Abstract
Accurate cerebral vasculature segmentation using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is critical for diagnosing and treating cerebrovascular diseases. However, conventional single-frame analysis methods often fail to capture fine vascular structures due to background noise, overlapping anatomy, and dynamic contrast flow. In this study, we propose a novel vessel-enhancing preprocessing technique using temporal differencing of DSA sequences to improve cerebrovascular segmentation accuracy. Our method emphasizes contrast flow dynamics while suppressing static background components by computing absolute differences between sequential DSA frames. The enhanced images were input into state-of-the-art deep learning models, U-Net++ and DeepLabv3+, for vascular segmentation. Quantitative evaluation of the publicly available DIAS dataset demonstrated significant segmentation improvements across multiple metrics, including the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC), Intersection over Union (IoU), and Vascular Connectivity (VC). Particularly, DeepLabv3+ with the proposed preprocessing achieved a DSC of 0.83 ± 0.05 and VC of 44.65 ± 0.63, outperforming conventional methods. These results suggest that leveraging temporal information via input enhancement substantially improves small and complex vascular structure extraction. Our approach is computationally efficient, model-agnostic, and clinically applicable for DSA.
1. Introduction
Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is crucial for diagnosing and treating cerebrovascular diseases, providing high-resolution, real-time intracranial vessel visualization [1,2]. DSA is the gold standard for detecting vascular pathologies, including aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, stenoses, and fistulas, often guiding therapeutic decisions when noninvasive techniques, such as computed tomography angiography and magnetic resonance angiography, are inconclusive [1]. Unlike static angiographic modalities, DSA provides excellent spatiotemporal resolution, capturing dynamic contrast through cerebral arteries and veins [3,4]. This enables real-time circulation observation, lesion hemodynamic evaluation, and endovascular procedure navigation, including thrombectomy and aneurysm coiling, using detailed roadmaps [4]. However, DSA sequence interpretation currently relies on manual frame-by-frame analysis by neurointerventional radiologists, which is labor-intensive, time-consuming, and subjective [5]. Automated DSA vessel segmentation could thus greatly assist clinical workflow by quantifying vascular anatomy and highlighting abnormalities for diagnosis and intervention planning.
Early studies on DSA segmentation focused on single frames or static composites, but these methods face critical limitations. Traditional techniques like thresholding and basic U-Net models can segment large vessels yet often misclassify static high-contrast structures such as skull edges or catheters [6,7,8]. Advanced architectures such as multiscale CNNs [9], dense networks [10], and edge-regularized models [11] have improved performance, while weakly supervised approaches using pseudolabels have been explored [12]. Nonetheless, single-frame methods struggle with low contrast in distal vessels, background artifacts, and anatomical overlap, leading to incomplete or unstable vessel maps. Since each frame captures only part of the contrast-filled vasculature, static segmentation frequently misses transient vessels [13], highlighting the need for sequence-based approaches that leverage temporal dynamics.
A DSA sequence is fundamentally a time series of images, and recent studies have utilized this temporal dimension to improve vascular segmentation [13]. Each frame captures contrast propagating through different vessel branches; integrating these frames reveals the full vascular anatomy and flow pattern [14]. Capturing such spatiotemporal dynamics can lead to more accurate segmentation than static frame analysis. The spatiotemporal U-Net, exemplified by the CAVE network, was one of the first models to process entire DSA sequences, significantly outperforming conventional U-Net and classical vessel filters on multicenter data [4]. Similarly, Wang et al. [15] proposed DSANet, which introduced a separate temporal encoding branch alongside spatial encoders to capture motion features across frames. By fusing temporal features, their model achieved state-of-the-art accuracy, outperforming single-frame methods. Despite these successes, sequence-based analysis presents challenges. Models must handle variable sequence lengths and complex motion patterns and require larger datasets and greater computational resources. The lack of publicly available annotated DSA sequences has also limited progress [13]. Moreover, as DSA is an invasive imaging modality, the availability of training data is more limited compared to noninvasive alternatives like retinal imaging. Nevertheless, with the emergence of datasets such as DIAS and DSCA and increasing evidence supporting the value of temporal information, there is a growing need to develop models that fully exploit the spatiotemporal nature of DSA.
Another important factor in DSA segmentation is the design of model inputs and preprocessing to enhance vessel visibility. Input preparation can significantly impact deep learning performance [16]. Traditional vessel enhancement methods, such as adaptive thresholding, segment vessels based on local intensity statistics [6], but they are highly sensitive to noise and intensity variations. Multiscale vesselness filters like the Frangi filter have also been used to highlight tubular structures; however, they require additional steps like thresholding or clustering, which introduce extra parameters and variability. For example, applying a Frangi filter followed by k-means clustering yields segmentation results that vary significantly depending on the binarization threshold [17]. These limitations highlight the drawbacks of fixed, handcrafted preprocessing: a single static filter cannot account for the variability in patient anatomy, contrast timing, or residual bone structures. To overcome this, researchers have developed trainable preprocessing modules. Iyer et al. [18] proposed the Angiographic Processing Network (APN) for coronary angiography, which learns optimal enhancement strategies jointly with a DeepLabv3+ backbone. This approach significantly improved segmentation by adapting contrast and denoising filters to each image. In cerebral DSA, Qin et al. [19] introduced a tensor completion method to separate background layers from angiograms. While effective in isolating vessel signals, this method may blur temporal information and reintroduce background noise, particularly if the background does not conform to low-rank assumptions. Additionally, tensor completion requires tuning multiple hyperparameters (e.g., lambda values, iteration counts), making results sensitive to parameter settings. Overall, both the content and quality of model inputs are critical. Preprocessing techniques that effectively emphasize vascular structures can enhance segmentation, but methods must also handle variability and noise robustly to be clinically reliable.
In this study, we propose a novel input design that leverages temporally differenced DSA images for driving deep learning segmentation. While previous approaches in cerebrovascular segmentation have focused predominantly on single-frame DSA analysis or handcrafted enhancement techniques, they often fall short in capturing the full extent of dynamic vascular structures, particularly in cases with complex hemodynamics or subtle microvessels. Our proposed method introduces a novel preprocessing strategy that leverages temporal differencing between sequential DSA frames to emphasize dynamic contrast flow and suppress static anatomical backgrounds.
This approach is fundamentally distinct from prior vessel enhancement techniques in the following key aspects:
- (1)
- Temporal flow sensitivity: Rather than relying on static frame-wise vesselness filters (e.g., Frangi or thresholding), we harness inter-frame intensity changes to detect perfusion dynamics, which directly reflect physiological blood flow;
- (2)
- Model-agnostic enhancement: The preprocessing output is compatible with any deep learning segmentation model, providing architecture-independent performance gains;
- (3)
- Topology-preserving enhancement: By amplifying time-variant vascular structures, the method significantly improves the connectivity of thin and branching vessels.
From a clinical perspective, this method offers several advantages:
- (1)
- Improved microvessel detection: Enhancing vessels that transiently opacify during contrast flow increases the detection sensitivity for pathologies involving fine vasculature, such as collateral circulation in ischemic stroke or microaneurysms;
- (2)
- Reduction of false positives: Suppressing static non-vascular structures (e.g., bones, catheter artifacts) mitigates misclassification, thereby reducing clinician burden in post-processing;
- (3)
- Feasibility for real-time application: The proposed technique is computationally efficient and can be integrated into existing clinical pipelines with minimal overhead, potentially enabling near real-time cerebrovascular assessment.
Our work presents a novel and efficient preprocessing pipeline that enhances static segmentation with temporal information, enabling more accurate and robust cerebrovascular delineation. This innovation lays the groundwork for broader applications in real-time interventional imaging and AI-assisted diagnostics in neurovascular care.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Proposed Cerebrovascular Extraction Technique in Time-Series DSA Images
Figure 1 shows the proposed framework for cerebrovascular extraction using a time-series DSA image.
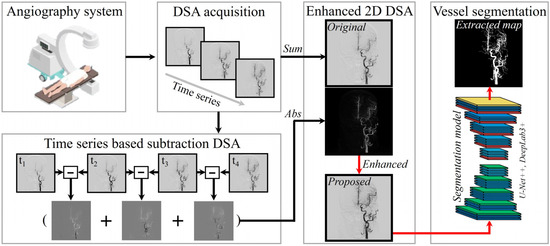
Figure 1.
Simplified framework for an improved vascular extraction method that utilizes differential images of time-series DSA images.
Initially, the DSA image was acquired in real time using an angiography system. Assuming the initially acquired DSA image was denoted , subsequent images were acquired up to the nth image (, depending on the frame acquisition performance of the system. To emphasize the vascular characteristics, the absolute value of the summed differences between consecutive DSA images in the time series was calculated, as expressed in Equation (1):
The absolute value was used to isolate contrast agent-induced changes, as the intensity of the regions through which the contrast agent has passed may be reversed. Subsequently, an angiographic information change map, , was obtained, and a minimal intensity projection (MinIP) image was obtained from a time-series DSA image. MinIP images (or original images) incorporate information from all frames to show complete angiography [2]. Obtaining an appropriate number of frames during MinIP image acquisition can improve vascular contrast. However, a high-performance DSA imaging system capable of extended acquisition may be required, or increased radiation exposure may not be allowed in clinical practice due to patient safety concerns. Therefore, we tried to overcome this problem through t* map. The original image and t* map were processed through an elemental multiplication operation (), as shown in Equation (2), to generate a blood-vessel-enhanced image.
When the process in Equation (2) is performed, the noise amplification problem [20]—a known limitation of conventional enhancement algorithms—could be overcome, as it selectively emphasizes angiographic regions exhibiting high rate of change. Figure 2a illustrates the step-by-step construction and enhancement process of the vessel-specific image used for segmentation. The leftmost image represents the conventional 2D MinIP image, which is a static projection combining the lowest intensity values across a time-series DSA sequence. While MinIP images provide a comprehensive overview of vascular anatomy, they also retain non-vessel background structures with minimal contrast change, such as bones, catheters, or overlapping tissues, which can confuse segmentation models. The middle image shows the temporal difference map, created by computing the absolute sum of intensity differences between consecutive DSA frames. This map captures regions where contrast intensity changes over time, which corresponds directly to the passage of contrast medium through blood vessels. In contrast, background regions with static intensity across frames are suppressed. This difference map, denoted as , effectively isolates dynamic vascular signals from static anatomical noise. The rightmost image is the vessel-enhanced image, generated by performing an element-wise multiplication between the MinIP image and the temporal difference map. This process increases the relative intensity of pixels corresponding to dynamically opacified vessels while attenuating static background components. As a result, the final image delivers enhanced contrast in both large and small vessels, which may otherwise be overlooked due to low intensity or overlapping structures in the original MinIP image.
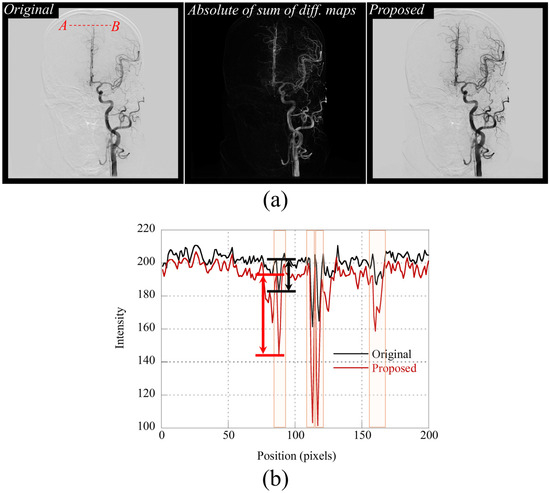
Figure 2.
(a) Illustrative images: 2D MinIP original image (left), the absolute map of the sum of differential images (middle), and the vessel-enhanced image (right) through the proposed method. (b) Intensity profiles drawn along the A–B line in (a).
This enhancement mechanism introduces novel information into the segmentation model:
- (1)
- It provides temporal context not present in static MinIP images;
- (2)
- It emphasizes regions of active contrast perfusion, aligning closely with true vascular structures;
- (3)
- It reduces the influence of irrelevant structures that remain static across frames.
By combining spatial and temporal cues into a single enhanced input, the model can better learn vessel boundaries and connectivity, especially for fine or distal vessels. Figure 2b shows the intensity profiles along the A–B line in Figure 2a. The red and black curves represent the intensity distributions of the proposed and original MinIP images, respectively. The difference in intensity across vessel boundaries is approximately twice as high in the proposed method compared to the original, indicating improved vessel-to-background contrast. This enhanced contrast facilitates better discrimination of microvascular structures by the segmentation network.
The proposed method was implemented in MATLAB (MathWorks, R2023a, Natick, MA, USA). Subsequently, cerebrovascular extraction was performed on the preprocessed images using a deep learning model.
2.2. DSA Sequences Dataset
This study utilized the Digital Subtraction Angiography Intracranial Artery Segmentation dataset (DIAS) [13], a publicly available benchmark for intracranial artery segmentation in DSA sequences. The images were acquired at the Beijing Tiantan Hospital during routine neurointerventional procedures performed between January 2019 and December 2021. All DSA sequences were anonymized and retrospectively collected with ethical approval.
From an original pool of over 1000 sequences, 120 DSA sequences (totaling 762 arterial phase frames) were selected according to the following inclusion criteria: clear arterial phase representation, minimal motion artifacts, and absence of duplication. Each sequence consisted of 4–14 frames captured at a fixed frame rate of 4 fps. All images had a resolution of 800 × 800 pixels and were obtained from either anteroposterior or lateral views. These sequences focused on patients diagnosed with intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (ICAS) or middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO).
To ensure annotation quality, each DSA frame was meticulously labeled by two medical students and subsequently verified by two experienced neurosurgeons. The annotations followed a semi-automatic protocol: initial keyframes from the early and late arterial phases were fully annotated, then the annotations were propagated across the entire sequence. This approach enabled efficient and accurate generation of ground-truth vessel masks. Additionally, two types of weak labels—including scribble annotations from novice users (SALE) and randomized skeleton-based drawings (RDFA)—were included to facilitate weakly supervised segmentation. Further dataset details are available in [13].
Publicly available datasets were used for this study. This retrospective study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Gachon University (1044396-202503-HR-051-01), which granted a waiver of informed consent due to the retrospective design. The IRB approval was issued on 2 April 2025.
2.3. Model Architecture and Training Conditions
The U-Net++ (L3) model [21] featured an encoder–decoder structure with a symmetrical design. The encoder path comprised sequential 3 × 3 convolutional layers, followed by ReLU activation [22], batch normalization [23], and max pooling layers for downsampling. The decoder path reversed this process through upsampling followed by convolution operations. U-Net++ incorporated nested and dense skip connections along with deep supervision, enabling refined multiscale feature aggregation and accelerated inference.
DeepLabv3+ is a state-of-the-art semantic segmentation model that combines atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) with an encoder–decoder architecture to capture multiscale contextual information while preserving spatial localization accuracy [24]. The backbone network employed for feature extraction was ResNet-50 [25], which delivered a robust initial representation. The total number of parameters in the DeepLabv3+ network with this configuration was approximately 43.9 million, significantly higher than the U-Net++ L3 model (12.1 million), thereby enabling deeper feature representation and improved performance in segmenting complex vascular structures. The encoder module comprised ResNet-50, which extracted hierarchical features through successive convolutional layers. The ASPP module employed parallel atrous (dilated) convolutions with varying rates to process multiscale contextual features, supplemented by global average pooling to capture image-level context. These features were then concatenated and passed to the decoder module, which applied bilinear up-sampling and 3 3 convolutions to refine the segmentation map to the original input resolution. Compared to U-Net++, which depended on nested skip connections and deep supervision, DeepLabv3+ utilized spatial pyramid pooling and encoder–decoder refinement, enhancing the detection of thin and branching vessels while maintaining computational efficiency. This architecture demonstrated particular efficacy in handling the morphological variability of intracranial vasculature in DSA sequences.
For model training, 188 augmented DSA images partitioned into training (73%), validation (11%), and test sets (16%) were used. The original 800 800-pixel images were cropped to 256 256-pixel patches for model input. Data augmentation included five-fold replication through random rotations (90°, 180°, and 270°) and horizontal flipping to enhance generalization across vessel orientations and anatomical variations.
Training was performed using the PyTorch framework (version 2.5.1) on a workstation running Windows 10 OS, a 2.13 GHz CPU, 128 GB of RAM, and an NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPU with 24 GB of RAM. The Adam optimizer was employed [26] with an initial learning rate of 1 × 10−5, and the categorical cross-entropy loss function was used for multi-class segmentation supervision. The model underwent training for 500 epochs with a batch size of 20.
2.4. Performance Evaluations
The quantitative performance of the proposed method was evaluated using established image segmentation metrics, providing a comprehensive assessment of accuracy, overlap, and topological integrity.
The Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) [27] and Intersection over Union (IoU) [28] were used to quantify the overlap between the segmented results and the ground-truth. DSC, defined as
where denotes the segmented image, and represents the reference image and is the degree of spatial overlap. Values closer to 1 indicate a higher accuracy. IoU, a stricter criterion than DSC, is given by
Both the DSC and IoU ranged from 0 to 1, with higher values indicating better segmentation performance.
In addition to the overlap metrics, traditional classification metrics were used to evaluate the pixel-level performance: accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and F1-score (F1) [29]. These are defined as follows.
TP, TN, FP, and FN represent true positives, true negatives, false positives, and false negatives, respectively. Accuracy offered a general indication of the overall prediction performance; however, in the presence of a class imbalance, such as a dominant background, its interpretability might be limited. Sensitivity quantified the ability of the model to correctly identify positive instances, which was crucial for minimizing false negatives. Specificity measured the proportion of true negatives that were accurately filtered, which was important for preventing unnecessary diagnoses. Precision evaluated the reliability of positive predictions. F1, as the harmonic mean of precision and sensitivity, provided a more balanced assessment of the overall model performance, particularly when data imbalance was present.
Finally, Vascular Connectivity (VC) [30] was used to evaluate the preservation of true vessel topology in predicted segmentations, particularly focusing on thin and branching vessels due to their clinical significance. The VC metric is defined as
where N represents the number of vessel segments, and and denote the ground-truth and predict centerlines of the p-th vessel segment, respectively. CE(⋅) computes the connectivity error between the predicted and ground-truth vessel trees, typically using geodesic or skeleton-based distance metrics. Lower VC values indicate superior connectivity. This metric was particularly valuable because high Dice or IoU scores might mask missed small vessels, whereas VC explicitly penalizes disconnected or fragmented vessel structures.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 3a,b display the MinIP DSA images and U-net++ segmentation results. In the vascular extraction results, green represented the reference map, pink indicated the model-extracted map, and white showed areas of overlap between the reference and prediction maps. The proposed method, using vessel-enhanced images as input, showed a higher cerebrovascular extraction accuracy compared to the baseline DSA image. Notably, Figure 3b reveals marked improvement in non-vascular region exclusion, confirming the preprocessing method’s significant performance in vascular extraction.
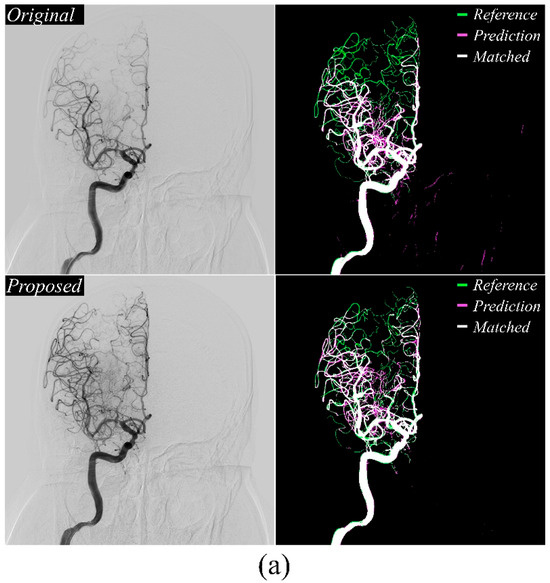
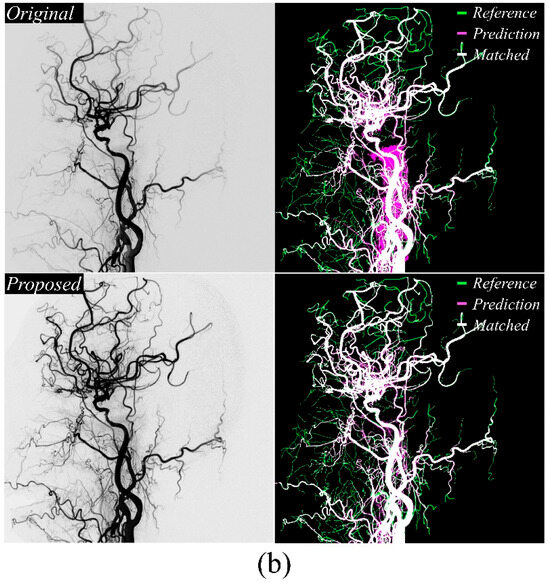
Figure 3.
Segmentation results based on the U-Net++ model are visualized. (a,b) illustrate the reference maps from the acquired DSA X-ray images with the segmentation outputs from both existing and newly proposed methods. The proposed method demonstrates a notable reduction in extravascular extraction errors during vessel segmentation.
Figure 4a,b present DeepLabv3+ cerebrovascular extraction results. The proposed method improved small vessel detection accuracy relative to conventional approaches and significantly reduced false-positive extractions in non-vascular regions, mirroring the performance gains observed with U-Net++.
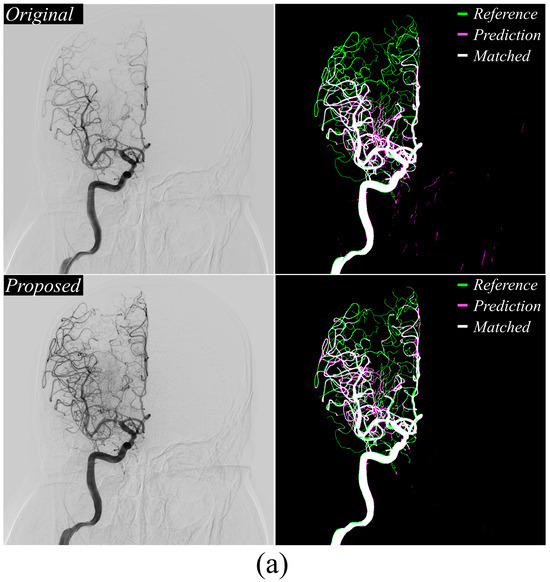
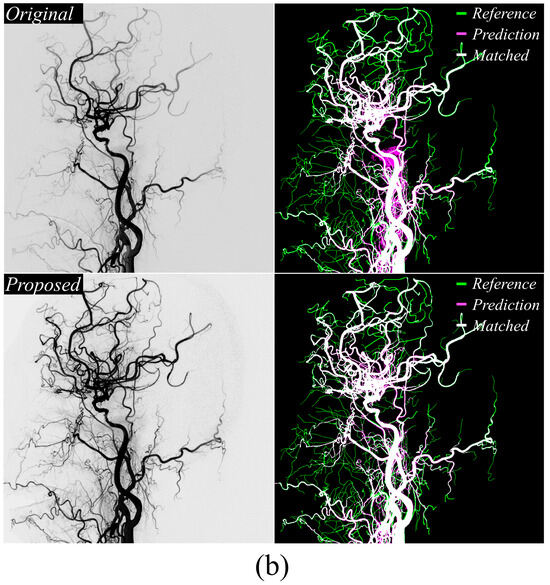
Figure 4.
Visualization of segmentation results of using the DeepLabv3+ model in (a) large vessel occlusion case and (b) normal case. They display the reference maps from the acquired DSA X-ray images with the segmentation outputs produced by the conventional and proposed methods. The application of the proposed approach demonstrated enhanced accuracy in microvessel extraction.
Table 1 summarizes the quantitative segmentation performance of the evaluated models, including U-Net++ and DeepLabv3+. Across all metrics, including DSC, IoU, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, F1-score, and VC, the proposed method consistently outperformed baseline approaches. For the U-Net++ model, the proposed method achieved a DSC of 0.79 ± 0.05, IoU of 0.68 ± 0.05, and VC of 65.46 ± 3.75, demonstrating significant improvement over the original input configuration (DSC: 0.71 ± 0.07; IoU: 0.56 ± 0.03; VC: 73.61 ± 5.83). Similarly, with DeepLabv3+, the proposed method yielded the highest overall scores, achieving a DSC of 0.83 ± 0.05, IoU of 0.70 ± 0.07, and F1-score of 0.92 ± 0.03, confirming its superior segmentation across both large and small vessel regions. Notably, the proposed method improved VC by approximately 31.90% when comparing DeepLabv3+ with U-Net++, with an absolute VC difference of 20.81 (from 65.46 ± 3.75 in U-Net++ to 44.65 ± 0.63 in DeepLabv3+). This substantial enhancement suggested that vessel-enhancing preprocessing substantially improved the topological continuity of segmented vessels, particularly for thin and branching microvascular structures.

Table 1.
Quantitative evaluation of vessel segmentation performance using the proposed preprocessing method with U-Net++ and DeepLabv3+ models.
These results demonstrated that the proposed preprocessing and input design significantly improve segmentation accuracy, particularly for fine and low-contrast vessels often missed by conventional approaches. Therefore, this method is particularly advantageous for microvessel extraction in cerebrovascular DSA sequences.
When an image of 800 800 pixels was secured with an average of 6 frames, about 0.04 s for MinIP and about 0.07 s for the proposed method were required. This indicates that the proposed method will not have much difficulty applying it to actual clinical practice, and if faster image processing is required, parallel processing and processing using a GPU can be considered.
However, a few limitations persist. First, the method intrinsically depended on the quality and temporal consistency of the acquired image series, despite its effectiveness in enhancing vascular structures through temporal differencing in DSA sequences [3,31]. In clinical practice, DSA sequences were frequently compromised by motion artifacts, variations in contrast injection timing, and irregular frame intervals. These issues could result in frame misalignment or irregular contrast propagation, corrupting the subtraction process and ultimately reducing segmentation accuracy. Misalignments might introduce spurious intensity changes in non-vascular regions, leading to false-positive results or distorted vessel morphology. Cerebrovascular images are highly sensitive to minor frame-to-frame inconsistencies due to the fine-scale branching patterns of cerebral vessels. To mitigate this, integrating explicit motion compensation strategies—such as image registration or temporal stabilization—as a preprocessing step prior to differencing could reliably enhance vascular structures.
Second, the algorithm inherently assumes uniform vascular signal changes across frames, which may not hold true in cases of delayed or pathological blood flow. In patients with severe stenosis, occlusion, or collateral circulation, contrast propagation through the vessels may be significantly delayed or spatially heterogeneous. Consequently, the temporal subtraction strategy may fail to capture vessels that opacify later or misclassify them as background, potentially leading to incomplete vascular segmentation, particularly in clinically critical regions. For example, time-resolved DSA analysis in acute ischemic stroke cases revealed delayed opacification of collateral vessels, which might have been overlooked if only early-phase frames or uniform temporal assumptions were considered [32]. To address this limitation, future implementation could incorporate temporally weighted subtraction or adaptive time-window selection methods to improve robustness in such clinical scenarios.
Third, the proposed preprocessing method’s use of absolute difference images may inadvertently amplify not only vascular signals but also the background noise and irrelevant fine structural textures. When imaging conditions are fixed, acquiring a greater number of frames can help reduce quantum noise and enhance vascular contrast. Conversely, a smaller number of frames may lead to increased noise levels, making vessel extraction more challenging. In this study, sequential DSA data consisting of five frames were used for analysis. Although denoising techniques, including non-local filters, are applied to suppress random noise prior to segmentation, residual elements—such as calcified tissue boundaries, catheter artifacts, or bone edges—may persist and interfere with accurate vessel extraction [33]. This effect becomes more pronounced in low-contrast regions or near anatomical structures with intensities comparable to those of vessels, leading to false positives in the segmentation output. Moreover, the absolute differencing approach inherently lacks flow-direction awareness. Specifically, it interprets any temporal intensity change as a potential vessel, irrespective of whether contrast flows forward, backward, or swirls. Consequently, in cases of abnormal hemodynamics—such as reflux, collateral retrograde filling, or turbulent flow—the algorithm may fail to delineate true vessel structures or misidentify flow artifacts as vessels. This limitation is particularly relevant in complex cerebrovascular pathologies, such as arteriovenous malformations or fistulas, where directional information is crucial for precise segmentation [34,35]. Future studies should explore integrating flow-sensitive metrics or direction-aware temporal differencing to mitigate this issue. In addition, there are plans to check the robustness of the proposal method according to changes in frame and x-ray tube current.
Finally, although the proposed preprocessing method demonstrated significant improvements in segmentation performance for the U-Net++ and DeepLabv3+ models, its generalizability across a broader range of deep learning architectures and imaging modalities remains unverified. To date, the method has only been evaluated on cerebral DSA sequences, and its applicability to other angiographic domains, including the coronary, peripheral, or abdominal vasculature, has not been established. In addition, variations in image resolution, noise profiles, and contrast injection protocols across different imaging systems may limit the current approach’s robustness. The dataset used in this study has difficulty in implementing these various situations, and it is necessary to perform model verification by establishing various dataset environments. In the current framework, the preprocessing and segmentation stages are handled separately, rather than being integrated into a unified end-to-end trainable system. This modular structure limits the model’s ability to simultaneously learn enhancement and segmentation features, which recent studies have shown to be beneficial. Incorporating learnable preprocessing layers or designing dual-branch architectures that jointly optimize both tasks could lead to more adaptive and data-driven vascular segmentation. Therefore, future studies should focus on incorporating the proposed enhancement mechanism into a fully differentiable framework to enable end-to-end training using the various datasets for better generalization and scalability.
In addition to the proposed temporal differencing approach, conventional contrast enhancement techniques such as histogram equalization and CLAHE can be considered for improving vascular visibility [36,37]. However, these methods rely solely on the redistribution of spatial intensity values and do not incorporate temporal information, which is critical for identifying dynamically opacified vessels in DSA sequences. As such, their effect is generally non-specific and may also enhance background noise or static anatomical structures. In contrast, our method emphasizes regions with temporal intensity changes, inherently aligning with the physiological behavior of contrast flow. Notably, these techniques are not mutually exclusive. It is possible to apply histogram equalization methods on top of our vessel-enhanced images to further enhance contrast, especially in low-contrast or distal vessel regions. Exploring such hybrid enhancement strategies and their effect on both visual quality and deep learning-based segmentation performance is a promising avenue for future research.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we propose a novel preprocessing method to enhance vascular segmentation performance in DSA sequences using the absolute differences between temporally sequential images. By emphasizing dynamic contrast flow and suppressing static background structures, the proposed method significantly improved segmentation outcomes in deep learning architectures such as U-Net++ and DeepLabv3+. Quantitative evaluations demonstrated significant gains in key performance metrics, including the DSC, IoU, and VC, particularly for fine vessel structures, which are typically challenging to extract. Our findings suggest that effective integration of temporal information through tailored input enhancement substantially improves the neural network’s ability to segment vascular regions in complex angiographic datasets. This method was computationally efficient and compatible with existing segmentation models, offering a practical solution for clinical DSA applications requiring high-precision microvascular delineation. In conclusion, this work contributed a robust, interpretable, and model-agnostic preprocessing technique that significantly enhanced deep-learning-based vascular segmentation and offers promising broader utilization in time-resolved angiographic imaging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: T.H., K.K. and Y.L.; methodology: T.H., S.H. and H.K.; software: E.D., H.K. and K.K.; validation: T.H., S.H. and Y.L.; formal analysis: T.H., S.H., H.K. and K.K.; investigation: E.D., H.K. and K.K.; writing—original draft preparation: T.H. and S.H.; writing—review and editing: K.K. and Y.L.; project administration: Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education (RS-2023-00239193).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Gachon University Institutional Review Board (1044396-202503-HR-051-01, approval date: 2 April 2025).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this study will be available upon request by the authors.
Acknowledgments
Thank you very much, Liu et al. research team, for providing the time-series DSA dataset.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| DSA | digital subtraction angiography |
| DSC | Dice Similarity Coefficient |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
| VC | Vascular Connectivity |
| CNN | convolution neural network |
| APN | Angiographic Processing Network |
| MinIP | minimal intensity projection |
| DIAS | Digital Subtraction Angiography Intracranial Artery Segmentation dataset |
| ICAS | intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis |
| MCAO | middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| SALE | scribble annotations from novice users |
| RDFA | randomized skeleton-based drawings |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| ASPP | atrous spatial pyramid pooling |
References
- Shaban, S.; Huasen, B.; Haridas, A.; Killingsworth, M.; Worthington, J.; Jabbour, P.; Bhaskar, S.M.M. Digital subtraction angiography in cerebrovascular disease: Current practice and perspectives on diagnosis, acute treatment and prognosis. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2022, 122, 763–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.H.; Jang, D.K.; Cho, B.R. Complications and risk factors after digital subtraction angiography: 1-year single-center study. J. Cerebrovasc. Endovasc. Neurosurg. 2022, 24, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, Q.; Mou, L.; Zhang, D.; Chen, D.; Shan, C.; Zhao, Y.; Su, R.; Guo, M. DSCA: A digital subtraction angiography sequence dataset and spatio-temporal model for cerebral artery segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2025, 44, 2515–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; van der Sluijs, P.M.; Chen, Y.; Cornelissen, S.; van den Broek, R.; van Zwam, W.H.; van der Lugt, A.; Niessen, W.J.; Ruijters, D.; van Walsum, T. CAVE: Cerebral artery-vein segmentation in digital subtraction angiography. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2024, 115, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakeda, S.; Korogi, Y.; Ohnari, N.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Moriya, J.; Oda, N.; Nishino, K.; Miyamoto, W. 3D digital subtraction angiography of intracranial aneurysms: Comparison of flat panel detector with conventional image intensifier TV system using a vascular phantom. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 839–843. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Cao, X.; Xu, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, H. An integrated global and local thresholding method for segmenting blood vessels in angiography. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X.; Cao, X.; Young, G.S.; Chen, H.; Xu, X. A neural network approach to segment brain blood vessels in digital subtraction angiography. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 185, 105159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Banerjee, A.; Choudhury, R.P.; Grau, V. Deep learning based coronary vessels segmentation in X-ray angiography using temporal information. Med. Image Anal. 2025, 102, 103496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, X. MDU-Net: Multi-scale densely connected U-Net for biomedical image segmentation. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2023, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, C.; Sun, K.; Guan, S.; Wang, Q.; Zong, R.; Liu, L. Multiscale dense convolutional neural network for DSA cerebrovascular segmentation. Neurocomputing 2020, 373, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Shi, Y.; Tan, T.; Liu, W.; Pan, X.; Deng, Y.; Gao, F.; Su, R. ERNet: Edge Regularization Network for cerebral vessel segmentation in digital subtraction angiography images. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 28, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vepa, A.; Choi, A.; Nakhaei, N.; Lee, W.; Stier, N.; Vu, A. Weakly Supervised Convolutional Neural Networks for Vessel Segmentation in Cerebral Angiography. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Tian, T.; Wang, L.; Xu, W.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Zhao, W.; Tian, S.; Pan, X.; Deng, Y.; et al. DIAS: A dataset and benchmark for intracranial artery segmentation in DSA sequences. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 97, 103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Xu, W.; Li, H.; Yang, H.; Gao, F. TSI-NET: A timing sequence image segmentation network for Intracranial Artery Segmentation in Digital Subtraction Angiography. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Athens, Greece, 27–30 May 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhassan, M.A.M.; Huang, C.; Yang, C.; Munea, T.L. DSANet: Dilated spatial attention for real-time semantic segmentation in urban street scenes. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 183, 115090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apivanichkul, K.; Phasukkit, P.; Dankulchai, P. Performance comparison of deep learning approach for automatic CT image segmentation by using window leveling. In Proceedings of the 13th Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON), Ayutthaya, Thailand, 19–21 November 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Asperen, V.; van den Berg, J.; Lycklama, F.; Marting, V.; Cornelissen, S.; van Zwam, W.H.; Hofmeijer, J.; van der Lugt, A.; van Walsum, T.; van der Sluijs, M.; et al. Automatic artery/vein classification in 2D-DSA images of stroke patients. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2022: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling, San Diego, CA, USA, 20 February–28 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, K.; Najarian, C.P.; Fattah, A.A.; Arthurs, C.J.; Soroushmehr, S.M.R.; Subban, V.; Sankardas, M.A.; Nadakuditi, R.R.; Nallamothu, B.K.; Figueroa, C.A. AngioNet: A convolutional neural network for vessel segmentation in X-ray angiography. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Jin, M.; Hao, D.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, S.; Zhao, J.; Fei, B. Accurate vessel extraction via tensor completion of background layer in X-ray coronary angiograms. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 87, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ameen, Z.; Sulong, G.; Rehman, A.; Al-Dhelaan, A.; Saba, T.; Al-Rodhaan, M. An innovative technique for contrast enhancement of computed tomography images using normalized gamma-corrected contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2015, 2015, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A nested U-Net architecture for medical image segmentation. Deep learning in medical image analysis and multimodal learning for clinical decision support. In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, C.; Mukherjee, T.; Pasiliao, E., Jr. ACMSE ’19. Proceedings of the 2019 ACM Southeast Conference; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorck, J.; Gomes, C.; Selman, B.; Weinberger, K.Q. Understanding batch normalization. In Proceedings of the Nips’18. Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; pp. 7705–7716. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2018; Volume 11211, pp. 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference for Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.H.; Warfield, S.K.; Bharatha, A.; Tempany, C.M.C.; Kaus, M.R.; Haker, S.J.; Wells, W.M.; Jolesz, F.A.; Kikinis, R. Statistical validation of image segmentation quality based on a spatial overlap index. Acad. Radiol. 2004, 11, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J.; Sadeghian, A.; Reid, I.; Savarese, S. Generalized intersection over union: A metric and a loss for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; Volume 2019, pp. 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, B.J.; Kitamura, F. Magician’s corner: 9. performance metrics for machine learning models. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2021, 3, e200126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, H.; Tian, T.; Cao, Z.; Pan, X.; Xu, W.; Jin, Y.; Gao, F. Full-resolution network and dual-threshold iteration for retinal vessel and coronary angiograph segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 4623–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zhang, D.; Mou, L.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhang, J. DSNet: A spatio-temporal consistency network for cerebrovascular segmentation in digital subtraction angiography sequences. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. MICCAI 2024, 15008, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.K.; Guo, W.Y.; Yang, H.C.; Lin, C.J.; Wu, C.F.; Gehrisch, S.; Kowarschik, M.; Wu, Y.T.; Chung, W.Y. Application of time-resolved 3d digital subtraction angiography to plan cerebral arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderman, M.; Holmin, S.; Andersson, T.; Palmgren, C.; Babic, D.; Hoornaert, B. Image noise reduction algorithm for digital subtraction angiography: Clinical results. Radiology 2013, 269, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Liu, X.; Fang, T.; Li, Y.; Min, X. DFA-Net: Dual multi-scale feature aggregation network for vessel segmentation in X-ray digital subtraction angiography. J. Big Data 2024, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, K.; Xiong, X.; Torio, E.; Du, R.; Juvekar, P.; Dorent, R.; Golby, A.; Frisken, S.; Haouchine, N. Spatiotemporal disentanglement of arteriovenous malformations in digital subtraction angiography. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2024, 12926, 129263B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owler, J.; Rockett, R. Influence of background preprocessing on the performance of deep learning retinal vessel detection. J. Med. Imaging 2021, 8, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, R.K.; Sachdeva, J.; Katoch, D. Segmentation of retinal blood vessels by a novel hybrid technique-principal component analysis (PCA) and contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE). Microvasc. Res. 2023, 148, 104477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).