Key Technologies for THz Wireless Link by Silicon CMOS Integrated Circuits
Abstract
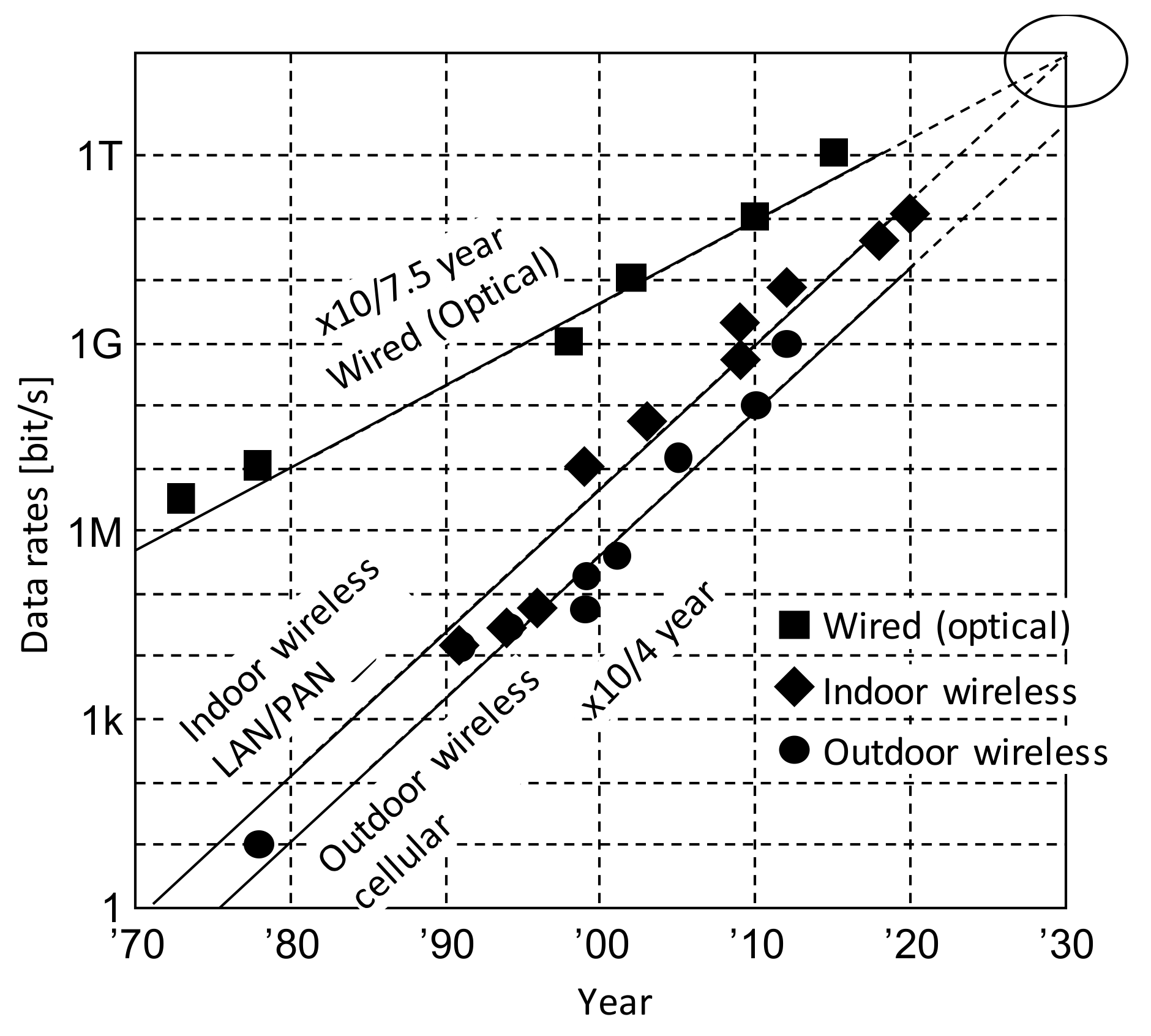
1. Introduction
2. 300 GHz Band Transceiver Using Silicon Integrated Circuits
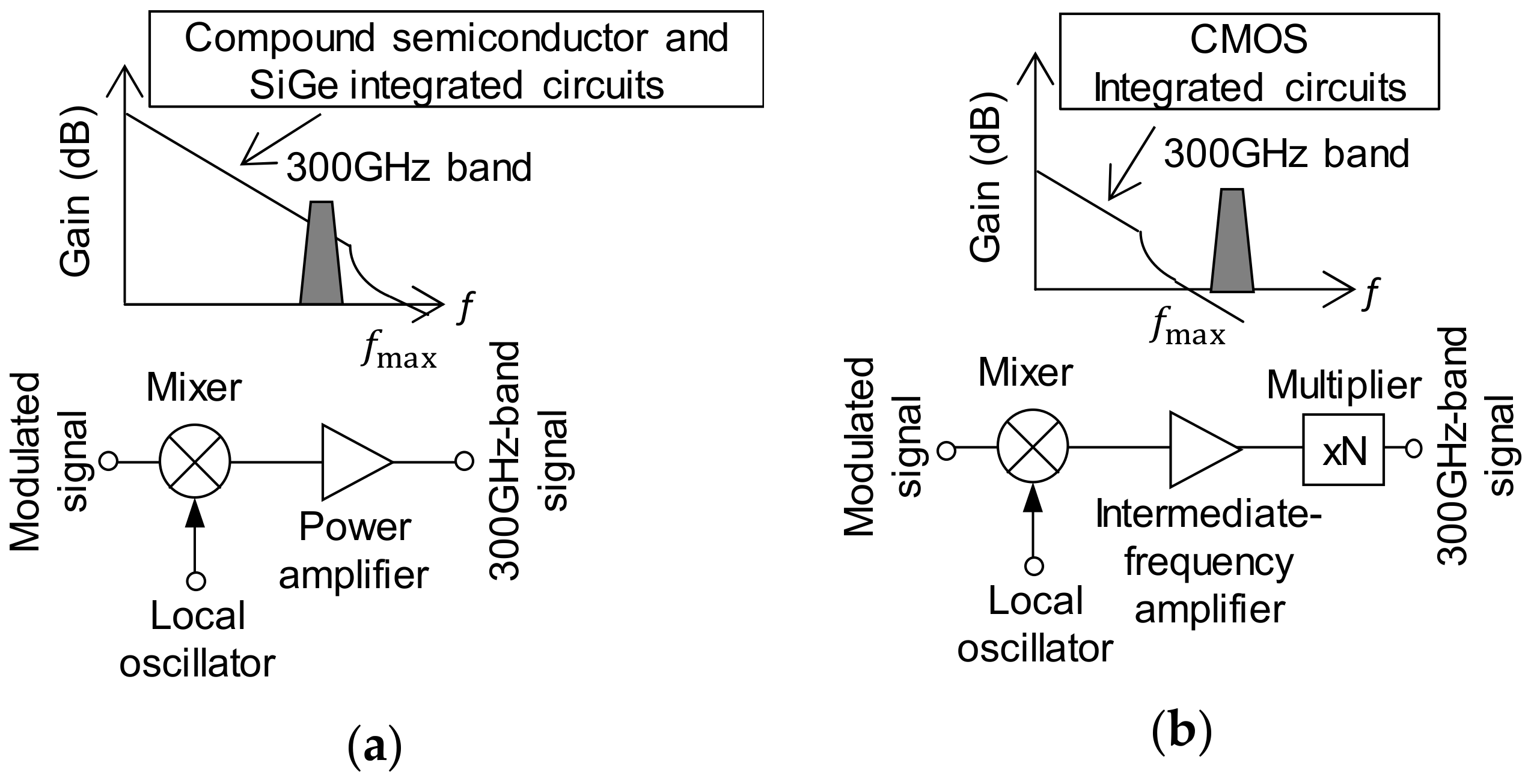
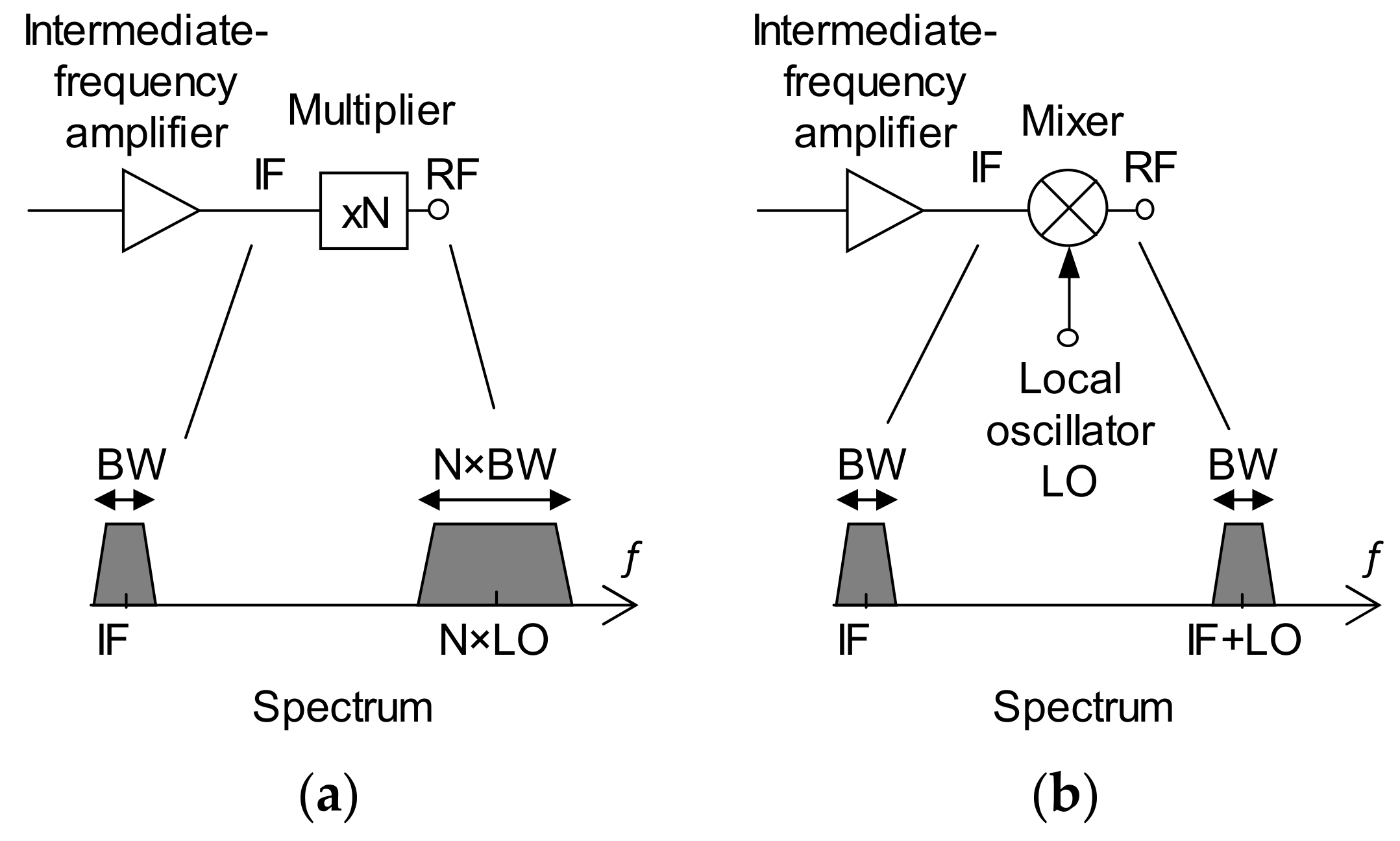
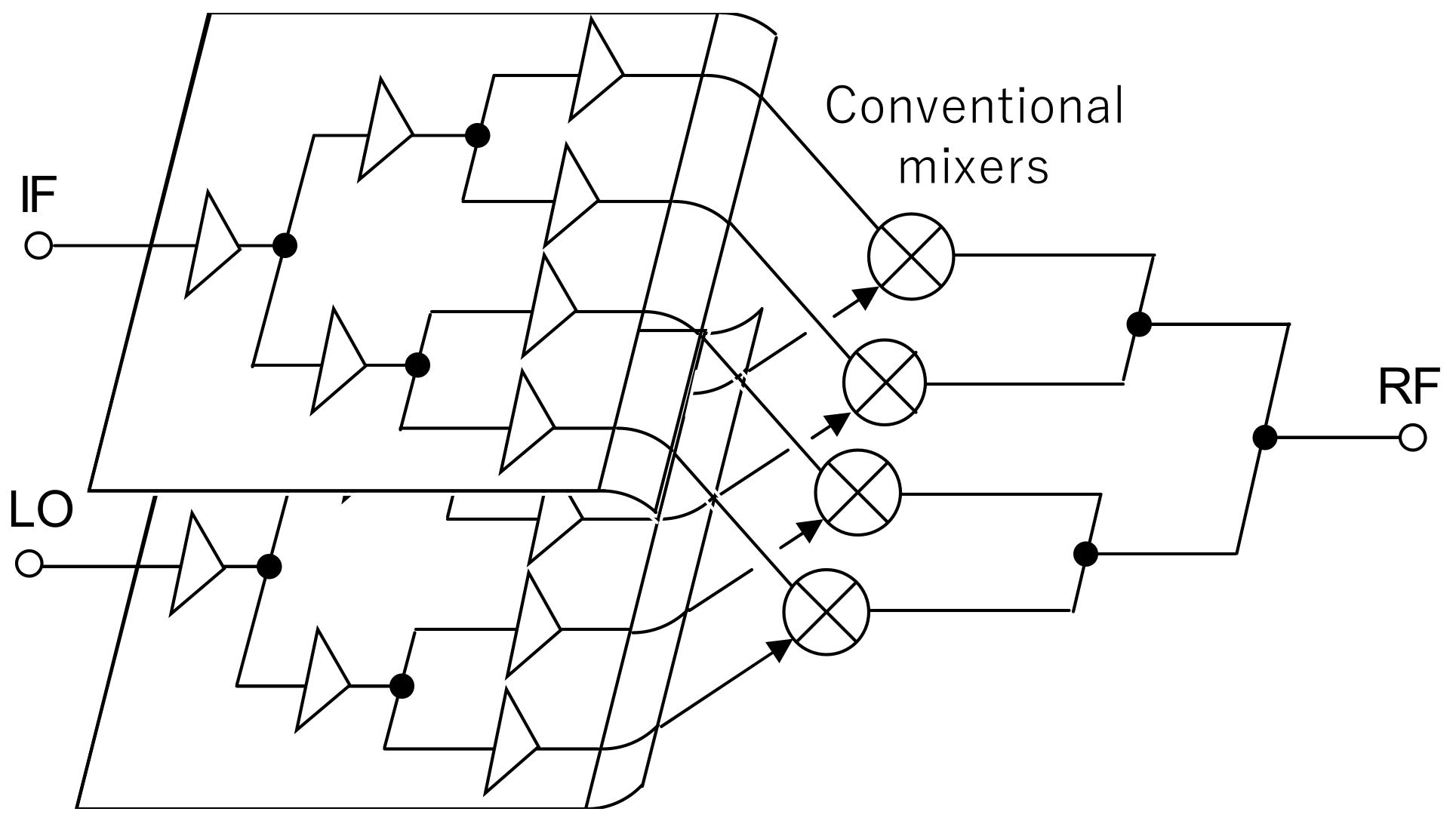
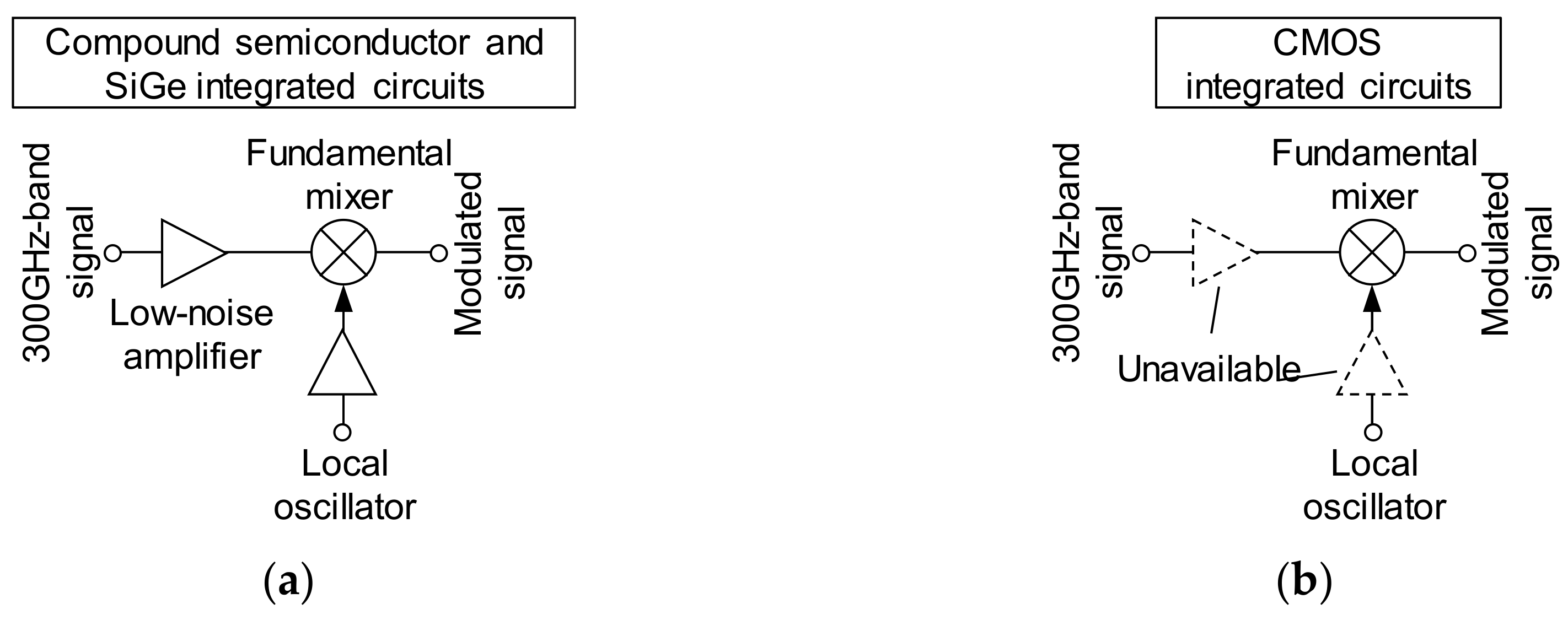
2.1. Integrated Circuit Realizing Terahertz Transceiver and Its Characteristics
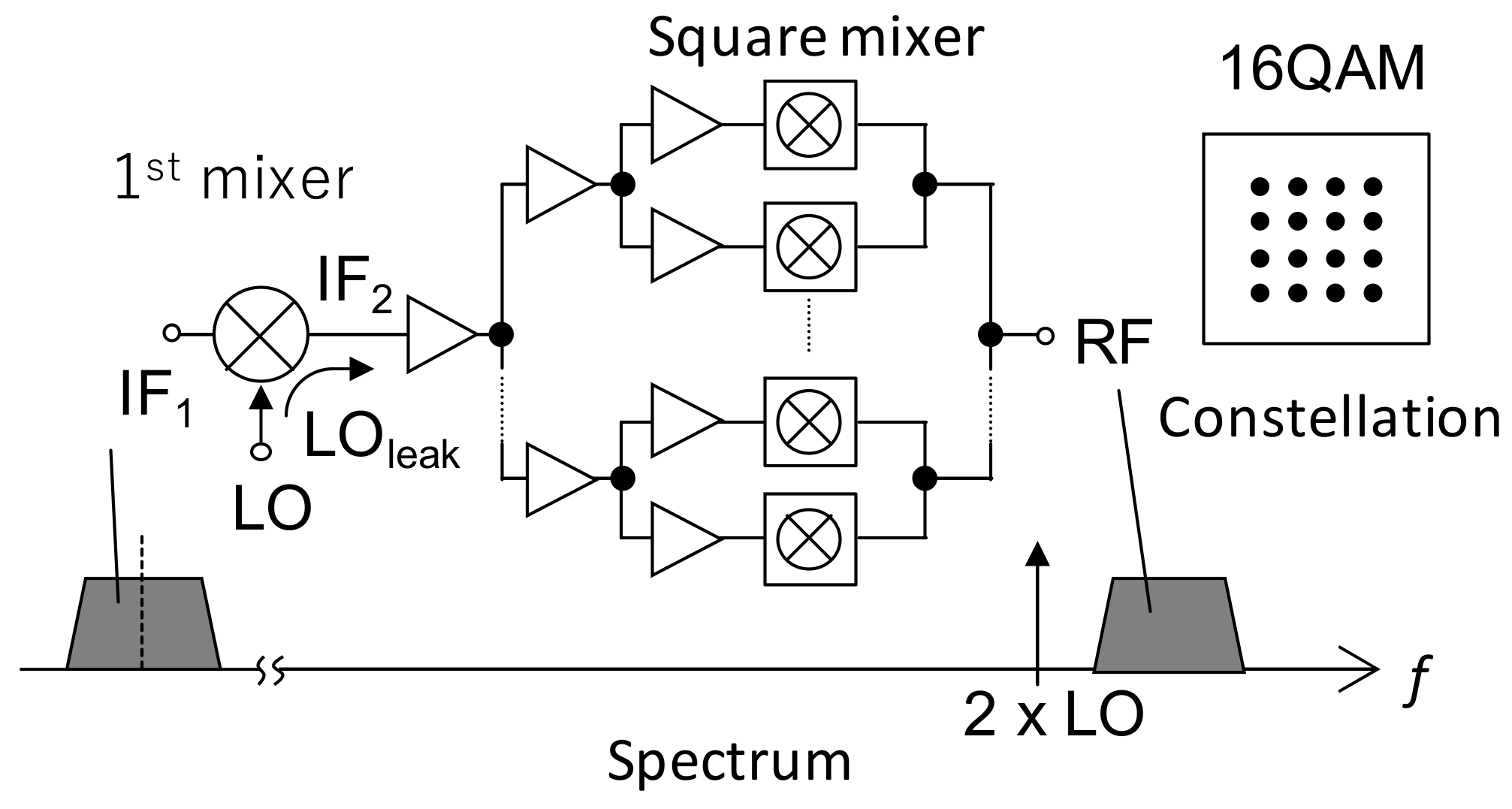
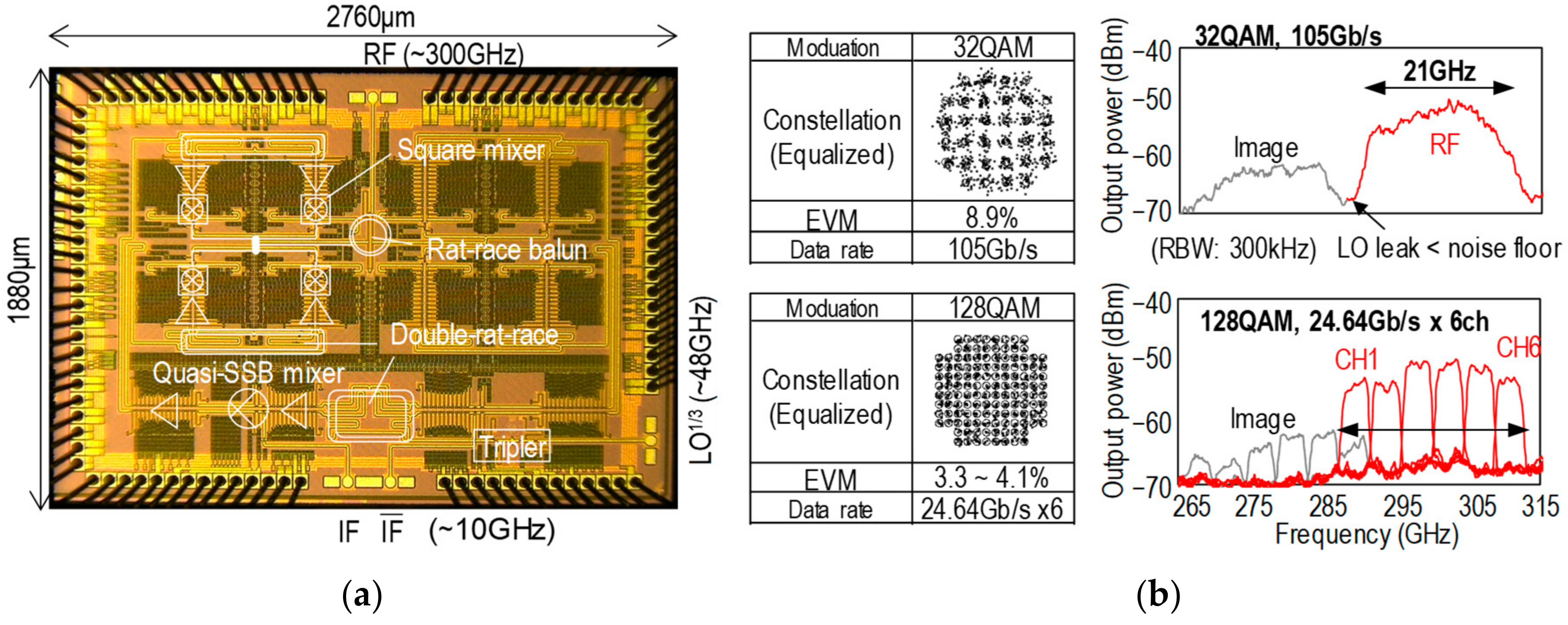
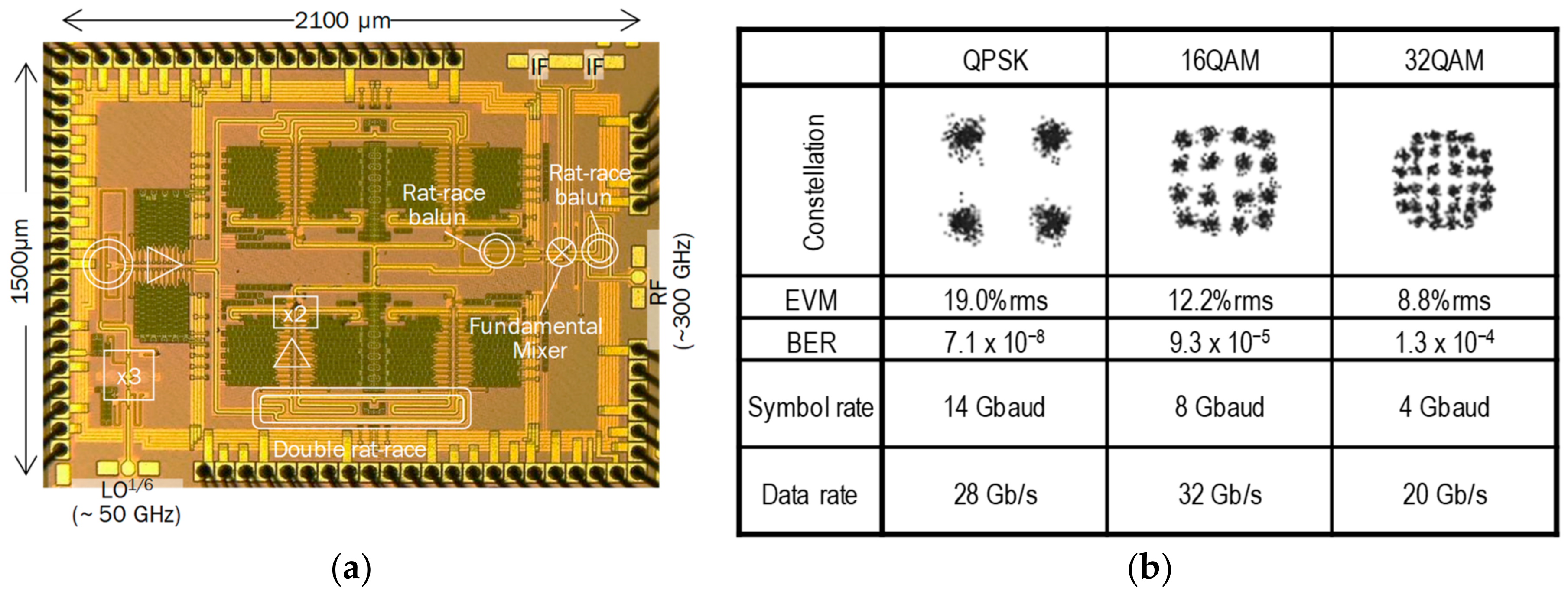
2.2. 300 GHz Band Transmitter Using Silicon Integrated Circuit
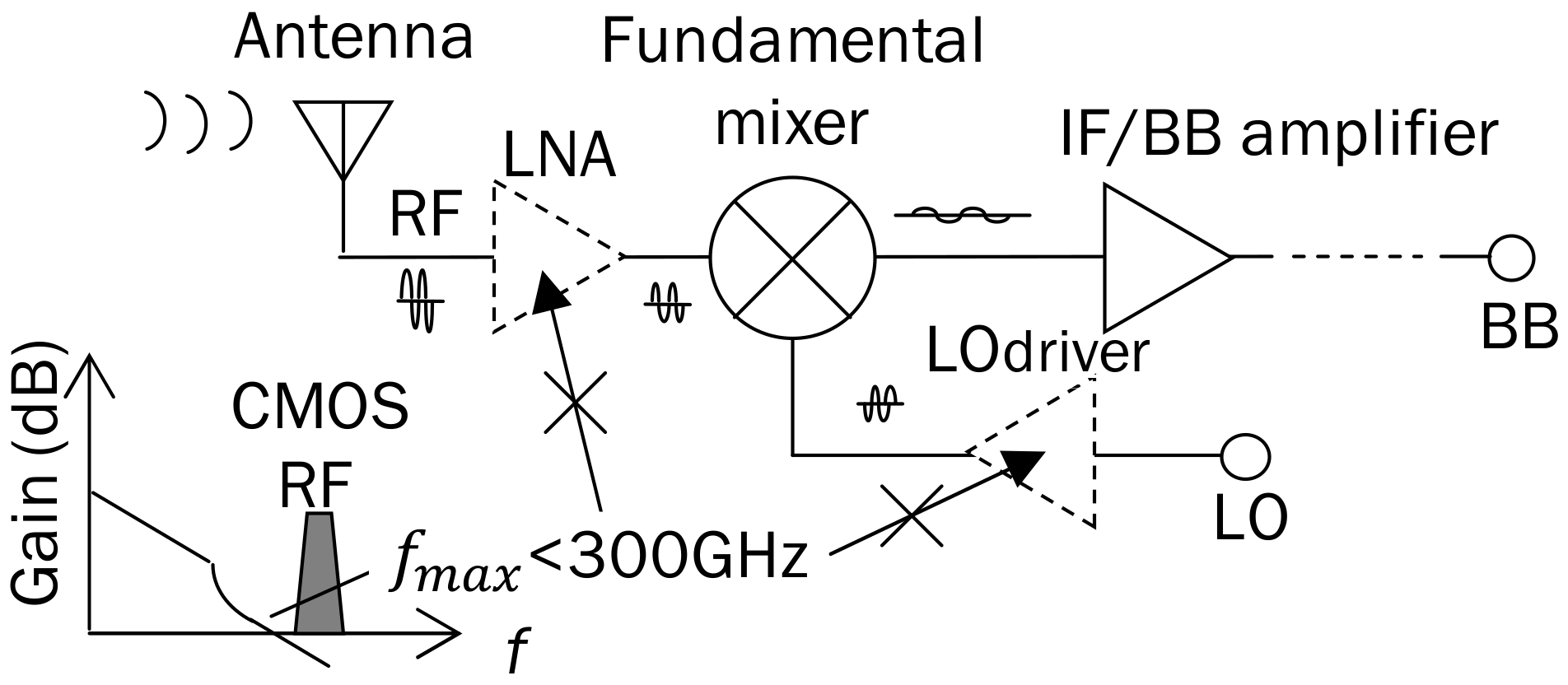
2.3. 300 GHz Band Receiver Using Silicon Integrated Circuit
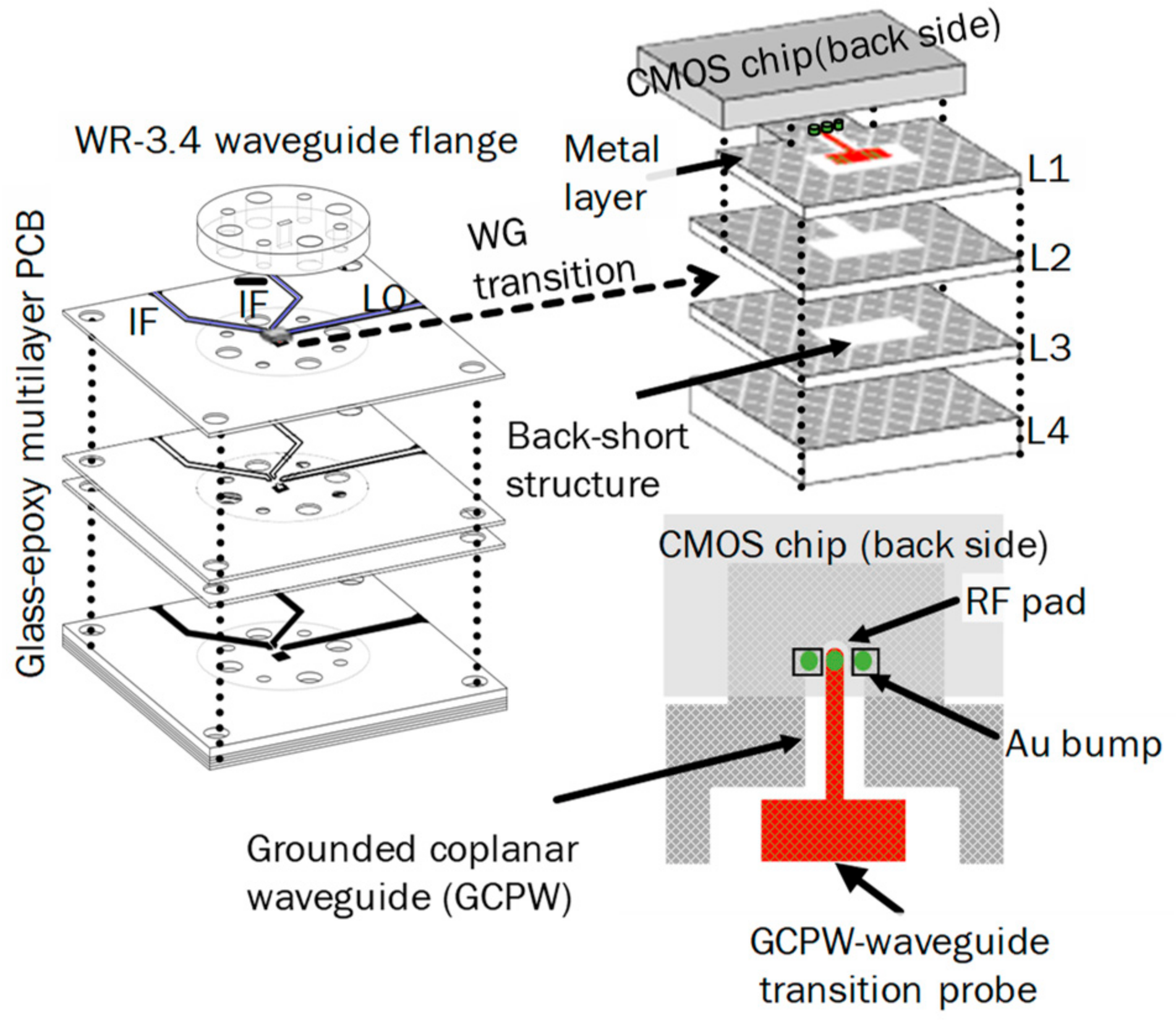
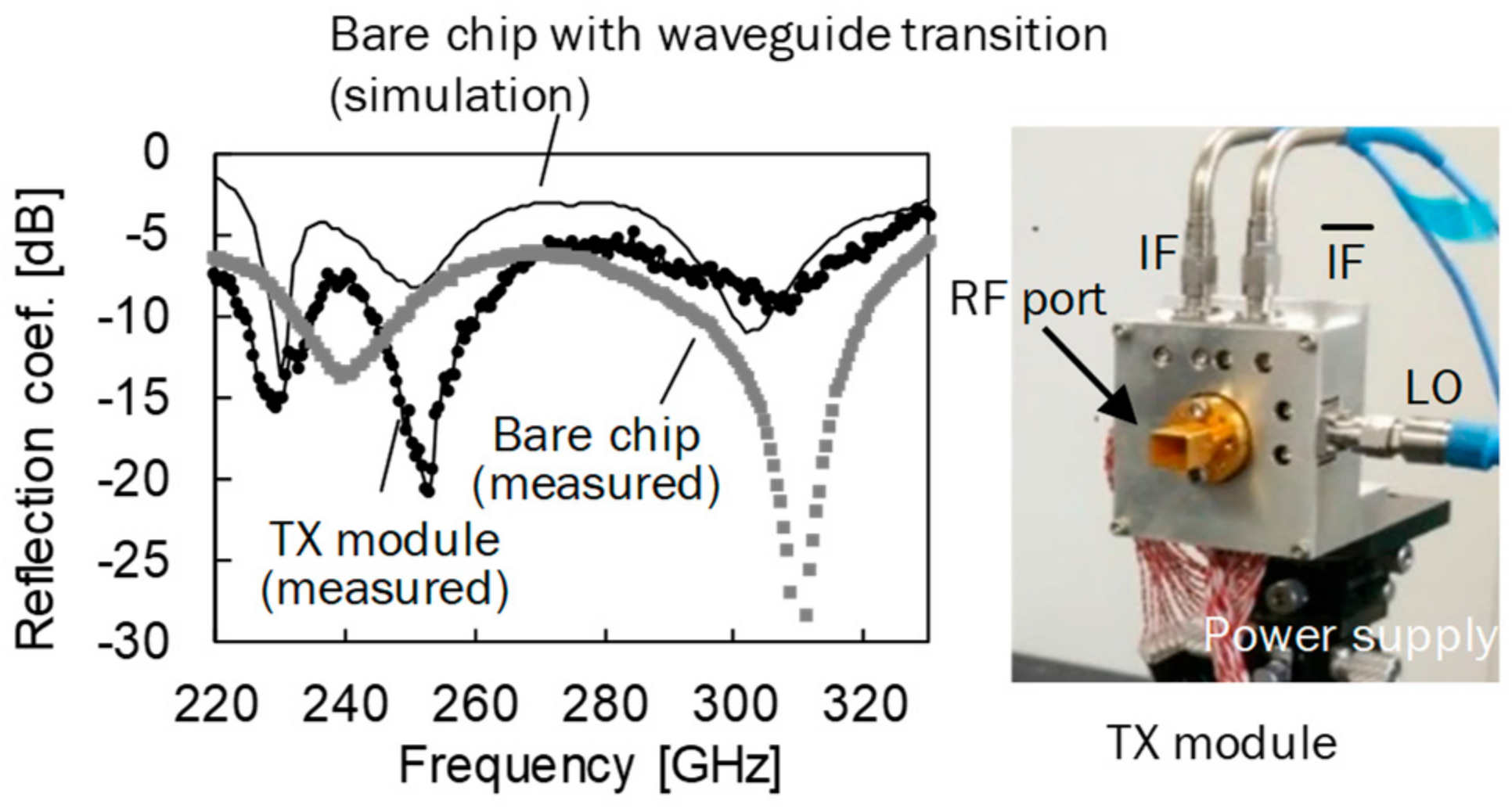
2.4. 300 GHz Band CMOS Transceiver Module
3. Features and Applications of 300 GHz Band Communication
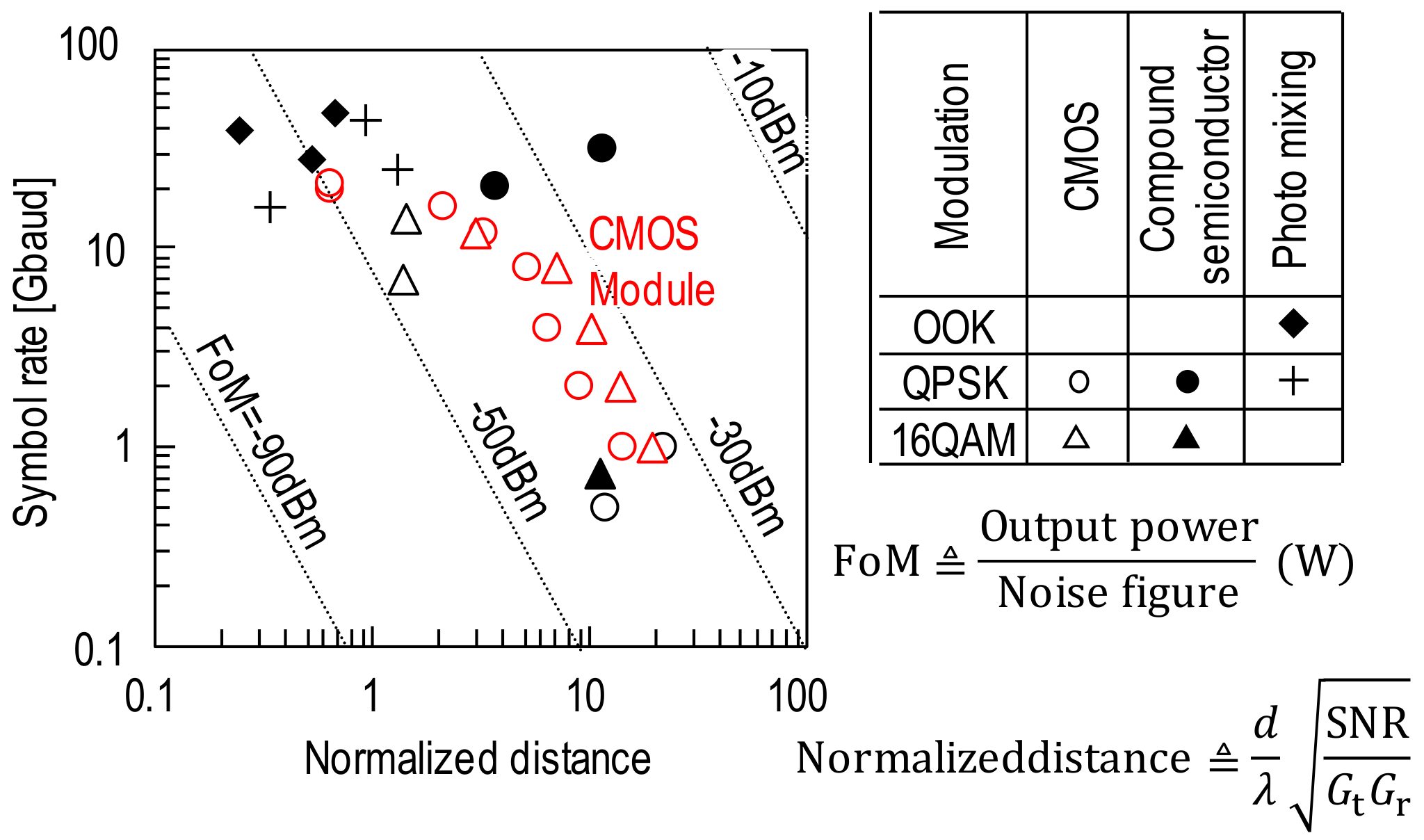
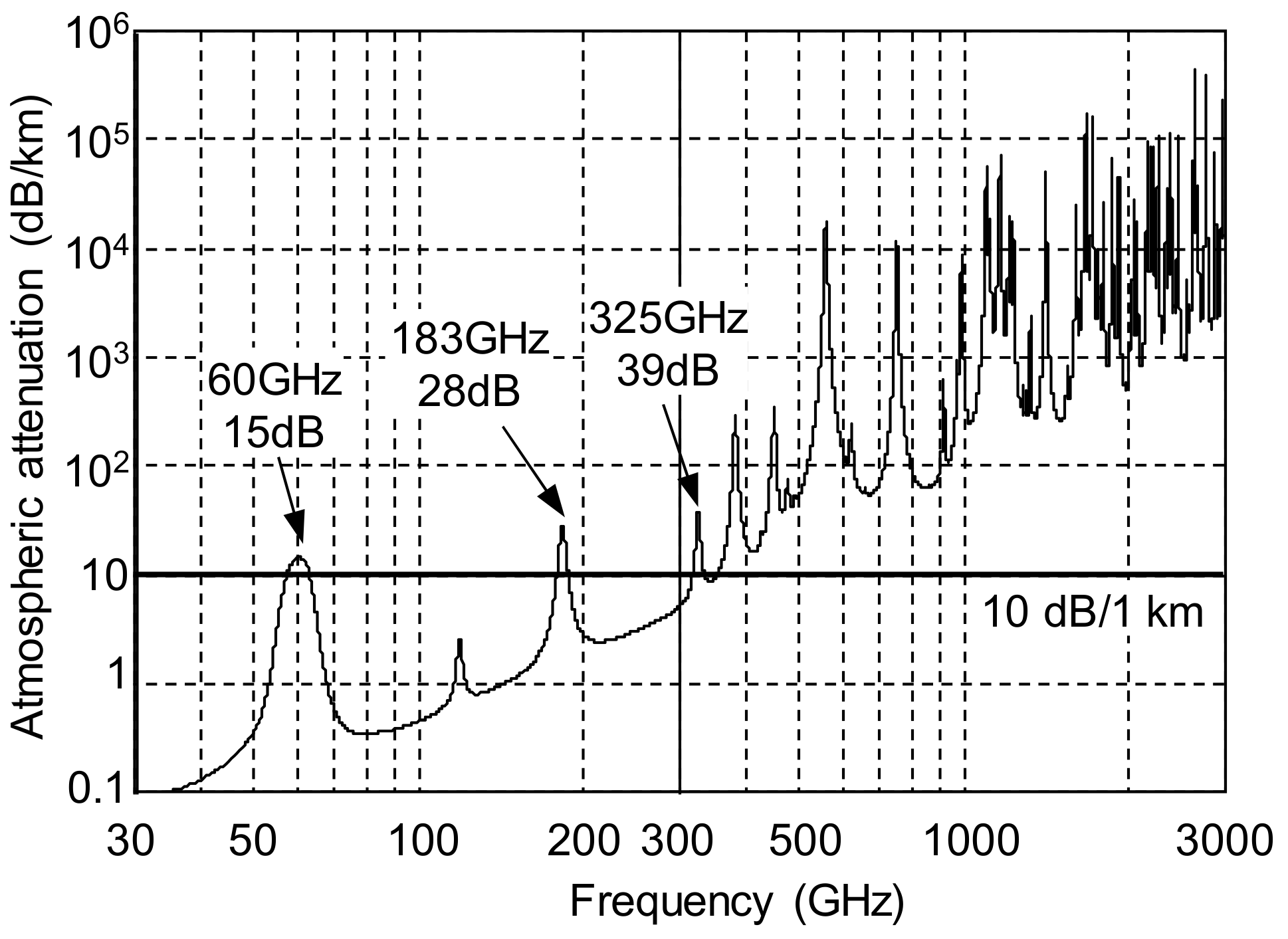
3.1. Characteristics of Terahertz Band Communication
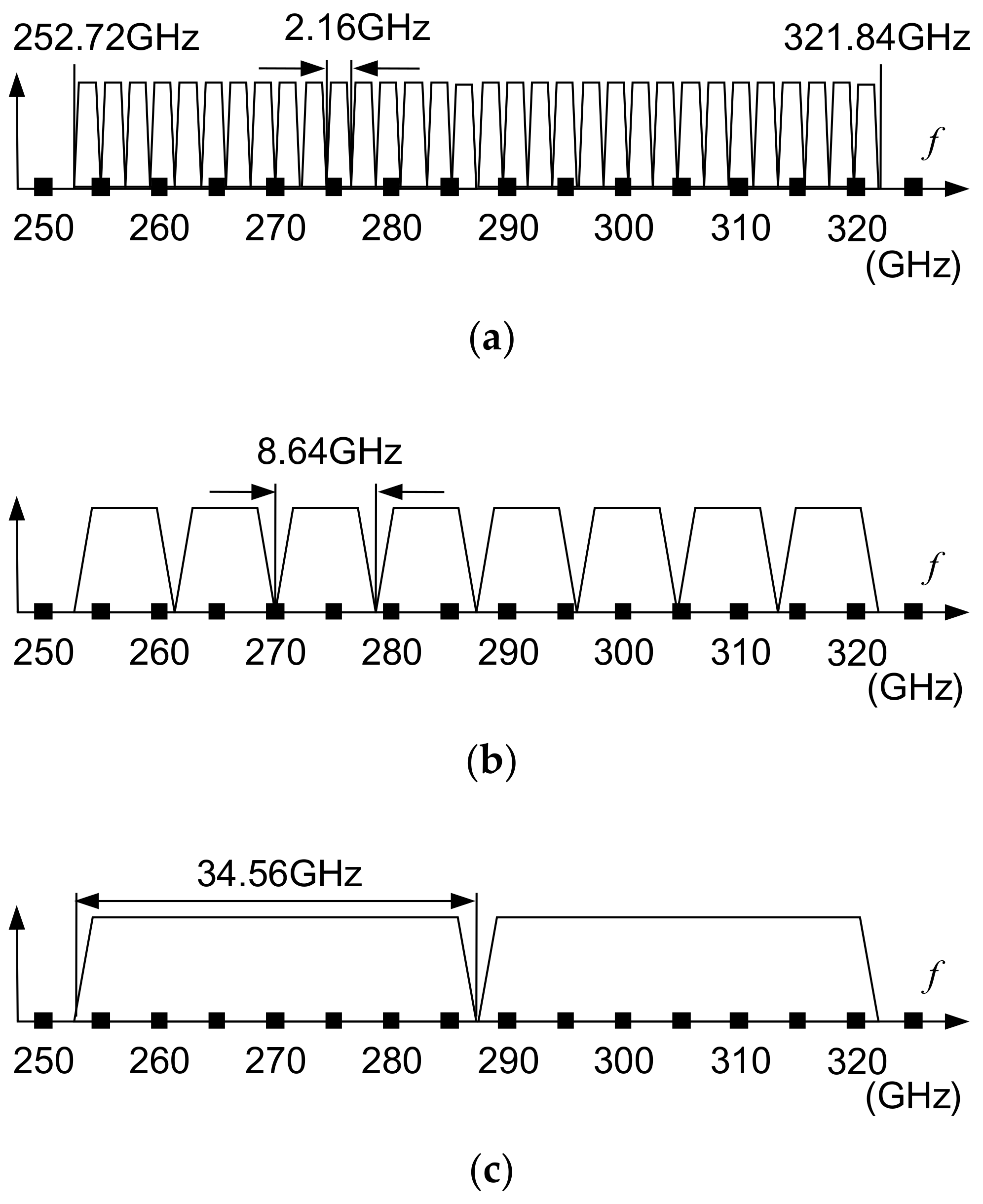
3.2. Application Examples of 300-GHz-Band Communication
3.3. Application Example of 300 GHz Band Communication
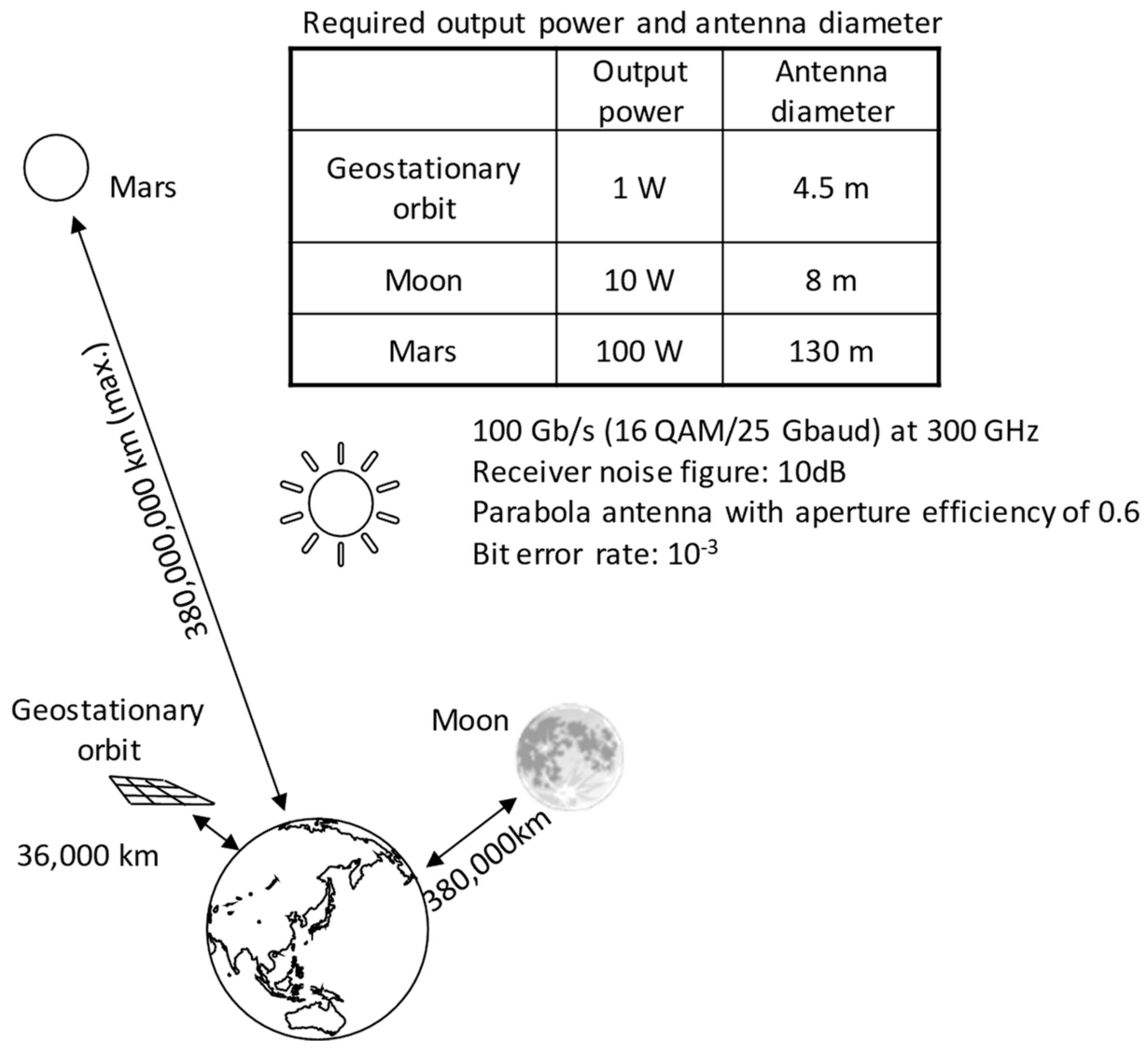
3.4. The Future of Terahertz Communication Spreading in Space
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kürne, T. IEEE 802.15-10-0320-02-0000-Tutorial_Igthz. Available online: https://mentor.ieee.org/802.15/dcn/12/15-12-0320-02-0thz-what-s-next-wireless-communication-beyond-60-ghz-tutorial-ig-thz.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Fujishima, M. Silicon integrated circuits creating new applications in terahertz communication. J. IEICE 2018, 101, 554–560. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Tonouchi, M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Telecommunication Union. Article 5: Frequency allocations. In Radio Regulations Article Edition of 2012; International Telecommunication Union (ITU): Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 37–178. Available online: http://search.itu.int/history/HistoryDigitalCollectionDocLibrary/1.41.48.en.101.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Resolution 767, The World Radiocommunication Conference (Geneva, 2015). Available online: https://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-r/oth/0c/0a/R0C0A00000C0016PDFE.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Nagatsuma, T.; Ducournau, G.; Renaud, C.C. Advances in terahertz communications accelerated by photonics. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deal, W.R.; Zamora, A.; Leong, K.; Liu, P.H.; Yoshida, W.; Zhou, J.; Lange, M.; Gorospe, B.; Nguyen, K.; Mei, X.B. A 670 GHz low noise amplifier with <10 dB packaged noise figure. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2016, 26, 837–839. [Google Scholar]
- Kallfass, I.; Boes, F.; Messinger, T.; Antes, J.; Inam, A.; Lewark, U.; Tessmann, A.; Henneberger, R. 64 Gbit/s transmission over 850m fixed wireless link at 240 GHz carrier frequency. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2015, 36, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, A.; Heinemann, B.; Rücker, H.; Barth, R.; Fischer, G.G.; Wipf, C.; Marschmeyer, S.; Aufinger, K.; Böck, J.; Boguth, S.; et al. Advanced heterojunction bipolar transistor for half-THz SiGe BiCMOS technology. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2015, 36, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, M.; Amakawa, S. Recent progress and prospects of terahertz CMOS. IEICE Electron. Express 2015, 12, 20152006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yun, J.; Yoon, D.; Kim, M.; Rieh, J.-S.; Urteaga, M.; Jeon, S. 300 GHz integrated heterodyne receiver and transmitter with on-chip fundamental local oscillator and mixers. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, N.; Grzyb, J.; Statnikov, K.; Malz, S.; Vazquez, P.R.; Föerster, W.; Heinemann, B.; Pfeiffer, U.R. A fully integrated 240-GHz direct-conversion quadrature transmitter and receiver chipset in SiGe technology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Techn. 2016, 64, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Thyagarajan, S.V.; Niknejad, A.M. A 240 GHz fully integrated wideband QPSK transmitter in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 2256–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, K.; Takano, K.; Amakawa, S.; Hara, S.; Kasamatsu, A.; Mizuno, K.; Takahashi, K.; Yoshida, T.; Fujishima, M. A 300 GHz CMOS transmitter with 32-QAM 17.5 Gb/s/ch capability over six channels. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2016, 51, 3037–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, K.; Amakawa, S.; Katayama, K.; Hara, S.; Dong, R.; Kasamatsu, A.; Hosako, I.; Mizuno, K.; Takahashi, K.; Yoshida, T.; et al. A 105Gb/s 300GHz CMOS transmitter. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2017; pp. 308–309. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, P.; Grzyb, J.; Sarmah, N.; Heinemann, B.; Pfeiffer, U. A 219-266 GHz fully-integrated direct-conversion IQ receiver module in a SiGe HBT technology. In Proceedings of the 12th European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 8–10 October 2017; pp. 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, S.; Katayama, K.; Takano, K.; Dong, R.; Watanabe, I.; Sekine, N.; Kasamatsu, A.; Yoshida, T.; Amakawa, S.; Fujishima, M. A 416-mW 32-Gbit/s 300-GHz CMOS receiver. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology (RFIT), Seoul, Korea, 30 August–1 September 2017; pp. 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, S.; Katayama, K.; Takano, K.; Dong, R.; Watanabe, I.; Sekine, N.; Kasamatsu, A.; Yoshida, T.; Amakawa, S.; Fujishima, M. A 32 Gbit/s 16QAM CMOS receiver in 300 GHz band. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Microwave Symposium (IMS2017), Honolulu, HI, USA, 4–9 June 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Kang, S.; Thyagarajan, S.; Alon, E.; Niknejad, A. A 260 GHz Fully Integrated CMOS Transceiver for Wireless Chip-to-Chip Communication. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Honolulu, HI, USA, 13–15 June 2012; pp. 48–49. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, K.; Katayama, K.; Hara, S.; Dong, R.; Mizuno, K.; Takahashi, K.; Kasamatsu, A.; Yoshida, T.; Amakawa, S.; Fujishima, M. 300-GHz CMOS transmitter module with built-in waveguide transition on a multilayered glass epoxy PCB. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS2018), Anaheim, CA, USA, 14–17 January 2018; pp. 154–156. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, K.; Katayama, K.; Amakawa, S.; Yoshida, T.; Fujishima, M. Wireless digital data transmission from a 300-GHz CMOS transmitter. Electron. Lett. 2016, 52, 1353–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, P.; Mendrok, J.; Kasai, Y.; Ochiai, S.; Seta, T.; Sagi, K.; Suzuki, K.; Sagawa, H.; Urban, J. AMATERASU: Model for Atmospheric TeraHertz Radiation Analysis and Simulation. J. Natl. Inst. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2008, 55, 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- International Telecommunication Union. Recommendation ITU-R P.676-11. In Attenuation by Atmospheric Gases; P Series Radiowave Propagation; International Telecommunication Union (ITU): Geneve, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: https://www.itu.int/dms_pubrec/itu-r/rec/p/R-REC-P.676-11-201609-I!!PDF-E.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Fujishima, M.; Amakawa, S. Integrated-Circuit Approaches to THz Communications: Challenges, Advances, and Future Prospects. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2017, 100, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friis, H. A note on a simple transmission formula. Proc. IRE 1946, 34, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P802.15.3d. Available online: http://www.ieee802.org/PARs/2015_11/15-15-0682-01-003d-3d-par-change.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Time is Money When It Comes to Microwaves. FT Magazine, 10 May 2013.
- IEEE Standard for High Data Rate Wireless Multi-Media Networks, Amendment 2: 100 Gb/s Wireless Switched Point-to-Point Physical Layer, IEEE Computer Society sponsored by the LAN/MAN standards committee. Available online: https://standards.ieee.org/standard/802_15_3d-2017.html (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Performance development. Available online: https://www.top500.org/statistics/perfdevel/ (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Kogge, P.; Bergman, K.; Borkar, S.; Campbell, D.; Carlson, W.; Dally, W.; Denneau, M.; Franzon, P.; Harrod, W.; Hill, K.; et al. Exascale computing study: Technology challenges in achieving exascale systems. DARPA IPTO Rep. 2008. Available online: http://www.cse.nd.edu/Reports/2008/TR-2008-13.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Mori, M.; Kagawa, H.; Saito, Y. Summary of studies on space solar power systems of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). Acta Astronaut. 2006, 59, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daines, G. NASA’s Journey to Mars; NASA: 2015. Available online: www.nasa.gov/content/nasas-journey-to-mars (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Masuda, N.; Yoshida, M.; Fujishita, Y.; Kobayashi, J.; Sekine, N.; Sugano, A. Development of 0.1/0.3 THz-band traveling wave tubes. IEICE Tech. Rep. 2015, 115, 111–116. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]



© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujishima, M. Key Technologies for THz Wireless Link by Silicon CMOS Integrated Circuits. Photonics 2018, 5, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics5040050
Fujishima M. Key Technologies for THz Wireless Link by Silicon CMOS Integrated Circuits. Photonics. 2018; 5(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics5040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujishima, Minoru. 2018. "Key Technologies for THz Wireless Link by Silicon CMOS Integrated Circuits" Photonics 5, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics5040050
APA StyleFujishima, M. (2018). Key Technologies for THz Wireless Link by Silicon CMOS Integrated Circuits. Photonics, 5(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics5040050




