Exploiting a Multi-Mode Laser in Homodyne Detection for Vacuum-Fluctuation-Based Quantum Random Number Generator
Abstract
1. Introduction
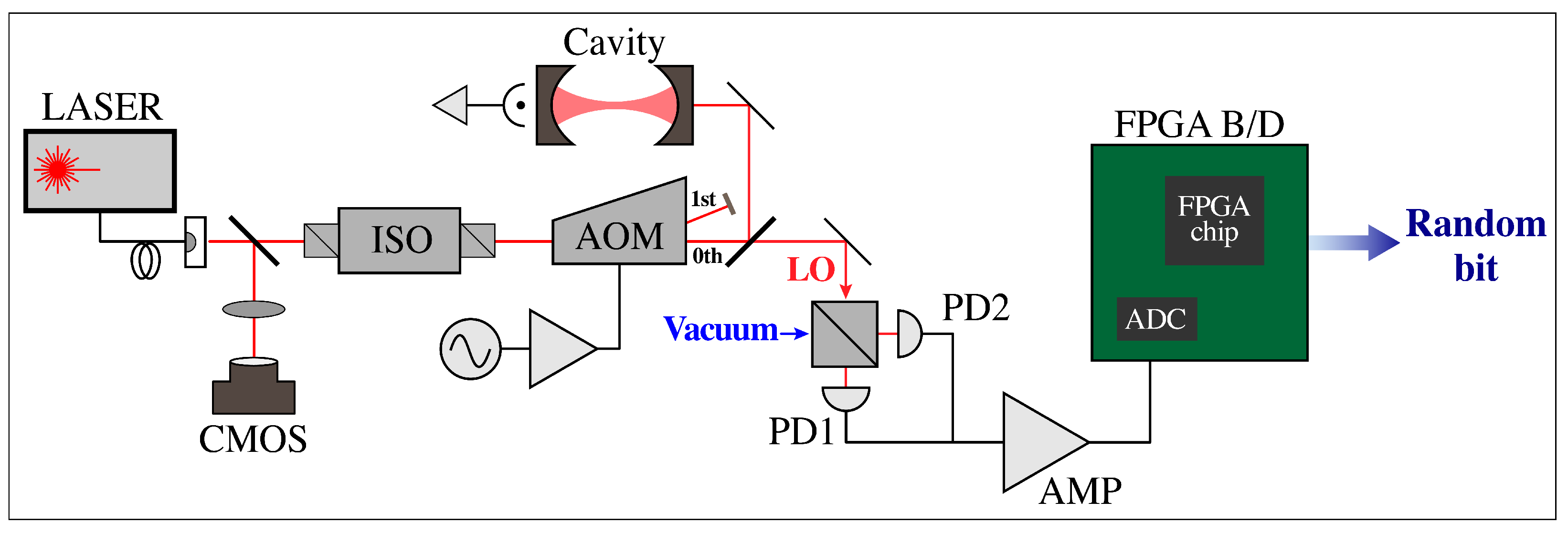
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Multi-Mode Lasers
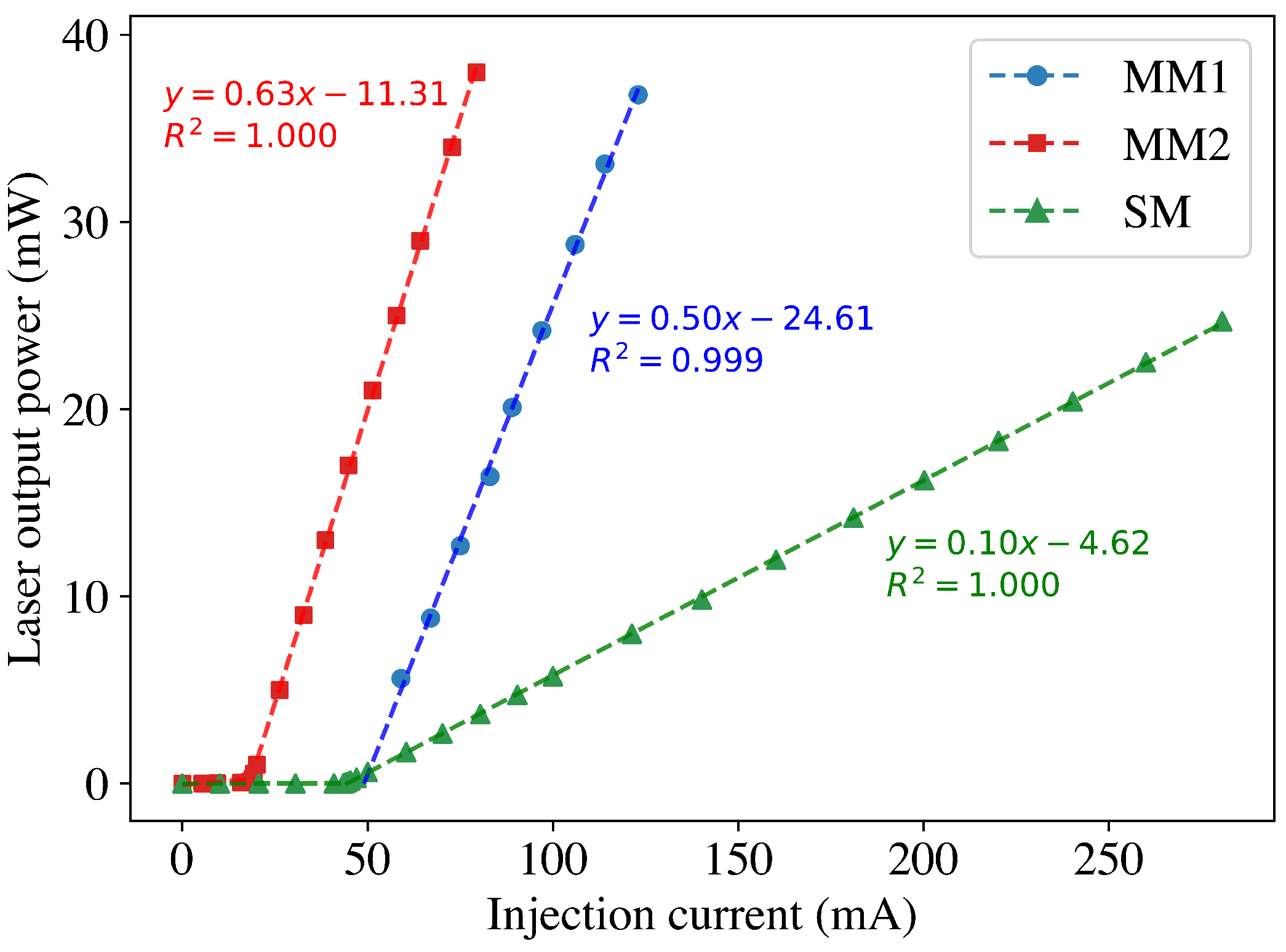
3.1.1. Optical Power Efficiency
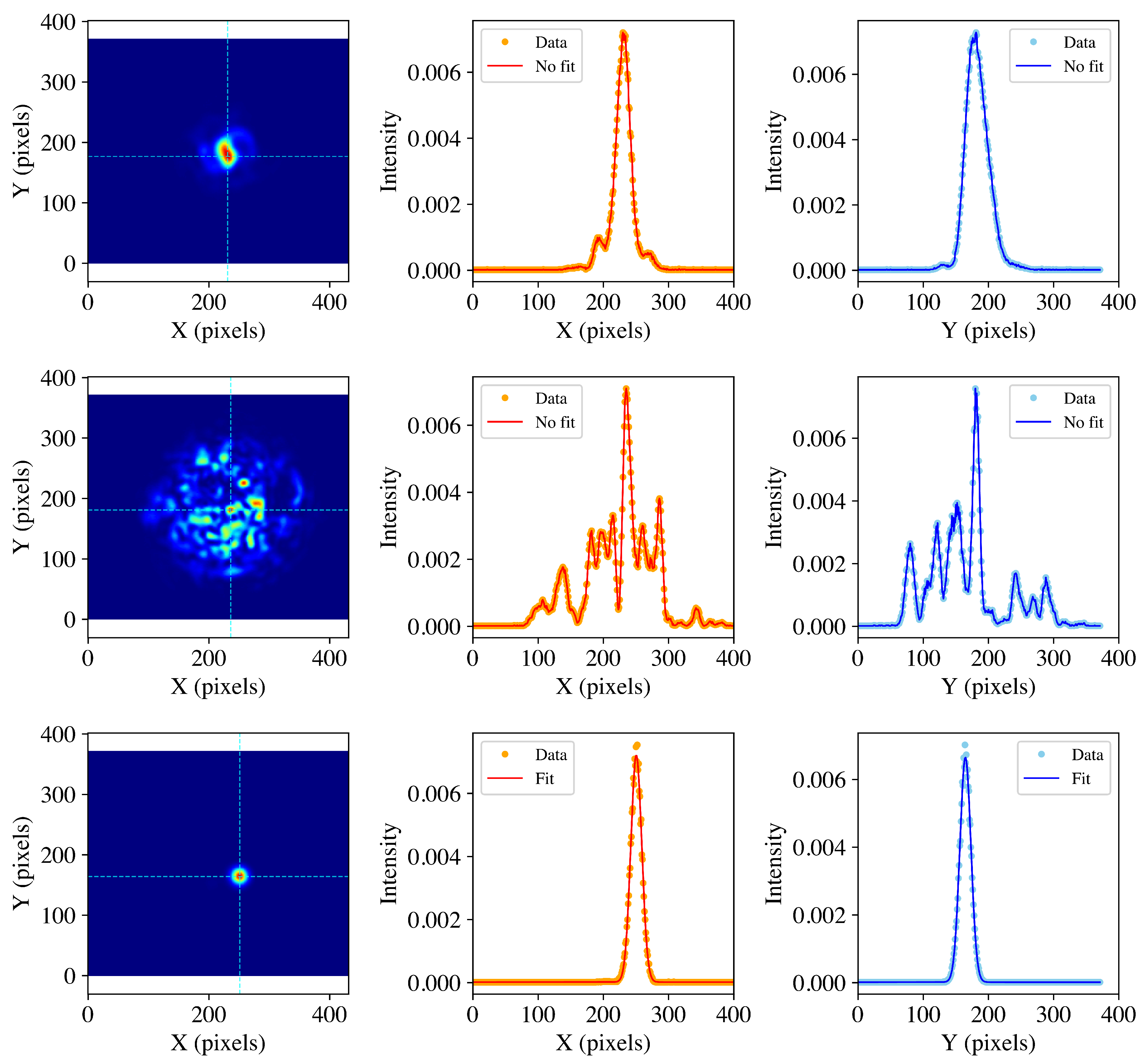
3.1.2. Transverse Mode
3.1.3. Longitudinal Mode
3.2. Analysis of Raw Entropy Data
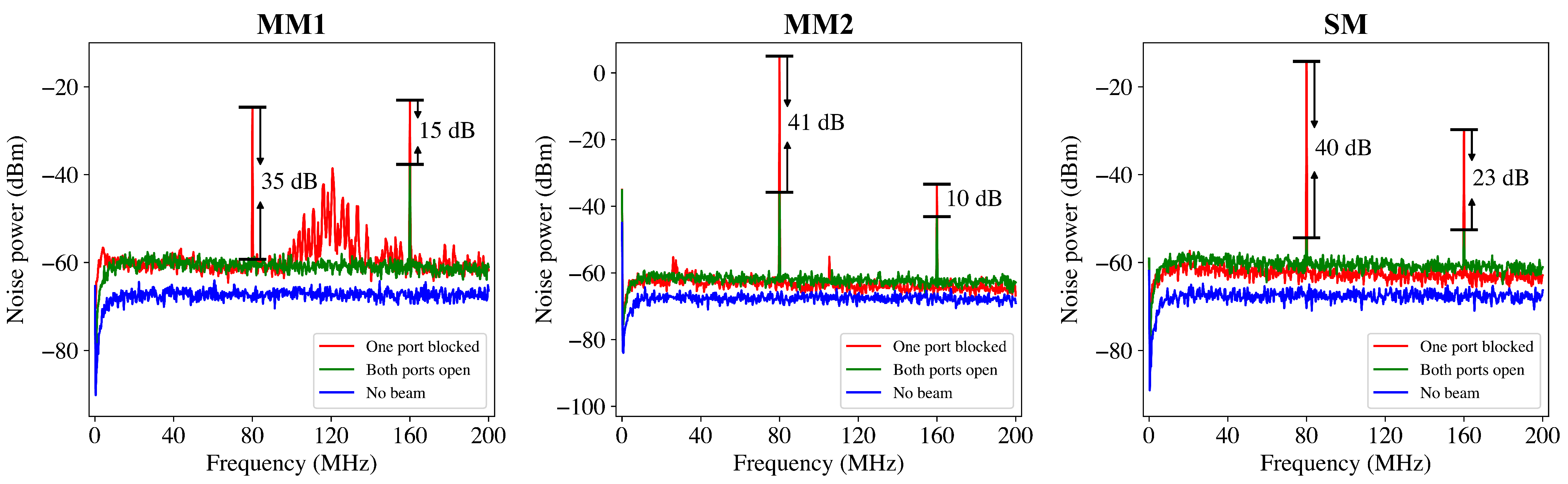
3.2.1. CMRR Comparison Between MM and SM
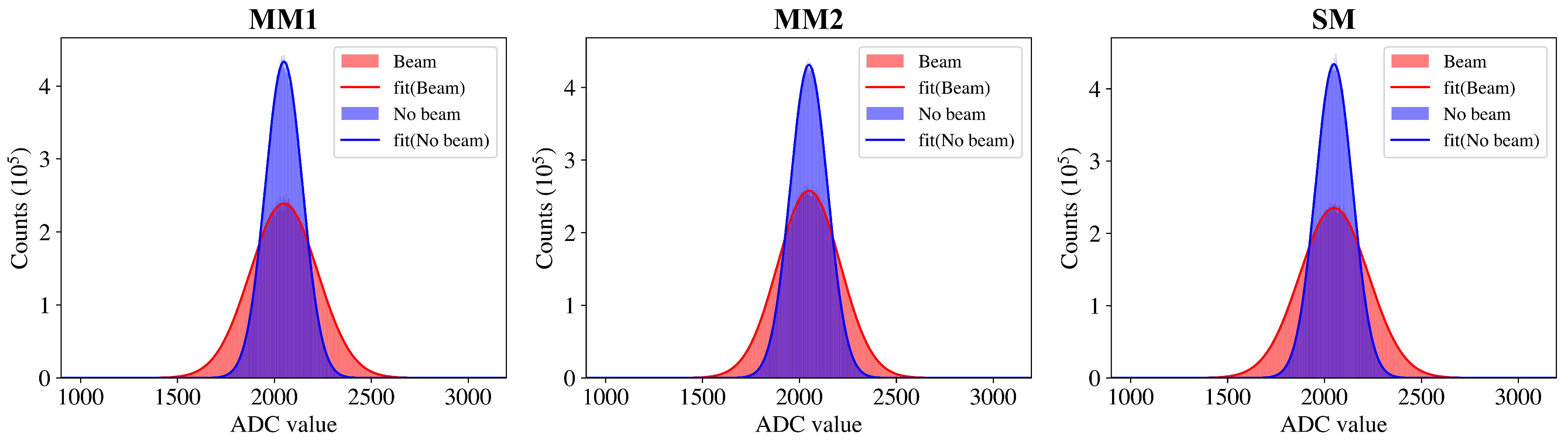
3.2.2. Min-Entropy and QCNR Estimation
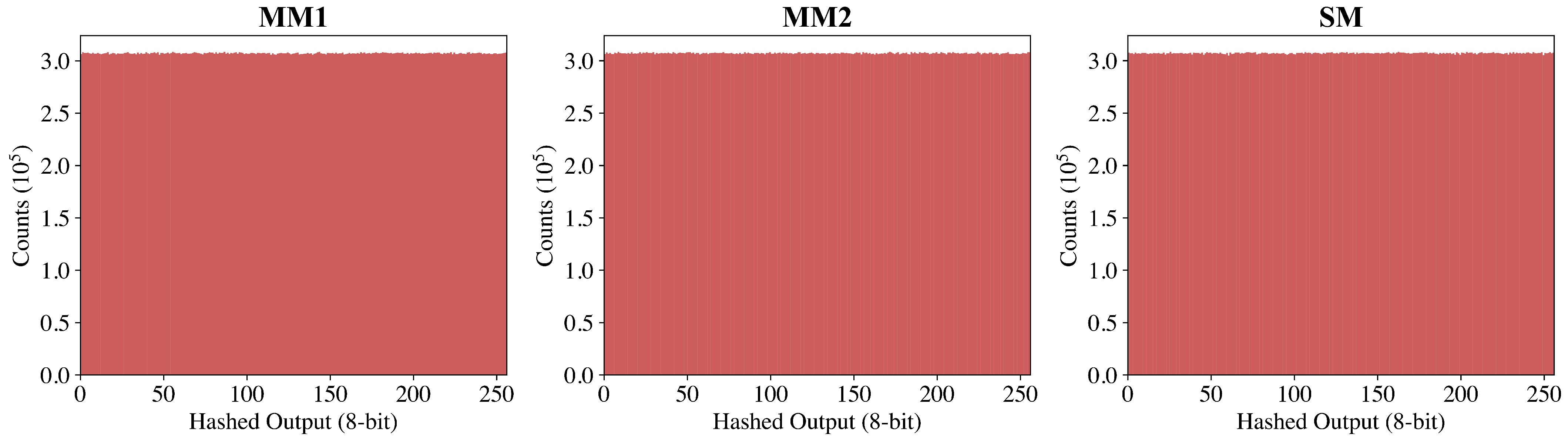
3.3. Full-Entropy Data Extraction Using SHA3-384
3.4. NIST Validation of Full-Entropy Data
3.4.1. Entropy and IID Assessment (SP 800-90B)
3.4.2. Statistical Test Suite (SP 800-22)
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bauke, H.; Mertens, S. Random numbers for large-scale distributed Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 066701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogorodnikov, V.A.; Prigarin, S.M. Numerical Modelling of Random Processes and Fields: Algorithms and Applications; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, S.; Beadling, P.; Ferencz, A. FPGA Implementation of Pseudo Random Number Generators for Monte Carlo Methods in Quantitative Finance. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Reconfigurable Computing and FPGAs, Cancun, Mexico, 3–5 December 2008; pp. 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, C.S.; Connelly, J.A. A noise-based IC random number generator for applications in cryptography. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 2000, 47, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stipčević, M. Quantum random number generators and their applications in cryptography. In Proceedings of the SPIE 8375, Advanced Photon Counting Techniques VI, Baltimore, MD, USA, 5–6 April 2012; Volume 837504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Ecuyer, P. Random numbers for simulation. Commun. ACM 1990, 33, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Ecuyer, P. Random Number Generation. In Handbook of Computational Statistics; Gentle, J.E., Härdle, W.K., Mori, Y., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 35–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H. Quantum-Mechanical Random-Number Generator. J. Appl. Phys. 1970, 41, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkassar, A.; Nicolay, T.; Rohe, M. Obtaining True-Random Binary Numbers from a Weak Radioactive Source. In Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2005; Gervasi, O., Gavrilova, M.L., Kumar, V., Laganà, A., Lee, H.P., Mun, Y., Taniar, D., Tan, C.J.K., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gude, M. Concept for a High Performance Random Number Generator Based on Physical Random Phenomena. Frequenz 1985, 39, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannalatha, V.; Mishra, S.; Pathak, A. A Comprehensive Review of Quantum Random Number Generators: Concepts, Classification and the Origin of Randomness. Quantum Inf. Process. 2023, 22, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Collantes, M.; Garcia-Escartin, J.C. Quantum random number generators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2017, 89, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, M.; Santori, C.; Spillane, S.M.; Beausoleil, R.G.; Munro, W.J. Secure self-calibrating quantum random-bit generator. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 75, 032334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennewein, T.; Achleitner, U.; Weihs, G.; Weinfurter, H.; Zeilinger, A. A fast and compact quantum random number generator. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2000, 71, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Wu, E.; Liang, Y.; Jian, Y.; Wu, G.; Zeng, H. Quantum random-number generator based on a photon-number-resolving detector. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 83, 023820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinetti, B.; Martin, A.; Zbinden, H.; Gisin, N. Quantum random number generation on a mobile phone. Phys. Rev. X 2014, 4, 031056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, M.A.; Jeffrey, E.R.; Akselrod, G.M.; Kwiat, P.G. Photon arrival time quantum random number generation. J. Mod. Opt. 2009, 56, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, M.; Leifgen, M.; Berlin, M.; Röhlicke, T.; Rahn, H.-J.; Benson, O. An ultrafast quantum random number generator with provably bounded output bias based on photon arrival time measurements. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 171105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Chi, Y.-M.; Lo, H.-K.; Qian, L. High-speed quantum random number generation by measuring phase noise of a single-mode laser. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.-Q.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Payne, F.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J.-W. The generation of 68 Gbps quantum random number by measuring laser phase fluctuations. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2015, 86, 063105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H. A Phase Fluctuation Based Practical Quantum Random Number Generator Scheme with Delay-Free Structure. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovic, V.; Marangon, D.G.; Lucamarini, M.; Yuan, Z.; Shields, A.J. Characterizing Phase Noise in a Gain-Switched Laser Diode for Quantum Random-Number Generation. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2021, 16, 054012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-Y.; Ding, Y.-Y.; Wang, S.; Yin, Z.-Q.; Chen, W.; He, D.-Y.; Huang, W.; Xu, B.-J.; Guo, G.-C.; Han, Z.-F. Compact Quantum Random Number Generation Using a Linear Optocoupler. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 3175–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, M.; Akbari, M.; Mirsadeghi, M.; Naeij, H.R.; Haghkish, N.; Hayeri, A.; Malekian, M. Quantum Random Number Generator Based on LED. J. Appl. Phys. 2024, 135, 084402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.R.S.; Salevan, J.C.; Li, X.; Roy, R.; Murphy, T.E. Fast Physical Random Number Generator Using Amplified Spontaneous Emission. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 23584–23597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyris, A.; Pikasis, E.; Deligiannidis, S.; Syvridis, D. Sub-Tb/s Physical Random Bit Generators Based on Direct Detection of Amplified Spontaneous Emission Signals. J. Light. Technol. 2012, 30, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Sanguinetti, B.; Lim, C.C.W.; Houlmann, R.; Zbinden, H. Quantum Random Number Generation for 1.25-GHz Quantum Key Distribution Systems. J. Light. Technol. 2015, 33, 2855–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Yang, J.; Fan, F.; Huang, W.; Li, D.; Xu, B. Compact Quantum Random Number Generator Based on Superluminescent Light-Emitting Diodes. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 123115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustard, P.J.; Moffatt, D.; Lausten, R.; Wu, G.; Walmsley, I.A.; Sussman, B.J. Quantum Random Bit Generation Using Stimulated Raman Scattering. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 25173–25180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, D.G.; Bustard, P.J.; Moffatt, D.J.; Nunn, J.; Lausten, R.; Sussman, B.J. Efficient Raman Generation in a Waveguide: A Route to Ultrafast Quantum Random Number Generation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 051117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.J.; Clark, A.S.; Xiong, C.; Mägi, E.; Steel, M.J.; Eggleton, B.J. Random Number Generation from Spontaneous Raman Scattering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 141112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, C.; Wittmann, C.; Sych, D.; Dong, R.; Mauerer, W.; Andersen, U.L.; Marquardt, C.; Leuchs, G. A Generator for Unique Quantum Random Numbers Based on Vacuum States. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tian, L.; Zou, H. Practical Quantum Random Number Generator Based on Measuring the Shot Noise of Vacuum States. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 063814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symul, T.; Assad, S.M.; Lam, P.K. Real-Time Demonstration of High Bitrate Quantum Random Number Generation with Coherent Laser Light. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 231103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, S.; Guo, H. 1.2-GHz Balanced Homodyne Detector for Continuous-Variable Quantum Information Technology. IEEE Photonics J. 2018, 10, 6803810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, H. Integrated Gbps Quantum Random Number Generator with Real-Time Extraction Based on Homodyne Detection. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2019, 36, B130–B136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Yu, S.; Guo, H. 6 Gbps Real-Time Optical Quantum Random Number Generator Based on Vacuum Fluctuation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 043105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, T.; Lupo, C.; Kordts, A.; Pacher, C.; Fürst, M.; Ricken, R.; Quiring, V.; Lenhard, A.; Mauerer, W.; Weinfurter, H.; et al. Homodyne-Based Quantum Random Number Generator at 2.9 Gbps Secure Against Quantum Side-Information. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Huang, J.; Qiao, G.-R.; Nie, Y.-Q.; Tang, W.; Chu, T.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J.-W. 18.8 Gbps Real-Time Quantum Random Number Generator with a Photonic Integrated Chip. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 264001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.J.; Silva, N.A.; Pinto, A.N.; Muga, N.J. Characterization of a Quantum Random Number Generator Based on Vacuum Fluctuations. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruynsteen, C.; Gehring, T.; Lupo, C.; Bauwelinck, J.; Yin, X. 100-Gbit/s Integrated Quantum Random Number Generator Based on Vacuum Fluctuations. PRX Quantum 2023, 4, 010330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, T.; Jia, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, X.; Shi, Y.; Wang, N.; Lu, Z.; Zou, J.; Li, Y. Compact Quantum Random Number Generator Based on a Laser Diode and a Hybrid Chip with Integrated Silicon Photonics. Photonics 2024, 11, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Standards and Technology. SHA-3 Standard: Permutation-Based Hash and Extendable-Output Functions; FIPS PUB 202; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Turan, M.S.; Barker, E.; Kelsey, J.; McKay, K.A.; Baish, M.L.; Boyle, M. Recommendation for the Entropy Sources Used for Random Bit Generation; NIST Special Publication 800-90B; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Rukhin, A.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.; Smid, M.; Barker, E.; Leigh, S.; Levenson, M.; Vangel, M.; Banks, D.; Heckert, A.; et al. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; NIST Special Publication 800-22 Rev.1a; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Hecht, E. The Laser. In Optics, 5th ed.; Pearson Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2017; Chapter 13.1.3; Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?title=Optics+Fifth&author=Hecht,+E.&publication_year=2017 (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Day, G.; Stubenrauch, D.F. Laser Far-Field Beam-Profile Measurements by the Focal Plane Technique; National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1978. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?title=Laser+Far-field+Beamprofile+Measurements+by+the+Focal+Plane+Technique&author=Day,+G.&author=Stubenrauch,+D.F.&publication_year=1978 (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Haw, J.Y.; Assad, S.M.; Lance, A.M.; Ng, N.H.Y.; Sharma, V.; Lam, P.K.; Symul, T. Maximization of Extractable Randomness in a Quantum Random-Number Generator. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2015, 3, 054004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, E.; Kelsey, J.; McKay, K.; Roginsky, A.; Sönmez Turan, M. Recommendation for Random Bit Generator (RBG) Constructions; NIST Special Publication 800-90C (4th Public Draft); National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2024. [CrossRef]

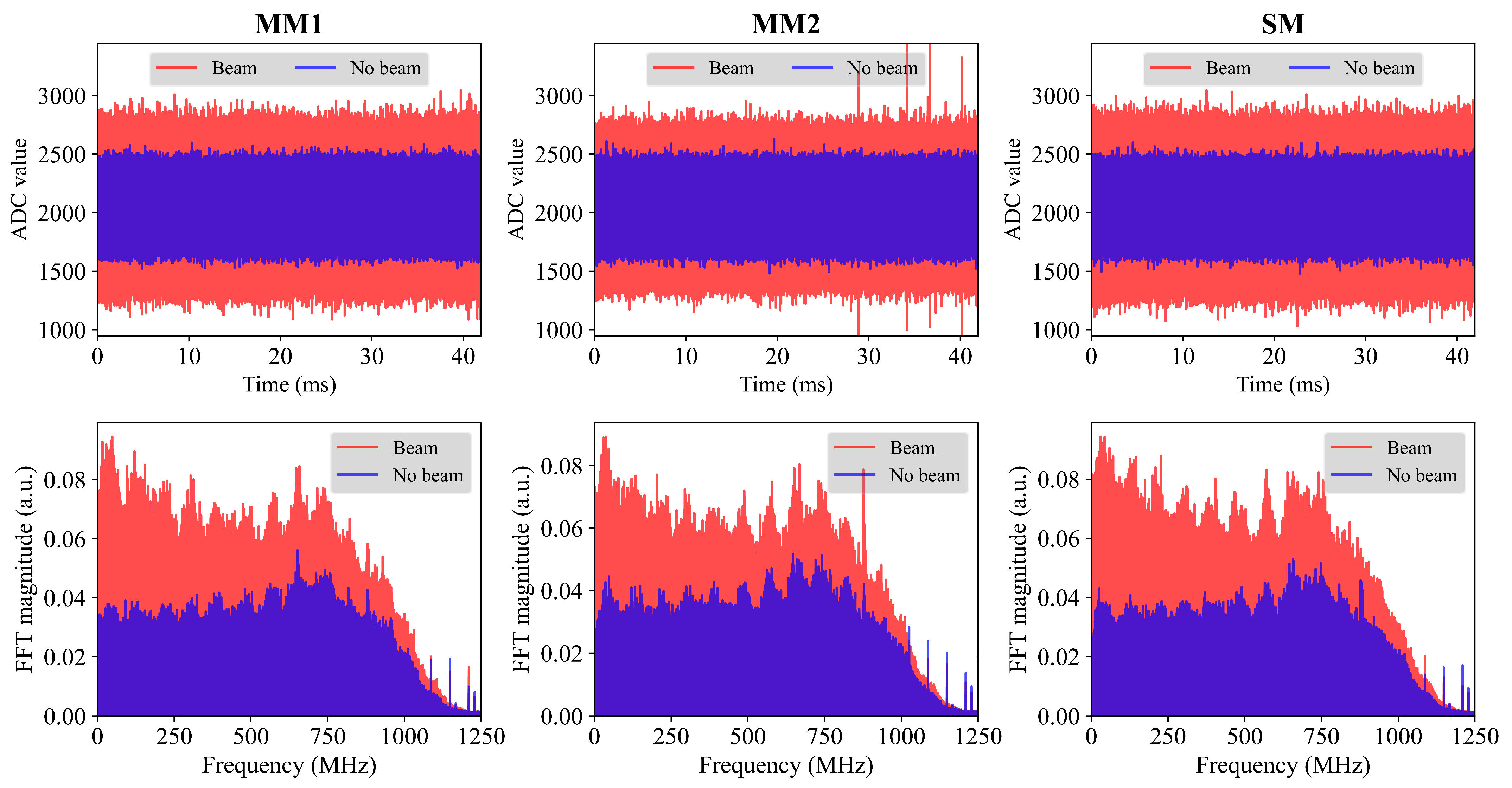
| MM1 | MM2 | SM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8.52 | 8.35 | 8.55 | |
| QCNR (dB) | 3.61 | 2.55 | 3.82 |
| MM1 | MM2 | SM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7.40 | 7.58 | 7.57 | |
| MM1 | MM2 | SM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7.986377 | 7.986643 | 7.986876 | |
| 0.999836 | 0.999840 | 0.999822 | |
| 7.986377 | 7.986643 | 7.986876 | |
| Chi-square test | Passed | Passed | Passed |
| LRS test | Passed | Passed | Passed |
| Permutation tests | Passed | Passed | Passed |
| Statistical Test | MM1 | MM2 | SM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prop. | p-Val. | Prop. | p-Val. | Prop. | p-Val. | |
| Frequency | 0.989 | 0.401 | 0.989 | 0.163 | 0.984 | 0.057 |
| Block Frequency | 0.987 | 0.666 | 0.984 | 0.883 | 0.983 | 0.699 |
| Cusum-Forward | 0.997 | 0.404 | 0.989 | 0.304 | 0.984 | 0.094 |
| Cusum-Reverse | 0.992 | 0.748 | 0.990 | 0.972 | 0.986 | 0.147 |
| Runs | 0.984 | 0.836 | 0.990 | 0.579 | 0.987 | 0.214 |
| Long Runs of Ones | 0.984 | 0.635 | 0.989 | 0.475 | 0.983 | 0.485 |
| Rank | 0.990 | 0.807 | 0.984 | 0.297 | 0.994 | 0.839 |
| Spectral DFT | 0.992 | 0.801 | 0.987 | 0.642 | 0.987 | 0.044 |
| Non-overlapping Templates | 0.989 | 0.725 | 0.992 | 0.936 | 0.984 | 0.602 |
| Overlapping Templates | 0.987 | 0.722 | 0.990 | 0.042 | 0.986 | 0.295 |
| Universal | 0.983 | 0.212 | 0.992 | 0.042 | 0.979 | 0.190 |
| Approximate Entropy | 0.979 | 0.466 | 0.992 | 0.247 | 0.987 | 0.844 |
| Random Excursions | 0.995 | 0.056 | 0.992 | 0.435 | 0.992 | 0.320 |
| Random Excursions Variant | 0.987 | 0.161 | 0.987 | 0.116 | 0.995 | 0.137 |
| Linear Complexity | 0.998 | 0.605 | 0.992 | 0.243 | 0.986 | 0.227 |
| Serial | 0.989 | 0.880 | 0.994 | 0.961 | 0.992 | 0.795 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Kim, S.; Park, C.; Choi, J.W. Exploiting a Multi-Mode Laser in Homodyne Detection for Vacuum-Fluctuation-Based Quantum Random Number Generator. Photonics 2025, 12, 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090851
Park S, Kim S, Park C, Choi JW. Exploiting a Multi-Mode Laser in Homodyne Detection for Vacuum-Fluctuation-Based Quantum Random Number Generator. Photonics. 2025; 12(9):851. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090851
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sooyoung, Sanghyuk Kim, Chulwoo Park, and Jeong Woon Choi. 2025. "Exploiting a Multi-Mode Laser in Homodyne Detection for Vacuum-Fluctuation-Based Quantum Random Number Generator" Photonics 12, no. 9: 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090851
APA StylePark, S., Kim, S., Park, C., & Choi, J. W. (2025). Exploiting a Multi-Mode Laser in Homodyne Detection for Vacuum-Fluctuation-Based Quantum Random Number Generator. Photonics, 12(9), 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090851





