Effective Failure Analysis for Packaged Semiconductor Lasers with a Simple Sample Preparation and Home-Made PEM System
Abstract
1. Introduction
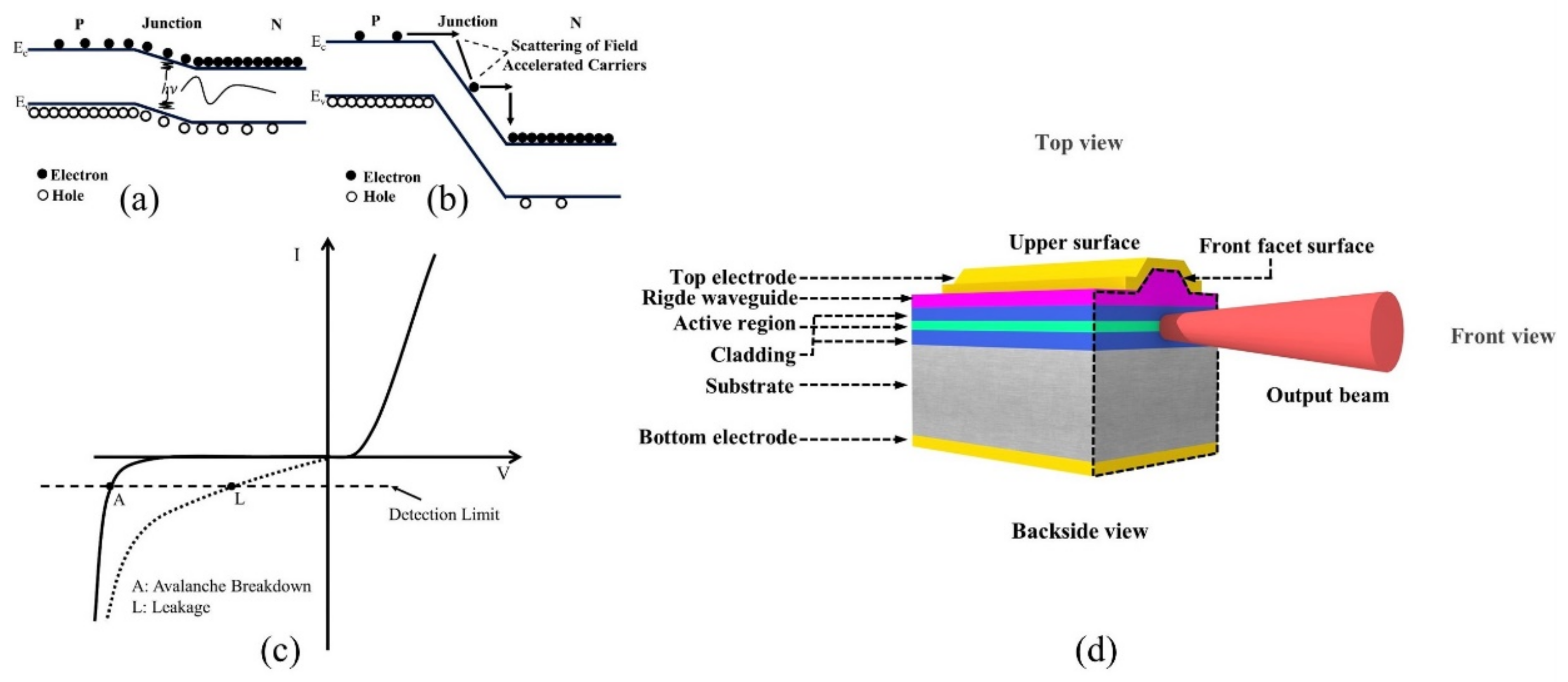
2. Principle of PEM
3. PEM Configuration
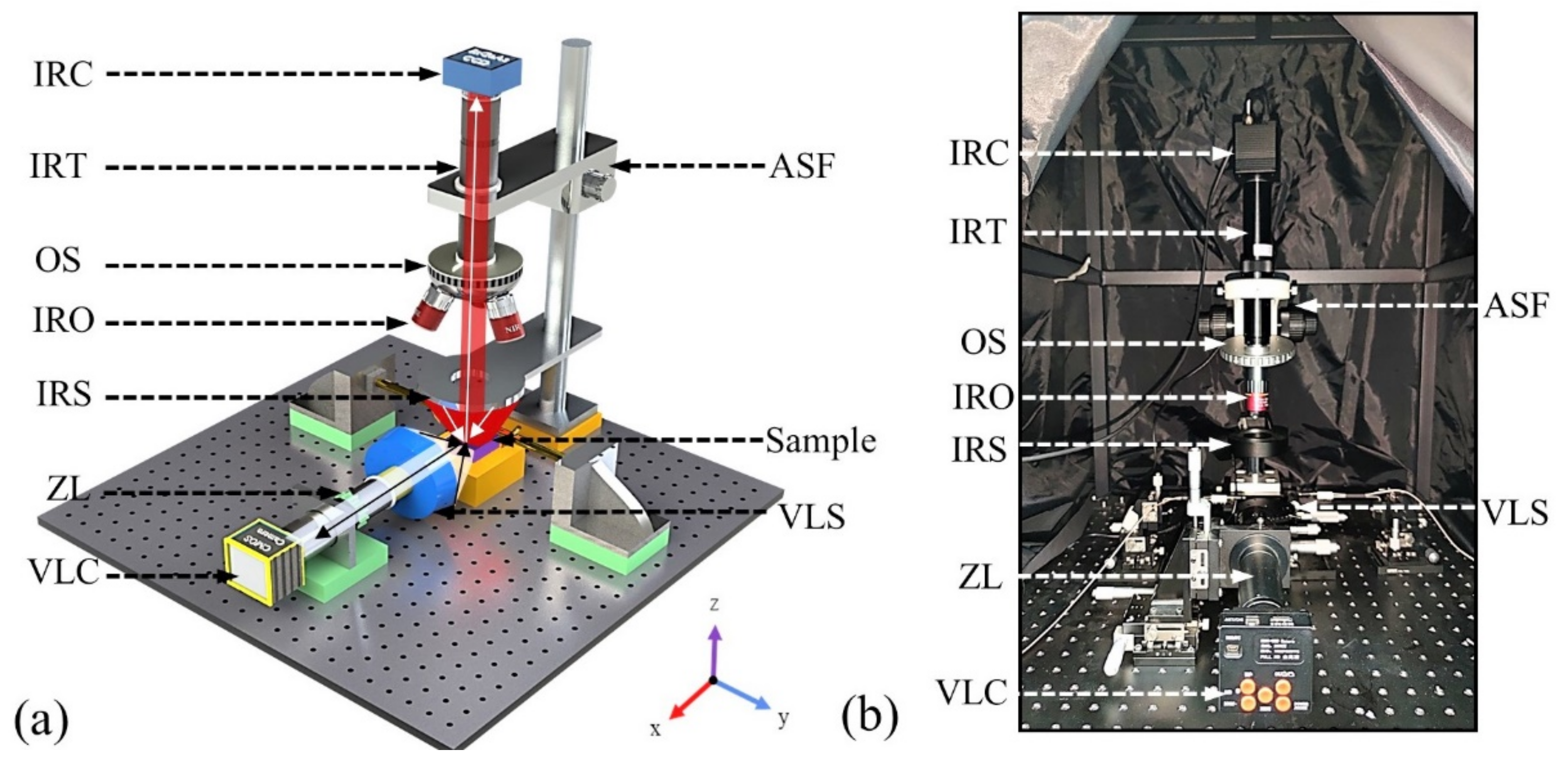
3.1. Type Ⅰ PEM
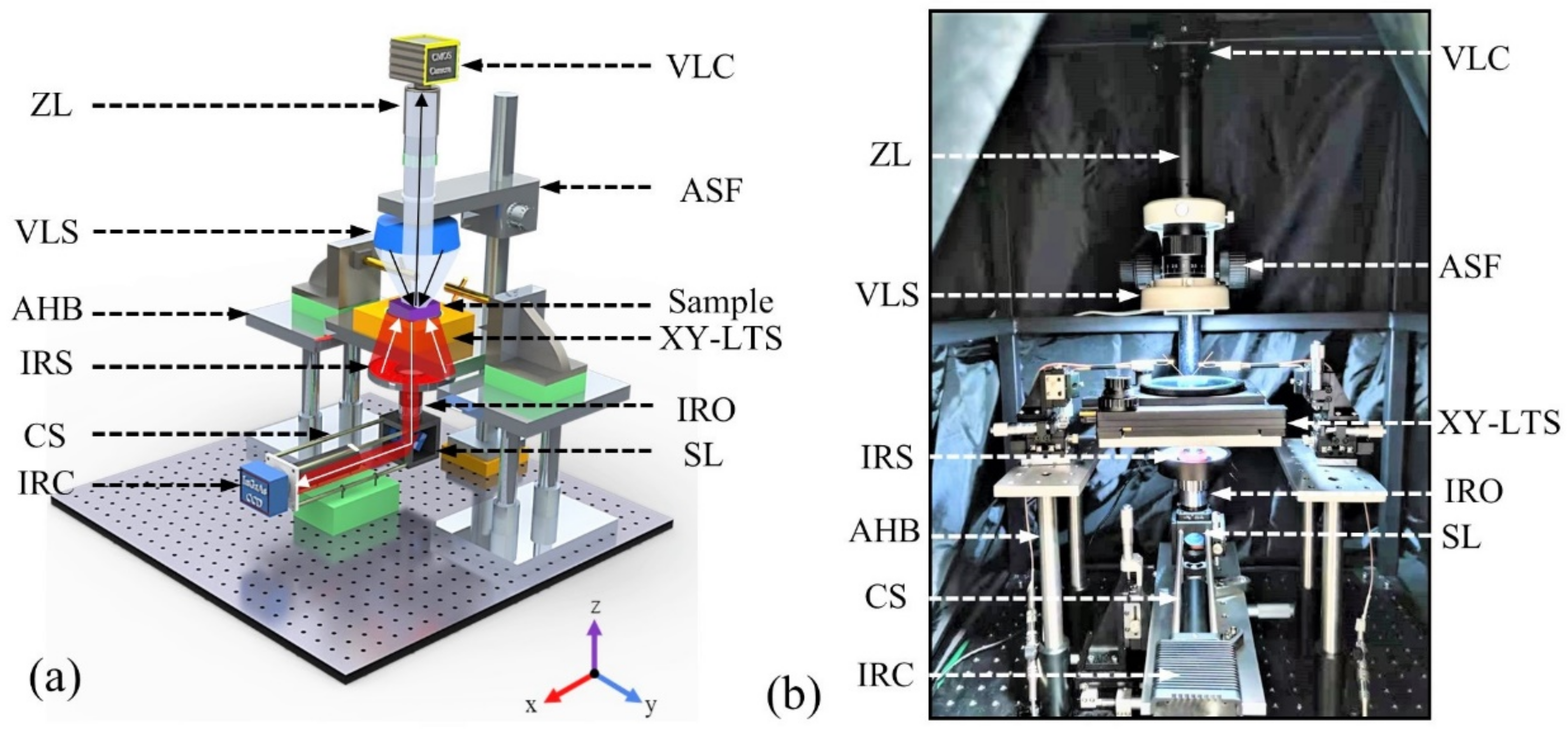
3.2. Type Ⅱ PEM
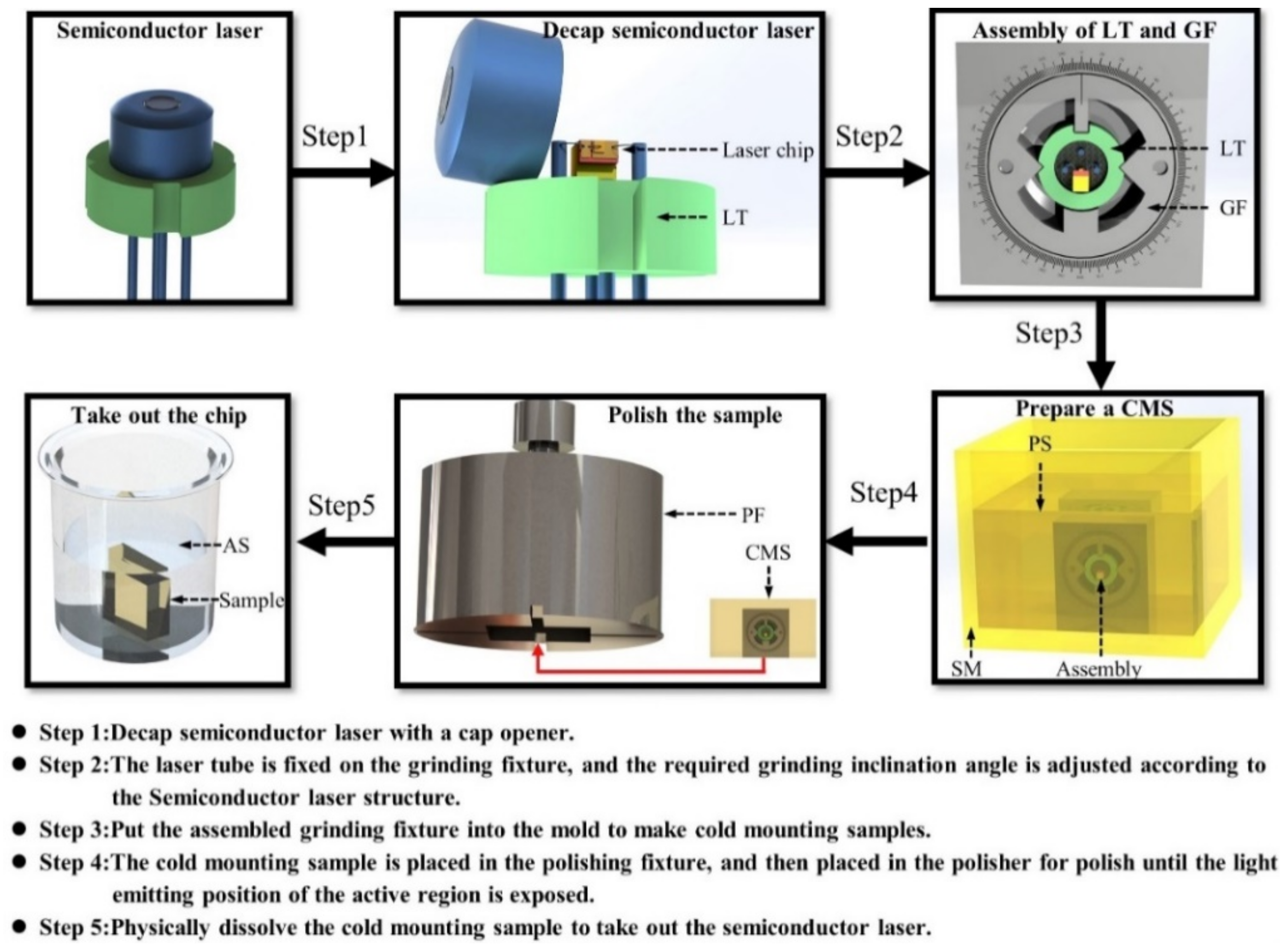
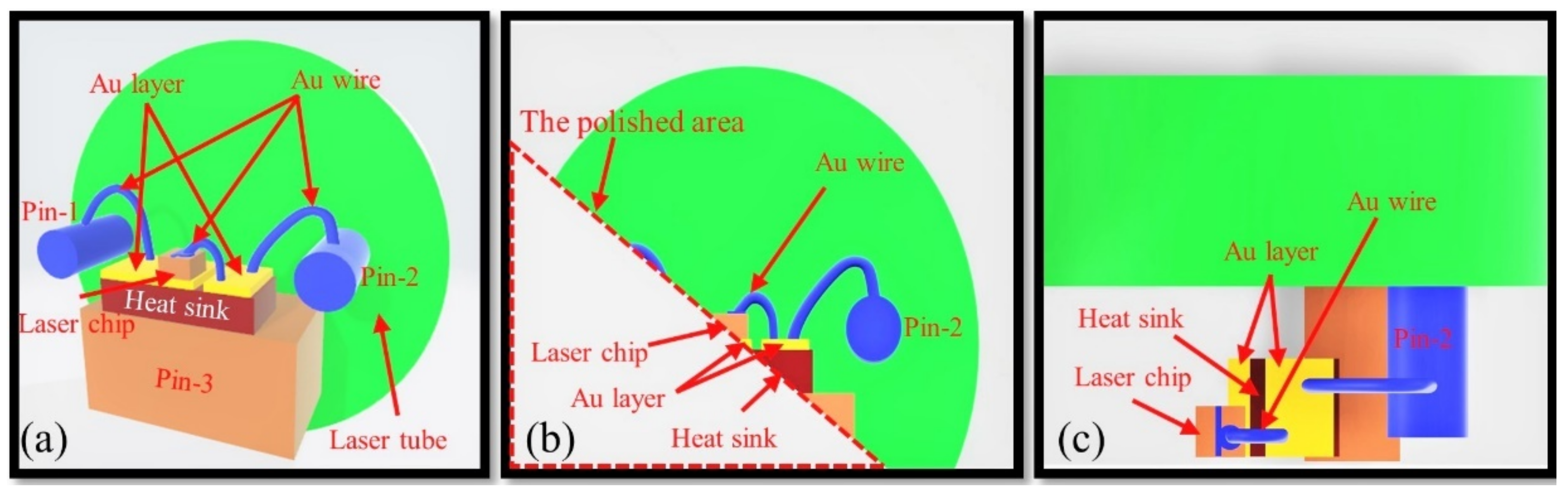
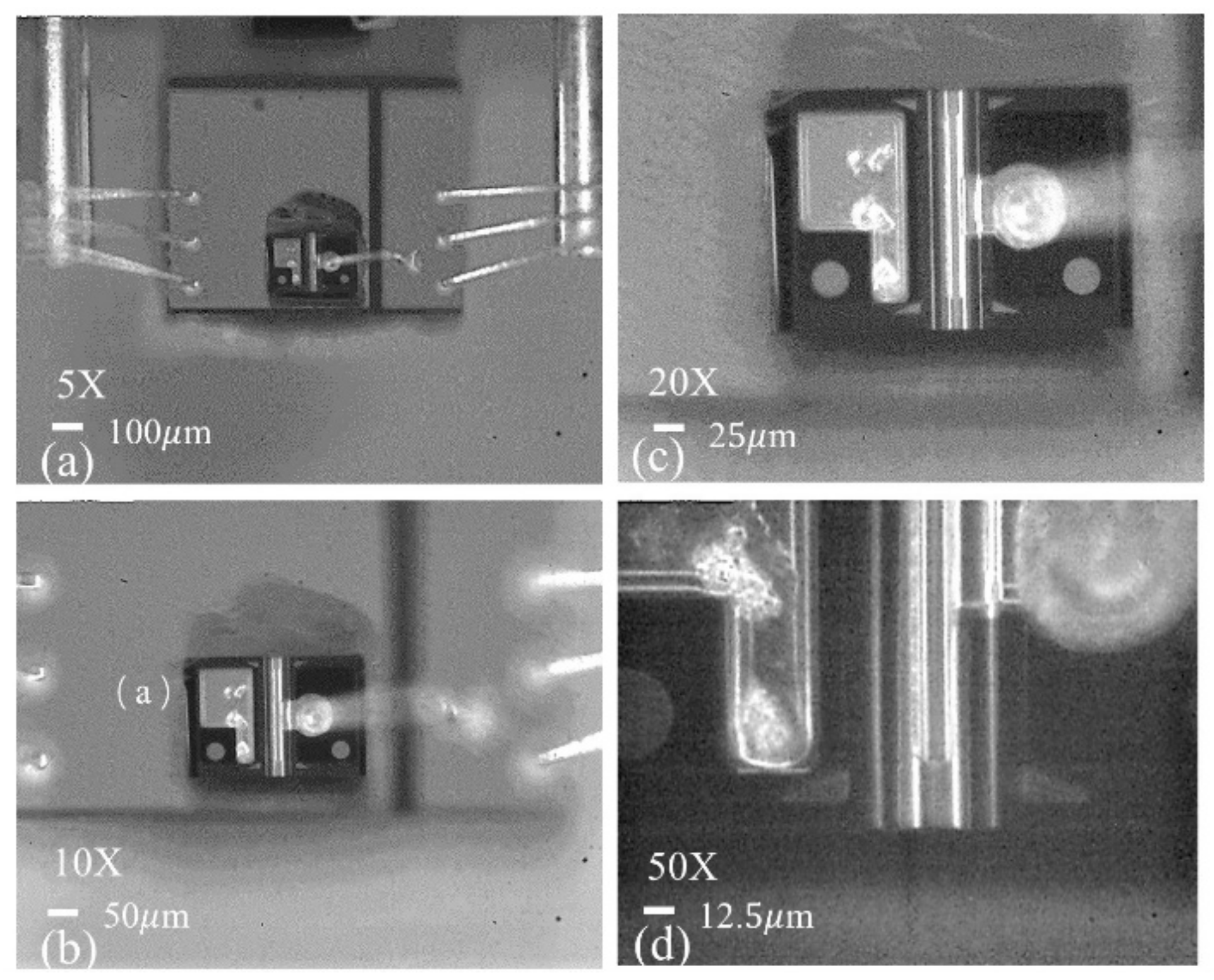
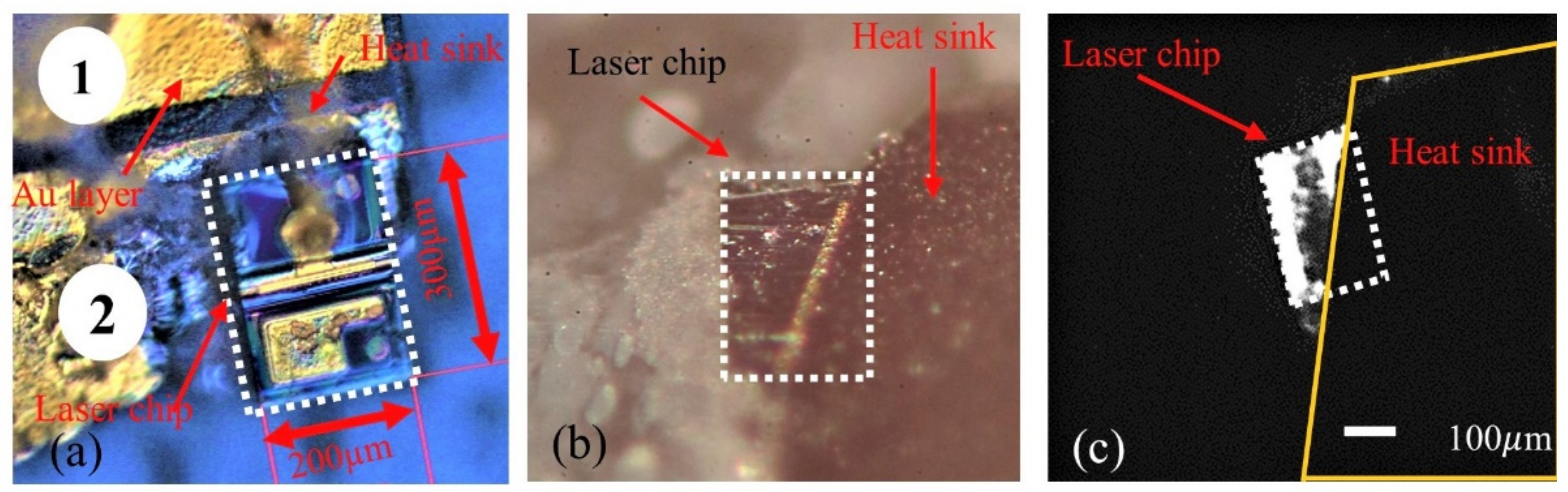
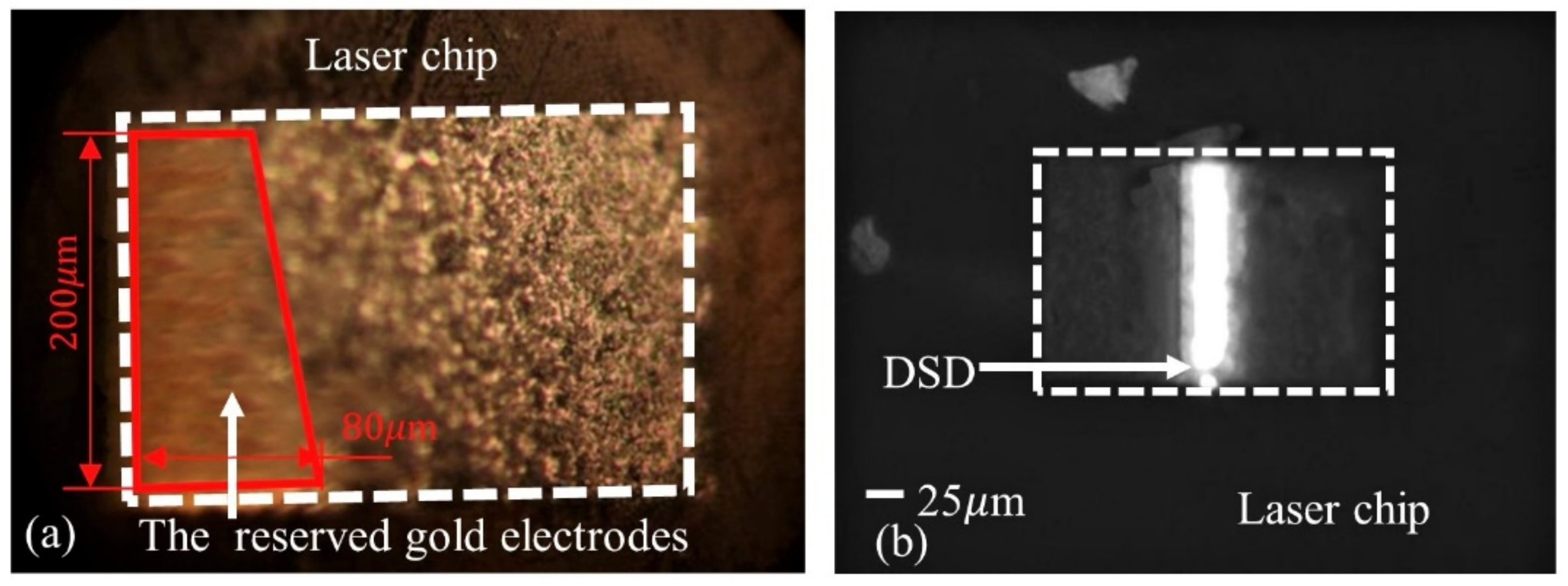
4. Sample Preparation Method for Failure Analysis
5. Results and Discussion
- The quantum well optical power in the ridge waveguide region was relatively large. Due to the large optical power, the temperature rises resulted in defects and even local melting and polycrystalline.
- There were trenches on both sides of the ridge waveguide. In the process of etching for forming the channel, lattice defects and surface defect states were generated. As impurities were accumulated at the channel after fabrication, defects continued to grow and climb to both sides in a large area.
- During the operation of the semiconductor laser, there was electrostatic breakdown, which caused COD on the facet. At the same time, the defects grew and diffused from the position where COD occurred to the inside of the active region during subsequent use, and finally appeared as a larger dark area in the active region.
- The substrate had dislocations, resulting in defects to be generated in the active area through dislocation gliding and climbing.
- The laser internal COD occurred, which caused local melting of the crystal lattice and a huge stress. During the stress release process, dislocations were generated.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hall, R.N.; Fenner, G.E.; Kingsley, J.D.; Soltys, T.J.; Carlson, R.O. Coherent light emission from GaAs junctions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1962, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, K.C.; Hockham, G.A. Dielectric-fibre surface waveguides for optical frequencies. Proc. Inst. Elec. Eng. 1966, 113, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranch, G.A.; Flockhart, G.M.; Kirkendall, C.K. Distributed Feedback Fiber Laser Strain Sensors. IEEE Sen. J. 2008, 8, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.F.; Dong, X.; Lv, H.J.; Hu, Y.X.; Yu, X.J.X.; Chen, F.; Liu, S.C. Real-time interrogation technology for a large-scale fiber-ring laser sensor array. IEEE Photon. J. 2017, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabi, L.; André, S.; Oliver, M.; Stefan, K.; Ludger, O. Investigations on laser welding of dissimilar joints of steel and aluminum using a high-power diode laser. J. Laser Appl. 2018, 30, 032422. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, M. Review of ladar: A historic, yet emerging, sensor technology with rich phenomenology. Opt. Eng. 2012, 51, 060901. [Google Scholar]
- Chapuran, T.E.; Toliver, P.; Peters, N.A.; Jackel, J.; Goodman, M.S.; Runser, R.J.; McNown, S.R.; Dallmann, N.; Hughes, R.J.; McCabe, K.P.; et al. Optical networking for quantum key distribution and quantum communications. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourley, P.L. Microstructured semiconductor lasers for high-speed information processing. Nature 1994, 371, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, S.W.; Fu, A.; Wong, A.B.; Ning, C.Z.; Yang, P.D. Semiconductor nanowire lasers. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S. The Roles of Structural Imperfections in InGaN-Based Blue Light-Emitting Diodes and Laser Diodes. Science 1998, 281, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Herrick, R.; Norman, J.; Turnlund, K.; Jan, C.; Feng, K.Y.; Gossard, A.C.; Bowers, J.E. Impact of threading dislocation density on the lifetime of InAs quantum dot lasers on Si. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 153507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontijo, I.; Qiu, Y.M.; Shapiro, A.A. Reliability of semiconductor laser packaging in space applications. In Proceedings of the 2008 2nd Electronics System-Integration Technology Conference, Greenwich, UK, 1–4 September 2008; pp. 1127–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Field, E.S.; Kletecka, D.E. Impact of contamination and aging effects on the long-term laser damage resistance of SiO2/HfO2/TiO2 high reflection coatings for 1054 nm. Opt. Eng. 2019, 58, 105105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistrali, F.; Sala, D.; Salmini, G.; Vanzi, M.; Fantini, F.; Giansante, M.; Zazzetti, L. ESD induced degradation mechanisms of InGaAsP/InP lasers. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 1992, 8, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, T.; Ogawa, M.; Endo, K.; Yonezu, H. Degradation of (AlGa)As DH lasers due to facet oxidation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1978, 32, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoedl, T.; Schwarz, U.T. Facet degradation of GaN heterostructure laser diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 97, 123102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, R.G. Diode laser degradation mechanisms: A review. Prog. Quantum Electron. 1991, 15, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J. Laser diode reliability: Crystal defects and degradation modes. C. R. Phys. 2003, 4, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanayeh, M.B.; Jaeger, A.; Schmid, W.; Tautz, S.; Brick, P.; Streubel, K. Investigation of dark line defects induced by catastrophic optical damage in broad-area AlGaInP laser diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, O.; Yamakoshi, S.; Komiya, S.; Akita, K.; Yamaoka, Y. Transmission electron microscope observation of dark-spot defects in InGaAsP/InP double-heterostructure light-emitting diodes aged at high temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1980, 36, 300–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, E.; Nakahara, K.; Shimaoka, M. Stress on junction-down-mounted ridge-waveguide laser diodes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 1756–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagdostar, S.; Souto, J.; Jiménez, J. CL as a tool for device characterisation: The case of laser diode degradation. Nano Ex. 2021, 2, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.J.; Sun, Q.; Feng, M.X.; Ge, X.T.; Ning, J.Q.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, H.W.; et al. Performance improvement of InGaN-based laser grown on Si by suppressing point defects. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 25943–25952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yellen, S.L.; Shepard, A.H.; Dalby, R.J.; Baumann, J.A.; Serreze, H.B.; Guido, T.S.; Soltz, R.; Bystrom, K.J.; Harding, C.M.; Waters, R.G. Reliability of GaAs-Based Semiconductor Diode Lasers: 0.6–1.1 μm. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1993, 29, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, O.; Imai, H.; Yamaguchi, A.; Komiya, S.; Umebu, I.; Kotani, T. Mechanism of catastrophic degradation in 1.3-μm V-grooved substrate buried-heterostructure lasers with the application of large pulsed currents. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 55, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Li, N.; Xie, C.; Carson, R.; Sun, X.Y.; Luo, W.L.; Zhao, L.; Helms, C.; Jensen, D.; Liu, C. Emcore VCSEL failure mechanism and resolution. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers XIV, San Francisco, CA, USA, 5 February 2010; p. 761504. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.H.; Lee, J.K.; Jang, D.H.; Cho, H.S.; Park, C.S.; Pyun, K.E. Characterization of catastrophic optical damage in Al-free InGaAs/InGaP 0.98 μm high-power lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEifresh, D.K.; Lopez, L.D.; Vacar, D. Reverse-bias emission sheds light on the failure mechanism of degraded vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 123113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, J.R. Microelectrionics Failure Analysis, 6th ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2011; pp. 279–281. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.C.; Pang, L.; Wang, C.P.; Huang, S.B.; Chen, C.L.; Chiang, P.F.; Lee, A.T.; Chu, M.T. Failure and degradation mechanisms of high-power white light emitting diodes. Microelectron. Reliab. 2010, 50, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushmaker, A.W.; Lingley, Z.; Brodie, M.; Foran, B.; Sin, Y. Optical Beam Induced Current and Time Resolved Electro-Luminescence in Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers During Accelerated Aging. IEEE Photonics J. 2019, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.S.; McElfresh, D.K. Categorizing light output degradation failures in LEDs using the relationship between defect revealing mechanisms responsible for electroluminescence (EL), cathodoluminescence (CL), EBIC, and reverse bias photoemission (RP). In Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4 April 1995; pp. 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, O.; Herrick, R.W. Failure Analysis of Semiconductor Optical Devices. In Book Materials and Reliability Handbook for Semiconductor Optical and Electron Devices; Ueda, O., Pearton, S.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 22. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, T.; Qiao, L.; Xia, M. Effective Failure Analysis for Packaged Semiconductor Lasers with a Simple Sample Preparation and Home-Made PEM System. Photonics 2021, 8, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8060184
Sun T, Qiao L, Xia M. Effective Failure Analysis for Packaged Semiconductor Lasers with a Simple Sample Preparation and Home-Made PEM System. Photonics. 2021; 8(6):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8060184
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Tianyu, Lei Qiao, and Mingjun Xia. 2021. "Effective Failure Analysis for Packaged Semiconductor Lasers with a Simple Sample Preparation and Home-Made PEM System" Photonics 8, no. 6: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8060184
APA StyleSun, T., Qiao, L., & Xia, M. (2021). Effective Failure Analysis for Packaged Semiconductor Lasers with a Simple Sample Preparation and Home-Made PEM System. Photonics, 8(6), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8060184




