Design and Simulation of an Ultra-Wide Field Optical Coherence Tomography Retinal Imaging System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design of the Ultrawide Field OCT Retinal Imaging System
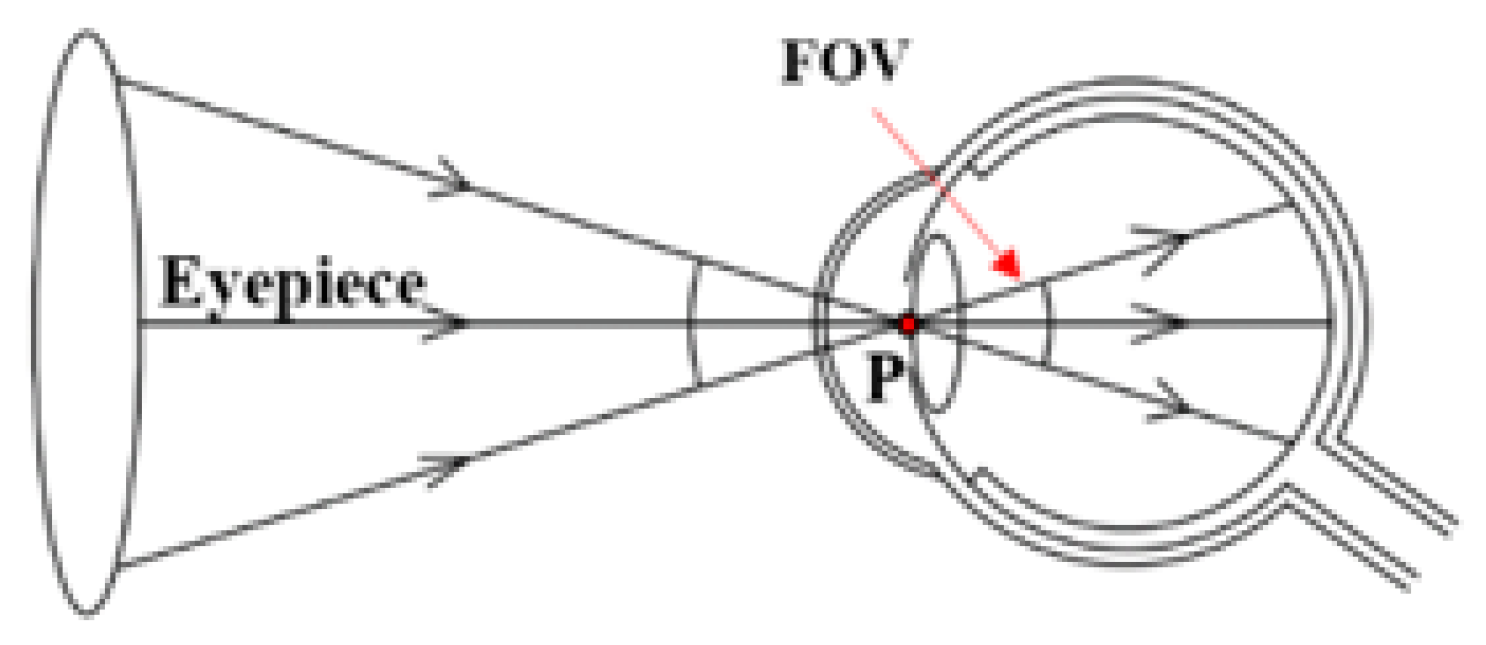
2.1. Definition of the FOV
2.2. Resolution of the OCT System
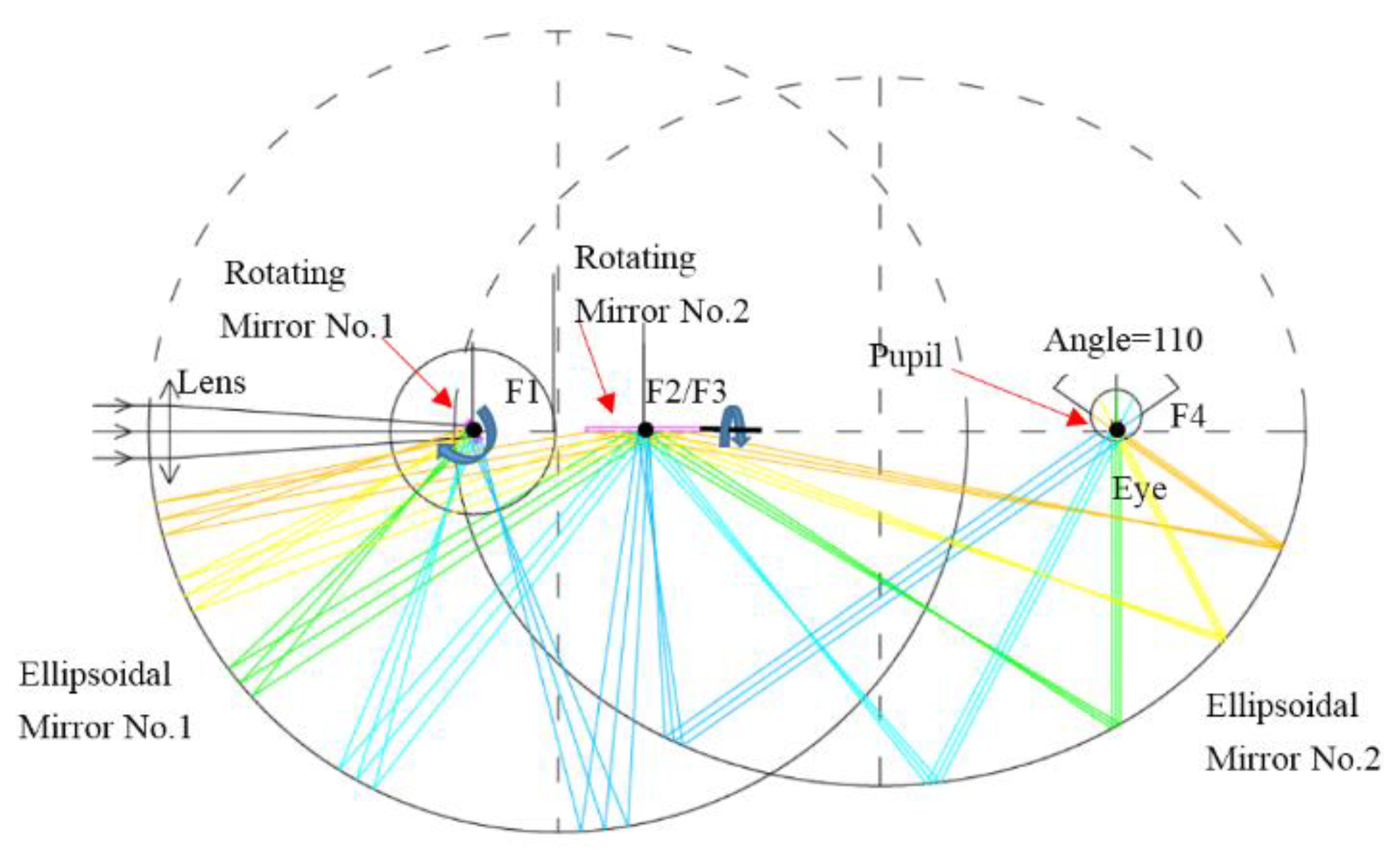
2.3. System Design
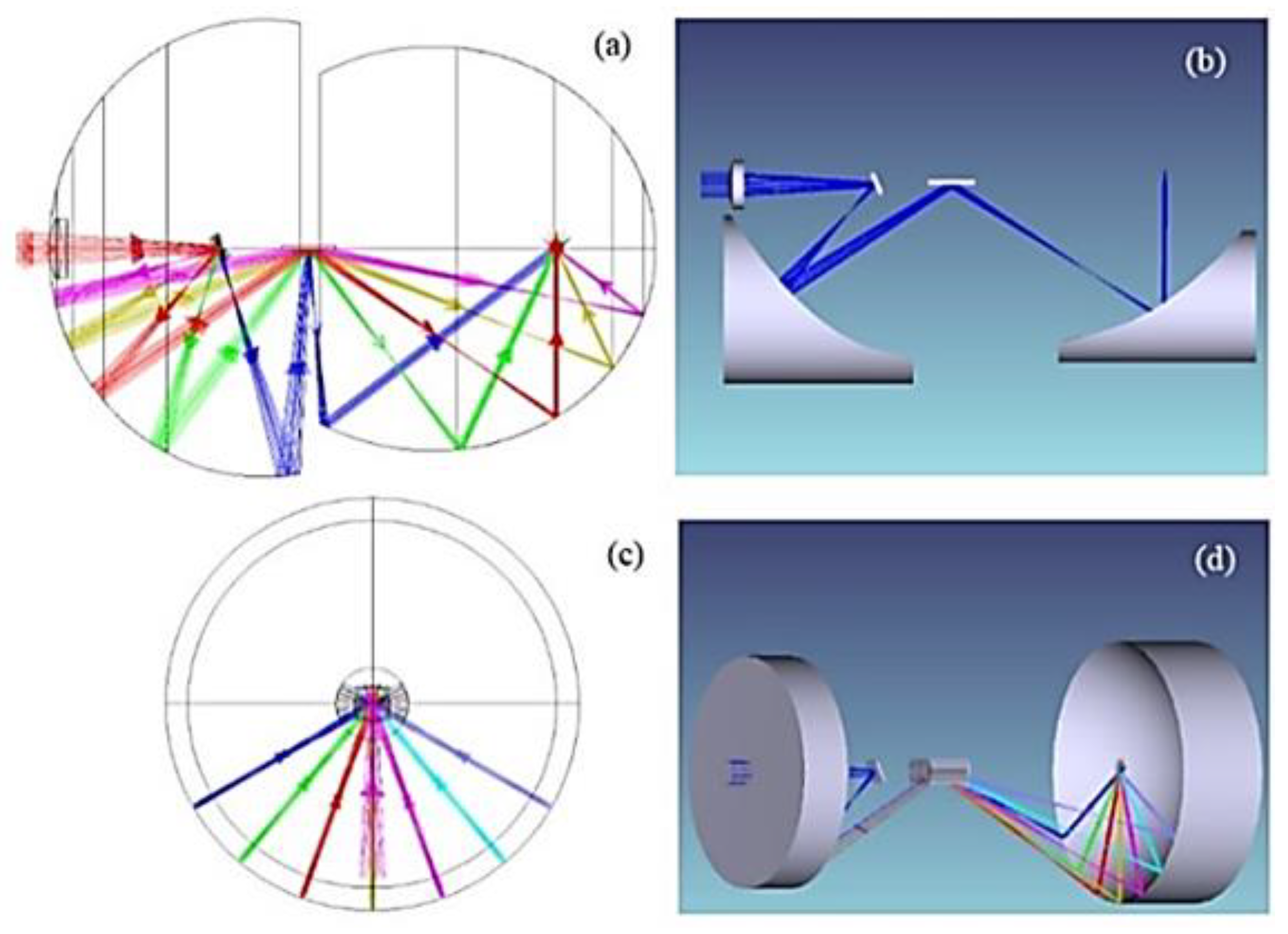
3. Simulation Methods
4. Results and Comparison
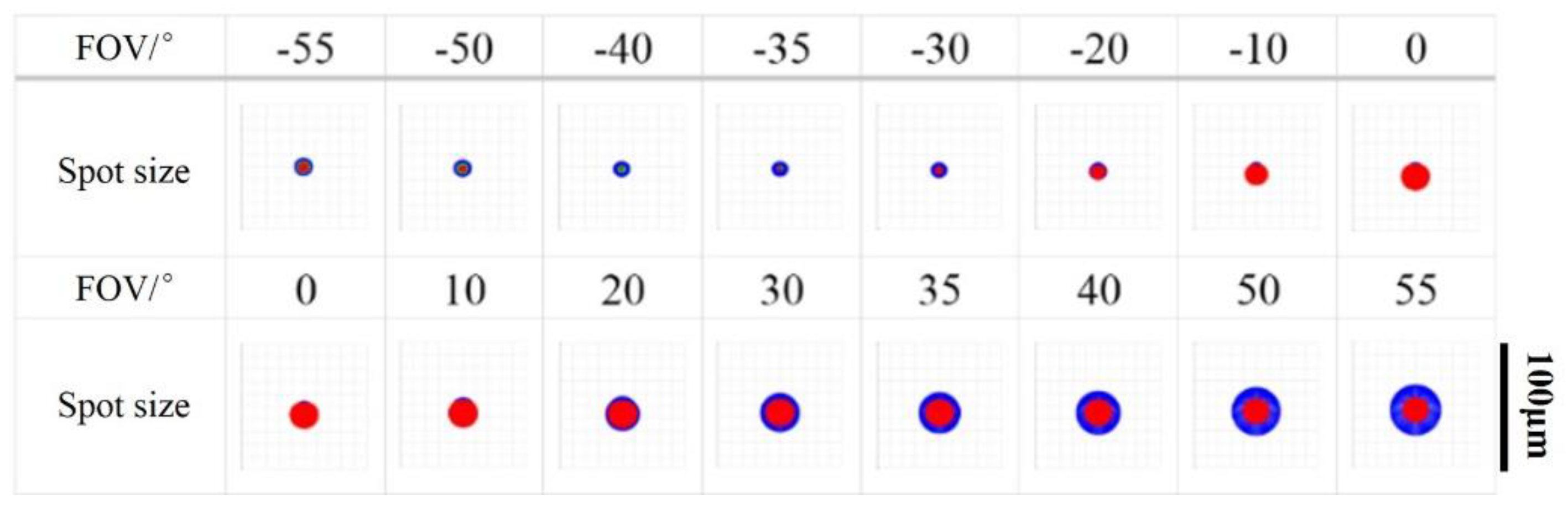
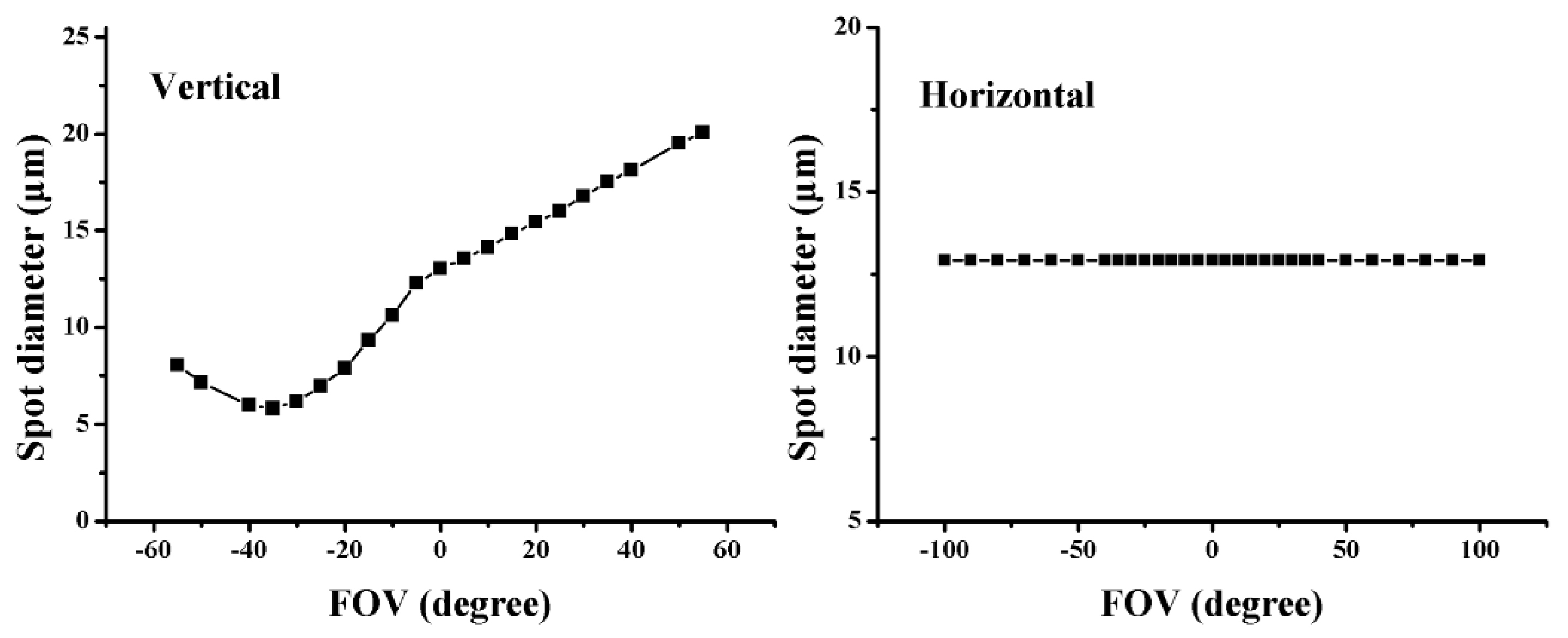
4.1. Inherent Aberration in the System
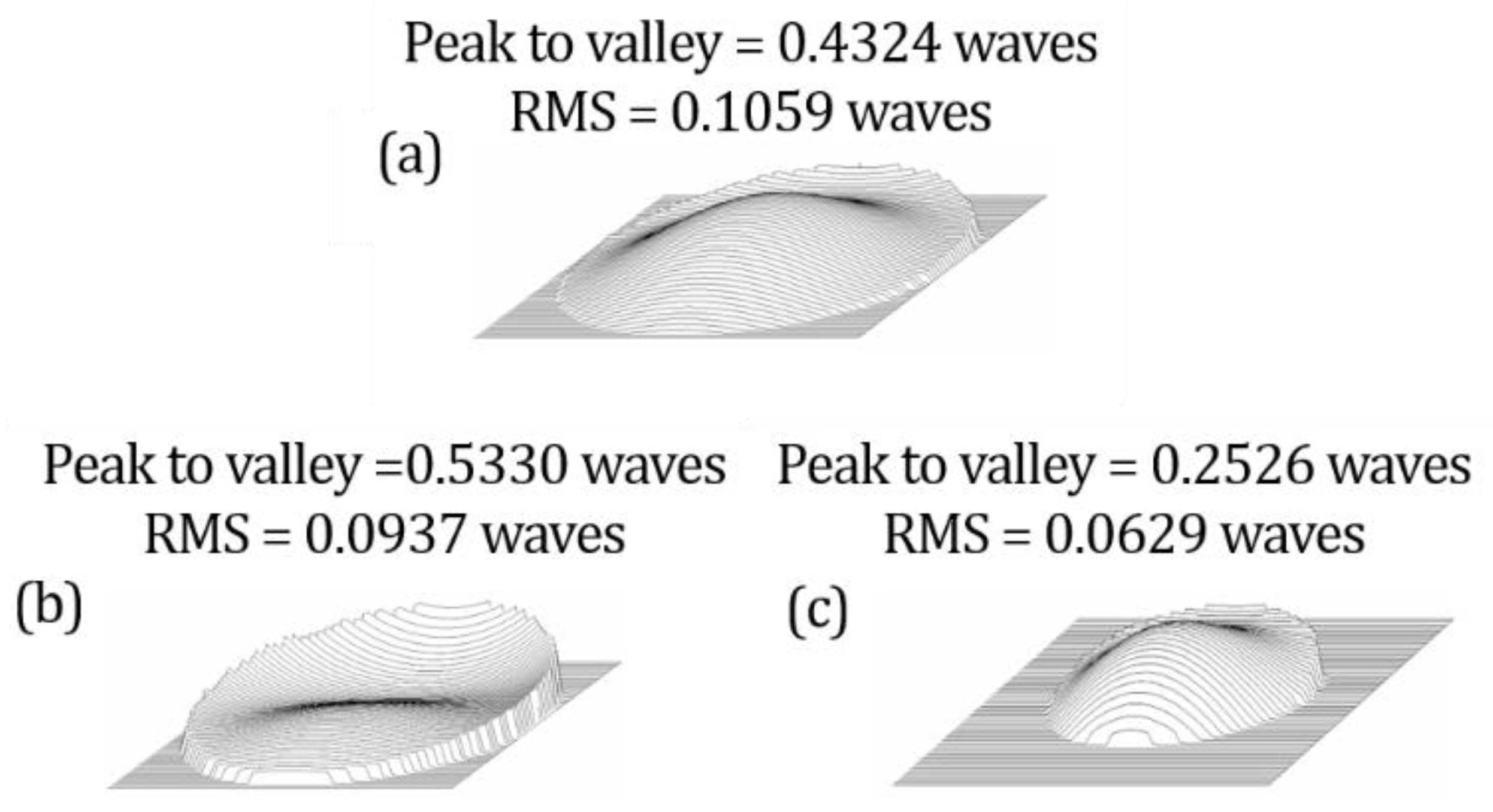
4.2. Aberrations in Retinal Imaging
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Puliafito, C.A.; et al. Optical coherence tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drexler, W.; Fujimoto, J.G. Optical Coherence Tomography: Technology and Applications, 3rd ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yuichiro, K.; Muka, M.; Shuichiro, H.; Yuichiro, O.; Kyoko, O.M. Areas of nonperfusion in peripheral retina of eyes with pathologic myopia detected by ultra-widefield fluorescein angiography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Falavarjani, K.G.; Kang, W.; Khadamy, J.; Sadda, S.R. Ultra-wide-field imaging in diabetic retinopathy: An overview. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2016, 28, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ying, L.; Giovanni, G.; Lam, B.L.; Rosenfeld, P.J. Automatic montage of SD-OCT data sets. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 26239–26248. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, K.; Kanno, J.; Gehlbach, P.L.; Yoneya, S. Montage Images of Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Eyes with Idiopathic Macular Holes. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2600–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregori, N.Z.; Lam, B.L.; Gregori, G.; Ranganathan, S.; Stone, E.M.; Morante, A.; Abukhalil, F.; Aroucha, P.R. Wide-Field Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Patients and Carriers of X-linked Retinoschisis. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choudhry, N.; Golding, J.; Manry, M.W.; Rao, R.C. Ultra-Widefield Steering-Based Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging of the Retinal Periphery. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.; Wieser, W.; Eigenwillig, C.M.; Biedermann, B.R.; Huber, R. Megahertz OCT for ultrawide-field retinal imaging with a 1050 nm Fourier domain mode-locked laser. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 3044–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, J.P.; Klein, T.; Kufner, C.L.; Wieser, W.; Neubauer, A.S.; Huber, R. Ultra-widefield retinal MHz-OCT imaging with up to 100 degrees viewing angle. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 1534–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polans, J.; Keller, B.; Carrascozevallos, O.M.; Larocca, F.; Cole, E.; Whitson, H.E.; Lad, E.M.; Farsiu, S.; Izatt, J.A. Wide-field retinal optical coherence tomography with wavefront sensorless adaptive optics for enhanced imaging of targeted regions. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 16–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, K.; Sewell, J.M.; Trempe, C.; Peto, T.; Travison, T.G. Comparison of image-assisted versus traditional fundus examination. Eye Brain 2013, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witmer, M.T.; Kiss, S. Wide-field Imaging of the Retina. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2013, 58, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network, Peripheral Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Lesions on Ultrawide-Field Fundus Images and Risk of DR Worsening over Time. Available online: https://public.jaeb.org/drcrnet/stdy/239 (accessed on 1 January 2015).
- Mo, J.; de Groot, M.; de Boer, J.F. Focus-extension by depth-encoded synthetic aperture in Optical Coherence Tomography. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 10048–10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polans, J.; Jaeken, B.; McNabb, R.P.; Artal, P.; Izatt, J.A. Wide-field optical model of the human eye with asymmetrically tilted and decentered lens that reproduces measured ocular aberrations. Optica 2015, 2, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaeken, B.; Artal, P. Optical quality of emmetropic and myopic eyes in the periphery measured with high-angular resolution. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 3405–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Order | Zernike Standard Coefficients/Waves | Aberration Meaning | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −55° | 0° | +55° | ||
| 4 | −0.85054148 | −0.03969461 | −0.12081888 | Defocus |
| 5 | 0.00000000 | 0.00000000 | 0.00000000 | Oblique astigmatism |
| 6 | −0.02730028 | −0.00247943 | −0.00020895 | 45° astigmatism |
| 7 | 0.08704811 | 0.08029944 | 0.02916162 | Vertical coma |
| 8 | 0.00000000 | 0.00000000 | 0.00000000 | Horizontal coma |
| 9 | −0.00087236 | −0.00002330 | −0.00000153 | Tilted trefoil |
| 10 | 0.00000000 | 0.00000000 | 0.00000000 | Horizontal trefoil |
| Order | Zernike Standard Coefficients/Waves | Aberration Meaning | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −40° | 0° | +40° | ||
| 4 | −0.04778938 | −0.01478089 | −0.08433465 | Defocus |
| 5 | 0.24196445 | −0.00512765 | −0.25042011 | Oblique astigmatism |
| 6 | −1.32105706 | −0.04584397 | −1.38152437 | 45° astigmatism |
| 7 | −0.07660711 | 0.01120033 | 0.09391515 | Vertical coma |
| 8 | −0.03552920 | −0.03162284 | −0.03574244 | Horizontal coma |
| 9 | −0.08725283 | 0.00008356 | 0.09332905 | Tilted trefoil |
| 10 | −0.01159125 | −0.00031933 | −0.01132933 | Horizontal trefoil |
| Order | Zernike Standard Coefficients/Waves | Aberration Meaning | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −40° | 0° | +40° | ||
| 4 | −0.10397192 | −0.01478089 | −0.12819229 | Defocus |
| 5 | −0.02110464 | −0.00512765 | 0.00707697 | Oblique astigmatism |
| 6 | 1.33305503 | −0.04584397 | 0.83154376 | 45° astigmatism |
| 7 | 0.01305138 | 0.01120033 | 0.01273088 | Vertical coma |
| 8 | −0.08885472 | −0.03162284 | 0.06125572 | Horizontal coma |
| 9 | −0.00258951 | 0.00008356 | −0.00220010 | Tilted trefoil |
| 10 | 0.12015452 | −0.00031933 | −0.08867846 | Horizontal trefoil |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, S.; Li, X.; Kang, J.; Wan, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Design and Simulation of an Ultra-Wide Field Optical Coherence Tomography Retinal Imaging System. Photonics 2021, 8, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8110476
Liang S, Li X, Kang J, Wan M, Wang J, Zhang J. Design and Simulation of an Ultra-Wide Field Optical Coherence Tomography Retinal Imaging System. Photonics. 2021; 8(11):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8110476
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Shanshan, Xinyu Li, Jiajing Kang, Mingming Wan, Jiahui Wang, and Jun Zhang. 2021. "Design and Simulation of an Ultra-Wide Field Optical Coherence Tomography Retinal Imaging System" Photonics 8, no. 11: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8110476
APA StyleLiang, S., Li, X., Kang, J., Wan, M., Wang, J., & Zhang, J. (2021). Design and Simulation of an Ultra-Wide Field Optical Coherence Tomography Retinal Imaging System. Photonics, 8(11), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8110476






