Secret Key Agreement for SISO Visible Light Communication Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We analyze a secret key agreement scheme in SISO VLC systems, explore the secret key rate performance, and derive the analytic expressions of bounds on secrecy key capacity.
- Based on the lower bound of secret key capacity, we consider the situation in which all receivers’ positions are unknown and uniformly distributed within the designated range. We analyze the average secret key capacity and discuss the improvement of the secret performance by employing a protected zone.
- Furthermore, we numerically analyze the distribution of the achievable secret key rate in a typical indoor VLC scenario, where the legitimate receiver is positioned at the center of the receiving plane and an eavesdropper is located at any position on the receiving plane or on the window.
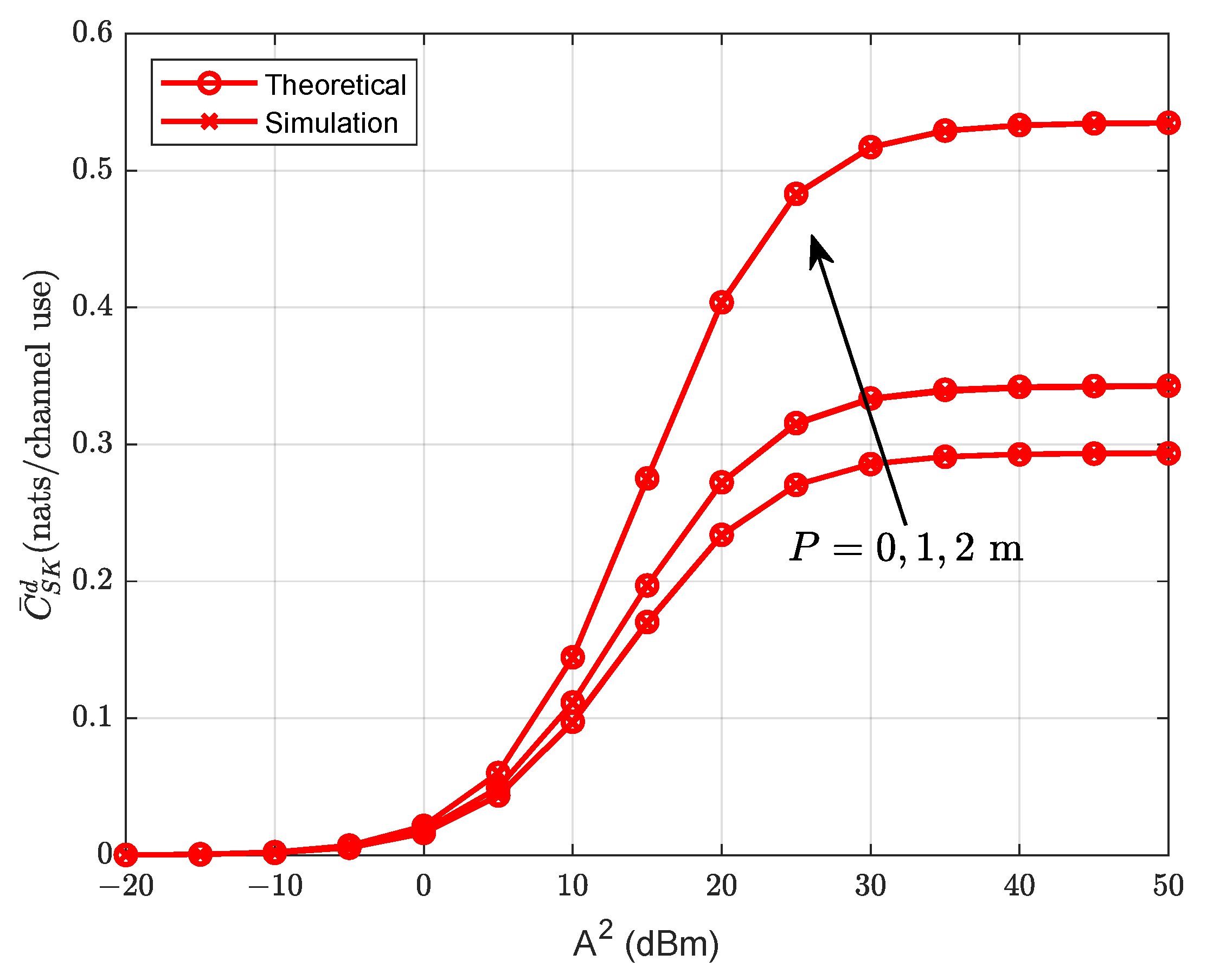
- Simulations are also presented to validate the theoretical analysis of the average secret key capacity and demonstrate the improved secrecy performance by introducing a protected zone.
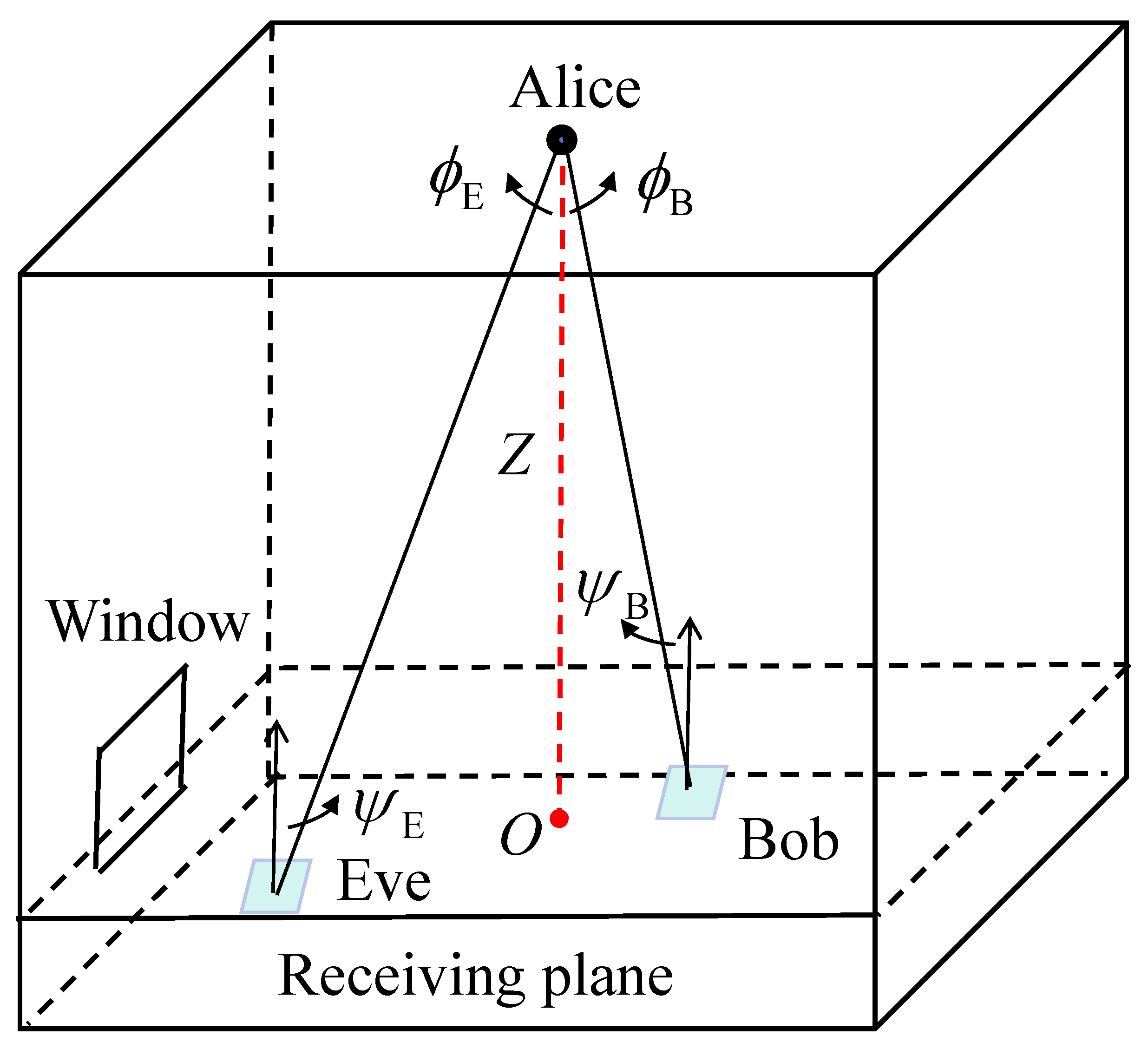
2. System Model
2.1. The VLC Channel Gain
2.2. Secret Key Agreement and Secret Key Capacity
3. Bounds on Secret Key Capacity
3.1. Lower Bound
3.2. Upper Bound
4. Secret Key Rate with Randomly Distributed Terminals
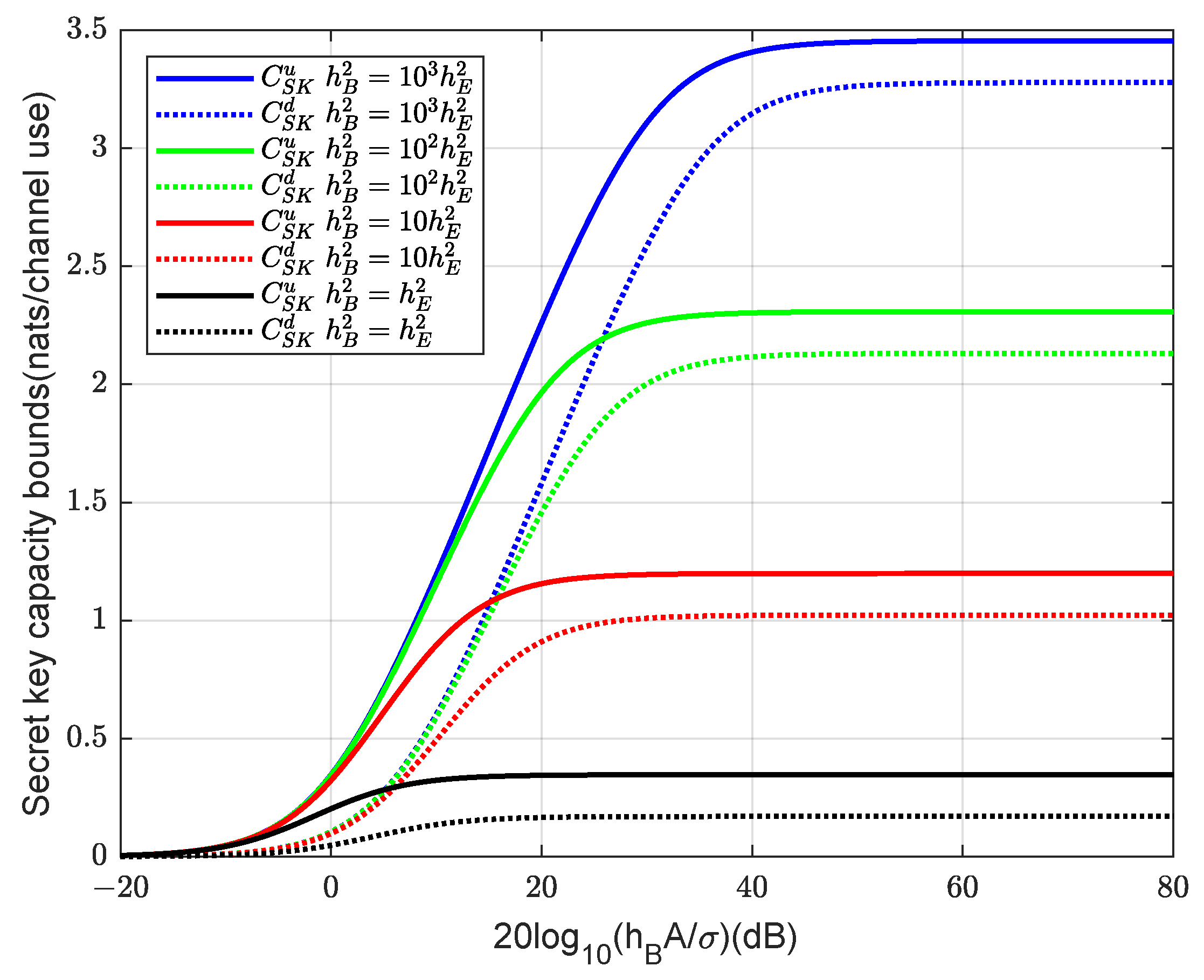
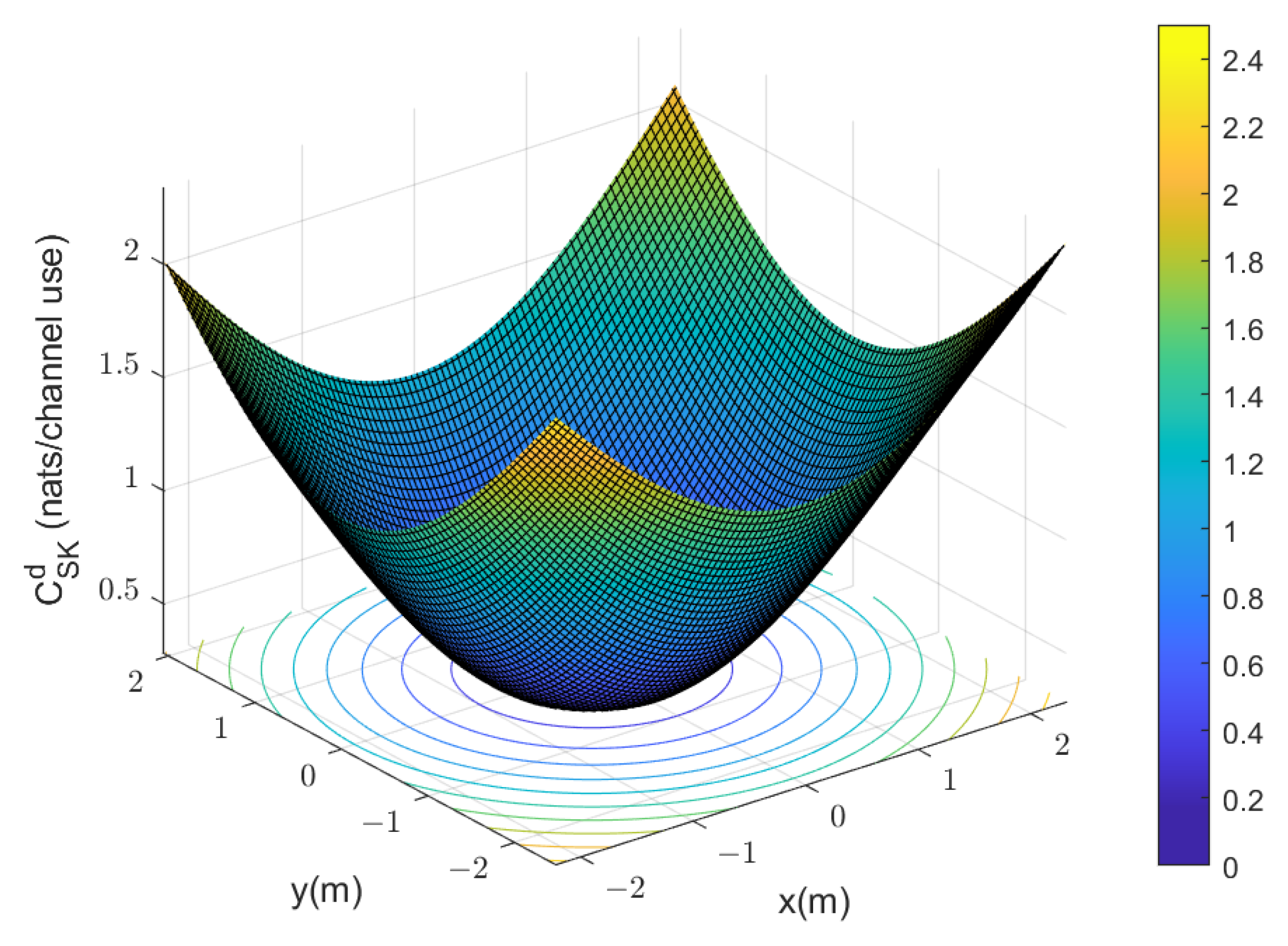
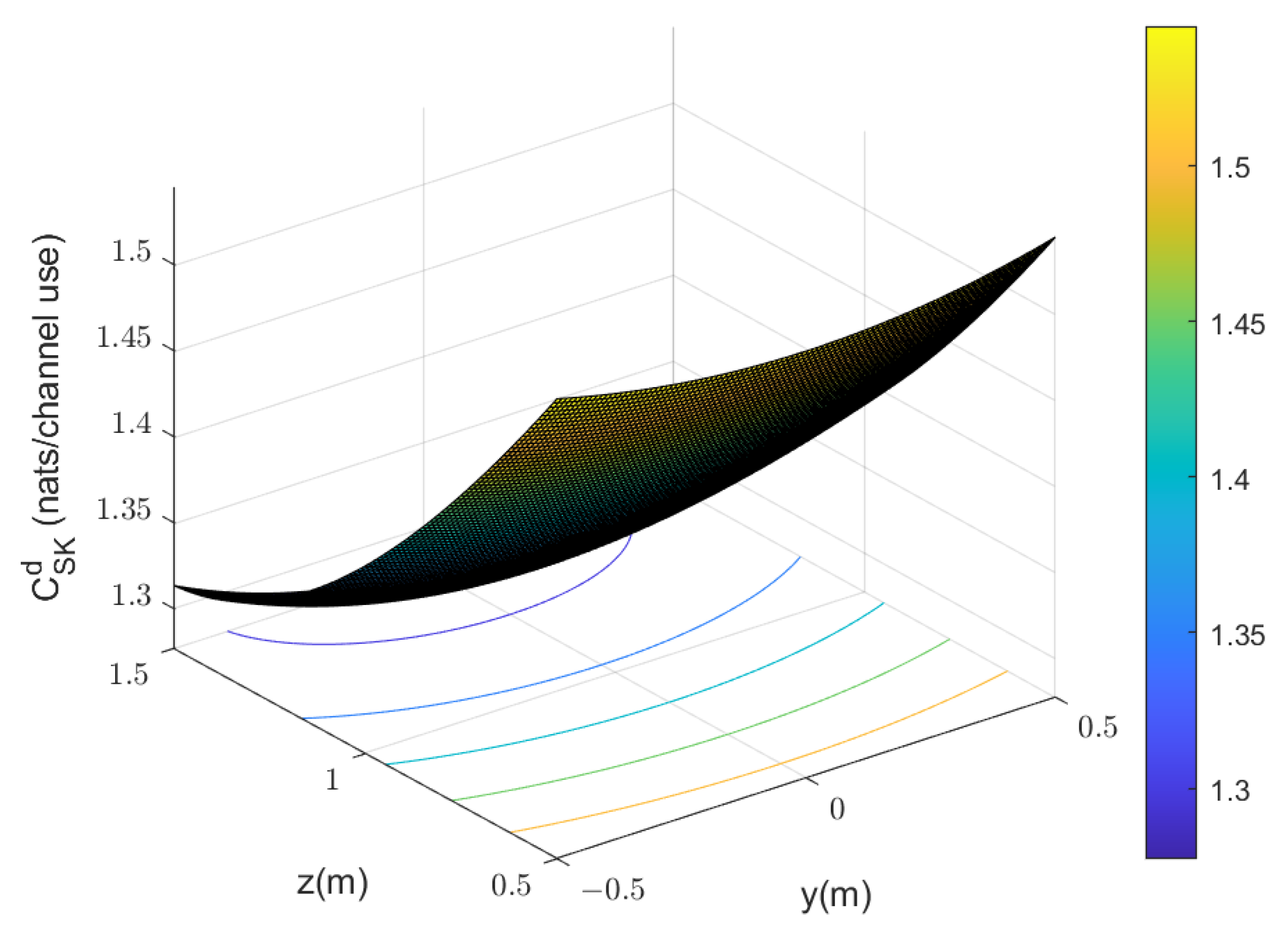
5. Simulation Results
5.1. Eve’s Known CSI
5.2. Randomly Distributed Terminals
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bloch, M.; Barros, J. Physical-Layer Security: From Information Theory to Security Engineering; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wyner, A.D. The wire-tap channel. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1975, 54, 1355–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaoui, M.A.; Soltani, M.D.; Tavakkolnia, I.; Ghrayeb, A.; Safari, M.; Assi, C.M.; Haas, H. Physical Layer Security for Visible Light Communication Systems: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 1887–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.B.; Wu, Y.; Lin, M.; Cheng, J. Physical-Layer Security for Indoor Visible Light Communications: Secrecy Capacity Analysis. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2018, 66, 6423–6436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Lampe, L. Physical-Layer Security for MISO Visible Light Communication Channels. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 1806–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Yang, L.L.; Hanzo, L. Optical Jamming Enhances the Secrecy Performance of the Generalized Space-Shift-Keying-Aided Visible-Light Downlink. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2018, 66, 4087–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yang, F.; Song, J.; Han, Z. Optimization on Multiuser Physical Layer Security of Intelligent Reflecting Surface-Aided VLC. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Du, X.; Guizani, M. Smart Jamming for Secrecy: Deep Reinforcement Learning Enabled Secure Visible Light Communication. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 17915–17928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, U. Secret key agreement by public discussion from common information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1993, 39, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlswede, R.; Csiszar, I. Common randomness in information theory and cryptography. I. Secret sharing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1993, 39, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, U.; Wolf, S. Secret-key agreement over unauthenticated public channels. I. Definitions and a completeness result. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2003, 49, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, U.; Wolf, S. Secret-key agreement over unauthenticated public channels—Part II: The simulatability condition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2003, 49, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, U.; Wolf, S. Secret-key agreement over unauthenticated public channels. II. Privacy amplification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2003, 49, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershey, J.; Hassan, A.; Yarlagadda, R. Unconventional cryptographic keying variable management. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1995, 43, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y. Generalized channel probing and generalized pre-processing for secret key generation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2023, 71, 1067–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, G.; Hu, A.; Ng, D.W.K. Exploiting malicious RIS for secret key acquisition in physical-layer key generation. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2023, 13, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X. Secure Key Distribution System Based on Optical Channel Physical Features. IEEE Photonics J. 2019, 11, 7205311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamant, R.; Casari, P.; Ardizzon, F.; Tomasin, S.; Sherlock, B.; Corner, T.; Neasham, J. Channel-Based Key Generation for Secure Underwater Acoustic Communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitinawarat, S.; Narayan, P. Secret Key Generation for Correlated Gaussian Sources. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2012, 58, 3373–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Goldenbaum, M.; Lai, L.; Poor, H.V. On Simultaneously Generating Multiple Keys in a Joint Source-Channel Model. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2017, 12, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi-Sadjadi, B.; Kiayias, A.; Mercado, A.; Yener, B. Robust key generation from signal envelopes in wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Alexandria, VA, USA, 2 November–31 October 2007; pp. 401–410. [Google Scholar]
- Rezki, Z.; Zorgui, M.; Alomair, B.; Alouini, M.S. Secret Key Agreement: Fundamental Limits and Practical Challenges. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A. Secret-Key Agreement for Security in Multi-Emitter Visible Light Communication Systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2016, 20, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Moliki, Y.M.; Alresheedi, M.T.; Al-Harthi, Y. Robust Key Generation From Optical OFDM Signal in Indoor VLC Networks. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2016, 28, 2629–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alresheedi, M.T. Improving the Confidentiality of VLC Channels: Physical-Layer Security Approaches. In Proceedings of the 2020 22nd International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Bari, Italy, 19–23 July 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komine, T.; Nakagawa, M. Fundamental analysis for visible-light communication system using LED lights. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2004, 50, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorgui, M.; Rezki, Z.; Alomair, B.; Alouini, M.S. Secret-Key Agreement with Public Discussion Subject to an Amplitude Constraint. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2016, 20, 1124–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M. Elements of Information Theory; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, G.; Ye, J.; Ding, Z. On Secure VLC Systems with Spatially Random Terminals. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Qiu, Y.; Lin, S.H.; Wang, J.B.; Lin, M.; Liu, C. On the Secrecy Performance of Random VLC Networks with Imperfect CSI and Protected Zone. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 14, 4176–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, F.P. Probability; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Arfaoui, M.A.; Ghrayeb, A.; Assi, C. Secrecy Rate Closed-Form Expressions for the SISO VLC Wiretap Channel with Discrete Input Signaling. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshafa, M.H.; Maraqa, O.; Moualeu, J.M.; Aboagye, S.; Ngatched, T.M.; Ahmed, M.H.; Gadallah, Y.; Di Renzo, M. RIS-assisted physical layer security in emerging RF and optical wireless communication systems: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Room dimensions | |
| Height of receivers | m |
| Semi-angle | |
| Receiver FOV | |
| The physical area of PD | 1 |
| Lens refractive index n | |
| Noise variance | −98.82 dBm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, D.; Zhang, J.; Xin, G.; Tian, K.; Xiao, X. Secret Key Agreement for SISO Visible Light Communication Systems. Photonics 2025, 12, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050498
Guo D, Zhang J, Xin G, Tian K, Xiao X. Secret Key Agreement for SISO Visible Light Communication Systems. Photonics. 2025; 12(5):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050498
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Dongqin, Jian Zhang, Gang Xin, Keming Tian, and Xingyu Xiao. 2025. "Secret Key Agreement for SISO Visible Light Communication Systems" Photonics 12, no. 5: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050498
APA StyleGuo, D., Zhang, J., Xin, G., Tian, K., & Xiao, X. (2025). Secret Key Agreement for SISO Visible Light Communication Systems. Photonics, 12(5), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050498





