Abstract
This work studies the problem of designing computer-generated holograms using phase-shifting masks limited to represent only a small number of discrete phase levels. This problem has various applications, notably in the emerging field of optogenetics and lithography. A novel regularized cost function is proposed for the problem at hand that penalizes the unfeasible phase levels. Since the proposed cost function is non-smooth, we derive proper proximal gradient algorithms for its minimization. Simulation results, considering an optogenetics application, demonstrate that the proposed proximal gradient algorithm yields better performance as compared to other algorithms proposed in the literature.
1. Introduction
The research area of optogenetics studies the targeted stimulation of neurons that have been previously functionalized with light-sensitive compounds, called opsins [1]. In particular, genetically designed opsins are properly placed by physicians to some area of the brain and are able to produce electrical signals when hit by light of a specific wavelength. In the sequel, structured light is used to target specific areas of the brain and thus stimulate the neurons to which the opsins have been attached. Achieving precise spatial specificity is very important in order to minimize unnecessary heating of the tissue that should not be stimulated. Due to the prospects that it offers for specified neuronal stimulation, the field of optogenetics has been embraced by the research community as an efficient tool towards demystifying the operation of the brain [2]. Indeed, the optogenetic method has the potential of stimulating a complex of neurons down to a single neuron. This unprecedented specificity and spatial flexibility cannot be matched by other deep brain stimulation techniques.
Furthermore, in many studies, short-term excitation is required to study the dynamics of the neuronal activity, since the impulse response function of networks is best obtained with spatiotemporally well-defined stimuli. In practice, such short-term stimulation of neurons can be achieved only via the use of ferroelectric Spatial Light Modulators (fSLMs) that are characterized by very fast response times when a new phase-shifting mask is loaded to the device [3,4]. Thus, short-term stimulation is achieved via such fast swapping of different phase-shifting masks that have been designed beforehand for this task. However, typical fSLMs are restricted to using only a small number of discrete phase levels, most commonly two or four, where in the latter case, two binary fSLMs are employed [5].
To this end, it is becoming important to devise methods that design accurate computer-generated holograms, using discrete level phase-shifting masks (PSMs). Previous works on this problem have mainly focused on lithography applications. In particular, the branch and bound algorithm and simulated annealing were employed in [6] for both binary and phase-shifting mask design. Furthermore, an iterative approach to generate binary masks was reported in [7]. The method of projections onto convex sets (POCS) was employed in [8] for the PSM design problem. Furthermore, a genetic optimization algorithm was employed in [9] to jointly optimize for the mask and the light source parameters. In contrast to the previous methods that rely upon optimization approaches for discrete variables, the work in [10] introduced a method suitable for gradient-based optimization algorithms that, in general, are less computationally expensive. The approach in [11] further extended the work in [10] and derived a gradient-based algorithm that was able to generate more general mask patterns. More recently, the emerging field of algorithm unrolling [12] was employed to derive fast versions of the algorithm that was proposed in [11]. In particular, in [13,14], the iterative algorithm of [11] was unfolded to neural networks of suitable structure, which were then trained in an unsupervised manner.
While most previous works for the problem of discrete-level phase-shifting mask design have mainly considered lithography applications, in this work the focus is on the application of optogenetics. When considering an optogenetics application, the problem is similar to that encountered in lithography applications, in the sense that a phase-shifting mask with limited phase levels must be designed. However, it must be emphasized that in lithography applications there are a number of other restrictions regarding manufacturability [15] that are not present in our case.
In this work, we extend our previous work in [4] that considered the problem of discrete-level phase-shifting mask design in optogenetics applications. Similar to [11], we follow a gradient-based regularized optimization approach. In more detail, in our previous work [4], it was shown that performance gains can be obtained by properly modifying the regularization term proposed in [11]. However, these modifications make the regularization term non-differentiable and, thus, proper optimization algorithms must be employed. The subgradient [16] method was used in our previous work in [4] to deal with the non-smooth regularization term. The present is different from our previous work in [4] in two aspects: (i) we propose a new form for the regularization term that is easier to handle analytically, and (ii) we derive a proximal gradient [17] type algorithm for the minimization. Simulation results are provided that demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
The rest of this manuscript is organized as follows. Section 2, contains our theoretical work. In more detail, Section 2.1 gives a mathematical formulation of the problem at hand and demonstrates why the globally optimal solution cannot be computed in practice. Section 2.2 provides the main ideas of our proposed approach, and Section 2.3 details the derivation of the proposed optimization algorithm. Numerical results that compare the performance of the proposed approach to other approaches are given in Section 3. Finally, Section 4 discusses the results in this work and outlines our future efforts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Problem Formulation
Let us consider that the input phase mask is denoted as , where denote the discrete spatial coordinates (pixels) on the SLM plane. As explained in the introduction, in this work we consider an application in which, due to technological limitations of the fSLM devices, is not allowed to take any value in , rather, only q equidistant phases are permitted, as denoted by
where q denotes the number of discrete phase levels, typically 2 or 4 for the considered application, and is the corresponding set of permissible phase values. We assume that monochromatic light from a proper laser source is reflected by the SLM device, thus generating the (input) light field
where denotes the intensity of the input light field and j denotes the complex imaginary unit. We also consider that is the input to an optical system that generates the output light field , as described by the relation
where the function describes the optical system under study. As an example, for lithography applications, is usually modeled as a low-pass Gaussian filter followed by an operation that computes the magnitude of the complex light field and the application of a sigmoid function [11]. In this work, for conducting our numerical simulations, we consider the optical path demonstrated in Figure 1, which consists of a 2f setup with focal length f followed by free-space propagation at a distance z. Since our focus is on an optogenetics application, the parameters of our simulation setup were selected so that the field-of-view at the target plane is an area of m.
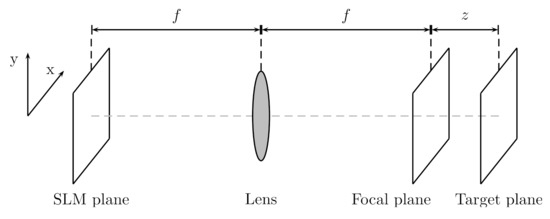
Figure 1.
The optical path considered for the simulations.
Clearly, the output light field is a function of the input light amplitude A and the phases . Given a desired response output intensity field , the optimal values and for the parameters A and are given as the solution to the following optimization problem
where denotes some suitable distance/cost function, for example, the mean square error (MSE) or any other, more elaborate, cost function as in [18]. It is easily seen that problem (4) is a combinatorial optimization problem in the sense that the optimal solution can be obtained by examining all possible phase-shifting masks and finding the one that yields the minimum cost, while the problem becomes even more complicated due to the continuous variable A. Thus, in practice, the optimal solution of (4) cannot be computed. A simple approach to circumvent this problem, and derive a sub-optimal solution, is to solve (4) by neglecting the constraint , letting , and then to replace each of the resulting phase values with the closest phase level from the constraint set . In the sequel, we refer to this approach as quantization.
2.2. The Proposed Approach
Trying to solve (4) while neglecting the constraint makes the problem significantly easier; however, the resulting solution (after quantization) exhibits poor performance, in the sense that the resulting output intensity will be significantly different from the desired intensity . To circumvent this effect, we employ the notion of regularized optimization. In essence, the method utilizes a modified cost function by adding a proper regularization part that penalizes values of the variables that do not satisfy the initial constraint. In more detail, we consider a cost function of the form
where the first term is recognized as the mean squared error between the intensity of the output light field and the desired intensity , whereas the second term is the regularization term, that is, it obtains greater value for phase values away from those in the set . The parameter , usually referred to as the regularizer, is some positive scalar that sets the relative importance between the mean squared error and the impact of the regularization. In our previous work [4], the regularization term was defined using
where is a positive scalar that controls the exact shape of the regularization terms in (6). It was experimentally shown in [4] that the value gives good results. However, it can be seen that the regularization term in (6) is a non-smooth function of when . Thus, the so-called subgradient method [16] was employed in [4] to minimize the resulting cost function that is suitable for such cases. The approach followed in this work is different from our previous work in [4] in two aspects.
Firstly, in place of the regularization term in (6) we propose here the term
where . Secondly, in this work, we derive a proximal gradient [17] type algorithm to deal with the fact that the considered regularization terms are non-smooth, while a subgradient type algorithm was used in [4]. It can be verified that the regularization terms in (6) and (7) give very similar values, when the value is used in (6). However, in this work, we prefer the form in (7) because it can lead to a closed form proximal operator, shown in Equation (14). The regularization term in (7) consists of a series of parts of second-degree polynomial functions, properly placed one next to the other, so as to have the desired regularization effect. In Figure 2a,b, we demonstrate the regularization terms and , respectively.
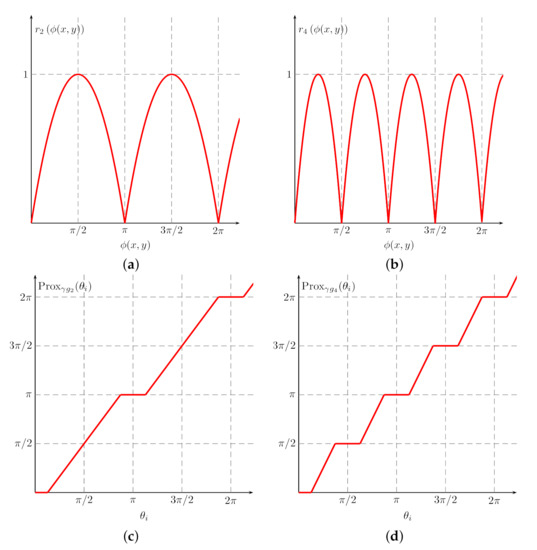
Figure 2.
Example plots for various regularization terms and proximal operators. (a) The regularization term for . (b) The regularization term for . (c) The proximal operator for . (d) The proximal operator for .
2.3. Derivation of the Proximal Gradient Algorithm
The cost function in (5) using the regularization term in (7) can be recognized as a cost function that consists of a smooth term (the mean square error) and a non-smooth term (the regularization part). Thus, the method of proximal gradient [17] can be employed for its minimization. The method is more commonly employed in convex optimization problems, but it can also be employed in non-convex problems [19] as it is the case in this work. Defining the vector that contains all the phase variables of our optimization problem, we also define
and
Using the above definitions, the considered optimization problem becomes
The proximal gradient algorithm is an iterative procedure that generates the estimates and at the n-th iteration. In particular, for the problem considered here, the algorithm consists of the following two equations
where is a properly selected positive step size parameter and is the so-called proximal operator, defined by
It can be easily verified that each of the variables in vector contributes two positive terms in the last minimization problem, and these two terms are independent of the terms that correspond to different variables. Thus, the minimization can be performed separately for each of the variables. After some calculations, it can be shown that the proximal operator for each scalar variable , , in the vector is given by
where and . Finally, the condition
must be satisfied for the previous expressions to be true. In Figure 2c,d, we demonstrate the form of the proximal operators for and , respectively. It can be observed that the effect of the proximal operator is (i) to quantize phase variables that are close to the discrete levels in the set , as shown by the flat regions in Figure 2c,d, and (ii) to apply a small “force” to the rest of the phase variables towards the closest discrete phase level in the set , as shown by the “ramp” regions in Figure 2c,d. Furthermore, it is very interesting to note that the derived proximal operator has a very similar form to the so-called soft-thresholding operator, employed in the context of the sparse coding problem [20].
3. Results
In this section, the results of our study are demonstrated. The simulation setup and parameters used were as follows: A square fSLM device, measuring mm along each dimension, was considered. We used monochromatic light with wavelength nm. The light reflected by the SLM travels through a 2f setup with focal length mm. In the sequel, for the scopes of reducing the considered pixel size, we consider free space propagation of the light along a distance equal to 10 mm, using a two step Frenel propagation method and a magnification parameter , as detailed in [21]. Thus, we arrive to a pixel size of around m at the target plane (see Figure 1).
Since we are considering an optogenetics application, the desired response intensity image was created as five, randomly placed, disks with a radius equal to 10 m, as it is demonstrated in Figure 3a, where each disk corresponds to the approximate size and shape of a neuronal soma in the mouse cerebral cortex [18]. In the same figure, we demonstrate the resulting images for various approaches, namely, simple phase quantization in Figure 3b, regularized optimization using the smooth regularizer of [11] in Figure 3c, regularized optimization using the non-smooth regularizer of [4] and the subgradient method in Figure 3d, regularized optimization using the proposed regularizer in Equation (7) and the proposed proximal gradient algorithm in Figure 3e and regularized optimization using a proximal gradient algorithm with an increasing , where is increased from zero to its final value 0.005 linearly over the 5000 iterations, shown in Figure 3f.
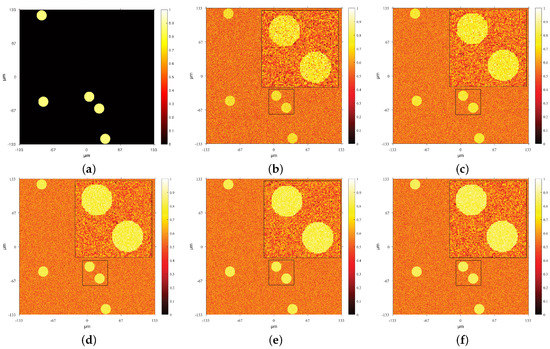
Figure 3.
Demonstrationof the resulting images (where the fifth root of the intensities multiplied by 1/2 has been used to amplify the details). All the results correspond to phase levels. Furthermore, the square regions have been magnified to better demonstrate the results. (a) Desired response intensity image, (b) non-regularized optimization followed by simple quantization to 2 phase levels, (c) regularized optimization using the regularizer in (6) with and (as used in [11]), (d) regularized optimization using the regularizer in (6) with and (as used in [4]), (e) regularized optimization using the regularizer in (7) with (proposed approach), and (f) regularized optimization using the regularizer in (7) where was linearly increased over 5000 iterations from 0 to 0.005.
Apart from the optical demonstration of the resulting images shown in Figure 3, the methods were also compared in terms of the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), defined using the MSE as
where the maximum value of the desired response intensity was , and the MSE is defined as
The results obtained can be seen in Table 1. It is evident from these results that the proposed approach offers significant performance improvements against the simple phase quantization approach as well as against the previously reported method [11]. In particular, for , the proposed approach offers more than 1.8 dB better performance as compared to the simple phase quantization approach, and 1 dB better performance as compared to the method of [11]. For , the proposed approach offers more than 1 dB better performance as compared to the simple phase quantization approach and about 0.5 dB as compared to the previously reported approach [11]. It is also interesting to note that our previously proposed algorithm in [4] and the approach proposed here give quite similar results, but with the approach proposed here always having better performance. In addition, Table 1 reveals that the approach in which the proximal gradient algorithm that utilizes a gradually increasing value for the regularizer , gave the best results. Finally, it can be seen that the performance gains of the various schemes become smaller as the number q of discrete phase levels increases. Note that for all the considered approaches, several experiments were conducted to yield the best values for the parameter , and these values also appear in Table 1. The PSNR values obtained for various algorithms as a function of the parameter can be seen in Figure 4, for the case .

Table 1.
PSNR values obtained by the various optimization approaches considered for various values for the number of discrete phase levels q. Note that for all approaches that employ regularized optimization, several experiments were conducted for various values of and the table gives the results that gave the best PSNR values and the corresponding value for .
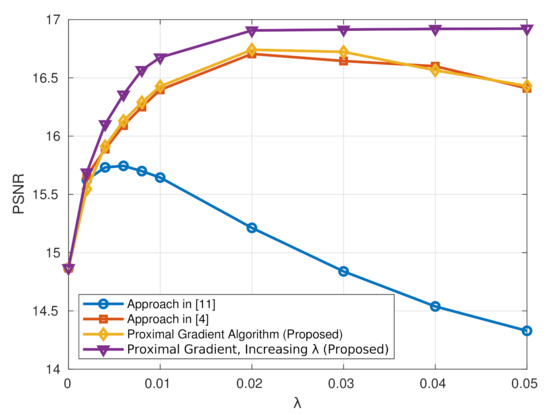
Figure 4.
PSNR values for various algorithms as a function of the parameter , for .
4. Discussion
In this work, the problem of designing few-level phase-shifting masks for computer-generated holograms was studied. This problem has applications in optogenetics but also in lithography, where such few-level phase-shifting masks are needed. For the problem at hand, we followed a gradient-based regularized optimization approach. Since the considered cost function is non-differentiable, we developed a novel proximal gradient type algorithm for its minimization. Simulation results were used to verify the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Future work will focus on the extension of the proposed approach so as to be able to take into account manufacturability constraints, as used in lithography applications. Furthermore, another line of research will focus on the unrolling of the proposed algorithm into a neural network of suitable structure, trained properly so as to derive a scheme with significantly smaller computational complexity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.A. (Dimitris Ampeliotis); A.A. and D.A. (Dimitris Alexandropoulos); methodology, D.A. (Dimitris Ampeliotis) and D.A. (Dimitris Alexandropoulos); software, D.A. (Dimitris Ampeliotis) and A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, D.A. (Dimitris Ampeliotis) and A.A.; writing—review and editing, C.P. and D.A. (Dimitris Alexandropoulos); visualization, A.A.; supervision, D.A. (Dimitris Alexandropoulos); project administration, D.A. (Dimitris Alexandropoulos); funding acquisition, D.A. (Dimitris Alexandropoulos) and C.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Social Fund-ESF) through the Operational Programme “Human Resources Development, Education and Lifelong Learning 2014–2020” in the context of the project “HOLOGEN” (MIS 5047121).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Deisseroth, K. Optogenetics. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiakoumou, E. Optical developments for optogenetics. Biol. Cell 2013, 105, 443–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmieder, F.; Klapper, S.D.; Koukourakis, N.; Busskamp, V.; Czarske, J.W. Optogenetic stimulation of human neural networks using fast ferroelectric spatial light modulator—Based holographic illumination. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ampeliotis, D.; Politi, C.; Anastasiou, A.; Alexandropoulos, D. A Regularized Optimization Approach for Optogenetic Stimulation using Ferroelectric SLMs. In SPIE Optical System Design (Computational Optics 2021); SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hamam, H.; de la Tocnaye, J.d.B. Fractional Talbot four-level phase-only holograms using ferroelectric liquid-crystal spatial light modulators. Opt. Lett. 1994, 19, 1654–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zakhor, A. Binary and phase shifting mask design for optical lithography. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 1992, 5, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, S.; Saleh, B.; De Leone, R. Binary image synthesis using mixed linear integer programming. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1995, 4, 1252–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pati, Y.; Kailath, T. Phase-shifting masks for microlithography: Automated design and mask requirements. JOSA A 1994, 11, 2438–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, A.; Fuehner, T.; Schnattinger, T.; Tollkuehn, B. Toward automatic mask and source optimization for optical lithography. In Proceedings of the Optical Microlithography XVII, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 24–27 February 2004; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5377, pp. 646–657. [Google Scholar]
- Poonawala, A.; Milanfar, P. OPC and PSM design using inverse lithography: A nonlinear optimization approach. In Optical Microlithography XIX; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006; Volume 6154, p. 61543H. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Arce, G.R. Generalized inverse lithography methods for phase-shifting mask design. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15066–15079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monga, V.; Li, Y.; Eldar, Y.C. Algorithm unrolling: Interpretable, efficient deep learning for signal and image processing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2021, 38, 18–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Arce, G.R. Model-driven convolution neural network for inverse lithography. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 32565–32584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zheng, X.; Arce, G.R. Fast inverse lithography based on dual-channel model-driven deep learning. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 20404–20421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.C.; Yu, P. Impacts of cost functions on inverse lithography patterning. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 23331–23342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, S.; Xiao, L.; Mutapcic, A. Subgradient Methods; Lecture Notes of EE392o; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2003; Volume 2004, pp. 2004–2005. [Google Scholar]
- Parikh, N.; Boyd, S. Proximal algorithms. Found. Trends Optim. 2014, 1, 127–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pégard, N.; Zhong, J.; Adesnik, H.; Waller, L. 3D computer-generated holography by non-convex optimization. Optica 2017, 4, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.; Tichatschke, R. Proximal point methods and nonconvex optimization. J. Glob. Optim. 1998, 13, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.D. Numerical Simulation of Optical Wave Propagation: With Examples in MATLAB; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; pp. 1–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).