis, 50 mg of the M1 adsorbent was dispersed in 50 mL of fluoride ion solution with a concentration of 10 mg/L, and the mixture was stirred for different periods, from 5 min to 24 h. The remaining fluoride concentration was determined as indicated above.
To assess the influence of interfering ions on fluoride adsorption, 50 mg of the M1 adsorbent was added to water samples containing 10 mg/L fluoride along with one of the following ions: (,
,
,
,
) at concentrations of 0.1, 1, and 10 mM. The mixtures were allowed to react for 2 h, after which the adsorbent was separated using a magnet, and the remaining fluoride concentration in the solution was measured.
4. Conclusions
The synthesized Fe3O4–ZrO2 nanoparticles demonstrated high efficiency in removing fluoride from aqueous solutions, with the Fe/Zr = 1:1 composition (M1) showing the highest fluoride adsorption capacity, reaching 70.8 mg/g at pH 3. The adsorption process followed the Temkin isotherm model, indicating strong interactions between the adsorbent and fluoride ions. Additionally, the nanoparticles exhibited excellent magnetic properties, allowing for easy separation using an external magnetic field, which enhances their potential for practical applications in water treatment. The adsorption capacity was found to be pH-dependent, with the highest efficiency observed at pH 3 and a decrease in performance at higher pH values due to electrostatic repulsion and competition with hydroxyl ions. However, fluoride adsorption remained over 60% across a range of pH values from 1 to 7, indicating that the material retains its adsorptive properties under different conditions, making it adaptable for various water treatment scenarios. Competitive ion studies showed that common anions like nitrate, chloride, and sulfate had a minimal effect on fluoride removal, indicating the selective nature of the adsorbent. However, bicarbonate, carbonate, and phosphate ions reduced the adsorption capacity due to their strong interactions with the adsorption sites. A comparative analysis with other fluoride adsorbents reported in the literature (Table 4) highlights the advantages of our adsorbent over alternative materials. While certain adsorbents exhibit higher fluoride uptake, many require complex synthesis methods, including solvothermal treatments, polymerization, or high-temperature calcination (500–700 °C), which increase energy consumption and production costs. Additionally, non-magnetic materials require additional separation steps, such as filtration or centrifugation, limiting their applicability. In contrast, our adsorbent combines high adsorption capacity, simple synthesis, and magnetic separation, making it a promising candidate for scalable and cost-effective water treatment solutions. Overall, our adsorbent shows great promise for selective fluoride removal from water, offering a balance of adsorption efficiency, magnetic separation, and minimal interference from most common ions. Its simple and scalable synthesis further supports its potential for real-world applications in addressing fluoride contamination in drinking water.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/inorganics13070248/s1, Figure S1: EDS spectrum of composite M1 (Fe3O4:ZrO2 = 1:1); Figure S2: EDS spectrum of composite M2 (Fe3O4:ZrO2 = 1:2); Figure S3: EDS spectrum of composite M3 (Fe3O4:ZrO2 = 1:4); Figure S4: FTIR spectra of the M1 composite before and after ion adsorptions; Table S1: Adsorption capacity (qe) and retention percentage of M1 composite over four adsorption–desorption cycles.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.Á.-M. and R.P.; methodology, I.Á.-M., J.A.P.-T., E.G.-A., P.E.C.-A., and R.P.; validation, I.Á.-M.; formal analysis, I.Á.-M., J.A.P.-T., E.G.-A., and P.E.C.-A.; investigation, I.Á.-M.; resources, P.E.C.-A., H.P.L.d.G., and R.P.; writing—original draft preparation, I.Á.-M. and J.A.P.-T.; writing—review and editing, E.G.-A., P.E.C.-A., H.P.L.d.G., and R.P.; visualization, I.Á.-M., J.A.P.-T., and E.G.-A.; supervision, P.E.C.-A., H.P.L.d.G., and R.P.; project administration, R.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
I. Águila Martínez and E. González-Aguiñaga thank Consejo Nacional de Humanidades, Ciencias y Tecnologías (CONAHCyT) for their scholarships (nos. 1002168 and 924183).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Materials Characterization Laboratory, Maria-Christian Albor (CIO) for her technical assistance in the SEM and EDS measurements, and Brenda Mata Ortega (Chemical Sciences Laboratory, Universidad de Guadalajara) for the FTIR measurements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L. A Zr-based coordination polymer for detection and adsorption of fluoride in water. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursaberi, T.; Hassanisadi, M.; Torkestani, K.; Zare, M. Development of zirconium (IV)-metalloporphyrin grafted Fe3O4 nanoparticles for efficient fluoride removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Zouboulis, A.I. Fluoride Removal from Water Sources by Adsorption on MOFs. Separations 2023, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.A.A.; Alam, J.; Qaid, S.M.H.; Shukla, A.K.; Al-Fatesh, A.S.; Alghamdi, A.M.; Fadhillah, F.; Osman, A.I.; Alhoshan, M. Fluoride removal using nanofiltration-ranged polyamide thin-film nanocomposite membrane incorporated titanium oxide nanosheets. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagtap, S.; Yenkie, M.K.; Labhsetwar, N.; Rayalu, S. Fluoride in drinking water and defluoridation of water. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2454–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waghmare, S.; Lataye, D.H.; Arfin, T.; Rayalu, S. Defluoridation by nano-materials, building materials and other miscellaneous materials: A systematic review. IJIRSET 2015, 4, 11998–12010. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Fluoride in Drinking-Water; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Available online: https://www.who.int/ (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Singh, J.; Singh, P.; Singh, A. Fluoride ions vs removal technologies: A study. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, P.; Dharaskar, S.; Pandian, S.; Panchal, H. Overview of fluoride removal from water using separation techniques. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, W.Z.; Deng, Z.Y. A comprehensive review of adsorbents for fluoride removal from water: Performance, water quality assessment and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 1362–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, X.; Shang, Y.; Gao, B. Removal of fluoride by carbohydrate-based material embedded with hydrous zirconium oxide nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27982–27991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Gupta, V.K. Advances in water treatment by adsorption technology. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 1, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, I.B.; Gupta, A.; Dubey, S.; Shafeeq, M.; Banerjee, P.; Sinha, A.S.K. Sol–gel synthesis of nanoparticles of gamma alumina and their application in defluoridation of water. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 77, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafshejani, L.D.; Tangsir, S.; Daneshvar, E.; Maljanen, M.; Lähde, A.; Jokiniemi, J.; Naushad, M.; Bhatnagar, A. Optimization of fluoride removal from aqueous solution by Al2O3 nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 238, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, C.; Yuan, K.; Gan, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D. Characterization and adsorption mechanism of ZrO2 mesoporous fibers for health-hazardous fluoride removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 346, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaeivelni, K.; Khodadoust, A.P. Adsorption of fluoride onto crystalline titanium dioxide: Effect of pH, ionic strength, and co-existing ions. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2013, 394, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y. Performance of granular zirconium-iron oxide in the removal of fluoride from drinking water. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3571–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savari, A.; Hamidi, A.; Farjadfard, S.; Omidvar, M.; Ramavandi, B. Zirconium-based materials for fluoride removal from aqueous environments: A literature review and scientometric analysis. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2023, 55, 100722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhizi, P.; Dandautiya, R.; Sahu, O. The efficiency of nano metakaolin modified with zirconium oxide for fluoride adsorption from aqueous solution. Next Nanotechnol. 2023, 3–4, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, F.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Hadizadeh, Z. Modification of Fe3O4 superparamagnetic nanoparticles with zirconium oxide; Preparation, characterization and its application toward fluoride removal. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 72058–72068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombuwala Dewage, N.; Liyanage, A.S.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D.; Mlsna, T. Fast nitrate and fluoride adsorption and magnetic separation from water on α-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 dispersed on Douglas fir biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lei, M.; Zeng, W.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, D.; Liu, C. Synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2-(-NH2/-COOH) nanoparticles and their application for the removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 20470–20479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchakipour, S.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Qaretapeh, M.Z.; Dashtian, K. Sustainable large-scale Fe3O4/carbon for enhanced polystyrene nanoplastics removal through magnetic adsorption coagulation. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.F.; Hassan, M.J.M.; Rheima, A.M. Adsorption of fast green dye onto Fe3O4 MNPs and GO/Fe3O4 MNPs synthesized by photo-irradiation method: Isotherms, thermodynamics, kinetics, and reuse studies. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2024, 6, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarchuk, T.; Soltys, L.; Macyk, W. Magnetic adsorbents for removal of pharmaceuticals: A review of adsorption properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 384, 122174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ouyang, G.; Han, R. Enhanced fluoride adsorption from aqueous solution by zirconium (IV)-impregnated magnetic chitosan graphene oxide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, F.; Sagredo, V.; Torres, T.; Márquez, G. Characterization of magnetite nanoparticles synthesized by the coprecipitation method. Cienc. Ing. 2019, 40, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Rojas, G.G.; López-Saucedo, F.; Vera-Graziano, R.; Mendizabal, E.; Bucio, E. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Medical Applications: Updated Review. Macromol 2022, 2, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstad, E.; Textor, M.; Reimhult, E. Stabilization and functionalization of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2819–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, Z.; Wei, J.; Yang, Z.; Ma, C.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.Y.; Zeng, G. Performance of magnetic zirconium-iron oxide nanoparticle in the removal of phosphate from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, E.; Feng, Q.; Yang, H.; Fan, J.; Mumtaz, S.; Begum, F. Synthesis of Fe3O4@mZrO2-Re (Re = Y/La/Ce) by using uniform design, surface response methodology, and orthogonal design & its application for As3+ and As5+ removal. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadjarodi, A.; Khodikar, R.; Ghafuri, H. Nanomagnetic zirconia-based sulfonic acid (Fe3O4@ZrO2-Pr-SO3H): A new, efficient and recyclable solid acid catalyst for the protection of alcohols: Via HMDS under solvent free conditions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 63480–63487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.M.; Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. Removal of pyrene and benzo(a)pyrene micropollutant from water via adsorption by green synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Magnetic properties of Fe3O4 stabilized zirconia. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1102204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbandian, L.; Patrikiadou, E.; Zaspalis, V.; Patrikidou, A.; Hatzidaki, E.; Papandreou, C.N. Magnetic nanoparticles in medical diagnostic applications: Synthesis, characterization and proteins conjugation. Curr. Nanosci. 2015, 12, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altass, H.M.; Khder, A.E.R.S. Surface and catalytic properties of triflic acid supported zirconia: Effect of zirconia tetragonal phase. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 411, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiyarasi, J.; Pandian, K. Selective and sensitive electrochemical detection of ATP in human serum samples at ZrO2 hallow spheres modified GCE. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 057524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaei, A.; Davoodnia, A.; Yadegarian, S. Nano-Fe3O4@ZrO2-SO3H as highly efficient recyclable catalyst for the green synthesis of fluoroquinolones in ordinary or magnetized water. Iran. J. Catal. 2018, 8, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, M.; Riaz, S.; Sanaullah, I.; Khan, U.; Sabri, A.N.; Naseem, S. Microwave assisted synthesis and antimicrobial activity of Fe3O4-doped ZrO2 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 10106–10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Fe3O4 stabilized zirconia: Structural, mechanical and optical properties. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 74, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U.; Yang, S. Remediating fluoride from water using hydrous zirconium oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dai, Y.; Lu, G.; Cao, Z.; Cheng, J.; Wang, K.; Wen, X.; Ma, W.; Wu, D.; Liu, C. Facile fabrication of high-contrast and light-colored marking on dark thermoplastic polyurethane materials. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 20787–20796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.J.; Jiang, Y.; Fok, J. Synthesis and properties of a high-capacity iron oxide adsorbent for fluoride removal from drinking water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 425, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, J.A.; Carr, P.W. Study of the fluoride adsorption characteristics of porous microparticulate zirconium oxide. J. Chromatogr. A 1991, 549, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Chang, C.; Hsu, T. Preparation and adsorptive application of novel superparamagnetic zirconia material. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 327, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhu, B.; Yang, W.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, L.; Liu, J. Fluoride removal performance and mechanism of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 233, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliyekkal, S.M.; Sharma, A.K.; Philip, L. Manganese-oxide-coated alumina: A promising sorbent for defluoridation of water. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3497–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Huang, Q.; Li, Q.; Yan, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H. Experimental and DFT calculation study on the efficient removal of high fluoride wastewater from metallurgical wastewater by kaolinite. Environ. Res. 2024, 260, 119604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhassan, S.I.; Wang, H.; He, Y.; Yan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, B.; Wang, T.; Gang, H.; Huang, L.; Jin, L.; et al. Fluoride remediation from on-site wastewater using optimized bauxite nanocomposite (Bx-Ce-La@500): Synthesis maximization, and mechanism of F─ removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurich, A.; Hofmann, J.; Oltrogge, R.; Wecks, M.; Gläser, R.; Blömer, L.; Mauersberger, S.; Müller, R.A.; Sicker, D.; Giannis, A. Improved Isolation of Microbiologically Produced (2R,3S)-Isocitric Acid by Adsorption on Activated Carbon and Recovery with Methanol. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revellame, E.D.; Fortela, D.L.; Sharp, W.; Hernandez, R.; Zappi, M.E. Adsorption kinetic modeling using pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws: A review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2020, 1, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. Characteristics of Elovich equation used for the analysis of adsorption kinetics in dye-chitosan systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, X. Efficient Fluoride Removal Using a CeO2/Attapulgite (ATP) Composite. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dada, A.O.; Olalekan, A.P.; Olatunya, A.M.; Dada, O. Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn2+ unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 3, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, F.; Akbar, J.; Iqbal, S.; Noreen, S.; Bukhari, S.N.A. Study of isothermal, kinetic, and thermodynamic parameters for adsorption of cadmium: An overview of linear and nonlinear approach and error analysis. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 3463724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günay, A.; Arslankaya, E.; Tosun, I. Lead removal from aqueous solution by natural and pretreated clinoptilolite: Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubinin, M.; Radushkevich, L.V. The equation of the characteristic curve of activated charcoal. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1947, 55, 327–329. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.; Chakrabarti, S.; Biswas, K.; Ghosh, U.C. Agglomerated nanoparticles of hydrous Ce(IV) + Zr(IV) mixed oxide: Preparation, characterization and physicochemical aspects on fluoride adsorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 307, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal Flórez, E. Adsorption isotherms for copper and lead removal from landfill leachate. Ing. Compet. 2024, 26, e-20912457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Liang, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, T.; Xu, Z.; Liu, G. Fabrication of a biomass-based hydrous zirconium oxide nanocomposite for preferable phosphate removal and recovery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 20835–20844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Tan, X.; Yu, T. Effectively arsenic(V) and fluoride removal in geothermal water using magnetic Fe3O4@MgO nanoparticles. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, A.; Wang, J.; Khan, M.S.; Farooq, U.; Riaz, N.; Nazir, A.; Mahmood, Q.; Hashem, A.; Al-Arjani, A.-B.F.; Alqarawi, A.A.; et al. Iron oxide (Fe3O4)-supported SiO2 magnetic nanocomposites for efficient adsorption of fluoride from drinking water: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption isotherm analysis. Water 2021, 13, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, T.J.; McKay, G.; Kadhim, A.; Joybari, M.M.; Balarak, D. Activated carbon prepared from hazelnut shell waste and magnetized by Fe3O4 nanoparticles for highly efficient adsorption of fluoride. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 4687–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, A.; Wang, J.; Riaz, N.; Khan, M.S.; Zeb, B.S.; Khan, I.A.; Akmal, M.; Khalid, A.; Khan, A.; Al-Harrasi, A.; et al. Optimizing the fluoride removal from drinking water through adsorption with mesoporous magnetic calcite nanocomposites. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Qiang, Z.; Chang, J.H.; Ben, W.; Qu, J. Synthesis of carbon-coated magnetic nanocomposite (Fe3O4@C) and its application for sulfonamide antibiotics removal from water. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Ma, C.; He, H.; Wei, L.; Xia, F. Preparation of Fe3O4/NiO Nanomaterials by Electrodeposition and Their Adsorption Performance for Fluoride Ions. Coatings 2024, 14, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiagar, S.; Mirazimi, H. Hydrothermal synthesis of Fe3O4-ZnO nanocomposites for removing fluoride from water. Progr Phys. Appl. Mat. 2024, 4, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, N.; Raissi, S.; Younes, M.K.; Elfil, H. Multifunctional nanoparticles as effective adsorbents for fluoride removal from synthetic and drinking waters: Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2024, 137, 3393–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Qin, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K. Double cross-linked chitosan sponge encapsulated with ZrO2/soy protein isolate amyloid fibrils nanoparticles for the fluoride ion removal from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Cai, X.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Jin, Z.; Meng, F.; Liu, N.; Wang, X.; Kong, L.; et al. Performance of a novelly-defined zirconium metal-organic frameworks adsorption membrane in fluoride removal. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2016, 484, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Wang, W.; Cao, M.; Yang, H.; Li, Y. Constructing hydrangea-like hierarchical zinc-zirconium oxide microspheres for accelerating fluoride elimination. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 317, 114133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Chen, L.; Jia, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.J.; Liu, J. Excellent fluoride removal performance by CeO2-ZrO2 nanocages in water environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Nasir, M. Development of Zr(IV)—Doped polypyrrole/zirconium (IV) iodate composite for efficient removal of fluoride from water environment. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 19, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Valadez Sanchez, E.P.; Bogdanova, E.; Bergfeldt, B.; Mahmood, A.; Ostvald, R.V.; Hashem, T. Efficient fluoride removal from aqueous solution using zirconium-based composite nanofiber membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).