Abstract
The synthesis of a series of six chloro[N-alkyl-N-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) complexes was successfully achieved, wherein allyl (3a), methoxymethyl (3b), benzyl (3c), 3-fluorobenzyl (3d), 4-fluorobenzyl (3e) and 4-methyl-benzyl (3f) substituents were grafted on the benzimidazole ring. The isolated silver N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complexes were identified by microanalyses and mass spectrometry and characterized by FT-IR and NMR spectroscopic techniques. Conclusive evidence for the structures of complexes 3c and 3d was provided by single-crystal X-ray crystallography. The in vitro inhibitory activity of the six Ag-NHC complexes was tested against trophozoites and cysts of the pathogenic Acanthamoeba castellanii strain and the efficacy sequence is as follows: 3d > 3c > 3f > 3a > 3b > 3e. At a concentration of 100 µM in complexes 3c, 3d and 3f and after 72 h of incubation, 5.3, 3.2 and 6.3% A. castellanii trophozoite viabilities were observed, respectively. The utilization of elevated silver(I) drug concentrations, 1000 µM, resulted in the near-total eradication of pathogenic protozoa.
1. Introduction
Acanthamoeba spp. are free-living amoebae that are widely distributed in soil, freshwater, and the air [1,2]. Some species have been identified as opportunistic human pathogens. These protozoa can cause severe infections, including Acanthamoeba keratitis (AK), which is a painful corneal disease and granulomatous amoebic encephalitis, which is a typically fatal infection of the central nervous system occurring in immunocompromised individuals [3,4,5]. Acanthamoeba species exhibit a biphasic life cycle, characterized by the alternating phase between a metabolically active trophozoite stage and a dormant cyst stage. The latter stage is distinguished by its resilience to environmental stress and therapeutic agents. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that both stages are capable of initiating infection [2,4].
AK has been identified as the most prevalent disease caused by Acanthamoeba. It primarily affects contact lens wearers, particularly those with corneal microtrauma or poor lens care practices, such as inadequate cleaning or exposure to contaminated water during activities like swimming or showering. The clinical manifestations include severe ocular pain, conjunctival hyperaemia, blurred vision, photophobia, and a foreign body sensation in the eye. Given the non-specific nature of these symptoms, they frequently masquerade as other forms of keratitis. This underscores the critical importance of a prompt and accurate diagnosis to avert severe consequences. In the absence of intervention, AK has the potential to escalate to a state of corneal ulceration, which may consequently lead to irreversible visual impairment or even total blindness [6,7,8,9].
Presently, there is an absence of an FDA-approved standard treatment protocol for AK. Treatment regimens generally consist of prolonged therapeutic interventions that incorporate topical antiseptics, such as polyhexamethylene biguanide and chlorhexidine, in combination with antimicrobials, including diamidines and azoles. Notwithstanding these therapeutic regimens, the degree of therapeutic success remains limited, and recurrence is not uncommon. Moreover, the majority of commercial contact lens disinfectants demonstrate an absence of amoebicidal activity against Acanthamoeba, thereby increasing the risk of infection for lens wearers [10,11,12]. These challenges underscore the pressing need to develop more effective, targeted therapeutic strategies for AK [13,14].
The exploration of organometallic compounds as potential drug candidates has emerged as a promising field within the bioinorganic chemistry [15,16]. Among these compounds, metal-N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complexes have attracted considerable attention in synthetic chemistry [17,18,19]. The introduction of NHCs into organometallic chemistry is attributed to Fischer in 1964. However, it was not until 1991 that a free NHC was successfully isolated, despite the existence of early reports of NHC metal complexes dating back to 1968 [20,21,22,23,24]. NHCs are distinguished by their robust stability, which is attributed to the coordination of two nitrogen atoms in close proximity, enabling them to form strong bonds with transition metals [25]. The bonding interactions between NHC ligands and metal centers are shaped by a combination of steric and electronic effects [26]. Initially, it was hypothesized that NHC complexes function exclusively as σ-donors. However, subsequent research has revealed a more intricate nature of these interactions. The inherent stability of NHCs, in conjunction with their facile synthesis, has resulted in their extensive utilization in the domain of coordination chemistry. Among metal-NHC complexes, Ag-NHC complexes are notable for their biological properties [27,28,29,30].
While biguanides, diamidines, and azoles have demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of Acanthamoeba, limitations such as prolonged treatment durations, toxicity to human corneal cells, and incomplete cyst eradication have prompted the exploration of novel agents [10,12]. Silver-based compounds, including silver nitrate, silver sulfadiazine, and silver acetate, have been recognized for their antimicrobial properties for a considerable duration. These compounds have been employed as effective microbiocidal agents for millennia [31,32,33,34]. Furthermore, studies have demonstrated the efficacy of silver nanoparticles in combating Acanthamoeba [35,36,37]. Notably, silver compounds exhibit minimal toxicity toward human cells, particularly mammalian cell membranes.
To date, and to the best of our knowledge, there has been no report of research on the use of silver-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes against A. castellanii. In the present article, we report on the synthesis of six chloro[N-alkyl-N-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) complexes, 3a–f (Figure 1), and their in vitro tests against A. castellanii.
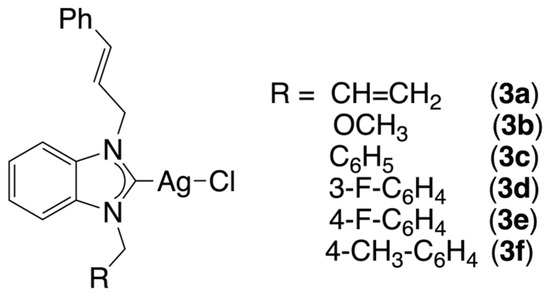
Figure 1.
Silver complexes 3a–f tested against Acanthamoeba castellanii in the present study.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Silver Complexes
Six silver(I) complexes (3a-f), namely chloro[1-cinnamyl-3-allyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3a), chloro[1-methoxymethyl-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3b), chloro[1-benzyl-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3c), chloro[1-(3-fluorobenzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3d), chloro[1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3e) and chloro[1-(4-methyl-benzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-ylidene]silver(I) (3f), were obtained in satisfactory yields (33–86%) from a reaction of Ag2O with the benzimidazolium salt (1a–f) in dichloromethane for 24 h at room temperature, with the reaction protected from light by aluminum foil (Scheme 1). The benzimidazolium salts 1a–f were previously prepared by alkylation of 1-cinnamyl-benzimidazole (2) and aryl chloride. Note that the alkyl substituents grafted on the benzimidazole only slightly modify the σ-donor properties of the N-heterocyclic carbenes. Indeed, the 1JCH constants demonstrate minimal variability within the range of 220–225 Hz (Table 1). This finding indicates that these ligands exhibit weak σ-donor properties, which are comparable to those of 1,3-dicyclohexyl-imidazolium salt [38].
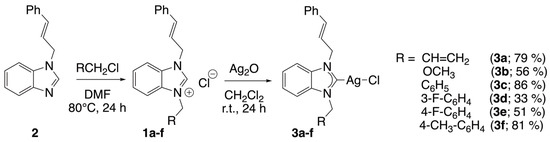
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of silver complexes 3a–f.

Table 1.
Spectroscopic data of silver(I) complexes 3a–f and their corresponding benzimidazolium salts 1a–f.
The silver(I) complexes demonstrated stability in the presence of air and moisture; however, they exhibited sensitivity to light. In the dark, these complexes remained stable in solution of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for at least three days. The characterization of the inorganic samples was performed using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H, 13C{1H}, and 19F{1H} NMR) and mass spectrometry (see the experimental section, Supplementary Materials and Table 1).
The benzimidazolium salts 1a–f exhibited a distinctive ν(CN) band within the FT-IR spectra, with a frequency range of 1556–1562 cm−1. Following the formation of silver complexes, no peaks were detected in this region, and a downshift was observed for the ν(CN) bands (1379–1394 cm−1). These values are in agreement with those previously observed by Panda, Ghosh and co-workers in the chloro[1-benzyl-3-tert-butylimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) complex (ν(CN) at 1375 cm−1) [40]. The observed change in stretching frequency can be attributed to a weakening of the CN bond, which becomes a partial double bond after coordination. This assertion is supported by the X-ray structures of two complexes (vide infra), in which the distances of carbon-nitrogen bonds are longer than that of a C=N bond (Table 1).
A thorough analysis of the 1H NMR spectra of the silver-NHC complexes (3a–f) revealed the absence of the downfield-shifted resonance (δ = 10.07–12.17 ppm) of the acid proton (NCHN) from the spectra of the N-heterocyclic carbene precursor salts, indicative of deprotonation of the benzimidazolium carbene. In the 13C{1H} NMR spectra of these salts, the signals from the carbon atom between the two nitrogen atoms (NCHN), present in the 142.71–144.26 ppm range, undergo significant deshielding after coordination to the silver atom. The analysis of the spectra of the complexes reveals the presence of NC(Ag)N carbon peaks in the 188.49–189.04 ppm range for 3a, 3d and 3e. As is the case with numerous silver(I) complexes, the signal in question could not be observed in the case of complexes 3b, 3c and 3f [41]. During the coordination step, the trans conformation of the double bond of the cinnamyl substituent remains unchanged, the coupling constant between the two protons of the double bond is approximately 16 Hz (Table 1).
A detailed analysis of the mass spectra of the six silver(I) complexes confirmed the successful formation of the desired complexes. Each organometallic compound displays a peak that corresponds to the cations [M − Cl]+ at m/z = 481.05, 385.05, 431.06 and 445.08 for complexes 3a, 3b, 3c and 3f, respectively and/or [M − Cl + CH3CN]+ at m/z = 422.07, 472.08, 490.08, 490.10 and 486.11 for complexes 3a, 3c, 3d, 3e and 3f, respectively, with the expected isotopic profiles.
2.2. Single-Crystal X-Ray Diffraction Studies
The formation of a silver(I) complex of the (NHC)Ag-Cl type was confirmed through two single-crystal X-ray diffraction studies of complexes 3c and 3d. The complexes exhibit centrosymmetric crystallization in the P triclinic space group, with the center of inversion situated at the midpoint of the [Ag2Cl2] bridge core.
The formation of dimers is achieved through the establishment of an additional Ag–Cl bond (Ag1–Cl1a of 2.968(3) and 2.9320(6) Å for complexes 3c and 3d, respectively), which are substantially longer than the direct Ag1–Cl1 bond (Ag1–Cl1 of 2.3854(13) and 2.3972(5) Å for complexes 3c and 3d, respectively) (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Dimer formation is frequently observed during the crystallization of (NHC)Ag-Cl complexes, as evidenced in chloro[1-(9-acridinyl)-3-methylimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) [42] or chloro[1-(N,N-diethylcarbamoylmethyl)-3-mesitylimidazol-2-ylidene]silver(I) [43] complexes.
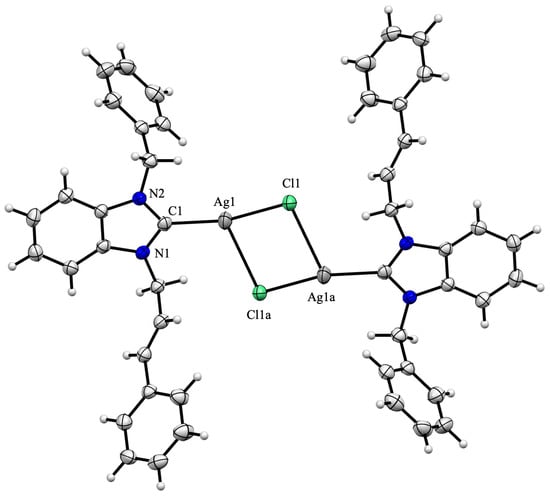
Figure 2.
Molecular structure of silver(I) complex 3c. The ORTEP drawing, with 50% probability thermal ellipsoid, shows the atom labelling. Important bond lengths (Å) and angles (°): Ag1-Cl1 2.3854(13), Ag1-Cl1a 2.968(3), Ag1-C1 2.096(3), N1-C1 1.350(4), N1-C2, 1.396(3), C1-Ag1-Cl1 163.55(7), Cl1-Ag1-Cl1a 86.49(6), Cl1a-Ag1-C1 109.24(9), N1-C1-Ag1 128.69(19), Ag1-C1-N2 125.1(2) and N2-C1-N1 105.7(2).
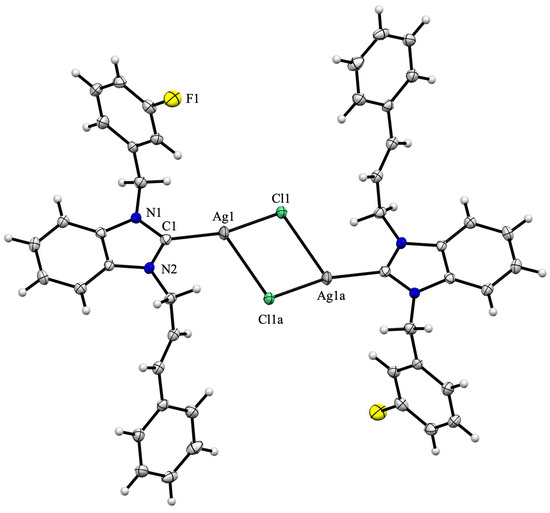
Figure 3.
Molecular structure of silver(I) complex 3d. The ORTEP drawing, with 50% probability thermal ellipsoid, shows the atom labelling. Important bond lengths (Å) and angles (°): Ag1-Cl1 2.3972(5), Ag1-Cl1a 2.9320(6), Ag1-C1 2.102(2), N1-C1 1.364(3), N1-C2, 1.355(3), C1-Ag1-Cl1 162.33(6), Cl1-Ag1-Cl1a 86.06(2), Cl1a-Ag1-C1 110.52(6), N1-C1-Ag1 125.43(15), Ag1-C1-N2 128.48(15) and N2-C1-N1 105.58(18).
The Ccarbene-Ag-Cl alignment is angled (C1-Ag1-Cl1 163.55(7) and 162.33(6)° for complexes 3c and 3d, respectively), and due to dimer formation, the Ag2Cl2 moiety is out of the plane of the benzimidazole ring, resulting in dihedral angles of 12.5 and 14.6° for complexes 3c and 3d, respectively. The Ag1-Cl1 (2.3854(13) and 2.3972(5) Å for complexes 3c and 3d, respectively) and Ag1-C1 distances (2.096(3) and 2.102(2) for complexes 3c and 3d, respectively) are within the usual range [44,45]. The two aromatic rings, which correspond to the cinnamyl and benzyl/3-fluorobenzyl substituents, are inclined toward the benzimidazole moiety, forming dihedral angles of 79.3/64.1° and 64.6/79.8°, respectively.
2.3. In Vitro Evaluation of Acanthamoeba castellanii
2.3.1. Effect on A. castellanii Trophozoites
The antiamoebic activities of the six silver(I) complexes (3a–f), the six benzimidazolium salts (1a–f), AgNO3, and Ag2O were evaluated against A. castellanii trophozoites after 24, 48 or 72 h of incubation at concentrations of 10, 100 or 1000 µM (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
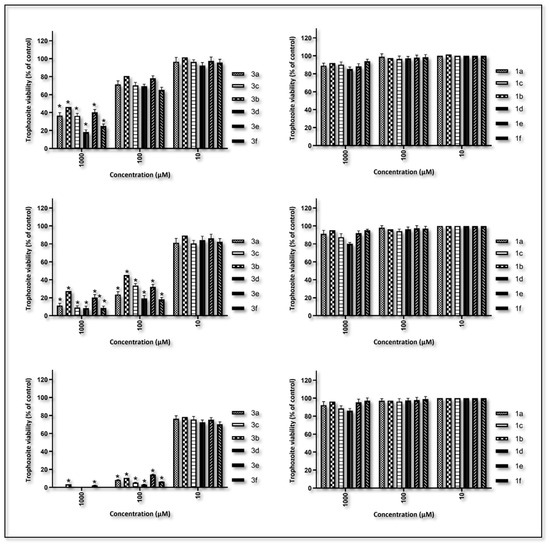
Figure 4.
The viability of trophozoites at concentrations of 1000, 100 and 10 µM against the silver(I) complex (3a–f) and the benzimidazolium salts (1a–f) was assessed after 24, 48 and 72 h against the pathogenic A. castellanii. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of four independent experiments (* p < 0.05 vs. control).
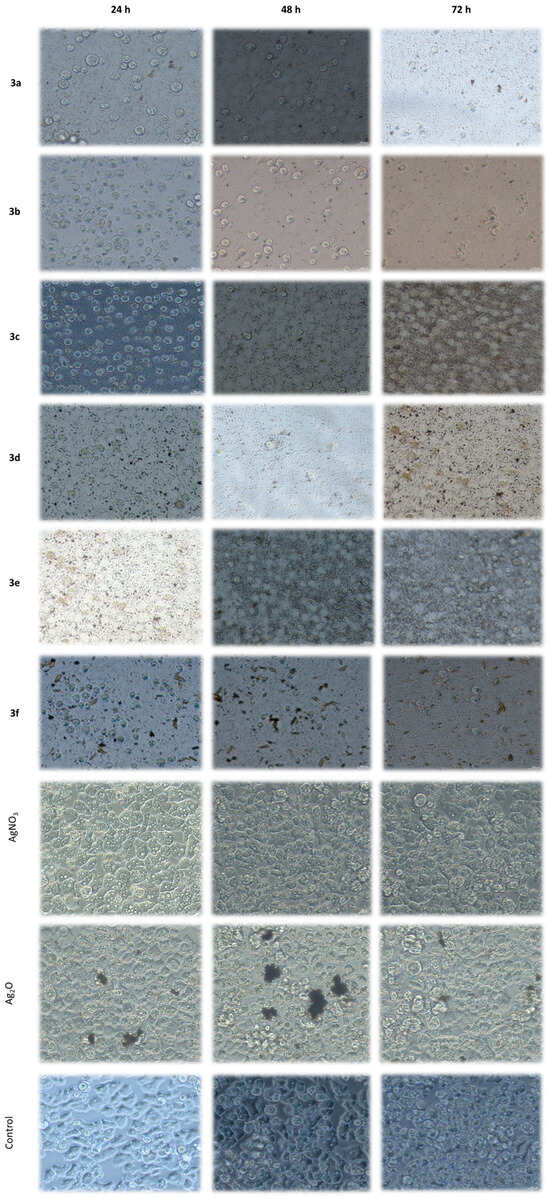
Figure 5.
Inverted microscope images showing the viability of A. castellanii trophozoites treated with 1000 µM concentrations of silver(I) complexes (3a–f), AgNO3 and Ag2O after 24, 48 and 72 h (magnification: 200×).
A significant decrease in trophozoite viability was observed to be time- and concentration-dependent. The silver(I) complexes 3a–f exhibited significantly higher antiamoebic activities than their corresponding benzimidazolium salts (1a–f). At the highest concentration (1000 µM), all complexes demonstrated strong trophozoite-killing effects within 24 h. Complexes 3a, 3c, 3d and 3f completely eliminated trophozoite viability within 72 h. The residual viability in the 3b and 3e treatments was 3.4 and 2.2%, respectively (p < 0.05). In contrast, the corresponding carbene precursor salts exhibited only minimal inhibition at this concentration, with no statistically significant reduction in viability compared with the control group.
Overall, efficacy was reduced at 100 µM, but a similar trend was observed. Complexes 3c, 3d and 3f exhibited significant activity, with 5.3, 3.2 and 6.3% trophozoite viability, respectively, recorded after 72 h (p < 0.05). Ligands at the same concentration did not demonstrate any inhibitory effects. At the lowest tested concentration (10 µM), the complexes displayed minimal activities. All ligands yielded viability rates comparable to those of the untreated control group.
As illustrated in Figure 4, the efficacy of silver(I) complexes 3a–f against A. castellanii exhibits variation in the following sequence: 3d > 3c > 3f > 3a > 3b > 3e. This sequence provides compelling evidence that the lipophilicity [46,47] of the silver(I) complexes does not significantly impact the efficacy of these drugs. In fact, the two complexes with the lowest calculated logP [48] (complexes 3a and 3b with logP of 3.99 and 3.42, respectively; Table 2) are the least effective against A. castellanii. This observation underscores the pivotal function of the arylmethyl substituent grafted on to the N-heterocyclic carbene. The nature (H, F or CH3) and position (meta or para) of the substituent carried on this aromatic cycle are also of crucial importance. Indeed, the 3d complex, which contains a fluorine atom in the meta position of the benzylic substituent, exhibits higher reactivity compared with its less polar 3e counterpart, which possesses the fluorine atom in para position on the aromatic ring.

Table 2.
Calculated logP [48] for silver(I) complexes 3a–f.
A study was conducted to ascertain the impact of AgNO3 and Ag2O on trophozoite viability. The study encompassed all concentrations and exposure times to ensure a comprehensive investigation. The findings indicate that neither compound exhibited a statistically significant reduction in trophozoite viability compared with untreated controls. Morphological evaluations substantiated these findings, disclosing the absence of cytopathic effects or aberrations from the conventional structure and motility of viable trophozoites (see Figure 5). The findings suggest that the silver salts examined were ineffective against Acanthamoeba trophozoites under these conditions, thereby emphasizing the enhanced efficacy and selectivity of the silver(I) complexes described in the present study.
2.3.2. Effect on A. castellanii Cysts
Following a 72 h observation period, no excystation or trophozoite formation was detected in cysts treated with complexes 3a, 3c, 3d or 3f at the highest tested concentration (1000 µM). This finding suggests the complete cysticidal activity of the complexes. Conversely, exposure to complexes 3b and 3e resulted in limited and delayed growth in cysts. Furthermore, minimal excystation was observed after 72 h at a concentration of 100 µM, and after 48 h at a concentration of 1000 µM, in cysts treated with complexes 3a, 3c, 3d and 3f. These results are of particular significance in light of the well-documented resistance of A. castellanii cysts to conventional antimicrobials [13]. The absence of any detectable activity by a ligand alone further emphasizes the importance of complexing with silver to achieve anti-amoebic potency.
At the lowest tested concentration (10 µM), none of the silver(I) complexes exhibited detectable cysticidal activity. In a similar manner, the ligands (1a–f) did not affect cyst viability at any time point (24, 48 or 72 h), and trophozoite outgrowth occurred at levels comparable to the untreated control. These results indicate that the ligands, when administered individually, were not efficacious against A. castellanii cysts under the conditions of the study. The present findings suggest that the silver(I) 3a–f complexes may offer an effective alternative or adjunctive therapeutic strategy by targeting both the trophozoite and cyst stages.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
The synthesis of silver(I) complexes was carried out under an inert atmosphere of argon with dried solvents. 1H, 13C{1H} and 19F{1H} NMR spectra were recorded with Bruker Avance III spectrometer (300 or 500 MHz). The spectra were calibrated according to the residual protonated solvent in CDCl3 (δ = 7.26 and 77.16 ppm for 1H and 13C, respectively) or in DMSO-d6 (δ = 2.50 and 39.52 ppm for 1H and 13C, respectively). 19F NMR spectra are given relative to external CCl3F. Chemical shifts and coupling constants are reported in ppm and Hz, respectively. ESI-TOF spectra were recorded on a Bruker MicroTOF spectrometer. Infrared spectra were recorded on a Bruker FT-IR Alpha-P spectrometer. 1-Cinnamyl-benzimidazole (2) [49], 1-benzyl-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazolium chloride (1c) [39], 1-(3-fluorobenzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazolium chloride (1d) [39], and 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazolium chloride (1e) [39] were prepared according to literature procedures.
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Benzimidazolium Salts
The 1-cinnamyl-benzimidazole (2) (234 mg, 1 mmol) was first dissolved in DMF (5 mL) before the addition of aryl chloride (1 mmol). The resulting solution was then subjected to a heating process at a temperature of 80 °C for a duration of 24 h. Subsequent to a period of cooling to room temperature, the salt underwent precipitation by the addition of Et2O (100 mL). The white solid was filtered and washed twice with Et2O (2 × 10 mL) prior to being dried under vacuum.
1-Cinnamyl-3-allyl-benzimidazolium chloride (1a): Yield: 36%; FT-IR: ν(CN) 1556 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 11.78 (s, 1H, NCHN), 7.79–7.74 (m, 1H, arom CH), 7.72–7.67 (m, 1H, arom CH), 7.64–7.58 (m, 2H, arom CH), 7.41–7.37 (m, 2H, arom CH), 7.34–7.28 (m, 3H, arom CH), 6.92 (d, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 15.9 Hz), 6.39 (dt, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 15.9 Hz, 3JHH = 6.7 Hz), 6.18–6.05 (m, 1H, CH=CH2), 5.52–5.46 (m, 4H, CH2CH=CH and CH=CH2), 5.31 (d, 2H, CH2CH=CH2, 3JHH = 6.0 Hz); 13C{1H} NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 143.88 (s, NCHN), 137.18 (s, CH=CHPh), 135.12, 131.67, 131.64, 128.99, 128.88, 127.30, 127.24, 127.08, 113.81, 113.78 (10 s, arom Cs), 129.71 (s, CH=CH2), 122.02 (s, CH=CH2), 120.32 (s, CH=CHPh), 50.37 (s, CH2CH=CHPh), 50.21 (s, CH2C=CH2) ppm. Elemental analysis (%): calcd for C19H19N2Cl (310.82): C: 73.42; H: 6.16; N 9.01; found C: 73.34; H: 6.21; N: 8.97.
1-Methoxymethyl-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazolium chloride (1b): Yield: 38%; FT-IR: ν(CN) 1556 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 11.94 (s, 1H, NCHN), 7.81 (d, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 9.0 Hz), 7.72 (d, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 9.0 Hz), 7.60–7.55 (m, 2H, arom CH), 7.34 (d, 2H, arom CH, 3JHH = 8.5 Hz), 7.26–7.19 (m, 3H, arom CH), 6.86 (d, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 15.5 Hz), 6.39 (d br, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 15.5 Hz), 6.03 (s, 2H, CH2OCH3), 5.42 (d, 2H, CH2CH=CH, 3JHH = 2.0 Hz), 3.46 (s, 3H, CH2OCH3); 13C{1H} NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 144.14 (s, NCHN), 137.35 (s, CH=CHPh), 135.03, 131.73, 131.16, 129.03, 128.89, 127.66, 127.59, 127.09, 114.42, 113.73 (10 s, arom Cs), 120.07 (s, CH=CHPh), 79.15 (s, CH2OCH3), 57.96 (s, CH2OCH3), 50.43 (s, CH2CH=CHPh) ppm. Elemental analysis (%): calcd for C18H19N2OCl (314.81): C: 68.67; H: 6.08; N 8.90; found C: 68.64; H: 6.01; N: 8.86.
1-(4-Methyl-benzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazolium chloride (1f): Yield: 90%; FT-IR: ν(CN) 1556 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 12.17 (s, 1H, NCHN), 7.73 (d, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 9.9 Hz), 7.60–7.50 (m, 3H, arom CH), 7.42–7.39 (m, 4H, arom CH), 7.36–7.28 (m, 3H, arom CH), 7.18 (d, 2H, arom CH, 3JHH = 8.1 Hz), 6.92 (d, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 15.6 Hz), 6.44 (dt, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 15.6 Hz, 3JHH = 6.6 Hz), 5.80 (s, 2H, CH2C6H4CH3), 5.50 (d, 2H, CH2CH=CH, 3JHH = 6.6 Hz), 2.32 (s, 3H, C6H4CH3); 13C{1H} NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 144.09 (s, NCHN), 139.55, 137.25, 131.73, 131.54, 130.23, 129.70, 129.06, 128.93, 128.50, 127.21, 127.11, 120.27, 113.92, 113.75 (14 s, arom Cs), 135.10 (s, CH=CHPh), 127.23 (s, CH=CHPh), 51.61 (s, CH2C6H4CH3), 50.30 (s, CH2CH=CHPh), 21.34 (s, C6H4CH3) ppm. Elemental analysis (%): calcd for C24H23N2Cl (374.90): C: 76.89; H: 6.18; N 7.47; found C: 77.02 H: 6.25, N: 7.39.
3.3. General Procedure for the Preparation of Silver Complexes
In a Schlenk tube, a solution of benzimidazolium salt (1.0 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (50 mL) was prepared under argon atmosphere. Subsequently, Ag2O (2.2 mmol) was added to the mixture, which was stirred in a dark environment at room temperature for a period of 24 h. Following this, the reaction mixture was filtered through a celite bed, and the volume of the resulting solution was reduced to approximately 5 mL. The silver complex was precipitated with the addition of Et2O (60 mL). The mixture was subsequently filtered, washed with Et2O, and then dried under vacuum.
Chloro[1-cinnamyl-3-allyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3a): Yield: 79%; FT-IR: ν(CN) 1387 cm−1; 1H NMR 300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.86–7.83 (m, 1H, arom CH), 7.78–7.74 (m, 1H, arom CH), 7.46–7.40 (m, 4H, arom CH), 7.30–7.21 (m, 3H, arom CH), 6.74 (d, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 15.9 Hz), 6.55 (dt, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 15.9 Hz, 3JHH = 6.1 Hz), 6.14–6.02 (m, CH=CH2), 5.28 (d, 2H, CH2CH=CH, 3JHH = 6.1 Hz), 5.25 (dd, 1H, CH=CH2, 3JHH = 9.9 Hz, 3JHH = 1.2 Hz), 5.20 (dd, 1H, CH=CH2, 3JHH = 17.1 Hz, 3JHH = 1.2 Hz), 5.13 (d, 2H, CH2CH=CH2, 3JHH = 5,4 Hz), 13C{1H} NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 188.49 (s, NCN), 135.66, 133.37, 133.34, 128.57, 128.01, 126.52, 124.58, 112.28, 112.25 (9 s, arom Cs), 133.36 (s, CH=CHPh), 124.04 (s, CH=CHPh), 124.02 (s, CH=CH2), 118.29 (s, CH=CH2), 50.87 (s, CH2CH=CHPh), 50.59 (s, CH2C=CH2) ppm. MS (ESI-TOF): m/z = 381.05 [M − Cl]+ and 422.07 [M − Cl + CH3CN]+ (expected isotopic profiles). Elemental analysis (%): calcd for C19H18N2AgCl (417.68): C: 54.64; H: 4.34; N 6.71; found C: 54.72; H: 4.39; N: 6.62.
Chloro[1-methoxymethyl-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3b): Yield: 56%; FT-IR: ν(CN) 1379 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.88–7.83 (m, 2H, arom CH), 7.49–7.47 (m, 2H, arom CH), 7.42 (d, 2H, arom CH, 3JHH = 7.0 Hz), 7.28 (t, 2H, arom CH, 3JHH = 7.2 Hz), 7.22 (t, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 7.2 Hz), 6.75 (d, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 16.0 Hz), 6.55 (dt, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 16.0 Hz, 3JHH = 6.0 Hz), 5.83 (s, 2H, CH2OCH3), 5.31 (d, 2H, CH2CH=CH, 3JHH = 6.0 Hz), 3.31 (s, 3H, CH2OCH3); 13C{1H} NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 135.57, 133.71, 133.12, 128.62, 128.08, 126.57, 124.49, 112.50, 112.48 (9 s, arom Cs), 133.40 (s, CH=CHPh), 124.46 (s, CH=CHPh), 80.01 (s, CH2OCH3), 56.19 (s, CH2OCH3), 50.73 (s, CH2CH=CHPh) ppm. MS (ESI-TOF): m/z = 385.05 [M − Cl]+ (expected isotopic profiles). Elemental analysis (%): calcd for C18H18N2OAgCl (421.67): C: 51.27; H: 4.30; N 6.64; found C: 51.18; H: 4.26; N: 6.57.
Chloro[1-benzyl-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3c). Yield: 86%; FT-IR: ν(CN) 1394 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 6.82 (d, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 9.9 Hz), 6.70 (d, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 9.9 Hz), 6.43–6.23 (m, 12H, arom CH), 5.71 (d, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 15.9 Hz), 5.52 (dt, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 15.9 Hz, 3JHH = 6.0 Hz), 4.70 (s, 2H, CH2Ph), 4.26 (d, 2H, CH2CH=CH, 3JHH = 6.0 Hz); 13C{1H} NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 136.43, 135.78, 133.69, 129.00, 128.79, 128.26, 128.24, 127.54, 126.71, 124.36, 124.32, 112.52, 112.51 (13 s, arom Cs), 133.48 (s, CH=CHPh), 124.57 (s, CH=CHPh), 52.17 (s, CH2Ph), 50.78 (s, CH2CH=CHPh) ppm. MS (ESI-TOF): m/z = 431.06 [M − Cl]+ and 472.08 [M − Cl + CH3CN]+ (expected isotopic profiles). Elemental analysis (%): calcd for C23H20N2AgCl (467.74): C: 59.06; H: 4.31; N 5.99; found C: 58.98; H: 4.35; N: 5.87.
Chloro[1-(3-fluorobenzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3d): Yield: 33%; FT-IR: ν(CN) 1385 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.85 (dd, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 7.5 Hz, 4JHH = 1.5 Hz), 7.72 (dd, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 7.0 Hz, 4JHH = 1.5 Hz), 7.45–7.35 (m, 5H, arom CH), 7.29–7.19 (m, 5H, arom CH), 7.14 (td, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 8.7 Hz, 4JHH = 2.5 Hz), 6.74 (d, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 16.0 Hz), 6.55 (dt, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 16.0 Hz, 3JHH = 6.0 Hz), 5.76 (s, 2H, CH2C6H4F), 5.30 (d, 2H, CH2CH=CH, 3JHH = 6.0 Hz); 13C{1H} NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 189.04 (s, NCN), 162.19 (d, CF, 1JCF = 244.9 Hz), 135.66, 133.54, 133.29, 128.58, 128.02, 126.53, 124.21, 124.17, 112.41, 112.28 (10 s, arom Cs), 139.11 (d, arom Cquat, 3JCF = 7.3 Hz), 133.29 (s, CH=CHPh), 130.87 (d, arom CH, 3JCF = 8.3 Hz), 124.57 (s, CH=CHPh), 123.36 (d, arom CH, 4JCF = 2.9 Hz), 114.94 (d, arom CH, 2JCF = 20.8 Hz), 114.30 (d, arom CH, 2JCF = 21.9 Hz), 51.32 (s, CH2C6H4F), 50.68 (s, CH2CH=CHPh); 19F{1H} NMR (282 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = -112.42 (s, C6H4F) ppm. MS (ESI-TOF): m/z = 490.08 [M − Cl + CH3CN]+ (expected isotopic profiles). Elemental analysis (%): calcd for C23H19N2FAgCl (485.73): C: 56.87; H: 3.94; N 5.77; found C: 56.85; H: 3.88; N: 5.74.
Chloro[1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3e): Yield: 51%; FT-IR: ν(CN) 1391 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.84 (d, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 9.0 Hz), 7.73 (d, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 9.0 Hz), 7.46–7.39 (m, 6H, arom CH), 7.28 (t, 2H, arom CH, 3JHH = 7.5 Hz), 7.22 (t, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 7.2 Hz), 7.17 (t, 2H, arom CH, 3JHH = 9.0 Hz), 6.74 (d, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 16.0 Hz), 6.54 (dt, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 16.0 Hz, 3JHH = 6.0 Hz), 5.72 (s, 2H, CH2C6H4F), 5.29 (d, 2H, CH2CH=CH, 3JHH = 6.0 Hz); 13C{1H} NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 188.64 (s, NCN), 161.76 (d, CF, 1JCF = 244.8 Hz), 135.67, 133.55, 133.25, 128.59, 128.04, 126.55, 124.16, 124.13, 112.40, 112.34 (10 s, arom Cs), 133.31 (s, CH=CHPh), 132.54 (d, arom Cquat, 4JCF = 3.1 Hz), 129.59 (d, arom CH, 3JCF = 8.4 Hz), 124.57 (s, CH=CHPh), 115.64 (d, arom CH, 2JCF = 21.7 Hz), 51.20 (s, CH2C6H4F), 50.68 (s, CH2CH=CHPh); 19F{1H} NMR (282 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = −114.15 (s, C6H4F) ppm. MS (ESI-TOF): m/z = 490.10 [M − Cl + CH3CN]+ (expected isotopic profiles). Elemental analysis (%): calcd for C23H19N2FAgCl (485.73): C: 56.87; H: 3.94; N 5.77; found C: 56.92; H: 4.11; N: 5.72.
Chloro[1-(4-methyl-benzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-ylidene]silver(I) (3f): Yield: 81%; FT-IR: ν(CN) 1387 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.83 (d, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 9.0 Hz), 7.73 (d, 1H, arom CH, 3JHH = 8.7 Hz), 7.45–7.39 (m, 4H, arom CH), 7.30–7.20 (m, 5H, arom CH), 7.12 (d, 2H, arom CH, 3JHH = 7.8 Hz), 6.72 (d, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 15.9 Hz), 6.53 (dt, 1H, CH=CHPh, 3JHH = 15.9 Hz, 3JHH = 6.0 Hz), 5.67 (S, 2H, CH2C6H4CH3), 5.27 (d, 2H, CH2CH=CH, 3JHH = 6.0 Hz), 2.23 (s, 3H, C6H4CH3); 13C{1H} NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 137.35, 135.65 133.31, 133.29, 129.33, 128.58, 128.02, 127.43, 126.54, 124.09, 124.06, 112.41, 112.33 (13 s, arom Cs), 133.52 (s, CH=CHPh), 124.57 (s, CH=CHPh), 51.79 (s, CH2C6H4CH3), 50.61 (s, CH2CH=CHPh), 20.64 (s, C6H4CH3) ppm. MS (ESI-TOF): m/z = 445.08 [M − Cl]+ and 486.11 [M − Cl + CH3CN]+ (expected isotopic profiles). Elemental analysis (%): calcd for C24H22N2ClAg (481.77): C: 59.83; H: 4.60; N 5.81; found C: 59.97 H: 4.49; N: 5.74.
3.4. X-Ray Crystal Structure Analysis
Single crystals of silver(I) complexes 3c and 3d, suitable for X-ray analysis, were obtained through the slow diffusion of Et2O into a CH2Cl2 solution of the complex. The crystal structures of complexes 3c and 3d were determined using, respectively, a Bruker APEX-II CCD and a Bruker PHOTON-III CPAD with Mo-Kα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å). The final structure was solved with SHELXT-2018/2 [50], which revealed the non-hydrogen atoms of the molecule. Following anisotropic refinement, the location of all hydrogen atoms was ascertained through the use of a Fourier difference map. The structure was refined with SHELXL-2019/3 [51] using the full-matrix least-square technique (use of F square magnitude; x, y, z, and βij for C, Cl, N, F and Ag atoms; x, y, and z in riding mode for H atoms) (Table 3). The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC) contains the supplementary crystallographic data for the structures. The data can be obtained free of charge via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures.

Table 3.
Selected crystallographic data for complexes 3c and 3d.
3.5. In Vitro Effects on A. castellanii
3.5.1. A. castellanii Strain and Culture
The A. castellanii PAT06 strain (sequence type T4, GenBank accession no. EF429131), which was previously isolated from a patient with severe AK, was utilized in the study. The strain was cultivated axenically in proteose peptone-yeast extract-glucose (PYG) medium. The cultures were maintained in 25 cm2 tissue culture flasks (Corning, USA) and incubated at 25 °C [52].
Trophozoites in the exponential growth phase (72–96 h) were harvested by centrifugation at 500× g for 10 min. Subsequently, the cell pellets were washed twice with a sterile Neff’s saline solution (1.2 g NaCl, 0.4 g MgSO4·H2O, 0.4 g CaCl2·2H2O, 1.42 g Na2HPO4, and 1.36 g KH2PO4 dissolved in 100 mL of distilled water). The cell concentrations were determined using a Neubauer hemocytometer, and the suspension was adjusted to a final concentration of 1 × 104 trophozoites/mL in PYG medium with ≥95% viability. The prepared suspension was utilized immediately for viability assays.
Mature cysts were obtained by culturing trophozoites on non-nutrient agar (NNA) plates presmeared with Escherichia coli, followed by incubation for six weeks at 25 °C. The resulting cysts were harvested by washing with a sterile Neff’s saline solution, with the concentration subsequently adjusted to 1 × 104 cysts/mL for the ensuing assays.
3.5.2. A. castellanii Trophozoites
Stock solutions of the silver(I) complexes and their respective ligands were prepared in 100% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Working solutions at final concentrations of 10, 100, and 1000 µM were prepared by diluting the stock solutions with PYG medium. The final DMSO concentration in all experimental groups, including the highest tested concentration, was standardized to 10% (v/v). AgNO3 and Ag2O were prepared in PYG medium at final concentrations of 10, 100, and 1000 µM.
A. castellanii trophozoites were seeded into sterile 24-well tissue culture plates at a density of 104 trophozoites per mL per well. Subsequently, the cultures were subjected to incubation with the test compounds at the designated concentrations for a duration of 24, 48 and 72 h at a temperature of 25 °C. Following the incubation period, the adherent trophozoites were meticulously detached using a sterile cell scraper and resuspended by gentle pipetting. The resulting cell suspensions were stained with 0.3% methylene blue for a period of 10 min. The viability of the trophozoites was determined by staining them with methylene blue, a method that distinguishes between viable (unstained) and non-viable (blue-stained) cells. The cell count was performed using a Neubauer hemocytometer under a light microscope. The percentage of viable trophozoites was subsequently calculated relative to the untreated control.
The control group consisted of trophozoites cultured in PYG medium alone. The solvent control group was maintained in PYG medium containing 10% (v/v) DMSO. All experiments were performed in quadruplicate.
3.5.3. A. castellanii Cysts
In order to assess the impact of silver(I) complexes and ligands on A. castellanii cysts, the cysts were prepared at a final concentration of 1 × 104 cysts/mL. Subsequently, the samples were subjected to incubation with the test compounds at the indicated concentrations at 25 °C for 24, 48 and 72 h.
Following the incubation period, the cyst suspensions were centrifuged and washed three times with sterile Neff’s saline. The treated cysts were then inoculated onto non-nutrient agar (NNA) plates that had been smeared with Escherichia coli and incubated at 25 °C for 14 days.
The viability of the cyst was monitored daily using phase-contrast microscopy. Cysts were considered viable if excystation occurred and motile trophozoites were observed. In the absence of trophozoite emergence, the cysts were considered non-viable.
3.6. Statistical Analysis
The experiments described herein were conducted in four independent biological replicates, with each replicate comprising technical triplicates. The results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). The statistical analysis was carried out using GraphPad Prism version 9.0. To assess the statistical significance of the observed variations among the multiple treatment groups, we employed a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), which was then followed by a Tukey’s multiple comparison test. For the purpose of performing for-a-value comparisons, a two-tailed Student’s t-test was utilized. In the context of statistical analysis, a p-value of less than 0.05 was determined to be statistically significant.
4. Conclusions
In summary, the present study described the synthesis of six new chloro[N-alkyl-N-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) complexes, with isolated yields ranging from 33 to 86%. These complexes were thoroughly characterized by a combination of analytical techniques, including FT-IR and NMR spectroscopic analyses, as well as microanalysis and mass spectrometry. Subsequently, a substantial in vitro inhibitory activity against trophozoites and cysts of the A. castellanii strain was exhibited, signifying a superior efficacy in comparison to the ligands and commercially available silver complexes as Ag2O and AgNO3. At a concentration of 100 µM, complexes bearing benzyl, 3-fluorobenzyl and 4-methyl-benzyl substituents on the benzimidazole ring exhibited significant activity, with 5.3, 3.2 and 6.3% trophozoite viability, respectively, recorded after 72 h. These findings provide substantial support for the preclinical development of silver-based NHC compounds as novel anti-Acanthamoeba agents, particularly for the treatment of AK. Subsequent studies will concentrate on the optimization of the substituents of the benzimidazole ligand in silver complexes and the investigation of their mode of action.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/inorganics13060204/s1, characterizing data of 1-cinnamyl-3-allyl-benzimidazolium chloride (1a) with Figure S1. FT-IR spectrum, Figure S2. 1H NMR spectrum and Figure S3. 13C{1H} NMR spectrum; characterizing data of 1-methoxymethyl-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazolium chloride (1b) with Figure S4. FT-IR spectrum, Figure S5. 1H NMR spectrum and Figure S6. 13C{1H} NMR spectrum; characterizing data of 1-(4-methyl-benzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazolium chloride (1f) with Figure S7. FT-IR spectrum, Figure S8. 1H NMR spectrum and Figure S9. 13C{1H} NMR spectrum; characterizing data of chloro[1-cinnamyl-3-allyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3a) with Figure S10. FT-IR spectrum, Figure S11. 1H NMR spectrum, Figure S12. 13C{1H} NMR spectrum and Figures S13 and S14. Mass spectrum (ESI-TOF); characterizing data of chloro[1-methoxymethyl-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3b) with Figure S15. FT-IR spectrum, Figure S16. 1H NMR spectrum, Figure S17. 13C{1H} NMR spectrum and Figure S18. Mass spectrum (ESI-TOF); characterizing data of chloro[1-benzyl-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3c) with Figure S19. FT-IR spectrum, Figure S20. 1H NMR spectrum, Figure S21. 13C{1H} NMR spectrum and Figure S22. Mass spectrum (ESI-TOF), characterizing data of chloro[1-(3-fluorobenzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3d) with Figure S23. FT-IR spectrum, Figure S24. 1H NMR spectrum, Figure S25. 13C{1H} NMR spectrum, Figure S26. 19F{1H} NMR spectrum and Figure S27. Mass spectrum (ESI-TOF); characterizing data of chloro[1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]silver(I) (3e) with Figure S28. FT-IR spectrum, Figure S29. 1H NMR spectrum, Figure S30. 13C{1H} NMR spectrum, Figure S31. 19F{1H} NMR spectrum and Figure S32. Mass spectrum (ESI-TOF); characterizing data of chloro[1-(4-methyl-benzyl)-3-cinnamyl-benzimidazol-2-ylidene]silver(I) (3f) with Figure S33. FT-IR spectrum, Figure S34. 1H NMR spectrum, Figure S35. 13C{1H} NMR spectrum and Figures S36 and S37. Mass spectrum (ESI-TOF).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.Ş. and D.S.; methodology, Z.A.-P., N.Ş. and D.S.; validation, Z.A.-P., N.Ş. and D.S.; formal analysis, Z.A.-P., N.Ş., S.H. and D.S.; investigation, Z.A.-P., N.Ş., S.H. and B.M.T.L.; resources, Z.A.-P. and D.S.; data curation, Z.A.-P., N.Ş. and D.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.A.-P., N.Ş. and S.H.; writing—review and editing, İ.Ö. and D.S.; visualization, Z.A.-P.; supervision, İ.Ö. and D.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Julia Walochnik from the Department of Medical Parasitology at the Clinical Institute of Hygiene at the University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, for providing the Acanthamoeba strain.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Geisen, S.; Fiore-Donno, A.M.; Walochnik, J.; Bonkowski, M. Acanthamoeba everywhere: High diversity of Acanthamoeba in soils. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3151–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schustera, F.L.; Visvesvara, G.S. Free-living amoebae as opportunistic and non-opportunistic pathogens of humans and animals. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 1001–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciano-Cabral, F.; Cabral, G. Acanthamoeba spp. as agents of disease in humans. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 273–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, R.; Khan, N.A. Biology and pathogenesis of Acanthamoeba. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.; Jain, V.; Goyal, M.K.; Radotra, B.D.; Khandelwal, N. Granulomatous amoebic meningoencephalitis. Neurol. India 2013, 61, 530–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Khan, N.A.; Walochnik, J. An update on Acanthamoeba keratitis: Diagnosis, pathogenesis and treatment. Parasite 2015, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederkorn, J.Y. The biology of Acanthamoeba keratitis. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 202, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wei, Z.; Cao, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Q. The global epidemiology and clinical diagnosis of Acanthamoeba keratitis. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varacalli, G.; Di Zazzo, A.; Mori, T.; Dohlman, T.H.; Spelta, S.; Coassin, M.; Bonini, S. Challenges in Acanthamoeba keratitis: A review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, F.; Tortori, A.; Vallino, V.; Galdiero, M.; Fea, A.M.; De Sanctis, U.; Reibaldi, M. Understanding Acanthamoeba keratitis: An in-depth review of a sight-threatening eye infection. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchele, M.L.C.; Nunes, B.F.; Filippin-Monteiro, F.B.; Caumo, K.S. Diagnosis and treatment of Acanthamoeba keratitis: A scoping review demonstrating unfavorable outcomes. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2023, 46, 101844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanselow, N.; Sirajuddin, N.; Yin, X.-T.; Huang, A.J.W.; Stuart, P.M. Acanthamoeba keratitis, pathology, diagnosis and treatment. Pathogens 2021, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, U.; Anwar, A.; Ong, S.-K.; Anwar, A.; Khan, N.A. Applications of medicinal chemistry for drug discovery against Acanthamoeba infections. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 462–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Batlle, M.; Sifaoui, I.; Rodríguez-Expósito, R.L.; Piñero, J.E.; Lorenzo-Morales, J. New insights in Acanthamoeba. Pathogens 2022, 11, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasser, G.; Ott, S.; Metzler-Nolte, N. Organometallic anticancer compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noffke, A.L.; Habtemariam, A.; Pizarro, A.M.; Sadler, P.J. Designing organometallic compounds for catalysis and therapy. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5219–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middya, P.; Chattopadhyay, S. An overview of synthesis, structure and biological application of N-heterocyclic carbene complexes of silver. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1324, 140842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceramella, J.; Catalano, A.; Mariconda, A.; D’Amato, A.; Aquila, S.; Saturnino, C.; Rosano, C.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Longo, P. Silver N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complexes as antimicrobial and/or anticancer agents. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, N.; Mosrati, M.A.; Merghni, A.; Özdemir, İ.; Sellami, H.; Bedchiche, K.; Krayiem, S.; Aifa, S.; Abdelmalek, D.; Sémeril, D. Synthesis, antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of silver(I) complexes with N-alkylbenzimidazole derivatives and their protein interaction modelling study. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1322, 140440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.O.; Maasböl, A. On the existence of a tungsten carbonyl carbene complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1964, 3, 580–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, W.A.; Köcher, C. N-Heterocyclic carbenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 36, 2162–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanzlick, H.-W.; Schönherr, H.-J. Direct synthesis of a mercury salt-carbene complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1968, 7, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öfele, K. 1,3-Dimethyl-4-Imidazolinyliden-(2)-Pentacarbonylchrom ein neuer Übergangsmetall-Carben-Komplex. J. Organomet. Chem. 1968, 12, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduengo, A.J., III; Kline, M.; Calabrese, J.C.; Davidson, F. Synthesis of a reverse ylide from a nucleophilic carbene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 9704–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, W.A. N-Heterocyclic carbenes: A new concept in organometallic catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1290–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, L.; Correa, A.; Costabile, C.; Jacobsen, H. Steric and electronic effects in the bonding of N-heterocyclic ligands to transition metals. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 5407–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasmari, S.; Ikhlef, S.; Boulcina, R.; Mokrani, E.H.; Bensouici, C.; Gürbüz, N.; Dündar, M.; Karcı, H.; Özdemir, İ.; Koç, A.; et al. New silver N-heterocyclic carbenes complexes: Synthesis, molecular docking study and biological activities evaluation as cholinesterase inhibitors and antimicrobials. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1238, 130399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, R.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M.A.; Jamil, Y. Synthesis of aryl linked binuclear silver N-heterocyclic carbene complexes, DNA interaction study and biological potentials. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 119, 108077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussaini, S.Y.; Haque, R.A.; Razali, M.R. Recent progress in silver(I)-, gold(I)/(III) -and palladium(II)-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes: A review towards biological perspectives. J. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 882, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, O.; González, S.; Higuera-Padilla, Á.R.; León, Y.; Coll, D.; Fernández, M.; Taylor, P.; Urdanibia, I.; Rangel, H.R.; Ortega, J.T.; et al. Remarkable in vitro anti-HIV activity of new silver(I)- and gold(I)-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes. Synthesis, DNA binding and biological evaluation. Polyhedron 2016, 110, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.R.W.; Anderson, R.A. The bactericidal effect of silver ions on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1968, 20, 1S–3S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melaiye, A.; Youngs, W.J. Silver and its application as an antimicrobial agent. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2005, 15, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banti, C.N.; Hadjikakou, S.K. Anti-proliferative and anti-tumor activity of silver(I) compounds. Metallomics 2013, 5, 569–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Nurchi, V.M.; Zoroddu, M.A. Medical uses of silver: History, myths, and scientic evidence. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 5923–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendiger, E.B.; Padzik, M.; Sifaoui, I.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; López-Arencibia, A.; Rizo-Liendo, A.; Bethencourt-Estrella, C.J.; San Nicolás-Hernández, D.; Chiboub, O.; Rodríguez-Expósito, R.L.; et al. Silver nanoparticles as a novel potential preventive agent against Acanthamoeba keratitis. Pathogens 2020, 9, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyyati, M.; Sasani, R.; Mohebali, M.; Ghazikhansari, M.; Kargar, F.; Hajialilo, E.; Rezaeian, M. Anti-Acanthamoeba effects of silver and gold nanoparticles and contact lenses disinfection solutions. Iran J. Parasitol. 2018, 13, 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Padzik, M.; Hendiger, E.B.; Chomicz, L.; Grodzik, M.; Szmidt, M.; Grobelny, J.; Lorenzo-Morales, J. Tannic acid-modified silver nanoparticles as a novel therapeutic agent against Acanthamoeba. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3519–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Kakalis, L.; Nolan, S.P.; Szostak, M. A simple 1H NMR method for determining the σ-donor properties of N-heterocyclic carbenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 60, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, N.; Zengin, S.; Özdemir, İ.; Sémeril, D. C-H activation of furanyl and thiofuranyl substrates catalyzed by trans-dichloro [1-cinnamyl-3-arylmethyl-benzimidazol-2-yliden]pyridine palladium(II) complexes. Polyhedron 2024, 261, 117144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Mohan, R.; Singh, J.K.; Samantaray, M.K.; Shaikh, M.M.; Panda, D.; Ghosh, P. Anticancer and antimicrobial metallopharmaceutical agents based on palladium, gold, and silver N-heterocyclic carbene complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 15042–15053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, J.C.; Youngs, W.J. Ag(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes: Synthesis, structure, and application. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 3978–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimeno, M.C.; Laguna, A.; Visbal, R. N-Heterocyclic carbene coinage metal complexes as intense blue-green emitters. Organometallics 2012, 31, 7146–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulloch, A.A.D.; Danopoulos, A.A.; Winston, S.; Kleinhenz, S.; Eastham, G. N-Functionalised heterocyclic carbene complexes of silver. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2000, 4499–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidlaw, G.; Wood, S.H.; Kennedy, A.R.; Nelson, D.J. An N-heterocyclic carbene with a saturated backbone and spatially-defined steric impact. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2019, 645, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutar, U.; Çelik, C.; Üstün, E.; Özdemir, N.; Sahin, N.; Sémeril, D.; Gürbüz, N.; Özdemir, İ. Benzimidazol-2-ylidene silver complexes: Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities, molecular docking and theoretical investigations. Inorganics 2023, 11, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asekunowo, P.O.; Haque, R.A.; Razali, M.R. A comparative insight into the bioactivity of mono- and binuclear silver(I)-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes: Synthesis, lipophilicity and substituent effect. Rev. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 37, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronga, L.; Varcamonti, M.; Tesauro, D. Structure-activity relationships in NHC-silver complexes as antimicrobial agents. Molecules 2023, 28, 4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Admetlab. Available online: https://admetlab3.scbdd.com/ (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Tan, K.L.; Vasudevan, A.; Bergman, R.G.; Ellman, J.A.; Souers, A.J. Microwave-assisted C-H bond activation: A rapid entry into functionalized heterocycles. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 2131–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT-Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, F.L. Cultivation of pathogenic and opportunistic free-living amebas. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).