Accurate, Extended-Range Indoor Visible Light Positioning via High-Efficiency MPPM Modulation with Smartphone Multi-Sensor Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
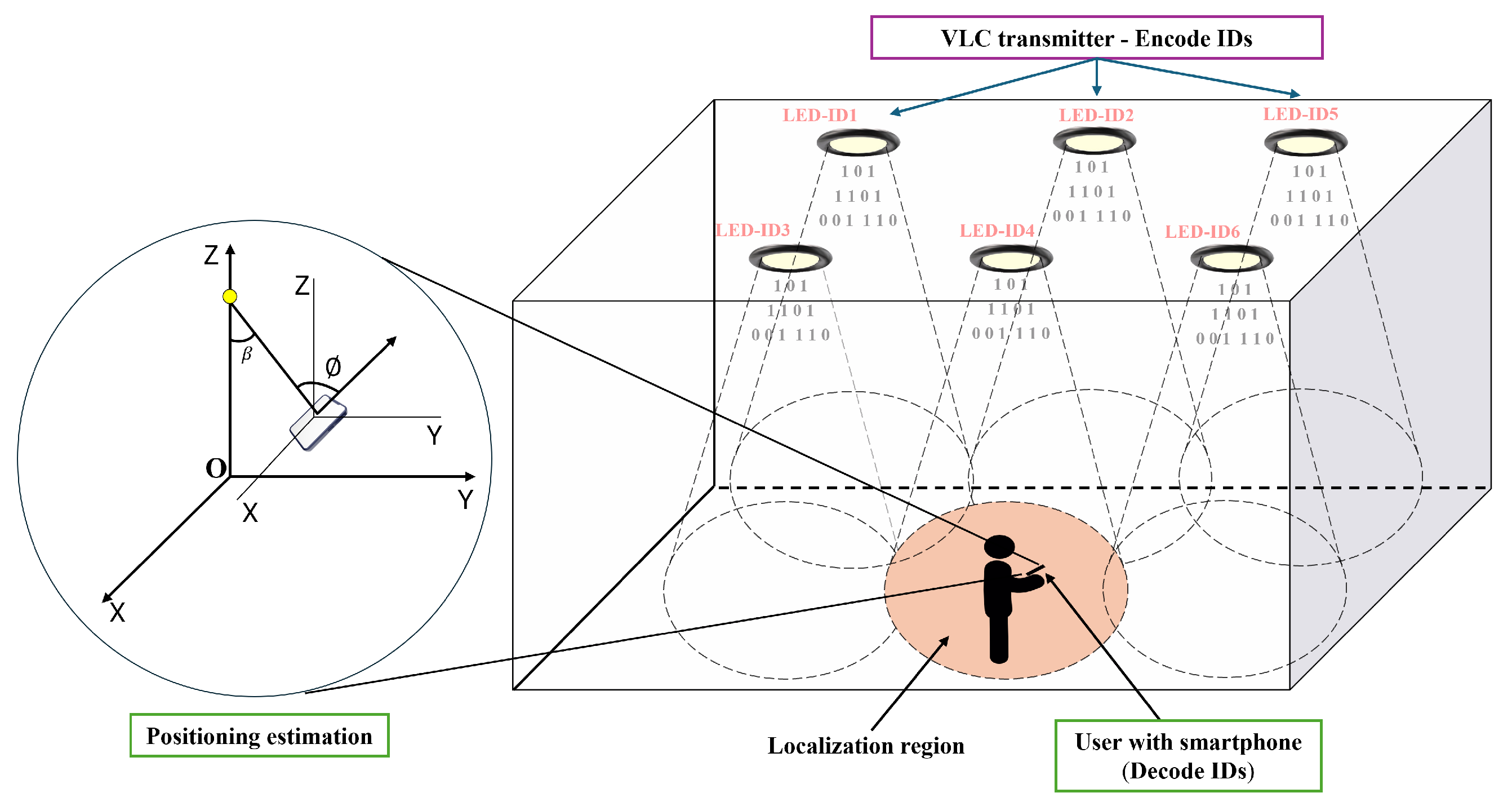
3. Overview of the Proposed VLC System for Indoor Positioning
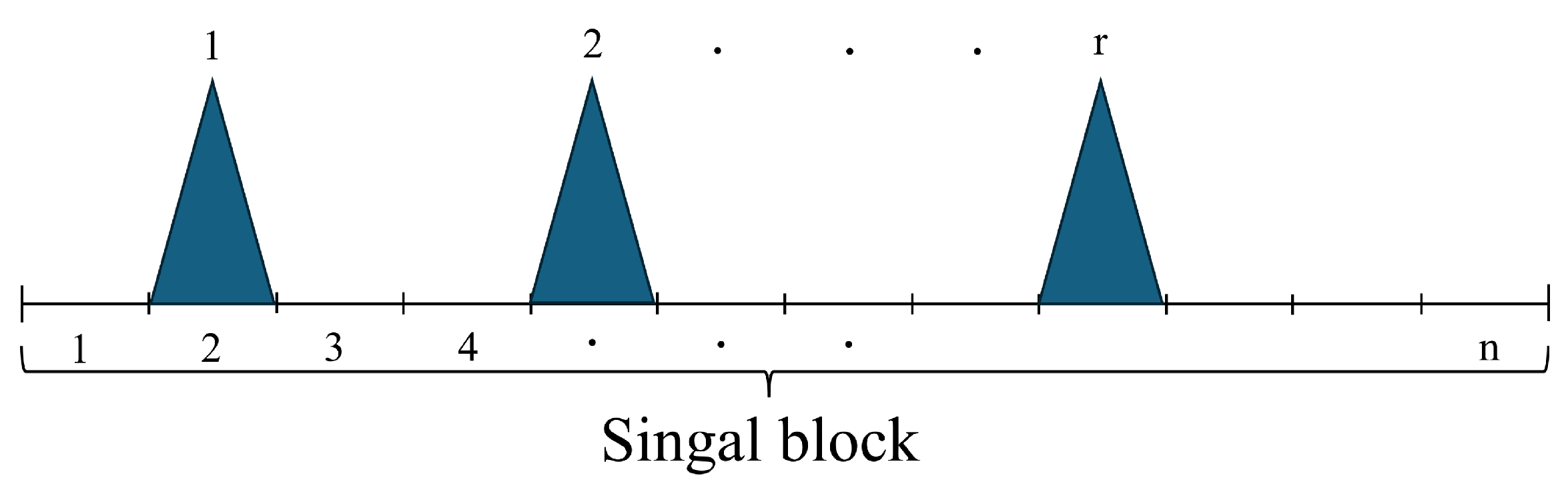
3.1. Proposed Modulation Scheme for Multi-LED ID Encoding
| Algorithm 1 Encoding elgorithm |
|
| Algorithm 2 Decoding algorithm |
|
3.2. Parameter Optimization Analysis
3.2.1. Frame Rate and Frequency Flicker
3.2.2. Transmission Distance and Dimension of LED
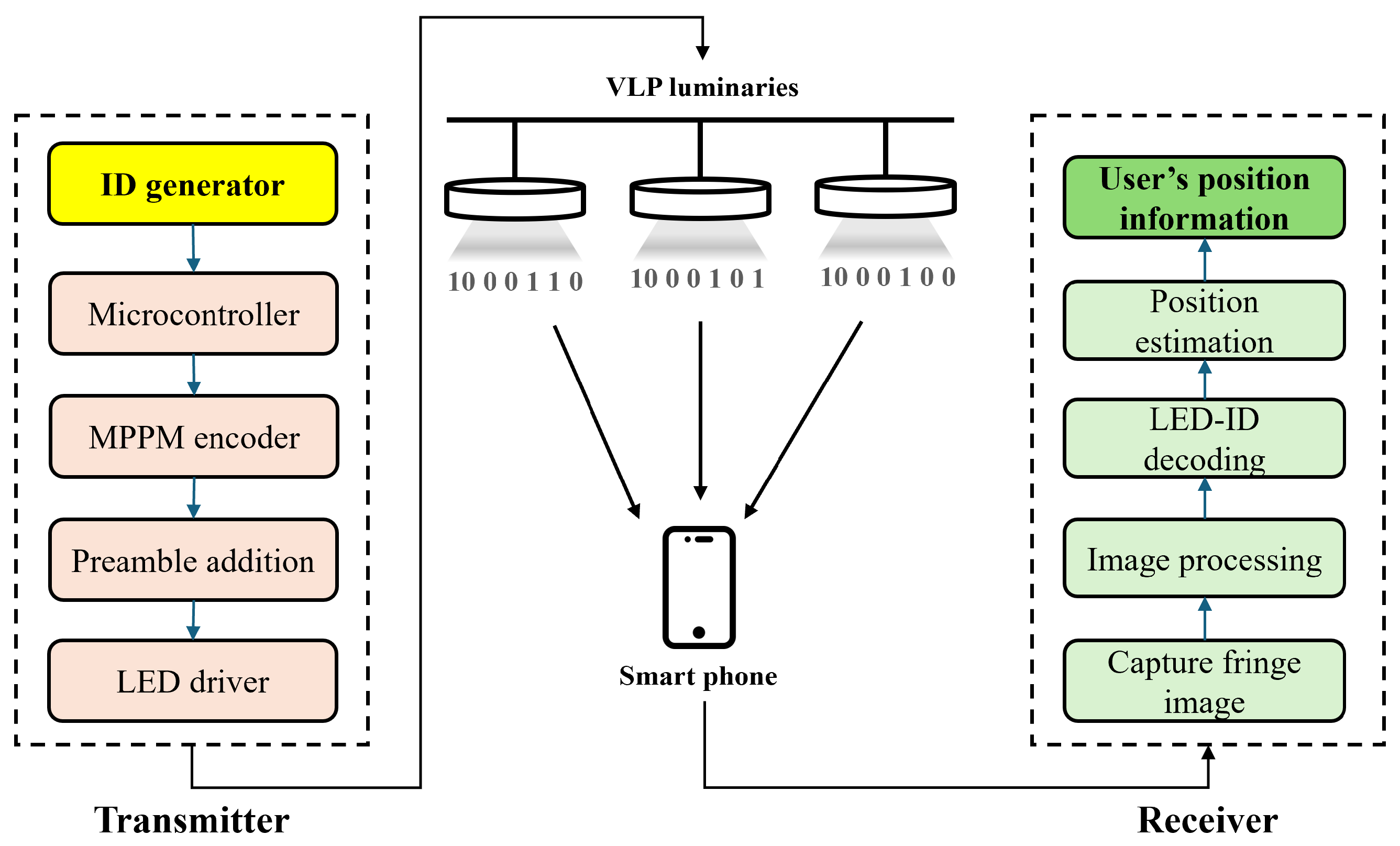
4. Proposed Visible Light Positioning System Architecture
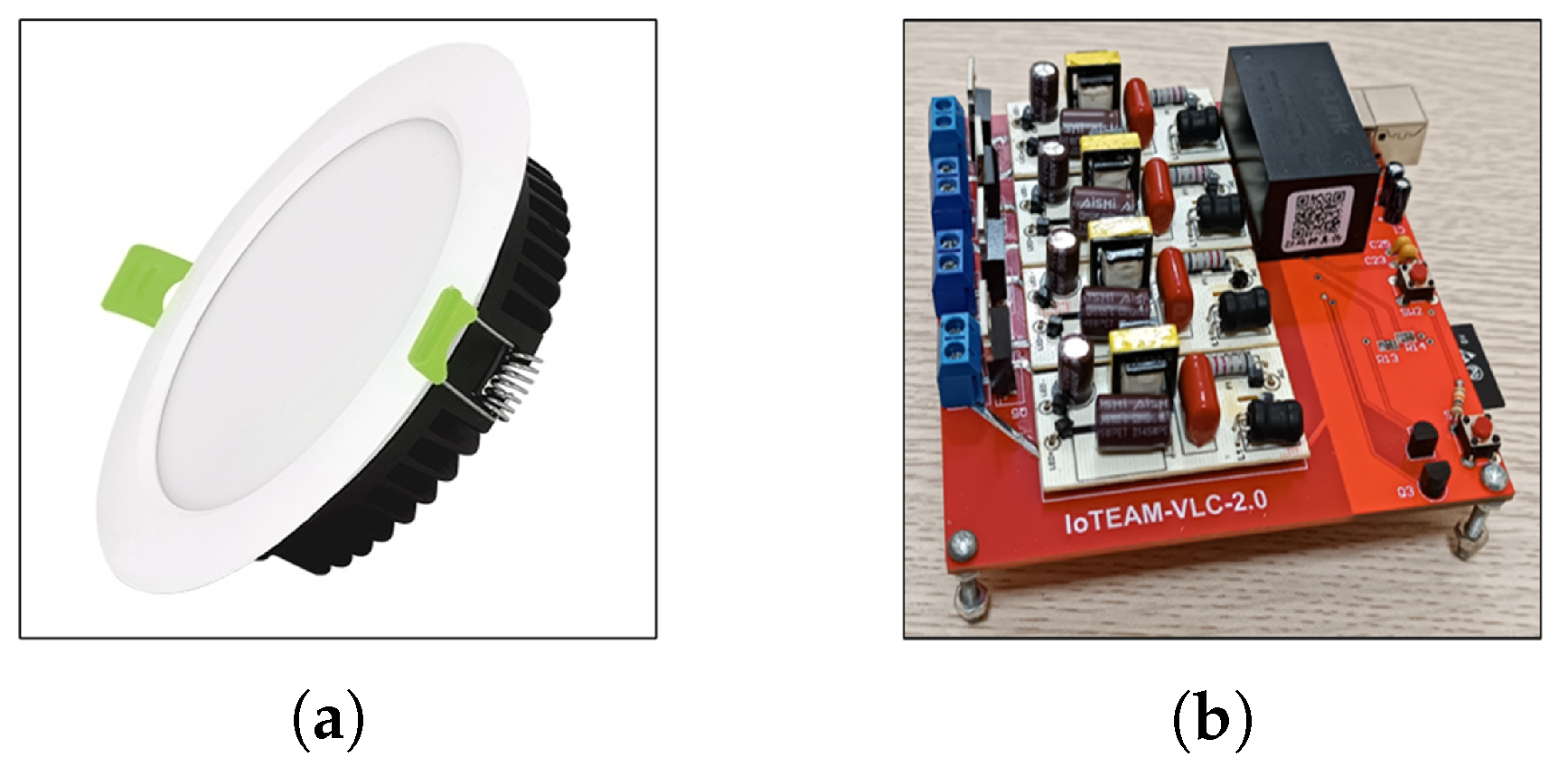
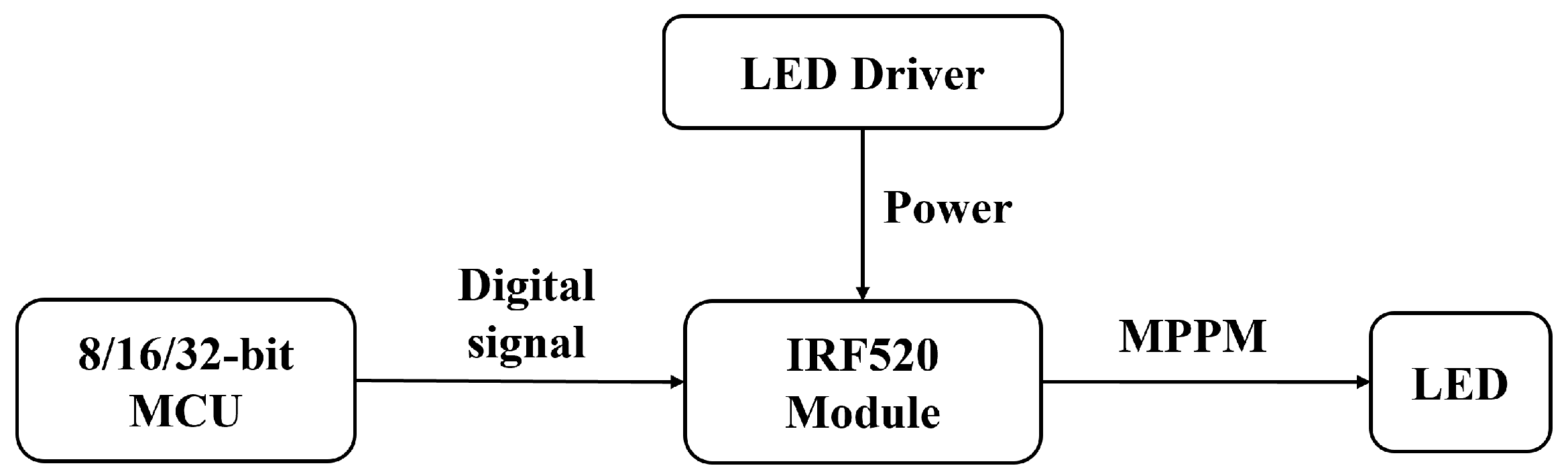
4.1. Transmitter Section
4.1.1. Transmitter Design
4.1.2. Transmitter LED Modulation
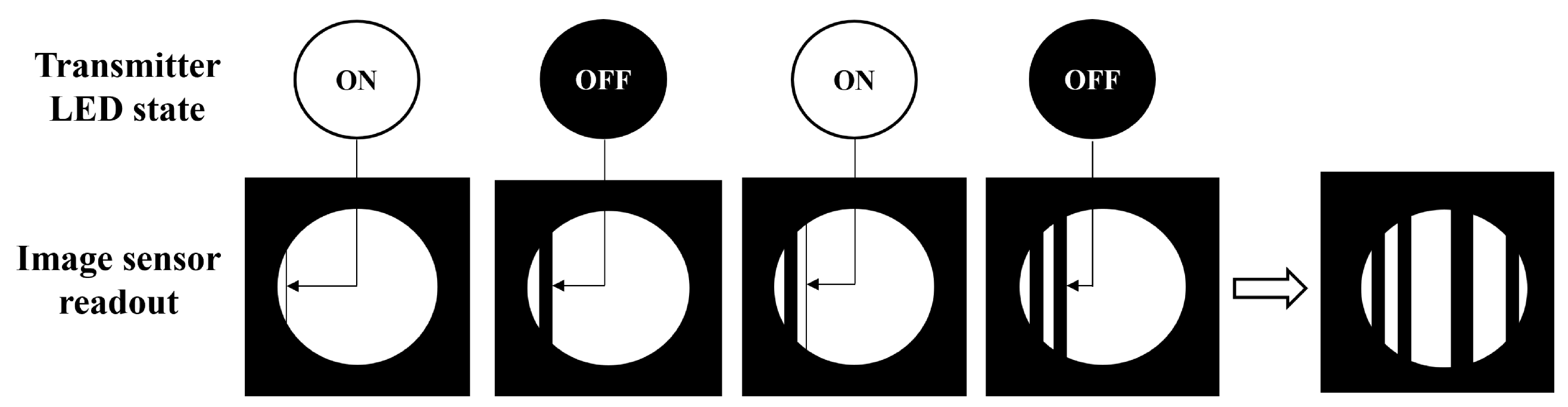
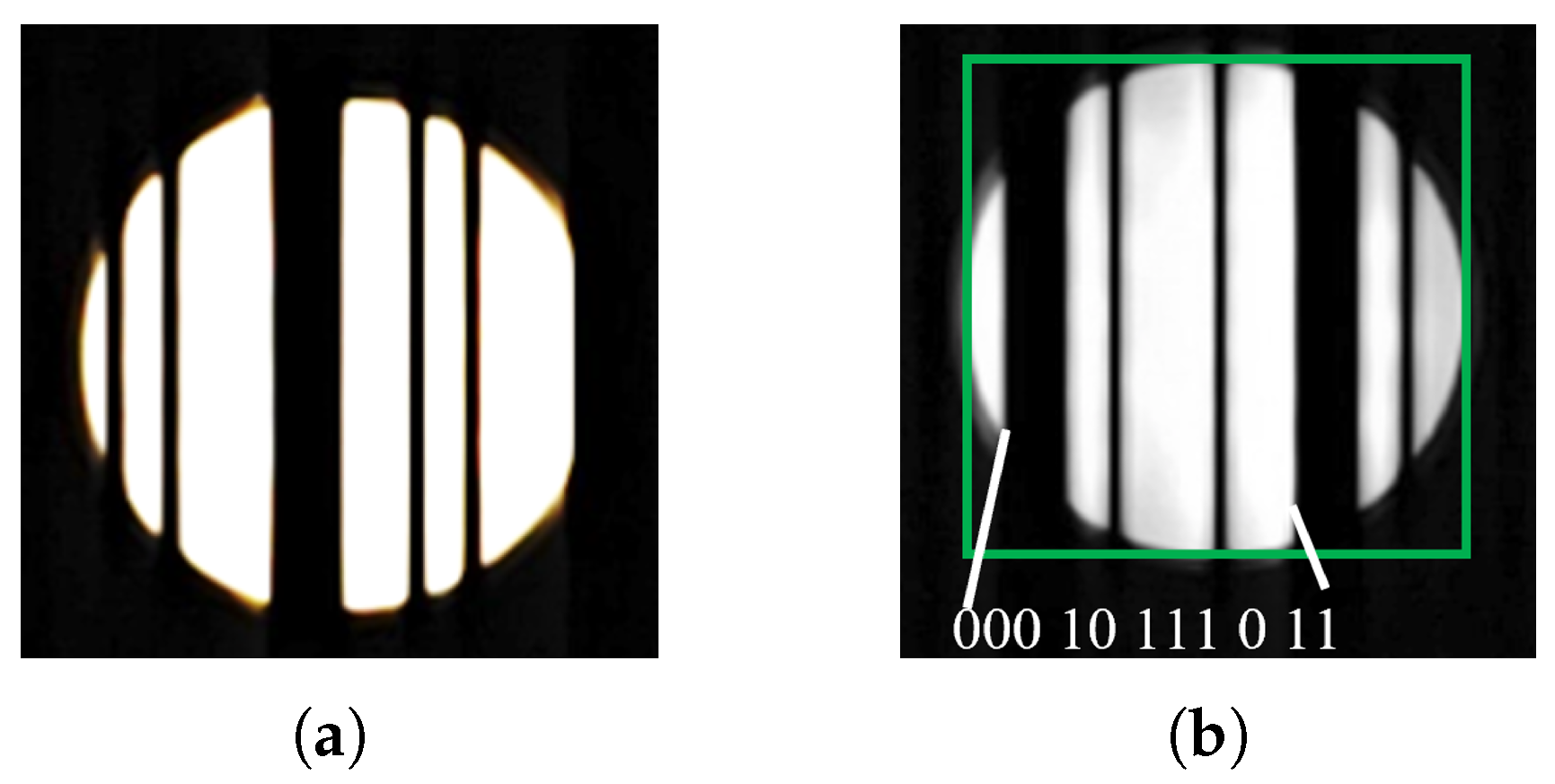
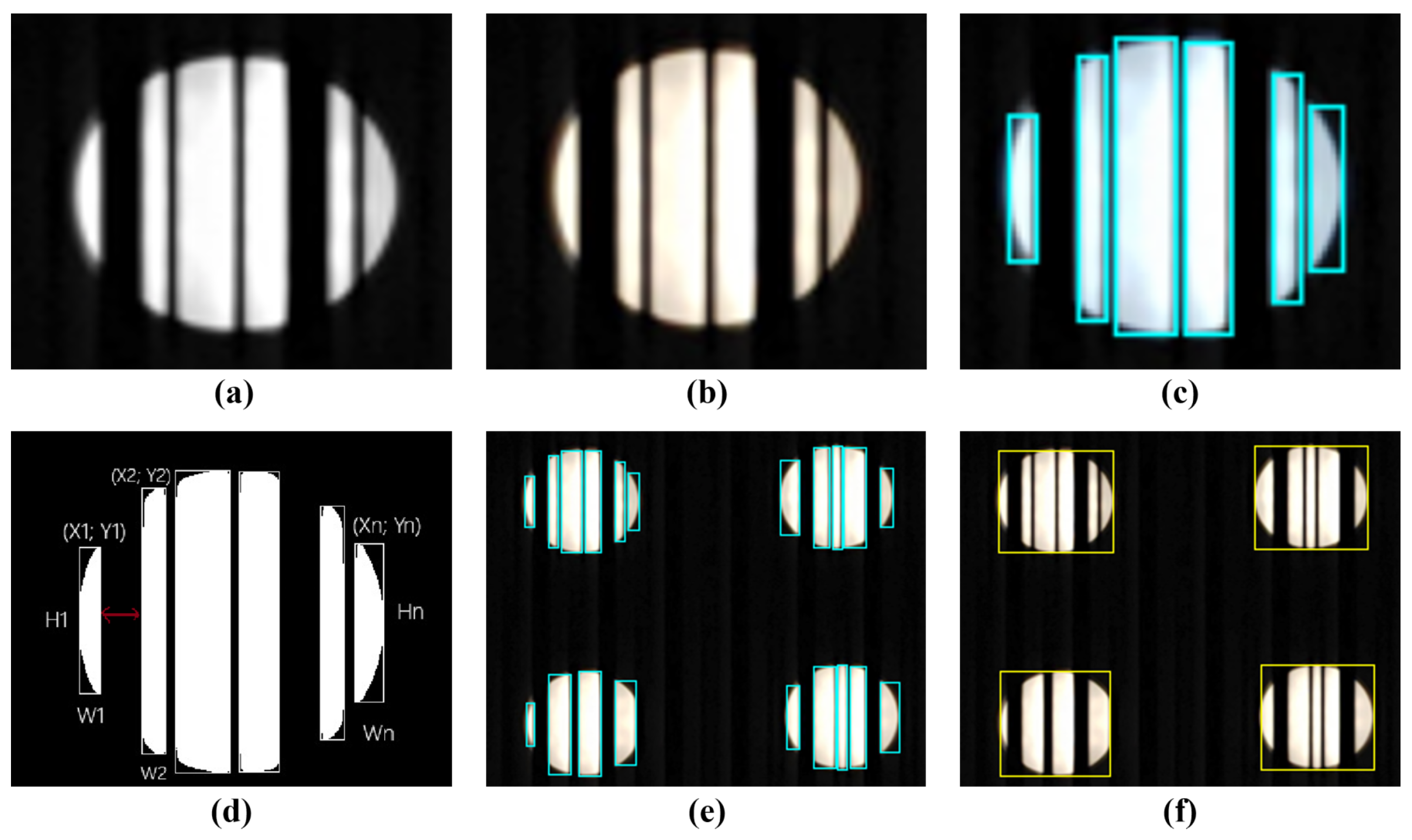
4.2. Image Processing Algorithm for LED–ID Feature Extraction
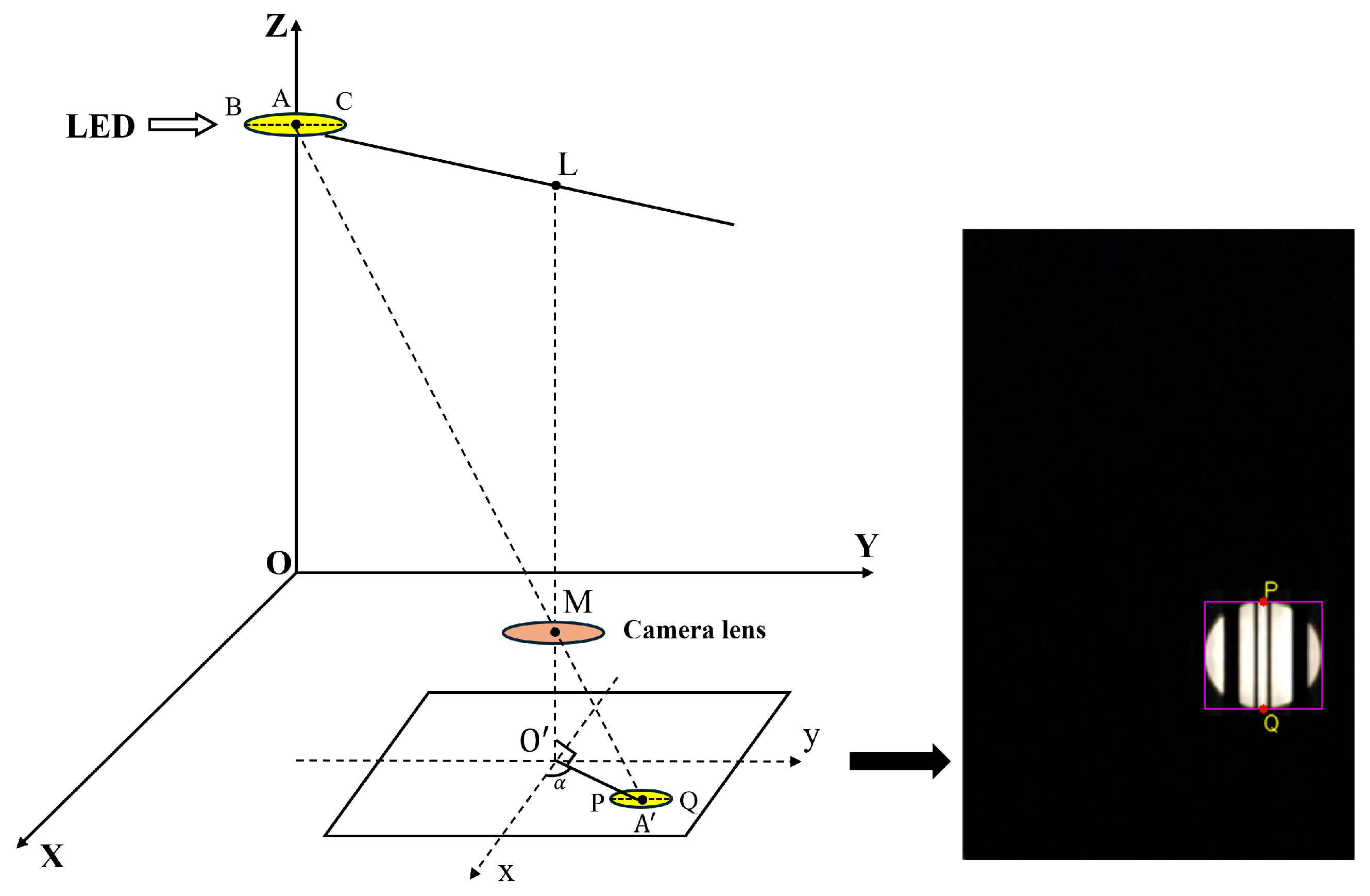
4.3. Position Estimation Algorithm
Basic Position of the Receiver
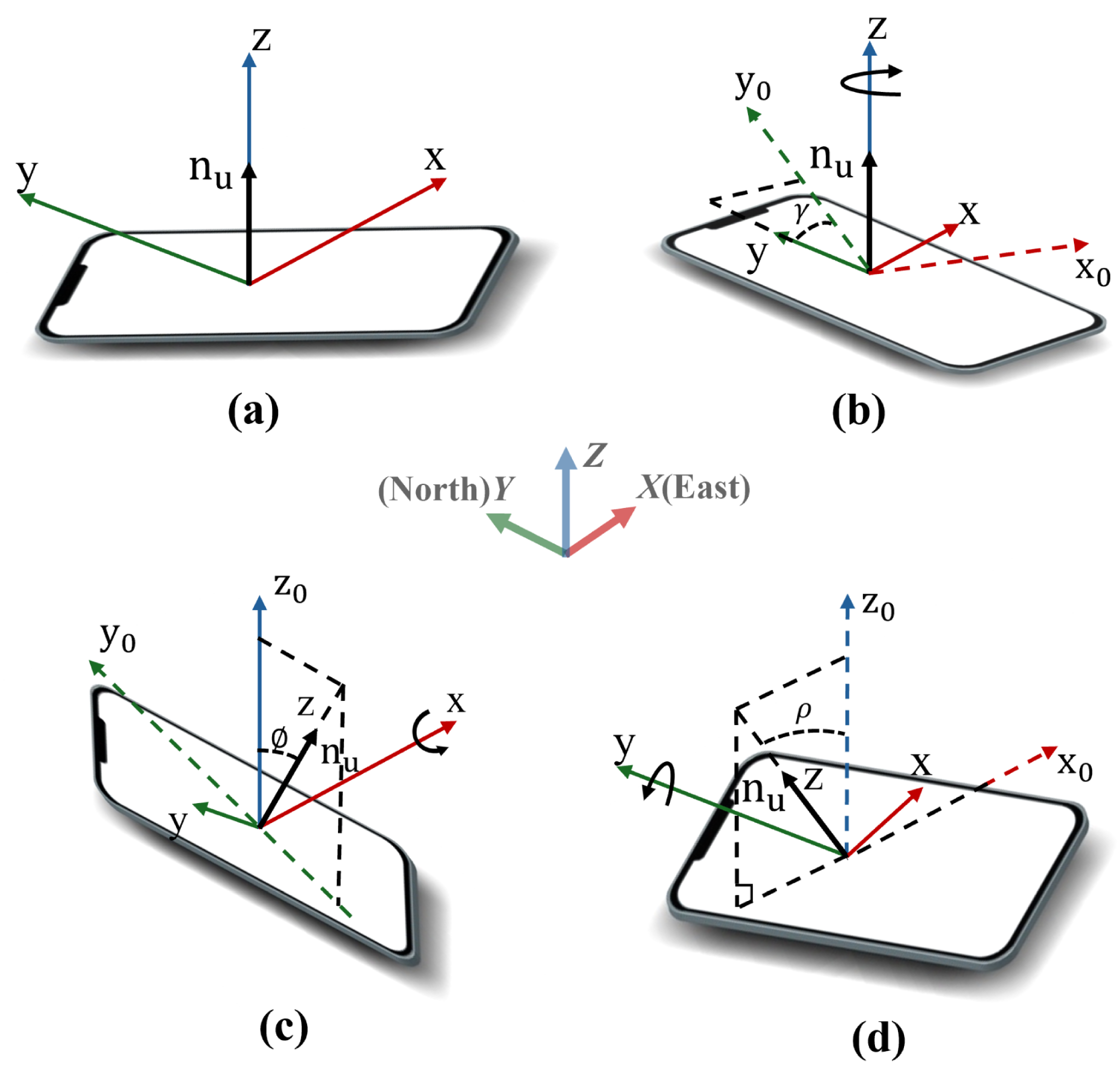
4.4. Estimating Position with Rotation Angles
5. Experiment and Results
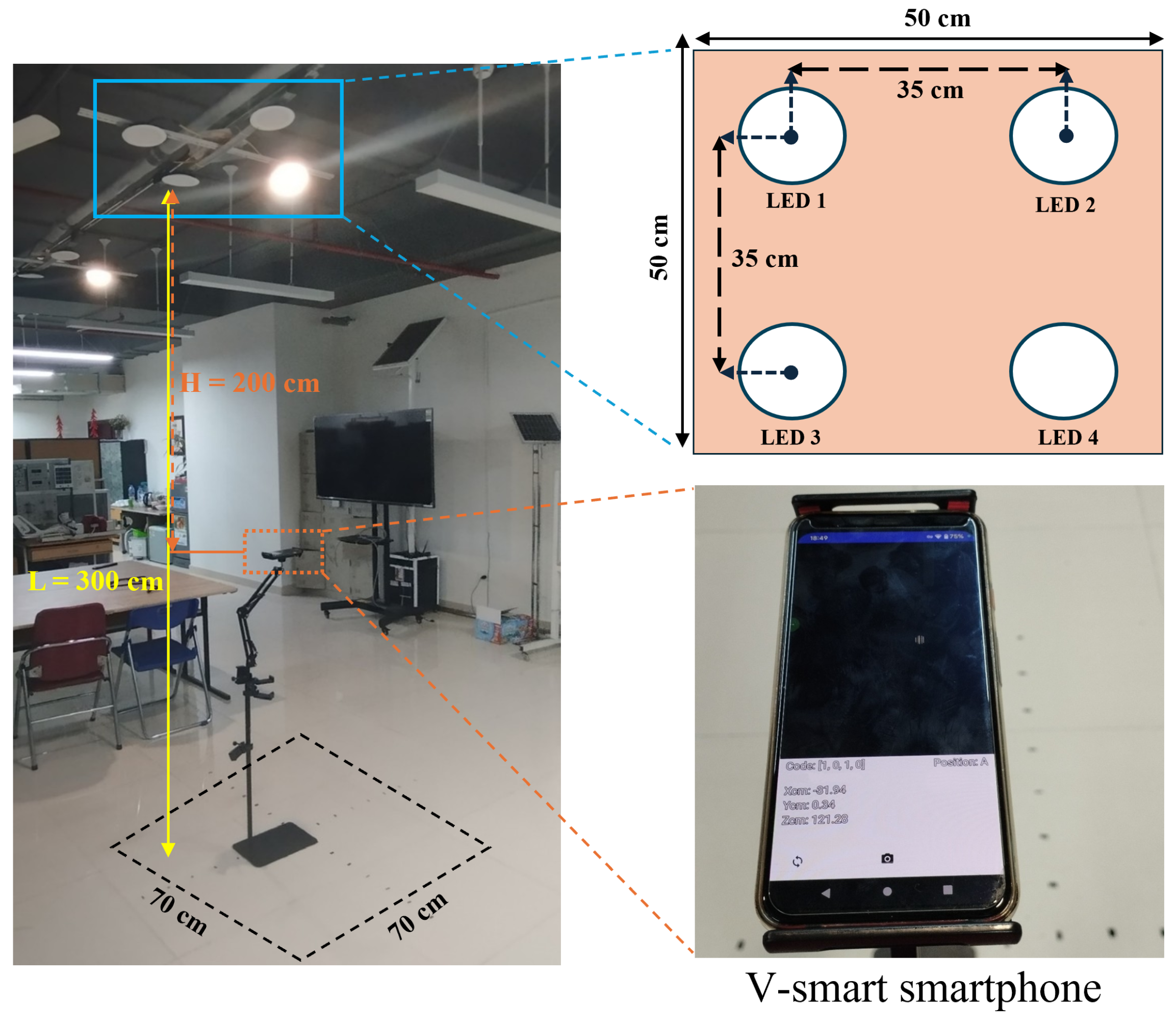
5.1. Experimental Setup
5.2. Experimental Results
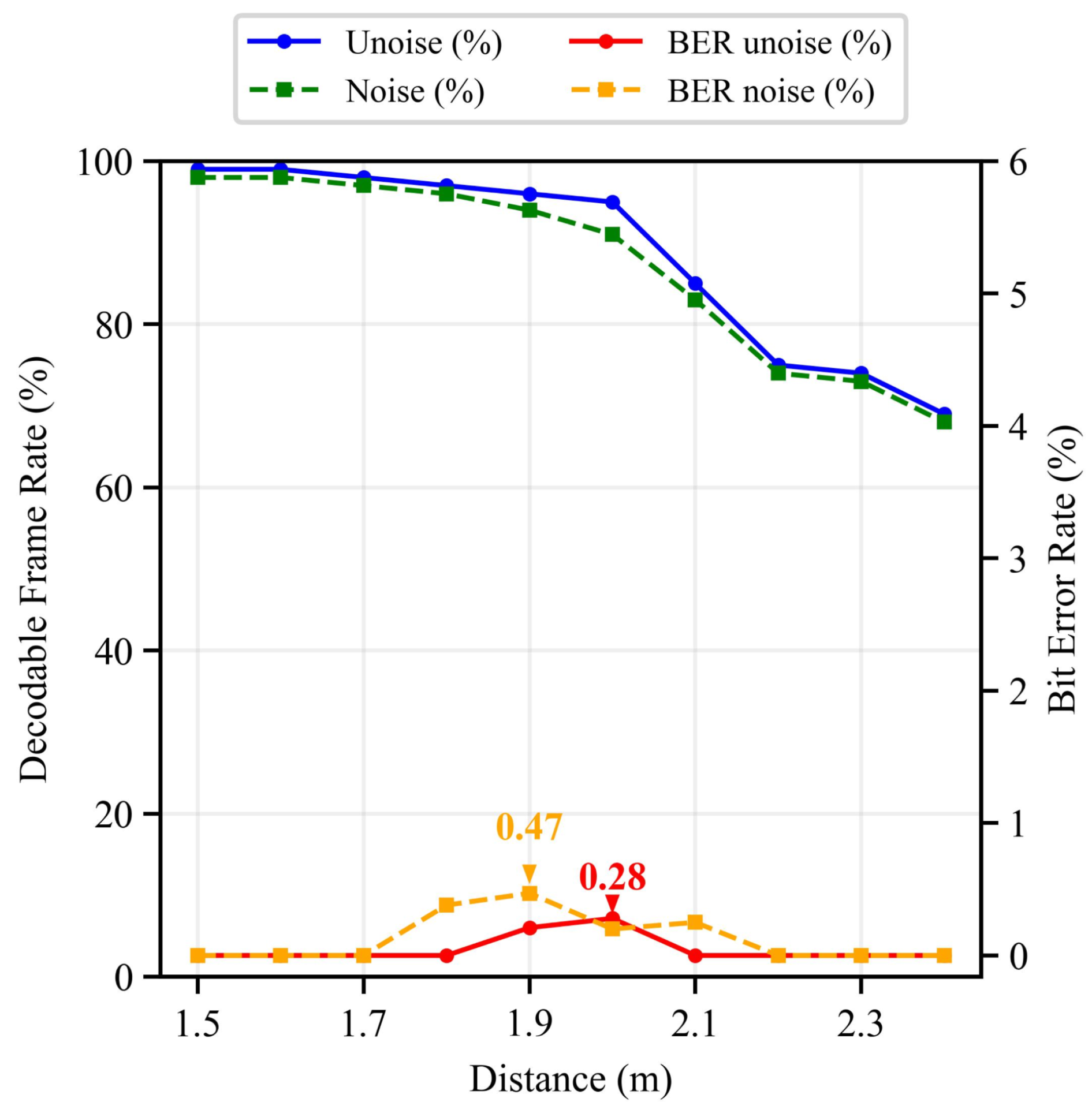
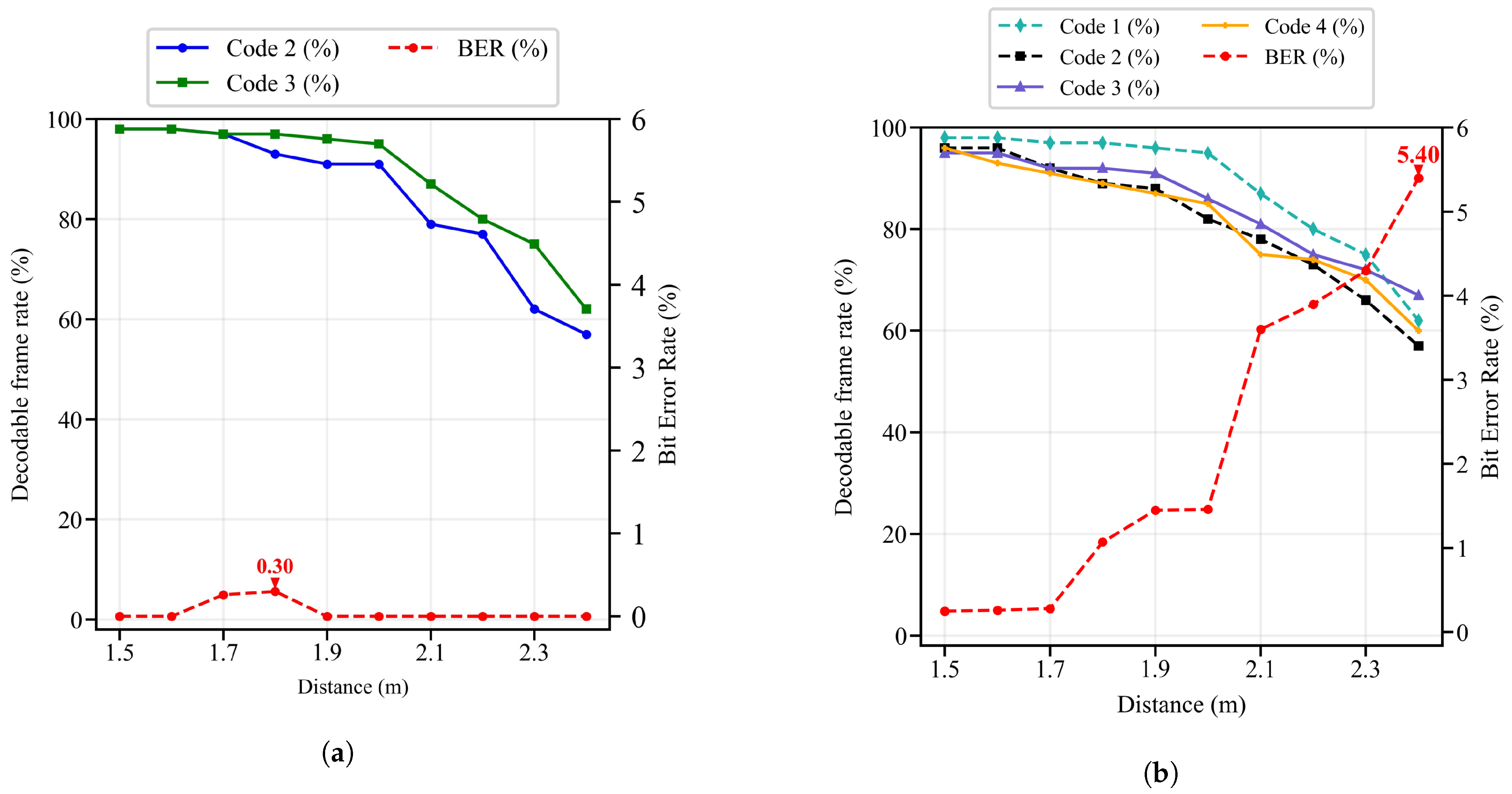
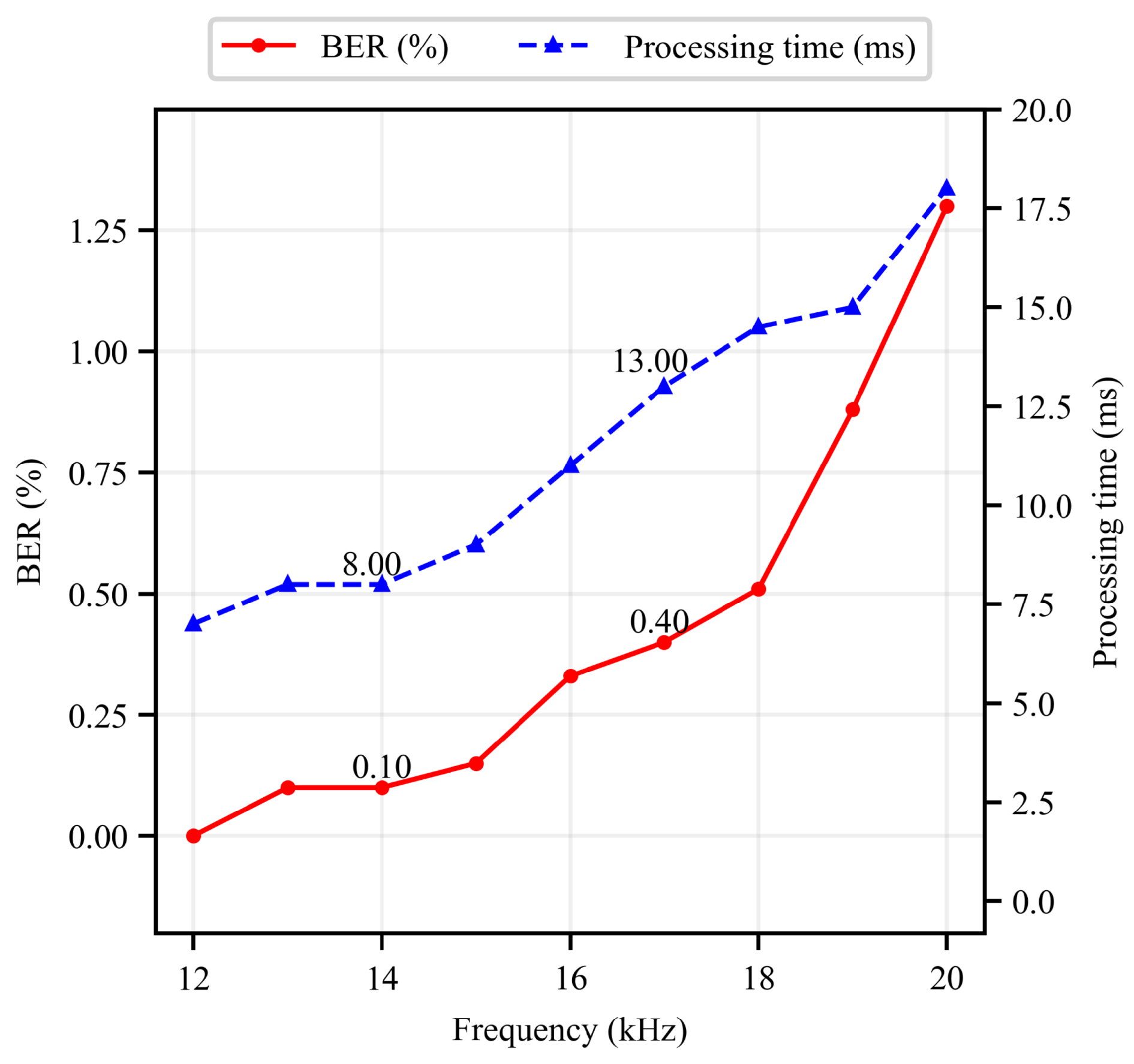
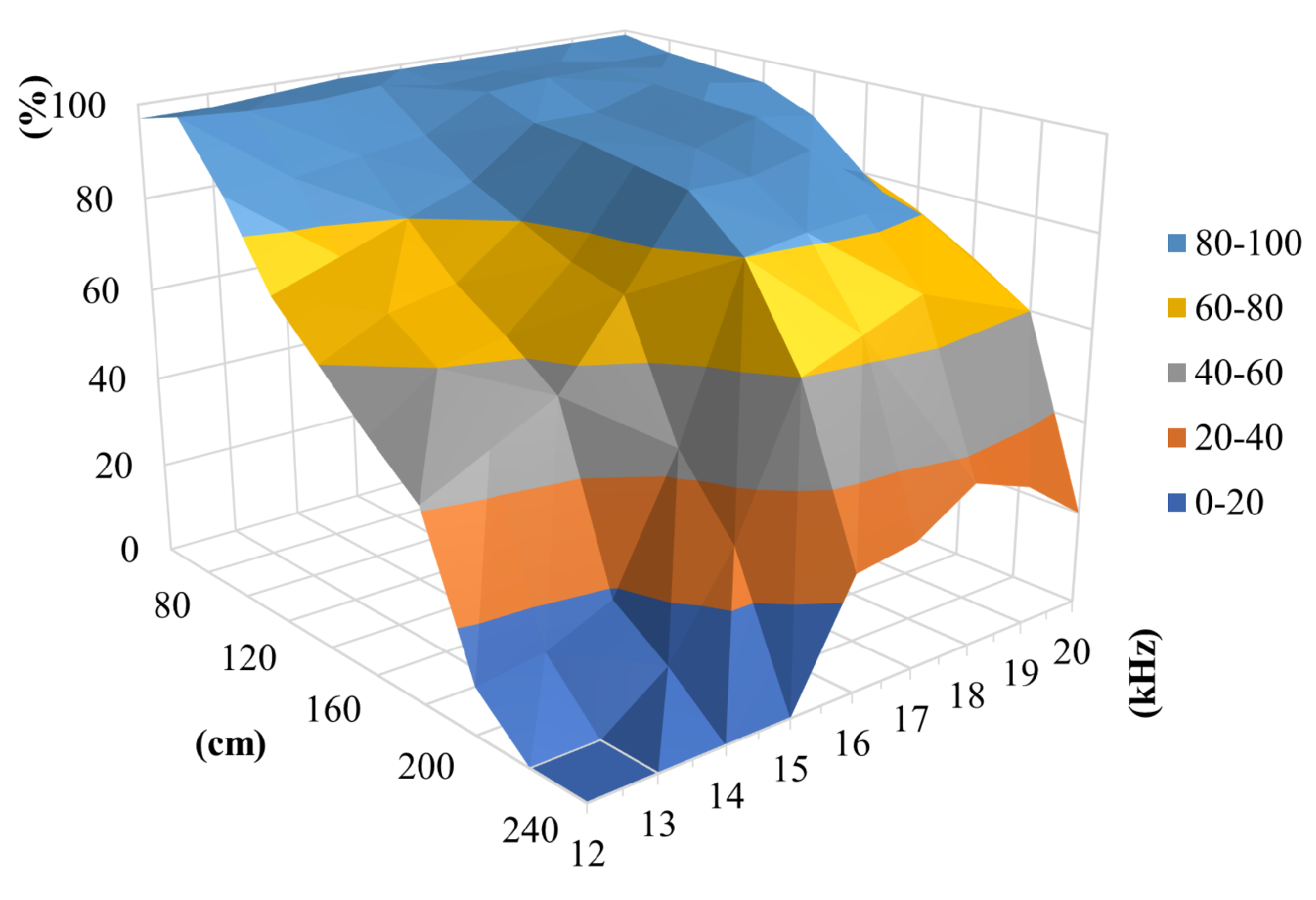
5.2.1. Decoding Error Rate
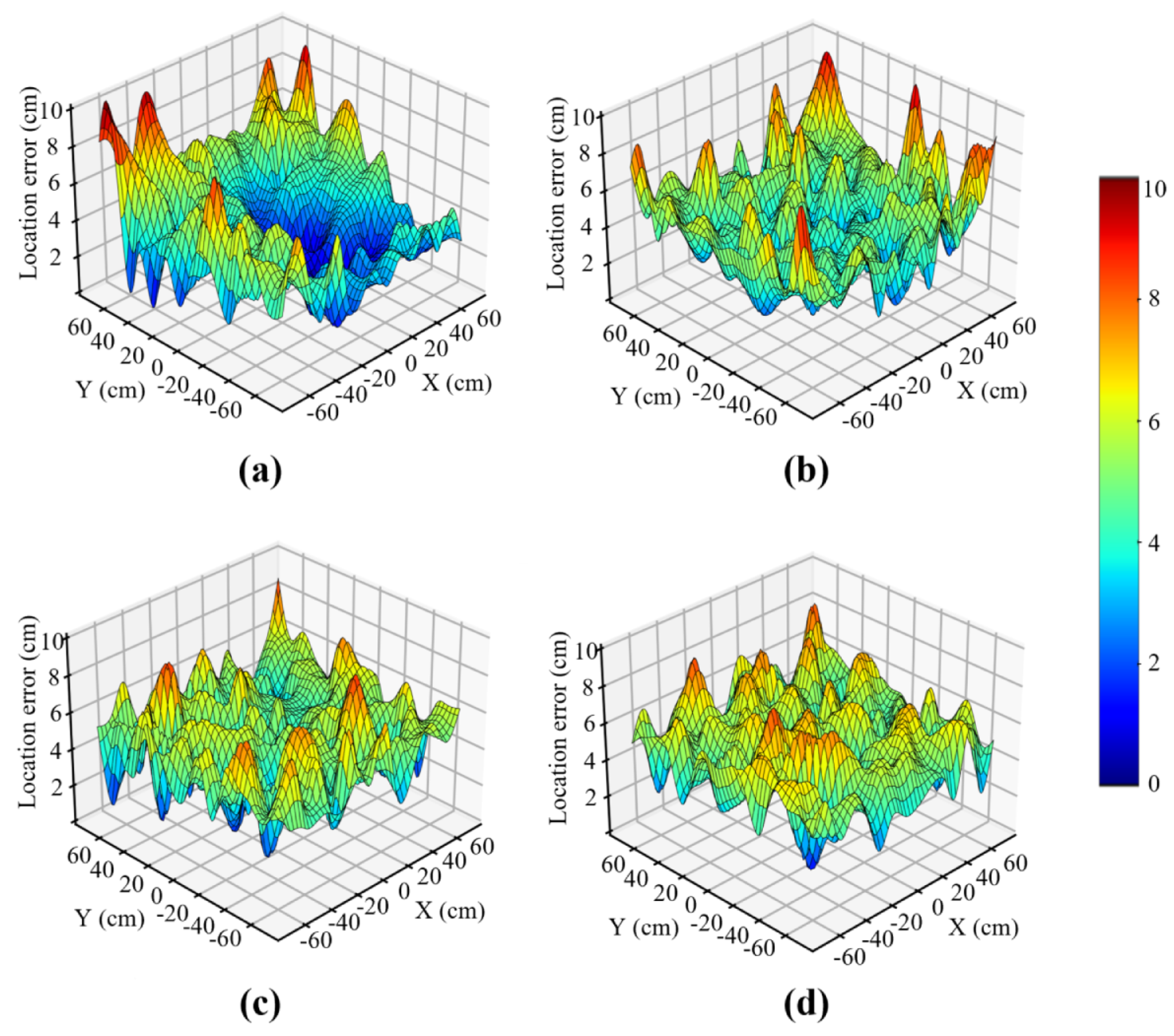
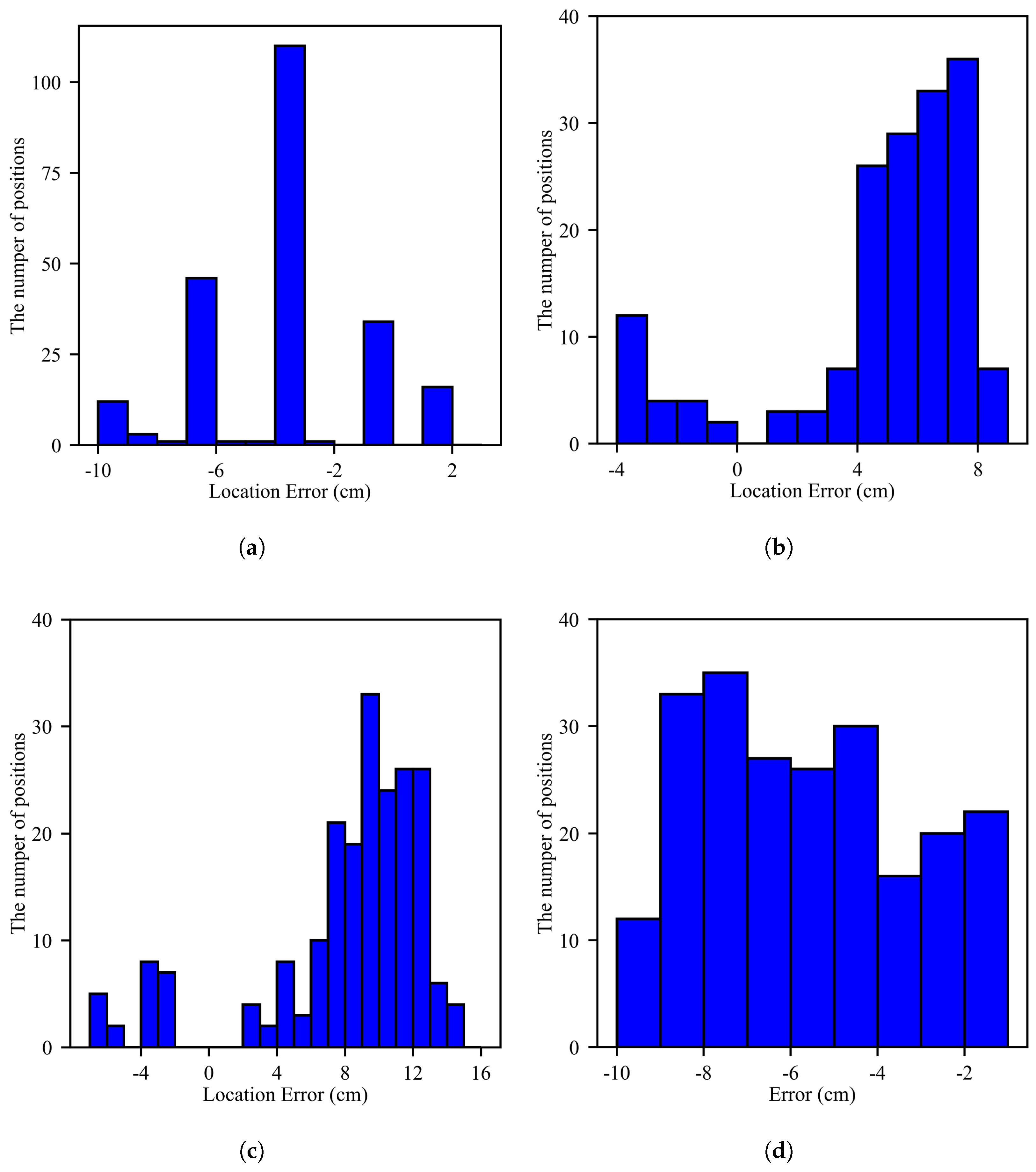
5.2.2. Position Accuracy
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vu, T.L.; Nguyen, T.; Kim, C.S.; Sin, E.B.; Jeong, J.; Jang, Y.M. Survey of indoor optical camera communication (OCC) systems for the Internet of lights. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 18–20 October 2017; pp. 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Saleh, S.S.; El-Badawy, E.S.A.; Aly, M.H. A comparative analysis of localization algorithms for visible light communication. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2021, 53, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Saputra, Y.M.; Huynh, N.V.; Nguyen, N.T.; Khoa, T.V.; Tuan, B.M.; Nguyen, D.N.; Hoang, D.T.; Vu, T.X.; Dutkiewicz, E.; et al. A Comprehensive Survey of Enabling and Emerging Technologies for Social Distancing—Part I: Fundamentals and Enabling Technologies. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 153479–153507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardari, D.; Closas, P.; Djuric, P.M. Indoor tracking: Theory, methods, and technologies. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftler, B.S.; Kadri, A.; Guvenc, I. Fundamental bounds on RSS-based wireless localization in passive UHF RFID systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 9–12 March 2015; pp. 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.; Sekercioglu, Y.; Neild, A. Visible light positioning: A roadmap for international standardization. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2013, 51, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Ghassemlooy, Z.; Lin, C.; Tang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. An Indoor Visible Light Positioning System Based on Optical Camera Communications. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2017, 29, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Son, Y.H.; Han, S.K. Three-dimensional visible light indoor localization using AOA and RSS with multiple optical receivers. J. Light. Technol. 2014, 32, 2480–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Wu, Y.; Wen, S.; Chen, H.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. A novel three-dimensional indoor positioning algorithm design based on visible light communication. Opt. Commun. 2017, 392, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Park, J.K.; Kim, J.T. Three-Dimensional VLC Positioning System Model and Method Considering Receiver Tilt. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 132205–132216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.M.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Han, S.K. Tilted receiver angle error compensated indoor positioning system based on visible light communication. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 888–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Chen, K.; Tan, G.; Lu, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; He, T. LIPS: A Light Intensity Based Positioning System For Indoor Environments. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2016, 12, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, A.; Lv, H.; Feng, L.; Song, W. Fusion of Visible Light Indoor Positioning and Inertial Navigation Based on Particle Filter. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Ho, S.W.; Vellambi, B.N. Indoor positioning system using visible light and accelerometer. J. Light. Technol. 2014, 32, 3306–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Nguyen, N.H. Mobile Application for Visible Light Communication Systems: An Approach for Indoor Positioning. Photonics 2024, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, S.; Roberts, R.; Lim, S.K. IEEE 802.15.7 visible light communication: Modulation schemes and dimming support. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2012, 50, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Lo, A.; Niemegeers, I. A survey of indoor positioning systems for wireless personal networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2009, 11, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.H.; Yoo, M. An in-depth survey of visible light communication based positioning systems. Sensors 2016, 16, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Shimada, S.; Murakami, H.; Watanabe, H.; Hashizume, H.; Sugimoto, M. ALiSA: A Visible-Light Positioning System Using the Ambient Light Sensor Assembly in a Smartphone. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 4989–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Cheng, H.C.; Yue, C.P. LiDR: Visible-Light-Communication-Assisted Dead Reckoning for Accurate Indoor Localization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 15742–15755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, K.; Keche, M. Accurate indoor visible light positioning method using four LEDs and a smartphone camera. Optik 2025, 331, 172346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.S.; Pannuto, P.; Hsiao, K.J.; Dutta, P. Luxapose: Indoor positioning with mobile phones and visible light. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, MOBICOM. Association for Computing Machinery, Maui, HI, USA, 7–11 September 9 2014; pp. 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Q. Wearables Can Afford: Light-weight Indoor Positioning with Visible Light. In Proceedings of the MobiSys 2015—Proceedings of the 13th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services. Association for Computing Machinery, Florence, Italy, 18–22 May 2015; p. 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.H.; Feng, X.; Hu, P.; Mohapatra, P. Visible Light Communication, Networking, and Sensing: A Survey, Potential and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 2047–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonen, T. Indoor Optical Wireless Systems: Technology, Trends, and Applications. J. Light. Technol. 2018, 36, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyadi, W.A.; Chung, Y.H.; Ghassemlooy, Z.; Hassan, N.B. Optical camera communications: Principles, modulations, potential and challenges. Electronics 2020, 9, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozawa, Y.; Habuchi, H. Enhancement of Optical Wireless Multi-Pulse PPM. In Proceedings of the IEEE GLOBECOM 2008—2008 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 30 November–4 December 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Khalighi, M.A.; Bourennane, S. Coded PPM and Multipulse PPM and Iterative Detection for Free-Space Optical Links. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2009, 1, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.B.; Tahir, M. Joint rate-brightness control using variable rate MPPM for LED based visible light communication systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 4604–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, H.; Nosu, K. MPPM: A method for improving the band-utilization efficiency in optical PPM. J. Light. Technol. 1989, 7, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Park, Y. Data rate enhancement of optical camera communications by compensating inter-frame gaps. Opt. Commun. 2017, 394, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gong, C.; Xu, Z. Experimental indoor visible light positioning systems with centimeter accuracy based on a commercial smartphone camera. IEEE Photonics J. 2018, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.D.; Purwita, A.A.; Zeng, Z.; Haas, H.; Safari, M. Modeling the random orientation of mobile devices: Measurement, analysis and LiFi Use Case. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2019, 67, 2157–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, K. Tilt Sensing Using Linear Accelerometers. In Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN3107; Freescale Semiconductor Inc.: Austin, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Pham-Nguyen, L.; Thi, H.N.; Viet, S.N.; Lan, H.N.T.; Si, H.H. Performance Analysis and Experiment of Data Transmission Rate of LEDs in Optical Camera Communication for Indoor Positioning System. In Proceedings of the 2022 11th International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences (ICCAIS), Hanoi, Vietnam, 21–24 November 2022; pp. 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Schemes | Time (ms) | Accuracy | Distance | Mobile Phone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALISA [19] | Not given | <0.21 m (90th percentile) | 1 m | Galaxy S10+ |
| LiDR [20] | 16 | <0.7 m (mean) | 1.5 m | Huawei P30 Pro |
| Amari and Keche [21] | Not given | 2 cm (mean) | 1.6 m | Nokia Lumia 1020 |
| Luxapose [22] | 9040 | 7 cm | 2.5 m | Nokia Lumia 1020 |
| PIXEL [23] | 1200 | 30 cm | 1–3 m | Samsung Galaxy S II |
| Ours | 30 | ∼10 cm | 2.4 m | Vsmart Aris |
| Parameter r (r) | Brightness Index () | No. of Symbols () | Bits/Symbol () |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.125 | 8 | 3 |
| 2 | 0.250 | 28 | 5 |
| 3 | 0.375 | 56 | 6 |
| 4 | 0.500 | 70 | 7 |
| 5 | 0.625 | 56 | 6 |
| 6 | 0.750 | 28 | 5 |
| 7 | 0.875 | 8 | 3 |
| ID Name | Symbol to Encode () | LED-ID Code | Modulated LED-ID Code (Payload) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LED-ID1 | 10 | 1010 | 101011 |
| LED-ID2 | 9 | 1001 | 110011 |
| LED-ID3 | 6 | 0110 | 110101 |
| LED-ID4 | 3 | 0011 | 101110 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, D.Q.; Nguyen, H.N. Accurate, Extended-Range Indoor Visible Light Positioning via High-Efficiency MPPM Modulation with Smartphone Multi-Sensor Fusion. Photonics 2025, 12, 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090859
Nguyen DQ, Nguyen HN. Accurate, Extended-Range Indoor Visible Light Positioning via High-Efficiency MPPM Modulation with Smartphone Multi-Sensor Fusion. Photonics. 2025; 12(9):859. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090859
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Dinh Quan, and Hoang Nam Nguyen. 2025. "Accurate, Extended-Range Indoor Visible Light Positioning via High-Efficiency MPPM Modulation with Smartphone Multi-Sensor Fusion" Photonics 12, no. 9: 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090859
APA StyleNguyen, D. Q., & Nguyen, H. N. (2025). Accurate, Extended-Range Indoor Visible Light Positioning via High-Efficiency MPPM Modulation with Smartphone Multi-Sensor Fusion. Photonics, 12(9), 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090859






