Flowline Optical Simulation to Refractive/Reflective 3D Systems: Optical Path Length Correction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
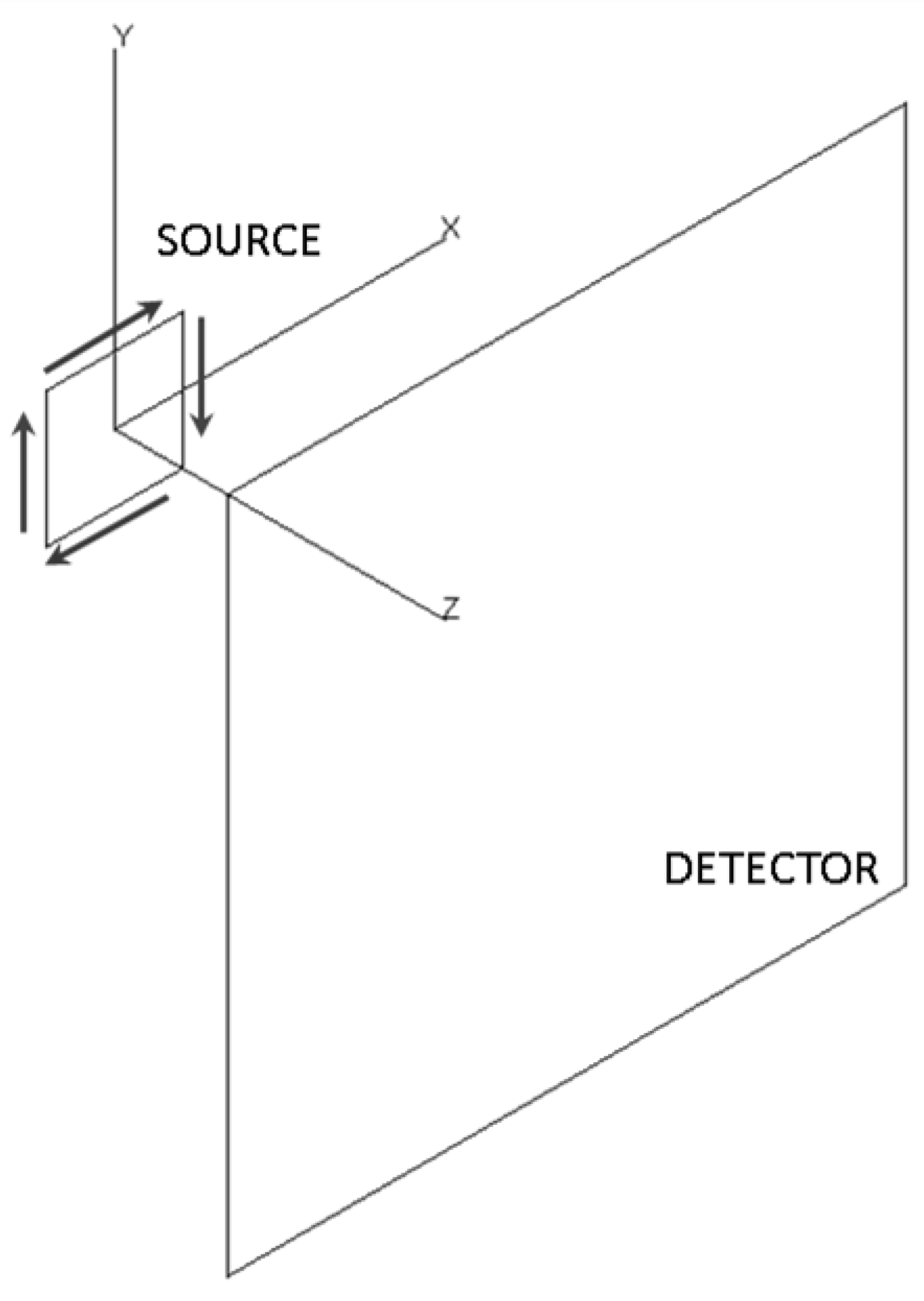
2. Theoretical Background and Flowline Methodology for 3D Optical Systems Analysis
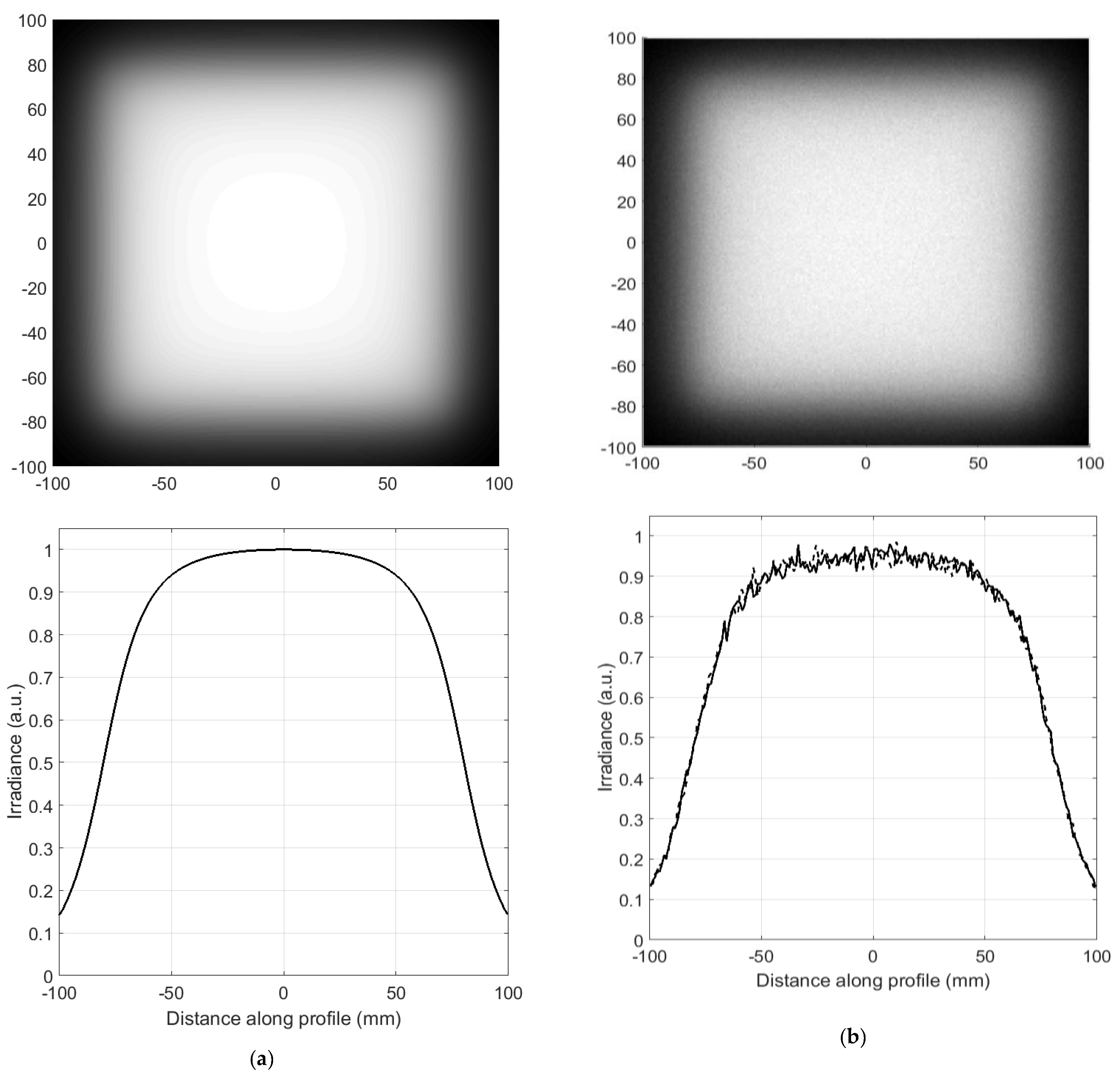
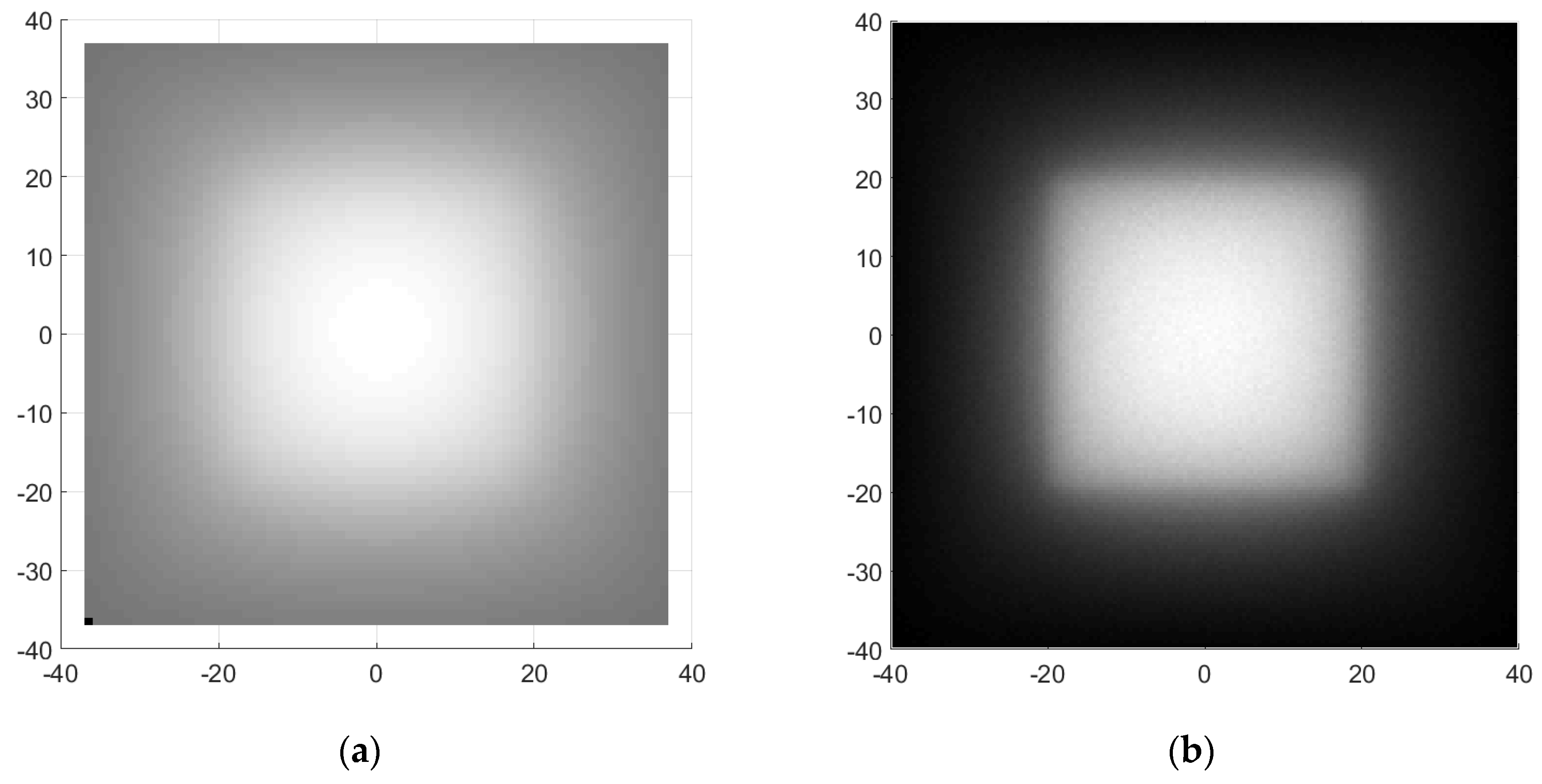
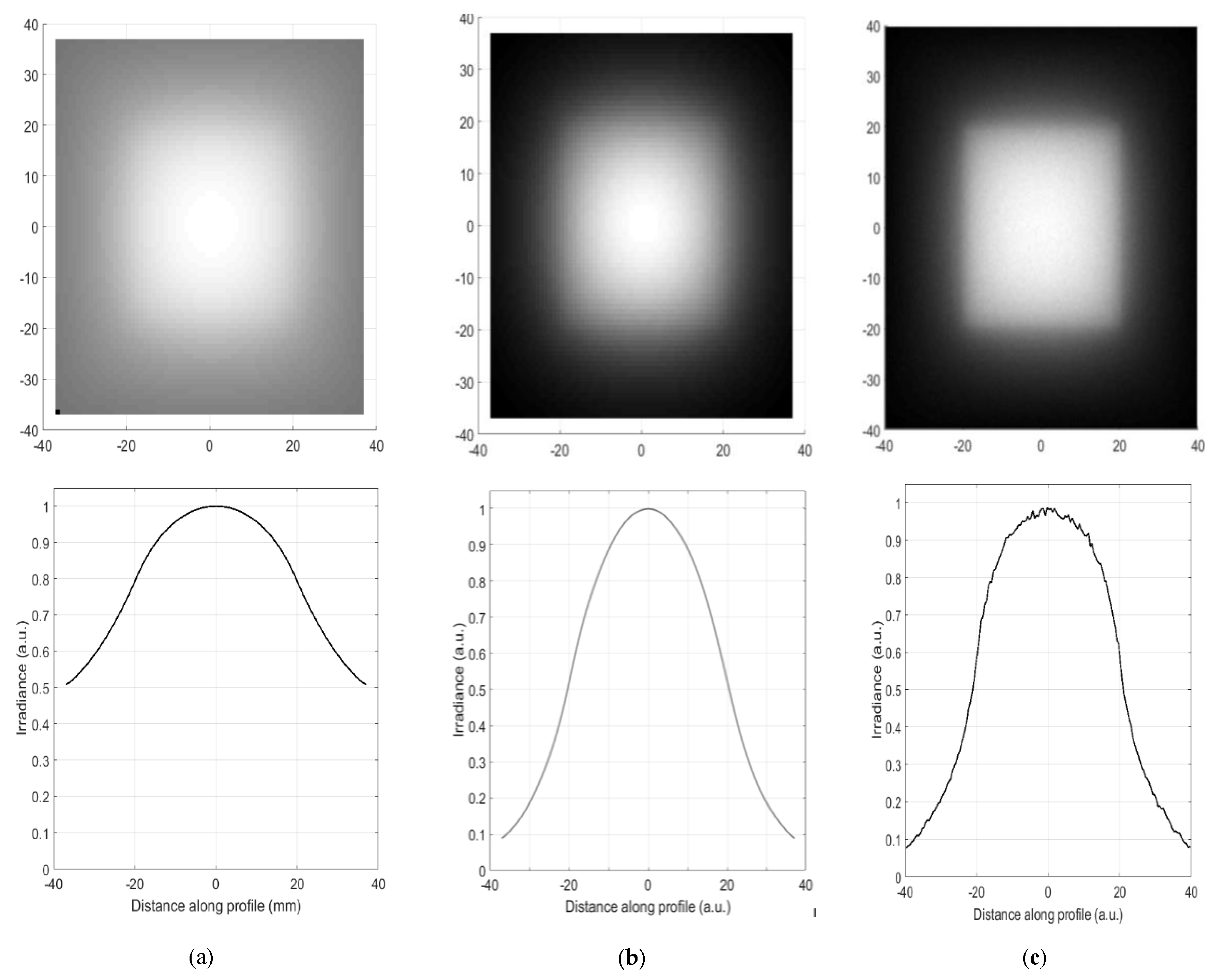
Irradiance Computation from J Vector for Simple Free Space 3D Non Symmetric Systems
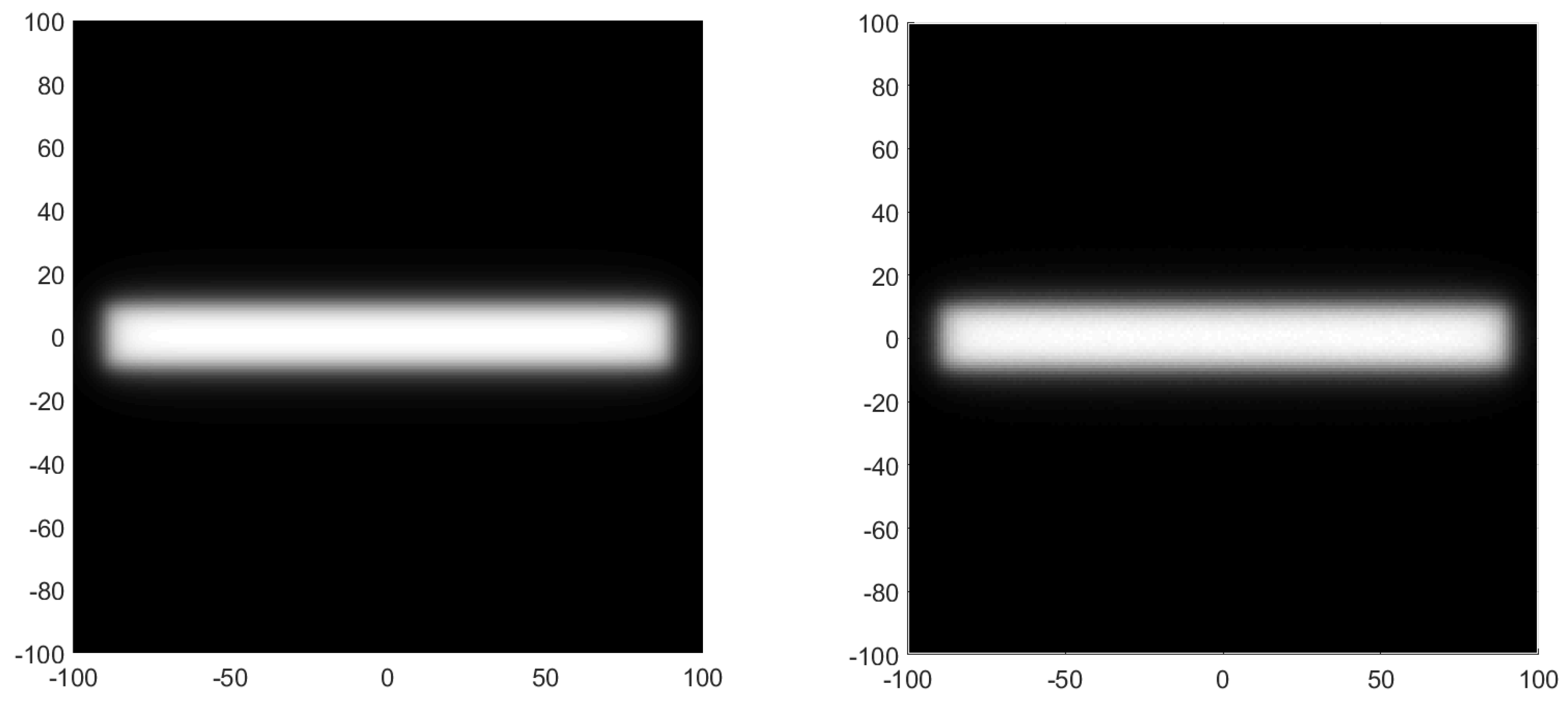
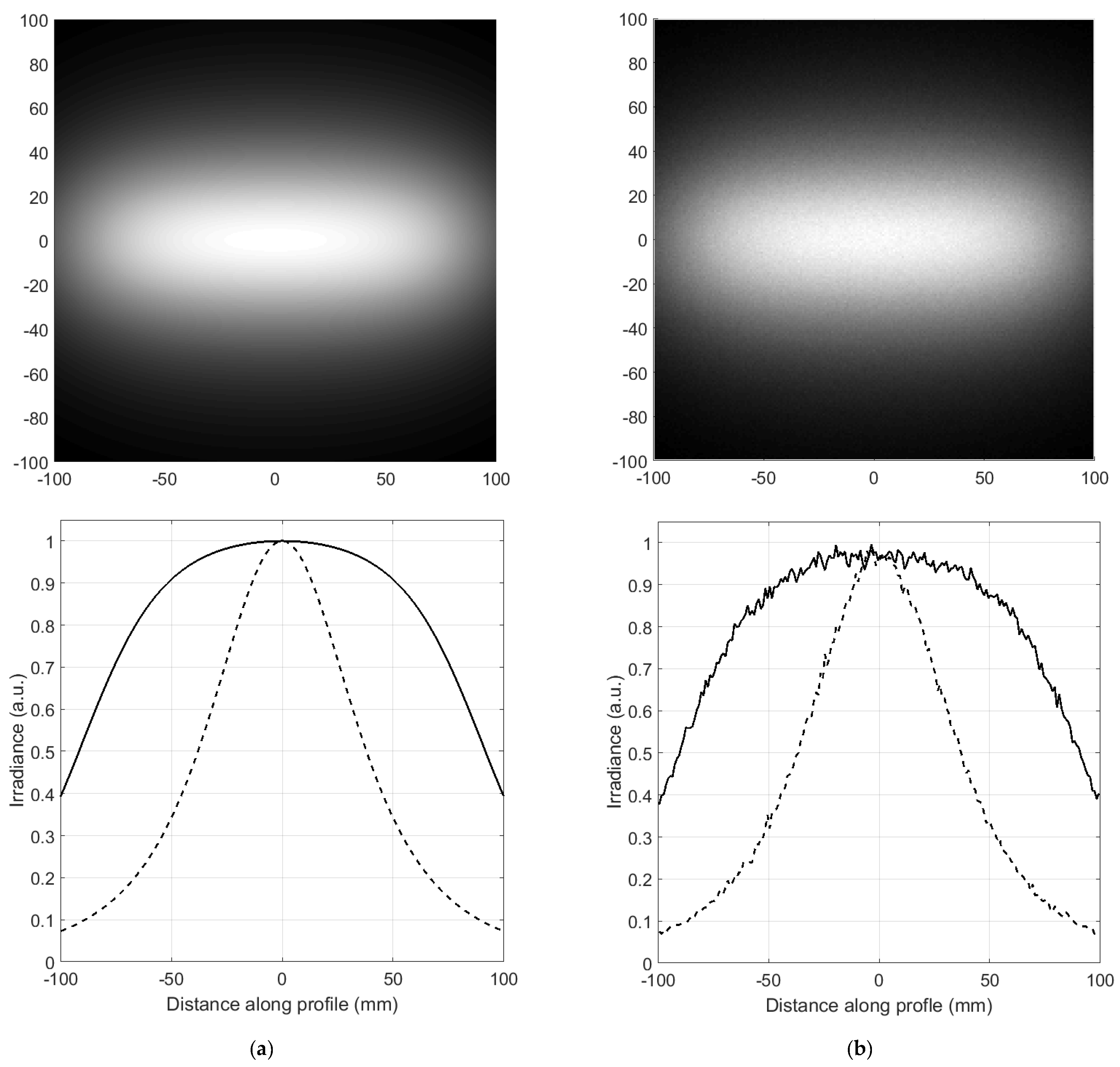
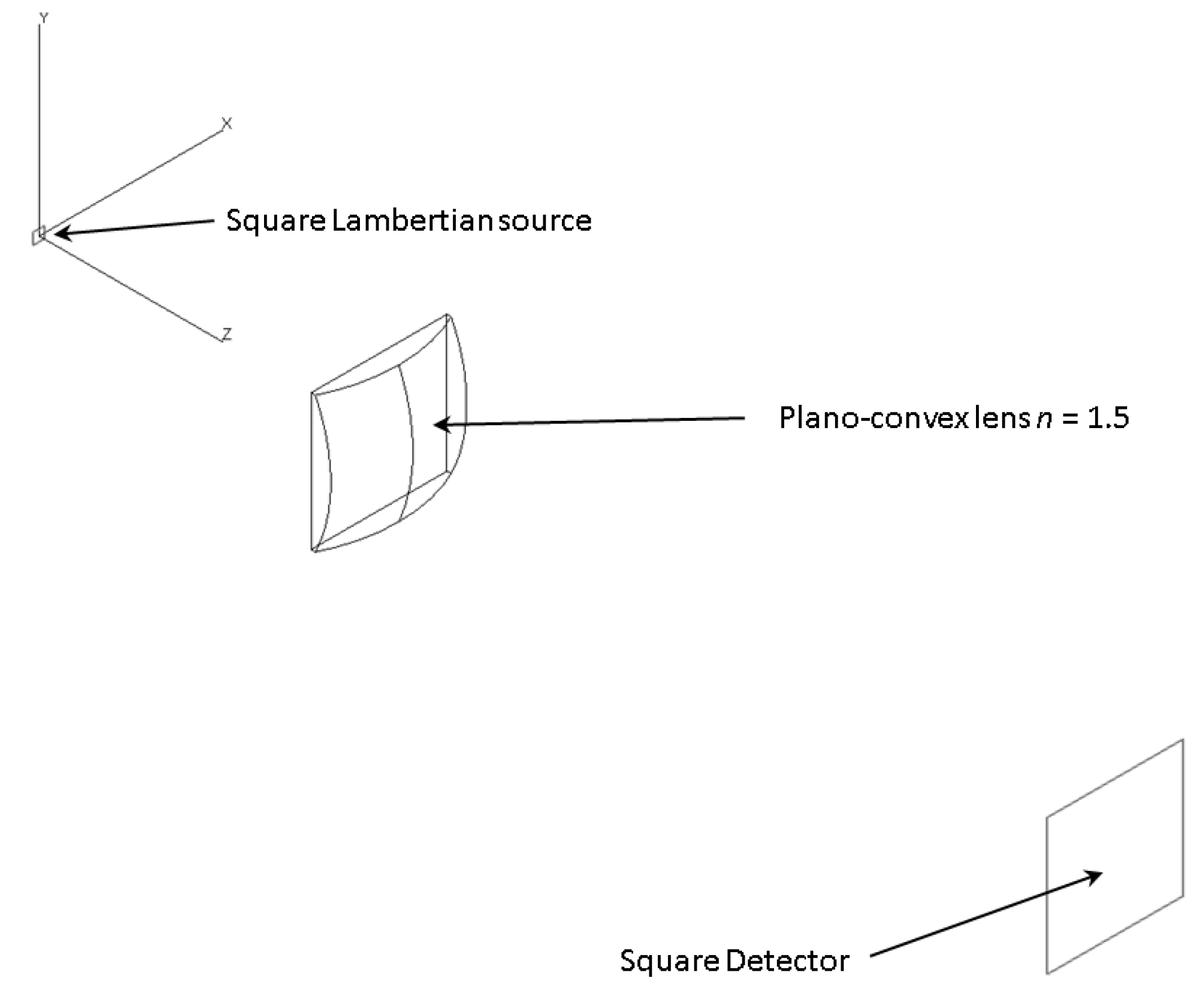
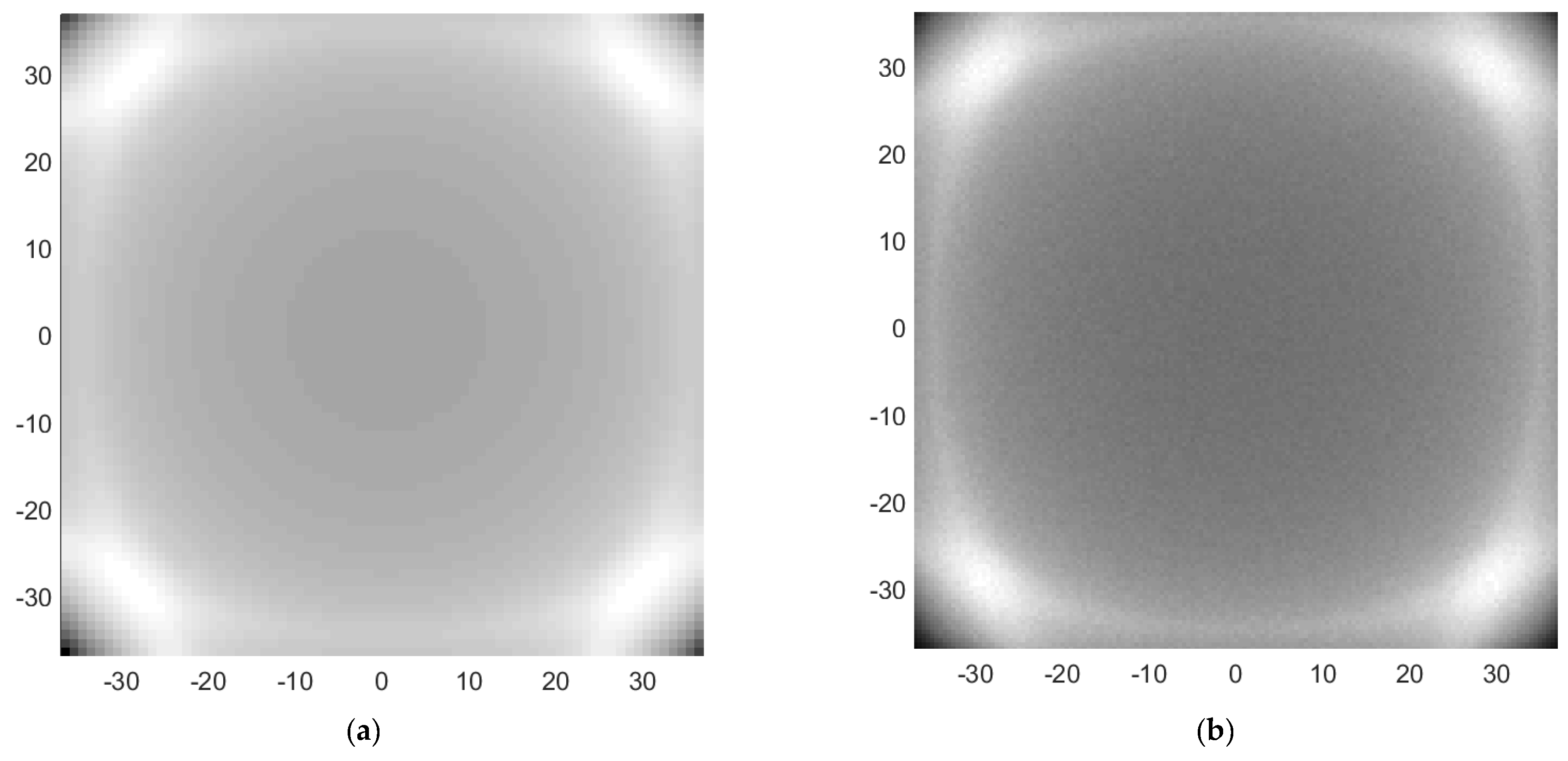
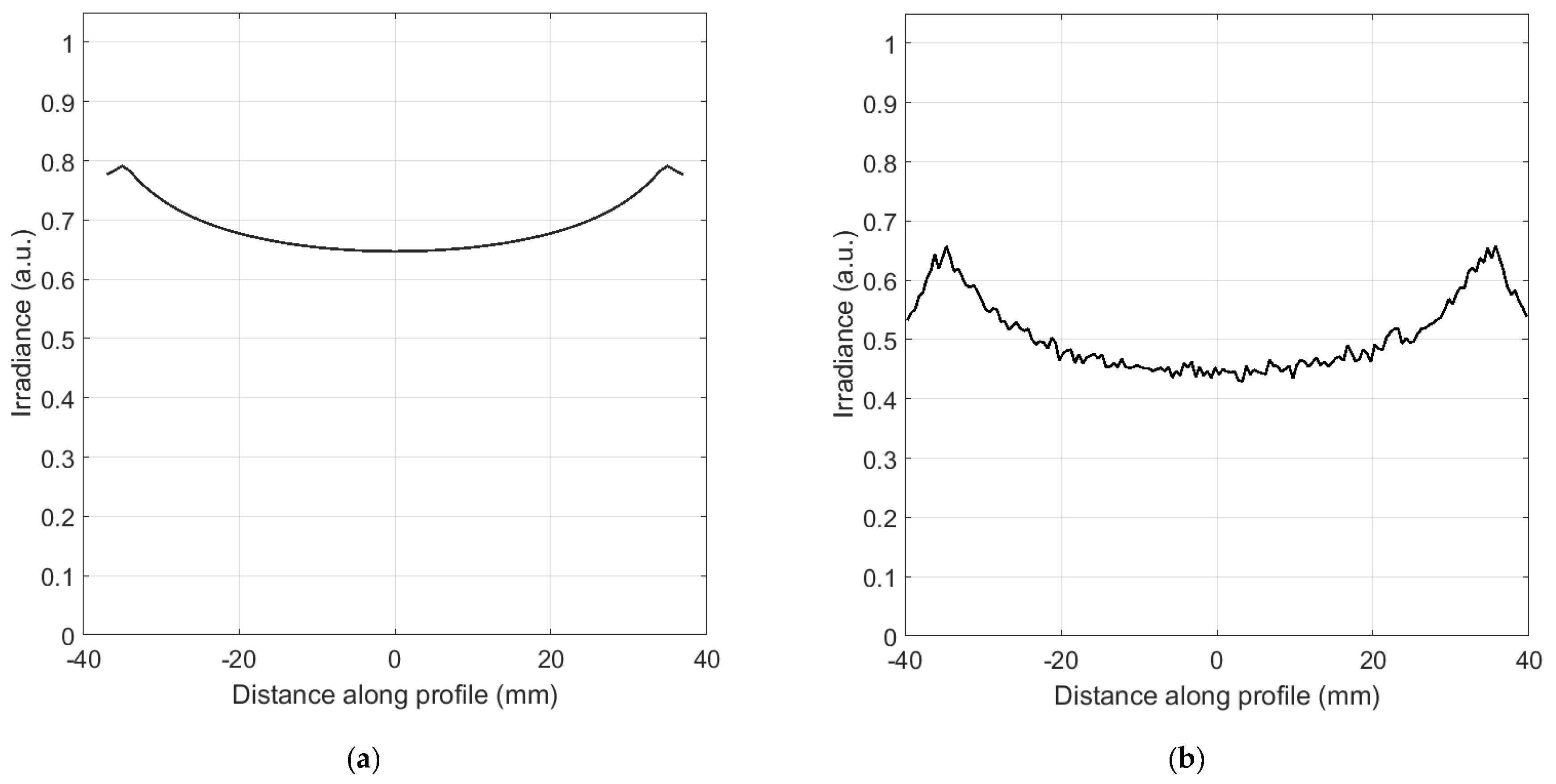
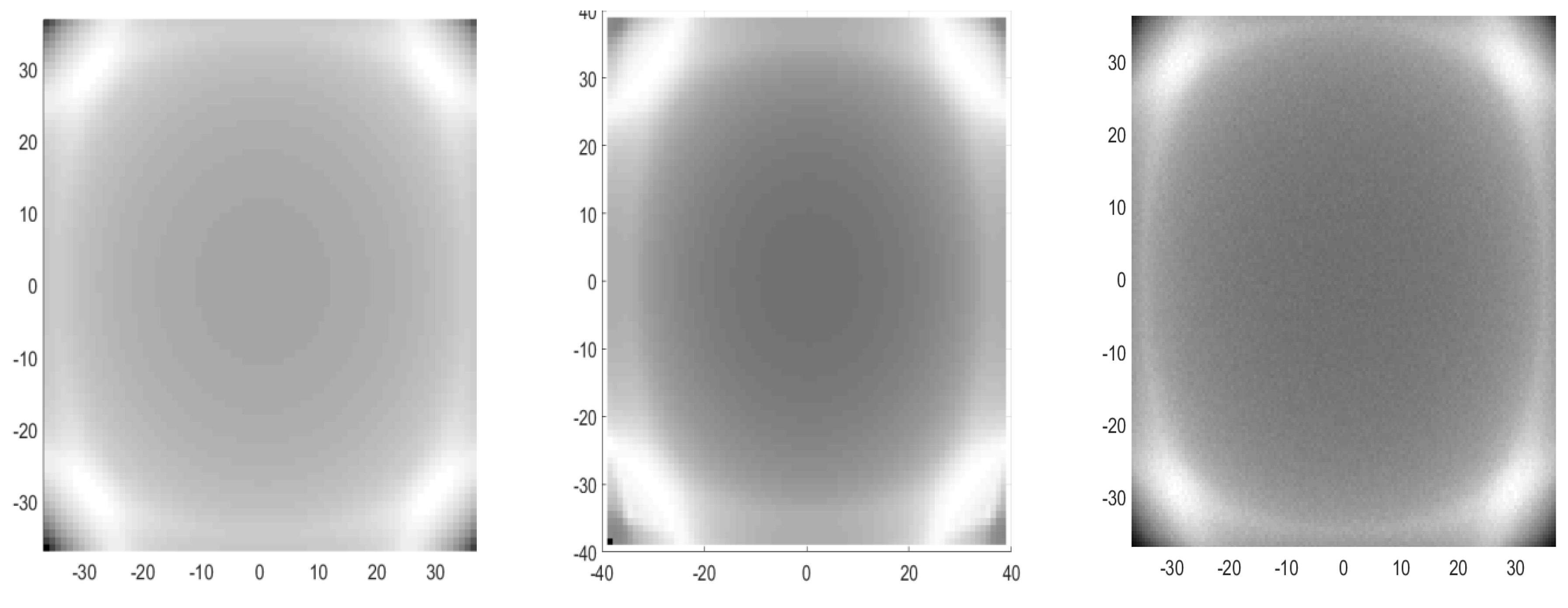
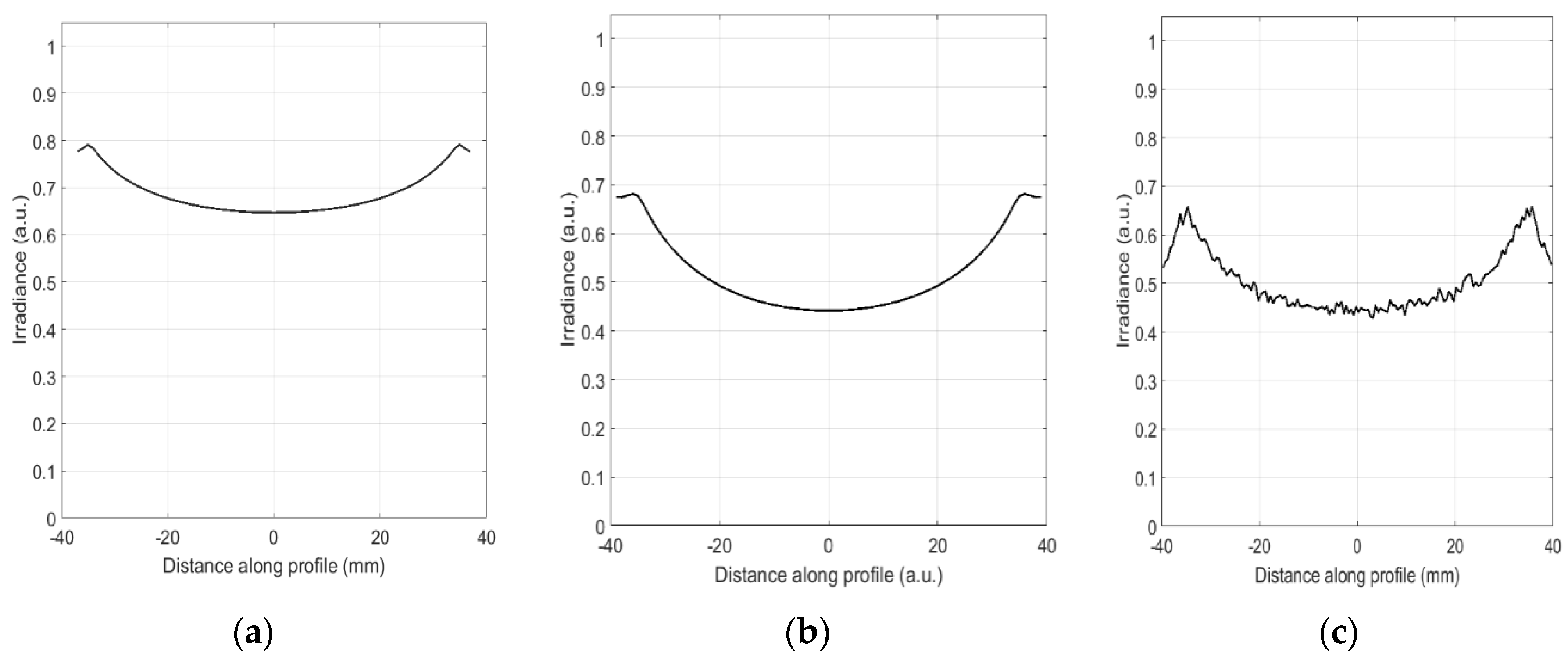
3. Irradiance Computation from J Vector for Asymmetric 3D Systems with Refractive Elements
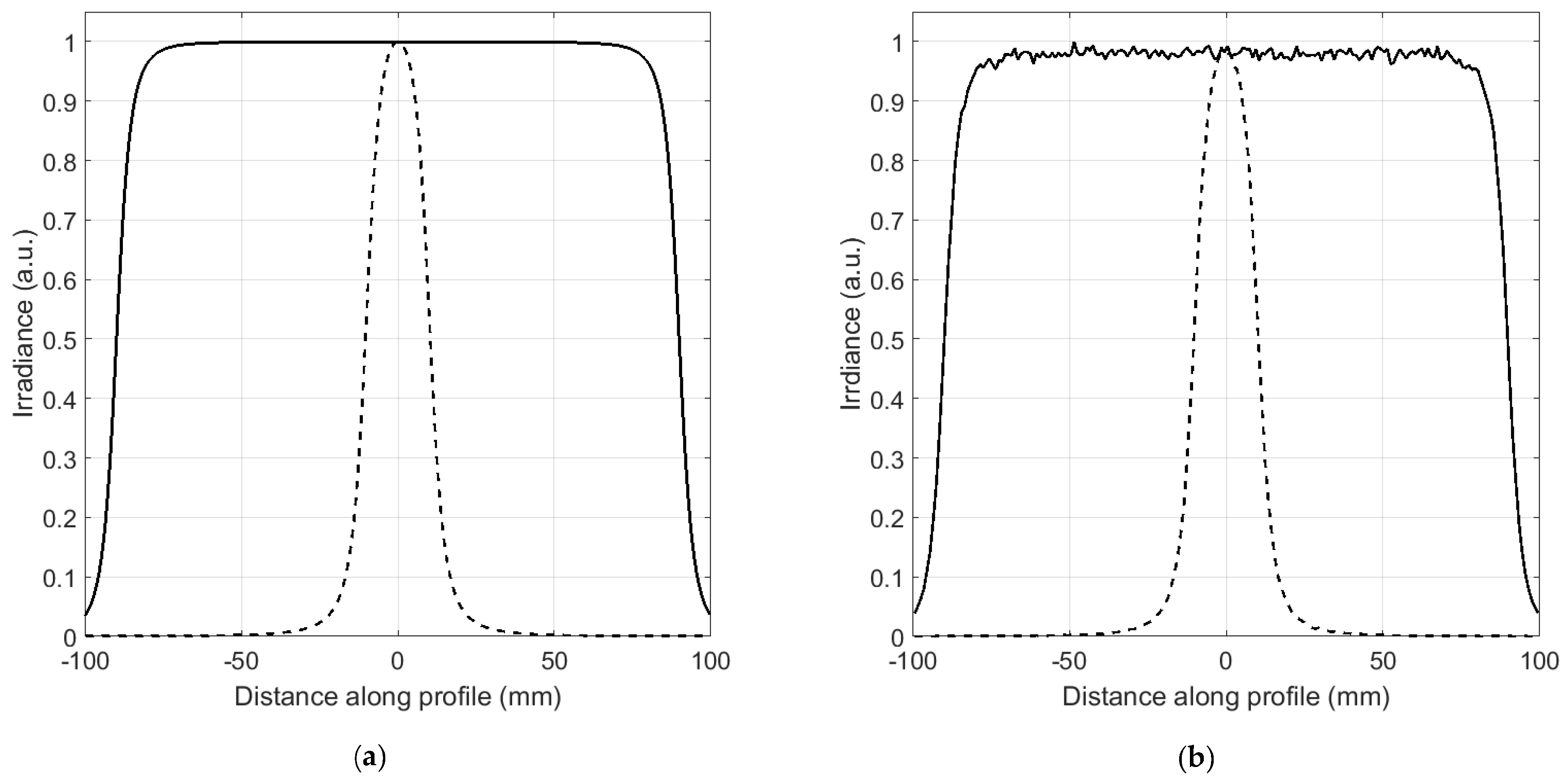
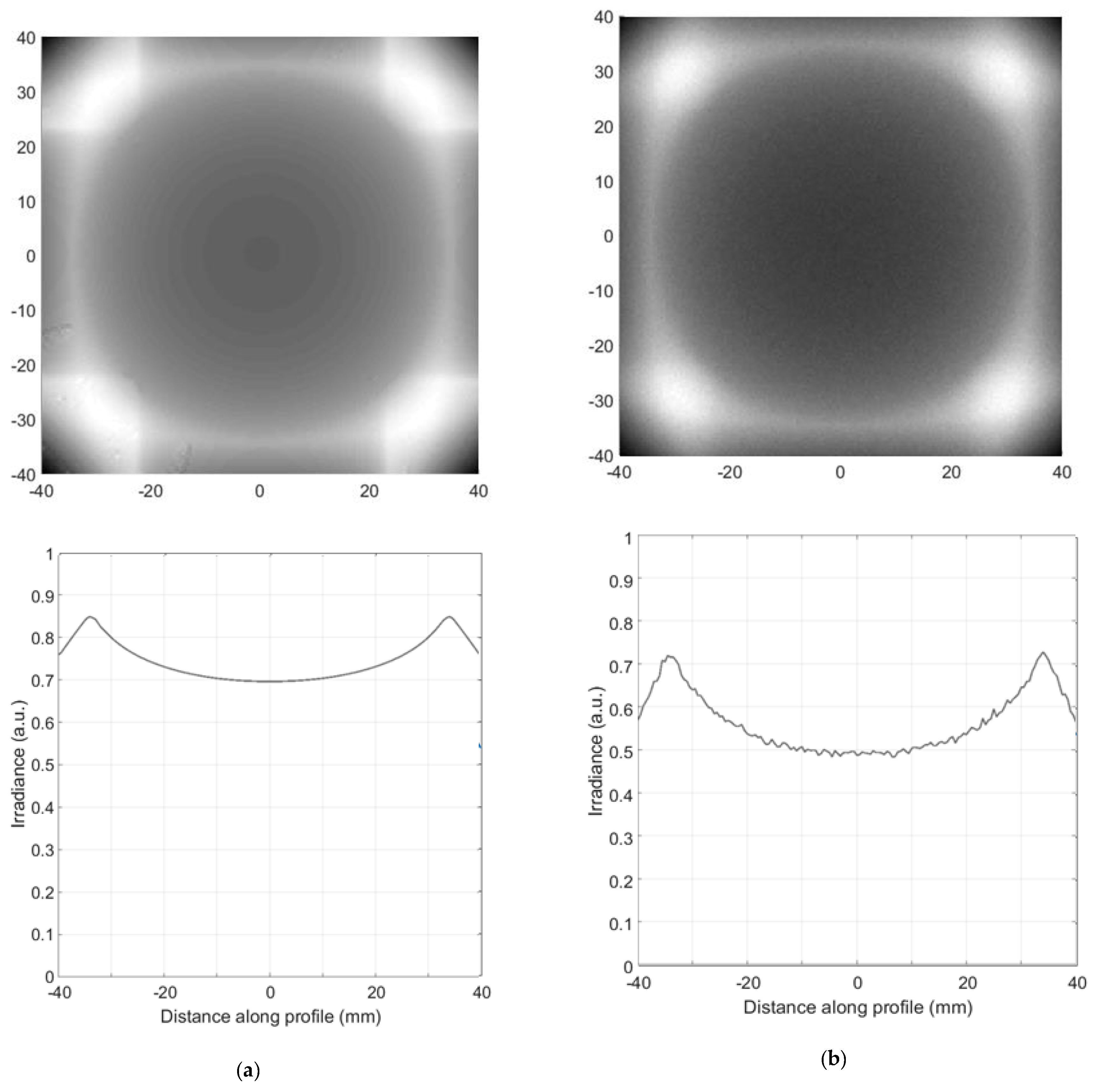
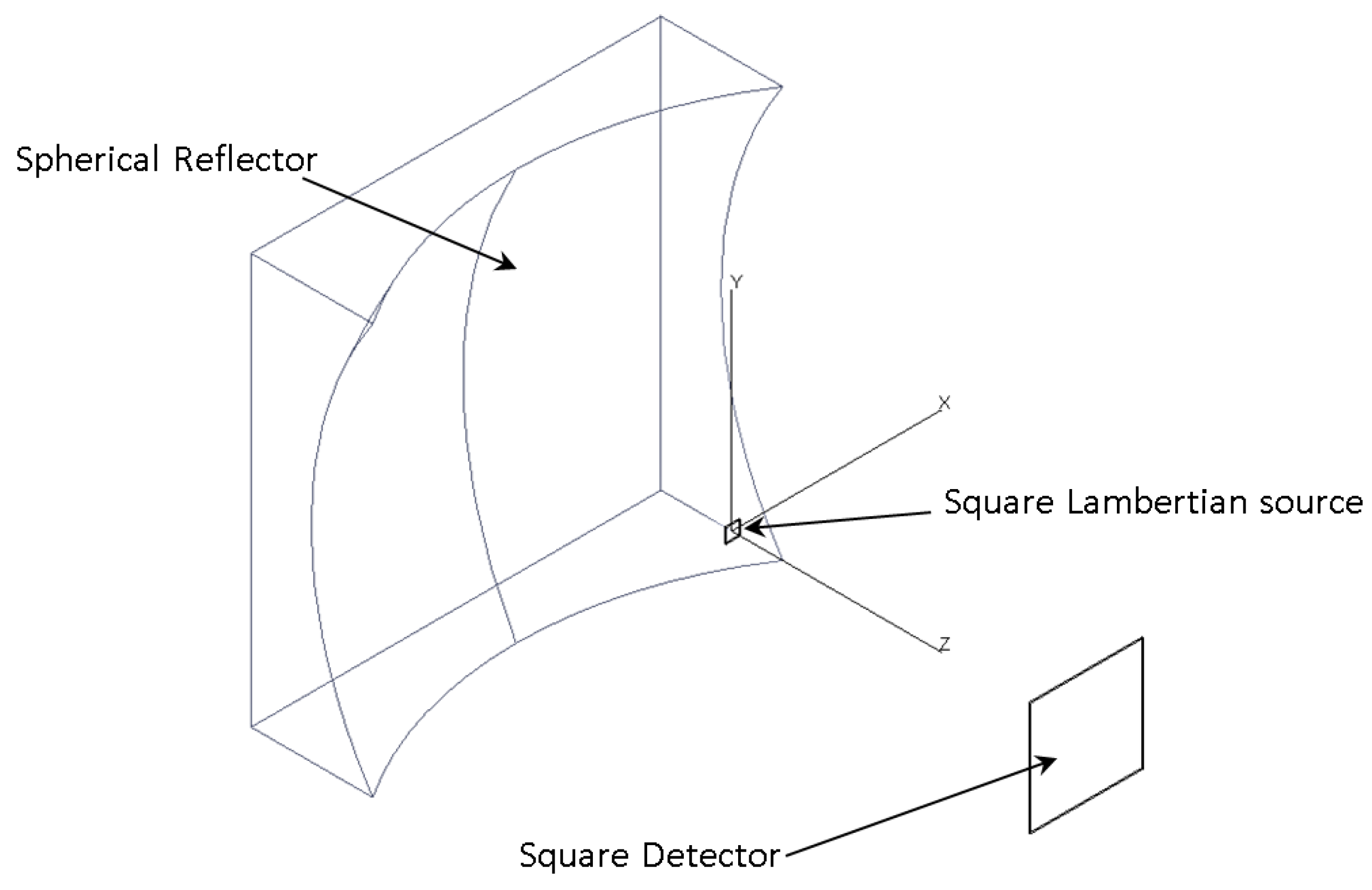
4. Irradiance Computation from J Vector for Asymmetric 3D Systems with Reflective Elements
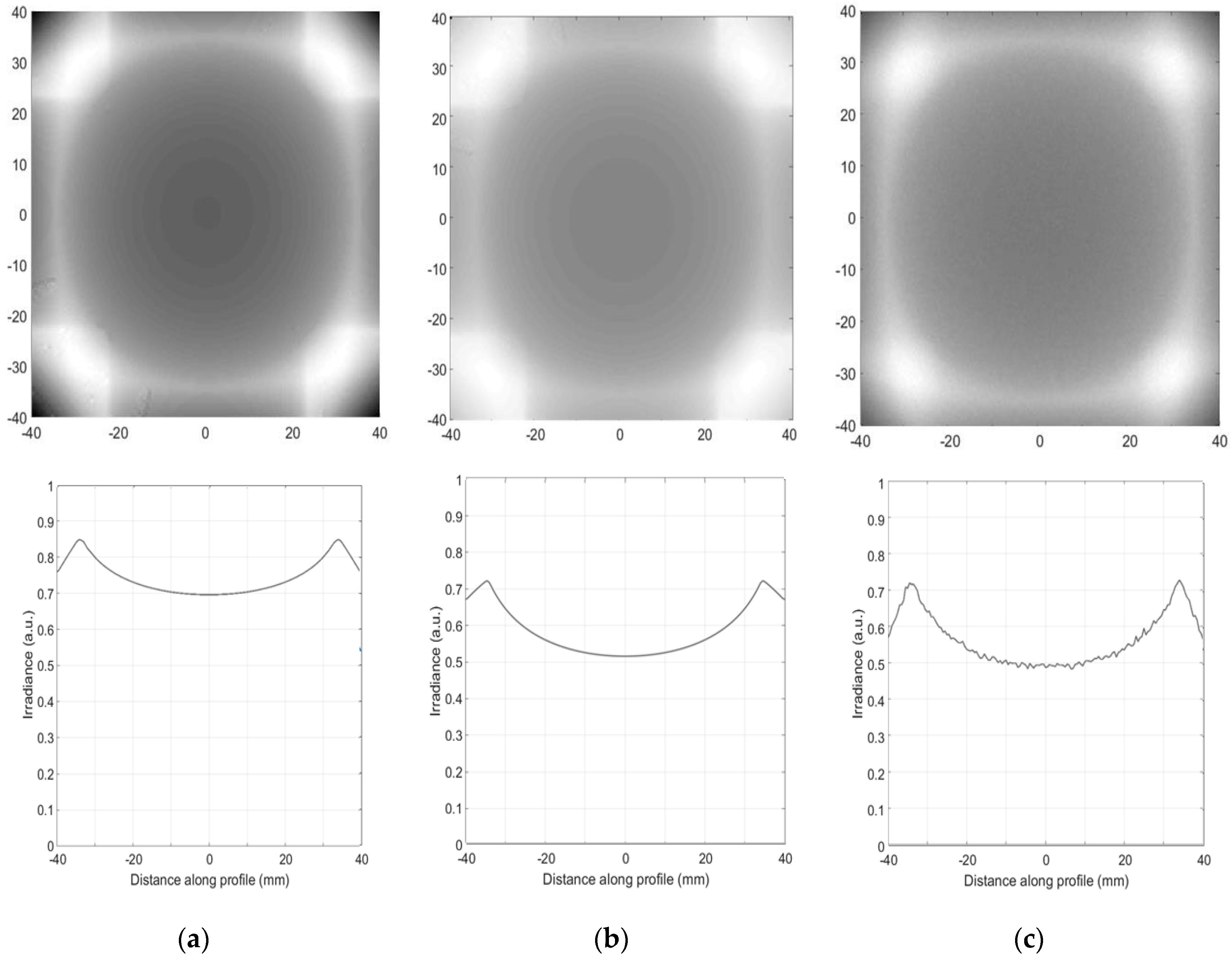
5. Optical Path Length Correction for Standard Vector Potential Method
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gershun, A. The light Field. J. Math. Phys. 1939, 18, 51–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, P.; Spencer, D.E. Photic Field; Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Winthrop, J.T. Propagation of Structural Information in Optical Wave Fields. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1971, 61, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.; Welford, W.T. Geometrical vector flux and some new nonimaging concentrators. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1979, 69, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.; Welford, W.T. Ideal flux concentrators as shapes that do not disturb the geometrical vector flux field: A new derivation of the compound parabolic concentrator. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1979, 69, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welford, W.T.; Winston, R. High Collection Nonimaging Optics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- García-Botella, A.; Fernández-Balbuena, A.A.; Vázquez, D.; Bernabeu, E.; González-Cano, A. Hyperparabolic Concentrators. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Botella, A. Ideal flux field dielectric concentrators. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 5357–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Botella, A.; Jiang, L.; Winston, R. Optical simulation-based on flowline method. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Nonimaging Optics: Efficient Design for Illumination and Solar Concentration XV, San Diego, CA, USA, 19–23 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tracepro Software. Available online: http://www.lambdares.com/ (accessed on 28 September 2019).
- Landau, L.D.; Lifschitz, E.M. The Classical Theory of Fields; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Winston, R. Flowline design and thermodynamic implications of the vector potential. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Nonimaging Optics: Efficient Design for Illumination and Solar Concentration XV, San Diego, CA, USA, 19–23 August 2018. [Google Scholar]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Botella, A.; Jiang, L.; Winston, R. Flowline Optical Simulation to Refractive/Reflective 3D Systems: Optical Path Length Correction. Photonics 2019, 6, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics6040101
García-Botella A, Jiang L, Winston R. Flowline Optical Simulation to Refractive/Reflective 3D Systems: Optical Path Length Correction. Photonics. 2019; 6(4):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics6040101
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Botella, Angel, Lun Jiang, and Roland Winston. 2019. "Flowline Optical Simulation to Refractive/Reflective 3D Systems: Optical Path Length Correction" Photonics 6, no. 4: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics6040101
APA StyleGarcía-Botella, A., Jiang, L., & Winston, R. (2019). Flowline Optical Simulation to Refractive/Reflective 3D Systems: Optical Path Length Correction. Photonics, 6(4), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics6040101





