Abstract
The first chlorido platinum(II) complex with a cyclometallated 1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)benzene ligand, Pt(bpyb)Cl, was prepared in 1999. Four years later, its luminescent properties were discovered. Since then, a huge number of studies have been dedicated to the synthesis and characterization of related complexes, and to their application in photonics, optoelectronics, bioimaging, and photodynamic therapy. The present review concerns the main results obtained in the last five years by our research group in Milan. After a brief introduction on Pt(bpyb)Cl complexes, we illustrate our recent investigations to show the Milanese contribution to the rapid growth of this platinum family.
1. Introduction
In the last thirty years, a huge amount of work has been devoted to the design and preparation of metal complexes for various fields of photonics such as nonlinear optics [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17], dye-sensitized solar cells [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29], electroluminescent devices [30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45], sensing [46,47,48], photocatalysis [49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56], bioimaging [57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69], and photodynamic therapy [70,71,72,73,74,75,76]. Among them, square planar platinum(II) complexes are of particular interest because (i) the strong spin–orbit coupling, SOC, accompanying the platinum center favors intersystem crossing to triplet excited states and their subsequent radiative decay and (ii) their geometrical structure allows the creation of bimolecular states either in the excited state (excimers), thanks to ligand–ligand or Pt–Pt intermolecular interactions, or in the ground state (dimers or higher aggregates). These bimolecular species can emit at lower energies with respect to the related isolated molecules, paving an efficient route for example for the preparation of deep-red/near infrared (NIR)-emitting materials, for color variation based on the local concentration, and even for the fabrication of white-light-emitting materials [30,36,37,42,43]. An interesting aspect is that the OLEDs’ emission color can be controlled by the concentration of the platinum(II) complex in the matrix used for the fabrication of the device’s blend emissive layer, as a consequence of the parallel emissions coming from the monomolecular and bimolecular excited states [36,37]. Numerous designs of square planar platinum(II) complexes have been considered, according to the nature of the ligands around the metal center. Although platinum is an expensive metal, today, a lot of work is devoted to the preparation of luminescent platinum complexes because the amount of compound needed for various applications, such as bioimaging, photodynamic therapy, and luminescent devices, is so limited that the cost of the metal does not represent a significant problem [75].
In 1999, Cardenas et al. found that 1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)benzene (bpybH) reacted with K2PtCl4 in acetic acid, affording Pt(bpyb)Cl, the first chlorido platinum(II) complex with a cyclometallated 1,3-bis(pyribin-2-yl)benzene ligand [77]. Four years later, Williams et al. discovered its amazing luminescent properties [78]. It is intensely luminescent at room temperature in a dilute deoxygenated dichloromethane solution, being characterized by an emission quantum yield (Φlum) of 0.60 and a luminescence lifetime (τ) of 7.2 μs. This is in contrast to [Pt(terpyridine)Cl]+, which is non-emissive due to the existence of low-lying d–d states that give a nonradiative decay route, putting in evidence that the introduction of the cyclometallating carbon atom intensifies the ligand-field strength and thus the d–d state energy, removing this decay pathway [79,80]. Moreover, the positive effect of the added rigidity of terdentate compared to bidentate binding appears by comparison with Pt(ppy)(Hppy)Cl (Hppy is phenylpyridine), which has a similar coordination sphere (one chlorido ligand, one cyclometallated benzene ring, and two pyridine rings) but displays a luminescence lifetime of 11.2 μs at 77 K which decreases to 641 ns at room temperature, whereas the luminescence lifetime of Pt(bpyb)Cl is the same at 77 K and 298 K, showing that the more rigid terdentate system hampers the distortion that leads to nonradiative decay in the bidentate system [80]. The emission quantum yield of Pt(bpyb) is an order of magnitude higher than that of the isomeric N^N^C-coordinated complex, a superiority which is due to the particularly short Pt–C bond in Pt(bpyb)Cl, leading to a higher ligand-field strength [80]. Thus, the excellent luminescent properties of Pt(bpyb)Cl can be explained by the combination of the short Pt–C bond and the high rigidity of the N^C^N ligand, minimizing nonradiative decay.
Since the high luminescence of Pt(bpyb)Cl was discovered [78], a growing number of studies have been devoted to the synthesis and characterization of related complexes. An interesting aspect of these platinum(II) complexes is that the presence of appropriate substituents, on the benzene or pyridine rings of the bpyb ligand, is an efficient way to control the color of the emission, maintaining high quantum yields [37]. Indeed, time-dependent (TD) density functional theory (DFT) calculations has shown that the frontier orbitals are concentrated on various parts of the complex, such that their energies can be varied independently [81,82]. As a matter of fact, in this family of complexes, in which the lowest energy triplet state has mostly a HOMO→LUMO character, the pyridine rings make the main contribution to the LUMO whereas the benzene ring dominates in the HOMO. Therefore, the presence of electron-donor groups on the benzene ring (which raises the HOMO energy) and electron-acceptor groups on the pyridine rings (which decreases the LUMO energy, particularly at the para position of the N atoms) would lead to a redshift of the emission. On the other hand, electron-acceptor groups on the benzene ring and electron-donor groups on the pyridine rings would cause a blueshift. The experimentally observed trend is in agreement with this design [79]. Moreover, Williams et al. utilized a different strategy to redshift the emission, consisting in the use of a dinuclear bis-terdentate chlorido platinum complex having two N^C^N units [83].
The effect of the ancillary ligand on the emission properties of platinum(II) complexes bearing a cyclometallated 1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)benzene ligand has also been investigated. The substitution of the chlorido ligand with an isothiocyanate or acetylide [75] allows them to maintain a high luminescence, whereas N^C^N-Pt–OPh complexes have a lower luminescent quantum yield than the related chlorido complexes, indicating that the ancillary ligand has an effect on the excited state properties of Pt(dpyb)X complexes, although the excited state is localized mostly in the Pt(N^C^N) moiety [84]. The substitution of the chlorido ligand with thiolates [85], isocyanide [86,87,88] or other halides [89] has also been studied, leading to novel highly luminescent N^C^N-platinum(II) complexes.
Fifteen years ago, some of us entered the world of Pt(bpyb)Cl complexes. We found the open and easy collaboration of various laboratories and people extraordinary, in particular J. A. Gareth Williams of the University of Durham who discovered for the first time the luminescent properties of this kind of complex. We feel that such spirit of collaboration is the strength of scientists, which make them unique. In the present review we wish to present the results obtained in the last five years in this Milanese adventure. These are divided in two parts: (i) 1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)benzene platinum(II) complexes with chloride as ancillary ligand and (ii) 1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)benzene platinum(II) complexes with other ancillary ligands.
2. 1,3-Bis(Pyridin-2-yl)benzene Platinum(II) Complexes with Chloride as Ancillary Ligand
Up to five years ago, the influence of the substituents on the 4-position of pyridine rings had been mostly studied with Pt(1,3-bis(4-R-pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl (R = H), in which the introduction of the electron-acceptor fluorine atoms on the benzene rings led to a blueshift of the emission, an aspect of great interest in the design of efficient blue phosphorescent complexes, which remains a challenge for the fabrication of blue emissive OLEDs [90,91,92]. It turned out that the emission energy of the monomolecular excited state follows a blueshift depending on the nature of the R group, going from 496 nm (R = CF3) to 472 nm (R = H) [93] to 453 nm (R = NMe2) [94]. All these platinum(II) compounds exhibited high luminescence quantum yields (Φlum = 0.50–0.87) and luminescence lifetimes in the range 5–10 μs. The influence of the introduction of a π-delocalized polarizable substituent on the 4-position of the pyridine rings was unknown.
Moreover, it was known that the introduction of a bulky group on the 5-position of the cyclometallated phenyl ring of the 1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-benzene ligand hampered the formation of excimers compared to the parental complex, due to the steric effect which prevented the face-to-face approach of a ground-state complex to a molecule in its excited state [95]. Therefore, the study of the influence of the introduction of bulky substituents on the 4-phenylpyridine unit was particularly appealing, since aggregate or excimer formation, and thus the phosphorescence properties, might be tuned by a suitable spatial arrangement of bulky groups. It appeared as a potential method to decrease π–π stacking and/or Pt–Pt interactions and obtain efficient blue OLEDs. In addition, the introduction of bulky aromatic groups could give a brighter emission both in solution and in the device.
These observations prompted us to prepare the complex with a simple phenyl substituent, Pt(1,3-bis(4-phenylpyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl (complex 1, Figure 1) [96], along with related complexes bearing various substituents on the 4-phenylpyridine unit, in order to understand their effect on the phosphorescence properties of this family of complexes. Namely, we investigated Pt(1,3-bis(4-(4-tert-butylphenyl)pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl (complex 2) [97], Pt(1,3-bis(4-(3,5-di-tert-butylphenyl)-pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl (complex 3) [97], Pt(1,3-bis(4-(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl (complex 4) [98], Pt(1,3-bis(4-(4-methoxy-2,6-dimethylphenyl)pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl (complex 5) [96], Pt(1,3-bis(4-triphenylamine-pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl (complex 6) [99], Pt(1,3-bis(4-triphenylamine-pyridin-2-yl)-5-triphenylamine-benzene)Cl (complex 7) [99], and Pt(1,3-bis(4-triphenylamine-pyridin-2-yl)-5-mesityl-benzene)Cl (complex 8) [99] (see Figure 1).
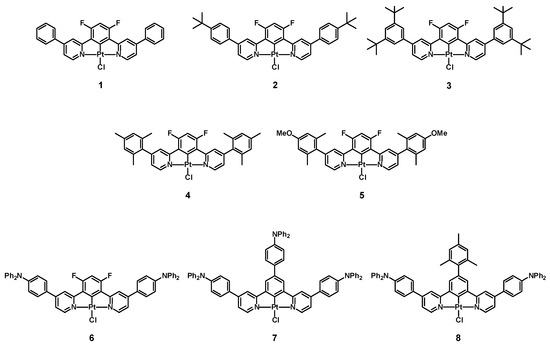
Figure 1.
Structure of complexes 1–8.
The photophysical parameters of the Pt(1,3-bis(4-R-pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl complexes (1–6) studied in our laboratories are shown in Table 1. In a CH2Cl2 solution, the absorption spectra of all complexes are characterized by high intensity bands at 260–320 nm, assigned to 1π–π* intraligand transitions of the cyclometallating 1,3-bis(4-R-pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene ligand, and bands of lower intensity in the range 340–420 nm, due to charge-transfer transitions between the cyclometallating N^C^N ligand and platinum(II) [96,97,98]; in the case of complex 6, the band around 423 nm is attributed to an intraligand charge transfer, from the triphenylamino substituent to the pyridine rings by analogy with related cyclometallated Ir(III) complexes, which covers the charge-transfer transition involving the N^C^N ligand and the platinum center. A weak absorption band in the range 467–471 nm is also observed for complexes 1–5, due to the formally spin-forbidden S0→T1 transition, helped by the spin–orbit coupling associated with the presence of platinum [96,97,98], similar to that of the related Pt(1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl complex [93] (467 nm, 140 M−1 cm−1). It is worth pointing out that the extinction coefficient associated with this weak transition is particularly high in the case of complexes 1–3 and 5, suggesting more efficient SOC routes [96].

Table 1.
Photophysical parameters of [Pt(1,3-bis(4-R-pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl] complexes 1–6 a.
Upon excitation at 330–380 nm in a dilute dichloromethane solution (5 · 10−6 M), complexes 1–5 are characterized by a vibrationally structured band with a high-energy emission maximum at 480 nm (1 and 2), 478 nm (3), and 471 nm (4 and 5), slightly redshifted with respect to Pt(1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl (467 nm) [93,96,97,98] and attributed to an emission from the T1 state. In contrast, complex 6 displays a broad emission at much lower energy (562 nm) upon excitation at 422 nm [99].
For complexes 1 and 2, as the concentration is augmented, a structureless, broad band grows in, with λmax at 704 nm and 697 nm, respectively, attributed to the formation of emissive, bimolecular excited states (excimers and/or aggregates). For complex 3, the related band, at 690 nm, is much less intense at the same concentration, probably due to the steric hindrance caused by the presence of two tert-butyl groups on the phenyl linked to the pyridine rings that inhibits the neighboring of two molecules [97]. Similarly, the corresponding band at 680 nm is weak upon the introduction of a 2,4,6-trimethyl phenyl substituent (complex 4) [98] or a 4-methoxy-2,6-dimethyl phenyl substituent (complex 5) [96] on the pyridine rings, because the two methyls ortho to the interannular C–C bond hamper the planar conformation that favors face-to-face intermolecular interactions (see Figure 2) [96,98]. In contrast, for complex 6 bearing a diphenylamino group on the phenylpyridine unit, the structureless broad band at 696 nm is very intense [99].
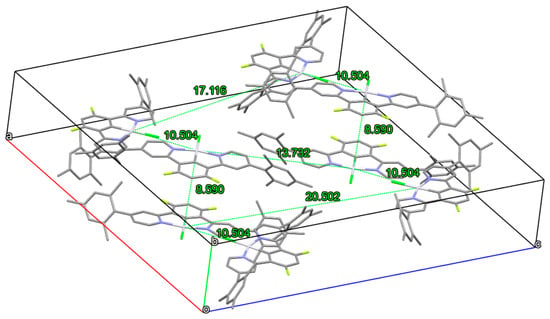
Figure 2.
X-ray structure of complex 4, unit cell with Pt–Pt distances. CCDC deposition number 2087747.
Complexes 1, 2, and 6 are characterized by an excellent luminescence quantum yield (Φlum = 0.89-0-90, Table 1) in dilute dichloromethane solution (5 · 10−6 M) [96,97,99], as determined with an integrating sphere, like the related Pt(1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl complex (Φlum = 0.80) [93]. Complexes 3–5 are even more luminescent (Φlum = 0.95–0.98) [96,97,98]. Under air-equilibrated conditions, the Φlum values are much lower (0.16–0.28 for complexes 1–5), owing to oxygen quenching; the value is even more reduced in the case of complex 6 (0.059). This quenching suggests an efficient production of singlet oxygen, putting in evidence the great potential of these platinum(II) complexes for photodynamic therapy [96,97,98,99].
The creation of aggregates and excimers of complexes bearing a cycloplatinated N^C^N ligand classically comes at the expense of the luminescence quantum yields [96]. An examination of the values in Table 1 shows than an increase in the concentration (2 · 10−4 M) does compromise the Φlum of complexes 1–4 and 6, but only slightly, the values remaining very high (0.53–0.66). Remarkably, the luminescence quantum yield of complex 5 (0.85) is even less affected by concentration than that of the other five compounds, probably due to the steric hindrance of the 4-methoxy-2,6-dimethyl phenyl substituents that inhibits the creation of emissive bimolecular species. In agreement with these observations, DFT calculations, performed on the dimers of some of these complexes, afforded a Pt–Pt distance of 4.88 Å, 6.31 Å, and 6.54 Å, for 1, 4, and 5, respectively. Thus, in 1 the presence of unsubstituted phenyls permits a closer approach of the two monomeric species; in 4, the approach is more difficult due to the presence of three methyls on the phenyls; in 5, the methoxy substituent in place of the methyl group at the para position of the phenyls renders the approach even more difficult, leading to a further increase in the Pt–Pt distance. As expected from these observations, the computed dimerization energy in dichloromethane, which gives an estimate of π–π and Pt–Pt interactions that allow the dimeric species to form, follows the order 1 (−43.34 kcal mol−1) < 4 (−47.4 kcal mol−1) < 5 (−50.5 kcal mol−1) [96].
In dilute deaerated dichloromethane solutions, complexes 1–5 are characterized by luminescence lifetime values in the range 3.5–4.8 μs [96,97,98], typical for N^C^N platinum(II) complexes such as Pt(1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl (τ = 6.6 μs) [93]. In contrast, complex 6 bearing a diphenylamino substituent at the para position of the 4-phenylpyridine unit is characterized by an unexpected very long lifetime (104 μs) [99].
The radiative kr decay constants of complexes 1–5 in a dilute dichloromethane solution, which can be calculated along with nonradiative knr from the τ and Φlum values (Table 1) assuming that the state which emits is obtained with unit efficiency, are in the range 2.0 · 105–2.5 · 105 s−1, about twice that of the parent Pt(1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl complex [93]. The kr of complex 6 is much lower (8.7 · 103 s−1) [99]. The higher Φlum values of complexes 3–5 compared to 1–2 can be reasonably attributed to suppressed nonradiative pathways, since their knr is lower. It is worth pointing out that an efficient mixing of metal orbitals into the excited state is important for a high spin–orbit coupling. In complex 6, the presence of the diphenylamino groups probably leads to low-energy excited states of intraligand character, leading to a particularly low kr and an abnormally long luminescence lifetime [96].
The peculiar photophysical properties of complex 6 prompted us to investigate those of related Pt(1,3-bis(4-triphenylamine-pyridin-2-yl)-4-R, 5-R’-6-R-benzene)Cl complexes with a triphenylamino (complex 7) or a mesityl substituent (complex 8) on the 5-position of the cyclometallated benzene ring instead of the fluorine atoms on the 4- and 6-positions (complex 6) [99]. The results are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Photophysical parameters of Pt(1,3-bis(4-triphenylamine-pyridin-2-yl)-4-R, 5-R’-6-R-benzene)Cl complexes 6–8 a.
The absorption spectra of complexes 7 and 8 are similar to that of complex 6. However, absorption bands at low energy (485–520 nm) are also observed for 7 and 8; they are very weak and attributed to the direct population of 3π–π* states helped by the SOC involving the Pt(II) center. This transition is not detected in the case of complex 6, reasonably due to its low molar extinction coefficient.
Upon excitation at 422 nm in dilute dichloromethane solution, complex 7 is characterized by an intense phosphorescent band with a maximum wavelength at 561 nm, similar to that of 6, whereas that of complex 8 is slightly blueshifted (549 nm). In any case, there is a strong redshift in the emission of 8 with respect to Pt(1,3-bis(pyridine-2-yl)-5-mesityl-benzene)Cl, which emits at 501 nm [95], due to the introduction of the triphenylamino group on the pyridine rings. An increase in the concentration of 7 and 8 also leads to the formation of bimolecular emissive states (around 704 and 727 nm, respectively).
Like 6, complexes 7 and 8 are bright emitters with similar Φlum values (Table 2). Moreover, as mentioned above, the luminescence lifetime measured for complex 6 is abnormally long (104 μs), 16 times longer with respect to the parent complex Pt(1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl. The lifetime of 8 is also quite long (50 μs), being seven times longer with respect to that of the related Pt(1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-5-mesityl-benzene)Cl complex [95]. In contrast, that of complex 7 is 6.6 μs, a value similar to that usually observed for N^C^N-platinum(II) complexes. The particularly long lifetimes of 6 and 8 is related to the nature of the substituent on the cyclometallated phenyl ring: it appears that an increase in the electron deficiency of the substituent (Ph3N <mesityl < F2Ph) makes the luminescence lifetime of the platinum complex longer [99]. It is worth pointing out that long lifetimes are of interest for many applications like bioimaging [99].
Complexes 1–8 constitute an interesting family of N^C^N-platinum(II) complexes, and some of them have already found applications. For example, complex 6 allowed the fabrication of both yellow-green and deep red OLEDs [99] whereas complex 4 turned out to be a springboard for blue OLEDs.
Furthermore, we were curious to exploit the known anticancer properties of Pt(II) complexes in the case of compounds presenting a terdentate N^C^N ligand [100]. Therefore, in 2025, we prepared two new compounds by conjugating a peptide nucleic acid (PNA) made of ten nucleobases together with a platinum(II) complex having a COOH group directly bound to the N^C^N scaffold or separated from it by an ethylene linker (complexes 9 and 10, respectively; Figure 3). The study pointed out not only the non-cytotoxic nature of the conjugates but also an improved phosphorescence of complex 10, presumably thanks to the long PNA chain able to protect the Pt(II) core from external quenching oxygen, resulting in Φlum > 0.37 even in the presence of air (Table 3).
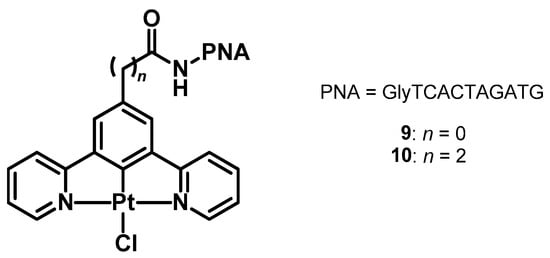
Figure 3.
Structure of complexes 9 and 10.

Table 3.
Photophysical parameters of complex 10 a.
3. 1,3-Bis(Pyridin-2-yl)benzene Platinum(II) Complexes with Other Ancillary Ligands
The chloride ancillary ligand on the Pt(II) center, which is present as a consequence of the use of K2PtCl4 as the source of the metal, can be easily replaced by other species, both anionic (acetylides, alkoxides, thiolates, azides, etc.) and neutral (carbenes, pyridines).
As it discussed and reported later, it appears evident that the effect of the substitution of the chloride ligand with other anionic species does not bring about a relevant modification in the emission wavelengths of the monomeric species in dilute solution, since a difference of only a few nanometers in the emission maxima can be observed. However, there is a significant effect on the emission quantum yield.
3.1. Complexes Bearing Thiolates as Ancillary Ligands
Important results were obtained in the case of heteroaromatic thiolates such as 1-phenyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiolate and 4-phenylthiazole-2-thiolate, leading to the synthesis and characterization of complexes 11–13 and 15–18 (Figure 4). While both thiolate ligands were tested on the N^C^N-Pt(II) complexes presenting a mesityl, a methyl, and a 2-thienyl substituent on the benzene ring, the phenyl-thiazole-thiolate was introduced also on the compound having a 4-NPh2-phenyl group.
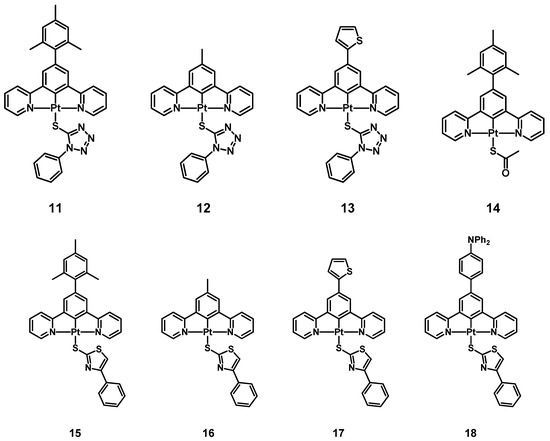
Figure 4.
Structure of complexes 11–18.
Thus, in 2020, we published a paper on complex 11, with a 1-phenyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiolate ligand, characterized by a high luminescence quantum yield both in a dilute dichloromethane solution (Φlum = 0.90) and in the solid state (Φlum = 0.62) [101]. The study of this complex, whose structure was determined by x-ray (Figure 5), put in evidence for the first time that N^C^N platinum(II) complexes with a suitable thiolate coligand could reach very good luminescence properties. Thus, other members of this family were investigated in 2022 [102,103] and in 2023 [104].
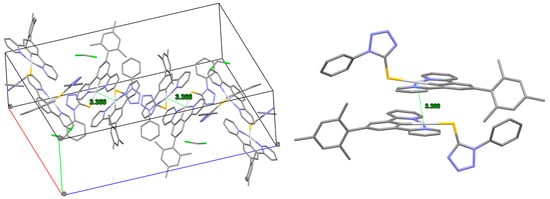
Figure 5.
X-ray structure of complex 11. On the left: unit cell with Pt–Pt distances; on the right: dimeric structure of the complex. CCDC deposition number 1979249.
It is important to point out that, as previously discussed, the emission wavelength depends purely on the substituent on the N^C^N scaffold and not on the ancillary ligand on the metal center: all complexes having a methyl or a mesityl group show an emission in the narrow range between 498 and 504 nm, while the presence of the 2-thienyl ring brings about a redshift of ~40 nm, reaching a maximum at 545 nm. The same trend is also valid for the lifetimes, these having a value of 7.3–8.1 μs in the case of mesityl and methyl groups, while reaching a longer range of 17.8–19.2 μs in the case of the thiophene.
Considering emission efficiency, the highest luminescent quantum yields were obtained for dilute solutions of 11, 13, and 17, reaching values of 0.90, 0.93, and 0.89, respectively.
Moreover, an investigation on the introduction of a non-aromatic thiolate on the metal center was performed in the case of compound 14, in which a simple thioacetate replaced the chloride in the N^C^N complex substituted with a mesityl moiety on the benzene ring (Figure 3). It turned out that the Φlum of this molecule was rather low (0.23), suggesting the importance of having a (hetero)aromatic thiolate or in general, a second ligand able to provide more steric hindrance on the Pt atom.
Table 4 and Table 5 report all the main photophysical parameters for the discussed complexes 11–14 and 15–18.

Table 4.
Photophysical parameters of [Pt(1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-5-R-benzene)Y] complexes 11–14. T1 = 1-phenyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiolate a.

Table 5.
Photophysical parameters of [Pt(1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-5-R-benzene)(T2)] complexes 15–18. T2 = 4-phenylthiazole-2-thiolate a.
Furthermore, compounds 11 and 17 were tested as dopants for the preparation of some OLED devices, having different amounts of the complex in the emissive layer. As a result, depending on the concentration of the complex, devices emitting yellow or green light were obtained [101,103].
3.2. Complexes Bearing Azides, Triazolates, and Acetylides as Ancillary Ligands
The use of an azide as ancillary ligand is particularly appealing because azido complexes of Pt(II) can find application in photoactivated chemotherapy, due to their ability not only to intercalate in DNA but also to photorelease azidyl radicals able to damage cancer cells [72]. Furthermore, this ancillary ligand can be the starting point for the well-known click reaction with an alkyne: as shown in the 2019 papers of Schatzschneider et al. [105,106], square planar platinum(II) complexes can easily react with an electron-poor alkyne at room temperature without the need of a catalyst to produce triazolate complexes. Once formed, such complexes can undergo isomerization to change the nitrogen atom they bind the metal with, passing from an N1- to an N2-triazole.
With the aim of studying this process, in 2024, we prepared and investigated azido complexes 19–21 (having a mesityl, methyl, and thienyl substituent, respectively, on the central benzene ring) [107]. Then, in the case of 19 and 21, the click reaction with diethyl acetylenedicarboxylate gave the new triazole derivatives 22 and 23. Figure 6 shows the molecular structure of complexes 19–23.
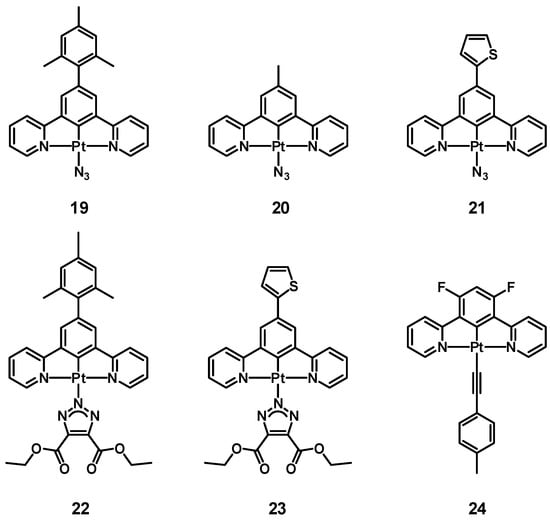
Figure 6.
Structure of complexes 19–24.
The x-ray structure of complexes 22 and 23 is shown in Figure 7.
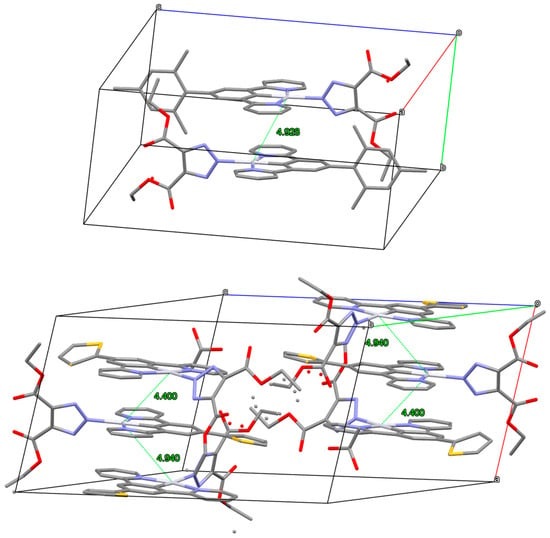
Figure 7.
X-ray structure of complexes 22 and 23. At the top: unit cell of 22 with Pt–Pt distances; at the bottom: unit cell of 23 with Pt–Pt distances. CCDC deposition numbers 2309868 and 2309869.
Also in the case of the introduction of an azide, and in the following click reaction, the emission energy does not change with respect to the parent chloride complex, but a variation in the absolute Φlum is observed: in the case of the mesityl-bearing complexes, the luminescence quantum yield of the deaerated diluted solution goes from 0.87 (19) to 0.96 (22). Similarly, in the compounds having a thienyl substituent, the quantum yield is increased from 0.79, for 21, to 0.94, for 23, after the click reaction.
Finally, in 2024, we reported a new complex in which the chloride ligand was replaced with an acetylide (compound 24, structure in Figure 6 and Figure 8) [108]. This compound, presenting two fluorine atoms on the cyclometallating benzene ring and a 4-methyl-phenylacetylide on the Pt center, gave a remarkable Φlum of ~0.43 and interesting second-order nonlinear optical properties.
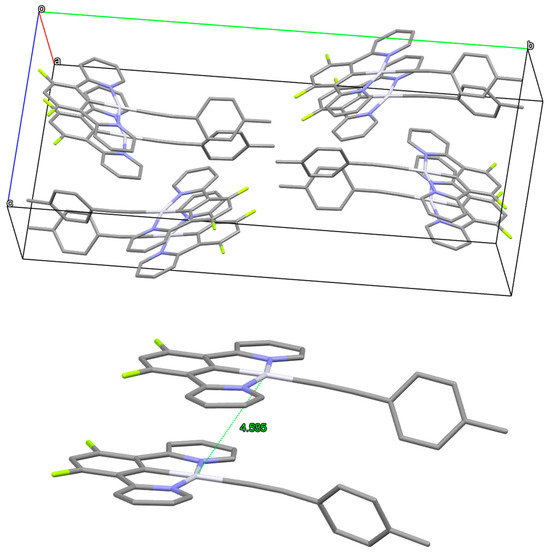
Figure 8.
X-ray structure of complex 24. At the top: unit cell with Pt-Pt distances; at the bottom: dimeric structure of the complex. CCDC deposition number 2357874.
All key data about the luminescent properties of the discussed complexes 19–24 are in Table 6.

Table 6.
Photophysical parameters of [Pt(1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-5-R-benzene)Y] complexes 19–23 and of complex 24. T1 = 1-phenyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiolate. Trz = 4,5-diethyl 1,2,3-triazolate-4,5-dicarboxylate a.
4. Conclusions
In the last five years, our investigations have produced information to help the research aimed at the design of luminescent 1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)benzene platinum(II) complexes of interest for electroluminescent devices and biomedicine.
It was shown that the introduction of a polarizable phenyl group on the position 4 of pyridine rings allowed to boost the luminescence properties. A further improvement of the quantum yields can be achieved with an appropriate functionalization of the 4-phenylpyridine unit. In particular, our studies showed that the introduction of bulky substituents was an efficient method to decrease π–π stacking and/or Pt–Pt interactions, allowing us to maintain very good quantum yields even in concentrated solutions and opening an appealing route for the fabrication of blue OLEDs. Thus, we put in evidence that the introduction of a bulky mesityl substituent on the pyridine rings of Pt(1,3-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl (complex 4) represented a springboard for the fabrication of efficient blue OLEDs. Moreover, we recently found that the steric hindrance of the 4-methoxy-2,6-dimethyl phenyl moiety on the pyridinyl rings (complex 5) was even better than that of a mesityl group at hampering the formation of bimolecular species. We plan to study its potential for the fabrication of blue OLEDs. Remarkably, the introduction of a diphenylamino group at the para position of the 4-phenylpyridine unit (complex 6) leads to a large redshift of the monomeric species emission (from 480 nm to 562 nm), to low-energy excited states of intraligand character, to a particularly low kr, and to an abnormally long luminescence lifetime (104 μs), one order of magnitude higher with respect to that of traditional N^C^N-platinum(II) complexes, of particular interest for bioimaging. This complex has already allowed the fabrication of deep red OLEDs.
In addition, we prepared new complexes by conjugating a peptide nucleic acid (PNA) with a platinum(II) complex having a COOH group directly bound to the N^C^N scaffold (complex 9) or separated from it by an ethylene linker (complex 10), putting in evidence the non-cytotoxic nature of the conjugates. In the case of complex 10, the long PNA chain can protect the Pt(II) core from external quenching oxygen, resulting in a Φlum > 0.37 even in the presence of air. This complex is particularly appealing for biomedicine. Azido complexes of Pt(II) such as 19 can find applications in photoactivated chemotherapy, for example, due to their potential ability to intercalate in DNA and to photorelease azidyl radicals able to damage cancer cells.
Our studies put in evidence that even N^C^N-platinum(II) complexes with a thiolate ancillary ligand can reach excellent luminescence properties. Thus, complex 11, with a 1-phenyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiolate ligand, is characterized by a high luminescence quantum yield both in a dilute dichloromethane solution (Φlum = 0.90) and in the solid state (Φlum = 0.62). The presence of the 1-phenyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiolate ligand plays an important role in inhibiting self-quenching intermolecular π–π stacking in the solid state, thus allowing this complex to reach large quantum yields. This new complex, characterized by an excellent solubility in organic solvents, which has already allowed the fabrication of convenient solution-processable OLEDs, opened the route to highly luminescent thiolate N^C^N-platinum(II) complexes.
In conclusion, during the last five years, our Milanese group, in collaboration with research groups in Durham, Rennes, Bologna, and Perugia, has made some important contributions to the design of novel N^C^N-platinum(II) complexes. We believe that there is a lot of room for new and enjoyable chemistry in this field for various applications such as electroluminescent devices and biomedicine. In particular, future work should be devoted to combining the presence of bulky substituents and electron-donor groups on the pyridines of N^C^N-platinum(II) complexes in order to reach not only true blue but also deep blue OLEDs. Another aspect that should be developed is the increase in their solubility in water, by the introduction of suitable substituents, in perspective of their application in biomedicine.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C., C.D., F.F., D.M., and D.R.; methodology, F.F. and D.R.; writing—original draft preparation, C.D., F.F., and D.R.; writing—review and editing, A.C., C.D., F.F., D.M., and D.R.; supervision, D.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
Our work is supported by the National Interuniversity Consortium of Materials Science and Technology and by the Università degli Studi di Milano. We deeply thank J.A. Gareth Williams (University of Durham, UK) for his qualified suggestions, scientific collaboration, and for helping us in getting in the field of N^C^N-platinum(II) complexes, Véronique Guerchais, Hubert Le Bozec, and Bertrand Carboni (Université de Rennes 1, CNRS, Institut des Sciences Chimiques de Rennes) and the Italian research groups of Simona Fantacci (Istituto di Scienze e Tecnologie Chimiche ‘‘Giulio Natta’’, CNR, Perugia), and Massimo Cocchi (Istituto per la Sintesi Organica e la Fotoreattività, CNR), Bologna) for scientific collaboration.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SOC | Spin–orbit coupling |
| NIR | Near infrared |
| OLED | Organic light-emitting diode |
| Φlum | Luminescence quantum yield |
| TD | Time-dependent |
| DFT | Density functional theory |
References
- Nalwa, H.S. Organometallic materials for nonlinear optics. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1991, 5, 349–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, N.J. Organometallic Compounds for Nonlinear Optics-The Search for En-light-enment! Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1995, 34, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bozec, H.; Renouard, T. Dipolar and Non-Dipolar Pyridine and Bipyridine Metal Complexes for Nonlinear Optics. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 2000, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bella, S.D. Second-order nonlinear optical properties of transition metal complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2001, 30, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzotti, M.; Ugo, R.; Roberto, D.; Bruni, S.; Fantucci, P.; Rovizzi, C. Organometallic Counterparts of Push−Pull Aromatic Chromophores for Nonlinear Optics: Push−Pull Heteronuclear Bimetallic Complexes with Pyrazine and trans -1,2-Bis(4-pyridyl)ethylene as Linkers. Organometallics 2002, 21, 5830–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, B.J.; Curati, N.R.M. Metal complexes for molecular electronics and photonics. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2004, 25, 147–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, C.E.; Humphrey, M.G. Nonlinear optical properties of transition metal acetylides and their derivatives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 725–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maury, O.; Le Bozec, H. Molecular Engineering of Octupolar NLO Molecules and Materials Based on Bipyridyl Metal Complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrall, J.P.; Dalton, G.T.; Humphrey, M.G.; Samoc, M. Organotransition metal complexes for nonlinear optics. Adv. Organomet. Chem. 2007, 55, 61–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Marinotto, D.; Righetto, S.; Roberto, D.; Tavazzi, S.; Escadeillas, M.; Guerchais, V.; Le Bozec, H.; Boucekkine, A.; et al. Cyclometalated 4-Styryl-2-phenylpyridine Platinum(II) Acetylacetonate Complexes as Second-Order NLO Building Blocks for SHG Active Polymeric Films. Organometallics 2013, 32, 3890–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, K.; Thirumoorthy, K.; Dragonetti, C.; Marinotto, D.; Righetto, S.; Colombo, A.; Haukka, M.; Palanisami, N. Ferrocene–quinoxaline Y-shaped chromophores as fascinating second-order NLO building blocks for long lasting highly active SHG polymeric films. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 11939–11943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Kaur, M.; Kaur, P.; Clays, K.; Singh, K. Ferrocene chromophores continue to inspire. Fine-tuning and switching of the second-order nonlinear optical response. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 343, 185–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, S.; Espa, D.; Artizzu, F.; Pilia, L.; Serpe, A.; Pizzotti, M.; Di Carlo, G.; Marchiò, L.; Deplano, P. Optically Multiresponsive Heteroleptic Platinum Dithiolene Complex with Proton-Switchable Properties. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 6763–6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, R.J.; Gauthier, S.; Achelle, S.; Groizard, T.; Kahlal, S.; Saillard, J.-Y.; Barsella, A.; Le Poul, N.; Robin Le Guena, F. Push–pull D–π-Ru–π-A chromophores: Synthesis and electrochemical, photophysical and second order nonlinear optical properties. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 3965–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attar, S.; Artizzu, F.; Marchik, L.; Espa, D.; Pilia, L.; Casula, M.F.; Serpe, A.; Pizzotti, M.; Orbelli Biroli, A.; Deplano, P. Uncommon Optical Properties and Silver-Responsive Turn-Off/On Luminescence in a PtII Heteroleptic Dithiolene Complex. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 10503–10512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagnani, F.; Colombo, A.; Malandrino, G.; Dragonetti, C.; Pellegrino, A.L. Luminescent 1,10-Phenanthroline β-Diketonate Europium Complexes with Large Second-Order Nonlinear Optical Properties. Molecules 2022, 27, 6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, S.; Fagnani, F.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Roberto, D.; Mathivathanan, L.; Palanisami, N. Effect of substitution on second-order nonlinear optical properties of ferrocene appended donor-π-acceptor Y-shaped trifluoromethyl imidazole chromophores. New J. Chem. 2024, 48, 14764–14772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Regan, B.; Grätzel, M. A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature 1991, 353, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vougioukalakis, G.C.; Philippopoulos, A.I.; Stergiopoulos, T.; Falaras, P. Contributions to the development of ruthenium-based sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2602–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragonetti, C.; Colombo, A.; Magni, M.; Mussini, P.; Nisic, F.; Roberto, D.; Ugo, R.; Valore, A.; Valsecchi, A.; Salvatori, P.; et al. Thiocyanate-Free Ruthenium(II) Sensitizer with a Pyrid-2-yltetrazolate Ligand for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 10723–10725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Roberto, D.; Valore, A.; Biagini, P.; Melchiorre, F. A simple copper(I) complex and its application in efficient dye sensitized solar cells. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2013, 407, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroni, M.; Favereau, L.; Planchat, A.; Akdas-Kilig, H.; Szuwarski, N.; Pellegrin, Y.; Blart, E.; Le Bozec, H.; Boujtita, M.; Odobel, F.J. Heteroleptic copper(I)–polypyridine complexes as efficient sensitizers for dye sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 9944–9947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malzner, F.J.; Prescimone, A.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Willgert, M. Exploring simple ancillary ligands in copper-based dye-sensitized solar cells: Effects of a heteroatom switch and of co-sensitization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4671–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, M.; Teuscher, J.; Saygili, Y.; Zhang, X.; Giordano, F.; Liska, P.; Hua, J.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Moser, J.-E.; Grätzel, M.; et al. Dye-sensitized solar cells for efficient power generation under ambient lighting. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, V.; Marchini, E.; Averardi, M.; Giorgini, L.; Muzzioli, S.; Dellai, A.; Argazzi, R.; Sanson, A.; Sangiorgi, N.; Caramori, S.; et al. New examples of Ru(ii)-tetrazolato complexes as thiocyanate-free sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 14543–14555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, N.; Agrawal, A.; Dhaka, V.S.; Surolia, P.K. Ruthenium complexes based dye sensitized solar cells: Fundamentals and research trends. Sol. Energy 2020, 207, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-García, A.B.; Benesperi, I.; Boschloo, G.; Concepcion, J.J.; Delcamp, J.H.; Gibson, E.A.; Meyer, G.J.; Pavone, M.; Pettersson, H.; Hagfeldt, A. Dye-sensitized solar cells strike back. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 12450–12550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housecroft, C.E.; Constable, E.C. Solar energy conversion using first row d-block metal coordination compound sensitizers and redox mediators. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 1225–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetouh, H.A.; Dissouky, A.E.; Salem, H.A.; Fathy, M.; Anis, B.; Kashyout, A.E.H. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of new alternative ruthenium complex for dye sensitized solar cells. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamovich, V.; Brooks, J.; Tamayo, A.; Alexander, A.M.; Djurovich, P.I.; D’Andrade, B.W.; Adachi, C.; Forrest, S.R.; Thompson, M.E. High efficiency single dopant white electrophosphorescent light emitting diodes. New J. Chem. 2002, 26, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotoyama, W.; Satoh, T.; Sawatari, N.; Inoue, H. Efficient organic light-emitting diodes with phosphorescent platinum complexes containing N^C^N-coordinating tridentate ligand. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 153505–153507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocchi, M.; Virgili, D.; Fattori, V.; Rochester, D.L.; Williams, J.A.G. N^C^N-Coordinated Platinum(II) Complexes as Phosphorescent Emitters in High-Performance Organic Light-Emitting Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.Y.; Ho, C.L. Heavy metal organometallic electrophosphors derived from multi-component chromophores. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 253, 1709–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.M.; Kwok, C.C.; Lai, S.W.; Rausch, A.F.; Finkenzeller, W.J.; Zhu, N.Y.; Yersin, H. Photophysical properties and OLED applications of phosphorescent platinum (II) Schiff base complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Ho, C.-L.; Wong, W.-Y.; Ma, D.; Wang, L.; Line, Z. Metallophosphors of platinum with distinct main-group elements: A versatile approach towards color tuning and white-light emission with superior efficiency/color quality/brightness trade-offs. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7472–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocchi, M.; Kalinowski, J.; Murphy, L.; Williams, J.A.G.; Fattori, V. Mixing of molecular exciton and excimer phosphorescence to tune color and efficiency of organic LEDs. Org. Electron. 2010, 11, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, J.; Fattori, V.; Cocchi, M.; Williams, J.A.G. Light-emitting devices based on organometallic platinum complexes as emitters. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2401–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildea, L.F.; Williams, J.A.G. Iridium and platinum complexes for OLEDs. In Organic Light-Emitting Diodes: Materials, Devices and Applications; Buckley, A., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013; ISBN 9780857094254. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yao, C.; Zhou, G. Highly Efficient Phosphorescent Materials Based on Platinum Complexes and Their Application in Organic Light-Emitting Devices (OLEDs). Platin. Met. Rev. 2013, 57, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, C.; Mauro, M. Recent advances in phosphorescent platinum complexes for organic light-emitting diodes. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 1459–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Guo, H.; Xu, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, G.; Ma, W.; Wu, Z. Enhancing Molecular Aggregations by Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonds to Develop Phosphorescent Emitters for High-Performance Near-Infrared OLEDs. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-C.; Sukpattanacharoen, C.; Chan, W.-H.; Huang, C.-C.; Hsu, H.-F.; Shen, D.; Hung, W.-Y.; Kungwan, N.; Escudero, D.; Lee, C.-S.; et al. Modulation of Solid-State Aggregation of Square-Planar Pt(II) Based Emitters: Enabling Highly Efficient Deep-Red/Near Infrared Electroluminescence. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.-C.; Wang, S.F.; Hu, Y.; Liao, L.-S.; Chen, D.-G.; Chang, K.-H.; Wang, C.-W.; Liu, S.-H.; Chan, W.-H.; Liao, J.-L.; et al. Overcoming the energy gap law in near-infrared OLEDs by exciton–vibration decoupling. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-F.; Su, B.-K.; Wang, X.-Q.; Wei, Y.-C.; Kuo, K.-H.; Wang, C.-H.; Liu, S.-H.; Liao, L.-S.; Hung, W.-Y.; Fu, L.-W.; et al. Polyatomic molecules with emission quantum yields >20% enable efficient organic light-emitting diodes in the NIR(II) window. Nat. Photonics 2022, 16, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housecroft, C.E.; Constable, E.C. TADF: Enabling luminescent copper(i) coordination compounds for light-emitting electrochemical cells. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 4456–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; El Moll, H.; Alenezi, K.M.; Khan, M.S.; Wong, W.Y. Functional Materials Based on Cyclometalated Platinum(II) β-Diketonate Complexes: A Review of Structure–Property Relationships and Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, A.S.-Y.; Yeung, M.C.-L.; Yam, V.W.-W. Arginine-Rich Peptide-Induced Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Water-Soluble Anionic Alkynylplatinum(II) Complexes: A Continuous and Label-Free Luminescence Assay for Trypsin and Inhibitor Screening. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 41143–41150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.Y.; Jin, G.Q.; Wang, M.X.; Gao, S.; Zhang, J.L. Recent progress in metal-based molecular probes for optical bioimaging and biosensing. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2022, 66, 102097–102107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minozzi, C.; Caron, A.; Grenier-Petel, J.-C.; Santandrea, J.; Collins, S.K. Heteroleptic Copper(I)-Based Complexes for Photocatalysis: Combinatorial Assembly, Discovery, and Optimization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5477–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, M.; Qi, R.; Shang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, R.; Xu, Z. Visible-Light-Driven, Copper-Catalyzed Decarboxylative C(sp3)−H Alkylation of Glycine and Peptides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15841–15846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Saito, K.; Matsukawa, H.; Yanagida, S.; Ebina, M.; Maegawa, Y.; Inagaki, S.; Kobayashi, A.; Kato, M. Immobilization of luminescent Platinum(II) complexes on periodic mesoporous organosilica and their water reduction photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2018, 358, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Sánchez, A.; Domingo-Legarda, P.; Cabrera, S.; Alemán, J. Visible light photocatalytic asymmetric synthesis of pyrrolo[1,2-a]indoles via intermolecular [3+2] cycloaddition. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 11303–11306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Zhou, B.; Luo, S.P.; Xu, Z.; Jin, H.; Liu, Y. P/N Heteroleptic Cu(I)-Photosensitizer-Catalyzed Deoxygenative Radical Alkylation of Aromatic Alkynes with Alkyl Aldehydes Using Dipropylamine as a Traceless Linker Agent. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 7563–7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Legarda, P.; Casado-Sánchez, A.; Marzo, L.; Alemán, J.; Cabrera, S. Photocatalytic Water-Soluble Cationic Platinum(II) Complexes Bearing Quinolinate and Phosphine Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 13845–13857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neerathilingam, N.; Prasanth, K.; Anandhan, R. Substituent-controlled selective synthesis of 1,2-diketones and internal alkynes from terminal alkynes and arylboronic acids via α-stilbene radicals obtained from heteroleptic Cu(I) complexes under visible light. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 8685–8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez de Segura, D.; Corral-Zorzano, A.; Alcolea, E.; Moreno, M.T.; Lalinde, E. Phenylbenzothiazole-Based Platinum(II) and Diplatinum(II) and (III) Complexes with Pyrazolate Groups: Optical Properties and Photocatalysis. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 1589–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Huang, C.; Li, F. Phosphorescent heavy-metal complexes for bioimaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2508–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggaley, E.; Weinstein, J.A.; Williams, J.A.G. Lighting the way to see inside the live cell with luminescent transition metal complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 1762–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggaley, E.; Botchway, S.W.; Haycock, J.W.; Morris, H.; Sazanovich, I.V.; Williams, J.A.G.; Weinstein, J.A. Long-lived metal complexes open up microsecond lifetime imaging microscopy under multiphoton excitation: From FLIM to PLIM and beyond. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, M.; Aliprandi, A.; Septiadi, D.; Kehr, N.S.; De Cola, L. When self-assembly meets biology: Luminescent platinum complexes for imaging applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4144–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.C.-C.; Lo, K.K.-W. Shining New Light on Biological Systems: Luminescent Transition Metal Complexes for Bioimaging and Biosensing Applications. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 8825–9014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, K.; Lyons, C.E.; Hartman, M.C.T. A platinum(II) complex of heptamethine cyanine for photoenhanced cytotoxicity and cellular imaging in near-IR light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10263–10267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yam, V.W.-W.; Law, A.S.-Y. Luminescent d8 metal complexes of platinum(II) and gold(III): From photophysics to photofunctional materials and probes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 414, 213298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, A.S.-Y.; Lee, L.C.-C.; Lo, K.K.-W.; Yam, V.W.-W. Aggregation and supramolecular self-assembly of low-energy red luminescent alkynylplatinum(II) complexes for RNA detection, nucleolus imaging, and RNA synthesis inhibitor screening. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 5396–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Chan, M.H.-Y.; Pan, M.; Li, Y.; Yam, V.W.-W. Supramolecular Assembly of Organoplatinum(II) Complexes for Subcellular Distribution and Cell Viability Monitoring with Differentiated Imaging. Angew. Chem. 2022, 61, e202210703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Ye, R.; Law, A.S.-Y.; Mao, Z.-W.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Yam, V.W.-W. Rational design of platinum(II) complexes with orthogonally oriented triazolyl ligand with emission enhancement characteristics for cancer chemotherapy in vivo. Sci. China 2023, 66, 2878–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrones Reyes, J.; Sherin, P.S.; Sarkar, A.; Kuimova, M.K.; Vilar, R. Platinum(II)-based optical probes for imaging quadruplex DNA structures via phosphorescence lifetime imaging microscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202310402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Xu, B.; Xu, Y.; Yue, L.; Chen, J.; Xie, G.; Zhao, J. Reblooming of the cis-bis(2-phenylpyridine) platinum(II) complex: Synthesis updating, aggregation-induced emission, electroluminescence, and cell imaging. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 19142–19152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, E.; Ramadurai, S.; Needham, S.R.; Baker, K.; Eastwood, T.A.; Weinstein, J.A.; Mulvihill, D.P.; Botchway, S.W. Fluorescence and phosphorescence lifetime imaging reveals a significant cell nuclear viscosity and refractive index changes upon DNA damage. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, R.E.; Sazanovich, I.V.; McKenzie, L.K.; Stasheuski, A.S.; Coyle, R.; Baggaley, E.; Bottomley, S.; Weinstein, J.A.; Bryant, H.E. Photodynamic killing of cancer cells by a platinum(II) complex with cyclometallating ligand. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzisideri, T.; Thysiadis, S.; Katsamakas, S.; Dalezis, P.; Sigala, I.; Lazarides, T.; Nikolakaki, E.; Trafalis, D.; Gederaas, O.A.; Lindgren, M.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a platinum(II)-c(RGDyK) conjugate for integrin-targeted photodynamic therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 141, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Clarkson, G.J.; Sadler, P.J. Dual action photosensitive platinum(II) anticancer prodrugs with photoreleasable azide ligands. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2019, 489, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, L.K.; Bryant, H.E.; Weinstein, J.A. Transition metal complexes as photosensitisers in one- and two-photon photodynamic therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 379, 2–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoditti, S.; Dabbish, E.; Russo, N.; Mazzone, G.; Sicilia, E. Anticancer activity, DNA binding, and photodynamic properties of a NˆCˆN-coordinated Pt(II) complex. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 10350–10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Soricellis, G.; Fagnani, F.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Roberto, D. Exploring the potential of NˆCˆN cyclometalated Pt(II) complexes bearing 1,3-di(2-pyridyl)benzene derivatives for imaging and photodynamic therapy. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2022, 541, 121082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Nepalia, A.; Bera, A.; Saini, D.K.; Chakravarty, A.R. A Platinum(II) boron-dipyrromethene complex for cellular imaging and mitochondria-targeted photodynamic therapy in red light. Chem. Asian J. 2023, 18, e202300667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, D.J.; Echavarren, A.M.; Ramirez de Arellano, M.C. Divergent Behavior of Palladium(II) and Platinum(II) in the Metalation of 1,3-Di(2-pyridyl)benzene. Organometallics 1999, 18, 3337–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A.G.; Beeby, A.; Davies, S.; Weinstein, J.A.; Wilson, C. An Alternative Route to Highly Luminescent Platinum(II) Complexes: Cyclometalation with N-C-N-Coordinating Dipyridylbenzene Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 8609–8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A.G. Photophysics and photochemistry of coordination compounds: Platinum. Top. Curr. Chem. 2007, 281, 205–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A.G. The coordination chemistry of dipyridylbenzene: N-deficient terpyridine or panacea for brightly luminescent metal complexes? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1783–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochester, D.L.; Develay, S.; Zális, S.; Williams, J.A.G. Localised to intraligand charge-transfer states in cyclometalated platinum complexes: An experimental and theoretical study into the influence of electron-rich pendants and modulation of excited states by ion binding. Dalton Trans. 2009, 1728–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotoyama, W.; Satoh, T.; Sato, H.; Matsuura, A.; Sawatari, N. Excited States of Phosphorescent Platinum(II) Complexes Containing N∧C∧N-Coordinating Tridentate Ligands: Spectroscopic Investigations and Time-Dependent Density Functional Theory Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 9760–9766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pander, P.; Zaytsev, A.V.; Sil, A.; Williams, J.A.G.; Lanoe, P.-H.; Kozhevnikov, V.N.; Dias, F.B. The role of dinuclearity in promoting thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) in cyclometallated, N^C^N-coordinated platinum(II) complexes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 10276–10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Turner, E.; Mahoney, V.; Madakuni, S.; Groy, T.; Li, J. Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Phosphorescent Pt(N∧C∧N)X Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 11276–11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarran, W.A.; Freeman, G.R.; Murphy, L.; Benham, A.M.; Kataky, R.; Williams, J.A.G. Platinum(II) Complexes of N^C^N-Coordinating 1,3-Bis(2-pyridyl)benzene Ligands: Thiolate Coligands Lead to Strong Red Luminescence from Charge-Transfer States. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 5738–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, W.; Che, C.-M. Luminescent Pincer-Type Cyclometalated Platinum(II) Complexes with Auxiliary Isocyanide Ligands: Phase-Transfer Preparation, Solvatomorphism, and Self-Aggregation. Organometallics 2013, 32, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, J.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yamawaki, K.; Yasuda, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Kanbara, T. Modulation of the Emission Mode of a Pt(II) Complex via Intermolecular Interactions. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 8726–8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Yamawaki, K.; Kimura, T.; Kuwabara, J.; Yasuda, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Kanbara, T. Multi-molecular emission of a cationic Pt(II) complex through hydrogen bonding interactions. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 4087–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pander, P.; Zaytsev, A.V.; Sil, A.; Williams, J.A.G.; Kozhevnikov, V.N.; Dias, F.B. Enhancement of thermally activated delayed fluorescence properties by substitution of ancillary halogen in a multiple resonance-like diplatinum(II) complex. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 4851–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Kong, X.; Yang, F.; Bian, H.-D.; Cheng, G.; Cook, T.R.; Zhang, Y. Deep Blue Phosphorescence from Platinum Complexes Featuring Cyclometalated N-Pyridyl Carbazole Ligands with Monocarborane Clusters (CB11H12−). Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 16707–16717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maganti, T.; Venkatesan, K. The Search for Efficient True Blue and Deep Blue Emitters: An Overview of Platinum Carbene Acetylide Complexes. ChemPlusChem 2022, 87, e202200014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Y.H.; Dang, V.Q.; Soares, J.V.; Wu, J.I.; Teets, T.S. Efficient blue-phosphorescent trans-bis(acyclic diaminocarbene) platinum(II) acetylide complexes. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 4857–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, A.F.; Murphy, L.; Williams, J.A.G.; Yersin, H. Improving the Performance of Pt(II) Complexes for Blue Light Emission by Enhancing the Molecular Rigidity. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, L.; Brulatti, P.; Fattori, V.; Cocchi, M.; Williams, J.A.G. Blue-shifting the monomer and excimer phosphorescence of tridentate cyclometallated platinum(II) complexes for optimal white-light OLEDs. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5817–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, S.J.; Rochester, D.L.; Thompson, A.L.; Howard, J.A.K.; Williams, J.A.G. Controlling Emission Energy, Self- Quenching, and Excimer Formation in Highly Luminescent N^C^N-Coordinated Platinum(II) Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 9690–9703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Soricellis, G.; Carboni, B.; Guerchais, V.; Williams, J.A.G.; Marinotto, D.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Fagnani, F.; Fantacci, S.; Roberto, D. New members of the family of highly luminescent 1,3-bis(4-phenylpyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluorobenzene platinum(II) complexes: Exploring the effect of substituents on the 4-phenylpyridine unit. Dalton Trans. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Soricellis, G.; Guerchais, V.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Fagnani, F.; Roberto, D.; Marinotto, D. Effect of the substitution of the mesityl group with other bulky substituents on the luminescence performance of [Pt(1,3-bis(4-mesityl-pyridin-2-yl)-4,6-difluoro-benzene)Cl]. Molecules 2025, 30, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.; De Soricellis, G.; Dragonetti, C.; Fagnani, F.; Roberto, D.; Carboni, B.; Guerchais, V.; Roisnel, T.; Cocchi, M.; Fantacci, S.; et al. Introduction of a mesityl substituent on pyridyl rings as a facile strategy for improving the performance of luminescent 1,3-bis-(2-pyridyl)benzene platinum(ii) complexes: A springboard for blue OLEDs. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 9702–9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.; De Soricellis, G.; Fagnani, F.; Dragonetti, C.; Cocchi, M.; Carboni, B.; Guerchais, V.; Marinotto, D. Introduction of a triphenylamine substituent on pyridyl rings as a springboard for a new appealing brightly luminescent 1,3-di-(2-pyridyl)benzene platinum(II) complex family. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 12161–12169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Acqua, R.M.; Fagnani, F.; Wojciechowska, M.; Marinotto, D.; Colombo, G.; Dalle-Donne, I.; Trylska, J.; Cauteruccio, S.; Colombo, A. Highly phosphorescent N^C^N platinum(ii)-peptide nucleic acid conjugates: Synthesis, photophysical studies and hybridization behaviour. Dalton Trans. 2025, 54, 3314–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragonetti, C.; Fagnani, F.; Marinotto, D.; di Biase, A.; Roberto, D.; Cocchi, M.; Fantacci, S.; Colombo, A. First member of an appealing class of cyclometalated 1,3-di-(2-pyridyl)benzene platinum(II) complexes for solution-processable OLEDs. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 7873–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagnani, F.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Roberto, D.; Marinotto, D. The intriguing effect of thiolates as co-ligands in platinum(II) complexes bearing a cyclometalated 1,3-di(2-pyridyl)benzene. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2022, 532, 120744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, D.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Fagnani, F.; Cocchi, M.; Marinotto, D. A Novel Class of Cyclometalated Platinum(II) Complexes for Solution-Processable OLEDs. Molecules 2022, 27, 5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagnani, F.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Roberto, D.; Marinotto, D. New members of a class of cyclometalated 1,3-di-(2-pyridyl)benzene platinum(II) complexes bearing a tetrazole-thiolate ancillary ligand. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2023, 550, 121446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Mawamba, V.; Schulz, E.; Löhr, M.; Hagemann, C.; Schatzschneider, U. IClick Reactions of Square-Planar Palladium(II) and Platinum(II) Azido Complexes with Electron-Poor Alkynes: Metal-Dependent Preference for N1 vs N2 Triazolate Coordination and Kinetic Studies with 1H and 19F NMR Spectroscopy. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 11508–11521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Moreth, D.; Schatzschneider, U. CNN Coordination Accelerates the iClick Reaction of Square-Planar Palladium(II) and Platinum(II) Azido Complexes with Electron-Poor Alkynes and Enables Cycloaddition with Terminal Alkynes. Organometallics 2021, 40, 2584–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagnani, F.; De Soricellis, G.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Roberto, D.; di Biase, A.; Fantacci, S.; Marinotto, D. Photophysical investigation of highly phosphorescent N^C^N platinum(II) azido complexes and their triazole derivatives. Dye. Pigment. 2024, 225, 112064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Fagnani, F.; Roberto, D.; Guerchais, V.; Roisnel, T.; Fantacci, S.; Marinotto, D. Multifunctional Organometallic Compounds: An Interesting Luminescent NLO-Active Alkynylplatinum (II) Complex. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 27, e202400478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).