Self-Mode-Locking and Frequency-Modulated Comb Semiconductor Disk Lasers
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Towards Self-Mode-Locking
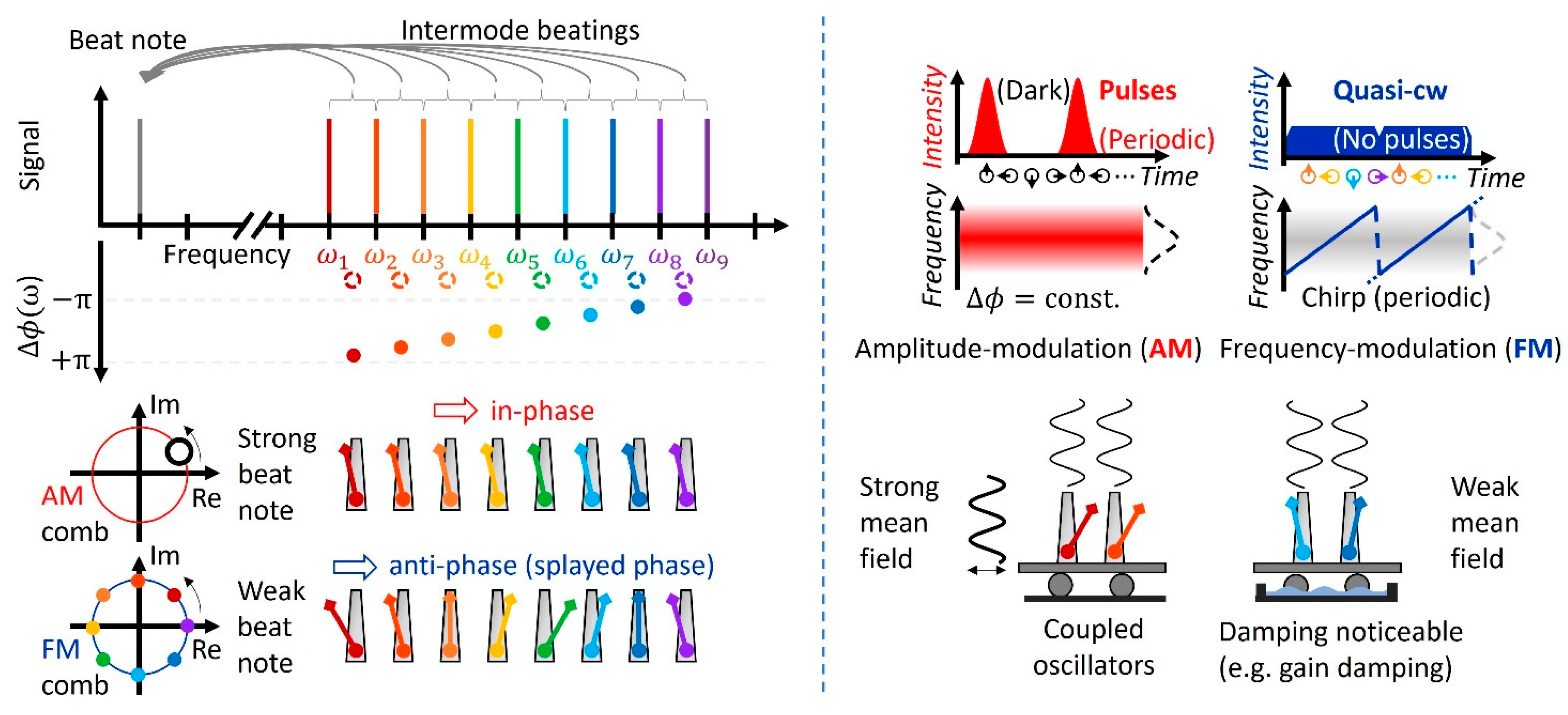
1.2. From Self-Mode-Locking to a Frequency-Modulated Comb
2. Methodology and Outcomes Summarized
2.1. Mechanism Behind Self-Mode-Locking in VECSELs
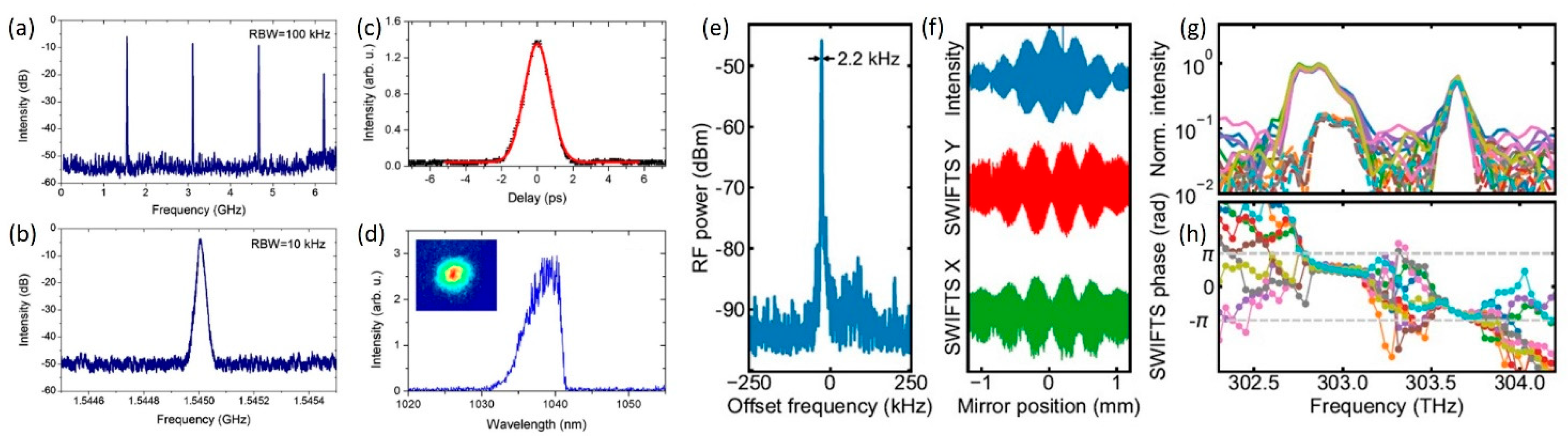
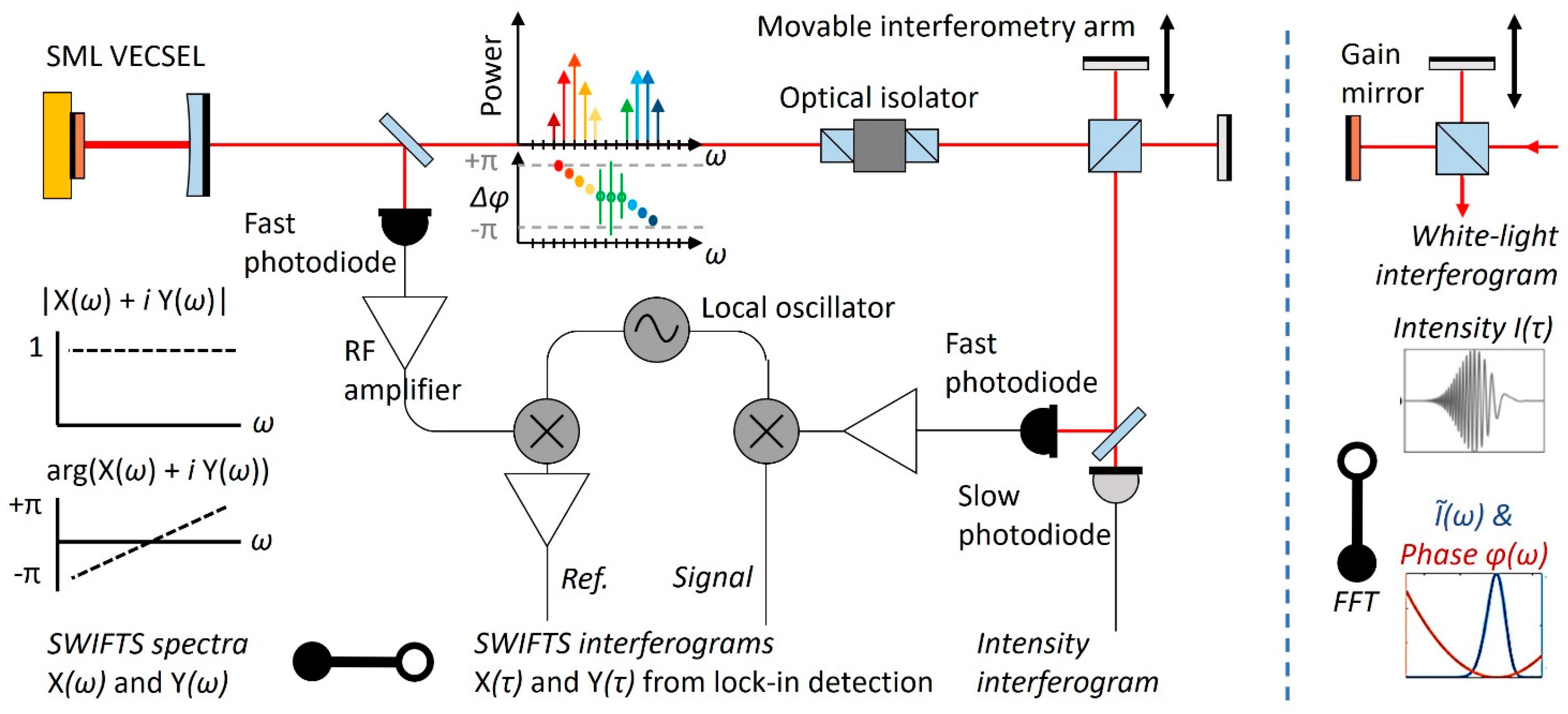
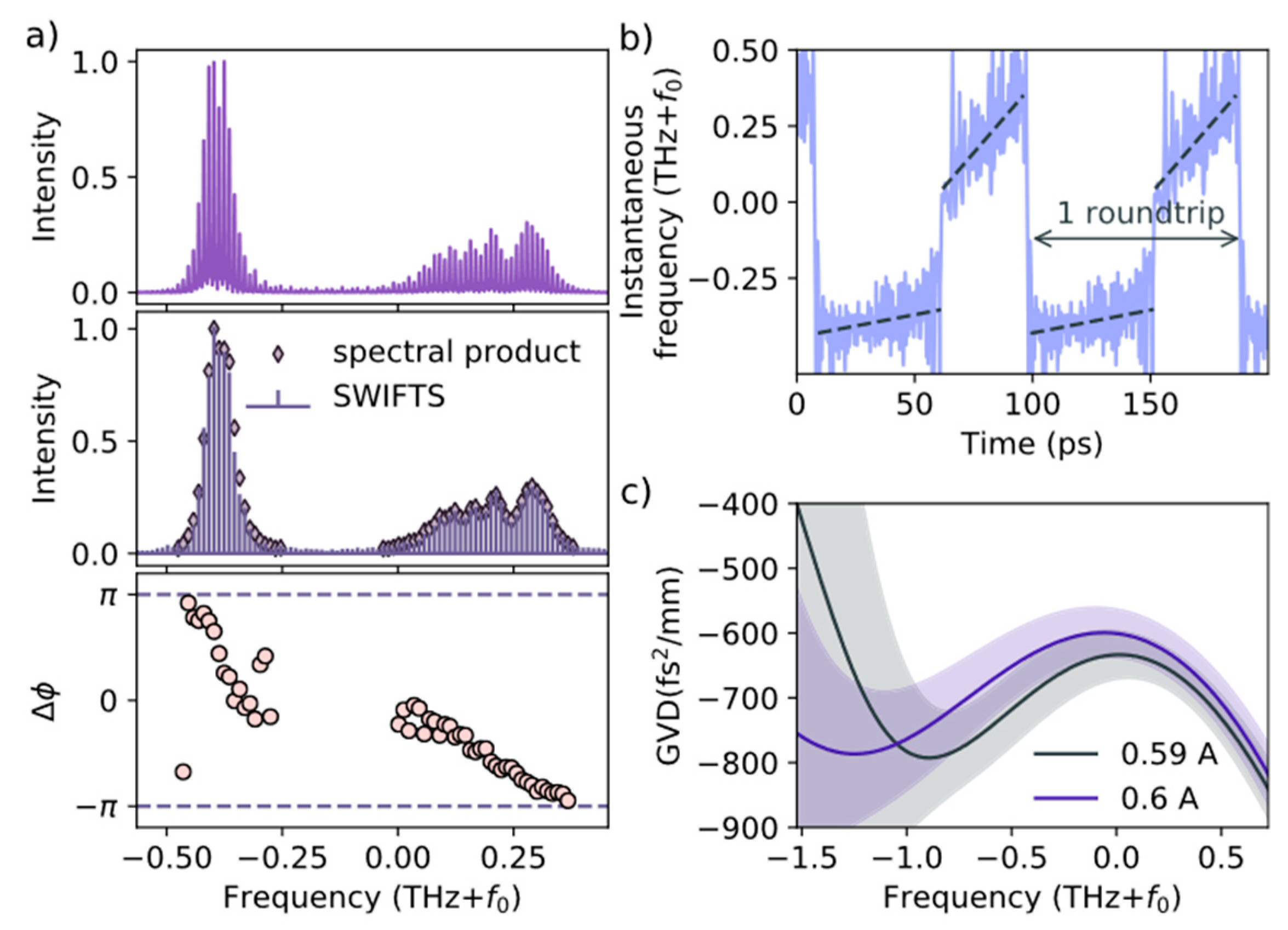
2.2. FM-Comb SML VECSEL and Shifted-Wave-Interference Fourier-Transform Spectroscopy (SWIFTS)
3. Applications and Outlook Comb V(E)CSEL
3.1. Dual-Comb Spectroscopy, Quantum Metrology, and More
3.2. Further Advances on Self-Mode-Locked VECSELs
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoogland, S.; Dhanjal, S.; Tropper, A.C.; Roberts, S.J.; Häring, R.; Paschotta, R.; Keller, U. Passively mode-locked diode-pumped surface-emitting semiconductor laser. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2000, 12, 1135–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetter, M.; Michler, P. Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers: VECSEL Technology and Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2021; ISBN 978-3-527-41362-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, U.; Tropper, A.C. Passively modelocked surface-emitting semiconductor lasers. Phys. Rep. 2006, 429, 67–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilma, B.W.; Mangold, M.; Zaugg CALink, S.M.; Waldburger, D.; Klenner, A.; Mayer, A.S.; Gini, E.; Golling, M.; Keller, U. Mode-locked semiconductor disk lasers. Light Sci. Appl. 2015, 4, e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaafar, M.A.; Rahimi-Iman, A.; Fedorova, K.A.; Stolz, W.; Rafailov, E.U.; Koch, M. Mode-locked semiconductor disk lasers. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2016, 8, 370–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, D.E.; Kean, P.N.; Sibbett, W. 60-fsec pulse generation from a self-mode-locked Ti: Sapphire laser. Opt. Lett. 1991, 16, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, U.; ’tHooft, G.W.; Knox, W.H.; Cunningham, J.E. Femtosecond pulses from a continuously self-starting passively mode-locked Ti:sapphire laser. Opt. Lett. 1991, 16, 1022–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopp, P.; Griebner, U.; Zorn Mund Weyers, M. Pulse repetition rate up to 92 GHz or pulse duration shorter than 110 fs from a mode-locked semiconductor disk laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 071103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaafar, M.; Richter, P.; Keskin, H.; Möller, C.; Wichmann, M.; Stolz, W.; Rahimi-Iman, A.; Koch, M. Self-mode-locking semiconductor disk laser. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 28390–28399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldburger, D.; Link, S.M.; Mangold, M.; Alfieri, C.G.E.; Gini, E.; Golling, M.; Tilma, B.W.; Keller, U. High-power 100 fs semiconductor disk lasers. Optica 2016, 3, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, K.G.; Tropper, A.C.; Beere, H.E.D.A.; Ritchie, B.; Kunert, B.; Heinen Stolz, W. 4.35 kW peak power femtosecond pulse mode-locked VECSEL for supercontinuum generation. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar]
- Gaafar, M.; Möller, C.; Wichmann, M.; Heinen, B.; Kunert, B.; Rahimi-Iman, A.; Stolz, W.; Koch, M. Harmonic self-mode-locking of optically pumped semiconductor disc laser. Electron. Lett. 2014, 50, 542–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husaini, S.; Bedford, R.G. Graphene saturable absorber for high power semiconductor disk laser mode-locking. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 161107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangold, M.; Golling, M.; Gini, E.; Tilma, B.W.; Keller, U. Sub-300-femtosecond operation from a MIXSEL. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 22043–22059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurain, A.; Kilen, I.; Hader, J.; Perez, A.R.; Ludewig, P.; Stolz, W.; Balakrishnan, G.; Koch, S.W.; Moloney, J.V. Modeling and experimental realization of modelocked VECSEL producing high power sub-100 fs pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 121113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Albrecht, A.R.; Nguyen, C.; Follman, D.; Cole, G.D.; Sheik-Bahae, M. Hybrid membrane-external-cavity surface-emitting laser. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 42470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilen, I.; Koch, S.W.; Hader, J.; Moloney, J.V. Fully microscopic modeling of mode locking in microcavity lasers. JOSAB 2015, 33, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, R.; Tong, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P. Dynamics Simulation of Self-Mode-Locking in a Semiconductor Disk Laser Using Delay Differential Equations. Photonics 2022, 9, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhu, R.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Tong, C.; Wang, L.; Song, Y. Dynamics Simulation and Experimental Investigation of Q-Switching in a Self-Mode-Locked Semiconductor Disk Laser. IEEE Photonics J. 2022, 14, 1548808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropper, C.; Hoogland, S. Extended cavity surface-emitting semiconductor lasers. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2006, 30, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlehahn, A.; Gaafar, M.; Vaupel, M.; Gschrey, M.; Schnauber, P.; Schulze, J.-H.; Rodt, S.; Strittmatter, A.; Stolz, W.; Rahimi-Iman, A.; et al. Single-photon emission at a rate of 143MHz from a deterministic quantum-dot microlens triggered by a mode-locked vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 041105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Lee, Y.C.; Liang, H.C.; Lin, K.Y.; Su, K.W.; Huang, K.F. Femtosecond high-power spontaneous mode-locked operation in vertical-external cavity surface-emitting laser with gigahertz oscillation. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 4581–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornaszewski, L.; Maker, G.; Malcolm, G.P.A.; Butkus, M.; Rafailov, E.U.; Hamilton, C.J. SESAM-free mode-locked semiconductor disk laser. Laser Photonics Rev. 2012, 6, L20–L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, A.R.; Wang, Y.; Ghasemkhani, M.; Seletskiy, D.V.; Cederberg, J.G.; Sheik-Bahae, M. Exploring ultrafast negative Kerr effect for mode-locking vertical external-cavity surface-emitting lasers. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 28801–28808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.C.; Tsou, C.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Huang, K.F.; Chen, Y.F. Observation of self-mode-locking assisted by high-order transverse modes in optically pumped semiconductor lasers. Laser Phys. Lett. 2014, 11, 105803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaafar, M.; Al Nakdali, D.; Möller, C.; Fedorova, K.A.; Wichmann, M.; Shakfa, M.K.; Zhang, F.; Rahimi-Iman, A.; Rafailov, E.U.; Koch, M. Self-mode-locked quantum-dot vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting laser. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 4623–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsou, C.H.; Liang, H.C.; Wen, C.P.; Su, K.W.; Huang, K.F.; Chen, Y.F. Exploring the influence of high order transverse modes on the temporal dynamics in an optically pumped mode-locked semiconductor disk laser. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 16339–16347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi-Iman, A.; Gaafar, M.; Möller, C.; Vaupel, M.; Zhang, F.; Al-Nakdali, D.; Fedorova, K.A.; Stolz, W.; Rafailov, E.U.; Koch, M. Self-mode-locked vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting laser. Proc. SPIE 2016, 9734, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bek, R.; Großmann, M.; Kahle, H.; Koch, M.; Rahimi-Iman, A.; Jetter, M.; Michler, P. Self-mode-locked AlGaInP-VECSEL. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 182105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriso, C.; Barua, A.; Mohiuddin, O.; Möller, C.; Ruiz-Perez, A.; Stolz, W.; Koch, M.; Rahimi-Iman, A. Signatures of a frequency-modulated comb in a VECSEL. Optica 2021, 8, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, R.; Wang, T.; Jiang, L.; Tong, C.; Song, Y.; Zhang, P. Intracavity third-harmonic generation in a continuous-wave/self-mode-locked semiconductor disk laser. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2023, 21, 051404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Hua, L.; Zhuang, B.; Tian, J.; Zhang, P.; Song, Y. Wavelength tunable self-mode locking semiconductor disk laser. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Optical and Photonic Engineering (icOPEN 2022), Online, 24–27 November 2022; p. 125502D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.; Hua, L.; Tian, J.; Mao, L.; Song, Y. Switching of several self-mode-locking states in an optically pumped semiconductor disk laser. Laser Phys. Lett. 2023, 20, 115801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhu, R.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Jiang, L.; Lu, H.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Z. Power scaling of a self-mode-locked vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 011106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chormet, B.; Blin, S.; Beaudoin, G.; Pantzas, K.; Sagnes, I.; Denet, S.; Garnache, A. Spontaneous mode locking of a multimode semiconductor laser under continuous wave operation. Front. Photonics 2023, 4, 1160251. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, K.G.; Tropper, A.C. Comment on SESAM-free mode-locked semiconductor disk laser. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 422–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornaszewski, L.; Maker, G.; Malcolm, G.P.A.; Butkus, M.; Rafailov, E.U.; Hamilton, C.J. Reply to comment on SESAM-free mode-locked semiconductor disk laser. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 555–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi-Iman, A. Self-mode-locked vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting laser, Chap. 12. In Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers: VECSEL Technology and Applications; Jetter, M., Michler, P., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2021; ISBN 978-3527413621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriso, C.; Kress, S.; Munshi, T.; Grossmann, M.; Bek, R.; Jetter, M.; Michler, P.; Stolz, W.; Koch, M.; Rahimi-Iman, A. Microcavity-enhanced Kerr nonlinearity in a vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting laser. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 11914–11929, Erratum in Opt. Express 2021, 29, 23290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriso, C.; Bergmeier, T.; Giannini, N.; Albrecht, A.R.; Sheik-Bahae, M.; Benis, S.; Faryadras, S.; Van Stryland, E.W.; Hagan, D.J.; Koch, M.; et al. Probing the ultrafast gain and refractive index dynamics of a VECSEL. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 119, 191105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardo, M.; Schwarz, B.; Kazakov, D.; Beiser, M.; Opacak, N.; Wang, Y.; Jha, S.; Hillbrand, J.; Tamagnone, M.; Chen, W.T.; et al. Frequency combs induced by phase turbulence. Nature 2020, 582, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, L.; Lippi, G.L. Phase instabilities in semiconductor lasers: A codimension-2 analysis. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 90, 05383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, L.; Lippi, G.L. Phase Instability in Semiconductor Lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 213902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, I.; Newbury, N.; Swann, W. Dual-comb spectroscopy. Optica 2016, 3, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, S.M.; Maas, D.J.H.C.; Waldburger, D.; Keller, U. Dual-comb spectroscopy of water vapor with a free-running semiconductor disk laser. Science 2017, 356, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugi, A.; Villares, G.; Blaser, S.; Liu, H.C.; Faist, J. Mid-infrared frequency comb based on a quantum cascade laser. Nature 2012, 492, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escoto, E.; Steinmeyer, G. Cage Solitons. Proc. SPIE 2020, 11263, 1126306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opacak, N.; Schwarz, B. Theory of frequency-modulated combs in lasers with spatial hole burning, dispersion, and Kerr nonlinearity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 243902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghoff, D. Unraveling the origin of frequency modulated combs using active cavity mean-field theory. Optica 2020, 7, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haus, H.A. Mode-locking of lasers. J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2000, 6, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillbrand, J.; Auth, D.; Piccardo, M.; Opačak, N.; Gornik, E.; Strasser, G.; Capasso, F.; Breuer, S.; Schwarz, B. In-Phase and Anti-Phase Synchronization in a Laser Frequency Comb. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 023901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, R.; Murdoch, S.G.; Watts, R.T.; Merghem, K.; Martinez, A.; Lelarge, F.; Accard, A.; Barry, L.P.; Ramdane, A. High performance mode locking characteristics of single section quantum dash lasers. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 8649–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterczewski, L.A.; Frez, C.; Forouhar, S.; Burghoff, D.; Bagheri, M. Frequency-modulated diode laser frequency combs at 2 μm wavelength. APL Photonics 2020, 5, 076111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, B.; Hillbrand, J.; Beiser, M.; Andrews, A.M.; Strasser, G.; Detz, H.; Schade, A.; Weih, R.; Höfling, S. Monolithic frequency comb platform based on interband cascade lasers and detectors. Optica 2019, 6, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, M.; Jouy, P.; Beck, M.; Faist, J. Evidence of linear chirp in mid-infrared quantum cascade lasers. Optica 2018, 5, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillbrand JAndrews AMDetz HStrasser, G.; Schwarz, B. Coherent injection locking of quantum cascade laser frequency combs. Nat. Photonics 2018, 13, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Täschler, P.; Forrer ABertrand, M.; Kapsalidis, F.; Beck, M.; Faist, J. Asynchronous upconversion sampling of frequency modulated combs. Laser Photonics Rev. 2023, 17, 220063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetser, J.; Dunn, T.J.; Walmsley, I.A.; Radzewicz, C.; Palese, S.; Miller, R.J.D. Characterization of an FM mode-locked Nd: YLF laser synchronized with a passively mode-locked dye laser. Opt. Commun. 1993, 97, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilen, I.; Hader, J.; Moloney, J.V.; Koch, S.W. Ultrafast nonequilibrium carrier dynamics in semiconductor laser mode locking. Optica 2014, 1, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardo, M.; Chevalier, P.; Schwarz, B.; Kazakov, D.; Wang, Y.; Belyanin, A.; Capasso, F. Frequency-Modulated Combs Obey a Variational Principle. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 253901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarterman, A.H.; Tyrk, M.A.; Wilcox, K.G. Z-scan measurements of the nonlinear refractive index of a pumped semiconductor disk laser gain medium. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 011105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, E.A.; Quarterman, A.H.; Turnbull, A.P.; Sverre, T.C.; Head CRTropper, A.C.; Wilcox, K.G. Nonlinear lensing in an unpumped antiresonant semiconductor disk laser gain structure. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2016, 28, 1395–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarterman, A.H.; Mirkhanov, S.; Smyth, C.J.C.; Wilcox, K.G. Measurements of nonlinear lensing in a semiconductor disk laser gain sample under optical pumping and using a resonant femtosecond probe laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 121113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriso, C.; Kress, S.; Munshi, T.; Grossmann, M.; Bek, R.; Jetter, M.; Michler, P.; Stolz, W.; Koch, M.; Rahimi-Iman, A. Wavelength and pump-power dependent nonlinear refraction and absorption in a semiconductor disk laser. Photon. Technol. Lett. 2020, 32, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik-Bahae, M.; Hutchings, D.; Hagan, D.; Van Stryland, E. Dispersion of bound electron nonlinear refraction in solids. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1991, 27, 1296–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghoff, D.; Yang, Y.; Hayton, D.J.; Gao, J.-R.; Reno, J.L.; Hu, Q. Evaluating the coherence and time-domain profile of quantum cascade laser frequency combs. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 1190–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Ren, D.; Burghoff, D. Sensitivity of SWIFT spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 6002–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diddams, S.; Diels, J.-C. Dispersion measurements with white-light interferometry. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1996, 13, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosteva, A.; Haiml, M.; Paschotta, R.; Keller, U. Noise-related resolution limit of dispersion measurements with white-light interferometers. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2005, 22, 1868–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voumard TWildi, T.; Brasch, V.; Álvarez, R.G.; Ogando, G.V.; Herr, T. AI-enabled real-time dual-comb molecular fingerprint imaging. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 6583–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villares, G.; Hugi, A.; Blaser, S.; Faist, J. Dual-comb spectroscopy based on quantum-cascade-laser frequency combs. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opačak, N.; Schneider, B.; Faist, J.; Schwarz, B. Impact of higher-order dispersion on frequency-modulated combs. Opt. Lett. 2024, 49, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakov, D.; Opačak, N.; Pilat, F.; Wang, Y.; Belyanin, A.; Schwarz, B.; Capasso, F. Cluster synchronization in a semiconductor laser. APL Photonics 2024, 9, 026104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiella, R.; Capasso, F.; Gmachl, C.; Sivco, D.L.; Baillargeon, J.N.; Hutchinson, A.L.; Cho, A.Y.; Liu, H.C. Self-Mode-Locking of Quantum Cascade Lasers with Giant Ultrafast Optical Nonlinearities. Science 2000, 290, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurgin, J.B.; Dikmelik, Y.; Hugi, A.; Faist, J. Coherent frequency combs produced by self frequency modulation in quantum cascade lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 081118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, J.; Youngblood, N.; Karpov, M.; Gehring, H.; Li, X.; Stappers, M.; Le Gallo, M.; Fu, X.; Lukashchuk, A.; Raja, A.S.; et al. Parallel convolutional processing using an integrated photonic tensor core. Nature 2021, 589, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Dumont, M.; Terra, O.; Wang, H.; Netherton, A.; Bowers, J.E. Broadband quantum-dot frequency-modulated comb laser. Light Sci. Appl. 2023, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Zeng, T.; Burghoff, D. Self-frequency-modulated laser combs. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2024, 125, 070503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, J.; Song, Y. Synchronized Dual-Pulse Self-Mode-Locked VECSELs. J. Light. Technol. 2025, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Meng, B.; Shang, J.; Zhang, X.; Tong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Z.; Wang, L. Self−Mode−Locked 2−μm GaSb−Based Optically Pumped Semiconductor Disk Laser. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Jiang, L.; Lu, H.; Song, Y.; Zhang, P. Mode-Locked Operation of High-Order Transverse Modes in a Vertical-External-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser. Sensors 2024, 24, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genty, G.; Salmela, L.; Dudley, J.M.; Brunner, D.; Kokhanovskiy, A.; Kobtsev, S.; Turitsyn, S.K. Machine learning and applications in ultrafast photonics. Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriso, C.D. Investigating Self-Mode-Locking in VECSELs: Nonlinear Lensing and Frequency-Modulated Combs; Philipps-Universitaet Marburg: Marburg, Germany, 2021; Available online: https://archiv.ub.uni-marburg.de/diss/z2021/0495 (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- Gaafar, M.A. Realization of a Kerr-Lens Mode-Locked Vertical-External-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser; Philipps-Universitaet Marburg: Marburg, Germany, 2015; Available online: https://archiv.ub.uni-marburg.de/diss/z2015/0403 (accessed on 23 May 2024).



| Ref. | Pulse Length (ps), [TBP] | Resonator Layout | Pulse Shaping Support | Presumed Key |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [22] | 0.65 | Linear | None | Saturable absorption (in gain mirror) |
| [23] | 0.93/1.5 | Z-shape [*] | Hard aperture/Soft aperture | Kerr lensing |
| [24] | 1.3, 1.0, 0.76, and 0.48, in order of increasing pump power, V-cavity (~0.9 to 1.8 by dispersion adjustment for lowest pump, V-cavity) | V-shape [*]/Linear | Hard aperture/Soft aperture (additionally, intracavity dispersion adjustment for pulse length tuning) | Kerr lensing |
| [25] | 0.93 [~0.45 (Gaussian)] | Linear | None (pump-to-mode size ratio) | Higher-order transverse modes (pump-power dependent onset) |
| [9,12] | 0.86 (~1 for 2nd, 3rd harmonic) [0.69/0.73/0.72 (sech21st/2nd/3rd)] | Z-shape [*] | Hard aperture | Kerr lensing |
| [26] | 0.83 at 30 °C (0.95 at 5 °C) [0.94/1.08 at 30°/5 °C (sech2)] | Linear | Hard aperture | Kerr lensing (n2 > 0) |
| [27] | 2.4 | Linear | Hard aperture | Kerr lensing (n2 > 0) |
| [28] | 3.5 | Linear | Hard aperture | Kerr lensing (n2 > 0) |
| [29] | 22 [0.33 (sech2)] | Linear | Soft aperture | Kerr lensing |
| [30] | - | Linear | (Soft aperture for pulsing, not part of article) | Four-wave mixing for frequency-modulated comb state (nonlinear lensing for pulsing, not part of article) |
| [19] | ~5 [~1.5 (Gaussian)] | Linear | Soft aperture | Kerr lensing |
| [31] | ~5 [~2.5 (Gaussian)] | V-shape [**] | Soft aperture | Kerr lensing |
| [32] | 4.3 | Linear | Soft aperture | Kerr lensing |
| [33] | 2.0, 2.0, 1.9, 1.7, 1.6, in order of increasing pump power (and 1.7, 1.6, 1.4, 1.4, 1.3 for high-order TM SML) | Linear | Soft aperture (outcoupler, for high-order-transverse-mode SML) | Kerr lensing |
| [34] | 1.9 [~0.82 (Gaussian)] | V-shape | Soft-aperture | Kerr lensing |
| [35] | ~2 | Linear | Dispersive cavity | Phase turbulence and mode–mode coupling through self-phase modulation and anomalous dispersion, together with time symmetry breaking (slow light-matter interaction compared to round-trip time) |
| Ref. | Experiment | Wavelengths (nm) | Effective n2 (10−16 m2/W) | Incidence Angle to Normal | Time Scales (Pulse Duration) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [61] | Z-scan (t-integrated, in reflection) | chip design 1040, lasing ~1050, probe 1064 | −1.5 [*], +0.5 (pump ~60 kW/cm2) up to +1.4 (highest pump ~90 kW/cm2) | ~10° | – (~10 ps pulses) |
| [62] | Z-scan (t-int., in refl.) | chip design 1035, lasing ~1025–1040, probe 1035 | ~−0.4 [*] | [~10°] | – (~0.23 ps pulses) |
| [63] | Z-scan (t-int., in refl.) | chip design 1040, probe 1035 | ~−0.6 [*], −0.7 (pump ~60 kW/cm2) −0.6 (highest pump ~75 kW/cm2) | [~10°] | – (~0.34 ps pulses) |
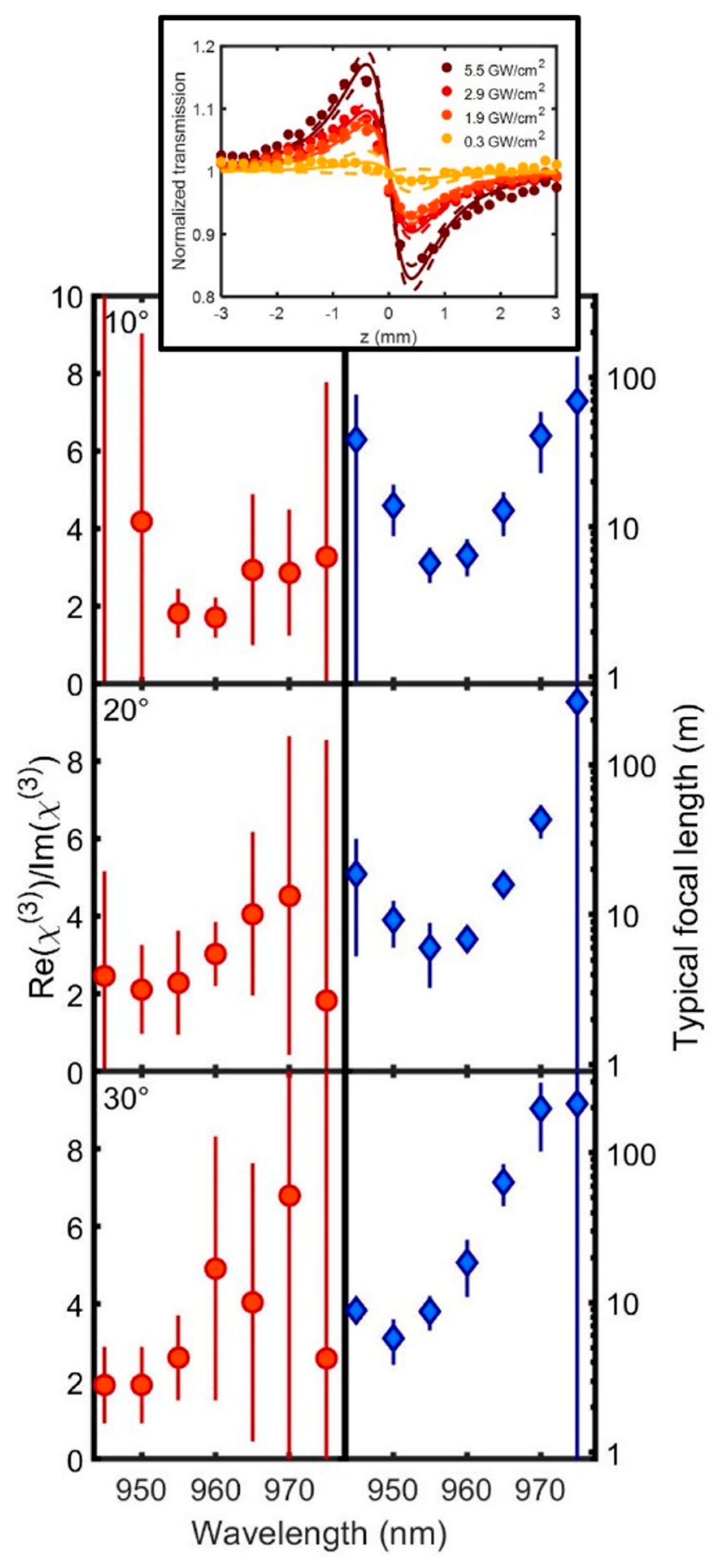
| [39] | Z-scan (t-int., in refl.) | chip design 960 (0°), ~960, 955, 950 for 10°, 20°, 30°, probe 930–975 | ~−4.5 to −5 [*] (at microcavity preference wavelength, PL peak position, LCF shaped) ~−0.5 to 1.5 [*] (at QW PL wavelength) | 10°, 20°, 30° | – (~0.15 ps pulses) |
| [64] | Z-scan (t-int., in refl.) | chip design 960 (0°, intracavity SiC on gain mirror) lasing ~960–970, probe 955–970 | ~−0.8 [*] (960 nm) ~−0.5 [*] (970 nm) −0.6 (above threshold pump ~4 kW/cm2) −0.3 (highest pump ~9 kW/cm2) | [~10°] | – (~0.15 ps pulses) |
| [40] | Beam-deflection (ultrafast) & Z-scan (t-int.) | chip design 1150 (0°, gain membrane on SiC), probe ~1150 | ~−1.2 [*] (Z-scan) corresponding to ~−3 calculated from beam-deflection meas. data [**] | 0° probe, all transmission geometry | 0.01–2.5 ps, pulses ~0.13 ps for pump/probe (~0.12 ps pulses) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahimi-Iman, A. Self-Mode-Locking and Frequency-Modulated Comb Semiconductor Disk Lasers. Photonics 2025, 12, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070677
Rahimi-Iman A. Self-Mode-Locking and Frequency-Modulated Comb Semiconductor Disk Lasers. Photonics. 2025; 12(7):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070677
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahimi-Iman, Arash. 2025. "Self-Mode-Locking and Frequency-Modulated Comb Semiconductor Disk Lasers" Photonics 12, no. 7: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070677
APA StyleRahimi-Iman, A. (2025). Self-Mode-Locking and Frequency-Modulated Comb Semiconductor Disk Lasers. Photonics, 12(7), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070677





