Real-Time Observer and Neuronal Identification of an Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Models
2.1. Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser Mathematical Model
Normalized Equations of EDFL
2.2. Mathematical Model of State Observer
2.3. Mathematical Model of RWFONN
3. Methodology and Description of the Process
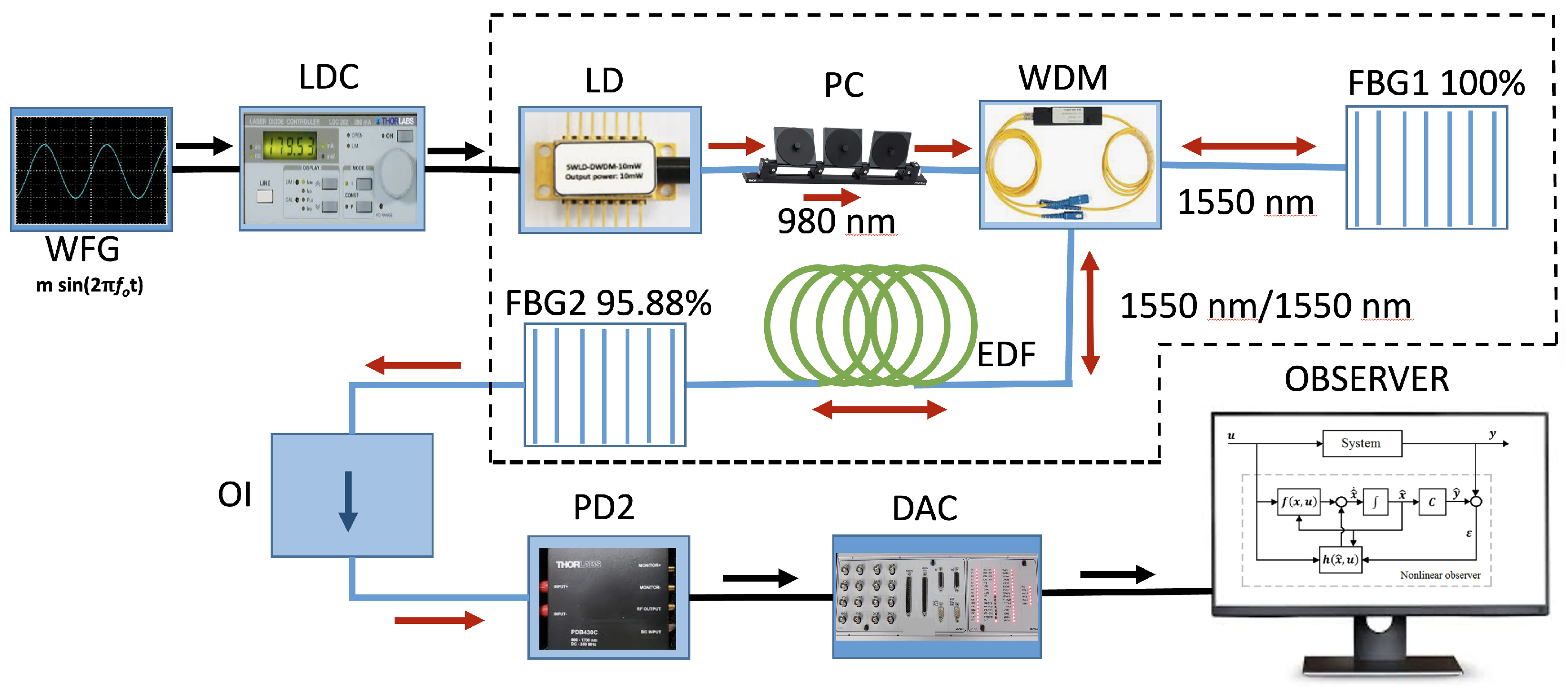
3.1. Experimental Setup
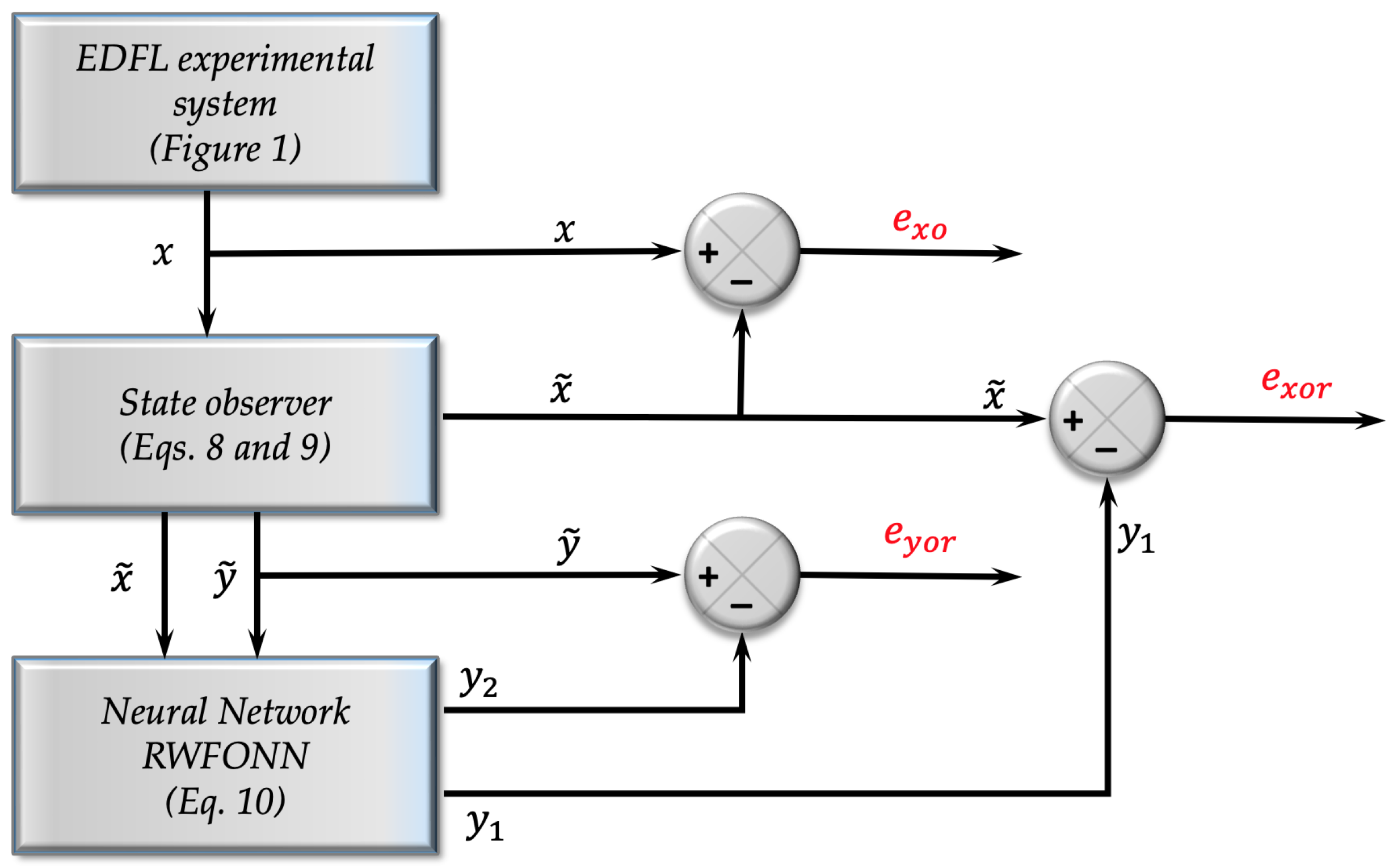
3.2. Schematic Implementation of State Observer in Real-Time
3.3. Temporary Rescaling
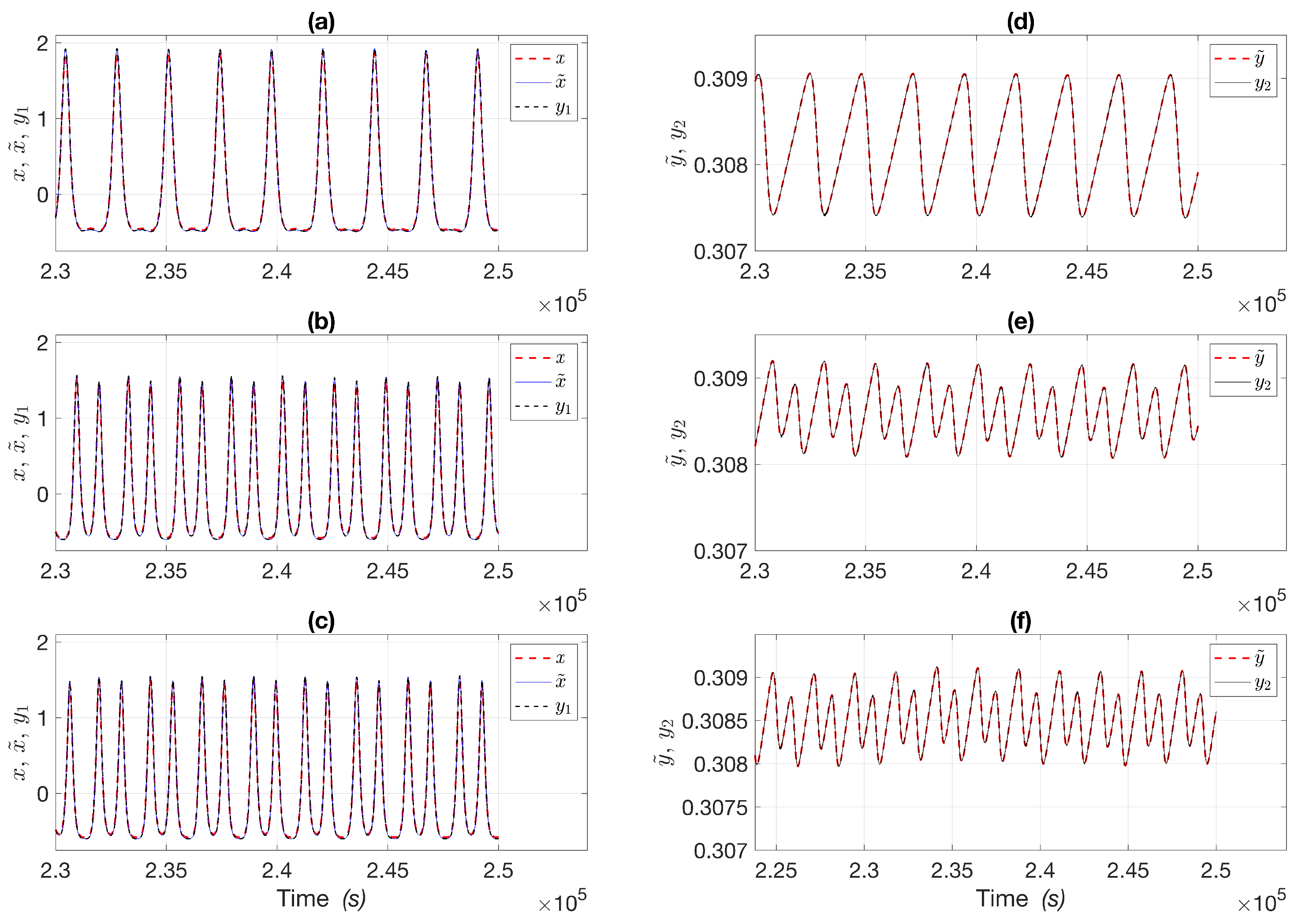
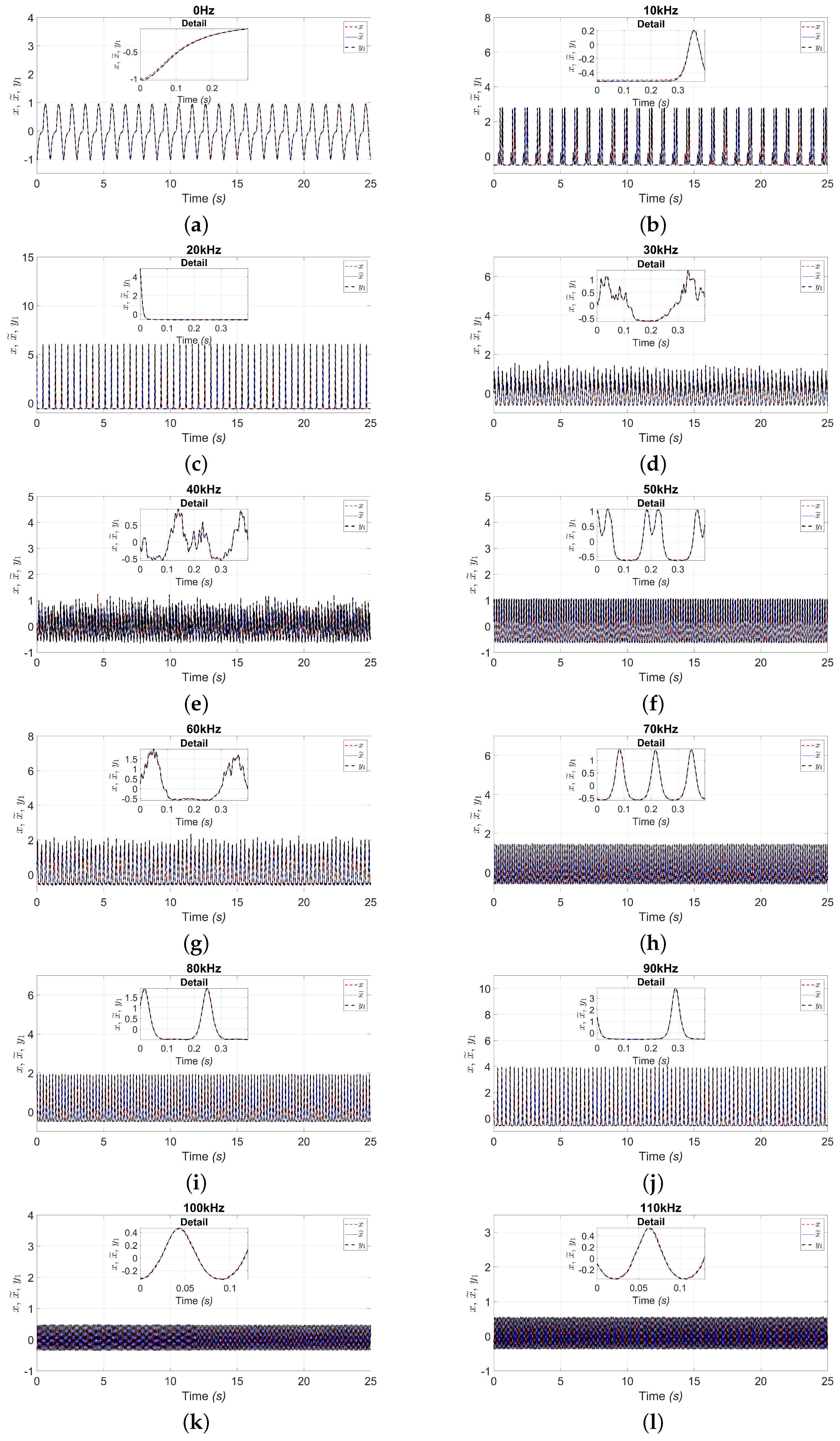
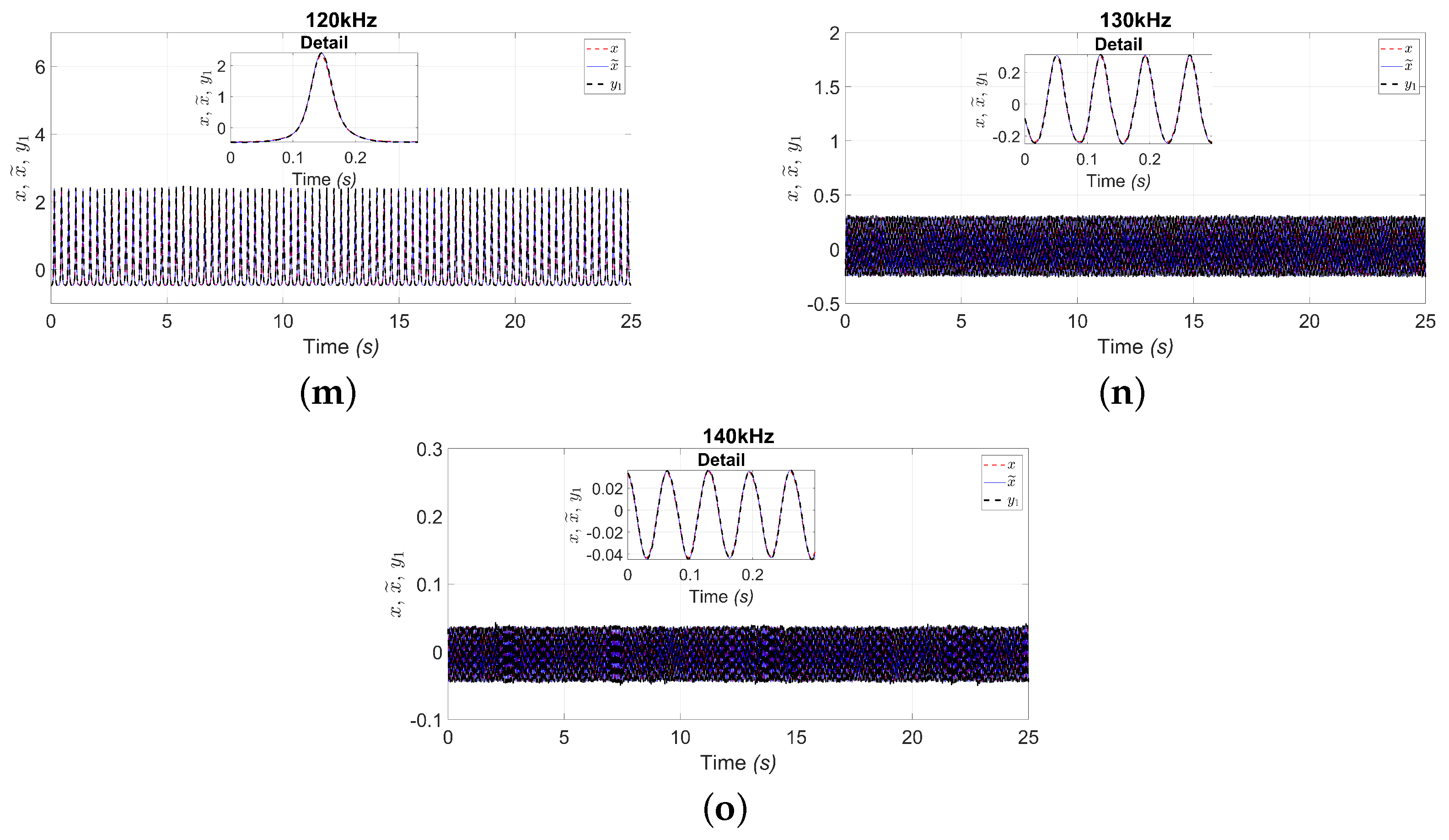
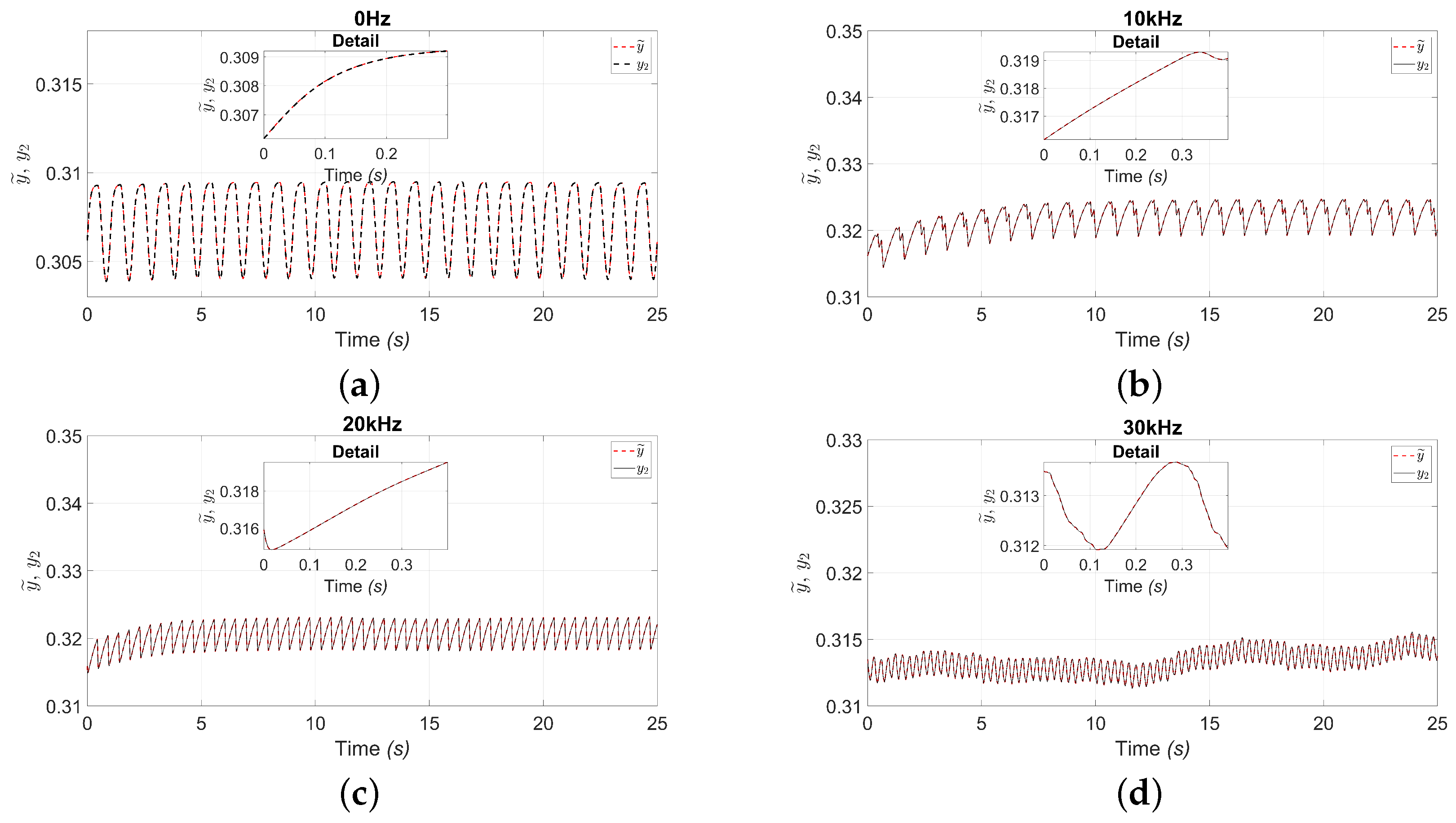
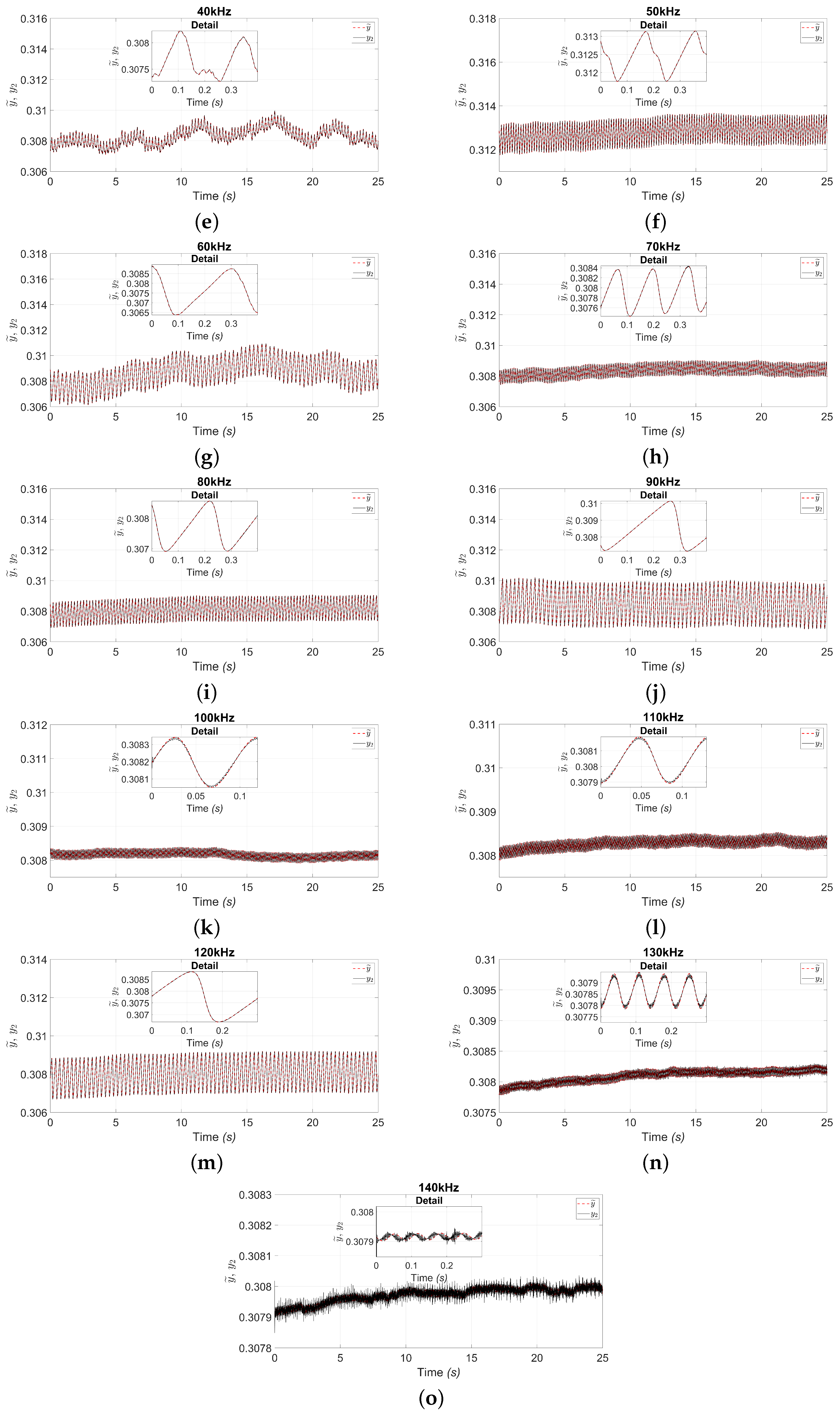
4. Real-Time Observer and Neural Identification Results
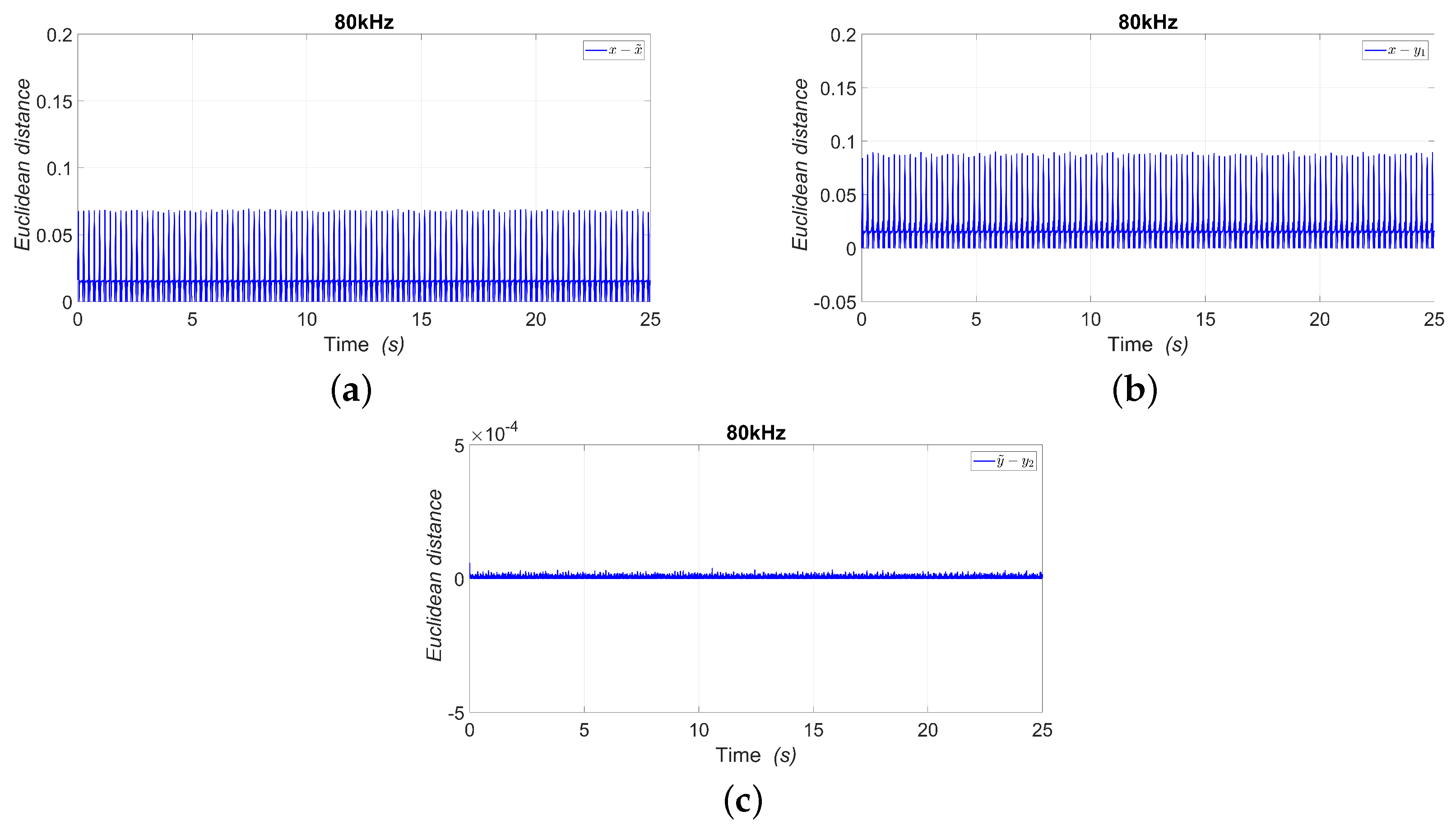
Euclidean Distance and MSE Metrics
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Stability Analysis
References
- Sulaiman, A.; Harun, S.W.; Ahmad, H. Erbium-doped fiber laser with a microfiber coupled to silica microsphere. IEEE Photonics J. 2012, 4, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, T.K. Erbium doped fiber lasers for long distance communication using network of fiber optics. Am. J. Opt. Photonics 2015, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Suzek, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; He, S.; Cheng, T.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Gindulyte, A.; Bryant, S.H. PubChem bioassay: 2014 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D1075–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, B. Erbium Doped Fiber Laser and Amplifier. Opt. Photonics J. 2014, 4, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meucci, R.; Ciofini, M.; Abbate, R. Suppressing chaos in lasers by negative feedback. Phys. Rev. E 1996, 53, R5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meucci, R.; Marc Ginoux, J.; Mehrabbeik, M.; Jafari, S.; Clinton Sprott, J. Generalized multistability and its control in a laser. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2022, 32, 083111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciofini, M.; Meucci, R.; Arecchi, F. Experimental control of chaos in a laser. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 52, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.H.; Kang, J.J.; Wu, H.H.; Lee, C.K.; Lin, G.R. Manipulation of operation states by polarization control in an erbium-doped fiber laser with a hybrid saturable absorber. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 4806–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombansen, U.; Gatej, A.; Pereira, M. Process observation in fiber laser–based selective laser melting. Opt. Eng. 2015, 54, 011008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konadu, K.A.; Yi, S.; Choi, W.; Abu-Lebdeh, T. Robust positioning of laser beams using proportional integral derivative and based observer-feedback control. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2013, 10, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Friedman, N.; Geiger, D.; Goldszmidt, M. Bayesian network classifiers. Mach. Learn. 1997, 29, 131–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, L.A.; Jurado, F. Continuous-time decentralized wavelet neural control for a 2 DOF robot manipulator. In Proceedings of the 2014 11th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control (CCE), Ciudad del Carmen, Mexico, 29 September–3 October 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Magallón-García, D.; García-López, J.; Huerta-Cuellar, G.; Jaimes-Reátegui, R.; Diaz-Diaz, I.; Ontanon-Garcia, L. Real-time neural identification using a recurrent wavelet first-order neural network of a chaotic system implemented in an FPAA. Integration 2024, 96, 102134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echenausía-Monroy, J.L.; Pena Ramirez, J.; Álvarez, J.; Rivera-Rodríguez, R.; Ontañón-García, L.J.; Magallón-García, D.A. A recurrent neural network for identifying multiple chaotic systems. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabessa, J.; Villa, A.E. A hierarchical classification of first-order recurrent neural networks. In International Conference on Language and Automata Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 142–153. [Google Scholar]
- Salgado, I.; Chairez, I. Nonlinear discrete time neural network observer. Neurocomputing 2013, 101, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogmus, D.; Genç, A.U.; Príncipe, J.C. A neural network perspective to extended Luenberger observers. Meas. Control 2002, 35, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, G. A multilayer recurrent neural network for on-line synthesis of minimum-norm linear feedback control systems via pole assignment. Automatica 1996, 32, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Poznyak, A.S. Robust Asymptotic Neuro Observer with Time Delay Term. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. IFAC-Affil. J. 2000, 10, 535–559. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, I.; Liu, Y.; Davis, P. Synchronization of chaotic semiconductor laser dynamics on subnanosecond time scales and its potential for chaos communication. Phys. Rev. A 2000, 62, 011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwiggeren, G.D.; Roy, R. Communication with chaotic lasers. Science 1998, 279, 1198–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, S.; Mirasso, C.R. Introduction to the feature section on optical chaos and applications to cryptography. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2002, 38, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsubo, J.; Davis, P. Chaotic optical communication. In Unlocking Dynamical Diversity: Optical Feedback Effects on Semiconductor Lasers; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 307–334. [Google Scholar]
- Soriano, M.C.; Ruiz-Oliveras, F.; Colet, P.; Mirasso, C.R. Synchronization properties of coupled semiconductor lasers subject to filtered optical feedback. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 046218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arecchi, F.T.; Harrison, R.G. Instabilities and Chaos in Quantum Optics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 34. [Google Scholar]
- Lacot, E.; Stoeckel, F.; Chenevier, M. Dynamics of an erbium-doped fiber laser. Phys. Rev. A 1994, 49, 3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehranchi, A.; Kashyap, R. Extremely efficient DFB lasers with flat-top intra-cavity power distribution in highly erbium-doped fibers. Sensors 2023, 23, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magallón-García, D.A.; López-Mancilla, D.; Jaimes-Reátegui, R.; García-López, J.H.; Huerta Cuellar, G.; Ontañon-García, L.J.; Soto-Casillas, F. Experimental State Observer of the Population Inversion of a Multistable Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser. Photonics 2024, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarchik, A.N.; Kir’yanov, A.V.; Barmenkov, Y.O.; Jaimes-Reátegui, R. Dynamics of an erbium-doped fiber laser with pump modulation: Theory and experiment. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2005, 22, 2107–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Cuellar, G.; Pisarchik, A.N.; Barmenkov, Y.O. Experimental characterization of hopping dynamics in a multistable fiber laser. Phys. Rev. E—Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2008, 78, 035202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reategui, R.J. Dynamic of Complex Systems with Parametric Modulation: Duffing Oscillators and a Fiber Laser. Ph.D. Thesis, Centro de Investigaciones en Optica Leon, Guanajuato, Mexico, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Magallón-García, D.A.; Ontanon-Garcia, L.J.; García-López, J.H.; Huerta-Cuéllar, G.; Soubervielle-Montalvo, C. Identification of chaotic dynamics in jerky-based systems by recurrent wavelet first-order neural networks with a morlet wavelet activation function. Axioms 2023, 12, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberti, L.; Lavor, C.; Maculan, N.; Mucherino, A. Euclidean distance geometry and applications. SIAM Rev. 2014, 56, 3–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters and Values | Parameters and Values |
|---|---|
| Parameters | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Frequency | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 kHz | 10.0 | 20.0 | 1.008 |
| 20 kHz | 30.0 | 50.0 | 2.449 |
| 30 kHz | 3.91 | 7.71 | 0.412 |
| 40 kHz | 3.25 | 10.0 | 0.265 |
| 50 kHz | 5.23 | 9.51 | 0.521 |
| 60 kHz | 7.11 | 10.0 | 0.701 |
| 70 kHz | 5.81 | 10.0 | 0.565 |
| 80 kHz | 6.31 | 9.33 | 0.652 |
| 90 kHz | 10.0 | 20.0 | 1.426 |
| 100 kHz | 1.06 | 2.13 | 0.177 |
| 110 kHz | 1.42 | 3.10 | 0.200 |
| 120 kHz | 7.05 | 10.0 | 0.725 |
| 130 kHz | 0.56 | 1.36 | 0.135 |
| 140 kHz | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.097 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magallón-García, D.A.; López-Mancilla, D.; Jaimes-Reátegui, R.; García-López, J.H.; Huerta-Cuellar, G.; Ontañon-García, L.J. Real-Time Observer and Neuronal Identification of an Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser. Photonics 2025, 12, 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12100955
Magallón-García DA, López-Mancilla D, Jaimes-Reátegui R, García-López JH, Huerta-Cuellar G, Ontañon-García LJ. Real-Time Observer and Neuronal Identification of an Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser. Photonics. 2025; 12(10):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12100955
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagallón-García, Daniel Alejandro, Didier López-Mancilla, Rider Jaimes-Reátegui, Juan Hugo García-López, Guillermo Huerta-Cuellar, and Luis Javier Ontañon-García. 2025. "Real-Time Observer and Neuronal Identification of an Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser" Photonics 12, no. 10: 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12100955
APA StyleMagallón-García, D. A., López-Mancilla, D., Jaimes-Reátegui, R., García-López, J. H., Huerta-Cuellar, G., & Ontañon-García, L. J. (2025). Real-Time Observer and Neuronal Identification of an Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser. Photonics, 12(10), 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12100955








