Abstract
We report the synthesis and characterization of five novel metal complexes. Three of them are vanadium complexes with the general formula [VO(Ln)2], where Ln are Schiff bases derived from the condensation of 2-carbaldehyde-8-hydroxyquinoline with either 4-(2-aminoethyl)morpholine (L1), 3-morpholinopropylamine (L2) or 1-(2-aminoethyl)piperidine (L3). The two other metal complexes are [Ni(L1)2] and [Fe(L1)2]Cl. They were characterized by analytical, spectroscopic (Fourier transform infrared, UV-visible absorption), and mass spectrometric techniques as well as by single-crystal X-ray diffraction (for all [VO(Ln)2] complexes and [Ni(L1)2]). While, in the crystal structure, the V(IV)O complexes show distorted square–pyramidal geometry with the ligands bound as bidentate through quinolate NO donors, the Ni(II) complex shows octahedral geometry with two ligand molecules coordinated through NNO donors. Stability studies in aqueous media revealed that the vanadium complexes are not stable, undergoing oxidation to VO2(L), which was corroborated by 51V NMR and MS. This behavior is also observed in organic media, though at a significantly slower rate. The Ni complex exhibited small spectral changes over time in aqueous media. Nonetheless, all compounds show enhanced stability in the presence of bovine serum albumin (BSA). Fluorescence studies carried out for the Ni(II) and Fe(III) complexes indicate reversible binding to albumin. The cytotoxicity of the L1 metal complexes was assessed on melanoma (B16F10 and A375) and colon cancer (CT-26 and HCT-116) cell lines, with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) as a reference drug. The V- and Ni complexes showed the lowest IC50 values (<10 μM) in either A375 or HCT-116 cells after 48 h of incubation, while the Fe(III) complex presented minimal antiproliferative effects. The complexes were generally more cytotoxic to human than murine cancer cells. Synergistic in vitro studies with 5-FU revealed antagonism in most cases, except in A375 cells, where an additive effect was observed for the combination with the V-complex. Overall, these compounds show promising potential for cancer treatment, mostly for melanoma.
1. Introduction
Cancer is currently one of the biggest public health challenges worldwide, and the prospects are that morbidity and mortality rates will continue to increase year after year [1]. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) predicts more than 35 million new cancer cases and 18.5 million deaths in the year 2050 [2,3], a 66 and 78% increase compared to the more than 21 million cases and 10 million deaths estimated for 2025, respectively [4,5].
The cancer therapeutic strategies currently available in the clinic range from the most conventional, such as surgery, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy, to the most recent and innovative, such as immunotherapy, targeted therapy, hormone therapy, and gene therapy, among others [6,7]. Despite low bioavailability, reduced specificity, significant side effects, and the emergence of resistance, chemotherapy still remains a widely used therapeutic choice [7,8]. Furthermore, the antineoplastic properties of cisplatin discovered in the 1960s aroused the interest of many researchers in the therapeutic potential of metal-based complexes [6,9]. Redox activity, variable coordination modes, as well as reactivity towards organic substrates are some of the unique characteristics that stand out [6,10,11]. Therefore, an ongoing and exciting area of research is the design of new metal complexes with better antineoplastic properties and lower side effects compared to cisplatin [7].
In recent decades, several classes of organic compounds, including many heterocyclic ligands, have been synthesized, as well as their complexes that have been screened as potential anticancer agents. Currently, there is considerable interest in 8-hydroxyquinoline (8-HQ) and its derivatives due to their versatile chemical properties and wide biological activity. They are excellent metal chelators, binding with high-affinity zinc, copper, and iron, and they have shown a broad spectrum of antimicrobial and anticancer activity. It has been shown that their ability to chelate metal ions affects their solubility, transport across cell membranes, and interaction with biological targets [12,13].
Our group has been exploring the bioactivity of 8-hydroxyquinolines by incorporating them in Schiff bases or hydrazones, which were coordinated with different metal ions and their potential in anticancer research. The conjugation of 8-HQ to the also biologically active benzothiazole yielded metal complexes with relevant cytotoxicity against several cancer cells [14], with the Zn(II) complex impairing tumor progression in vivo in a murine colon cancer mouse model [15,16]. V(IV)O and Cu(II) complexes of 8-HQ hydrazones showed antiproliferative activity against malignant melanoma (A375) and lung (A549) cancer cells, with all complexes showing much higher activity in A375 than in A549 cells. Zn(II) complexes of Schiff bases derived from 8-HQ and imidazole derivatives also showed antiproliferative activity on a wide panel of cancer cells, particularly for triple-negative breast cancer, in which they were comparable to cisplatin. In general, they also displayed much higher in vitro selectivity in cancer cells vs. normal cells than cisplatin [17].
Recently, we have reported the synthesis and characterization of three novel Schiff bases derived from the condensation of 2-carbaldehyde-8-hydroxyquinoline with amines containing morpholine or piperidine moieties. These ligands were reacted with Zn(II) and Cu(II) metal salts to obtain stable M(L)2 complexes. Their antiproliferative effects were evaluated on malignant melanoma cells and non-cancerous keratinocytes. All complexes demonstrated notable cytotoxicity (IC50 < 10 μM) but exhibited only moderate selectivity. The complexes were more potent than the free ligands, with Cu(II) complexes showing higher activity than the Zn(II) ones [18]. Given the promising results obtained with these compounds, we explored other biologically relevant transition metal ions. Iron is an endogenous essential metal ion, required for the activity of proteins and enzymes that carry out a broad range of functions, and therefore, it should impose low systemic toxicity. It is also a redox-active metal ion, involved in Fenton reactions, and could act through the generation of reactive oxygen species. Nickel and vanadium are considered “possibly essential trace metals” [19] and their toxicity depends, as for any other metal, on their concentration and speciation, with nickel being generally considered toxic due to carcinogenic effects. However, upon complexation with different ligands, these metal ions have shown promise for cancer therapy, due to numerous cellular effects [20]. Ni(II) is much less studied in this regard, but there are numerous reports of the anticancer effects of its compounds (e.g., [14,21,22]).
Therefore, herein, we report the synthesis and characterization (including new crystal structures) of V(IV)O complexes with three ligands (L1–L3) and Ni(II) and Fe(III) complexes with one ligand (L1). Their antiproliferative properties were evaluated in murine and human melanoma and colon cancer cells, as well as normal cells, to evaluate selectivity. Their potential for combinatory chemotherapy was explored with in vitro synergistic studies of the most promising complexes combined with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a clinically approved anticancer drug.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Complexes
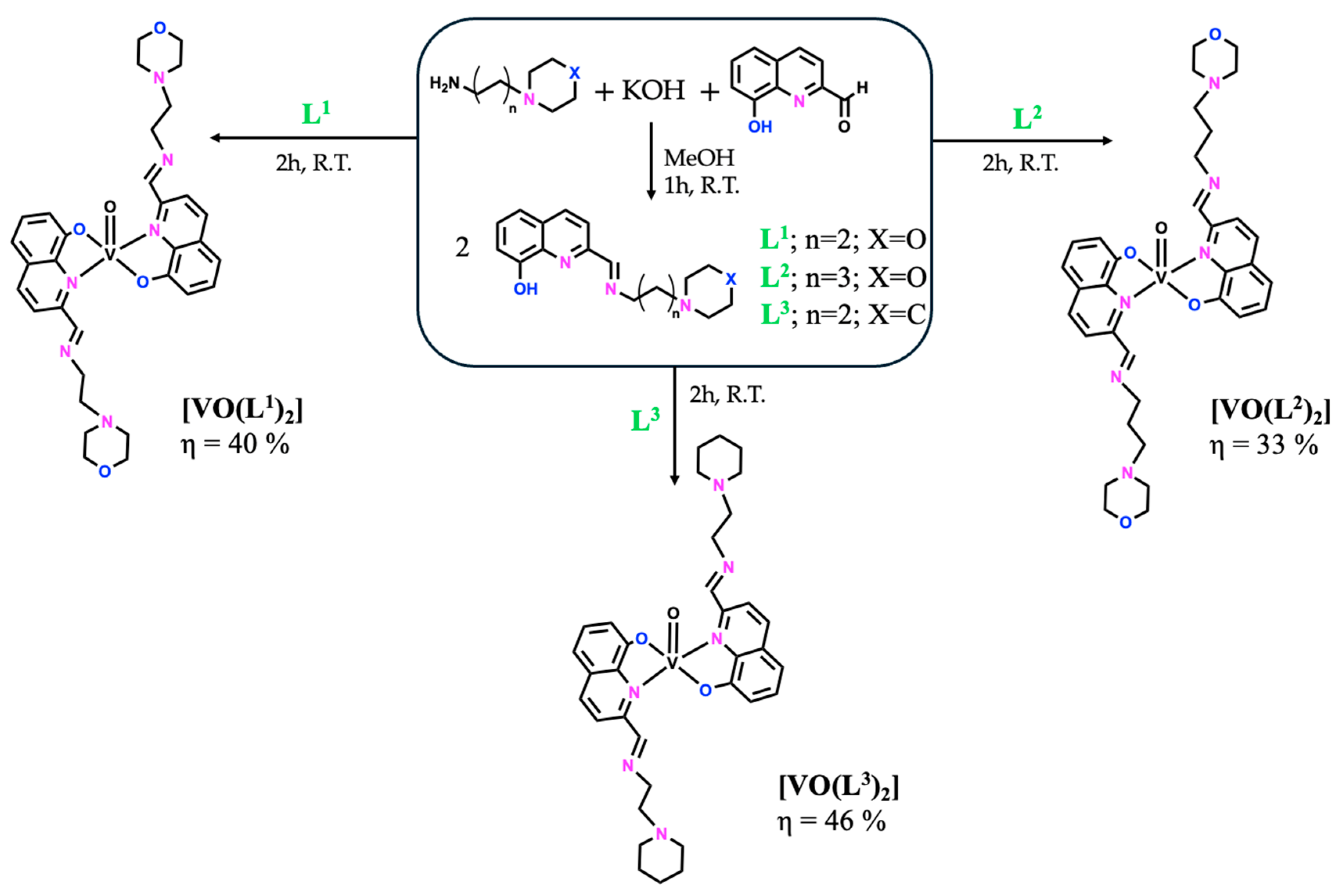
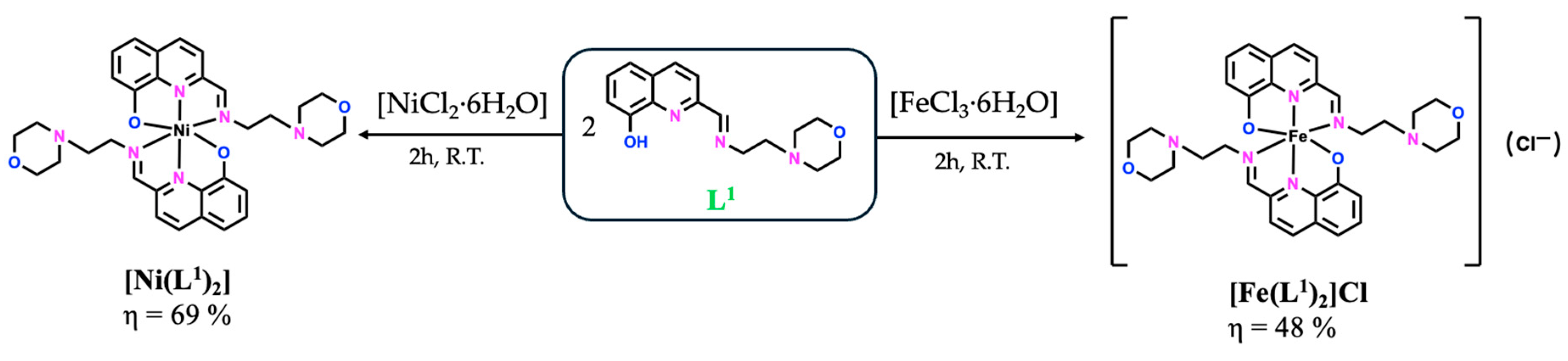
The compounds included in this report follow a previously synthesized family of Zn(II) and Cu(II) complexes bearing bioactive Schiff bases containing both 8-hydroxyquinoline and morpholine/piperidine heterocycles, evaluated for the treatment of human malignant melanoma [18]. The most promising results were obtained with the Cu(II) complexes, which were more active than the Zn(II) ones, but overall, they all showed high antiproliferative effects, regardless of the ligand moiety (below 10 μM after 48 h of incubation). Therefore, we decided to explore the metal effect by preparing other metal complexes, namely V(IV)O complexes with three Schiff bases (SB), L1–L3, as summarized in Figure 1, and Ni(II) and Fe(III) complexes only with the SB derived from (2-aminoethyl)morpholine (L1—Figure 2). All complexes were obtained in low to moderate yields (33–69%), and their full characterization (elemental analysis, mass spectrometry, FTIR, and UV–Vis spectroscopies) is described in the Materials and Methods Section 3. The mass spectrometry and FTIR spectra of all complexes are also presented in the Supplementary Materials section (Figure S1). Additionally, the vanadium complexes were characterized by EPR. Overall, the experimental data support the proposed structural formulae.
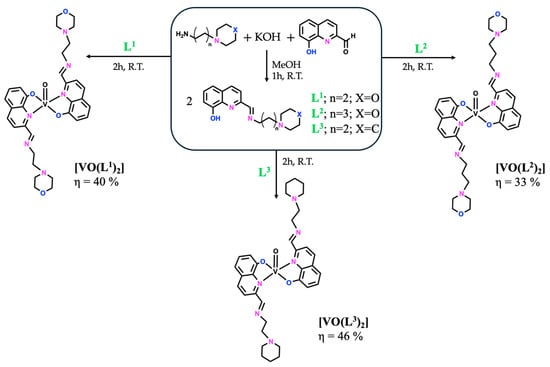
Figure 1.
General synthetic methodology to obtain the free ligands, L1–L3, and their respective [VO(Ln)2] compounds.
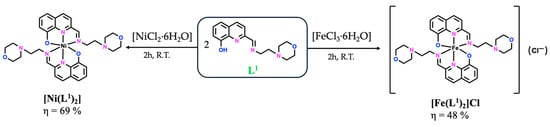
Figure 2.
General synthetic methodology to obtain the [Ni(L1)2] and [Fe(L1)2]Cl compounds.
Single crystals were obtained for all the V(IV)O–complexes and for the Ni(II)–complex, allowing the determination of their molecular structures by single-crystal X-ray diffraction (SC-XRD) analysis. Since crystals of the Fe(III)–based complex could not be obtained, its structural elucidation was addressed using the Evans NMR method (Materials and Methods Section 3) to calculate the magnetic susceptibility, providing additional insight regarding the complex electronic properties. The magnetic moment obtained in solution was 5.61 μB, consistent with a high-spin d5 configuration (S = 5/2, five unpaired electrons in an octahedral environment), similar to other reported Fe(III)–hydroxyquinoline based complexes [23,24,25]. Therefore, the proposed molecular structure is a cationic [Fe(L1)2]+ complex with an octahedral coordination sphere around the Fe(III) center in an NNO arrangement of donor atoms from two ligands and chloride as a counter ion, which elemental analyses corroborate.
The solid-state FTIR characterization of the complexes (Figure S2) shows spectra with a band corresponding to the stretching vibration of the azomethine moiety, ν(C=N), at ~1640 cm−1, as expected [17,18]. For all complexes, this band shifts to lower wavenumbers (between 1627 and 1643 cm−1) when compared to its frequency in the corresponding free ligands (1649 cm−1), which is indicative of a decrease in the bond order and coordination of the metal to the imine nitrogen lone pair [26]. The bands due to the ν(C=C) stretching vibrations of the quinoline unit are observed between 1500 and 1600 cm−1. For the oxidovanadium complexes, a sharp strong band is present between 966 and 987 cm−1, characteristic of the ν(V=O) stretching vibration [27,28,29]. Finally, the bands observed at ~3050 cm−1 and ~2950 cm−1 correspond to the C−H stretching vibrations of the 8-hydroxyquinoline and morpholine units, respectively.
The molecular absorption spectra of all complexes and the ligand L1 were recorded using 1.0 × 10−5–1.0 × 10−4 M solutions in DMSO, and the spectra are shown in Figure S3.
We have previously reported the electronic absorption spectra of the Schiff base ligand L1 in DMSO, which shows one intense absorption band at ~270 nm and two shoulders in the region of 260−400 nm, assigned to intraligand n → π* transitions of the azomethine group. The π → π* transitions of the aromatic rings of the 8-hydroxyquinoline moiety are below the cutoff of the solvent [18]. After complexation, only the Ni(II) complex shows a clear bathochromic shift, whereas the bands of the V(IV)O and Fe(III) complexes appear nearly in the same wavelength as in the spectra of the corresponding ligand. Given that the Ni(II) complex has the lowest oxidation state of the series, it experiences smaller crystal field splitting (<Δo) and is expected to have absorption bands shifted towards lower energy. Additionally, all three complexes of L1 show the presence of a broad band in the visible region that can be ascribed to ligand-to-metal charge-transfer (LMCT) and probably overlapping low intensity d-d bands. Due to the limited solubility of the complexes and the weak intensity of d−d bands (Laporte forbidden), these are not clearly visible or assigned in the spectra recorded for the metal complexes. The V(IV)O−complexes of L1 and L2, both derived from the same chromophore (morpholine), are almost equal, while the complex containing L3 shows some differences, particularly in the position of the CT band, and the intensity of the π → π* transitions.
To further characterize the compounds and establish their solid-state structure, diffuse reflectance spectra were measured, and a Kubelka–Munk transformation was performed to allow comparison with the UV-Vis absorption spectra in DMSO. The remission functions deduced from the spectral reflectance measurements are included in Figure S3, and Table 1 lists their wavelength. The [Ni(L1)2] complex shows several broad bands in the visible region: (i) between 420 and 720 nm, the broad band seems to be composed of three bands centered at ca. 485, 525, and 600 nm, which we assign to one CT band and two d-d bands; (ii) in the NIR, there is another band that can also be assigned to a d-d transition. This is in agreement with an octahedral environment around d8 Ni(II), which gives rise to three bands, with one of them in the NIR region [30]. For the [Fe(L1)2]Cl complex, since the magnetic measurements indicated a high-spin d5 configuration, the d-d bands are spin-forbidden and weak. Thus, we assign the band at 488 nm to a CT band and the broad band tailoring from this one into the visible region to d-d bands. For V(IV)O d1 complexes with square–pyramidal C4v symmetry, three (or four) transitions are expected [31]. The spectra included in Figure S3d for the three complexes show broad bands between 350 and 550 nm, which seems to be an overlap of at least two bands that we assign to CT and d-d bands. Shoulders at ca. 580 nm and a broad band in the NIR (770–810 nm) are probably due to the other two d-d bands.

Table 1.
Wavelength of the bands (nm) from the UV-Vis absorption spectra in solution (DMSO and 5%DMSO/HEPES, 10 mM, pH 7.4) and the remission functions deduced from the diffuse reflectance spectra for the metal complexes.
2.2. Single Crystal X-Ray Diffraction
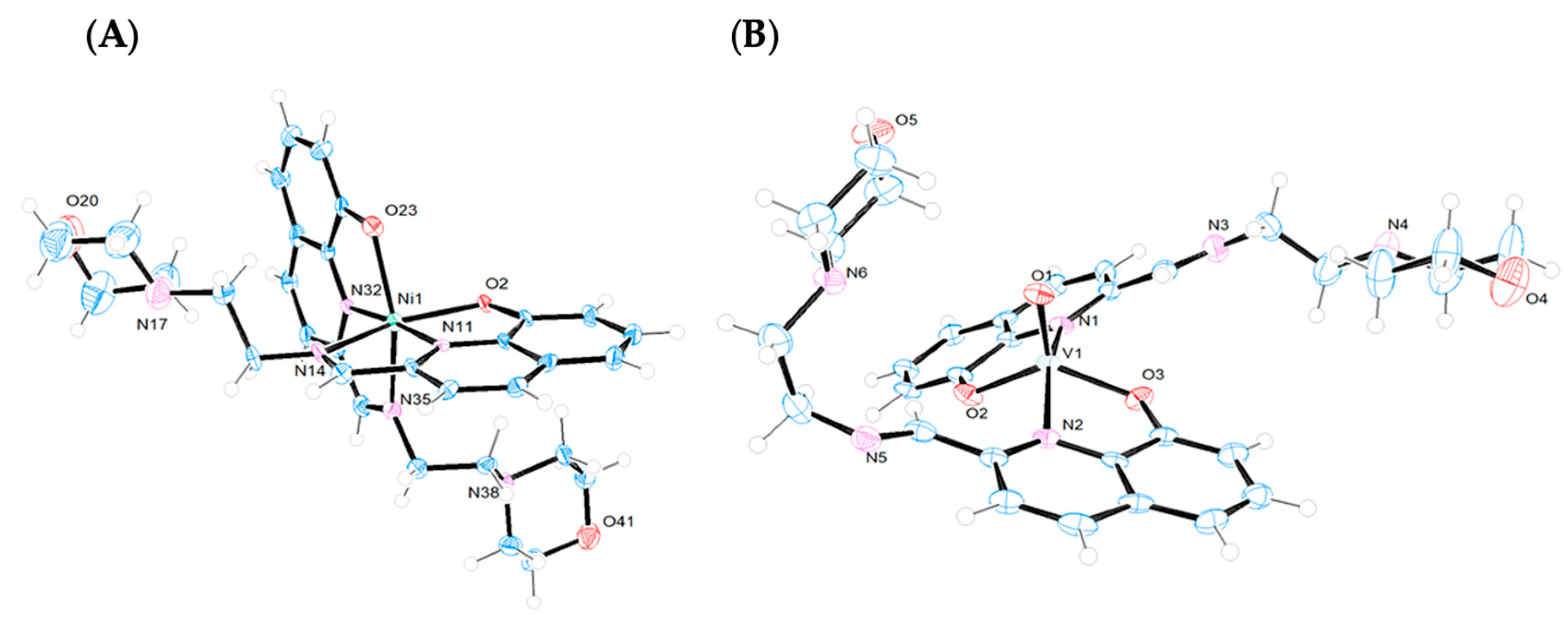
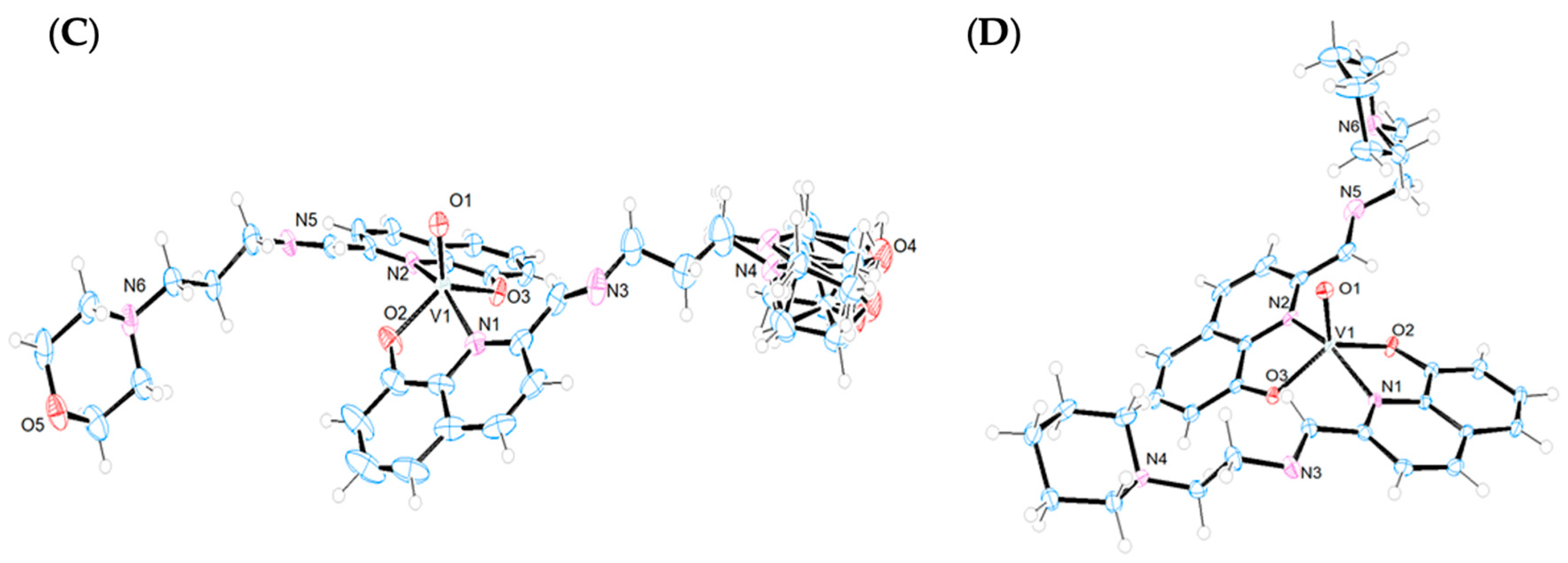
The crystal structures of the Ni(II) and V(IV)O complexes were solved by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. Figure 3 displays the ORTEP diagrams of their molecular structures. The main crystallographic data and selected bond distances and angles can be found in the Supplementary Materials (Table S1).
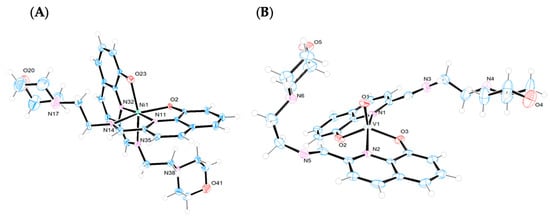
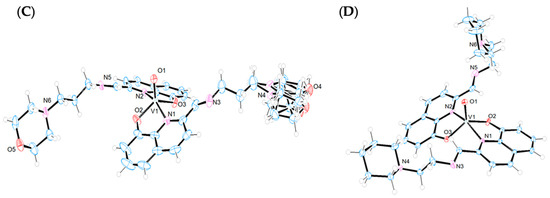
Figure 3.
X-ray structures (ORTEP plots with ellipsoids at 50% probability level) and labeling scheme for (A) [Ni(L1)2], (B) [VO(L1)2], (C) [VO(L2)2], and (D) [VO(L3)2] complexes determined by SC-XRD.
The [Ni(L1)2] complex crystallizes in the monoclinic system, space group P1 21/n1, with two crystalographically independent enantiomers within the racemic crystal (Figure S4). The complex displays a six-coordinated Ni(II) ion with a distorted octahedral geometry (Figure 3A), where two monodeprotonated 8-hydroxyquinoline-imine ligands coordinate through their NNO donor atoms in a meridional fashion. The phenolate moieties and imine nitrogen atoms adopt a cis orientation [O2-Ni-O23 = 93.5° and N11-Ni-N35 = 99.9°], while the quinoline nitrogen atoms are trans to each other [N11-Ni-N32 = 176.3°]. This coordination pattern has been previously observed in other Ni(II) complexes containing 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives [32].
The distortion in the angles around Ni(II), and consequently in the octahedral coordination sphere, arises from the geometrical constraints imposed by the NNO binding mode of the tridentate ligands, whose angles are slightly less than 90°. The Ni–Nimine bond distances are generally longer than the Ni–Nquinoline [Ni-N35 = 2.185 Å and Ni-N14 = 2.188 Å vs. Ni-N11 = 1.966 Å and Ni-N32 = 1.966 Å]. However, the Ni–Nimine bonds in this complex are shorter than those reported for other Ni(II) complexes with 8-hydroxyquinoline-imine ligands [32]. On the other hand, the bond distances in the complex are, in general, longer than those observed in other six-coordinated Ni(II) complexes bearing N,N,O-salicylaldiminato ligands [33]. The distortion parameters calculated using the OctaDist program are summarized in Table S2.
Both intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds are present in the structure (i) between neighboring ligands via oxygen atoms and the aliphatic hydrogens of the imine substituents [O2-H37A = 2.646 Å and O23-H16B = 2.775 Å] as well as [O2A-H37C = 2.794 Å and O23A-H16D = 2.698 Å] (Figure S5A) and (ii) between enantiomeric molecules, where oxygen atoms interact with imine [O23-H34A = 2.293 Å] and aromatic hydrogen atoms [O2-H30A = 2.954 Å and O23-H30A = 2.485 Å] from neighboring molecules (Figure S5B). The crystal packing along the a, b, and c axis is displayed in Figure S6.
Complexes [VO(Ln)2] (n = 1–3) crystallizes in the triclinic system, space group P-1. In all cases, the coordination environment around the V(IV) ion is closer to a distorted square–pyramidal geometry than to a trigonal bipyramid, as indicated by the Reedijk’s τ factor, which is 0.49, 0.44, and 0.43 for [VO(Ln)2] (n = 1–3), respectively (τ = 0 for a square–pyramid and τ = 1 for a trigonal bipyramid) [34] (Figure 3B–D). The distortions in the square–pyramidal geometries are more pronounced than those observed in other V(IV)O complexes with different Schiff bases [35,36]. In all three compounds, the V(IV) is coordinated to two deprotonated ligands that act as bidentate donors through the quinoline nitrogen atoms (N1, N2) and the phenolate oxygen atoms (O2, O3). Both ligands occupy the basal positions with the nitrogen atoms and oxygen atoms arranged trans to each other, while the fifth axial coordination site is occupied by the vanadyl O atom (O1). The axial V1-O1 bonds [1.594(4) Å for L1; 1.589(3) Å for L2; 1.5887(18) Å for L3] are shorter than the basal V1-O2 [1.915(4) Å for L1; 1.912(2) Å for L2; 1.9221(18) Å for L3] and V1-O3 [1.912(4) Å for L1; 1.912(3) Å for L2; 1.9163(18) Å for L3] bonds, consistent with the double bond character of the V=O group. This trend is observed for other oxidovanadium(IV)–complexes reported in the literature [37]. The O–V–N angles of the chelate ligands reflect the geometric constraints imposed by these ligands, with values ranging from 79.74(8)° to 80.59(8)° across the three complexes. The angles O2-V-O3 [129.95(18) for L1; 131.30(12) for L2; 131.89(8) for L3] and N1-V-N2 [159.77(18) for L1; 158.12(12) for L2; 158.04(8) for L3] indicate that the vanadium centers are displaced out of the plane towards the apical oxygen atoms, O1.
Intramolecular hydrogen bonds between the phenolate oxygen atoms and the hydrogen atoms of the iminic carbons (HC=N) [O2-H26 = 2.349 Å and O3-H10 = 2.549 Å for L1; O2-H27 = 2.550 Å and O3-H10 = 2.329 Å for L2; O2-H27 = 2.366 Å and O3-H10 = 2.507 Å for L3] appear to contribute to the stabilization of the structures (Figure S7). Notably, in compounds [VO(Ln)2] (n = 1 and 3), weak hydrogen bonds are observed between the vanadyl oxygen atoms and hydrogen atoms from the morpholine and piperidine rings [O1-H30A = 2.708 Å for [VO(L1)2] and O1-H31B = 2.805 Å for [VO(L3)2]]. However, in compound [VO(L2)2], this interaction is absent, likely due to the different spatial arrangement of the aminopropylmorpholine chain, which contains one additional carbon atom compared to the others’ two ligands. The crystal packing of the three complexes reveals π-stacking interactions (3.310–3.619 Å) between the quinoline rings of neighboring molecules, which contribute to unit cell formation. Additionally, the arrangement of the apical vanadyl oxygen atoms within the unit cells is noteworthy. In compounds with shorter ligand chains, [VO(Ln)2] (n = 1 and 3), these oxygen atoms are positioned close to each other, promoting intermolecular hydrogen bonding between the oxygen atoms of one molecule and the aromatic protons of a neighboring molecule, further stabilizing the structure. In contrast, in [VO(L2)2], which features the longest ligand chain, these interactions are not favored, leading to an alternate arrangement in which the oxygen atoms are positioned opposite to each other (Figure S8A–C).
2.3. EPR Characterization
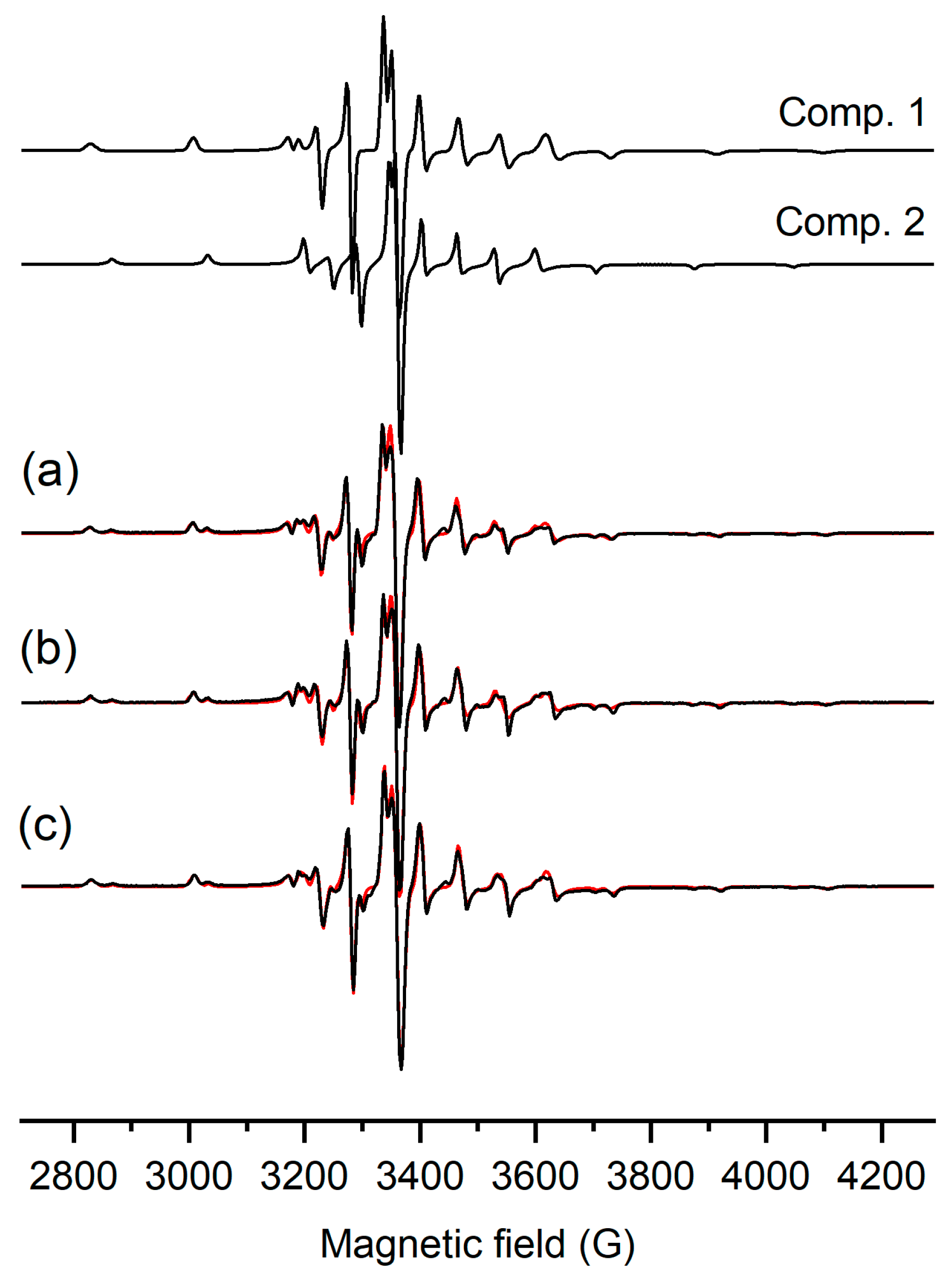
The oxidation state of vanadium in the complexes was confirmed by EPR spectroscopy. The X-band frozen solution (20% MeOH/DMSO) EPR spectra obtained for compounds [VIVO(L1)2], [VIVO(L2)2], and [(VIVO(L3)2] are shown in Figure 4. The eight lines of hyperfine splitting of a parallel and perpendicular orientation prove the interaction of S = ½ with the nucleus spin of vanadium. All three spectra can be interpreted as the sum of two components. These, obtained for the three different complexes, can be described with the same EPR data sets, suggesting that the coordination is identical and the difference in side chains has no spectral effect. Only the ratio of the components changed slightly, close to 70% of component 1 and 30% of component 2 (Figure 4). Component 1 was simulated using the spin Hamiltonian parameters g⊥ = 1.976, g|| = 1.945, A⊥ = 58 × 10−4 cm−1, and A|| = 165 × 10−4 cm−1, and component 2 was simulated with g⊥ = 1.975, g|| = 1.948, A⊥ = 52 × 10−4 cm−1, and A|| = 153 × 10−4 cm−1. These EPR parameters fall within the range of typical oxidovanadium(IV) compounds with N2O2 donor sets [38,39,40]; however, the difference shows two different arrangements of the ligands. Component 2 is the complex with a higher ligand field in the equatorial plane (smaller A||), while component 1 is a complex with a somewhat lower ligand field.
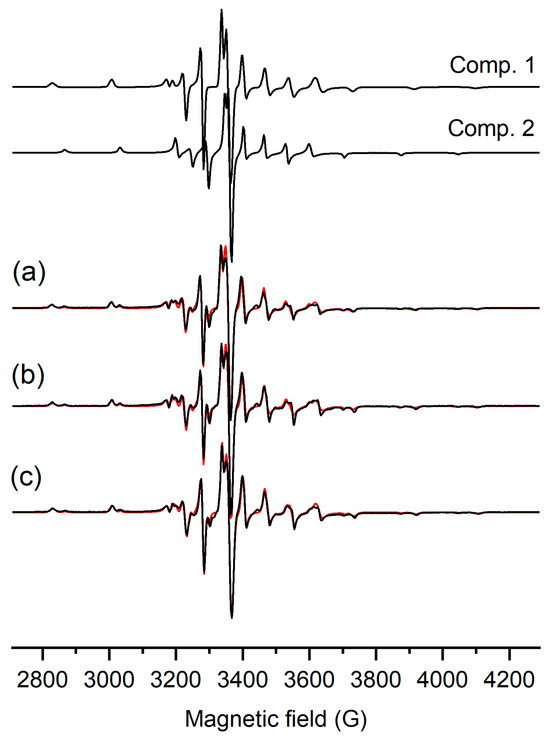
Figure 4.
Experimental (black) and simulated (red) frozen solution EPR spectra (77 K) of (a) [VO(L1)2], (b) [VO(L2)2], and (c) [VO(L3)2] complexes dissolved in 20% (v/v) MeOH/DMSO solution with the obtained component EPR spectra. The ratio of comp. 1/comp. 2 was 70/30, 67/33, and 76/24% for [VO(L1)2], [VO(L2)2], and [VO(L3)2], respectively.
The crystal structures obtained for the [VO(Ln)2] (n = 1–3) complexes show a strongly distorted square–pyramidal geometry, similar to the bis-ligand oxidovanadium(IV) complex of 2,5-dimethyl-8-hydroxyquinoline reported by Joanna Palion-Gazda et al. [38] for which the EPR parameters g⊥ = 1.977, g|| = 1.958, A⊥ = 48 × 10−4 cm−1, and A|| = 155 × 10−4 cm−1 were obtained in frozen DMSO solution. These data are close to the parameters of component 2, suggesting that the solid-phase stabilized geometry appears as a minor component (30%) in solution. The higher A|| value in component 1 suggests a quinoline oxygen of one ligand turned axially and the fourth equatorial position being filled by a methanol molecule. Changing the second ligand coordination into an equatorial–axial mode often occurs when the ligands contain larger substituents. An example of this is the bis-ligand complex of 5-(isopropoxycarbonyl)pyridine-2-carboxylato) with oxidovanadium(IV) (Figure S9), for which the measured EPR data, g⟂ = 1.985, A⟂ = 60 × 10−4 cm−1, gII = 1.945, and AII = 167 × 10−4 cm−1 [41], are close to the parameters obtained for component 1. Consequently, we can propose a similar octahedral geometry for component 1 (see Figure S10), detected in higher amounts in solution. However, another possibility cannot be excluded, involving the loss of a ligand and the formation of V(IV)O(Ln)+ (n = 1–3). This process could drive the formation of V(V)O2(Ln) (n = 1–3), which was observed by HR-MS, and oxidation, which was corroborated by NMR measurements (see below). The oxidovanadium(IV) species could have a tridentate ligand and a methoxide, completing the coordination sphere. The low intensity of the EPR spectra of all complexes is in agreement with early oxidation taking place in DMSO.
2.4. Stability Studies in Organic and Aqueous Media
Evaluating the stability of the metal compounds in solution, particularly in aqueous environments at physiological pH, is crucial before conducting biological assessments. The EPR measurements indicate the occurrence of dynamic processes upon dissolution of the V-complexes in organic solvents, such as DMSO/MeOH mixtures. The complexes should be soluble in water and resist hydrolysis and decomposition if the biologically active species is the dissolved compound. If not, understanding the solution behavior is crucial to propose an active species. Therefore, the stability of the complexes was first assessed by UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy, and the spectra of the complexes were recorded with time in 100% organic medium (DMSO) and in an aqueous buffer (5% DMSO/HEPES, 10 mM, pH 7.4) by diluting DMSO stock solutions of the complexes. The evaluation of the ligand L1 was previously reported [18] and showed no decomposition in both organic and aqueous solutions within 10 h. Hydrolysis was observed in aqueous solution for longer periods of time.
As observed in Figures S11 and S12, [Ni(L1)2] and [Fe(L1)2]Cl complexes, at biologically relevant concentrations, are reasonably stable for up to 24 h in DMSO. However, the [VO(L1)2] complex is unstable in this organic solvent, showing isosbestic points and a loss of the charge-transfer band with time. Moreover, if we compare the changes observed in this system with the spectrum measured for the ligand in the same solvent (Figure S13), we can propose that one ligand molecule is lost since new bands develop with maxima in the same wavelengths as L1: at 355 and 312 (sh) nm. Therefore, for all the vanadium complexes the most probable process occurring is the oxidation of the V(IV)O2+ center to a V(V)O2+, which can exist as a monomeric species or a dimeric one [V(V)O2(Ln)]2 (n = 1–3), which are difficult to distinguish by UV-Vis spectroscopy solely. This is further supported by the variation of the LMCT bands in DMSO, since V(V) complexes typically present LMCT bands centered at around 350–400 nm [27,42].
In a physiological pH-buffered solution containing a much lower DMSO content (5% DMSO/HEPES, 10 mM, pH 7.4), no spectral changes are observed (Figure S12). However, a more detailed analysis of the band positions (energies) suggests that the same process occurs but probably at a significantly faster rate, not detected in the used timeframe. Therefore, we propose that the following reactions occur in solution under air (O2):
V(IV)O(Ln)2 + S ⇌ V(IV)O(Ln)2S
V(IV)O(Ln)2S + S ⇌ V(IV)O(Ln)S2 + (Ln)
2 V(IV)O(Ln)S + O2 + S ⇌ 2 V(V)O2(Ln) ⇌ [V(V)O2(Ln)]2
S = solvent molecule, n = 1–3
The first two species agree with the EPR observations. The faster changes observed in water, which is more polar, also support this hypothesis. These processes also account for the fact that the neutral V(IV)O(Ln)2 (n = 1–3) species probably has higher thermodynamic stability than the cationic V(IV)O(Ln)+ (n = 1–3), if we consider the stability constants found for mono- and bis-ligand species determined for the Cu(II) and Zn(II) complexes [18], and, thus, it is unreasonable to assume that ligand loss occurs independently of metal oxidation. The V(V) complexes are likely to feature the ligand coordinated in a tridentate manner, as the chelate effect may promote the coordination of the imine nitrogen and enhance the stability of the more Lewis acidic V(V) center.
To clarify this, 51V NMR spectra were measured for the complex dissolved in 100% DMSO-d6 and in 5% DMSO/D2O immediately after dissolution and after 24 h (Figure S14). The spectra clearly show the presence of a peak at ca. -500 ppm, which can be assigned to a V(V)-containing species. The chemical shift is solvent-dependent, and the peak is broader in DMSO due to the higher viscosity of this solvent. So, these studies confirm the oxidation of the complex in solution, which is common for V(IV) species as previously shown for related V(IV)O(8-hydroxyquinolate)2 complexes [43]. However, as discussed above, the formed species likely retains one ligand molecule in a tridentate coordination.
To further confirm this hypothesis, high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) studies were carried out in DMSO/ABIC buffer (pH 7.4) at times: 0 and 30 min as well as 1 h and 24 h. The results allowed us to assign the oxidized species to [V(V)O2(Ln)], which showed the expected isotopic pattern for all V-complexes (Figures S15–S17). Based on this observation, we hypothesize that V(V)O2(Ln) is the vanadium biologically active species. To simplify terminology in cellular studies, we refer to the selected [VO(L1)2] compound as the “V-complex.”, i.e., the species originated by the [VO(L1)2] complex in solution. As for other V(V) species, we identified a dioxidovanadium complex (only for VO(L1)2) bearing one hydrolyzed 8HQ Schiff base ligand, which is not present after 24 h. We also detected residual amounts of the original V(IV)O complexes at time 0, which were no longer present after 24 h. This indicates a rapid oxidation process that occurs immediately upon dissolution in aqueous media and is nearly complete within 24 h. In addition, two V(IV)O species were identified at time 0 in low amounts: one containing two 8-hydroxyquinoline (8HQ) hydrolyzed Schiff bases and another with one intact Schiff base ligand and one hydrolyzed 8HQ Schiff base. These species were not detected after 24 h. Also, HR-MS analysis further confirmed the presence of the free Schiff base ligands corresponding to each V-complex. Table S3 summarizes the list of all identified species.
The Ni(II) complex exhibited a different effect since it was stable in 100% organic solvent but showed small changes in aqueous media (Figures S11 and S12). These changes included a slight loss in the charge-transfer (CT) band intensity as the concentration increased. The band centered at 296 nm decreased by 35% within 2 h and then remained mostly unchanged. Nevertheless, given these changes and the high stability results observed in the presence of bovine serum albumin (Section 2.5), we proceeded with further biological testing of the compound, assuming that most of it remains intact in solution.
Additionally, comparison of the spectra measured in both solvents (at time 0, see Table 1) and the remission functions deduced from the spectral reflectance measurements in the solid state (Figure S18) allow further conclusions: (i) the d-d bands are not observed in solution due to their low intensity (Laporte forbidden) and the low concentrations used; (ii) the lowest energy band observed in solution probably has a charge-transfer character; (iii) immediately after dissolution in DMSO, the CT band appears to be in the same region as in the solid state, indicating that the complexes present a similar structure in the solid state and DMSO; and (iv) for the Ni complex, the only observed differences in both solvents are in the CT band energy, and it may simply be due to solvent effects, and not a change in coordination.
2.5. Interaction Studies with BSA
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) is commonly used as a model protein and widely used as a substitute for human serum albumin (HSA) when studying the interaction between bioactive compounds and serum proteins. This is due to its affordability, easy availability, and significant structural similarity to HSA, sharing 76% of its amino acid sequence [44]. It is also the major component of fetal bovine serum (FBS), a supplement added to mammalian cell cultures during in vitro experiments. Notably, the ability of BSA to form complexes with drugs increases the solubility and bioavailability of these compounds.
To assess how BSA influences the stability of the complexes, equimolar mixtures of the complexes with BSA in 5% DMSO/HEPES (10 mM, pH 7.4) were prepared. The mixtures were monitored over time by UV-visible spectroscopy to track changes. Figure S19 depicts detailed data from these observations, and the key results are highlighted here. Despite the Ni- and V-based complexes showing lower stability in aqueous media, in the presence of BSA, all complexes were stable. The charge-transfer bands did not decrease their intensity, even after 24 h. As already observed for related compounds [17,18], two isosbestic points can be observed and are probably related to an equilibrium between two species, the free complex and complex–BSA adducts.
To evaluate the possibility of the interaction occurring near the Trp-212 residue of BSA, fluorescence spectroscopy was used. Trp-212 is located within a hydrophobic pocket in subdomain IIA, making it sensitive to environmental changes nearby. When this residue becomes exposed to solvent molecules and excited at 295 nm, its fluorescence emission decreases (quenching). Thus, fluorimetric titrations can help to reveal if the compounds interact with this specific site. Titrations were carried out as detailed in the Materials and Methods Section 3, and Figures S20 and S21 show the fluorescence quenching data for the [Ni(L1)2] and [Fe(L1)2]Cl complexes. The V-complex was not studied since it did not show adequate stability in DMSO, the solvent required for the dissolution of the complex. Given that the fluorescence titration experiment requires several hours to complete, the instability of the complex in DMSO renders this approach unsuitable for obtaining reliable data.
For both the [Ni(L1)2] and [Fe(L1)2]Cl complexes, the Stern–Volmer plots (I0/I vs. [Q]) showed an upward curvature that was fitted with a second-order equation, probably indicating that static and dynamic quenching processes may occur, as already observed for related compounds [18]. Determining the dynamic quenching constant would require fluorescence lifetime studies, which fall outside the scope of the work. The Stern–Volmer constants (KSV), shown in Table 2, were determined by fitting the lower quencher concentration range data, where a linear relationship is observed. Both complexes exhibit Stern–Volmer constants of the order of 105, indicating high quenching efficiencies within the range of reversible binding [18].

Table 2.
Fluorescence quenching parameters: % quenching at molar ratio complex–BSA = 5:1; Stern−Volmer quenching constant and R2 coefficient, binding constants from Scatchard plot (log k), and R2 coefficient.
If an adduct is formed between the compound and the protein, employment of the Scatchard Equation (5) [45] allows the determination of the binding constant (k) and the number of binding sites for these systems (Figures S20 and S21). This gives further evidence that the binding is stronger for [Ni(L1)2] than for [Fe(L1)2]Cl. Given that the Ni complex is neutral and Fe complex is cationic, this agrees with binding in a hydrophobic region such as near the Trp-residue.
Although BSA may provide some degree of stabilization for the Ni(II) and Fe(III) complexes, the vanadium complexes appear to undergo rapid decomposition in aqueous environments, and their stability under these conditions remains limited.
2.6. In Vitro Antiproliferative Properties of Metal-Based Complexes
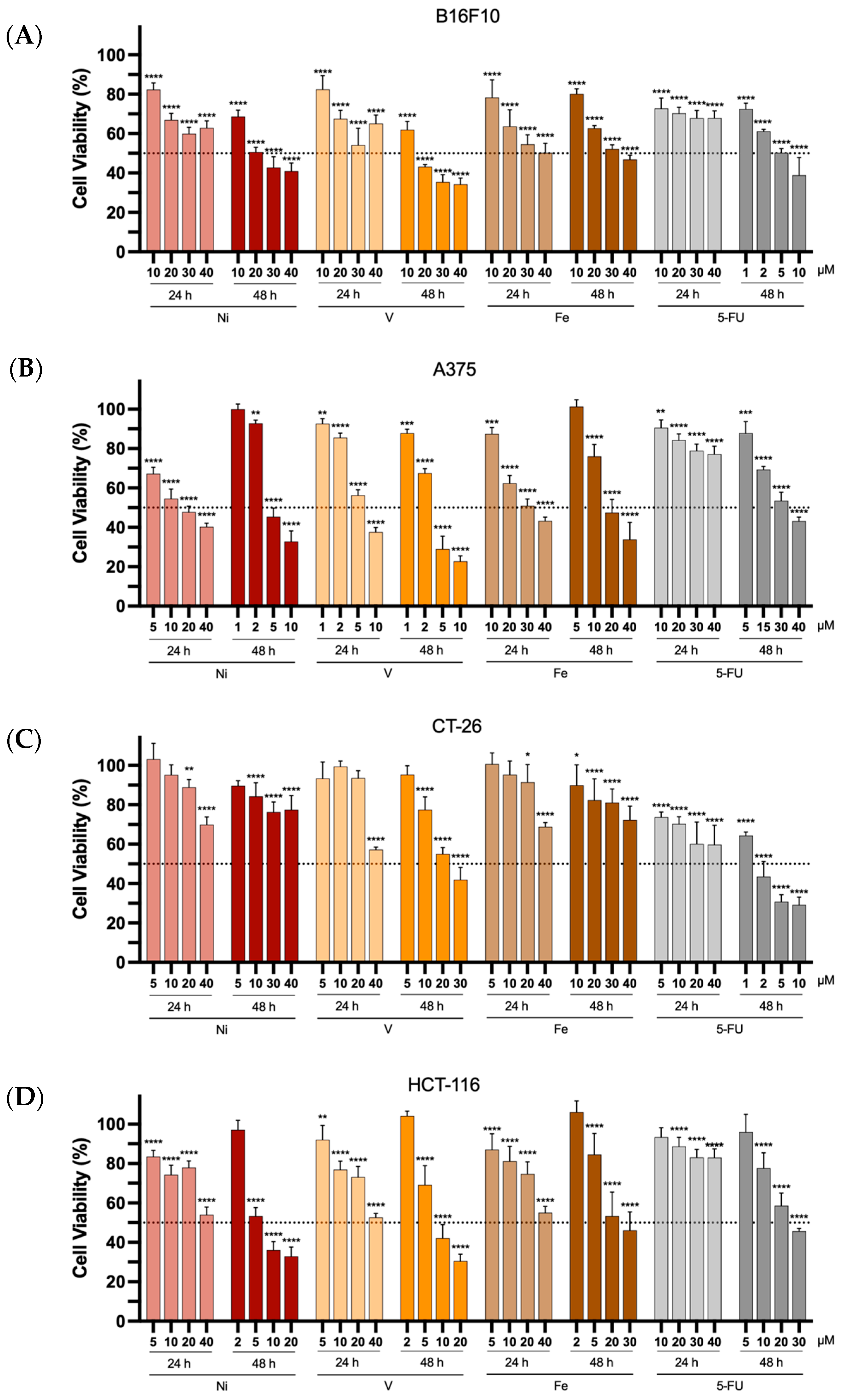
The antiproliferative properties of all metal complexes from L1 were evaluated in murine and human melanoma (B16F10 and A375, respectively) and colon cancer (CT-26 and HCT-116, respectively) cell lines using the MTT assay. The Ni-, V- and Fe-based complexes, as well as 5-FU, used as the positive control, were incubated with the different cell lines for a period of 24 and 48 h. The selection of 5-FU as a positive control was based on this drug being widely used in the clinic for the treatment of cancer, and specifically for melanoma and colon cancer [46,47,48]. Furthermore, the concentrations tested for each compound (from 1 to 40 μM) were selected to evaluate their cytotoxic properties. The cancer cell line viability can be seen in Figure 5.
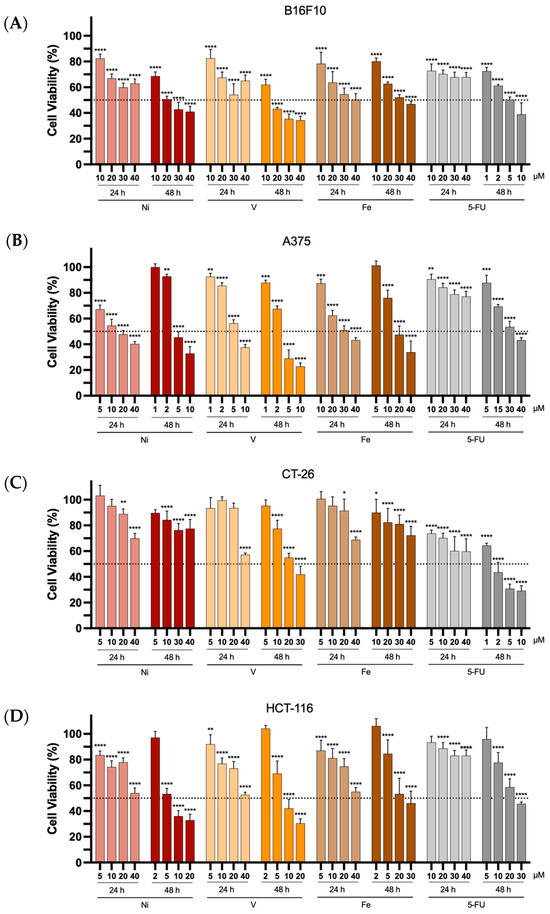
Figure 5.
In vitro antiproliferative properties of the Ni-, V-, and Fe-based complexes towards B16F10 (A), A375 (B), CT-26 (C), and HCT-116 (D) cancer cell lines, 24 or 48 h after incubation at different concentrations (1 to 40 μM). 5-FU was used as a positive control. Results are presented as mean ± SD of at least four independent experiments with six replicates per condition. The dotted line represents 50% cell viability. Statistical analysis was performed by comparing data of each compound at the different tested concentrations with negative control (100% cell viability) using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Šidák’s test. Differences between groups were considered statistically significant when p-value < 0.05. * p < 0.0332, ** p < 0.0021, *** p < 0.0002, and **** p < 0.0001 vs. negative control.
The results in the tested melanoma and colon cancer cell lines showed a clear trend towards a decrease in cell viability as a function of increasing the concentration of the compounds (either metal complexes or 5-FU) and exposure time.
In general, 24 h after incubation, the complexes did not reduce cell viability by more than 50% for concentrations ranging from 1 to 40 μM. An exception was found for the human melanoma cell line, A375, which exhibited a reduction in cell viability greater than 50% for all three metal-based complexes under study. The positive control, 5-FU, an anticancer drug commonly used in the treatment of melanoma and colon cancer [46,47,48], displayed a lower cytotoxic effect, presenting a cell viability superior to 60% for all tested concentrations after 24 h of incubation for all cancer cell lines. Longer incubation times with the different compounds resulted in increased antiproliferative properties, as indicated by the reduced concentrations required for the 48 h incubation period, especially for the Ni- and V-complexes. [Fe(L1)2]Cl exhibited relatively modest antiproliferative properties. A similar tendency of increased cytotoxicity with prolonged incubation time was also observed for 5-FU. Notably, the Ni(II) and Fe(III) complexes exhibited the lowest antiproliferative properties towards the murine colon cancer cell line CT -26 for both tested incubation periods (24 and 48 h).
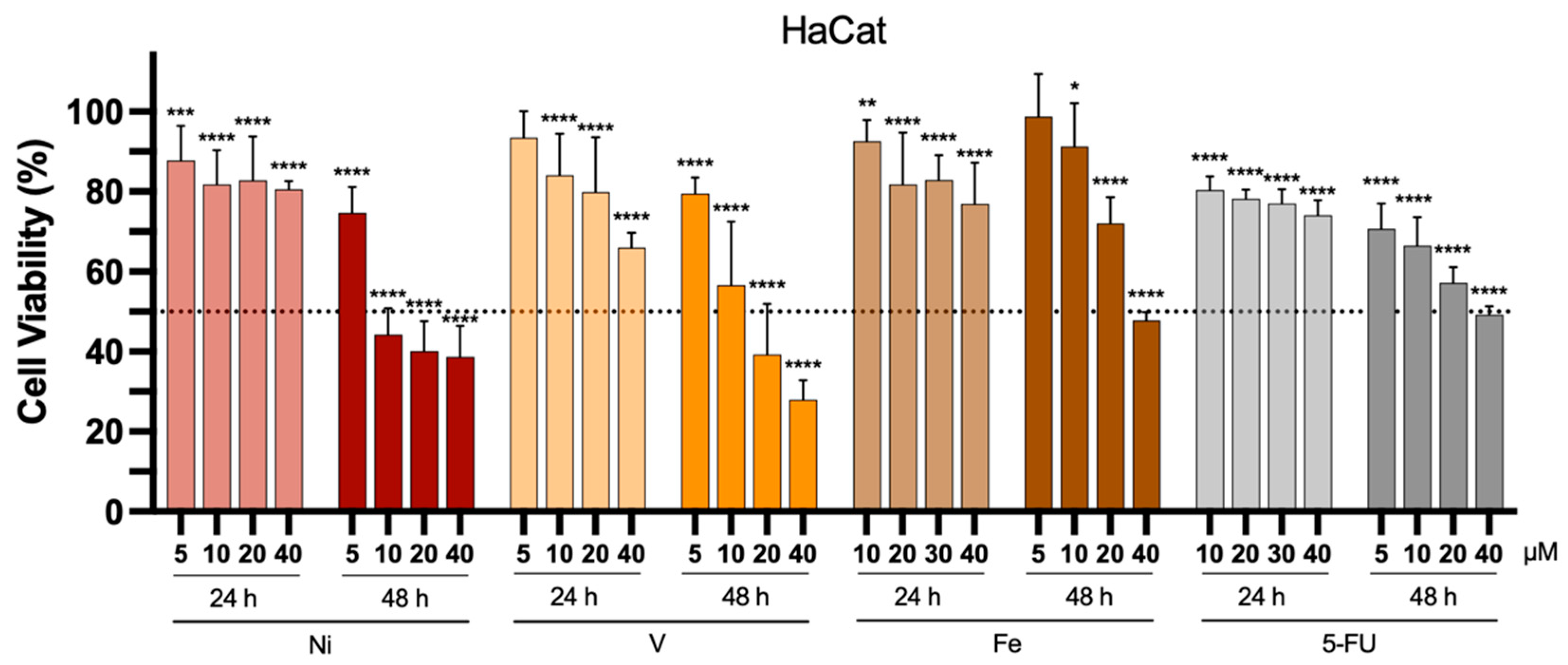
When developing antitumor compounds, assessing their specificity for tumor cells is crucial. To verify this specificity, it is necessary to test these compounds on healthy cells as well. In this study, we selected the human keratinocyte cell line (HaCat) for this purpose. Figure 6 presents the impact of each complex and 5-FU on HaCat cell viability 24 and 48 h after incubation at concentrations ranging from 5 to 40 μM.
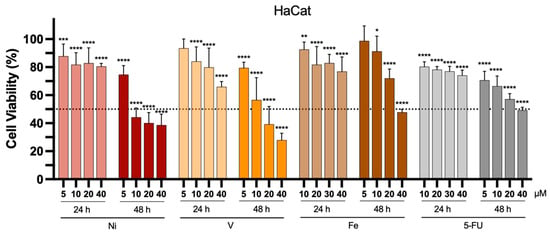
Figure 6.
In vitro antiproliferative properties of the Ni-, V-, and Fe-based complexes towards healthy human keratinocytes HaCat cell lines, 24 or 48 h after incubation at different concentrations (5 to 40 μM). 5-FU was used as a positive control. Results are presented as mean ± SD of at least four independent experiments with six replicates per condition. The dotted line represents 50% cell viability. Statistical analysis was performed by comparing data of each compound at the different tested concentrations with negative control (100% cell viability) using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Šidák’s test. Differences between groups were considered statistically significant when p-value < 0.05. * p < 0.0332, ** p < 0.0021, *** p < 0.0002, and **** p < 0.0001 vs. negative control.
Similar to what was observed for cancer cell lines, a more pronounced reduction in cell viability was also noted in healthy human keratinocyte cells after 48 h of incubation. This effect was particularly evident at higher concentrations, either for the metal-based complexes or 5-FU. The IC50 values obtained for the tested cancerous and healthy cell lines are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Half-inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of the Ni-, V-, and Fe-based complexes and 5-FU towards murine and human melanoma and colon cancer cell lines, as well as healthy human keratinocytes, after 24 or 48 h of incubation.
Results are presented as mean ± SD of at least four independent experiments with six replicates per condition. IC50 values were determined according to Calado and co-workers [49].
Interestingly, and looking closely at the IC50 values obtained for the metal complexes 48 h after incubation in the different cell lines, a superior antiproliferative activity towards human cell lines compared to the murine ones was observed. Moreover, as previously noticed in Figure 5, although the Ni-(II) and V-complexes exhibited low IC50 values in the micromolar range against the B16F10 cell line (21.1 and 15.4 µM, respectively), in A375, the correspondent values were 4.3 and 3.6 µM, and in HCT-116, they were 5.9 and 8.5 µM. In turn, the murine colorectal cancer cell line (CT-26) demonstrated decreased susceptibility to the complexes. Nevertheless, the lowest IC50 value of the three metal-based complexes in this cell line was achieved for the vanadium complex (22.8 µM). On the other hand, the Fe(III) complex showed the lowest antiproliferative effect in all tested cell lines. Regarding the 48 h incubation period, 5-FU, unlike the metal-based complexes, presented higher antiproliferative activity against murine cell lines compared to human ones. The standard log dose–response curves for the different complexes and 5-FU are available in the Supplementary Materials section (Figures S22 and S23).
Promising results similar to those observed in this study have also been reported for other 8-hydroxyquinoline metal complexes, highlighting the potential of these metallodrugs in the treatment of diverse cancer types. Our study, focused on V(IV)O complexes derived from 8-hydroxyquinoline benzohydrazones, showed IC50 values below ca. 6 μM in A375 melanoma cells; however, the incubation time was longer at 72 h [50]. In previous studies, the Zn(II) and Cu(II) complexes of the same ligand [18] presented IC50 values in the same range as the Ni- and V-complexes: 10.3 and 7.7 μM, respectively, against the A375 cell line, although viability was determined with a different assay (CellTiter-Glo 3D kit), and so it is not completely comparable.
It should be noted that since the V-complex oxidizes and originates V(V)O2L, as shown in the stability studies, we do not state that the antiproliferative effect is from the V(IV)O(L)2 species but probably from the species that form in aqueous solution, V(V)O2L + HL.
As previously discussed, assessing the selectivity of compounds for tumor cells versus healthy cells is a critical aspect in the development of new treatments. In this context, the selectivity index (S.I.) is a key metric used to measure this specificity. It is defined as the ratio of the IC50 values of a compound in healthy vs. cancerous cell lines. Higher S.I. values indicate greater selectivity, suggesting that the compound is more effective at targeting cancer cells and potentially safer for healthy tissues [51]. The S.I. values of each complex towards each cancer cell line tested are depicted in Table 4.

Table 4.
Selectivity index (S.I.) of [Ni(L1)2], V-complex, and [Fe(L1)2]Cl, as well as 5-FU in murine and human melanoma and colon cancer cell lines. Data was obtained after a 48 h incubation period.
Different authors define selectivity for varying threshold values, with some considering an S.I. of 1 [52,53], while others considering 2 [54] or 3 [55]. Despite these differences, high S.I. values indicate superior cytotoxicity towards cancer cells compared to healthy ones. In our study, the S.I. values for the tested complexes were generally low, indicating limited selectivity against the melanoma and colorectal cell lines under study. The highest S.I values were observed for human cell lines A375 and HCT-116, whereas 5-FU exhibited higher S.I. values in murine cell lines B16F10 and CT-26. These results are comparable with our previously published work, where Zn(II) and Cu(II) complexes bearing the same ligand presented S.I. values around 1–2 for human melanoma [18]. Nevertheless, it is interesting that the V-complex has the highest S.I. value of the three metal complexes under study, better than the reference drug 5-FU for the human melanoma cell line.
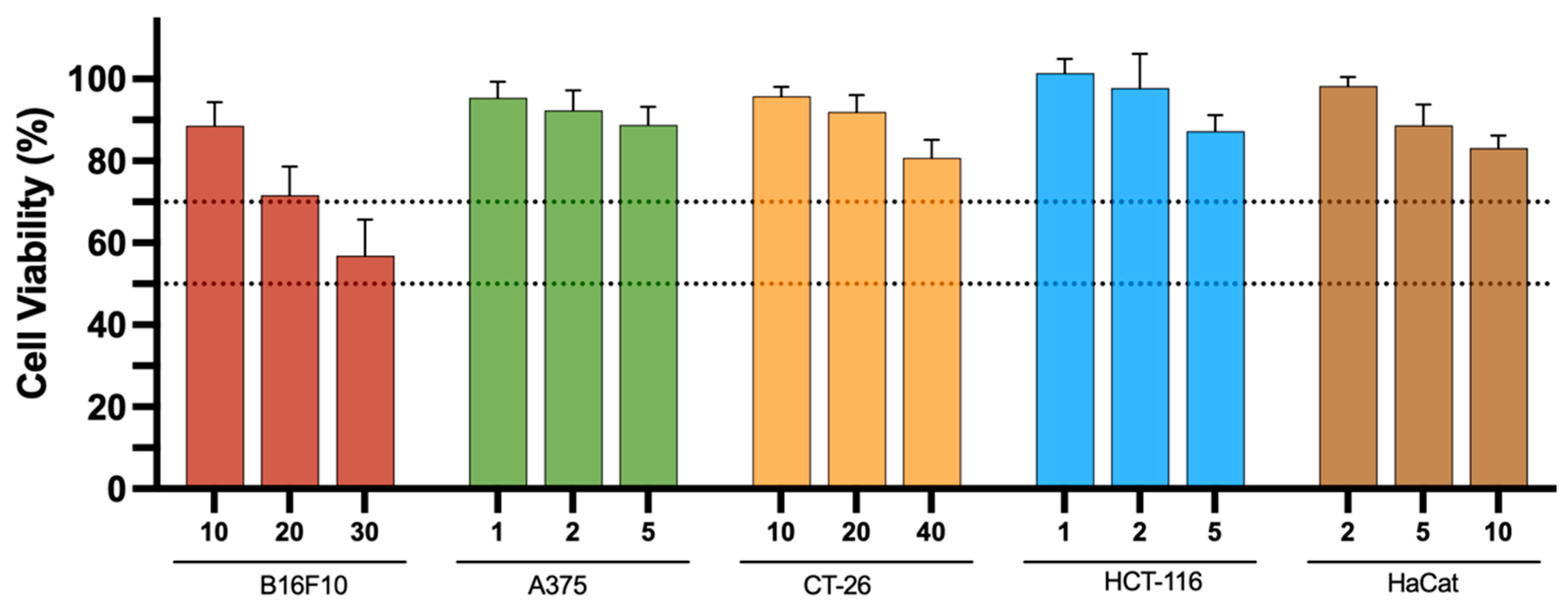
Finally, given that metal-based complexes consist of a central metal ion coordinated to surrounding ligands that modulate the chemical, physical, and biological properties of the complexes [56,57], it is crucial to determine whether the observed antiproliferative activity is primarily due to the ligand or the metal complex. To address this, the ligand used in the design of the complexes, L1, was evaluated after 48 h of incubation (Figure 7). The results show that the ligand does not exhibit significant antiproliferative properties against the melanoma and colon cancer cell lines we tested, as cell viability remained above 70% (upper dashed line) across the entire range of tested concentrations. An exception was observed for the B16F10 cell line, in which, for the highest concentration (30 μM), a cell viability of around 55% was obtained. Nevertheless, the IC50 values for the V- and Ni-based complexes were 21 and 15 μM, respectively. We can therefore conclude that the cytotoxicity observed in most cell studies with the V-complex is mainly due to the V(V)O2L species, since the free ligand is only moderately cytotoxic.
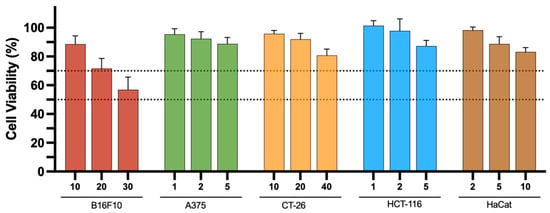
Figure 7.
In vitro antiproliferative properties of ligand, L1, towards B16F10, A375, CT-26, and HCT-116 cancer cell lines as well as healthy keratinocyte (HaCat) cell lines, 48 h after incubation at different concentrations (1 to 40 μM). Results are presented as mean ± SD of at least four independent experiments with six replicates per condition. The dotted lines represents 50 and 70% cell viability, respectively.
We previously reported the antiproliferative properties of Cu, Ni, Ru, and Fe complexes of an 8-hydroxyquinoline benzothiazole Schiff base [14]. The preliminary screening conducted using murine and human colon cancer (CT-26 and HCT-116, respectively) cell lines showed that most complexes, as well as the ligand, exhibited high antiproliferative activity across the tested cell lines, with the Ni(II) complex presenting IC50 values towards CT-26 and HCT-116 colon cancer cells of 11.0 ± 2.3 and 8.6 ± 2.0 (at 48 h), respectively [14].
Furthermore, Pinho and collaborators [58,59] evaluated the antiproliferative effects of a copper complex, containing a 1,10-phenanthroline-type ligand, against several cancer cells, including melanoma (B16F10, A375 and MNT-1), colon (CT-26 and HCT-116), and pancreatic (Bx-PC3 and PANC-1) cancers. IC50 values of 5 µM or lower were found for the copper complex. In addition, although the 1,10-phenanthroline ligand alone displayed IC50 values within a similar range, these were generally higher than those of the Cu-complex. Nevertheless, in a murine colon cancer model, treatment with 1,10-phenanthroline did not result in tumor regression, showing a similar effect to the negative control group (untreated animals) [58].
2.7. In Vitro Synergistic Effect of Metal-Based Complexes in Combination with 5-FU
The investigation of potential synergism in anticancer therapies is a critical aspect of modern oncology research. In clinical practice, the use of multiple cytostatic compounds is a common strategy to maximize antitumor effects, exploit diverse mechanisms of action, and mitigate the development of drug resistance [60,61]. This approach aligns with the growing body of evidence suggesting that combination therapies often yield superior outcomes compared to monotherapies [60,62]. Given the promising results observed for the Ni- and V-based complexes, we aimed to evaluate their potential synergistic effect when combined with the well-established chemotherapeutic agent 5-FU.
The cytotoxic effect of combining [Ni(L1)2] and the V-complex with 5-FU was assessed 48 h after incubation in B16F10 and A375 melanoma cells and CT-26 and HCT-116 colon cancer cells by the MTT assay. Concentrations tested were based on IC50 values previously obtained for the three compounds under study (depicted in Table 2). They ranged from ¼ IC50 to 2 IC50 of each isolated compound, which resulted in the following ratios between the Ni(II) or V-complex and 5-FU: (a) for B16F10, the ratio of [Ni(L1)2]:5-FU was 5.25:1, and for V-complex:5-FU, it was 4:1; (b) for A375, the ratio of [Ni(L1)2]:5-FU was 1.25:8.5, and for V-complex:5-FU, it was 1:8.5; (c) for CT-26, the ratio of [Ni(L1)2]:5-FU was 10:0.5, and for V-complex:5-FU, it was 6.25:0.5; (d) for HCT-116, the ratio of [Ni(L1)2]:5-FU was 1.25:6.25, and for V-complex:5-FU, it was 4.5:12.5. The IC50 values using the mentioned combinations are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Half-inhibitory concentrations (IC50) (in µM) of combinations of metal complexes with 5-FU: [Ni(L1)2] + 5-FU and V-complex + 5-FU towards B16F10, A375, CT-26, and HCT-116 cell lines, after 48 h of incubation.
The IC50 values were calculated, and the obtained results revealed a consistent pattern across all cell lines, as IC50 values for the combination treatments ([Ni(L1)2] + 5-FU and V-complex + 5-FU) generally fall between those of the individual compounds. In the murine cell lines, a reduction in the IC50 values was observed for the Ni(II) and V-complexes when combined with 5-FU. However, this reduction results from the high cytotoxic properties (low IC50 values) of 5-FU towards the B16F10 and CT-26 cell lines: 4.1 and 1.7 μM, respectively. On the other hand, in the human cell lines, an opposite effect was observed as an increase in the IC50 values was achieved for Ni(II) and V-complexes when combined with 5-FU. The two metal-based complexes in isolated form presented IC50 values below 10 μM (from 3.6 to 8.5 μM) and, when combined with 5-FU, ranged from 18.4 to 27.8 μM.
Building upon the obtained IC50 values, we evaluated the nature of the interactions between the metal-based complexes and 5-FU using the CI method. As implemented in CompuSyn, the CI approach provides a quantitative measure of the degree of drug interaction in terms of synergism, additivity, or antagonism [64,65]. This method is particularly valuable as it considers both the potency (IC50) and the shape of the dose–effect curve (Fraction affected (Fa) plot) for each compound and their combinations, which can be found in the Supplementary Materials section (Figures S24 and S25). By analyzing the CI values at various effect levels, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of how the metal-based complexes interact with 5-FU across a range of concentrations.
The CI values for the combined therapies of [Ni(L1)2] + 5-FU and V-complex + 5-FU across four different cancer cell lines, B16F0, A375, CT-26, and HCT-116, can be found in the Supplementary Materials section (Table S4). The results reveal a consistent pattern of antagonism across the majority of the tested cell lines when combining the Ni(II) or V-complex with 5-FU, with the exception of the A375 cell line, where an additive effect was observed for the V-complex + 5-FU combination. These findings align with previous studies exploring combinations of metallodrugs with 5-FU [66,67,68,69].
Furthermore, in Zoetemelk et al. [68], their objectives aimed to identify effective cell line-specific low-dose folinic acid/5-FU/oxaliplatin/irinotecan combinations towards colon cancer cell lines (DLD1, SW620, LS174T, and HCT-116) that outperform the already used clinical combined therapies. The in vitro results demonstrated only a synergistic effect between folinic acid and 5-FU, and additivity, or even antagonism, between the other combination drugs was observed, aligning with our results. However, cisplatin combined with 5-FU has demonstrated synergistic effects in cervical carcinoma cells, the HeLa cell line, by inducing apoptosis and suppressing cell growth [70], which differs from the antagonistic outcomes seen with the Ni(II) and V-complexes combinations, but using another type of cells.
In conclusion, while the present in vitro results indicate a trend towards antagonism in the combinations of the [Ni(L1)2] complex and V-complex with 5-FU, it is essential to recognize that these findings may not fully translate into clinical settings. Metallodrugs can yield beneficial outcomes in patients, suggesting that further exploration of these combinations in vivo is warranted to better understand their therapeutic potential.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
8-hydroxy-2-quinolinecarboxaldehyde, 4-(2-aminoethyl)morpholine, 3-morpholinopropyl amine, 1-(2-aminoethyl)piperidine, nickel(II) chloride hexahydrate, and 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazine ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Vanadium(IV) oxide sulfate pentahydrate and iron(III) chloride hexahydrate were obtained from Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany) and Scharlau (Barcelona, Spain), respectively. Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), ammonium bicarbonate (ABIC), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Cell culture medium, fetal bovine serum (FBS), and antibiotics were purchased from Invitrogen (Thermo Fisher Scientific; Waltham, MA, USA). All the remaining reagents were of analytical grade, and the deionized water was purified through a Millipore system (Burlington, MA, USA).
3.2. Apparatus
The electronic UV−vis absorption spectra were measured on a Cary 60 UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, CA, USA). Infrared (IR, 4000−400 cm−1) spectra were recorded on a Jasco FT/IR 4100 spectrophotometer (Jasco Europe s.r.l., Madrid, Spain) in KBr pellets. C, H, and N elemental analysis were carried out on a FISONS EA 1108 CHNS-O (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) apparatus at Laboratório de Análises of Instituto Superior Técnico. ESI-MS spectra of methanolic solutions of the compounds were measured on a LCQ Fleet TM ion trap mass spectrometer from Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA in both the positive and negative ion modes. CW-EPR spectra were recorded using a BRUKER EleXsys E500 spectrometer (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). The microwave frequency was 9.45 GHz. Fluorescence measurements were performed on a PerkinElmer LS55 spectrofluorometer ( PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with a xenon lamp and in quartz cells with 10 mm optical path; these were steady-state measurements performed at room temperature. HR-MS spectra were recorded on an IMPACT II hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight (QTOF) mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany), equipped with an electrospray ionization source (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany) by flow injection analysis (FIA). Spectra were acquired in the positive electrospray ionization mode ESI (+). Internal calibration was performed for the sodium formate cluster using High-Precision Calibration (HPC) mode.
3.3. Diffuse Reflectance
Diffuse reflectance measurements were conducted using a 6-around-1 fiber bundle reflectance probe (with 6.35 mm diameter steel ferrule and 400 µm core fibers). The probe’s 6-fiber leg was connected a deuterium–tungsten light source, providing continuous illumination from 215–2500 nm while the single-fiber leg was coupled a Flex RES UV-Vis-NIR spectrometer (Sarspec, Porto, Portugal), offering a spectral resolution of 2 nm.
To minimize specular reflection, the probe was mounted at 80° relative to the sample surface. Solid samples were prepared by mixing the target compound powder with barium sulfate (BaSO4) powder in a 1:10 weight ratio. The mixture was then placed into a sample holder and gently pressed to achieve a flat and uniform surface. Barium sulfate, known for its >98% reflectivity from 250 to 1000 nm, was used as a reference standard. Diffuse reflectance spectra were evaluated using the Kubelka–Munk (K-M) function F(R∞):
which describes the behavior of the light path through an infinitely thick and densely-packed dispersing medium as a function of the back-scattering (S) and absorption (k) coefficients [71].
3.4. Magnetic Susceptibility
The magnetic susceptibility of the Fe(III) complex in solution was estimated by 1H NMR using Evan’s method [72]. Briefly, a complex solution of known concentration in an appropriate deuterated solvent was placed in an NMR tube containing a sealed capillary of the deuterated solvent, DMSO-d6. The solvent shift (in Hz) at the probe’s temperature of 302.15 K was recorded on a Bruker Avance 400 MHz Spectrometer (Bruker Avance II, Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). μeff (in μB) was then calculated by reported procedures [73,74,75]. Solvent density corrections were not necessary, given the dilution of the sample (ca. 16 μM); the molar susceptibility value χM was corrected for diamagnetic contributions using Pascal’s constants.
3.5. EPR Measurements and Evaluation of the Spectra
For the EPR measurements, the following parameters were used: a microwave power of 13 mW, a modulation amplitude of 5 G, and a modulation frequency of 100 kHz. The VO(IV) compounds were first dissolved in DMSO (0.5 mL). Then, 200 μL was transferred to a quartz EPR tube and MeOH (50 μL) was added. The samples were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and the spectra measured at ~77 K (liquid nitrogen temperature). The EPR spectra were simulated with EPR software (version 2013) developed by Rockenbauer and Korecz [76]. Axial g- and vanadium hyperfine A-tensors (IV = 7/2) were considered. As for the description of the spectral linewidths, orientation-dependent α, β, and γ parameters were used, in which α, β, and γ define the linewidths through Equation (2):
where MI denotes the magnetic quantum number of the vanadium ion.
σMI = α + βMI + γMI2
3.6. Synthesis and Characterization
A one-pot reaction was used to synthesize the metal-based complexes, starting with the synthesis of the ligand as previously reported [18].
To a methanolic solution (20 mL) of the corresponding amine (2 mmol) and KOH (2 mmol), 8-hydroxy-2-quinolinecarboxaldehyde (2 mmol) was added. The orange solution was stirred at room temperature for one hour. Then, [NiCl2·6H2O], [VOSO4·5H2O], or [FeCl3·6H2O] (1 mmol) were added, and the reaction mixture was stirred for two hours at room temperature. The solvent was evaporated and the solid precipitate was dissolved in dichloromethane, filtered, and recrystallized with diethyl ether (for the [Fe(L1)2]Cl complex) or n-hexane. Good-quality crystals, suitable for SC-XRD studies, were obtained for the [Ni(L1)2] and all [VO(Ln)2] complexes.
[VO(L1)2]: The complex was obtained from the reaction with 4-(2-aminoethyl)morpholine. Yield: 40%; Elemental analyses calcd. for C32H36N6O5V·0.3H2O (641.02 g/mol) (%): C: 59.96, H: 5.75, N: 13.11. Found (%): C: 60.0, H: 5.8, N: 13,0. Mass spectrometry MS (ESI+): m/z (calcd): 636.22, found: 635.86 [M+H+]. UV-vis: [DMSO, λmax/nm (ε/M−1 cm−1)]: 270 (4.50 × 104), 362 (sh), 423 (2.90 × 103). FTIR [KBr, cm−1]: 3041 (νC−H aromatic); 2951, 2852 and 2808 (νC−H aliphatic); 1640, 1563 and 1450 (νC=N and νC=C aromatic); 1106 (νC−O), 984 (νV=O).
[VO(L2)2]: The complex was obtained from the reaction with 3-morpholinopropylamine. Yield: 33%; Elemental analyses calcd. for C34H40N6O5V·0.5H2O (672.68 g/mol) (%): C: 60.71, H: 6.14, N: 12.49. Found (%): C: 61.1, H: 6.1, N: 12.1. Mass spectrometry MS (ESI+): m/z (calcd): 664.25, found: 6634.92 [M+H+]. UV-vis: [DMSO, λmax/nm (ε/M−1 cm−1)]: 270 (5.9 × 104), 346(sh) (4.7 × 103), 425 (2.56 × 103). FTIR [KBr, cm−1]: 2948 (νC−H aromatic); 2874 and 2770 (νC−H aliphatic); 1638, 1562 and 1450 (νC=N and νC=C aromatic); 1107 (νC−O), 966 (νV=O).
[VO(L3)2]: The complex was obtained from the reaction with 1-(2-aminoethyl)piperidine. Yield: 46%; Elemental analyses calcd. for C34H40N6O3V·H2O (640.67 g/mol) (%): C: 63.74, H: 6.38, N: 13.30. Found (%): C: 63.5, H: 6.5, N: 12.8. Mass spectrometry MS (ESI+): m/z (calcd): 632.27, found: 632.12 [M+H+]. UV-vis: [DMSO, λmax/nm (ε/M−1 cm−1)]: 267 (5.9 × 104), 286 (sh) (2.4 × 104), 308 (sh) (1.3 × 104), 345 (sh) (4.6 × 103), 412 (1.9 × 103). FTIR [KBr, cm−1]: 2932 (νC−H aromatic); 2845 and 2797 (νC−H aliphatic); 1643, 1562 and 1449 (νC=N and νC=C aromatic); 1104 (νC−O), 987 (νV=O).
[Ni(L1)2]: The complex was obtained from the reaction with 4-(2-aminoethyl)morpholine. Yield: 69%; Elemental analyses calcd. for C32H36N6NiO4·H2O (645.39 g/mol) (%): C: 59.55, H: 5.93, N: 13.02. Found (%): C: 59.0, H: 6.0, N: 13.0. Mass spectrometry MS (ESI+): m/z (calcd): 627.23, found: 627.07 [M+H+]. UV−vis: [DMSO, λmax/nm (ε/M−1 cm−1)]: 268 (2.80 × 104), 304 (2.65 × 104), 357 (sh), 376 (sh), 526 (2.35 × 103). FTIR [KBr, cm−1]: 3053 (νC−H aromatic); 2958, 2867 and 2816 (νC−H aliphatic); 1627, 1592 and 1449 (νC=N and νC=C aromatic); 1112 (νC−O).
[Fe(L1)2]Cl: The complex was obtained from the reaction with 4-(2-aminoethyl)morpholine. Yield: 48%; Elemental analyses calcd. for C32H36N6O4FeCl·0.4H2O (667.18 g/mol) (%): C: 57.61, H: 5.56, N: 12.60. Found (%): C: 57.6, H: 5.7, N: 12.6. Mass spectrometry MS (ESI+): m/z (calcd): 625.53, found 624.12 [M-Cl]. UV-vis: [DMSO, λmax/nm (ε/M−1 cm−1)]: 270 (4.09 × 104), 454 (sh). FTIR [KBr, cm−1]: 3047 (νC−H aromatic); 2956, 2852 and 2806 (νC−H aliphatic); 1639, 1557 and 1453 (νC=N and νC=C aromatic); 1115 (νC−O).
3.7. Single-Crystal X-Ray Diffraction
The experimental data were measured on a Bruker D8 QUEST ECO triple-circle diffractometer system equipped with a ceramic X-ray tube (Mo Kα, λ = 0.71076 Å) and a Bruker Triumph doubly curved silicon crystal monochromator. Images were integrated using the Bruker SAINT software package (version 8.40A) with a narrow-frame algorithm. The data were corrected for absorption effects using the multi-scan method (SADABS). All structure were solved and refined using the Bruker SHELXTL Software Package (v6.14).
[Ni(L1)2]: A brown, block-like specimen of C32H36N6NiO4, of approximate dimensions 0.060 mm× 0.140 mm × 0.400 mm, was selected for the X-ray crystallographic analysis. In total, 1960 frames were collected. The integration of the data was performed using a monoclinic unit cell that yielded a total of 19632 reflections to a maximum θ angle of 27.55° (0.77 Å resolution), of which 11939 were independent (average redundancy 1.644, completeness = 99.8%, Rint = 4.93%, Rsig = 5.69%) and 9304 (77.93%) were greater than 2σ(F2). The final cell constants of a = 26.768(5) Å, b = 8.1639(14) Å, c = 29.333(5) Å, β = 108.654(5)°, and volume = 6073.4(18) Å3 are based on the refinement of the XYZ-centroids of 5767 reflections above 20 σ(I) with 5.755° < 2θ < 43.57°. The ratio of minimum to maximum apparent transmission was 0.721. The calculated minimum and maximum transmission coefficients (based on the crystal size) are 0.7710 and 0.9600.
The structure was solved and refined, using the space group P 1 21/n 1, with Z = 8 for the formula unit, C32H36N6NiO4. The final anisotropic full-matrix least-squares refinement on F2 with 777 variables converged at R1 = 13.88% for the observed data and wR2 = 36.75% for all data. The goodness of fit was 1.184. The largest peak in the final difference electron density synthesis was 3.473 e−/Å3 and the largest hole was −1.971 e−/Å3 with an RMS deviation of 0.227 e−/Å3. Based on the final model, the calculated density was 1.372 g/cm3 and F(000), 2640 e−.
[VO(L1)2]: A yellow, plate-like specimen of C32H36N6O5V, of approximate dimensions 0.040 mm× 0.080 mm × 0.500 mm, was used for the X-ray crystallographic analysis. In total, 636 frames were collected. The integration of the data was performed using a triclinic unit cell that yielded a total of 30164 reflections to a maximum θ angle of 21.72° (0.96 Å resolution), of which 3606 were independent (average redundancy 8.365, completeness = 99.8%, Rint = 14.34%, Rsig = 7.75%) and 2761 (76.57%) were greater than 2σ(F2). The final cell constants of a = 7.6001(11) Å, b = 14.218(2) Å, c = 14.728(2) Å, α = 74.717(8)°, β = 85.421(8)°, γ = 87.560(8)°, and volume = 1529.9(4) Å3 are based upon the refinement of the XYZ-centroids of 4566 reflections above 20 σ(I) with 5.378° < 2θ < 49.77°. The ratio of minimum to maximum apparent transmission was 0.666. The calculated minimum and maximum transmission coefficients (based on the crystal size) are 0.8350 and 0.9850.
The structure was solved and refined g with the space group P-1, with Z = 2 for the formula unit, C32H36N6O5V. The final anisotropic full-matrix least-squares refinement on F2 with 397 variables converged at R1 = 7.37%, for the observed data and wR2 = 17.34% for all data. The goodness of fit was 1.109. The largest peak in the final difference electron density synthesis was 0.880 e−/Å3 and the largest hole was −0.421 e−/Å3 with an RMS deviation of 0.086 e−/Å3. On the basis of the final model, the calculated density was 1.380 g/cm3 and F(000), 666 e−.
[VO(L2)2]: A yellow, plate-like specimen of C34H40N6O5V, of approximate dimensions 0.030 mm × 0.060 mm × 0.260 mm, was used for the X-ray crystallographic analysis. A total of 635 frames were collected. The integration of the data using a triclinic unit cell yielded a total of 38041 reflections to a maximum θ angle of 27.80° (0.76 Å resolution), of which 7530 were independent (average redundancy 5.052, completeness = 99.2%, Rint = 12.53%, Rsig = 11.06%) and 4612 (61.25%) were greater than 2σ(F2). The final cell constants of a = 9.1625(7) Å, b = 13.5197(10) Å, c = 14.0148(10) Å, α = 70.945(3)°, β = 89.556(3)°, γ = 78.208(3)°, and volume = 1603.0(2) Å3 are based upon the refinement of the XYZ-centroids of 5336 reflections above 20 σ(I) with 5.331° < 2θ < 51.67°. The ratio of minimum to maximum apparent transmission was 0.899. The calculated minimum and maximum transmission coefficients (based on crystal size) are 0.9120 and 0.9890.
The structure was solved and refined using the space group P -1, with Z = 2 for the formula unit, C34H40N6O5V. The final anisotropic full-matrix least-squares refinement on F2 with 478 variables converged at R1 = 7.79%, for the observed data and wR2= 16.43% for all data. The goodness-of-fit was 1.054. The largest peak in the final difference electron density synthesis was 0.777 e−/Å3 and the largest hole was −0.591 e−/Å3 with an RMS deviation of 0.080 e−/Å3. On the basis of the final model, the calculated density was 1.375 g/cm3 and F(000), 698 e−.
[VO(L3)2]: A yellow, needle-like specimen of C34H40N6O3V, with approximate dimensions 0.010 mm × 0.050 mm × 0.400 mm, was selected for the X-ray crystallographic analysis. A total of 1034 frames were collected. The integration of the data was performed using a triclinic unit cell that yielded a total of 71917 reflections to a maximum θ angle of 28.44° (0.75 Å resolution), of which 7611 were independent (average redundancy 9.449, completeness = 99.1%, Rint = 11.97%, Rsig = 6.51%) and 5864 (77.05%) were greater than 2σ(F2). The final cell constants of a = 7.8654(4) Å, b = 13.4661(7) Å, c = 14.7366(7) Å, α = 77.628(2)°, β = 87.379(2)°, γ = 86.519(2)°, and volume = 1520.93(13) Å3 are based upon the refinement of the XYZ-centroids of 9902 reflections above 20 σ(I) with 5.830° < 2θ < 56.30°. The ratio of minimum to maximum apparent transmission was 0.894. The calculated minimum and maximum transmission coefficients (based on the crystal size) are 0.8650 and 0.9960.
The structure was solved and refined, using the space group P -1, with Z = 2 for the formula unit, C34H40N6O3V. The final anisotropic full-matrix least-squares refinement on F2 with 397 variables converged at R1 = 6.54%, for the observed data and wR2= 11.45% for all data. The goodness of fit was 1.125. The largest peak in the final difference electron density synthesis was 0.342 e−/Å3 and the largest hole was −0.569 e−/Å3 with an RMS deviation of 0.078 e−/Å3. On the basis of the final model, the calculated density was 1.379 g/cm3 and F(000), 666 e−.
CCDC 2388547, 2429973, 2429972, and 2388548 contain the supplementary crystallographic data for [VO(L1)2], [VO(L2)2], [VO(L3)2], and [Ni(L1)2], respectively. These data can be obtained free of charge from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/ (accessed on 23 February 2025).
3.8. Stability Studies by UV-Vis and 51V NMR Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry
Stock solutions of each complex were freshly prepared in DMSO and diluted with HEPES buffer (10 mM, pH 7.4), ensuring that the organic solvent content was less than 5% (v/v). The samples were maintained at room temperature, in the absence of light, and monitored by UV−vis absorption spectroscopy for six consecutive hours, and a final measurement was carried out after 24 h.
The 51V NMR spectra of the V-complexes were recorded in DMSO-d6 and a mixture of DMSO/D2O at 0 h and 24 h time points. 51V chemical shifts (δV) were referenced relative to neat VOCl3 as an external standard.
The V(IV)O compounds were dissolved in DMSO (1 mg/mL), and then 200 μL of the stock was added to 1 mL of ABIC buffer (50 mM) at pH 7.4. The HR-MS spectra were recorded immediately after dissolution and after 1 h and 24 h.
3.9. Interaction with BSA
For the measurement of UV−vis spectrophotometric data, bovine serum albumin (BSA) stock solutions were prepared from the lyophilized protein in HEPES buffer (10 mM, pH 7.4) and hydrated for 24 h in the refrigerator. For the evaluation of the interaction of the metal complexes with BSA, 1:1 molar ratios of BSA and [Ni(L1)2] (54 and 261 μM), [VO(L1)2] (40 and 156 μM) and [Fe(L1)2]Cl (51 and 310 μM) complexes in 5% (v/v) DMSO/HEPES were prepared. The first measurement was made immediately after mixing the complex and BSA solutions and another after 30 min. For the next six hours, the spectrum was recorded hourly, and a final measurement was made at 24 h. Spectra were measured between 260 and 900 nm, with quartz cuvettes of 1.0 cm optical path.
The steady-state fluorescence titrations were performed with a 0.5−1.0 μM BSA solution (in HEPES buffer) and were recorded between 310 and 500 nm, using λexc = 295 nm, after addition of the solutions of the complexes directly to the cuvette (optical path of 1.0 cm). To correct and minimize the inner filter and reabsorption interferences [77,78], UV−vis spectra of each sample were measured and used. Additionally, solutions with the same concentration of complex and no BSA were recorded and used as blank spectra. The data were analyzed by fitting the second-order Equation (3), which accounts for both static and dynamic quenching:
where I0 and I are the fluorescence intensities in the absence and presence of quencher (Q) and KS and KD are the static and dynamic quenching constants. The Stern–Volmer equation was used in the range of low quencher concentrations to determine the Stern–Volmer quenching constant (KSV), a measure of the quenching strength, according to Equation (4):
The Scatchard plot allowed the determination of the binding constant (k) and the number of binding sites per protein (n), with the use of the modified Stern–Volmer equation:
3.10. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
In vitro antiproliferative activity and synergism assays were performed in the human immortalized keratinocyte cell line, HaCat, (CLS 300493, Cell Line Service GmbH, Eppelheim, Germany), murine and human melanoma cell lines B16F10 (ATCC® CRL-6475™) and A375 (ATCC® CRL-1619™), as well as in murine and human colorectal cancer cell lines CT-26 (ATCC® CRL-263™) and HCT-116 (ATCC® CCL-247™), respectively. HaCat, B16F10, A375, and HCT-116 cells were grown in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) with high glucose (4500 mg/L). In its turn, CT-26 cells were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) 1640 medium. Both culture mediums were supplemented with 10% of FBS, 100 IU/mL of penicillin, and 100 µg/mL of streptomycin further designed as complete medium. Cell lines were incubated at 37 °C and 5% CO2 environment and maintained every 2–3 days until a confluence of about 80% was reached.
3.11. Assessment of the Antiproliferative Activity
In vitro antiproliferative properties of increasing concentrations of Ni-, V-, and Fe-based complexes and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) towards murine and human cell lines were evaluated by the MTT assay [79]. For this, murine (B16F10) and human (A375) melanoma cells and murine (CT-26) and human (HCT-116) colorectal cancer cells as well as human immortalized keratinocytes (HaCat) were seeded at a concentration of 5 × 104 cells/mL in 96-well plates and allowed to adhere overnight at 37 °C under a 5% CO2 atmosphere. On the next day, the medium was replaced by freshly complete medium in the absence (negative control corresponding to 100% cell viability) or presence of increasing concentrations of the compounds under study for 24 and 48 h at the same culture conditions described above. Concentrations tested for the metal-based complexes and 5-FU ranged from 1 to 40 μM. After the respective incubation period, the medium was discarded, cells were washed twice with PBS at pH 7.4, and 50 μL of MTT at 0.5 mg/mL in incomplete medium was added to all wells. Finally, after an incubation period of 1 to 3 h in an atmosphere at 37 °C and 5% CO2, the formed formazan crystals were dissolved by adding 200 μL of DMSO to each well. Absorbance at 570 nm was measured in a microplate reader (BioTekTM EL×800TM Absorption Microplate Reader; BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT, USA) and the percentage of cell viability was determined in relation to the negative control, according to Equation (6):
where Abssample is the absorbance of cells incubated with tested compounds and Absnegative control is the absorbance of cells exposed only to complete medium corresponding to 100% cell viability.
In addition, the cytotoxic effect of the ligand used for the design of metal-based complexes (L1) was also evaluated. L1 was tested after 48 h of incubation at selected concentrations according to the IC50 values of metal-based complexes that demonstrated the best antiproliferative properties in cancer cells (Ni- and V-based complexes).
Furthermore, the selectivity index (S.I.) of each complex to cancer cells was calculated using Equation (7):
3.12. In Vitro Synergistic Studies
The synergistic effect of the selected metal-based complexes (Ni- and V-based complexes) with 5-FU was evaluated in murine and human melanoma (B16F10 and A375, respectively) and colon cancer (CT-26 and HCT-116, respectively) cell lines after 48 h of incubation. Selected concentrations were based on the respective IC50 values for compounds under study in isolate form (ranging from ¼ to 2-fold the IC50 value) [80]. The combination index (CI) method of Chou and Talalay [64,81] and CompuSyn 1.0 software (ComboSyn, Inc.) were used to calculate the possible synergistic effect of compound combinations [82]. CI reflects the interaction between drugs and is based on the comparison between the combined and individual drug concentrations necessary to achieve a specific effect (Fraction affected or Fa, meaning dead cells), distinguishing between synergistic, additive, or antagonistic effects according to the respective CI: CI < 0.8 indicates synergism, 0.8 < CI < 1.2 indicates additivity, and CI > 1.2 indicates antagonism [65,80]. The final CI value was calculated by taking the mean of the CIs obtained at FA 50, 75, and 90% [65]. Additionally, Fa-CI plots between the levels of different fractions affected against the CI values reflecting the type of interactions between Ni- and V-based complexes with 5-FU can be found in the Supplementary Materials section.
3.13. Statistical Analysis
Results were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of at least three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 9® (GraphPad Software Inc.; Boston, MA, USA), and comparison among groups was analyzed by using a two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Šidák’s test. Differences between groups were considered statistically significant when the p-value < 0.05.
4. Conclusions
Herein, we report the synthesis of V(IV)O, Ni(II), and Fe(III) complexes bearing the previously synthesized Schiff base, L1, which contains 8-hydroxyquinoline and a morpholine heterocycle. Two V(IV)O complexes with changes in the heterocycle (piperidine) or in the spacer length were also prepared (L2 and L3). All compounds were fully characterized by analytic, spectroscopic, and spectrometric techniques. Additionally, the Ni(II) and all V(IV)O complexes were also characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction.
The crystal structures revealed versatile coordination modes: [Ni(L1)2] exhibited a distorted octahedral geometry with two crystallographically independent enantiomers, while all [VO(L)2] complexes displayed a distorted square–pyramidal geometry.
The solution behavior was studied, and some complexes exhibited limited stability in organic/aqueous solution, which was significantly improved in the presence of BSA. The V(IV)O complexes are stable in the solid state but easily oxidized in solution, especially in aqueous media, yielding a V(V)O2L neutral species after the loss of one ligand molecule. 51V NMR and HR-MS studies support these dynamic processes in polar solvents. The complex–BSA interaction was corroborated by fluorescence studies (except for the vanadium complexes), which indicated a high quenching efficiency within the range of reversible binding.
All complexes tested in melanoma and colon cancer cell lines were more cytotoxic towards human cancer cells, A375 and HCT-116, than murine ones. Furthermore, the new complexes displayed lower IC50 values than 5-FU in human cancer cells. The lowest IC50 value of the three metal complexes was achieved for the V-complex, while [Fe(L1)2]Cl had the lowest antiproliferative effect in all tested cell lines. The complexes were also tested in a normal cell line, which showed that they are not particularly selective towards cancer cells, except the V-complex towards A375 melanoma cells (S.I of 4). Combination studies revealed antagonism with 5-FU, except for an additive effect observed in the A375 cell line with the V-complex.
In conclusion, [Ni(L1)2] and the species-originated V-complex exhibited the most promising biological activities, with low micromolar IC50 values in human tumor cells and an additive effect in combination with 5-FU for the vanadium complex. Efforts to improve bioavailability and targeting are ongoing, with nickel and vanadium complexes being incorporated into liposomes and PLGA nanoparticles, respectively, for evaluation in murine models.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/inorganics13050150/s1, Figure S1. ESI-MS spectra of complexes [VO(L1)2], [VO(L2)2], [VO(L3)2], [Ni(L1)2] and [Fe(L1)2]Cl, in MeOH (positive mode). Figure S2. FTIR spectra of the [VO(L1)2], [VO(L2)2], [VO(L3)2], [Ni(L1)2] and [Fe(L1)2]Cl compounds, overlaid with their respective ligand spectra, measured in KBr pellets. The main bands are labeled for clarity. Figure S3. UV-Vis absorbance spectra of (a) the metal complexes, [Ni(L1)2], [VO(L1)2] and [Fe(L1)2]Cl and corresponding ligand, L1, (already reported and shown for comparison) in DMSO (concentrations between 40–90 μM); (b) the V(IV)O complexes (~40 μM), (c) Remission functions deduced from the spectral reflectance measurements for the metal complexes [Ni(L1)2], [VO(L1)2] and [Fe(L1)2]Cl in the solid state and d) Remission functions deduced from the spectral reflectance measurements for the V(IV)O complexes in the solid state. Figure S4. Crystal structures and labeling schemes for enantiomers of [Ni(L1)2]. Figure S5. (A) Intramolecular and (B) intermolecular hydrogen bonds for [Ni(L1)2]. Figure S6. Packing of [Ni(L1)2] along the (A) a axis, (B) b axis and (C) c axis. Figure S7. Intramolecular hydrogen bonds for complex (A) [VO(L1)2]; (B) [VO(L2)2] and (C) [VO(L3)2]. Figure S8. π-stacking interactions in the packing of (A) [VO(L1)2]; (B) [VO(L2)2] and (C) [VO(L3)2]. Figure S9. SC-XRD structure of aqua-bis(5-(isopropoxycarbonyl)pyridine-2-carboxylato)-oxidovanadium(IV) hemihydrate for which the obtained EPR data are close to component 1. Figure S10. Proposed geometry for component 1 of [V(IV)O(L2)2] obtained by simple geometry optimization. Figure S11. UV-vis spectra of the [Ni(L1)2], [Fe(L1)2]Cl and [VO(L1)2] complexes in 100% DMSO from time zero to the 24 h measurement. Figure S12. UV-vis spectra of the [Ni(L1)2], [Fe(L1)2]Cl, [VO(L1)2], [VO(L2)2] and [VO(L3)2] complexes in 5% DMSO/HEPES (10 mM, pH 7.4) from time zero to the 24 h measurement. Figure S13. Comparison of the spectra of L1 (in black) and [VO(L1)2] at time zero (blue) and at 24 h after dissolution (orange) in 100% DMSO. Figure S14. 51V NMR spectra of the vanadium complex [VO(L1)2] after dissolution in 5%DMSO/D2O (6.4 mM) and 100%DMSO-d6 (24.4 mM) at 0 h (A) and 24 h (B). Figure S15. HR-MS spectrum of the oxidized species [VO2(L1)], after 24 h in DMSO/ABIC: simulated (top) and experimental (bottom), [M+H]+ m/z 368.080970 (+2.5 ppm). Figure S16. HR-MS spectrum of the oxidized species [VO2(L2)], after 24 h in DMSO/ABIC: simulated (top) and experimental (bottom), [M+H]+ m/z 382.096620 (+2.6 ppm). Figure S17. HR-MS spectrum of the oxidized species [VO2(L3)], after 24 h in DMSO/ABIC: simulated (left) and experimental (right), [M+H]+ m/z 366.101706 (+2.2 ppm). Figure S18. Comparison of the UV-Vis absorption spectra (in DMSO and 5%DMSO:HEPES) and the remission functions deduced from the spectral reflectance measurements of the solid-state complexes. The absorbance is in arbitrary units for the purpose of comparison. Figure S19. UV-vis spectra of equimolar mixtures of BSA and the [Ni(L1)2], [Fe(L1)2]Cl and [VO(L1)2] or complexes in 5% DMSO/HEPES (10 mM, pH 7.4), from time zero to the 24 h measurement. Figure S20. (A) Fluorescence emission (I) titration of BSA (1.5 μM) with [Ni(L1)2] complex (λexc = 295 nm). (B) Fitting of I0/I (λem = 355 nm) vs. [Ni(L1)2] with a second-order equation [I0/I = 2.75 × 1010 x2 − 1.05× 105 x + 1.45; R2 = 0.993]. (C) Fitting of I0/I (λem = 355 nm) vs. [Ni(L1)2] according to the Stern–Volmer equation (represented in the graph); (D) Scatchard plot at 355 nm obtained from steady-state (I0/I) measurements for [Ni(L1)2] (0–11 μM), [BSA] ~ 1.5 μM, and λex = 295 nm, obtaining n = 1.3 and log k = 6.79, R2 = 0.997. Figure S21. (A) Fluorescence emission (I) titration of BSA (2.5 μM) with [Fe(L1)2]Cl complex (λexc = 295 nm). (B) Fitting of I0/I (λem = 340 nm) vs. [Fe(L1)2]Cl] with a second-order equation [I0/I = 4.0 × 109 x2 − 1.18 × 105 x + 1.0046; R2 = 0.9997]. (C) Fitting of I0/I (λem = 340 nm) vs. [Fe(L1)2]Cl complex according to the Stern–Volmer equation (represented in the graph). (D) Scatchard plot at 340 nm obtained from steady-state (I0/I) measurements for [Fe(L1)2]Cl (0–15 μM), [BSA] ~ 1.5 μM, and λex = 295 nm, obtaining n = 1.2 and log k = 5.95, R2 = 0.999. Figure S22. Dose–response curves for cell viability in the presence of [Ni(L1)2] (Ni), V-complex (V) and [Fe(L1)2]Cl (Fe) complexes towards B16F10 (a), A375 (b), CT-26 (c) and HCT-116 (d) cancer cell lines, 24 or 48 h after incubation at different concentrations (1 to 40 μM). 5-FU was used as a positive control. Results are presented as mean ± SD of at least four independent experiments with six replicates per condition. Figure S23. Dose–response curves for cell viability in the presence of [Ni(L1)2] (Ni), V-complex (V) and [Fe(L1)2]Cl (Fe) complexes towards healthy human keratinocytes HaCat cell lines, 24 or 48 h after incubation at different concentrations (1 to 40 μM). 5-FU was used as a positive control. Results are presented as mean ± SD of at least four independent experiments with six replicates per condition. Figure S24. Fraction affected (Fa) plot showing the dose vs. the effect of [Ni(L1)2] complex (Ni) and 5-FU in monotherapy and combination against cancer cell lines: (a) B16F10, (b) A375, (c) CT-26 and (d) HCT-116. Figure S25. Fraction affected (Fa) plot showing the dose vs. effect of V-complex complex and 5-FU in monotherapy and combination against cancer cell lines: (a) B16F10, (b) A375, (c) CT-26 and (d) HCT-116. Table S1. Selected bond lengths (Å) and angles (°) for [Ni(L1)2] and [VO(Ln)2] (n = 1–3) complexes. Table S2. Octahedral distortion parameters for [Ni(L1)2] calculated with OctaDist program. Table S3. List of identified compounds obtained by HR-MS (positive mode) for complexes [VO(L1)2], [VO(L2)2] and [VO(L3)2] in 20%DMSO/ABIC buffer, and their relative intensities (%) 0 h and 24 h. 8HQ-Ald: 8-hydroxyquinoline-2-carbaldehyde. Table S4. Combination index (CI) values of [Ni(L1)2] + 5-FU and V-complex + 5-FU after 48 of incubation with B16F10, A375, CT-26 and HCT-116 cell lines.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.G. and I.C.; methodology, J.L., L.C.-R., Í.N., N.V.M., X.F., I.R., A.M.M.A., C.P.R., M.M.G., and I.C.; formal analysis and investigation, J.L., L.C.-R., Í.N., A.A., M.D., N.V.M., X.F., I.R., A.M.M.A., C.P.R., M.M.G., and I.C.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L., L.C.-R., and Í.N.; writing—review and editing, L.C.-R., C.P.R., M.M.G., and I.C.; supervision, L.C.-R., C.P.R., M.M.G., and I.C.; funding acquisition, C.P.R. and I.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) for financial support under project references UIDB/00645/2020, UIDP/00645/2020, UIDB/04138/2020, UIDP/04138/2020, UIDB/00100/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDB/00100/2020), accessed on 29 April 2025, UIDP/00100/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDP/00100/2020), accessed on 29 April 2025, LA/P/0056/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/LA/P/0056/2020), accessed on 29 April 2025, PTDC/MED-QUI/31721/2017, and PTDC/QUI-QIN/0586/2020, as well as for the PhD fellowships SFRH/BD/148044/2019 and UI/BD/153626/2022. The Portuguese NMR and mass spectrometry IST-UL are acknowledged for access to the equipment. I. R. acknowledges AGAUR (Generalitat de Catalunya, projects 2021-SGR-00442) and MICINN (PID2022-136892NB-I00).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lopes, J.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Gaspar, M.M.; Reis, C.P. How to Treat Melanoma? The Current Status of Innovative Nanotechnological Strategies and the Role of Minimally Invasive Approaches like PTT and PDT. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Global Cancer Observatory, Cancer Tomorrow—Estimated Number of New Cases of Cancer from 2022 to 2050. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en/dataviz/isotype?years=2050&single_unit=500000&types=0 (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Global Cancer Observatory, Cancer Tomorrow—Estimated Number of Deaths of Cancer from 2022 to 2050. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en/dataviz/isotype?years=2050&single_unit=500000&types=1 (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Global Cancer Observatory, Cancer Tomorrow—Estimated Number of New Cases of Cancer from 2022 to 2025. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en/dataviz/isotype?years=2025&single_unit=500000&types=0 (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Global Cancer Observatory, Cancer Tomorrow—Estimated Number of Deaths of Cancer from 2022 to 2025. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en/dataviz/isotype?years=2025&single_unit=500000&types=1 (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Lucaciu, R.L.; Hangan, A.C.; Sevastre, B.; Oprean, L.S. Metallo-Drugs in Cancer Therapy: Past, Present and Future. Molecules 2022, 27, 6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, S.; Nath, P.; Das, A.; Datta, A.; Baildya, N.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Pathak, S. A review on metal complexes and its anti-cancer activities: Recent updates from in vivo studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 171, 116211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debela, D.T.; Muzazu, S.G.; Heraro, K.D.; Ndalama, M.T.; Mesele, B.W.; Haile, D.C.; Kitui, S.K.; Manyazewal, T. New approaches and procedures for cancer treatment: Current perspectives. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 205031212110343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Singh, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, H.; Sonawane, P.; Pathak, P.; Grishina, M.; Pal Yadav, J.; Verma, A.; Kumar, P. Metal Complexes in Cancer Treatment: Journey So Far. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202300061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndagi, U.; Mhlongo, N.; Soliman, M. Metal complexes in cancer therapy—An update from drug design perspective. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2017, 11, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolmaleki, S.; Aliabadi, A.; Khaksar, S. Riding the metal wave: A review of the latest developments in metal-based anticancer agents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 501, 215579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, V.; Vecchio, G. 8-Hydroxyquinolines in medicinal chemistry: A structural perspective. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 120, 252–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Luxami, V.; Paul, K. Insights of 8-hydroxyquinolines: A novel target in medicinal chemistry. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 108, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, N.; Farinha, P.F.; Pinho, J.O.; Luiz, H.; Mészáros, J.P.; Galvão, A.M.; Costa Pessoa, J.; Enyedy, É.A.; Reis, C.P.; Correia, I.; et al. Metal Coordination and Biological Screening of a Schiff Base Derived from 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Benzothiazole. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, N.; Albino, M.; Ferreira, A.; Escrevente, C.; Barral, D.; Pessoa, J.; Reis, C.; Gaspar, M.; Correia, I. Liposomal Formulations of a New Zinc(II) Complex Exhibiting High Therapeutic Potential in a Murine Colon Cancer Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, N.; Bulut, I.; Sergi, B.; Pósa, V.; Spengler, G.; Sciortino, G.; André, V.; Ferreira, L.P.; Biver, T.; Ugone, V.; et al. Promising anticancer agents based on 8-hydroxyquinoline hydrazone copper(II) complexes. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1106349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côrte-Real, L.; Sergi, B.; Yildirim, B.; Colucas, R.; Starosta, R.; Fontrodona, X.; Romero, I.; André, V.; Acilan, C.; Correia, I. Enhanced selectivity towards melanoma cells with zinc(II)-Schiff bases containing imidazole derivatives. Dalton Trans. 2024, 53, 9416–9432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côrte-Real, L.; Pósa, V.; Martins, M.; Colucas, R.; May, N.V.; Fontrodona, X.; Romero, I.; Mendes, F.; Pinto Reis, C.; Gaspar, M.M.; et al. Cu(II) and Zn(II) Complexes of New 8-Hydroxyquinoline Schiff Bases: Investigating Their Structure, Solution Speciation, and Anticancer Potential. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 11466–11486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoroddu, M.A.; Aaseth, J.; Crisponi, G.; Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Nurchi, V.M. The essential metals for humans: A brief overview. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 195, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crans, D.C.; Yang, L.; Haase, A.; Yang, X. Health benefits of vanadium and its potential as an anticancer agent. In Metallo-Drugs: Development and Action of Anticancer Agents; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 251–280. [Google Scholar]
- Ay, B.; Şahin, O.; Saygıdeğer Demir, B.; Saygideger, Y.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Mahmoudi, G.; Safin, D.A. Antitumor effects of novel nickel–hydrazone complexes in lung cancer cells. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 9064–9072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, B.; Gönül, İ.; Demir, B.S.; Saygıdeğer, Y.; Kani, İ. Synthesis, structural characterization and in vitro anticancer activity of two new nickel complexes bearing imine bonds. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 114, 107824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, C.P.; Yildizhan, Y.; Adiguzel, Z.; Pavan, F.R.; Campos, D.L.; Pessoa, J.C.; Ferreira, L.P.; Tomaz, A.I.; Correia, I.; Acilan, C. New ternary iron(II) aminobisphenolate hydroxyquinoline complexes as potential therapeutic agents. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 8702–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amolegbe, S.A.; Adewuyi, S.; Akinremi, C.A.; Adediji, J.F.; Lawal, A.; Atayese, A.O.; Obaleye, J.A. Iron(III) and copper(II) complexes bearing 8-quinolinol with amino-acids mixed ligands: Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial investigation. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 8, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, V.; Matos, C.P.; Canelas, C.; Pessoa, J.C.; Tomaz, A.I.; Starosta, R.; Correia, I.; León, I.E. New ternary Fe(III)-8-hydroxyquinoline–reduced Schiff base complexes as selective anticancer drug candidates. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2022, 236, 111961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, Part B, 5th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, M.R.; Sarkar, B.; Avecilla, F.; Correia, I. Vanadium(IV and V) complexes of pyrazolone based ligands: Synthesis, structural characterization and catalytic applications. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 17343–17364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembaremba, T.O.; Correia, I.; Hosten, E.C.; Kuznetsov, M.L.; Gerber, W.J.; Pessoa, J.C.; Ogunlaja, A.S.; Tshentu, Z.R. New V IV O-complexes for oxidative desulfurization of refractory sulfur compounds in fuel: Synthesis, structure, reactivity trend and mechanistic studies. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 16687–16704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, I.; Roy, S.; Matos, C.P.; Borovic, S.; Butenko, N.; Cavaco, I.; Marques, F.; Lorenzo, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Moreno, V.; et al. Vanadium(IV) and copper(II) complexes of salicylaldimines and aromatic heterocycles: Cytotoxicity, DNA binding and DNA cleavage properties. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 147, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figgis, B.N.; Hitchman, M.A. Ligand Field Theory and Its Applications; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0471986203. [Google Scholar]
- Ballhausen, C.J.; Gray, H.B. The Electronic Structure of the Vanadyl Ion. Inorg. Chem. 1962, 1, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Gao, T.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Z.; Han, Z.; Lu, G.-L.; Lin, J. Nickel(II) complexes bearing 8-hydroxyquinoline-imine ligands: Synthesis and catalysis in hydrosilylation of aldehydes and ketones. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1294, 136539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Hao, Z.; Han, Z.; Lin, J.; Lu, G.-L. Nickel Complexes Bearing N,N,O-Tridentate Salicylaldiminato Ligand: Efficient Catalysts for Imines Formation via Dehydrogenative Coupling of Primary Alcohols with Amines. Organometallics 2021, 40, 3843–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, A.W.; Rao, T.N.; Reedijk, J.; van Rijn, J.; Verschoor, G.C. Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopic properties of copper(II) compounds containing nitrogen–sulphur donor ligands; the crystal and molecular structure of aqua[1,7-bis(N-methylbenzimidazol-2′-yl)-2,6-dithiaheptane]copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1984, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Benítez, L.J.; Jiménez-Cruz, P.; Cureño-Hernández, K.E.; Solano-Peralta, A.; Flores-Álamo, M.; Flores-Parra, A.; Gracia-Mora, I.; Castillo-Blum, S.E. [VIVO]2+ complexes: Structure, unusual magnetic properties and cytotoxic effect. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 480, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, L.d.S.; da Cruz, J.W., Jr.; Bucalon, D.H.; Romera, S.; dos Santos, M.P.; Lião, L.M.; Vizotto, L.; Martins, F.T.; Dockal, E.R. Synthesis, characterization and crystal structure of racemic vanadyl and uranyl salen-type complexes. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1228, 129656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutradhar, M.; Roy Barman, T.; Mukherjee, G.; Drew, M.G.B.; Ghosh, S. Synthesis, structural characterization and electrochemical activity of oxidovanadium(IV/V) complexes of a diprotic ONS chelating ligand. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2010, 363, 3376–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palion-Gazda, J.; Luz, A.; Raposo, L.R.; Choroba, K.; Nycz, J.E.; Bieńko, A.; Lewińska, A.; Erfurt, K.; Baptista, P.V.; Machura, B.; et al. Vanadium(IV) Complexes with Methyl-Substituted 8-Hydroxyquinolines: Catalytic Potential in the Oxidation of Hydrocarbons and Alcohols with Peroxides and Biological Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micera, G.; Pecoraro, V.L.; Garribba, E. Assessing the Dependence of 51 V A z Value on the Aromatic Ring Orientation of V IV O 2+ Pyridine Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 5790–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, I.; Adão, P.; Roy, S.; Wahba, M.; Matos, C.; Maurya, M.R.; Marques, F.; Pavan, F.R.; Leite, C.Q.F.; Avecilla, F.; et al. Hydroxyquinoline derived vanadium(IV and V) and copper(II) complexes as potential anti-tuberculosis and anti-tumor agents. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2014, 141, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gätjens, J.; Meier, B.; Adachi, Y.; Sakurai, H.; Rehder, D. Characterization and Insulin-Mimetic Potential of Oxidovanadium(IV) Complexes Derived from Monoesters and -carboxylates of 2,5-Dipicolinic Acid. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 2006, 3575–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, M.R.; Khan, A.A.; Azam, A.; Ranjan, S.; Mondal, N.; Kumar, A.; Avecilla, F.; Pessoa, J.C. Vanadium complexes having [VIVO]2+ and [VVO2]+ cores with binucleating dibasic tetradentate ligands: Synthesis, characterization, catalytic and antiamoebic activities. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalese, G.; Machado, I.; Correia, I.; Pessoa, J.C.; Bilbao, L.; Pérez-Diaz, L.; Gambino, D. Exploring oxidovanadium(iv) homoleptic complexes with 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives as prospective antitrypanosomal agents. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 17756–17773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujacz, A.; Zielinski, K.; Sekula, B. Structural studies of bovine, equine, and leporine serum albumin complexes with naproxen. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2014, 82, 2199–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. (Ed.) Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-387-31278-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ewert de Oliveira, B.; Junqueira Amorim, O.H.; Lima, L.L.; Rezende, R.A.; Mestnik, N.C.; Bagatin, E.; Leonardi, G.R. 5-Fluorouracil, innovative drug delivery systems to enhance bioavailability for topical use. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahm, W.J.; Gwillim, E.C.; Badiavas, E.V.; Nichols, A.J.; Kirsner, R.S.; Boggeln, L.H.; Shen, J.T. Treating Melanoma in Situ During a Pandemic with Telemedicine and a Combination of Imiquimod, 5-Fluorouracil, and Tretinoin. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-H.; Ro, E.J.; Yoon, J.-S.; Mizutani, T.; Kang, D.-W.; Park, J.-C.; Il Kim, T.; Clevers, H.; Choi, K.-Y. 5-FU promotes stemness of colorectal cancer via p53-mediated WNT/β-catenin pathway activation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calado, S.; Eleutério, C.; Mendes, E.; Rocha, M.d.J.; Francisco, A.P.; Gaspar, M.M. Nanoformulations of a Triazene Analogue with Specific Affinity to Human Melanoma. J. Nanosci. Adv. Technol. 2016, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, N.; Bulut, I.; Pósa, V.; Sergi, B.; Sciortino, G.; Pessoa, J.C.; Maia, L.B.; Ugone, V.; Garribba, E.; Enyedy, É.A.; et al. Solution chemical properties and anticancer potential of 8-hydroxyquinoline hydrazones and their oxidovanadium(IV) complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2022, 235, 111932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Gangrade, A.; Jana, A.; Mandal, B.B.; Das, N. Design, Synthesis, Characterization, and Antiproliferative Activity of Organoplatinum Compounds Bearing a 1,2,3-Triazole Ring. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronina, T.; Bartmańska, A.; Popłoński, J.; Rychlicka, M.; Sordon, S.; Filip-Psurska, B.; Milczarek, M.; Wietrzyk, J.; Huszcza, E. Prenylated Flavonoids with Selective Toxicity against Human Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Hussain, O.; Phillips, R.M.; Kaminsky, W.; Kollipara, M.R. Neutral and cationic half-sandwich arene d 6 metal complexes containing pyridyl and pyrimidyl thiourea ligands with interesting bonding modes: Synthesis, structural and anti-cancer studies. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, L.L.F.; Silva, M.B.; Moreira, R.O.; Cardoso, A.P.; Fernandes, C.; Horn, A.; de Aquino Almeida, J.C.; Kanashiro, M.M. In Vitro and In Vivo Relevant Antineoplastic Activity of Platinum(II) Complexes toward Triple-Negative MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tram, N.T.T.; Anh, D.H.; Thuc, H.H.; Tuan, N.T. Investigation of chemical constituents and cytotoxic activity of the lichen Usnea undulata. Vietnam J. Chem. 2020, 58, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karges, J.; Stokes, R.W.; Cohen, S.M. Metal complexes for therapeutic applications. Trends Chem. 2021, 3, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricker, S.P. Metal based drugs: From serendipity to design. Dalton Trans. 2007, 4903–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, J.O.; da Silva, I.V.; Amaral, J.D.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Casini, A.; Soveral, G.; Gaspar, M.M. Therapeutic potential of a copper complex loaded in pH-sensitive long circulating liposomes for colon cancer management. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, J.O.; Amaral, J.D.; Castro, R.E.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Casini, A.; Soveral, G.; Gaspar, M.M. Copper Complex Nanoformulations Featuring Highly Promising Therapeutic Potential in Murine Melanoma Models. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doostmohammadi, A.; Jooya, H.; Ghorbanian, K.; Gohari, S.; Dadashpour, M. Potentials and future perspectives of multi-target drugs in cancer treatment: The next generation anti-cancer agents. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, A.C.; Chidley, C.; Sorger, P.K. A curative combination cancer therapy achieves high fractional cell killing through low cross-resistance and drug additivity. eLife 2019, 8, e50036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, R.B.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer systematic review: Combination therapy in combating cancer background. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-C. Theoretical Basis, Experimental Design, and Computerized Simulation of Synergism and Antagonism in Drug Combination Studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug Combination Studies and Their Synergy Quantification Using the Chou-Talalay Method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijnsdorp, I.V.; Giovannetti, E.; Peters, G.J. Analysis of Drug Interactions. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Clifton, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 731, pp. 421–434. ISBN 9781617790799. [Google Scholar]
- Balsa, L.M.; Ferretti, V.; Sottile, M.; Nunes, P.; Costa Pessoa, J.; Correia, I.; León, I.E. New copper(II) and oxidovanadium(IV) complexes with a vitamin B6 Schiff base: Mechanism of action and synergy studies on 2D and 3D human osteosarcoma cell models. Dalton Trans. 2024, 53, 3039–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrián-Blasco, E.; Gascón, S.; Rodríguez-Yoldi, M.J.; Laguna, M.; Cerrada, E. Novel Gold(I) Thiolate Derivatives Synergistic with 5-Fluorouracil as Potential Selective Anticancer Agents in Colon Cancer. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 8562–8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoetemelk, M.; Ramzy, G.M.; Rausch, M.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Drug-Drug Interactions of Irinotecan, 5-Fluorouracil, Folinic Acid and Oxaliplatin and Its Activity in Colorectal Carcinoma Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.; Amaral, J.D.; Capela, R.; Perry, M.d.J.; Braga, C.; Gaspar, M.M.; Piedade, F.M.; Bijlsma, L.; Roig, A.; Pinto, S.N.; et al. Necroptosis induced by ruthenium (II) complexes as mitochondrial disruptors. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, E.-K.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, C.-J.; Park, J.-S. Analysis of the in vitro synergistic effect of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin on cervical carcinoma cells. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer Off. J. Int. Gynecol. Cancer Soc. 2006, 16, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, R.W.; MacNeil, J.D. Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy in Environmental Problem-Solving; CRC Press: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Garland, C.W.; Nibler, J.W.; Shoemaker, D.P. Experiments in Physical Chemistry, 8th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, E.M. Utilizing the Evans method with a superconducting NMR spectrometer in the undergraduate laboratory. J. Chem. Educ. 1992, 69, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piguet, C. Paramagnetic Susceptibility by NMR: The “Solvent Correction” Removed for Large Paramagnetic Molecules. J. Chem. Educ. 1997, 74, 815–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.M.R.; Mahmudov, K.T.; Guedes da Silva, M.F.C.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Copper(II) and iron(III) complexes with arylhydrazone of ethyl 2-cyanoacetate or formazan ligands as catalysts for oxidation of alcohols. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 10071–10083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockenbauer, A.; Korecz, L. Automatic computer simulations of ESR spectra. Appl. Magn. Reson. 1996, 10, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, A.; Prieto, M. Ribonuclease TI and Alcohol Dehydrogenase Fluorescence Quenching by Acrylamide. J. Chem. Educ. 1993, 70, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquês, J.T.; de Almeida, R.F.M. Application of Ratiometric Measurements and Microplate Fluorimetry to Protein Denaturation: An Experiment for Analytical and Biochemistry Students. J. Chem. Educ. 2013, 90, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, J.O.; Matias, M.; Marques, V.; Eleutério, C.; Fernandes, C.; Gano, L.; Amaral, J.D.; Mendes, E.; Perry, M.J.; Moreira, J.N.; et al. Preclinical validation of a new hybrid molecule loaded in liposomes for melanoma management. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 157, 114021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C.; Martin, N. CompuSyn for Drug Combinations and for General Dose-Effect Analysis—User’s Guide; ComboSyn, Inc.: Paramus, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, T.-C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C.; Martin, N. CompuSyn Software for Drug Combinations and for General Dose—Effect Analysis, and User’s Guide; ComboSyn, Inc.: Paramus, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).