Reinforcement Learning Compensatory-Based Fully Actuated Control Method for Risley Prisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Module
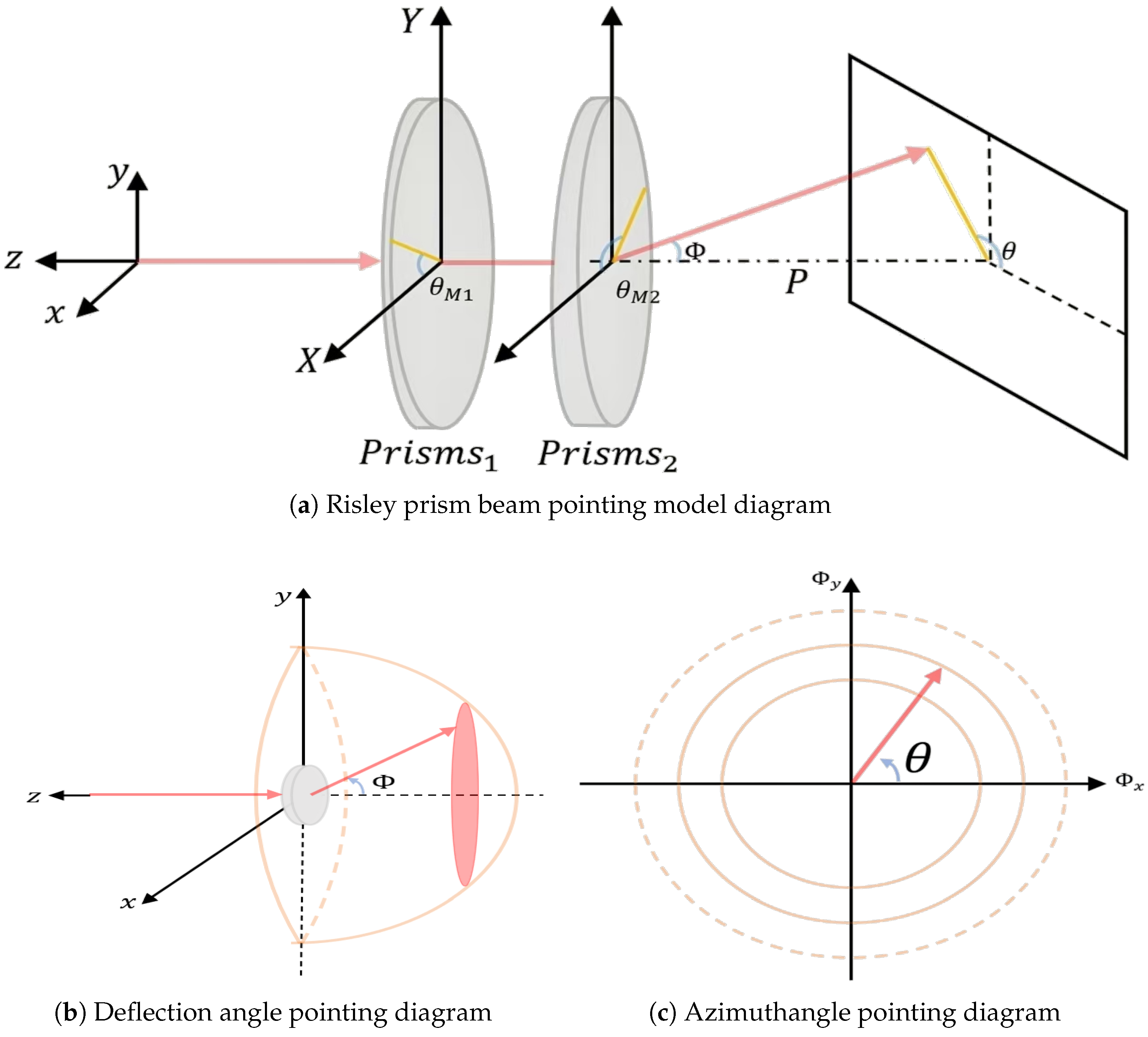
2.1. Risley Prism Beam Pointing Model
2.2. Motor Control Models
2.3. Risley Prism Beam Control Model
3. Methods
3.1. Fully Actuated Controller Design
3.2. Reinforcement Learning Compensator Design
3.2.1. Actor–Critic Network Design
3.2.2. Algorithm Implementation
3.3. Stability Analysis
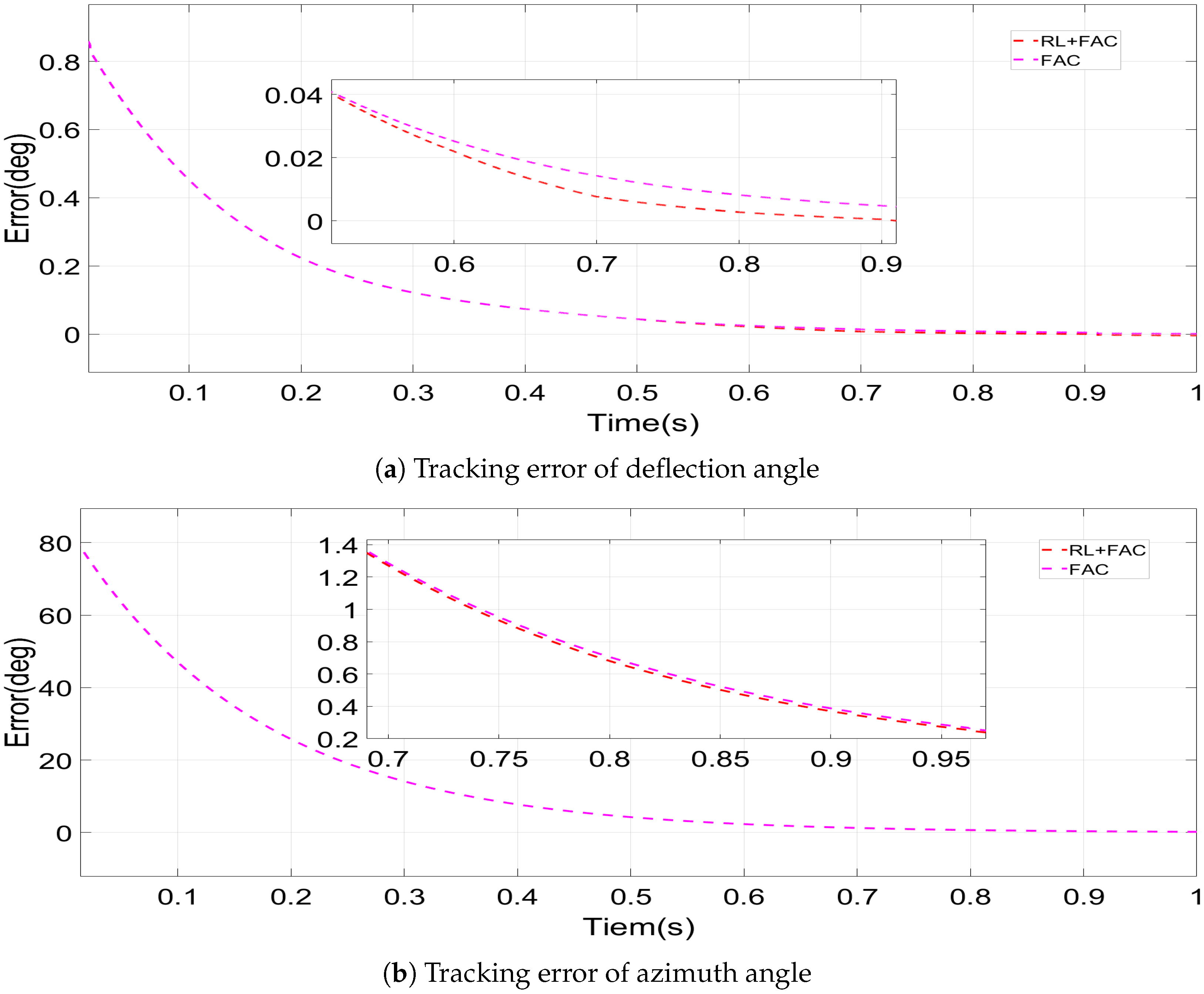
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Han, J.; Wang, C.; Xie, M.; Liu, P.; Cao, Y.; Jing, F.; Wang, F.; Su, Y.; Meng, X. Beam Scanning and Capture of Micro Laser Communication Terminal Based on MEMS Micromirrors. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Sun, M.; He, M.; Jia, S.; Xie, Z.; Yao, B.; Wang, W. Development current status and trends analysis of deep space laser communication (cover paper·invited). Hongwai Yu Jiguang Gongcheng/Infrared Laser Eng. 2024, 53, 20240247. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Xu, L.; Liang, X.; Dai, J. Multi-Beam Focusing and Deflecting Characteristics of Liquid Crystal Optical Phased Array. Photonics 2025, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaktionov, I.; Toporovsky, V.; Nikitin, A.; Rukosuev, A.; Alexandrov, A.; Sheldakova, J.; Laskin, A.; Kudryashov, A. Software and hardware implementation of the algorithm for 2-mirrors automatic laser beam alignment system. In Laser Beam Shaping XXIII; The Society of Photo–Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE): San Diego, CA, USA, 2023; Volume 12667, pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, W.J.; Wang, Y.C.; Lian, B.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Deng, X.W.; Zhao, J.P.; Zhou, W. Automatic alignment technology in high power laser system. In Proceedings of the XX International Symposium on High-Power Laser Systems and Applications 2014, Chengdu, China, 25–29 August 2014; Volume 9255, pp. 862–865. [Google Scholar]
- Burkhart, S.C.; Bliss, E.; Nicola, P.D.; Kalantar, D.; Lowe-Webb, R.; McCarville, T.; Nelson, D.; Salmon, T.; Schindler, T.; Villanueva, J.; et al. National Ignition Facility system alignment. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 1136–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahari, S.A.; Raj, A.; Soumya, S. Control of fast steering mirror for accurate beam positioning in FSO communication system. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on System, Computation, Automation and Networking (ICSCAN), Puducherry, India, 30–31 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Torales, G. Risley prisms applications: An overview. Adv. 3OM Opto-Mechatronics Opto-Mech. Opt. Metrol. 2021, 12170, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostaszewski, M.; Harford, S.; Doughty, N.; Huffman, C.; Sanchez, M.; Gutow, D.; Pierce, R. Risley prism beam pointer. In Free-Space Laser Communications VI; SPIE: Denver, CO, USA, 2006; Volume 6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, L.; Yun, M.; Wang, L.; Xu, N. Double prisms for two-dimensional optical satellite relative-trajectory simulator. In Free-Space Laser Communications IV; SPIE: Denver, CO, USA, 2004; Volume 5550, pp. 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Yi, W.; Sun, W.; Liu, L. Tilting double-prism scanner driven by cam-based mechanism. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 5788–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, F.; Ren, H.; Liu, J. Pointing Error Correction of Risley-Prism System Based onParticle Swarm Algorithm. Acta Opt. Sin. 2021, 41, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Third-order theory of the Risley-prism-based beam steering system. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Ruled surfaces generated by Risley prism pointers: I. Pointing accuracy evaluation and enhancement based on a structural analysis of the scan field inside the pointer. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2021, 38, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Risley prisms as a conformal transformation device. I. Complex and graphic analyses of mapping images conformality. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2022, 39, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. Risley prisms as a conformal transformation device: II. Derivatives of the absolute functions and an attributive analysis of the control singularities. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2022, 39, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, K.; Peng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, C.; Ren, G.; Li, A.; Sun, W.; Liu, X.; et al. Improvement of pointing accuracy for Risley prisms by parameter identification. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 7358–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Peng, Q.; Chen, K.; Fu, C.Y. High precision pointing system based on Risley prism: Analysis and simulation. In Proceedings of the XX International Symposium on High-Power Laser Systems and Applications 2014, Chengdu, China, 25–29 August 2015; Volume 9255, pp. 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, Y.; Hei, M.; Liu, G.; Fan, D. Motion control of the wedge prisms in Risley-prism-based beam steering system for precise target tracking. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, Y.; Hei, M.; Liu, G.; Fan, D. Pointing error analysis of Risley-prism-based beam steering system. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 5775–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fan, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, G. Beam steering limitation of a Risley prism system due to total internal reflection. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 6079–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, P.; Jiang, G.; Hu, F.; Fan, S. Limits on field of view for Risley prisms. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 9114–9122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, L.; Zou, Z.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X.; Fan, S.; Fan, D. Singularity Problem Analysis of Target Tracking Based on Risley Prisms. Acta Opt. Sin. 2025, 45, 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Xia, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yuan, J.; Shi, J.; Liu, X.; Tu, Q.; Tang, T.; et al. Robust Risley prism control based on disturbance observer for system line-of-sight stabilization. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 3463–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Li, J.; Fan, Y.; Shi, J.; Huang, Y. Enhancing pointing accuracy in Risley prisms through error calibration and stochastic parallel gradient descent inverse solution method. Precis. Eng. 2025, 93, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Huang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Shi, J.; Xia, H.; Li, J. Rotational Risley prisms: Fast and high-accuracy inverse solution and application based on back propagation neural networks. Measurement 2025, 242, 116007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Torales, G.; Flores, J.L.; Munoz, R.X. High precision prism scanning system. In Sixth Symposium: Optics in Industry; SPIE: Monterrey, Mexico, 2007; Volume 6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuxiang, Y.; Ke, C.; Jinying, L.; Congming, Q. Closed-Loop Control of Risley Prism Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Application, Guangzhou, China, 27–29 March 2020; pp. 481–488. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.; Holly, E.; Lillicrap, T.; Levine, S. Deep reinforcement learning for robotic manipulation with asynchronous off-policy updates. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 3389–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Closed form analytical inverse solutions for Risley-prism-based beam steering systems in different configurations. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 4302–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.; Zhou, B.; Yang, X. Fully actuated system theory and applications: New developments in 2023. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2024, 55, 2419–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G. High-order fully actuated system approaches: Part I. Models and basic procedure. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2021, 52, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G. High-order fully actuated system approaches: Part II. Generalized strict-feedback systems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2021, 52, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinelli, F.; Hocquet, G.; Singh, S.; Baldi, P. From Reinforcement Learning to Deep Reinforcement Learning: An Overview. In Braverman Readings in Machine Learning: Key Ideas from Inception to Current State; Lecture Notes in Artificial, Intelligence; Rozonoer, L., Mirkin, B., Muchnik, I., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11100, pp. 298–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Yan, P.; Guan, X. Deep Reinforcement Learning: From Q-Learning to Deep Q-Learning. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing (ICONIP 2017), PT IV, Guangzhou, China, 14–18 November 2017; Liu, D., Xie, S., Li, Y., Zhao, D., ElAlfy, E., Eds.; Volume 10637, pp. 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S. The Advance of Reinforcement Learning and Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Big Data and Algorithms (EEBDA), Changchun, China, 25–27 February 2022; pp. 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.R. Fully Actuated System Approach for Control: An Overview. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 7285–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G. High-order fully actuated system approaches: Part III. Robust control and high-order backstepping. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2021, 52, 952–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, J. A deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm based on averaged state-action estimation. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 101, 108015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsiklis, J.; Van Roy, B. An analysis of temporal-difference learning with function approximation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1997, 42, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Xia, Y.; Yuan, L.; Wen, P.; Zhang, W.; Ding, K.; Fan, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, J. Fast and high-precision tracking technology for image-based closed-loop cascaded control system with a Risley prism and fast steering mirror. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 8555–8571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]















| Parameters | Meaning | Value |
|---|---|---|
| B | (N·m·s/rad) | |
| 1 | ||
| J | (kg·m2) | |
| (N·m·s/rad) | ||
| (V·s/rad) | ||
| n | ||
| 16 |
| Test | Deviation Deflection Range | Azimuthal Deflection Range |
|---|---|---|
| Test 1 | ||
| Test 2 | –16° | 80° |
| Test 3 | –360° | |
| Test 4 | –16° | –220° |
| Test 5 | –16° | –360° |
| Test 6 | –12° | –360° |
| IAE of Deflection Angle (deg) | IAE of Azimuth Angle (deg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | FAC | FAC+RL | FAC | FAC+RL |
| Test 1 | 0.3743 | 0.3429 | 16.9534 | 15.8186 |
| Test 2 | 0.1290 | 0.1161 | 13.6840 | 13.1700 |
| Test 3 | 0.0436 | 0.0385 | 2.1370 | 1.9340 |
| Test 4 | 0.1423 | 0.1383 | 21.2093 | 20.1940 |
| Test 5 | 0.1308 | 0.1214 | 2.1394 | 1.9322 |
| Test 6 | 0.0844 | 0.0736 | 2.5133 | 2.3081 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, R.; Xie, M.; Xue, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, F. Reinforcement Learning Compensatory-Based Fully Actuated Control Method for Risley Prisms. Photonics 2025, 12, 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090885
Xing R, Xie M, Xue H, Wang J, Wang F. Reinforcement Learning Compensatory-Based Fully Actuated Control Method for Risley Prisms. Photonics. 2025; 12(9):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090885
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Runqiang, Meilin Xie, Haoqi Xue, Jie Wang, and Fan Wang. 2025. "Reinforcement Learning Compensatory-Based Fully Actuated Control Method for Risley Prisms" Photonics 12, no. 9: 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090885
APA StyleXing, R., Xie, M., Xue, H., Wang, J., & Wang, F. (2025). Reinforcement Learning Compensatory-Based Fully Actuated Control Method for Risley Prisms. Photonics, 12(9), 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090885





