Probing Layered Tissues by Backscattering Mueller Matrix Imaging and Tissue Optical Clearing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Samples
2.2.1. Design of Tissue Phantoms
2.2.2. TOC Procedures of Tissue Phantoms
2.2.3. Living Skin Samples
2.3. Polarization Feature Extraction Techniques
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. TOC Dynamics of Different Layered Phantoms
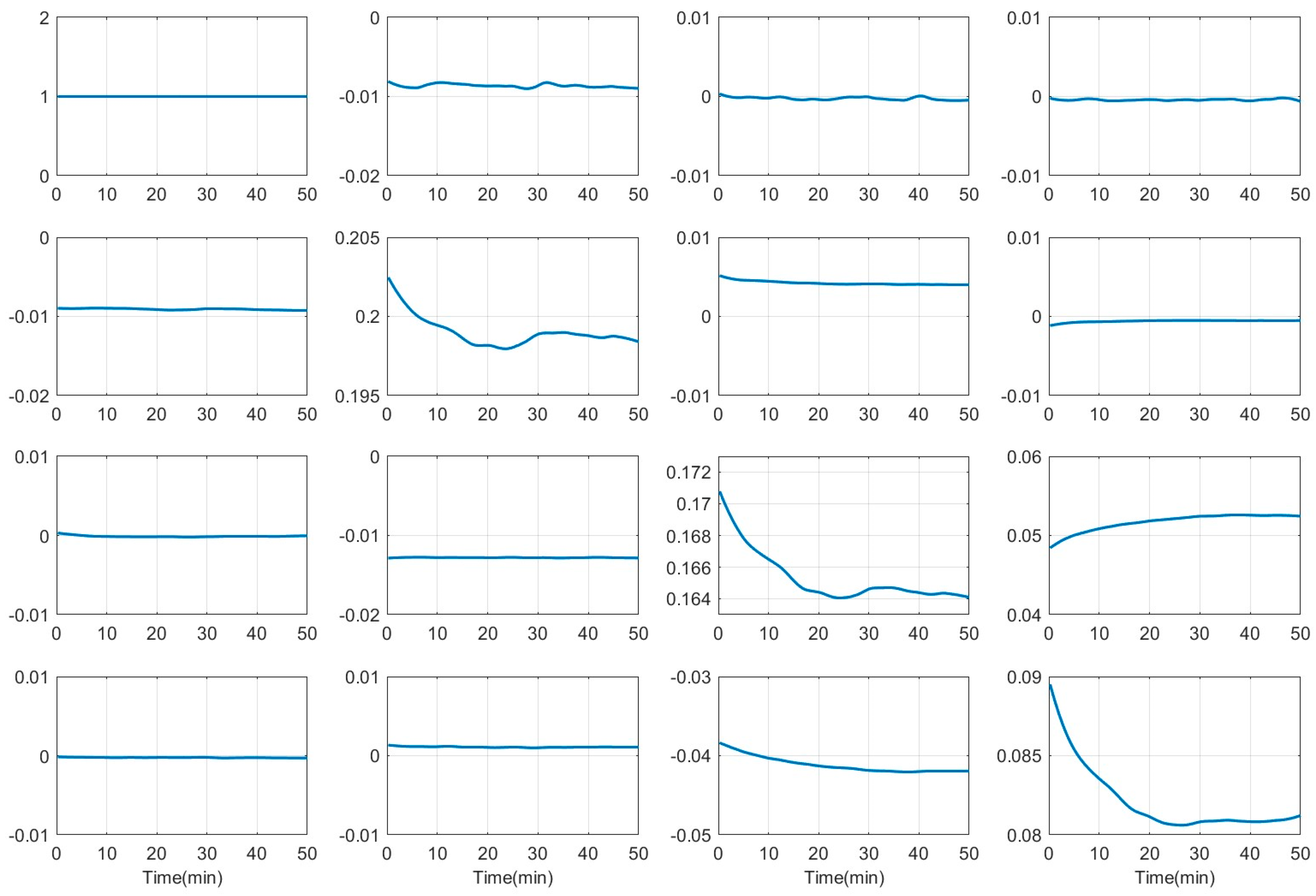
3.1.1. Variation of Mueller Matrix during TOC
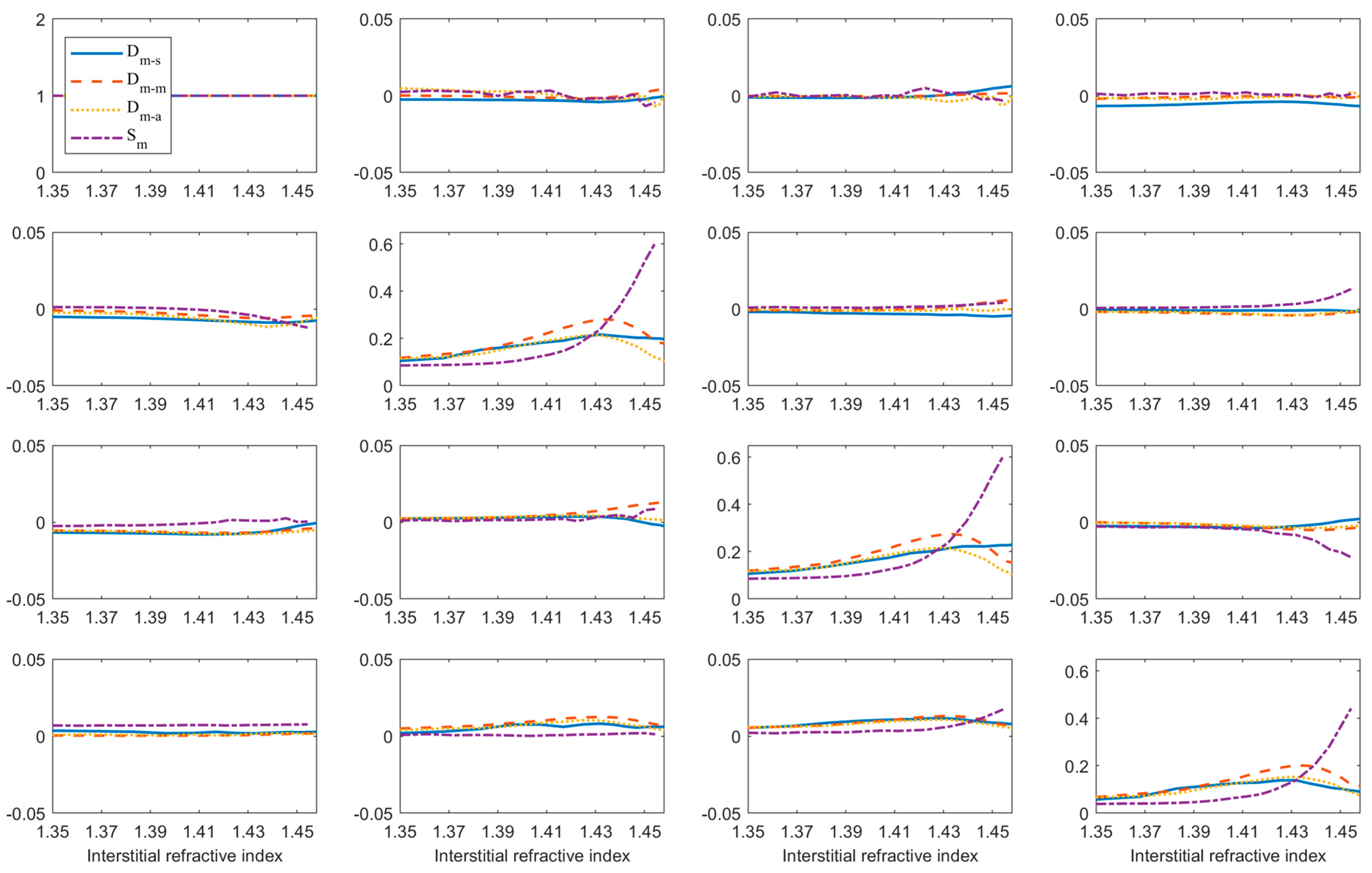
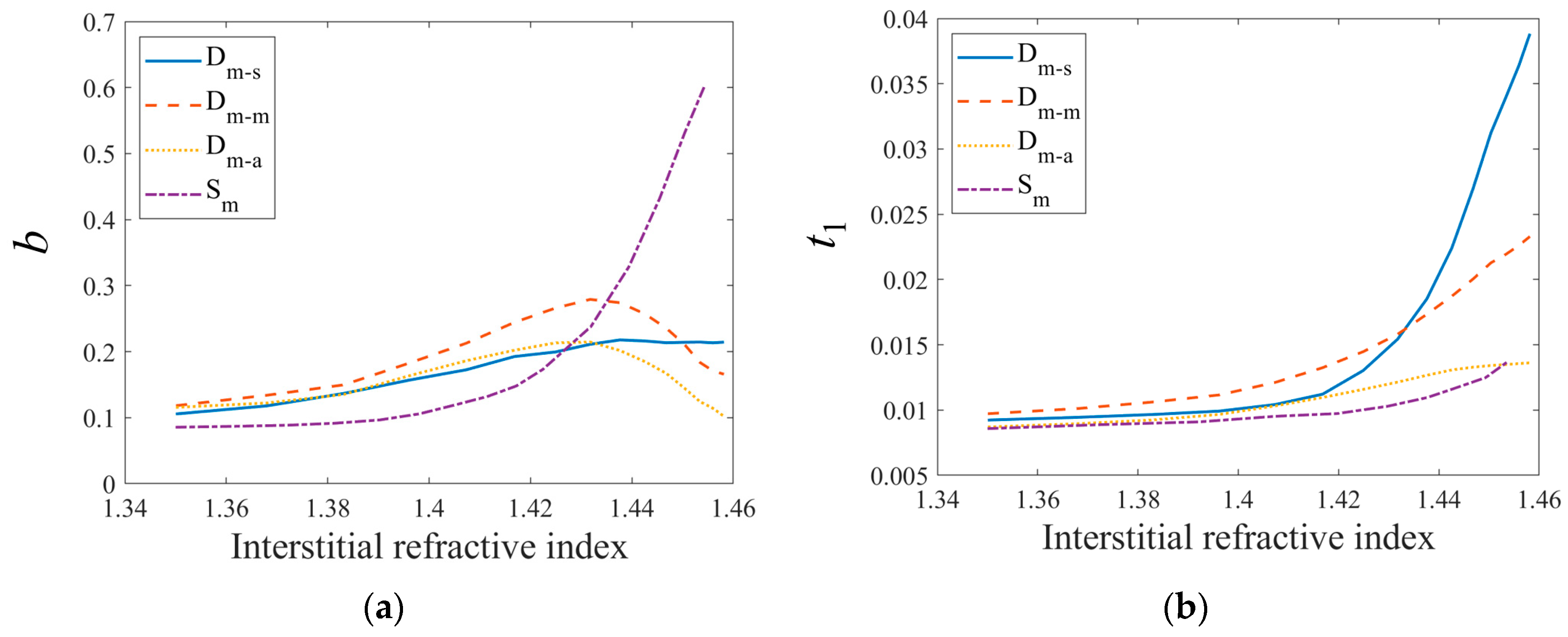
3.1.2. Variation of PBPs during TOC
3.2. Extracting Microstructural Information of the Upper and Lower Layers via the TOC Process
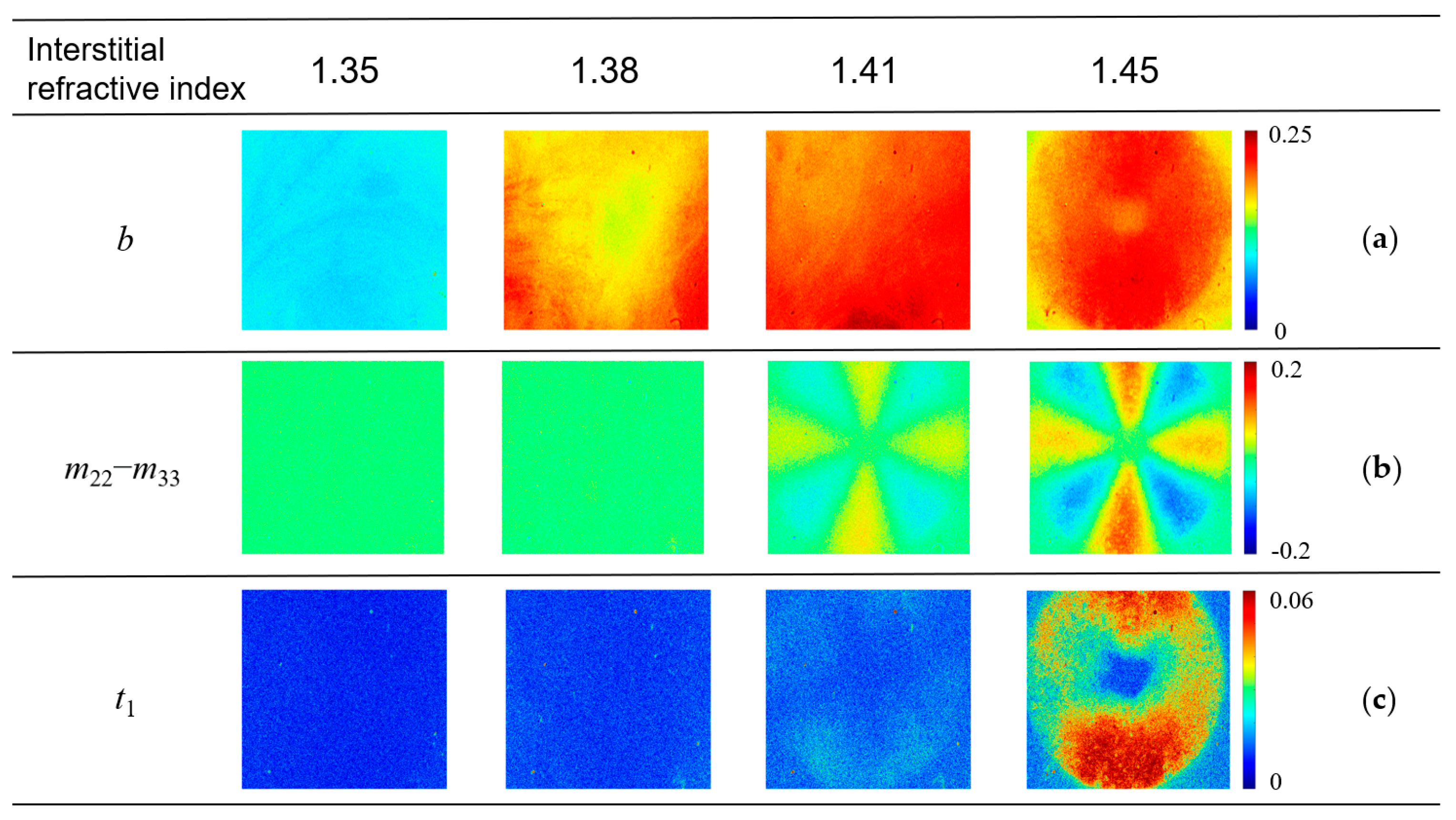
3.2.1. Changes in PBP Images during TOC
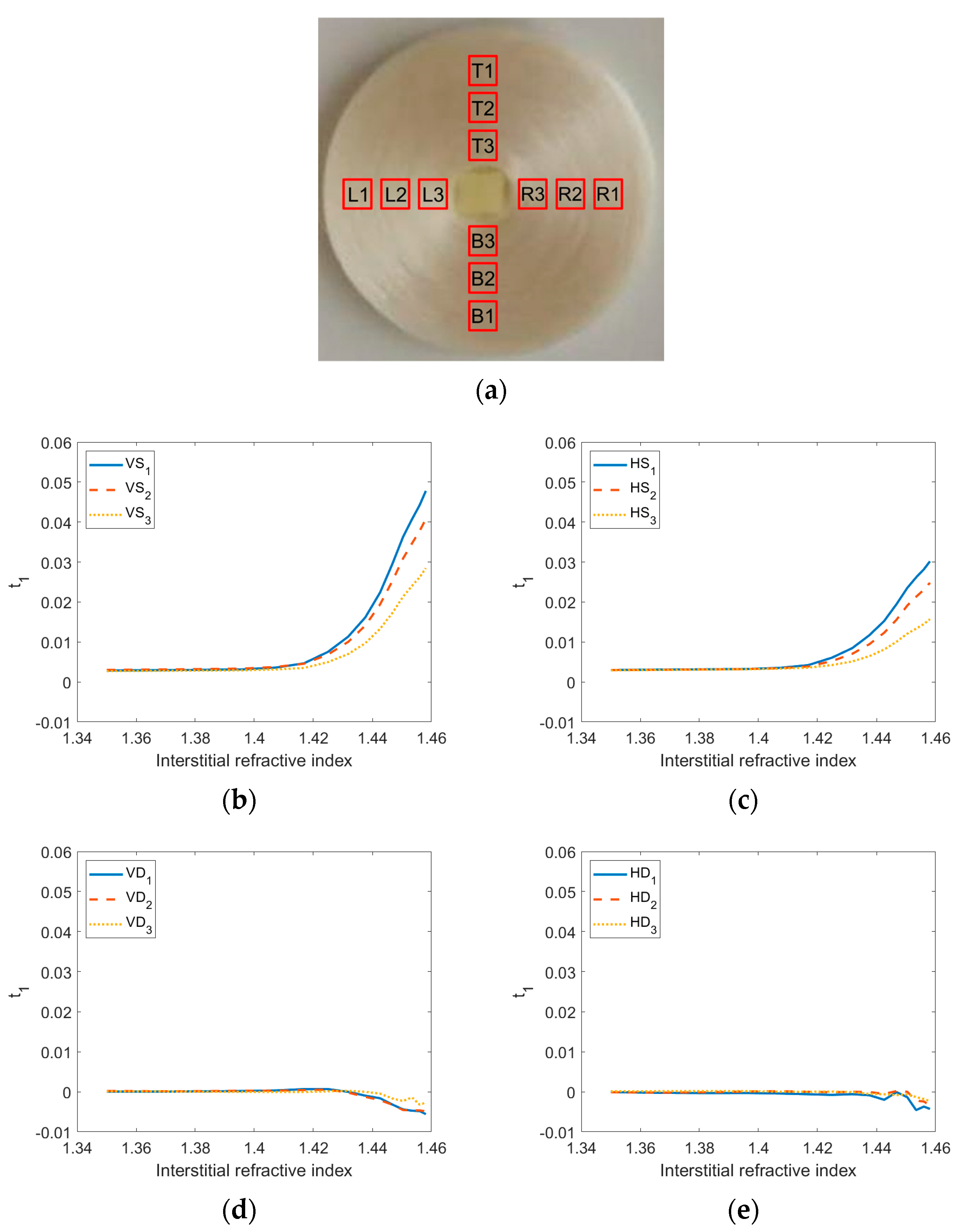
3.2.2. Influence of Oblique Incident Illumination
3.3. Probing Layered Structures in Living Skin Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghosh, N.; Vitkin, A. Tissue polarimetry: Concepts, challenges, applications, and outlook. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 110801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Elson, D.S. Mueller polarimetric imaging for surgical and diagnostic applications: A review. J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 950–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierangelo, A.; Benali, A.; Antonelli, M.R.; Novikova, T.; Validire, P.; Gayet, B.; De Martino, A. Ex-vivo characterization of human colon cancer by Mueller polarimetric imaging. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurjar, R.S.; Backman, V.; Perelman, L.T.; Georgakoudi, I.; Badizadegan, K.; Itzkan, I.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S. Imaging human epithelial properties with polarized light-scattering spectroscopy. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1245–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunnen, B.; Macdonald, C.; Doronin, A.; Jacques, S.; Eccles, M.; Meglinski, I. Application of circularly polarized light for non-invasive diagnosis of cancerous tissues and turbid tissue-like scattering media. J. Biophotonics 2015, 8, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schucht, P.; Lee, H.R.; Mezouar, H.M.; Hewer, E.; Raabe, A.; Murek, M.; Zubak, I.; Goldberg, J.; Kövari, E.; Pierangelo, A.; et al. Visualization of White Matter Fiber Tracts of Brain Tissue Sections With Wide-Field Imaging Mueller Polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 4376–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villiger, M.; Lorenser, D.; McLaughlin, R.A.; Quirk, B.C.; Kirk, R.W.; Bouma, B.E.; Sampson, D.D. Deep tissue volume imaging of birefringence through fibre-optic needle probes for the delineation of breast tumour. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roa, C.; Du Le, V.N.; Mahendroo, M.; Saytashev, I.; Ramella-Roman, J.C. Auto-detection of cervical collagen and elastin in Mueller matrix polarimetry microscopic images using K-NN and semantic segmentation classification. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 2236–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, S.; Ramella-Roman, J.; Lee, K. Imaging skin pathology with polarized light. J. Biomed. Opt. 2002, 7, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushenko, Y.A.; Tomka, Y.Y.; Dubolazov, A.V.; Telen’ga, O.Y. Diagnostics of optical anisotropy changesin biological tissues using Müller matrix. Quantum Electron. 2011, 41, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zeng, N.; He, H.; Liu, C.; Du, E.; He, Y.; Ma, H. Retardance of bilayer anisotropic samples consisting of well-aligned cylindrical scatterers and birefringent media. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yao, Y.; Si, L.; Liu, Y.; He, H.; Ma, H. Probing layered structures by multi-color backscattering polarimetry and machine learning. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 4324–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuchin, V.; Maksimova, I.; Zimnyakov, D.; Kon, I.; Mavlyutov, A.; Mishin, A. Light propagation in tissues with controlled optical properties. J. Biomed. Opt. 1997, 2, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuchin, V.V. Optical clearing of tissues and blood using the immersion method. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhi, Z.; Wen, X.; Luo, Q. Imaging dermal blood flow through the intact rat skin with an optical clearing method. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 026008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Shi, R.; Ma, N.; Tuchina, D.; Tuchin, V.; Zhu, D. Skin optical clearing potential of disaccharides. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 081207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, C.; Meglinski, I. Backscattering of circular polarized light from a disperse random medium influenced by optical clearing. Laser Phys. Lett. 2011, 8, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, B.B.K.; Khatami, S.S.; Ansari, M.A.; Jahangiri, F.; Latifi, H.; Tuchin, V.V. Method for tissue clearing: Temporal tissue optical clearing. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 4222–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchin, V.V.; Genina, E.A.; Tuchina, E.S.; Svetlakova, A.V.; Svenskaya, Y.I. Optical clearing of tissues: Issues of antimicrobial phototherapy and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 180, 114037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, I.; Carvalho, S.; Henrique, R.; Oliveira, L.; Tuchin, V.V. Kinetics of Optical Properties of Colorectal Muscle During Optical Clearing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2019, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, I.; Carvalho, S.; Silva, V.; Henrique, R.; Oliveira, L.; Tuchin, V. Kinetics of optical properties of human colorectal tissues during optical clearing: A comparative study between normal and pathological tissues. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 121620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, T.; Shao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H. Probing Dynamic Variation of Layered Microstructure Using Backscattering Polarization Imaging. Photonics 2022, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Meng, R.; Qi, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liao, R.; Ma, H. Fast Mueller matrix microscope based on dual DoFP polarimeters. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 1676–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogue, B.W.; Patterson, M.S. Review of tissue simulating phantoms for optical spectroscopy, imaging and dosimetry. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 041102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterworth, M.D.; Tarte, B.J.; Joblin, A.J.; Van Doorn, T.; Niesler, H.E. Optical transmission properties of homogenised milk used as a phantom material in visible wavelength imaging. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 1995, 18, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tasic, A.Z.; Djordjevic, B.D.; Grozdanic, D.K.; Radojkovic, N. Use of mixing rules in predicting refractive indexes and specific refractivities for some binary liquid mixtures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1992, 37, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.C.; Dong, Y.; Wan, J.C.; He, H.H.; Aziz, T.; Ma, H. Polaromics: Deriving polarization parameters from a Mueller matrix for quantitative characterization of biomedical specimen. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 034002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Liu, T.; He, H.; Wu, J.; Ma, H. Distinguishing anisotropy orientations originated from scattering and birefringence of turbid media using Mueller matrix derived parameters. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 4092–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; He, H.; Zeng, N.; Du, E.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; He, Y.; Ma, H. Characterizing the microstructures of biological tissues using Mueller matrix and transformed polarization parameters. Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 5, 4223–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; He, H.; Zeng, N.; Du, E.; Guo, Y.; Peng, C.; He, Y.; Ma, H. Probing microstructural information of anisotropic scattering media using rotation-independent polarization parameters. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 2949–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
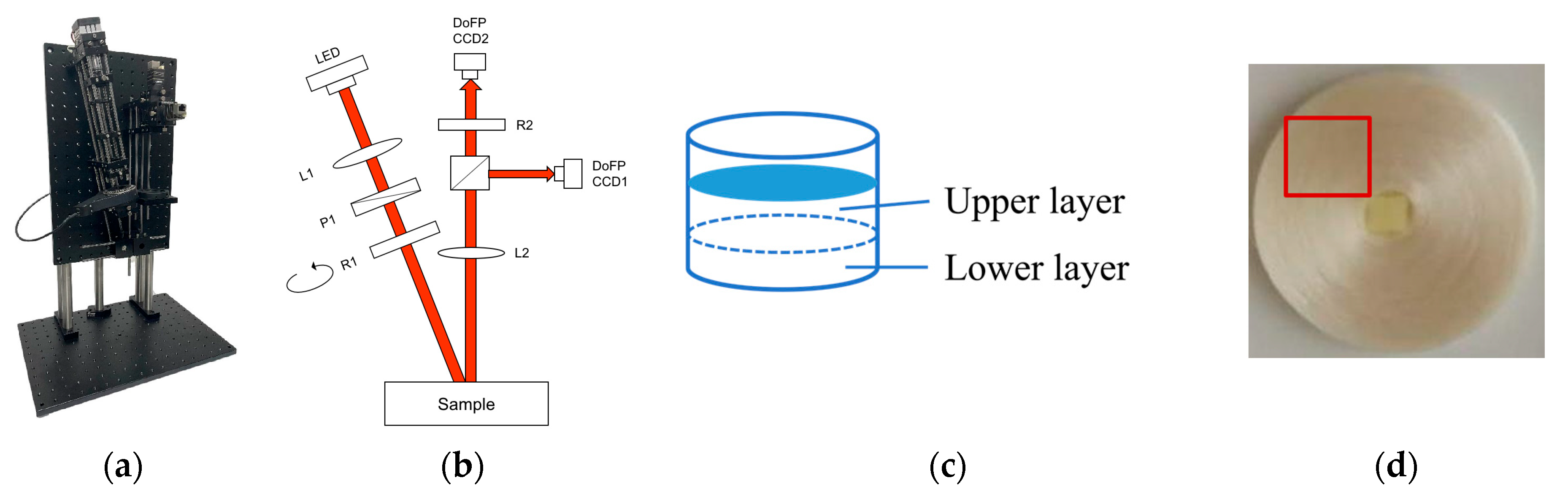


| Type | Name | Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
| Single-layer sample | Sm | 5 cm milk |
| Double-layer samples | Dm-s | Upper layer: 0.3 cm milk Lower layer: concentrically aligned silk fibers |
| Dm-m | Upper layer: 0.3 cm milk Lower layer: porcine skeletal muscle | |
| Dm-a | Upper layer: 0.3 cm milk Lower layer: porcine adipose |
| Regions of Analysis | Definition |
|---|---|
| Vertical analysis | Summation: |
| Difference: | |
| Horizontal analysis | Summation: |
| Difference: | |
| Overall analysis | Summation: |
| Difference: |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, Q.; Bu, T.; Huang, T.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H. Probing Layered Tissues by Backscattering Mueller Matrix Imaging and Tissue Optical Clearing. Photonics 2024, 11, 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11030237
Lai Q, Bu T, Huang T, Sun Y, Wang Y, Ma H. Probing Layered Tissues by Backscattering Mueller Matrix Imaging and Tissue Optical Clearing. Photonics. 2024; 11(3):237. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11030237
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Qizhi, Tongjun Bu, Tongyu Huang, Yanan Sun, Yi Wang, and Hui Ma. 2024. "Probing Layered Tissues by Backscattering Mueller Matrix Imaging and Tissue Optical Clearing" Photonics 11, no. 3: 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11030237
APA StyleLai, Q., Bu, T., Huang, T., Sun, Y., Wang, Y., & Ma, H. (2024). Probing Layered Tissues by Backscattering Mueller Matrix Imaging and Tissue Optical Clearing. Photonics, 11(3), 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11030237






