Electrical Features of Liquid Crystal Composition Doped with Cobalt Ferrite: Possible Sensing Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
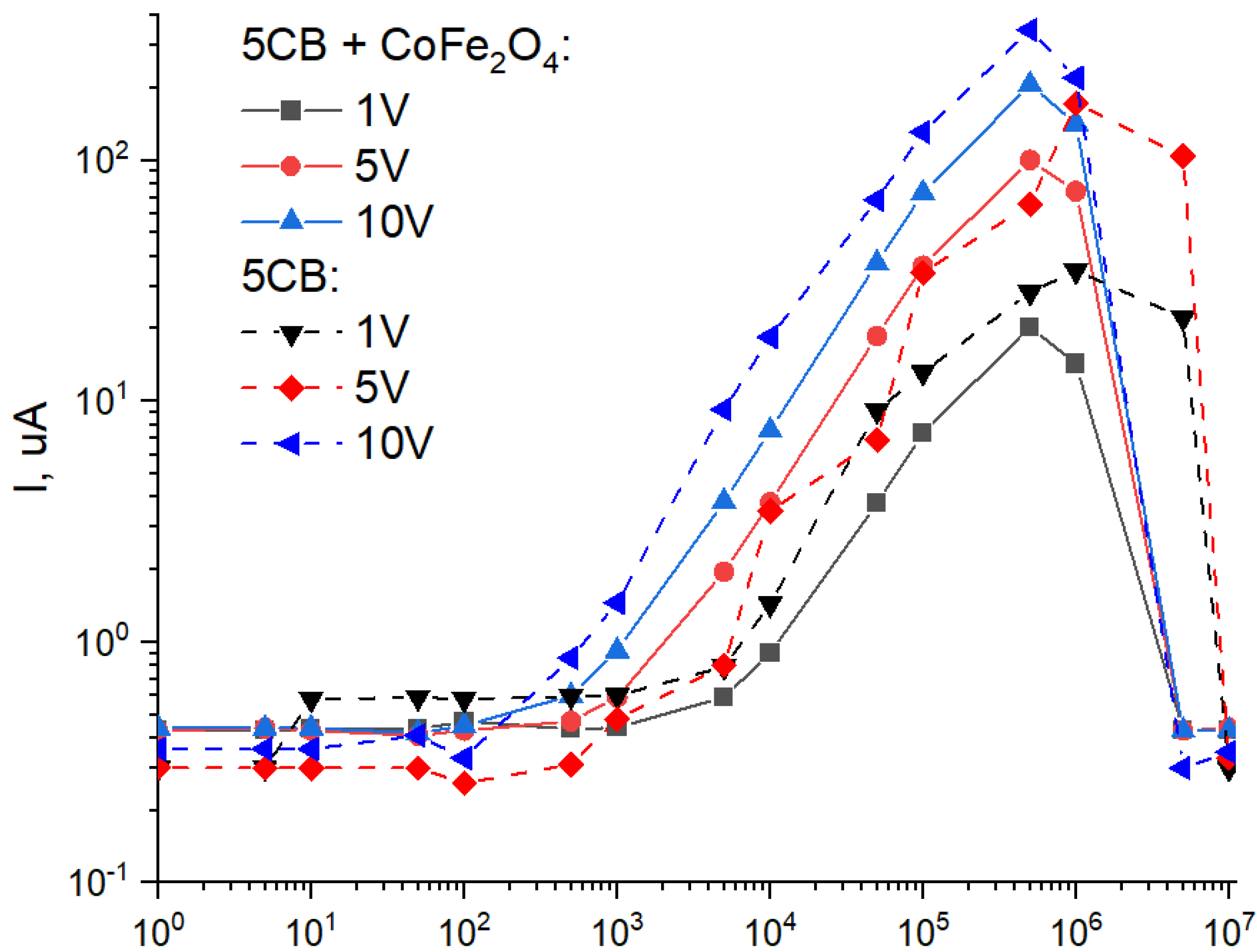
2. Results
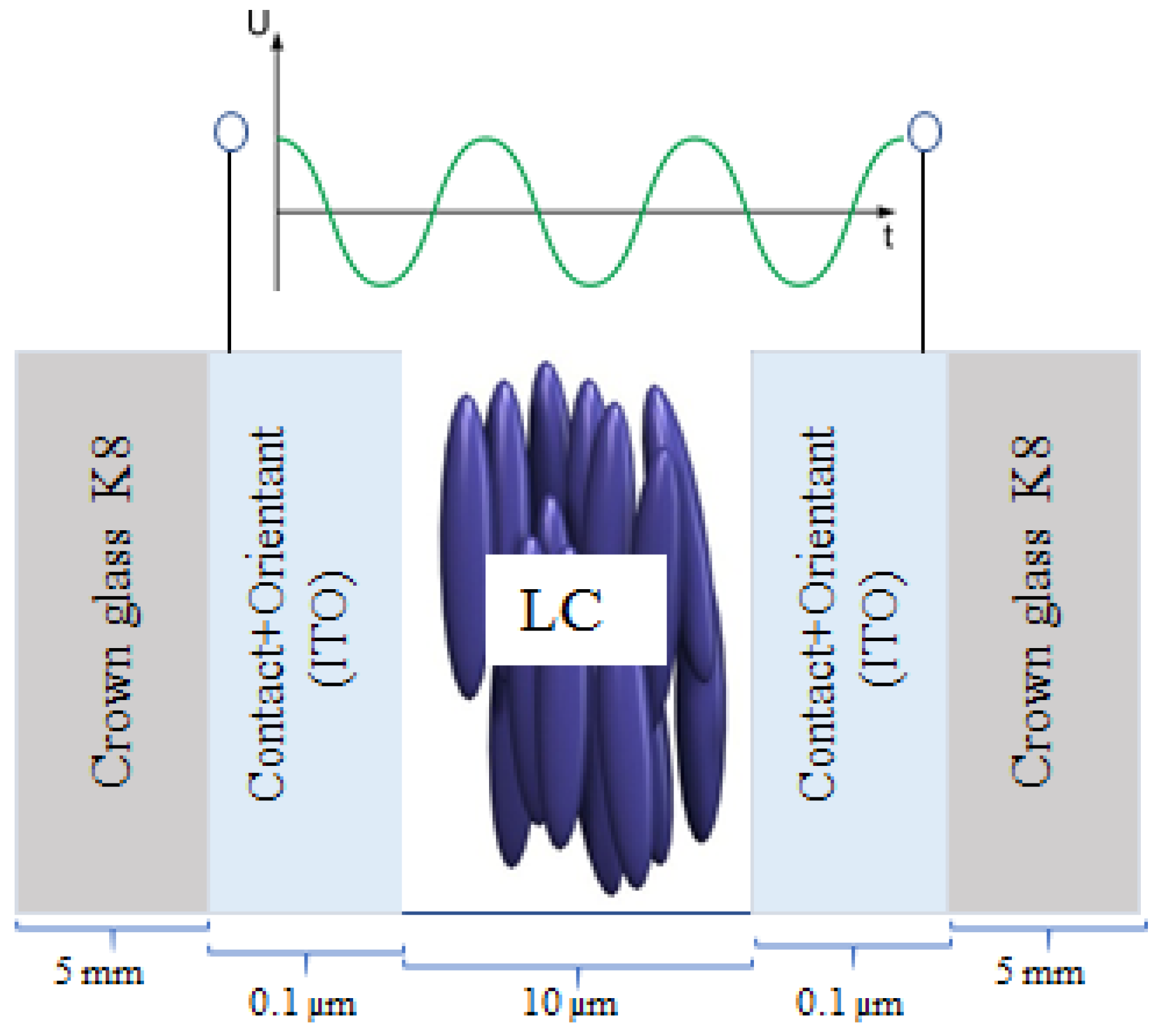
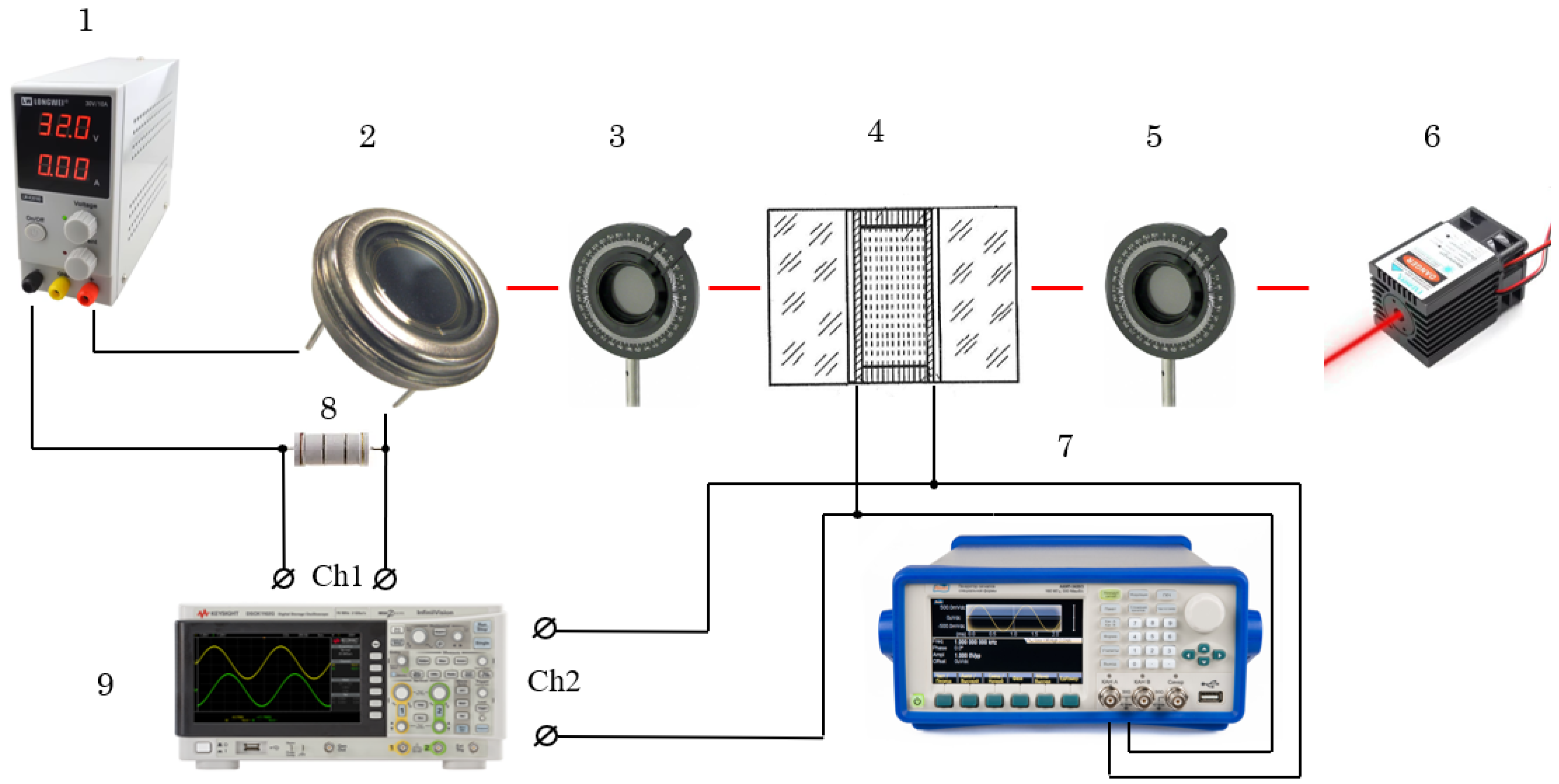
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasil’ev, A.A.; Kasacent, D.; Kompanets, I.N.; Parfenov, A.V. Spatial Light Modulators; Radio & Svyaz’: Moscow, Russia, 1987; 320p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- McEwen, R.S. Liquid crystals, displays and devices for optical processing. J. Phys. B Sci. Instrum. 1987, 20, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, F.; Cipparrone, G.; Umeton, C.; Arabia, G.; Chidichimo, G. Optical nonlinearities induced by thermal effects in polymer dispersed liquid crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1989, 54, 896–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, I.C.; Wood, M.V.; Shih, M.Y.; Chen, P.H. Extremely nonlinear photosensitive liquid crystals for image sensing and sensor protection. Opt. Express 1999, 4, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.N. Nanophotonics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; 432p. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, S.-T.; Lee, B.R.; Gim, M.-J.; Park, K.-W.; Song, M.-H.; Choi, S.-W. Liquid-crystalline blue phase laser with widely tunable wavelength. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3002–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, I.C. Holographic grating formation in dye- and fullerene C60-doped nematic liquid-crystal film. Opt. Lett. 1995, 20, 2137–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Yin, K.; Wu, S.-T. Reflective polarization volume gratings for high efficiency waveguide-coupling augmented reality displays. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 27008–27014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Yoshida, H.; Ozaki, M. Tunable polarization volume gratings based on blue phase liquid crystals. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Ohara, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Noda, K.; Sasaki, T.; Kawatsuki, N.; Ono, H. Temperature dependence of the diffraction efficiency of circular polarization gratings made by liquid crystal molecules with anisotropic absorption. Opt. Mater. Express 2024, 14, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahle, M.; Kasdorf, O.; Kitzerow, H.-S.; Liang, Y.; Feng, X. Electrooptic Switching in Graphene-Based Liquid Crystal Cells. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 543, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, Z.; Bai, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, K. Fast testing of partial camera lenses based on a liquid crystal spatial light modulator. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 6420–6429. Available online: https://opg.optica.org/ao/abstract.cfm?URI=ao-61-22-6420 (accessed on 13 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Hadjichristov, G.B. Control of Coherent Light Through Microperiodic Director Modulation in Nematic Films Under Low-Voltage DC Electric Field. Materials 2023, 16, 6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, K. Phase-Only Liquid-Crystal-on-Silicon Spatial-Light-Modulator Uniformity Measurement with Improved Classical Polarimetric Method. Crystals 2023, 13, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Han, J.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Song, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhu, J. Advanced liquid crystal-based switchable optical devices for light protection applications: Principles and strategies. Light Sci. Appl. 2023, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Hsieh, L.-H.; Chien, H.-W. Enhanced Solar Cell Conversion Efficiency Using Birefringent Liquid Crystal Polymer Homeotropic Films from Reactive Mesogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21319–21327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, Q.; Lan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Liquid-crystal-based fiber laser sensor for non-invasive gas detection. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 4508–4511. Available online: https://opg.optica.org/ol/abstract.cfm?URI=ol-48-17-4508 (accessed on 13 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Shadkami, R.; Chan, P.K. A Numerical Study on the Performance of Liquid Crystal Biosensor Microdroplets. Crystals 2023, 13, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Du, W.; Shao, F.; Li, S.; Kuai, Y.; Cao, Z.; Xu, F.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Peng, G.-D.; et al. Voltage, thermal and magnetic field fiber sensors based on magnetic nanoparticles-doped photonic liquid crystal fibers. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 25372–25384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Patterned Liquid Crystal Polymer Thin Films Improved Energy Conversion Efficiency at High Incident Angles for Photovoltaic Cells. Polymers 2024, 16, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudreyko, A.; Chigrinov, V.; Neyts, K.; Chausov, D.; Perestoronina, A. Photonic Devices with Multi-Domain Liquid Crystal Structures. Crystals 2024, 14, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigrinov, V.G.; Kudreyko, A.A.; Podgornov, F. Optically rewritable liquid crystal displays: Properties and performance. Crystals 2021, 11, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhong, G.C.; Chen, T.J.; Lin, Y.-T.; Wu, J.-J.; Yang, Y.J. Effect of chiral dopant on electro-optical properties of nematic liquid crystal cells under in-plane switching and non-uniform vertical electric fields. Opt. Mater. Express 2014, 4, 2468–2477. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Weng, C. Tuning Electro-Optical Properties Through Polymerization Monomer Content in PSVA Liquid Crystal Displays: Simulation and Experimentation. Polymers 2024, 16, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, J.; Lai, Y.; Sun, J.; Shang, J.; Zhao, S. A Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle-Doped Photo-Alignment Layer and Liquid Crystal Layer for Optimizing the Rewriting Speed and the Response Time of Optically Driving Liquid Crystal Displays. Crystals 2022, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soref, R.A.; Rafuse, M.J. Electrically controlled birefringence of thin nematic films. Appl. Phys. 1972, 43, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar]
- Casasent, D. Performance Evaluation of Spatial Light Modulators. Appl. Opt. 1979, 18, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, G.P. Optical properties of a liquid crystal image transducer at normal incidence: Mathematical analysis and applications to the off-state. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1980, 70, 287–300. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, G.P. Optical properties of a liquid crystal image transducer at normal incidence: Mathematical analysis and applications to the on-state. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1980, 70, 843–856. [Google Scholar]
- Macfaden, A.J.; Wilkinson, T.D. Characterization, design, and optimization of a two-pass twisted nematic liquid crystal spatial light modulator system for arbitrary complex modulation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2017, 34, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, S. Development and Prospect of Viewing Angle Switchable Liquid Crystal Devices. Crystals 2022, 12, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Cheng, M.; Kong, D.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.J. Switchable liquid crystal lenticular microlens arrays based on photopolymerization-induced phase separation for 2D/3D autostereoscopic displays. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, O.V.; Kovalchuk, T.M.; Garbovskiy, Y. Eliminating Ambiguities in Electrical Measurements of Advanced Liquid Crystal Materials. Crystals 2023, 13, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zid, M.; Cordoyiannis, G.; Kutnjak, Z.; Kralj, S. Criticality Controlling Mechanisms in Nematic Liquid Crystals. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, C.-H.; Oh, S.-W. Review of Angular-Selective Windows with Guest–Host Liquid Crystals for Static Window Applications. Crystals 2024, 14, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W. Frequency-stable liquid crystal lenses using a circumferentially segmented concentric electrode. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 48315–48328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Sinha, A. Nanoscale surface metrology with a liquid crystal-based phase-shifting angular shearing interferometer. Opt. Lett. 2024, 49, 1705–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparyan, P.K.; Margaryan, H.L.; Abrahamyan, V.K.; Sargsyan, T.K.; Hakobyan, N.H. Switchable anisotropic diffraction mode filter based on fork-like liquid crystal gratings. Appl. Opt. 2024, 63, 8712–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronov, A.A.; Bachiller, C.; Villacampa, B.; Boria, V.E. Development of Reconfigurable High-Frequency Devices Using Liquid Crystal in Substrate-Integrated Gap Waveguide Technology. Crystals 2024, 14, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Fan, F.; Zhao, H.-J.; Liu, J.; Ji, Y.-Y.; Cheng, J.-R.; Chang, S.-J. Active broadband unidirectional focusing of terahertz surface plasmons based on a liquid-crystal-integrated on-chip metadevice. Photonics Res. 2024, 12, 2148–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanina, N.V. Fullerene-dispersed liquid crystal structure: Dynamic properties and self-organization processes. Physics-Uspekhi 2005, 48, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanina, N.V. New optical effects in liquid crystals: Self-organization and dynamic properties of fullerene-doped nematic mesophase. Proc. SPIE 2005, 5947, 594704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanina, N.V.; Komolkin, A.V.; Yevlampieva, N.P. Variation of the Orientational Order Parameter in a Nematic Liquid Crystal–COANP–C70 Composite Structure. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2005, 31, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanina, N.V.; Zubtsova, Y.A.; Toikka, A.S.; Likhomanova, S.V.; Zak, A.; Tenne, R. Temporal properties of liquid crystal cell with WS2 nanoparticles: Mesophase sensitization and relief features. Liq. Cryst. Their Appl. 2020, 20, 34–40. Available online: http://nano.ivanovo.ac.ru/journal/ru/articles/article.php?year=2020&issue=1&first_page=34 (accessed on 31 March 2020). [CrossRef]
- Kamanina, N. Refractive Properties of Conjugated Organic Materials Doped with Fullerenes and Other Carbon-Based Nano-Objects. Polymers 2023, 15, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamanina, N.V.; Toikka, A.S.; Barnash, Y.V.; Redka, D.N.; Lihkomanova, S.V.; Zybtsova, Y.A.; Kyzhakov, P.V.; Jovanovic, Z.; Jovanovic, S. Functioning features of liquid crystalline cells doped with CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Liq. Cryst. Their Appl. 2022, 22, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanina, N.; Kukharchik, A.; Kuzhakov, P.; Vasilyev, P. Nano-structured conducting layers based on ITO and their modified properties. In Proceedings of the 14th Israeli Russian Bi-National Workshop “The Optimization of the Composition, Structure and Properties of Metals, Oxides, Composites, Nano and Amorphous Materials”, Ariel, Israel, 12–16 July 2015; pp. 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Toikka, A.; Ilin, M.; Kamanina, N. Perspective Coatings Based on Structured Conducting ITO Thin Films for General Optoelectronic Applications. Coatings 2024, 14, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toikka, A.S.; Kamanina, N.V. Surfaces modifications in functional layers for liquid crystal devices. St. Petersburg Polytech. Univ. J. Phys. Math. 2024, 17, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, S.; Spreitzer, M.; Tramšek, M.; Trontelj, Z.; Suvorov, D. Effect of Oleic Acid Concentration on the Physicochemical Properties of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 13844–13856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanina, N.V.; Vasiliev, P.Y.; Studenov, V.I. Polarizing Films for the Visible Range of the Spectrum with a Nanostructured Surface Based on Carbon Nanoparticles. Russian Patent No. RU 2426157 C1, 10 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
| Systems | The Amplitude of the Control Voltage, V | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 10 | |
| 5CB | 0.245 | 0.390 | 1.17 |
| 5CB + CoFe2O4 | 0.58 | 0.59 | 0.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barnash, Y.; Jovanović, S.; Jovanović, Z.; Kamanina, N. Electrical Features of Liquid Crystal Composition Doped with Cobalt Ferrite: Possible Sensing Applications. Inorganics 2025, 13, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040107
Barnash Y, Jovanović S, Jovanović Z, Kamanina N. Electrical Features of Liquid Crystal Composition Doped with Cobalt Ferrite: Possible Sensing Applications. Inorganics. 2025; 13(4):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040107
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarnash, Yaroslav, Sonja Jovanović, Zoran Jovanović, and Natalia Kamanina. 2025. "Electrical Features of Liquid Crystal Composition Doped with Cobalt Ferrite: Possible Sensing Applications" Inorganics 13, no. 4: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040107
APA StyleBarnash, Y., Jovanović, S., Jovanović, Z., & Kamanina, N. (2025). Electrical Features of Liquid Crystal Composition Doped with Cobalt Ferrite: Possible Sensing Applications. Inorganics, 13(4), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040107









