Abstract
Boron Neutron Capture Therapy is a re-emerging therapy for the treatment of cancer, and the development of new neutron-reactive nuclei carriers with enhanced efficiency is of great importance. In this work we propose three new boron-based solid compounds, of formulas [Ca(H2O)6](C14H8O6B)2 (CaSB), [Cu(C14H8O6B)] (CuSB), and [Li(C14H8O6B)(H2O)] (LiSB), usable as nanoparticles for the carriage of the 10B isotope. The copper atom in CuSB was introduced because it is known that its presence magnifies the effect of the radiation on cells. Furthermore, the lithium atom in LiSB also allows us to include the 6Li isotope, which can take part in the nuclear reactions, enhancing the efficiency of the anti-cancer treatment. The compounds were characterized with single-crystal X-ray diffraction to compare the densities of the reactive isotopes in the materials, a key parameter related to the efficiency of the materials. In this work, we used a computational method to calculate the dose absorbed by a tumor mass treated with nanoparticles of the compounds in order to select the most efficient one for the therapy. The results reported in this work are encouraging.
1. Introduction
Among the radiation techniques used to treat cancer, Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) is a re-emerging therapy due to its advantages of target therapy and low toxicity. In fact, it can overcome radio-resistance in different types of cancers, inducing minimal damage to the adjacent normal tissues [1]. It consists in the irradiation of cancer cells carrying the boron-10 isotope with thermal neutrons. When a thermal neutron is captured by the boron-10 isotope, a nuclear (n,α) reaction occurs: the unstable boron-11 isotope forms and decays into a lithium-7 and an α particle, which release a large amount of energy along their short pathway.
The efficacy of this technique requires a suitable selective concentration of the boron-10 isotope into cancer cells rather than the healthy cells, and for this reason, a lot of efforts are being made to develop more selective boron delivery agents [2]. Several boron-10-containing molecules were prepared and studied, but the low difference in boron concentration between tumor tissues and healthy tissues is still not satisfactory to justify the application of BNCT on a large scale.
Recently, boron-10-enriched nanoparticles were proposed as boron delivery agents, since in each nanoparticle hundreds of thousands of boron atoms were concentrated, and furthermore, the surface of nanoparticles can be easily modified with specific biomarkers to systematically penetrate inside the target tumor cells [3,4,5,6].
Boron-10 is not the only isotope that can produce a nuclear reaction with thermal neutrons; lithium-6 nuclei can capture neutrons to yield tritium and α particles that release energy into the cells. The combination of the nuclear reaction of both isotopes could greatly improve the efficacy of the Neutron Capture Therapy (NCT).
In our previous work, two compounds containing both boron and lithium, of formulas Li[(C6H12O6)2B]·2H2O (LiMB) and Li5[(C4H4O6)2B]·5.5H2O (LiTB) (M = mannitol, T = L-(+)-tartrate), were synthesized with 6Li and 10B isotopes, and their behavior under thermal neutron radiation was tested [7]. The preliminary tests were encouraging, although not quantitatively conclusive, and the necessity to synthesize more efficient compounds was reported.
In this work, we propose three new solid salicylatoborate complexes, of formulas [Ca(H2O)6](C14H8O6B)2·4H2O (CaSB), [Cu(C14H8O6B)2] (CuSB), and [Li(C14H8O6B)(H2O)] (LiSB), as new boron and/or lithium delivery agents for the NCT. In general, salicylatoborate complexes are considered inexpensive, stable materials, usually non-toxic [8]. In our previous work [9], we developed, for analogue compounds, a method to both obtain particles of nanoscale dimension and to suitably cover them in order to permit their encapsulation in biological tumor cells. Thus, we are confident that we will also be able to reduce to nanoscale the dimension of the particles of the present compounds, and, due to the presence of many OH groups in the salicylate fragments, to exploit the same method to suitably functionalize the nanoparticle surface, which allows them to be concentrated into tumor tissues.
CuSB was synthesized since Cu2+ ions were found to enhance the radiosensitivity of cells towards gamma rays [10].
In this work, we employed a computational method to calculate the dose (D) absorbed by a tumor mass. To perform these calculations, the three compounds investigated in this work were characterized with the single-crystal X-ray diffraction technique (XRD), in order to calculate the concentration of the neutron-reactive isotopes in the nanoparticles. The calculations were also performed on the LiMB and LiTB compounds for comparison. The calculation method reported in this work allows for the preliminary prediction of the compound with the best therapeutic efficacy for the NCT before the testing at the neutron source.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Syntheses
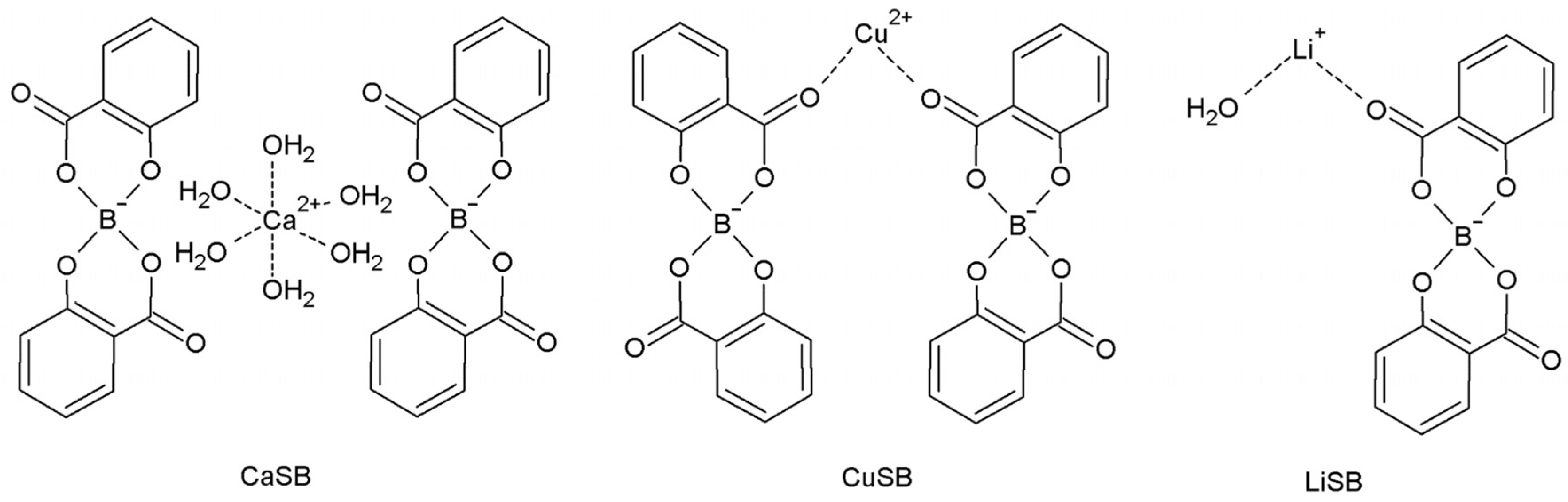
The salicylatoborate compounds were synthesized by mixing salicylic acid, boric acid, and an inorganic base (a metal hydroxide or carbonate), and dissolving the reagents in warm water. An esterification reaction occurs, where the boric acid hydroxyl groups react with those of the salicylate, and the metal atom is coordinated by the oxygen atoms of either water molecules or the salicylate fragment. In Scheme 1, the molecular schemes of the three products obtained are reported.
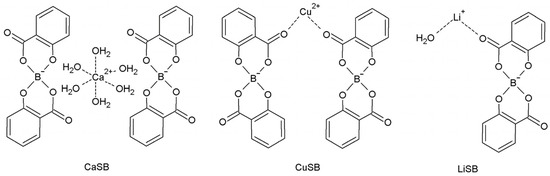
Scheme 1.
Molecular schemes of the salicylatoborate compounds.
The diesters of boric acid, based on aromatic or aliphatic diols, are known to be thermodynamically stable, almost indissociable in water, non-toxic, and inexpensive [8]. The products obtained precipitated directly in crystals suitable for the XRD characterization or quickly spontaneously recrystallized.
2.2. X-Ray Crystal Structures
2.2.1. Crystal Structure of CaSB
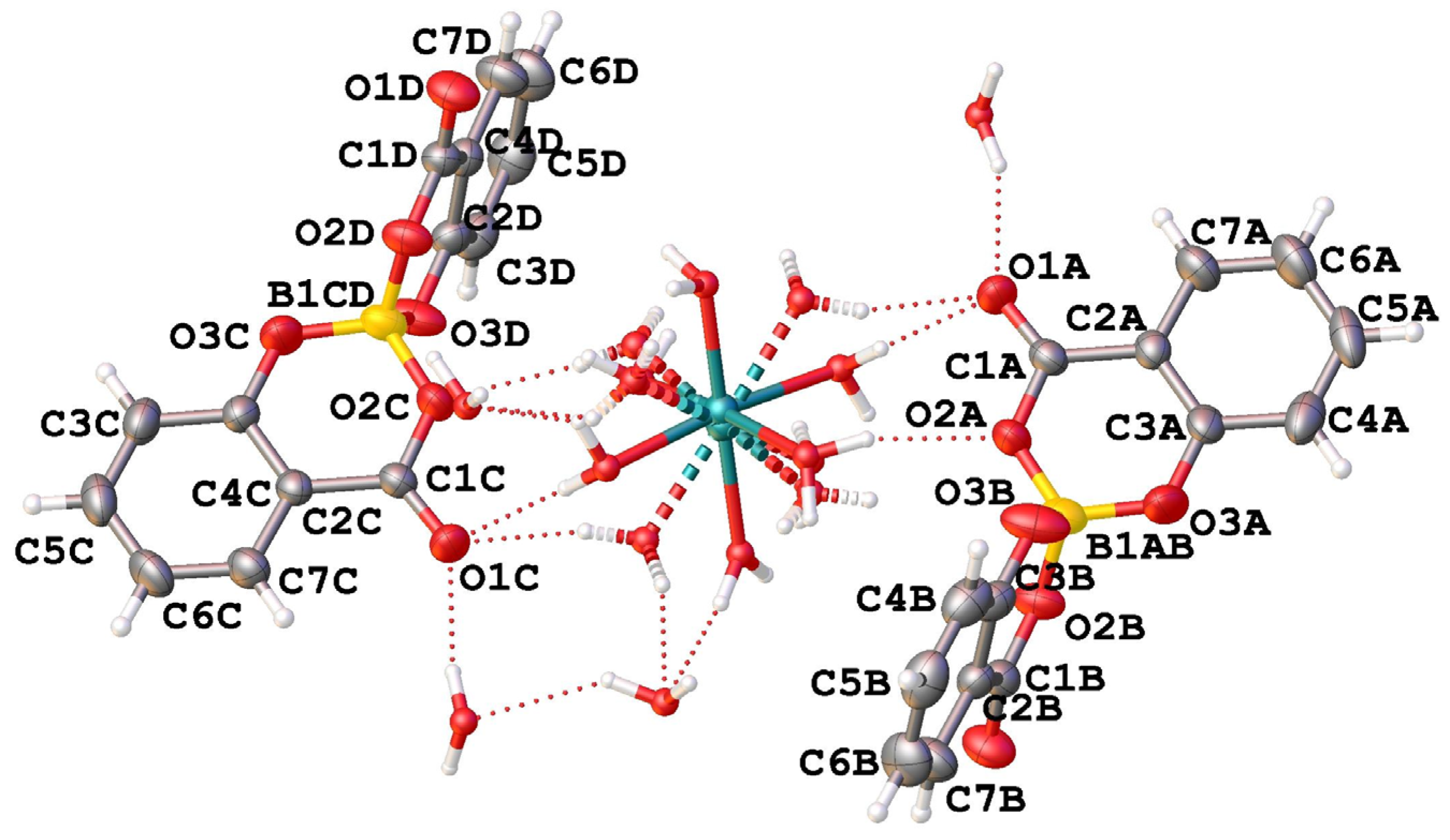
The asymmetric unit of compound CaSB consists of two salicylatoborate units (one boron atom covalently bonded to two salicylate fragments) connected through hydrogen bonds to one disordered [Ca(H2O)6]2+ complex, and to four water molecules embedded in the crystal structure (Figure 1).
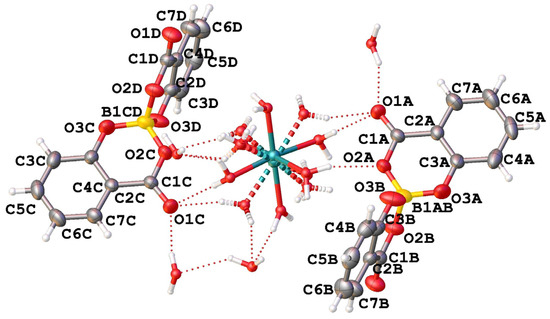
Figure 1.
View of the asymmetric unit of [Ca(H2O)6](C28H16O12B)2·4H2O (CaSB) with atom labelling.
In the crystal packing, the salicylatoborate units are intercalated by the calcium exahydrated complexes and by the free water molecules in a three-dimensional lattice. The relevant bond distances are reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Relevant bond distances (Å) from X-ray data for the LiSB compound.
In each unit cell, there are eight boron atoms, and the density of the boron atoms in the crystals is 2.256 × 1027 atoms/m3.
2.2.2. Crystal Structure of CuSB
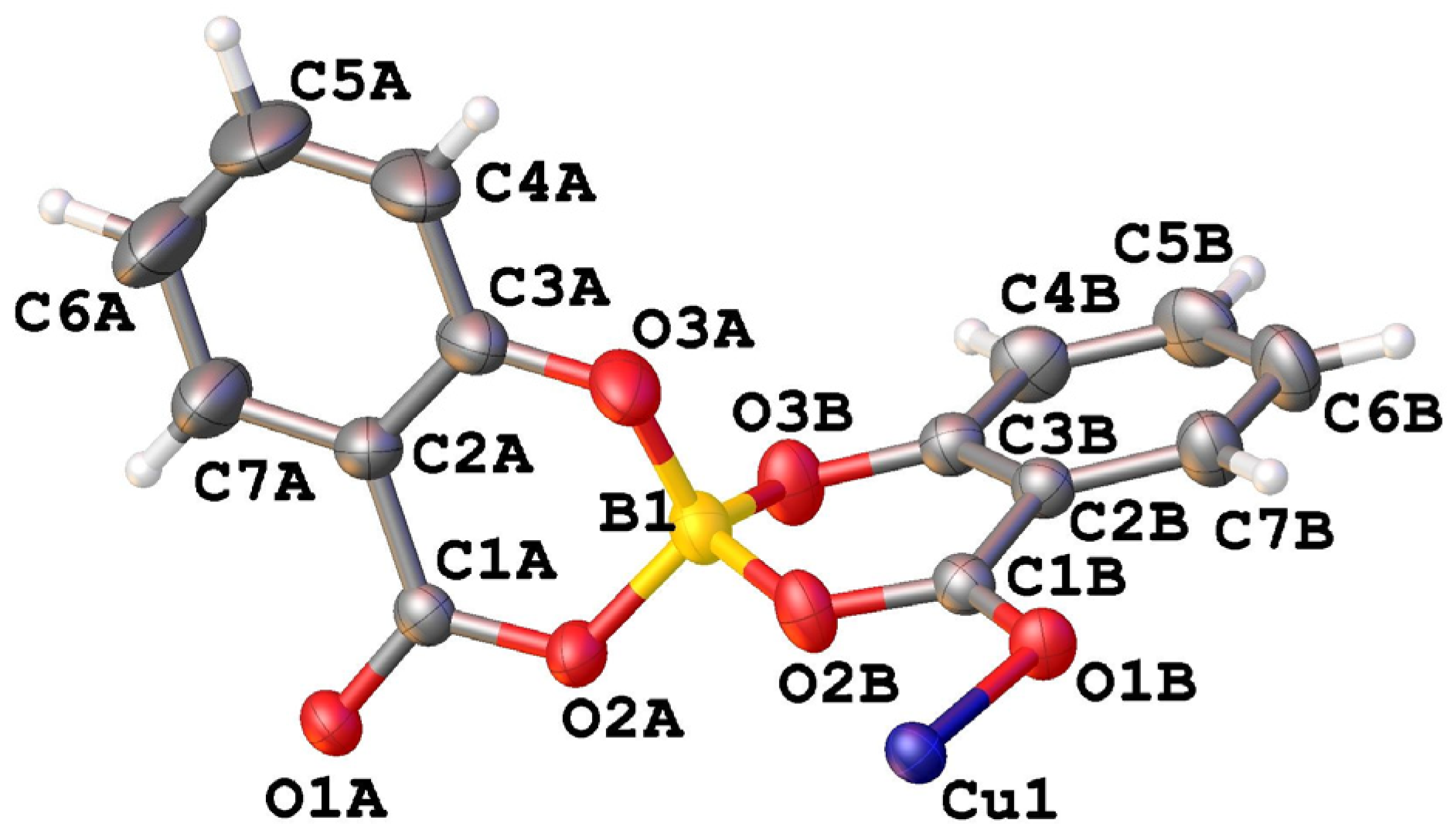
The asymmetric unit of CuSB contains half of the copper ion and one salicylatoborate ligand (Figure 2).
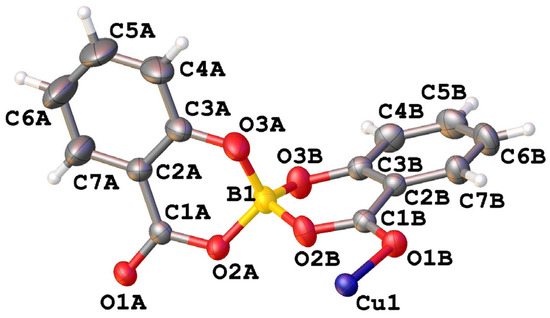
Figure 2.
View of the asymmetric unit of [Cu(C14H8O6B)2] (CuSB) with atom labelling.
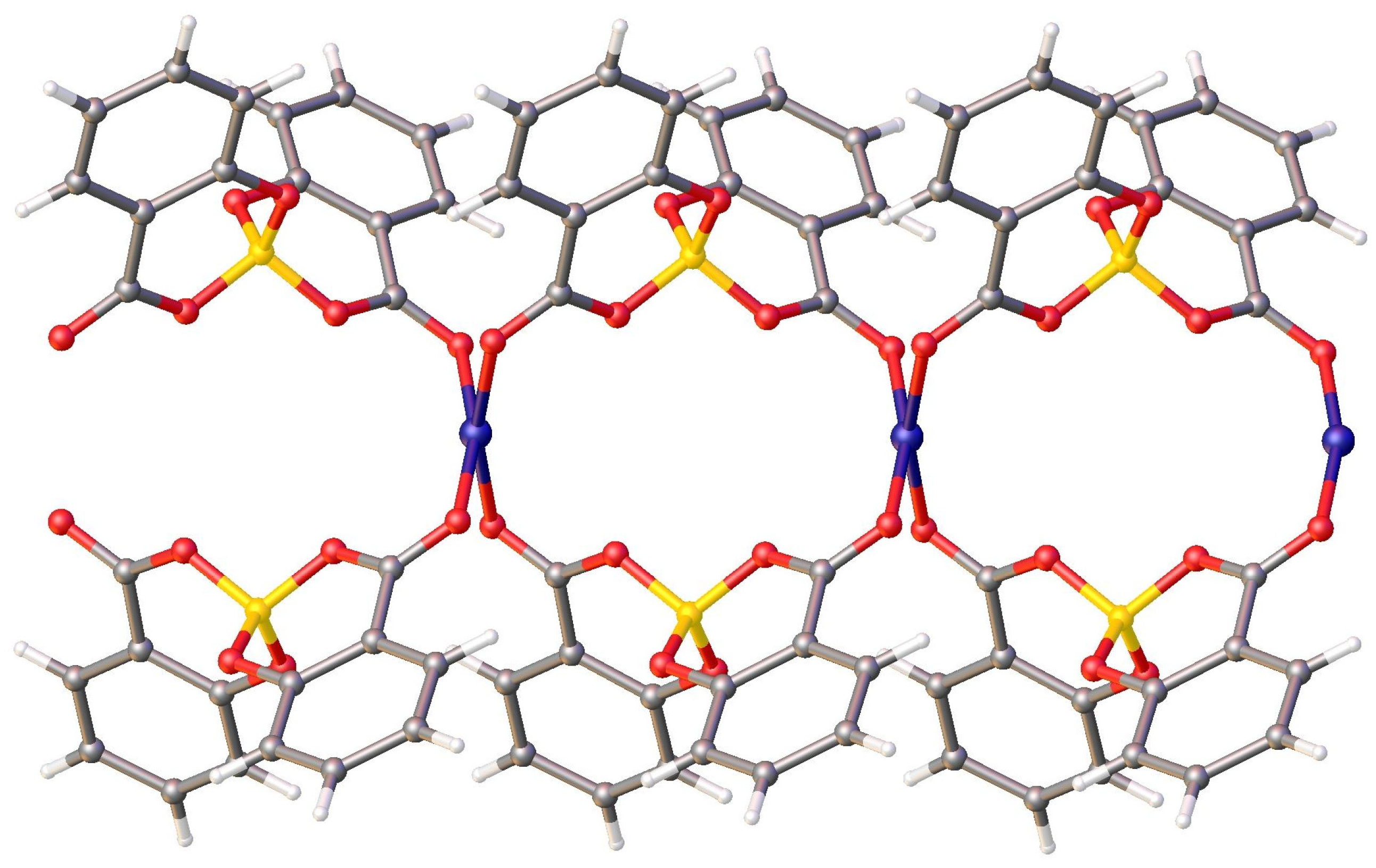
In the crystal packing, each copper ion is coordinated by four salicylatoborate ligands, and each salicylatoborate ligand bridges two copper ions, forming an infinite row along the b axis, i.e., a one-dimensional polymeric structure (1D Metal Organic Framework, Figure 3). The rows are joined through strong hydrogen bonds that connect the hydrogens of the aromatic ring of the salicylate to the carboxylic oxygen bonded to the metal. Relevant bond distances are reported in Table 1.
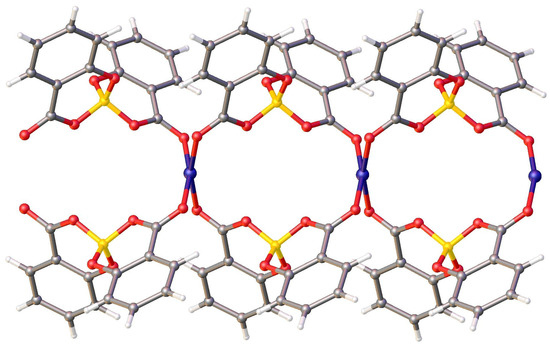
Figure 3.
View of the packing motif of CuSB.
In each unit cell, there are two boron atoms, and the density of the boron atoms is 1.533 × 1027 atoms/m3.
2.2.3. Crystal Structure of LiSB
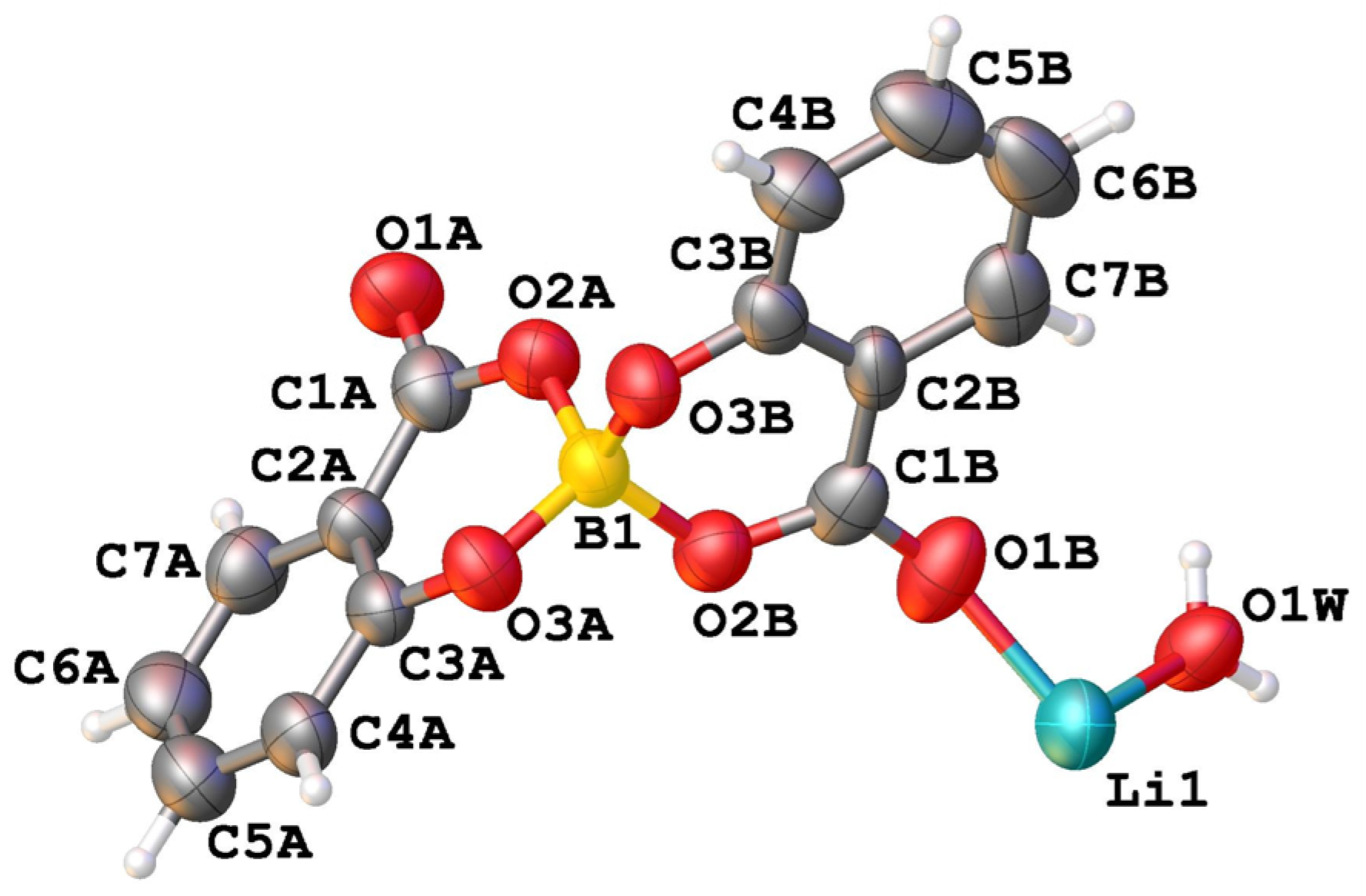
The asymmetric unit of compound LiSB consists of one boron atom covalently bonded to two salicylate molecules, one Li+ ion, and one water molecule coordinated to the lithium atom. (Figure 4).
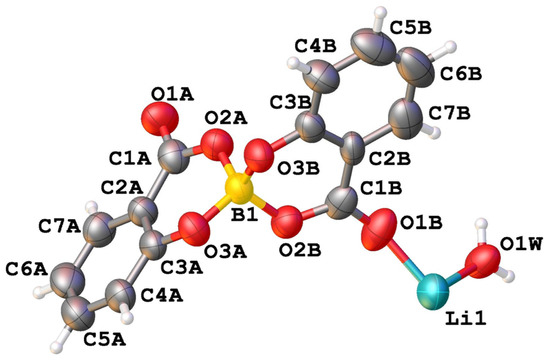
Figure 4.
View of the asymmetric unit of [Li(C14H8O6B)(H2O)] (LiSB) with atom labelling.
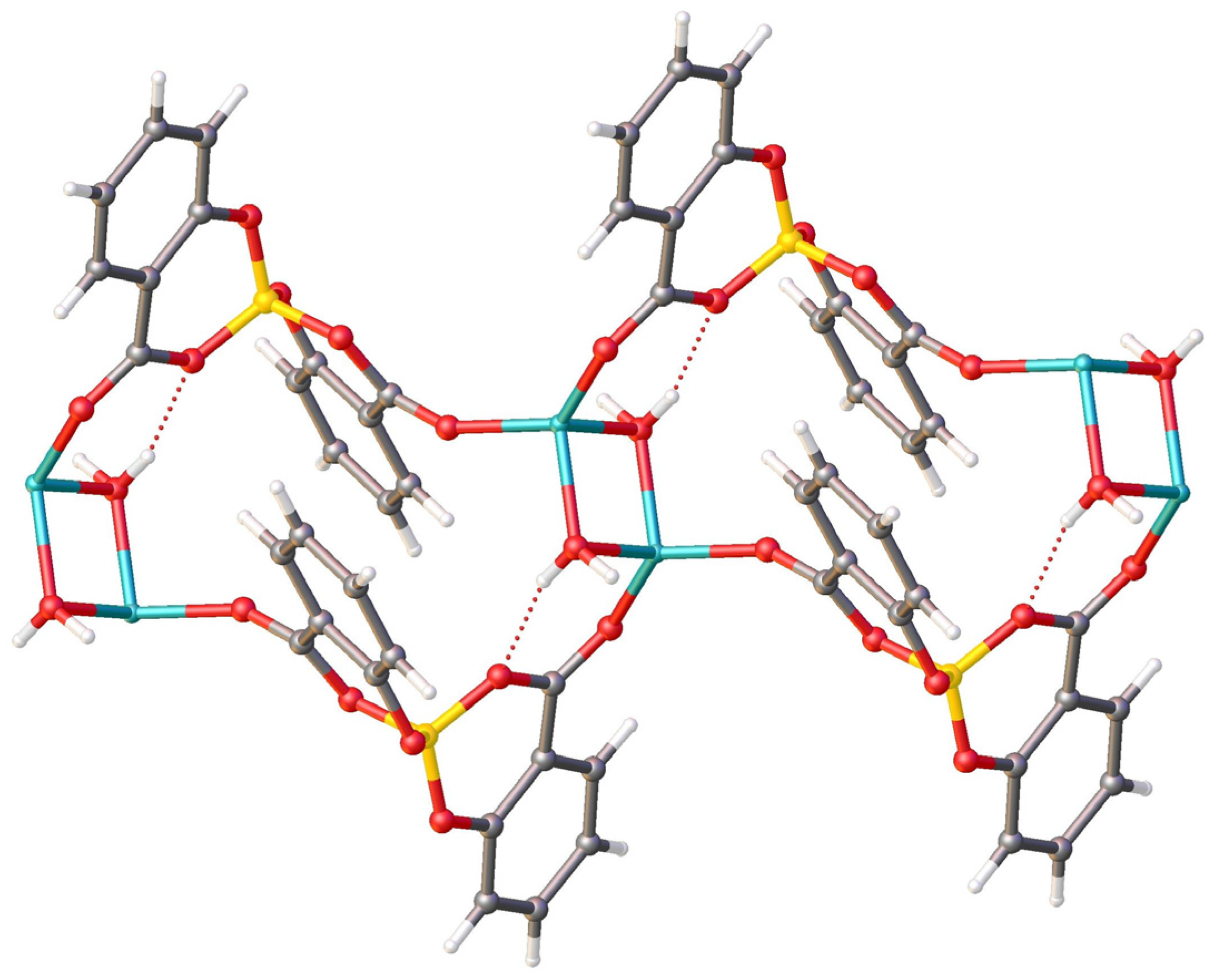
Along the b-axis direction, the water molecules bridge two lithium ions, and each salicylatoborate ligand also bridges two lithium ions, forming an infinite row, i.e., a one-dimensional polymeric structure (1D Metal Organic Framework, Figure 5). The rows are joined through strong hydrogen bonds that connect the hydrogens of the water molecules to the oxygen atoms of the carboxylic groups of the salicylate fragments. The relevant bond distances are reported in Table 1.
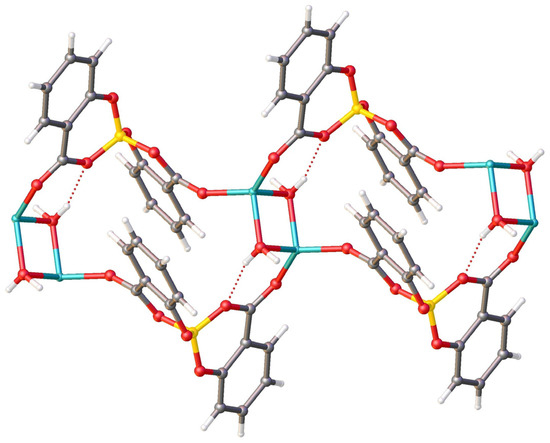
Figure 5.
View of the packing motif of LiSB.
In each unit cell, there are four boron and four lithium atoms (cell volume = 1304.51 Å3), and the density of the boron and lithium atoms is 2.954 × 1027 atoms/m3.
2.3. Calculation of the Dose (D) Absorbed by a Tumor Mass
The dose absorbed by a tumor mass depends on the energy deposited in the tumor tissue by the particles along their paths. This, in turn, depends on the particle’s kinetic energy, its charge, mass, and range. The calculations performed evaluate a realistic value of D. However, given the uncertainty on the tumor dimension and the density of the neutron-reactive isotopes inside each tumor cell, in this work, we provide only a comparison of the therapeutic efficiency of the different compounds. For these reasons, the calculations were performed considering, for all the compounds, the same spherical tumor diameter (5 mm), number of nanoparticles inside each tumor cell (100), dimension of the nanoparticles (diameter 175 nm, the medium size between the smaller nanoparticles obtained with the grinding method proposed in ref. [9]), and a homogeneous distribution of 10B and/or 6Li in the tumor mass. These values were chosen considering that the nanoparticles should be able to concentrate inside a tumor cell. The model of tumor proposed is a little distant from real tumors, which are usually heterogeneous, and therefore, the drug can be unevenly distributed. However, the calculations cannot take into account this aspect, since in this case, the number of calculations to do would increase exponentially and would become quite prohibitive. Since the aim of the theoretical method is not the simulation of a real tumor situation but the discrimination of the more promising compound for the radiotherapy, the model used is a compromise between a possible real situation and the time consumed for calculations.
The calculation of the dose rate Ḋ (the dose absorbed by the tumor in the unit of time) is based on the following nuclear reactions, taking into account the different densities of the neutron-reactive isotopes in the three materials:
10B + n → 7Li + α + 2.31 MeV
6Li + n → 3H + α + 4.78 MeV
The Ḋ values depend on the total energy developed by the reaction (that is divided between the two particles produced), on the cross section of the reaction, on the individual energy of the particles produced, and on the value of the Linear Energy Transfer of each particle.
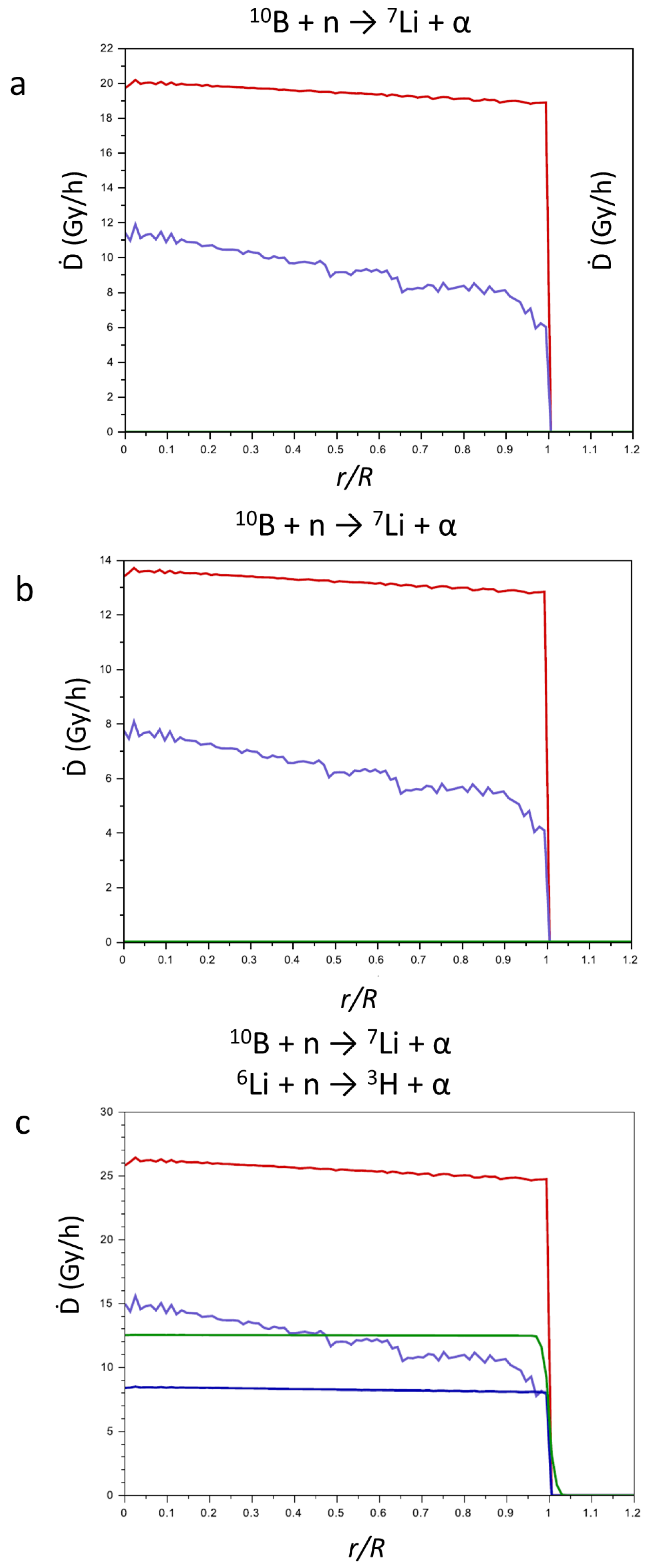
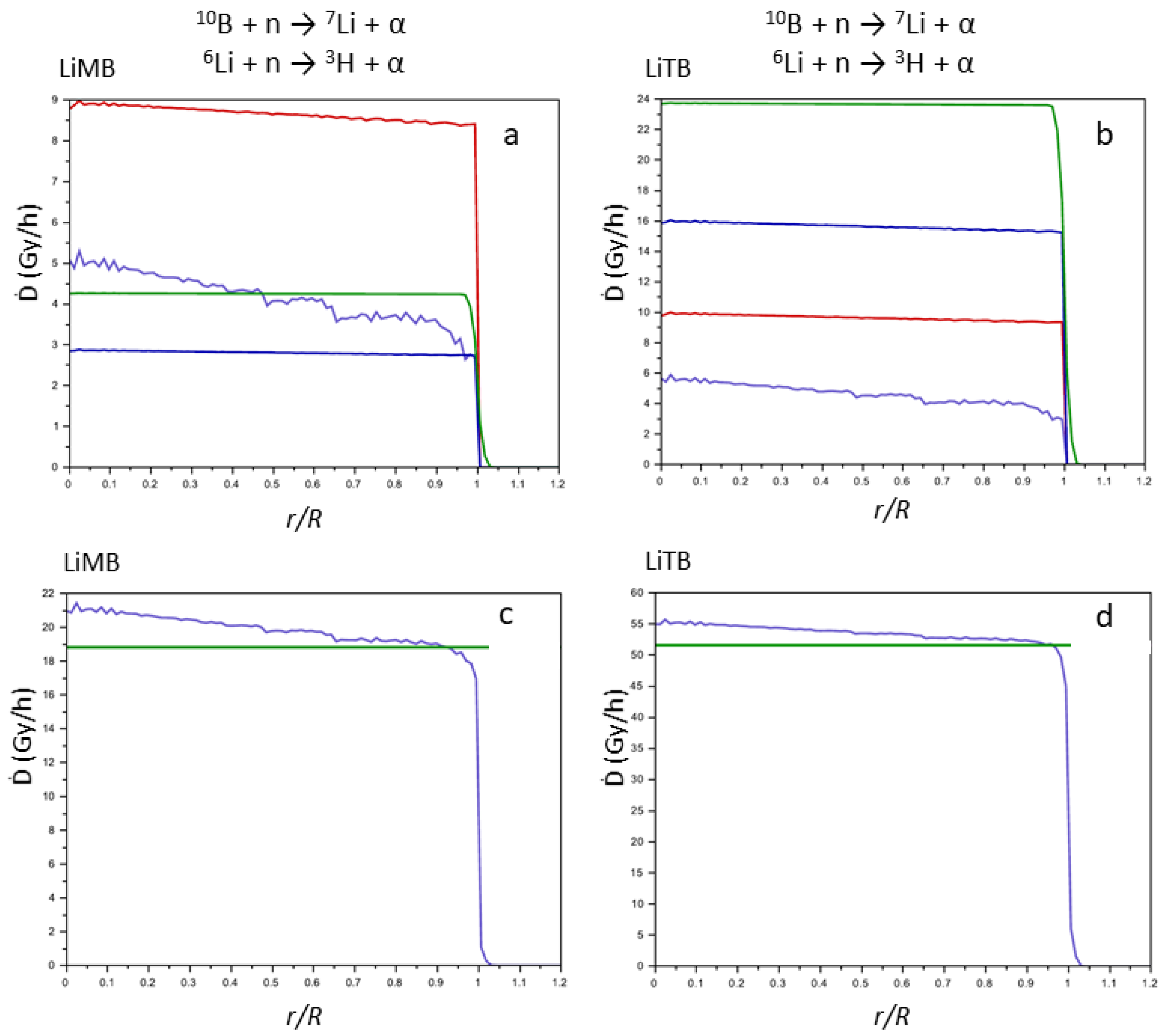
In Figure 6, the contributions of the products of the above-reported reactions to the Ḋ values (Gy h−1) in function of the reduced radius r/R (r = point in which the contribution was calculated; R = radius of the tumor mass) are reported. For CaSB (a) and CuSB (b), only the products of reaction (1) are considered, while for LiSB (c), the contributions of the products of reaction (2) are also considered. Since the range of the products is very short in comparison to the tumor dimension, the contributions of the products to the Ḋ values drastically decrease near the surface of the tumor.
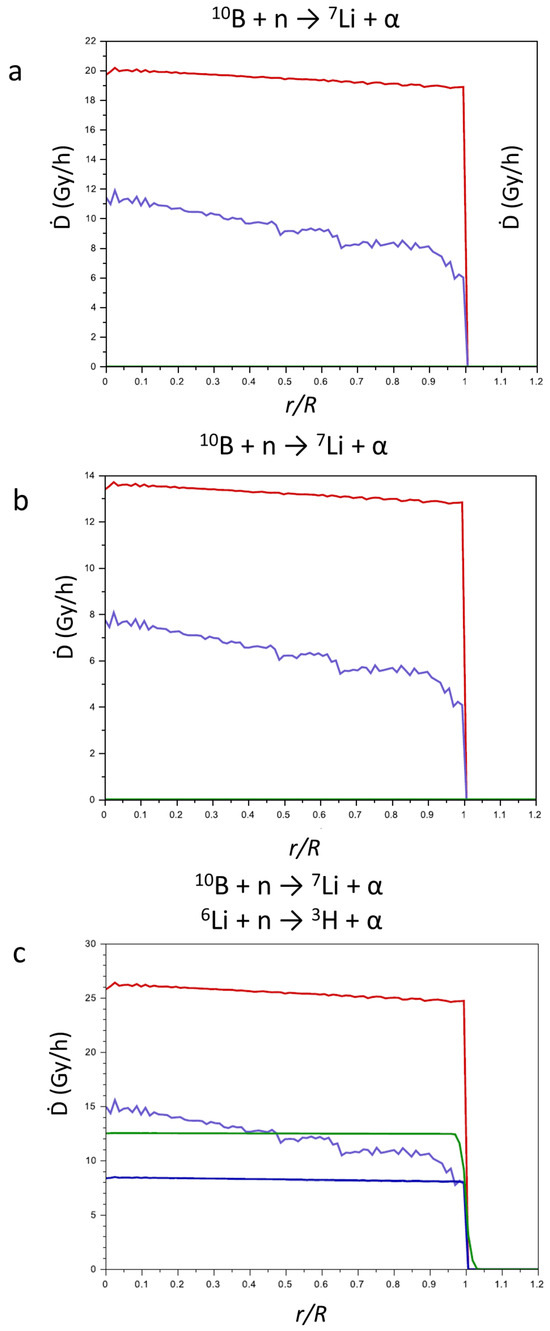
Figure 6.
Contributions of the products of the nuclear reactions (1) and (2) to the Ḋ values vs. r/R for CaSB (a), CuSB (b), and LiSB (c). 7Li, violet line; α from Equation (1), red line; 3H, green line; α from Equation (2), blue line.
Comparing the three pictures in Figure 6, for all the particles produced, the value of Ḋ is quite constant while varying r/R. As expected, the products of reaction (1) show the highest Ḋ values, since most of the parameters that influence the energy transfer are more favorable compared to reaction (2). In fact, the major contribution to the transfer of energy is the cross section of 10B with respect to neutron capture (neutron flux 2.35 × 1013 m−2 s−1), which is more than four times higher compared to 6Li (4210.71 vs. 1030.19 b, respectively).
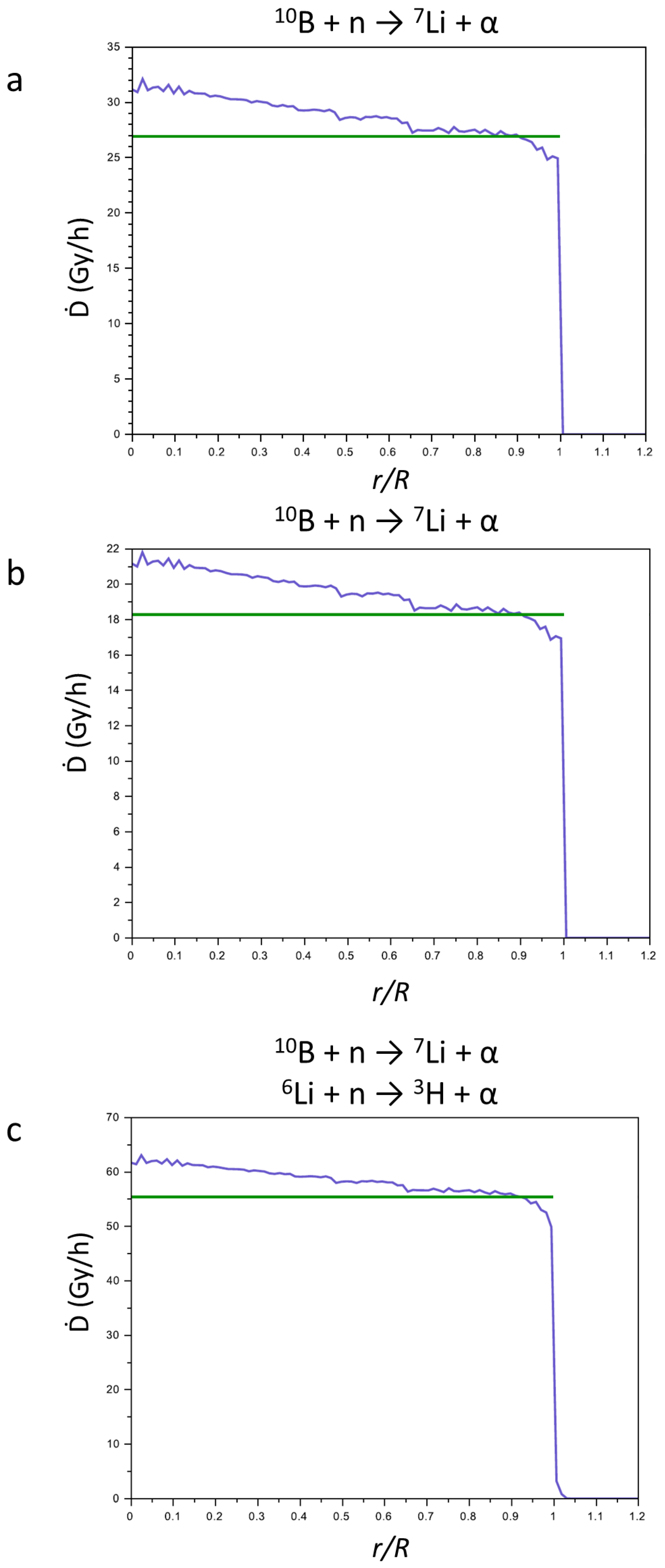
In Figure 7, the sums of the contributions to the Ḋ values of the products of reactions (1) and (2) for CaSB (a), CuSB (b), and LiSB (c) are reported. The green lines represent the Ḋ values averaged on the sphere of the tumor mass, and their values are reported in Table 2. For all compounds, the Ḋ values, being different for each compound, slightly decrease from the center to the periphery of the tumor mass.
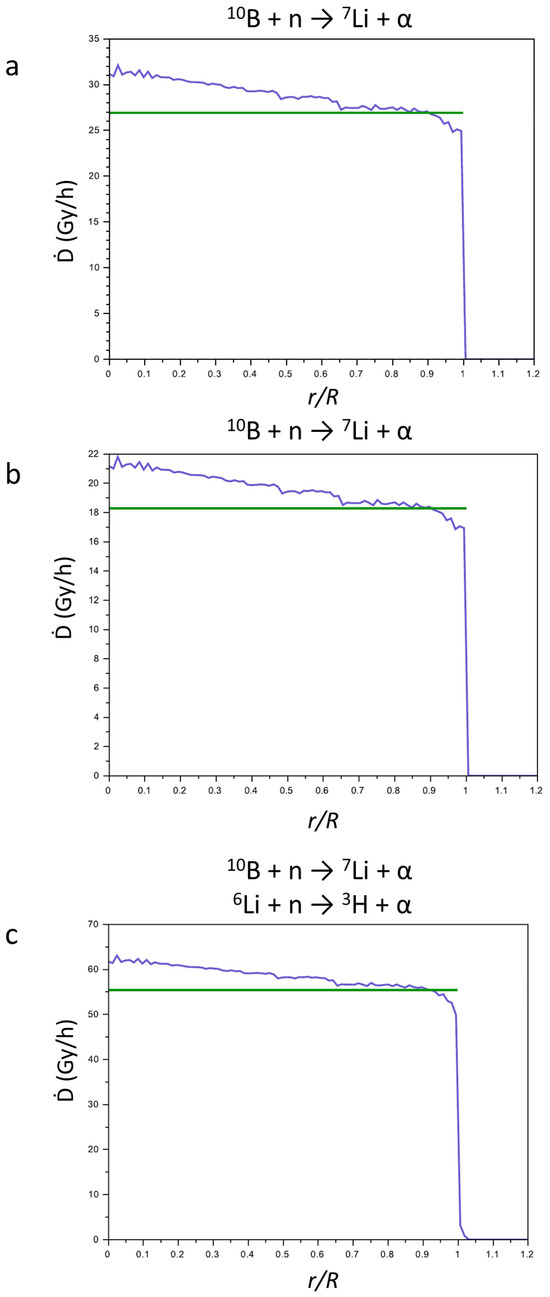
Figure 7.
Sum (blue line) of the contribution of the Ḋ values of the products of the nuclear reactions for CaSB (a), CuSB (b), and LiSB (c). The green line represents the Ḋ values averaged on the sphere of the tumor mass.

Table 2.
Densities of the isotopes 10B and 6Li and total Ḋ values for all the compounds.
Table 2 also reports the density of the reactive isotopes in the materials, which was calculated from the density of the boron and lithium atoms in the crystal structure, taking into account the percentage of each isotope in the commercial enriched reagents (99% for H310BO3 and 95% for 6LiCO3).
The total Ḋ values of CaSB, CuSB, and LiSB vary according to the densities of the reactive isotopes. The addition of 6Li to the compounds enhances the efficiency of the LiSB for the NCT.
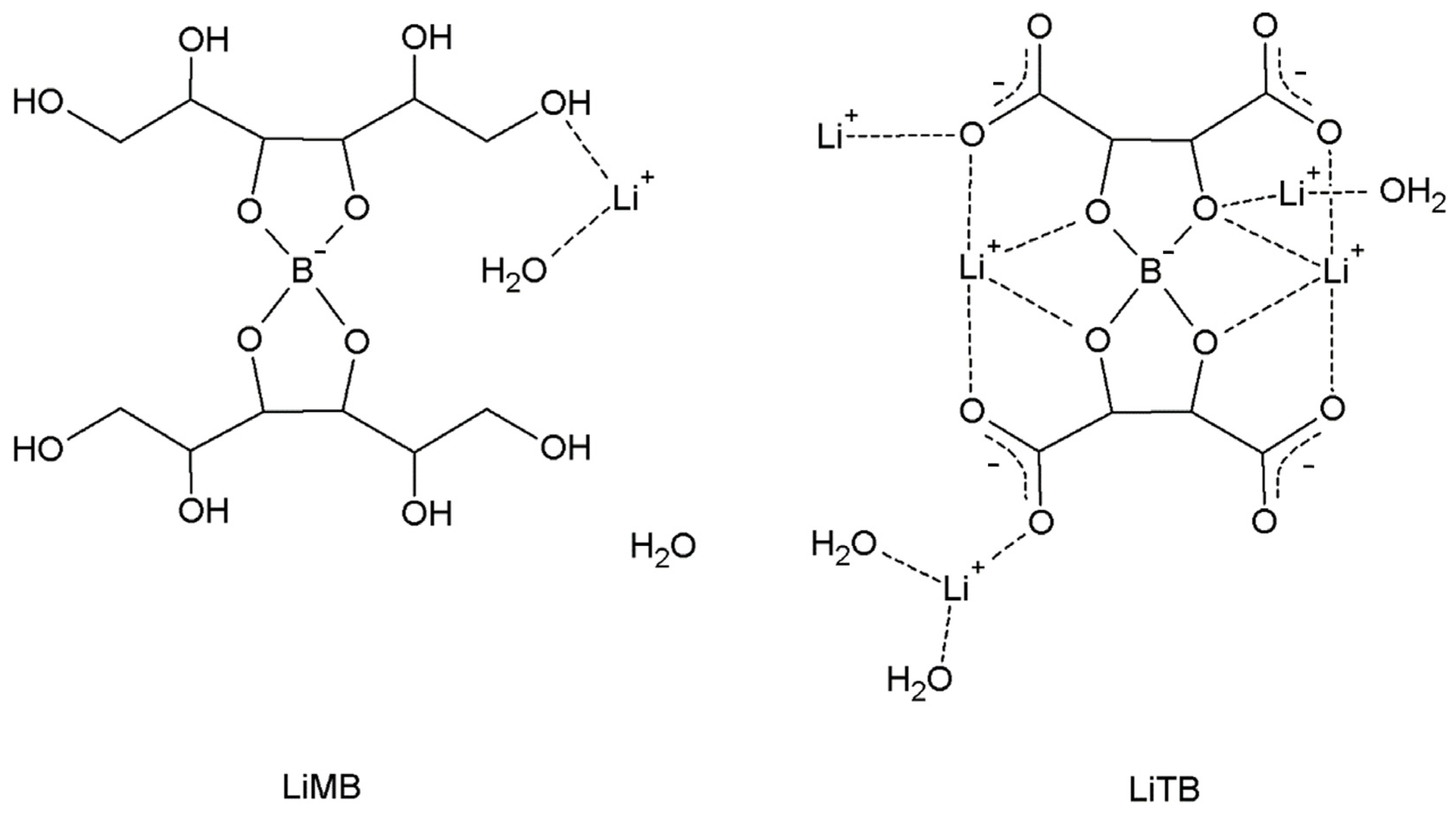
In Scheme 2, the molecular schemes of LiMB and LiTB, whose crystal structure was published in our previous work [7], are reported. In Figure 8, for these two compounds, the same graphs as in Figure 6 and Figure 7 are reported.
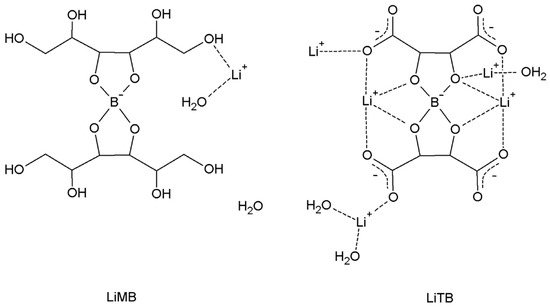
Scheme 2.
Molecular schemes of LiMB and LiTB.
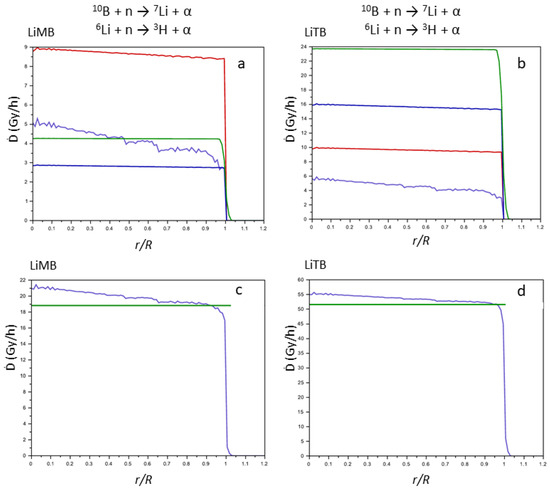
Figure 8.
Contributions of the products of the nuclear reactions to the Ḋ values (Gy h−1) vs. (r/R) for LiMB (a) and LiTB (b) (7Li, violet line; α from Equation (1), red line; 3H, green line; α from Equation (2), blue line). Sum (blue line) of the contributions of the products of the nuclear reactions for LiMB (c) and LiTB (d) (the green line represents the Ḋ values averaged on the sphere of the tumor mass).
In LiMB and LiTB, both boron and lithium are present, as in LiSB, but the averaged Ḋ values are lower since their 10B + 6Li density is also lower (Table 2). However, the averaged Ḋ values for LiTB are slightly lower than for LiSB, despite the fact that the 10B + 6Li density is greater. This indicates that the largest contribution to the averaged Ḋ values is from the products of the boron reaction rather than the lithium ones, since the cross section of Equation (1) is higher than that of Equation (2), and the higher presence of the 6Li in the LiTB is not able to counterbalance the contribution of the 10B. Thus, to design more efficient compounds for the NCT, it is more convenient to enhance the density of 10B rather than the density of 6Li. However, in a chemical synthesis, the lithium cation is easier to introduce in a compound compared to the boron atom, and thus, 6Li can be an easy expedient to enhance the performance of the compounds for the NCT.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Syntheses
All the reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Darmstadt, Germany) and used as received.
3.1.1. Synthesis of [Ca(H2O)6](C14H8O6B)2·4H2O (CaSB)
A total of 5 mmol of salicylic acid, 1.25 mmol of calcium hydroxide, and 2.50 mmol of boric acid were dissolved in 10 mL of warm water (323 K). The solution was evaporated at room temperature for a few days, and during the evaporation, faint green crystals of CaSB precipitated. The crystals were dried at room temperature.
3.1.2. Synthesis of [Cu(C14H8O6B)2] (CuSB)
A total of 5 mmol of salicylic acid, 1.25 mmol of copper hydroxide, and 2.50 mmol of boric acid were dissolved in 10 mL of warm water (323 K) to obtain a light green solution with some undissolved residue. After keeping steel the solution at 288 K, crystalline needles formed in a few days. In about two more days, some of the crystals grew to fairly large green transparent crystals, which were filtered and dried in air. In a closed vial, the crystals slowly lost water and, after a few months, yielded dark green crystals of CuSB.
3.1.3. Synthesis of [Li(C14H8O6B)(H2O)] (LiSB)
A total of 5 mmol of salicylic acid (5 mmol), 1.5 mmol of lithium carbonate, and 2.5 mmol of boric acid were added to about 5 mL of ethanol, and the mixture was warmed at 323 K until all the solids were dissolved. The solution was slowly evaporated at 290 K, and after a few hours, a white crystalline powder of LiSB precipitated. The crystals were dried at room temperature.
3.2. Single Crystal X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
X-ray diffraction data were collected at room temperature using a Xcalibur AtlasS2 Gemini R Ultra diffractometer (Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Wrocław, Poland). Data were collected with mirror monochromatized Cu-Kα (1.5418 Å) radiation. The CrysAlisPro (Version 1.171.37.31) [11] package was used for data collection and integration, SHELXT [12] for solving, SHELXL [13] for refinement, and Olex2 [14] for graphics. All atoms but hydrogen were refined with anisotropic thermal factors. Even if the hydrogen peaks were observed in the difference Fourier maps, hydrogen atoms were calculated and refined riding with the Uiso = 1.2 or 1.5 Ueq of the connected atom.
3.2.1. Crystal Data for CaSB
Monoclinic, space group P21/c, Z = 4, a = 9.8996(3), b = 12.4244(3) Å, c = 28.8806(8), β = 93.556(2)°, V = 3545,4(2) Å3, 49769 reflections collected of which 6194 unique (Rint = 0.0617). R1 = 0.1031 (I > 2σ(I)), wR2 = 0.3803 (all data).
3.2.2. Crystal Data for CuSB
Monoclinic, space group P2/n, Z = 2, a = 12.6250(2), b = 6.5216(1) Å, c = 16.7556(2), β = 108.988(1)°, V = 1304.51(3) Å3, 12674 reflections collected of which 2317 unique (Rint = 0.0235). R1 = 0.0300 (I > 2σ(I)), wR2 = 0.0815 (all data).
3.2.3. Crystal Data for LiSB
Monoclinic, space group P21/c, Z = 4, a = 10.720(5), b = 8.347(4) Å, c = 15.446(6), β = 101.52(4)°, V = 1354.3(10) Å3, 6161 reflections collected of which 1417 unique (Rint = 0.1003). R1 = 0.0604 (I > 2σ(I)), wR2 = 0.1576 (all data).
The interested reader can find further details on crystal data, data collection, least-squares refinements, and bond angles in the Supporting Information (Tables S1–S4, Section S1) and CIF files (CCDC 2408779-2408781).
3.3. Calculation of the Dose (D) Absorbed by a Tumor Mass
The algorithm begins by calculating the loss of energy in each point along a radius of the spherical tumor (in our simulation, 100 points) from the flux of particles emitted by each element of volume in the tumor. This flux is, in turn, evaluated by calculating the nuclear reaction rate in each element of volume and integrating it over the sphere, taking into account the distance between the element of volume emitting the radiation and the point where we want to obtain the dose rate. Details are reported in the Supporting Information (Section S2).
The reaction cross sections were evaluated by averaging the experimental σ (ϵ) over the Boltzmann distribution at 311 K.
The thermal neutron flux used is 2.35 × 1013 m−2s−1. As suggested by the International Atomic Energy Agency for BNCT applications [15], a thermal distribution was used for the neutron flux. In a spherical tumor of arbitrary diameter 5 mm, 100 nanoparticles of diameter 175 nm of each compound were considered inside each tumor cell.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we reported three new solid salicylatoborate complexes for application as nanoparticles for the NCT. These nanoparticles are inexpensive and non-toxic materials, easily functionalizable on the surface in order to improve their concentration in tumor tissues. The XRD structures were of fundamental importance for the calculation of the densities of the reactive boron and lithium isotopes, which allowed us to employ a computational method to calculate the dose absorbed by the spherical tumor mass in order to preliminarily test their therapeutic efficacy for the NCT. This method was also applied to two other similar compounds containing boron and lithium with mannitol or tartaric acid, published in our previous work.
The calculated dose rate is in good agreement with the values of the 10B + 6Li densities in the compounds, except for the comparison of the Ḋ values for LiTB and LiSB, due to the higher cross section of the 10B reaction compared to the 6Li.
Among all the compounds studied, the LiSB gives the highest dose absorbed by the tumor mass, and thus it results in being the most efficient compound according to our model calculations, demonstrating that the synergy between the boron-10 and the lithium-6 isotopes enhances the efficacy of the NCT.
The density of the reactive nuclides in a compound is the only parameter that we can partially control. It can be precisely calculated from the XRD structure and thus allows both for the calculation of the dose absorbed by a tumor and the quantification of the amount of drug needed for a given therapy. Therefore, the method used in this work can be useful to both determine the therapeutic efficacy of a new compound and help design new ones with higher efficiency for the NCT. As expected, along with the density of the neutron-reactive isotopes in the material, among the most important parameters influencing the absorbed dose by a tumor mass are the cross sections for neutron capture of the nuclides involved in the nuclear reactions.
In conclusion, in this work, we propose a simple and relatively fast method for the preliminary discrimination of the most promising compound for therapeutic NCT applications. The assumptions made in the tumor-nanoparticle model used for the calculations do not take into account any type of tumor cells or other biological parameters, but once the most promising compound has been chosen, we can focus future experimental efforts on it, limiting the time and costs of the research.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/inorganics13050136/s1, Table S1: Crystal data and structure refinements for CaSB, CuSB, and LiSB. Table S2: Bond Angles for CaSB. Table S3: Bond Angles for CuSB. Table S4: Bond Angles for LiSB.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.M. and C.C.; data curation, C.C.; formal analysis, A.C.; funding acquisition, P.B.; investigation, D.M. and A.C.; methodology, D.M. and C.C.; validation, P.B. and A.C.; writing—original draft, D.M.; writing—review and editing, P.B. and C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by MUR (Ministero dell’Università e della Ricerca), funded by the Italian Government.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, L.; Li, Y. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy: Current status and challenges. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 788770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedunchezhian, K.; Aswath, N.; Thiruppathy, M.; Thirugnanamurthy, S. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy–A Literature Review. J. Clin. Diag. Res. 2016, 10, ZE01–ZE04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, R.L. Critical review, with an optimistic outlook, on Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). Appl. Rad. Isot. 2014, 88, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, K.C.; Lai, P.D.; Chiang, C.-S.; Wang, P.-J.; Yuan, C.-J. Neutron capture nuclei-containing carbon nanoparticles for destruction of cancer cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuthala, N.; Vankayala, R.; Li, Y.-N.; Chiang, C.-S.; Hwang, K.C. Engineering novel targeted boron-10-enriched theranostic nanomedicine to combat against murine brain tumors via MR imaging-guided boron neutron capture therapy. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuthala, N.; Shanmugam, M.; Yao, C.-L.; Chiang, C.-S.; Hwang, K.C. One step synthesis of 10B-enriched 10BPO4 nanoparticles for effective boron neutron capture therapeutic treatment of recurrent head-and-neck tumor. Biomaterials 2022, 290, 121861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marabello, D.; Benzi, P.; Beccari, F.; Canepa, C.; Cariati, E.; Cioci, A.; Costa, M.; Durisi, E.A.; Monti, V.; Sans Planell, O.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of new lithium and boron based Metal Organic Frameworks with NLO properties for application in Neutron Capture Therapy. Processes 2020, 8, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, D.A.; Zümreoglu-Karan, B.; Hökelek, T.; Şahin, E. Boric acid complexes with organic biomolecules: Mono-chelate complexes with salicylic and glucuronic acids. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2010, 363, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabello, D.; Antoniotti, P.; Benzi, P.; Beccari, F.; Canepa, C.; Barge, A.; Boscaro, V.; Gallicchio, M.; Peira, E. Synthesis, characterization and cell uptake of nanoparticles for a novel approach to radionuclide therapy: A feasibility study. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Nano Sci. 2019, 8, 230. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj, S.; Chabita (Saha), K.; Chakrabortya, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Saha, A. Influence of copper (II) ions and its derivatives on radiosensitivity of Escherichia coli. Rad. Phys. Chem. 2007, 76, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CrysAlisPro, Version 1.171.37.31; Release 14-01-2014 CrysAlis171.NET; Agilent Technologies UK Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2014.
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT-Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Cryst. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Physical Dosimetry and Determination of Neutron Field Parameters. In Advances in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Chapter 4; p. 29. Available online: https://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/Publications/PDF/CRCP-BOR-002_web.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).