Electrohydrodynamically Printed Microlens Arrays with the High Filling Factor near 90%
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
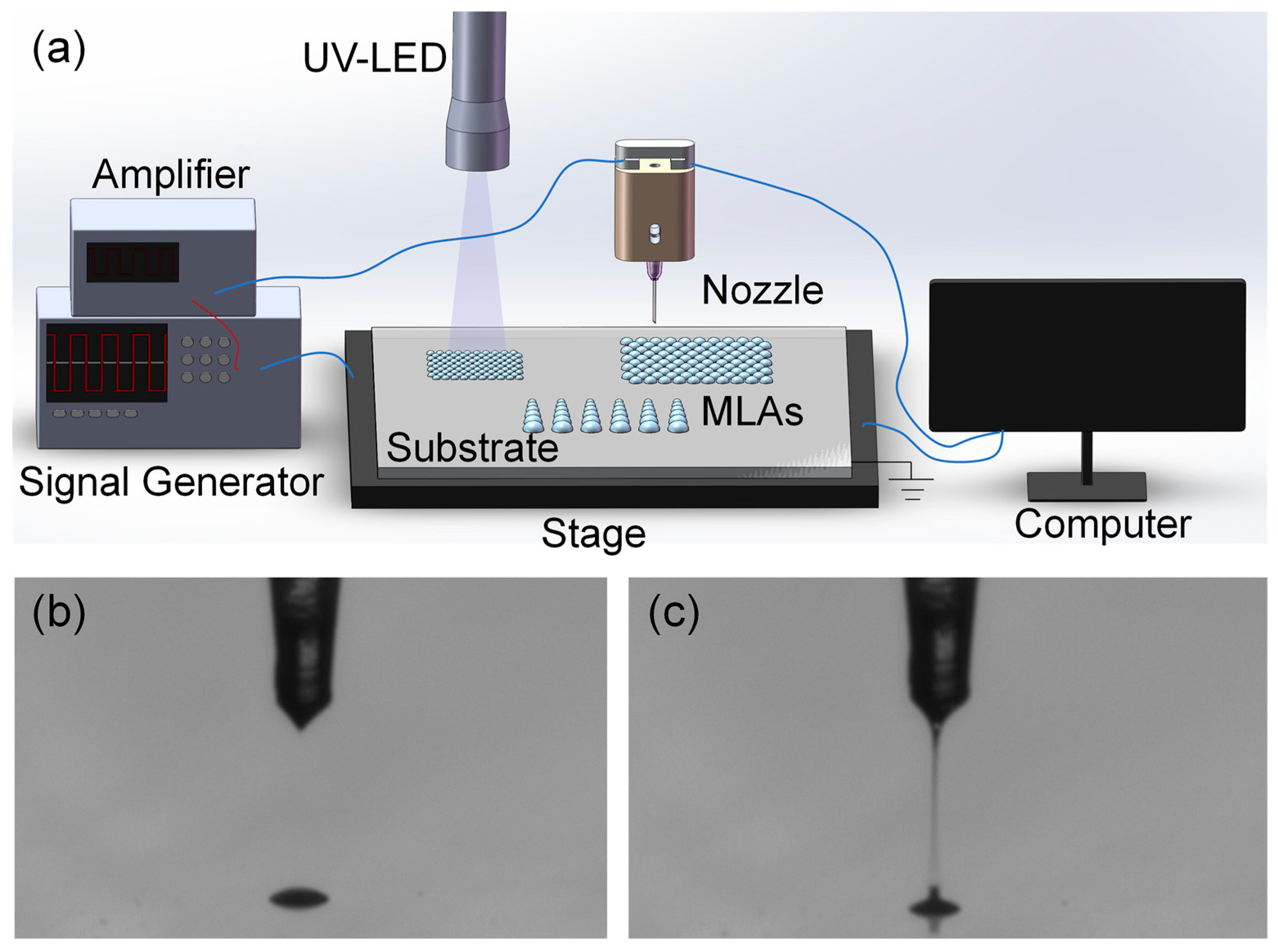
2.1. Experimental System
2.2. MLAs Fabrication
- (1)
- The glass slides were selected as the substrate in our experiments. They were ultrasonically cleaned with acetone and isopropyl alcohol for 15 min, respectively. Then, the glass slides were dried with nitrogen gas and UVO treatment for 20 min;
- (2)
- The UV-curing optical adhesives NOA 61, NOA 63, and NOA 68 (all from Norland Products, Inc., Jamesburg, NJ, USA) were used to print MLAs with a square wave electrical pulse (DC bias: 580 V, amplitude: 200 V, frequency: 100 Hz, duty cycle: 60%);
- (3)
- When the E-jet printing process was completed, the printed MLAs were cured by a UV-LED (wavelength: 365 nm, exposure intensity: 100 mW/cm2).
2.3. Characterization and Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
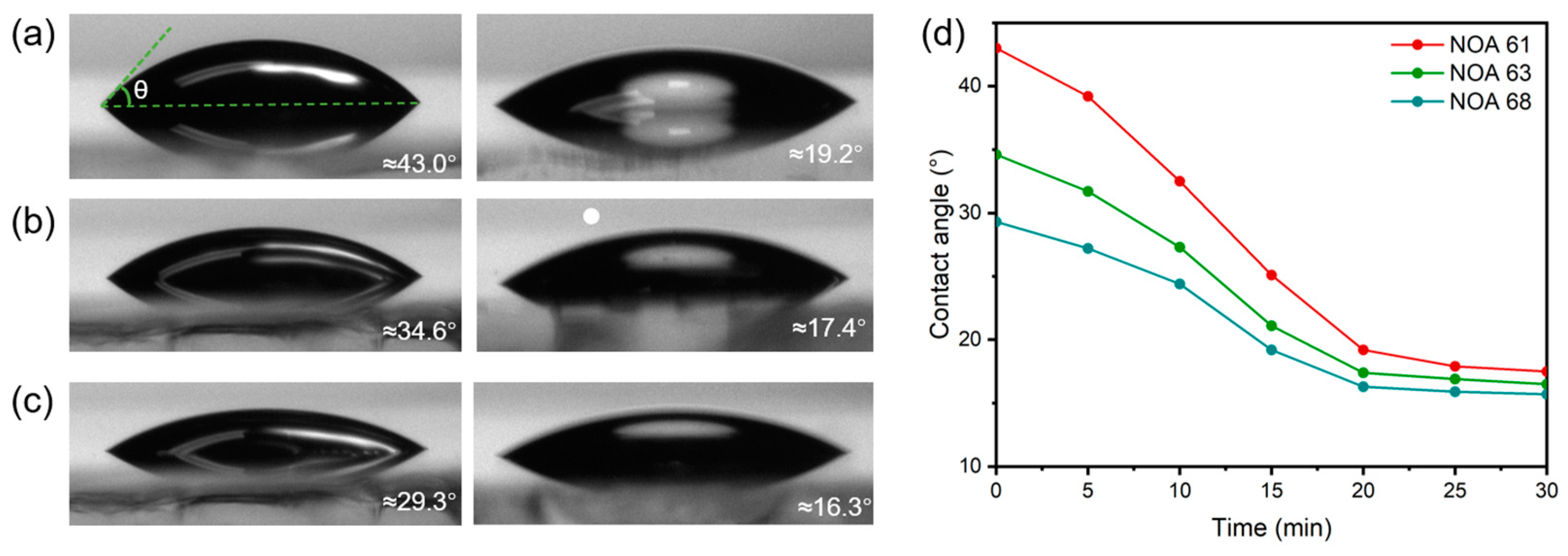
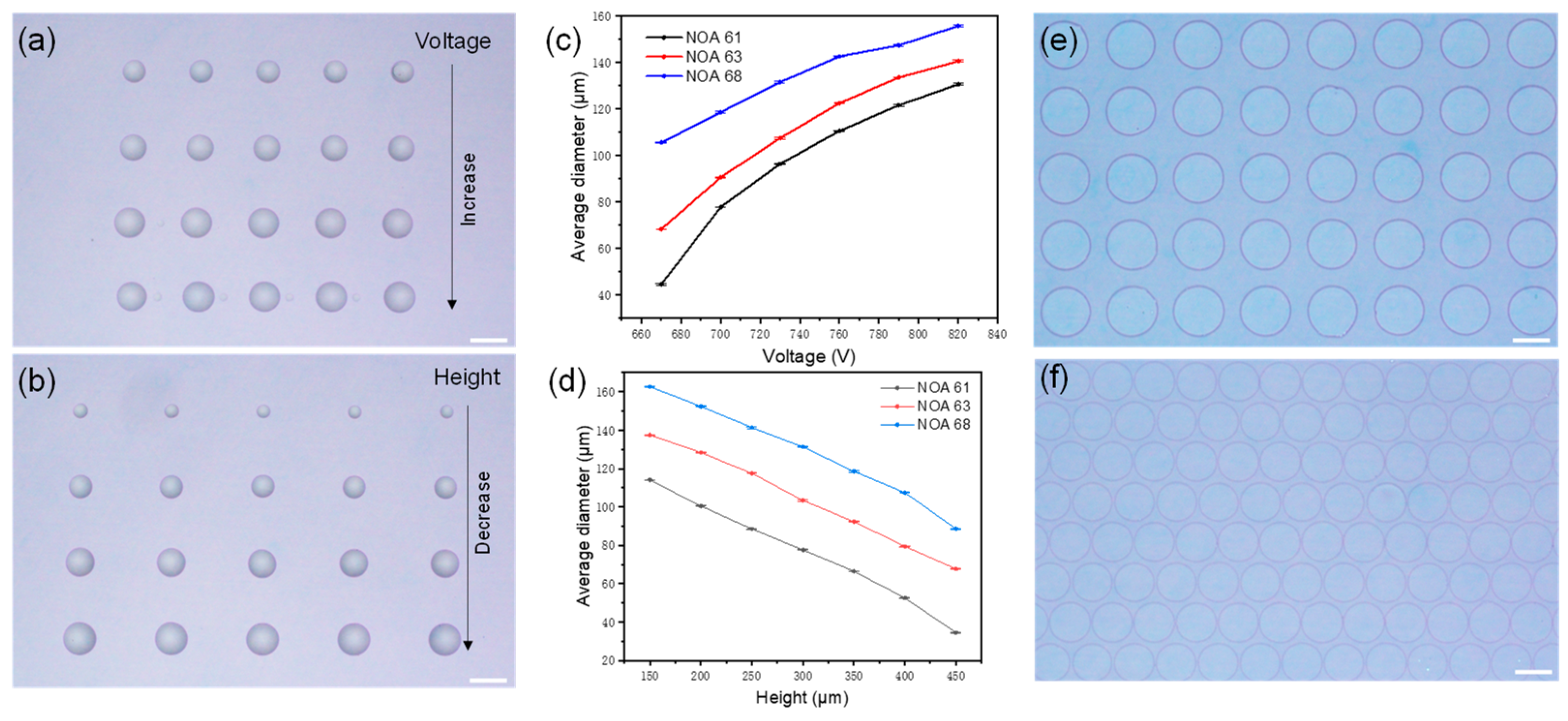
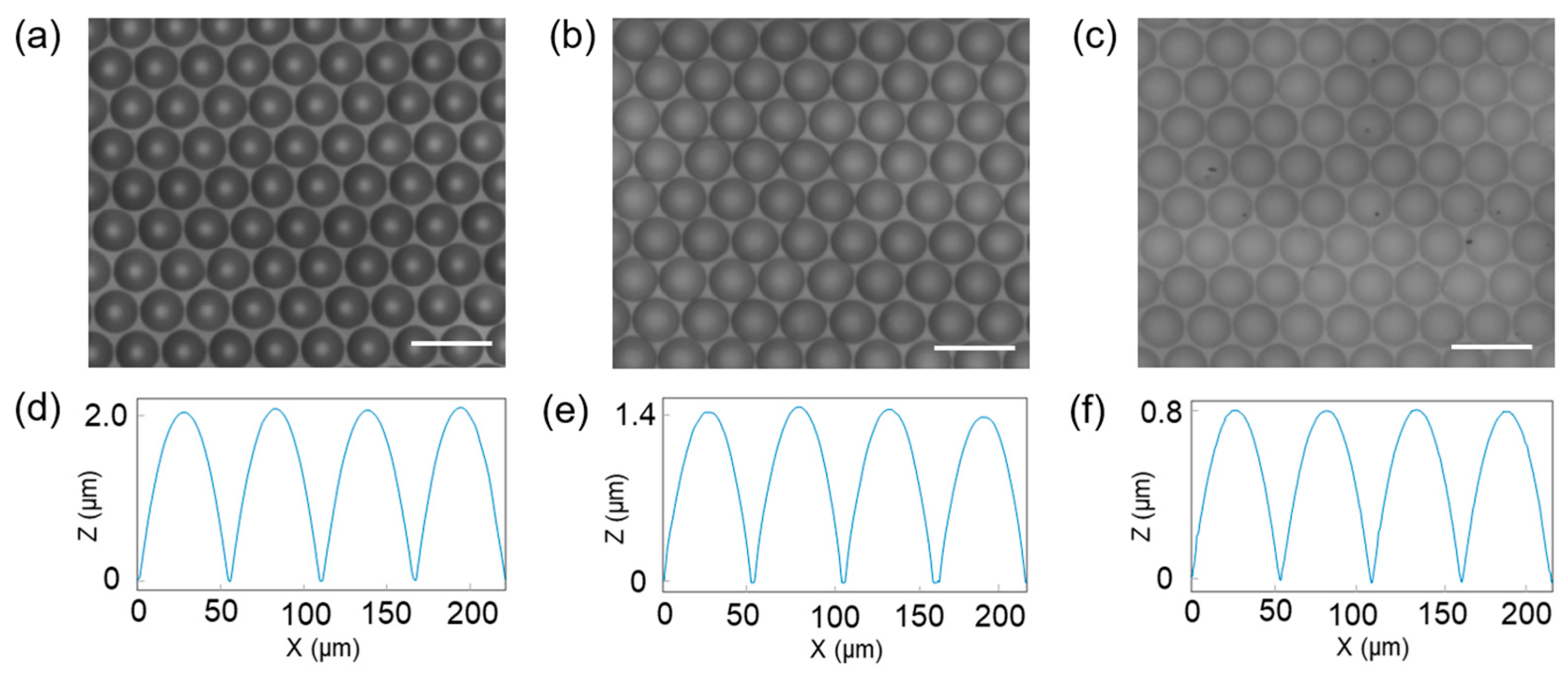
3.1. Fabrication of MLAs
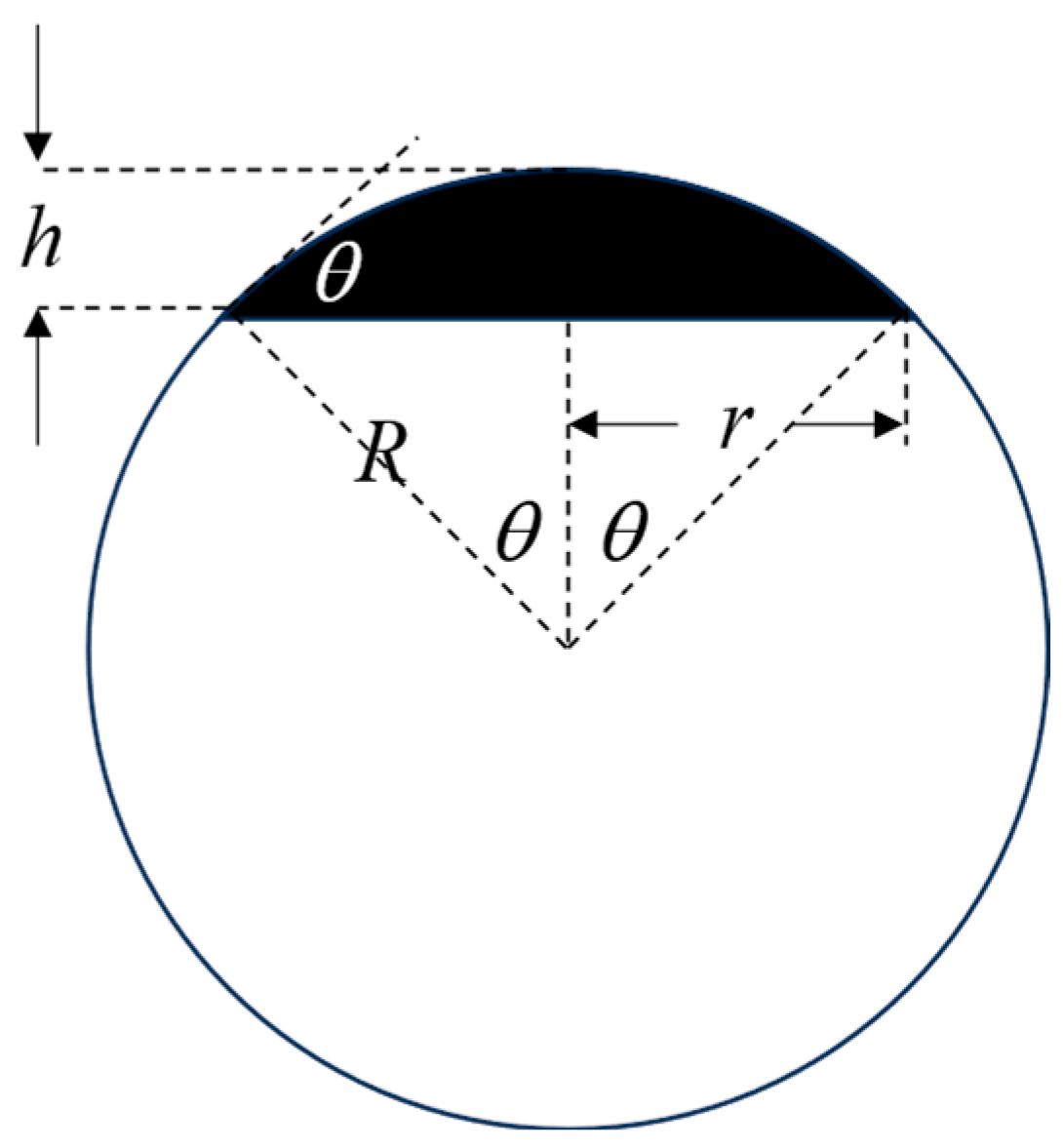
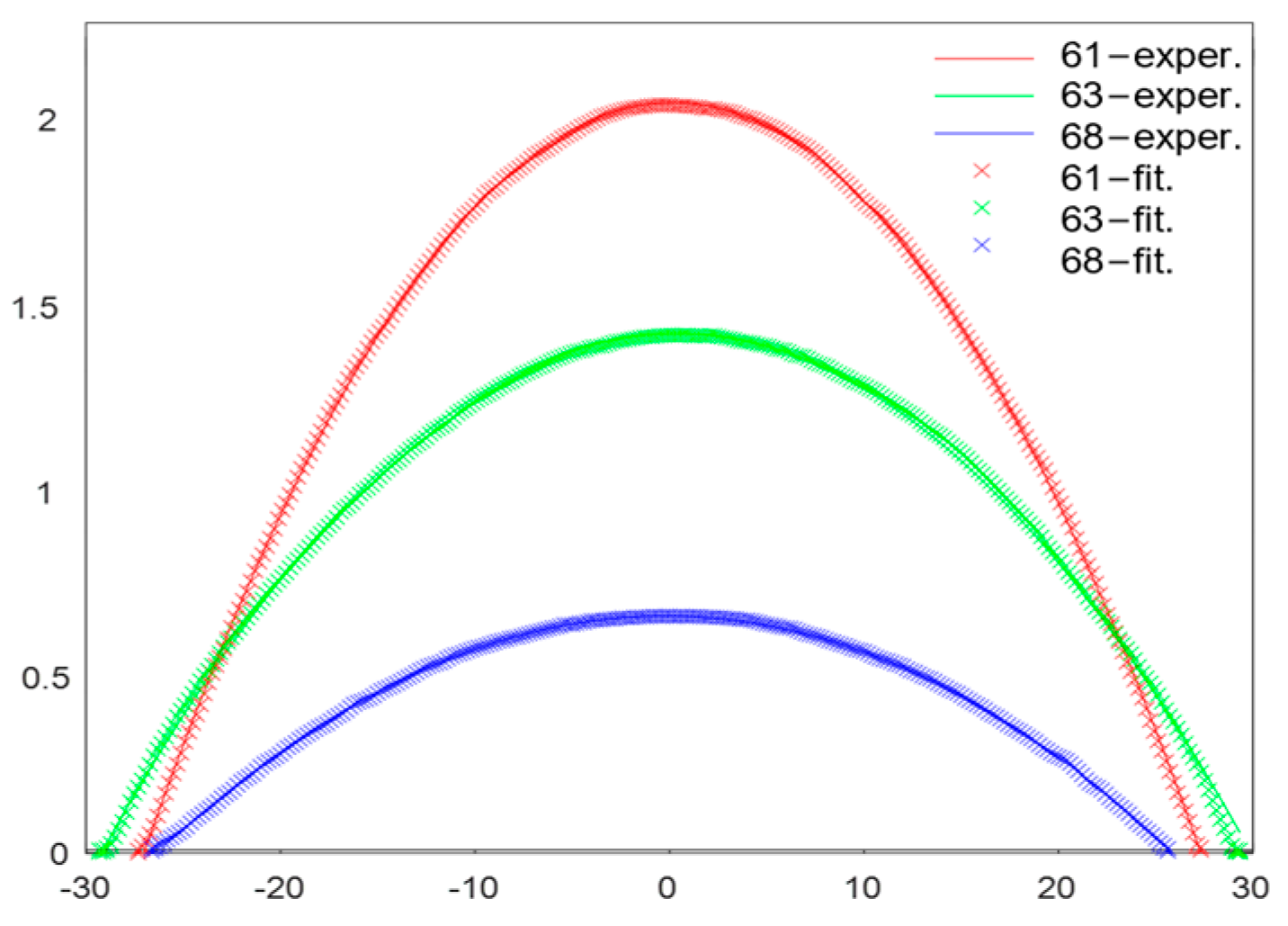
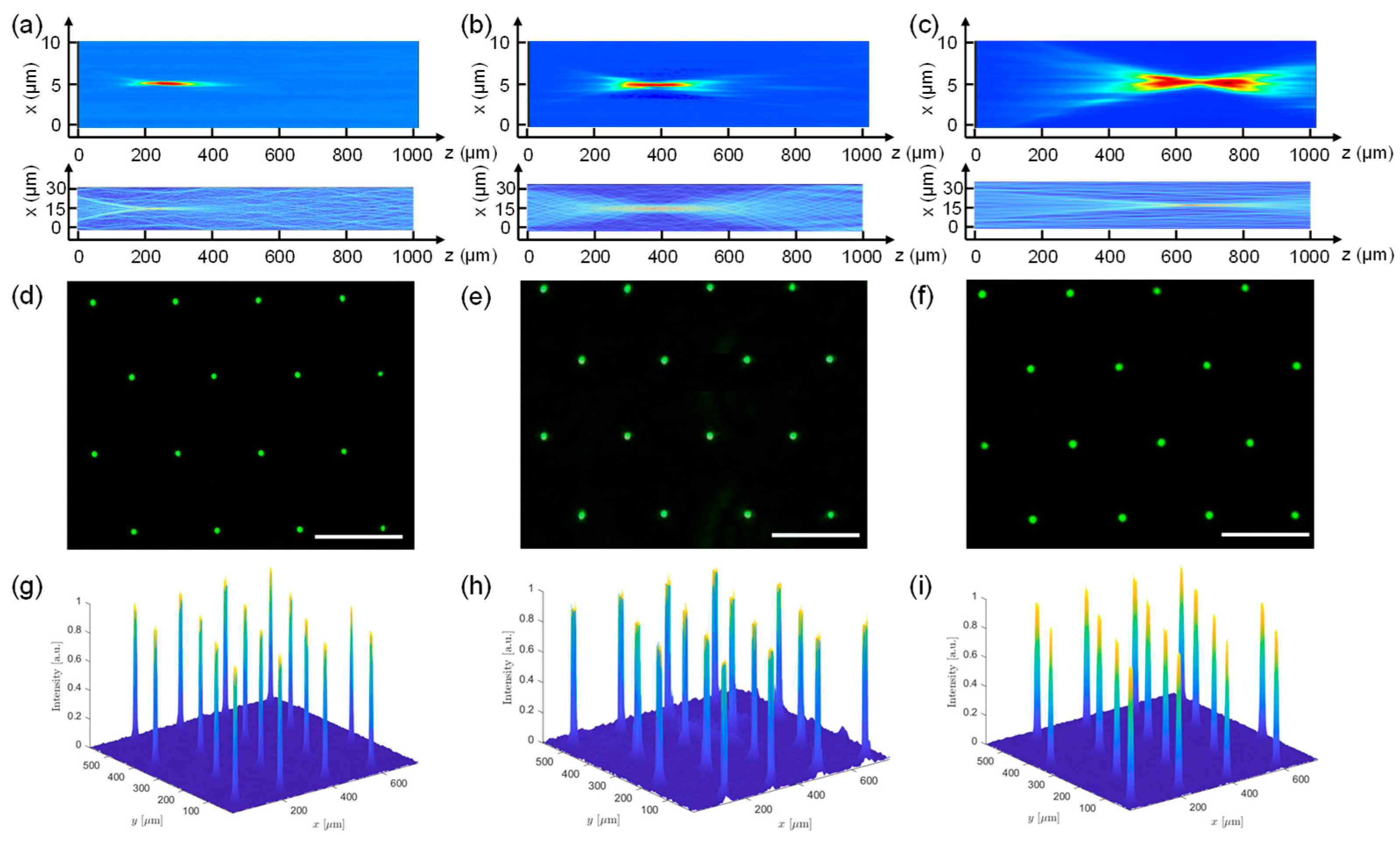
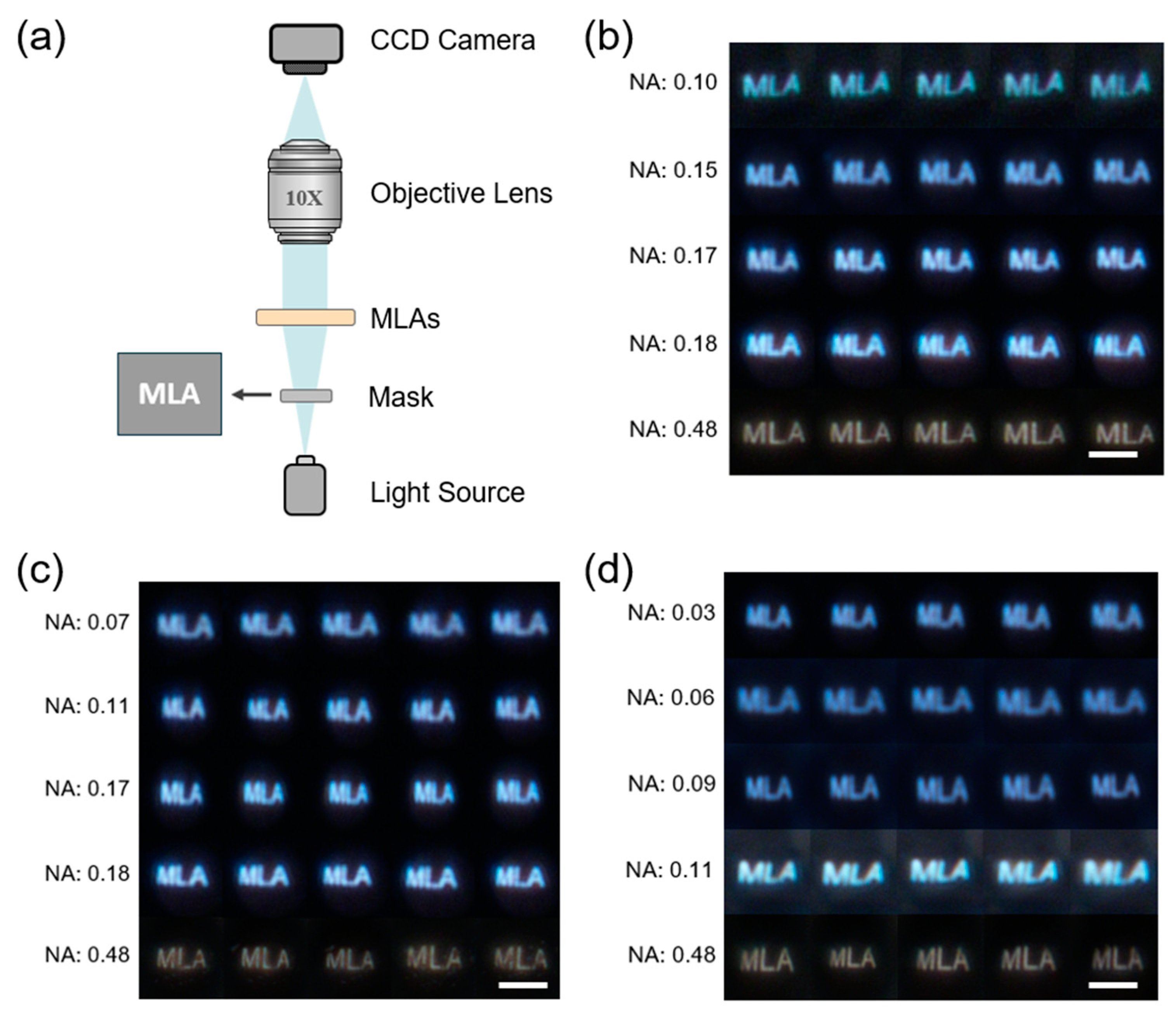
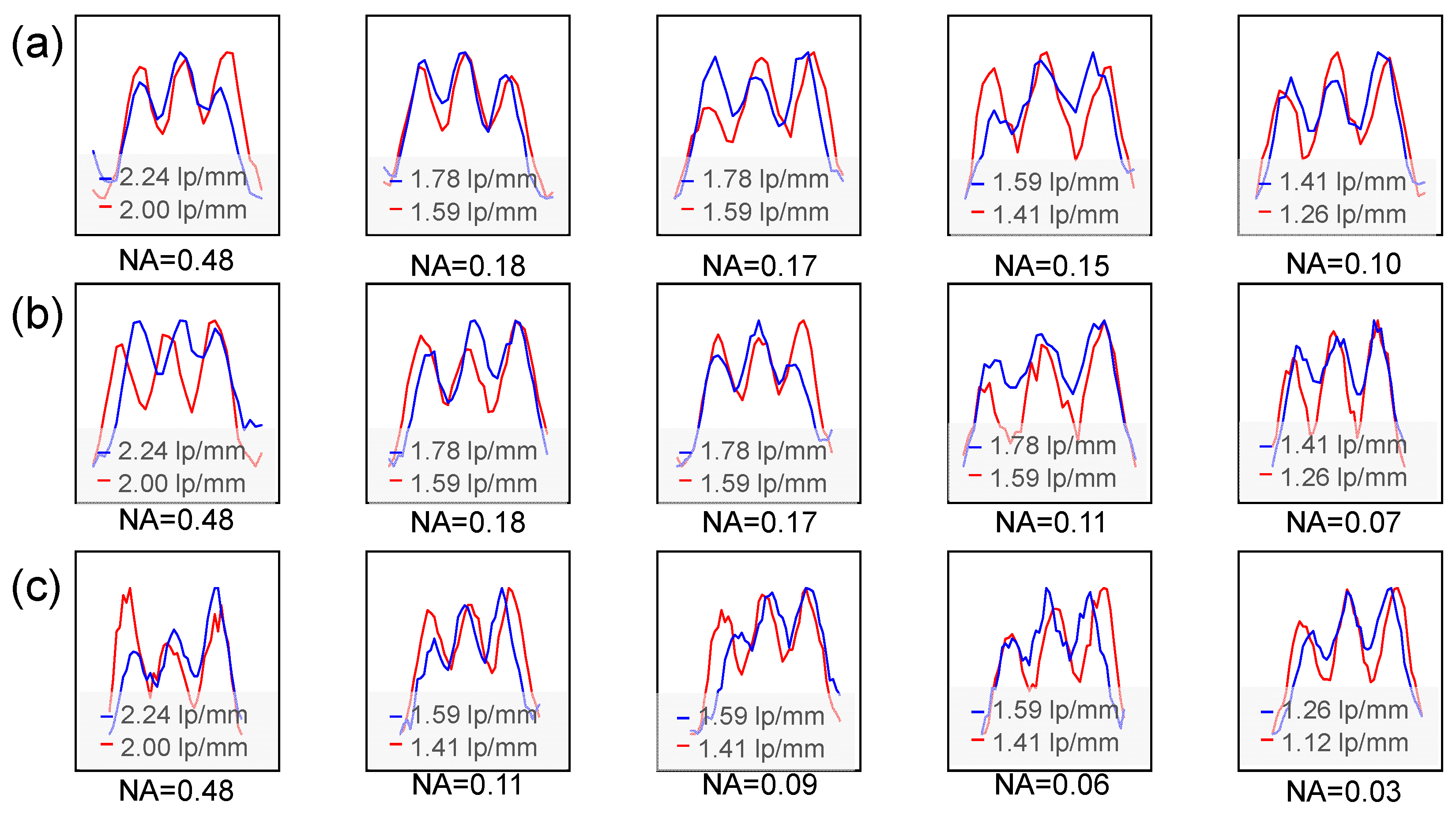
3.2. Optical Characterization of MLAs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho, Y.H.; Chen, K.Y.; Peng, K.Y.; Tsai, M.C.; Tian, W.C.; Wei, P.K. Enhanced light out-coupling of organic light-emitting diode using metallic nanomesh electrodes and microlens array. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 8535–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhu, P.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Song, R.; Ee, Y.K.; Kumnorkaew, P.; Gilchrist, J.F.; Tansu, N. Light extraction efficiency enhancement of III-Nitride light-emitting diodes by using 2-D close-packed TiO2 microsphere arrays. J. Disp. Technol. 2013, 9, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.R.; Le, H.B.; Ji, W.Y.; Ko, K.J.; Park, S.; Yoo, S.; Kang, J.W. Improving light extraction of flexible OLEDs using a mechanically robust Ag mesh/ITO composite electrode and microlens array. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 5444–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Bian, H.; Du, G.; Yong, J.; Shan, C.; Hou, X. Dragonfly-eye-inspired artificial compound eyes with sophisticated Imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 26, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Xu, W.; Hu, X.; Zhu, W.; Yue, T.; Zhang, C.; Yan, F.; Chen, L.; Lezec, H.J.; Lu, Y.; et al. Trilobite-inspired neural nanophotonic light-field camera with extreme depth-of-field. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Mei, X.; Pan, A.; Sun, X.; Liu, B.; Cui, J. Artificial compound eyes prepared by a combination of air-assisted deformation, modified laser swelling, and controlled crystal growth. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Elshobaki, M.; Ye, Z.; Park, J.M.; Noack, M.A.; Ho, K.M.; Chaudhary, S. Microlens array induced light absorption enhancement in polymer solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 4297–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.D.; Cao, W.; Cassidy, V.; Eom, S.H.; Zhou, R.; Yang, L.; You, W.; Xue, J. A universal optical approach to enhancing efficiency of organic-based photovoltaic devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6900–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, M.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.K.; Yang, S.S. Concentrating microlens array mounted on an InGaP/GaAs/Ge solar cell for photovoltaic performance enhancement. Sol. Energy 2013, 91, 374–380. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Wu, K.; Cheng, J.; Li, P.; Zheng, J. The micro-optic photovoltaic behavior of solar cell along with microlens curved glass substrate. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2015, 96, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.Q.; Chin, W.H.; Sun, Y.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D. A novel lab-on-chip platform with integrated solid phase PCR and supercritical angle fluorescence (SAF) microlens array for highly sensitive and multiplexed pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Yu, W.; Meng, X.; Sun, A.; Xue, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, S. Real-time quantitative phase imaging based on transport of intensity equation with dual simultaneously recorded field of view. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Xu, J.; Niu, L.G.; Wu, S.Z.; Midorikawa, K.; Sugioka, K. In-channel integration of designable microoptical devices using flat scaffold-supported femtosecond-laser microfabrication for coupling-free optofluidic cell counting. Light Sci. Appl. 2015, 4, e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Xia, H.; Li, W.; Kong, D.; Ma, Z.; Cheng, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Luo, D.; et al. Electrohydrodynamically printed microlens arrays with controllable curvature based on surface functionalization. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 46, 103935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lu, H. Self-assembled microlens array with controllable focal length formed on a selective wetting surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 7826–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Z.Z.; Feng, X.; Lu, B. Fabrication of microlens array with controllable high NA and tailored optical characteristics using confined ink-jetting. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 442, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.T.; Liu, Y.J.; Sun, X.W.; Luo, D. A negative-positive tunable liquid-crystal microlens array by printing. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 4317–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Tu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Yang, Z.Y. High fill factor microlens array fabrication using direct laser writing and its application in wavefront detection. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 4460–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; Conrad, D. Micro lens arrays made by CO2-laser radiation. Proc. SPIE 2020, 11478, 1147806. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, Y.; Li, S.; Qian, J.; Xiao, Y.; Fu, S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, M. Fabrication of large-area microwells on Polydimethylsiloxane films by femtosecond laser ablation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 130, 106330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Cao, X.W.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.Z.; Chen, Q.D.; Juodkazis, S.; Sun, H.B. Control of diameter and numerical aperture of microlens by a single ultra-short laser pulse. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 5149–5152. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Cai, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Yuan, D.; Ma, Z.; Bai, Z.; Kong, D.; Cen, M.; Xu, S.; et al. Responsive liquid crystal network microstructures with customized shapes and predetermined morphing for adaptive soft microoptics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 31776–31787. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.; Cheng, M.; Kong, D.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.J. Switchable liquid crystal lenticular microlens arrays based on photopolymerization-induced phase separation for 2D/3D autostereoscopic displays. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Kong, D.; Ma, Z.; Cen, M.; Wang, J.; Yuan, D.; Li, K.; Cheng, M.; Xu, S.; Luo, D.; et al. Optically anisotropic, electrically tunable microlens arrays formed via single-step photopolymerization-induced phase separation in polymer/liquid-crystal composite materials. Light Adv. Manuf. 2023, 4, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Si, G.; Liu, Y.J. Optically isotropic, electrically tunable liquid crystal droplet arrays formed by photopolymerizationinduced phase separation. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 2723–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, G.; Weng, Y.; Weng, X.; Zhou, X.; Wu, C.; Guo, T.; Yan, Q.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Y. Large-scale microlens arrays on flexible substrate with improved numerical aperture for curved integral imaging 3D display. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11741. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Peng, Y.; Peng, R.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, T. Fabrication of large-scale microlens arrays based on screen printing for integral imaging 3D display. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24248–24255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, H.; Ding, Y.; Xu, M. Low voltage liquid crystal microlens array based on polyvinyl alcohol convex induced vertical alignment. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 48, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, M.; Lu, H.; Ding, Y. A polyvinyl alcohol microlens array with controlled curvature on discontinuous hydrophobic surface. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. Rapid fabrication of curved microlens array using the 3D printing mold. Optik 2018, 156, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, Q.; Fang, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, S.; Dai, B. Fabrication of a microlens array with controlled curvature by thermally curving photosensitive gel film beneath microholes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16604–16609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, C.; Liu, C.; Yu, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, T.; Qiao, Y.; Yu, W. Fabrication and characterization of a polymeric curved compound eye. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2019, 29, 055008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, M.; Qiu, J.; Ye, H. Fabrication of high fill-factor aspheric microlens array by dose-modulated lithography and low temperature thermal reflow. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.U.; Hardy, M.; Kang, S.J.; Barton, K.; Adair, K.; Mukhopadhyay, D.K.; Lee, C.Y.; Strano, M.S.; Alleyne, A.G.; Georgiadis, J.G.; et al. High-resolution electrohydrodynamic jet printing. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhou, P.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zou, W.; Luo, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L. In situ electrohydrodynamic jet printing-based fabrication of tunable microlens arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 39550–39560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.W.; Kim, K.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Shim, Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Song, J.Y.; Park, J.U. High-resolution printing of 3D structures using an electrohydrodynamic inkjet with multiple functional inks. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4322–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onses, M.S.; Sutanto, E.; Ferreira, P.M.; Alleyne, A.G.; Rogers, J.A. Mechanisms, capabilities, and applications of high-resolution electrohydrodynamic jet printing. Small 2015, 11, 4237–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chen, S. Over 32.5% efficient top-emitting quantum-dot LEDs with angular-independent emission. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 30039–30045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; LV, L.; Hu, F. Photoresist microlens arrays fabricated by nanoimprint technique to improve the photoelectric conversion efficiency of solar cells. Coatings 2022, 12, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Disintegration of water drops in an electric field. Proc. R. Soc. A 1964, 280, 383–397. [Google Scholar]
- John, R. UV/ozone cleaning of surfaces. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1985, 3, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, T.D.; Coninck, J.D. The influence of solid–liquid interactions on dynamic wetting. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 96, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Schambach, M.; Schlisske, S.; Jin, Q.; Mertens, A.; Rainer, C.; Sosa, G.H.; Heizmann, M.; Lemmer, U. Fabrication of microlens arrays with high quality and high fill factor by inkjet printing. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2200677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Du, G.; Bian, H.; Zhang, D.; Si, J.; Yun, F.; Hou, X. Rapid fabrication of large-area concave microlens arrays on PDMS by a femtosecond laser. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 9382–9385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, L.; Liu, W.; Gong, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Kong, D.; Du, Q.; Xu, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.J. Electrohydrodynamically Printed Microlens Arrays with the High Filling Factor near 90%. Photonics 2025, 12, 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050446
Zhong L, Liu W, Gong H, Li Y, Zhao X, Kong D, Du Q, Xu B, Zhang X, Liu YJ. Electrohydrodynamically Printed Microlens Arrays with the High Filling Factor near 90%. Photonics. 2025; 12(5):446. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050446
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Linkun, Weixuan Liu, Hongbo Gong, Ye Li, Xueqian Zhao, Delai Kong, Qingguo Du, Bing Xu, Xiaoli Zhang, and Yan Jun Liu. 2025. "Electrohydrodynamically Printed Microlens Arrays with the High Filling Factor near 90%" Photonics 12, no. 5: 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050446
APA StyleZhong, L., Liu, W., Gong, H., Li, Y., Zhao, X., Kong, D., Du, Q., Xu, B., Zhang, X., & Liu, Y. J. (2025). Electrohydrodynamically Printed Microlens Arrays with the High Filling Factor near 90%. Photonics, 12(5), 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050446






