A Miniaturized Electrothermal-MEMS-Based Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Handheld Microscope
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
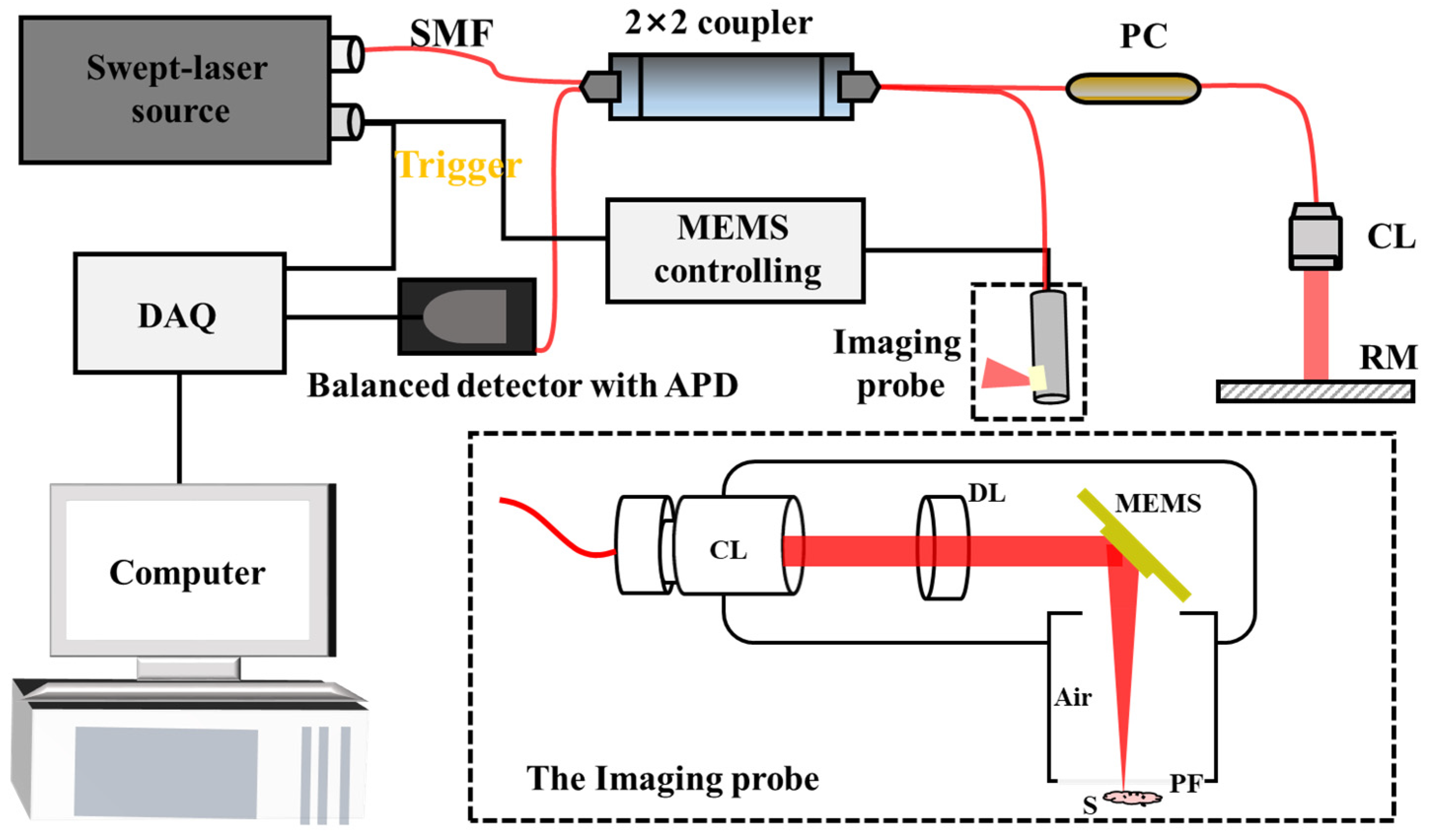
2.1. System Configuration and the Imaging Probe Design
2.2. Sample Preparation and Experimental Process
2.3. Data Acquisition and Processing
3. Results
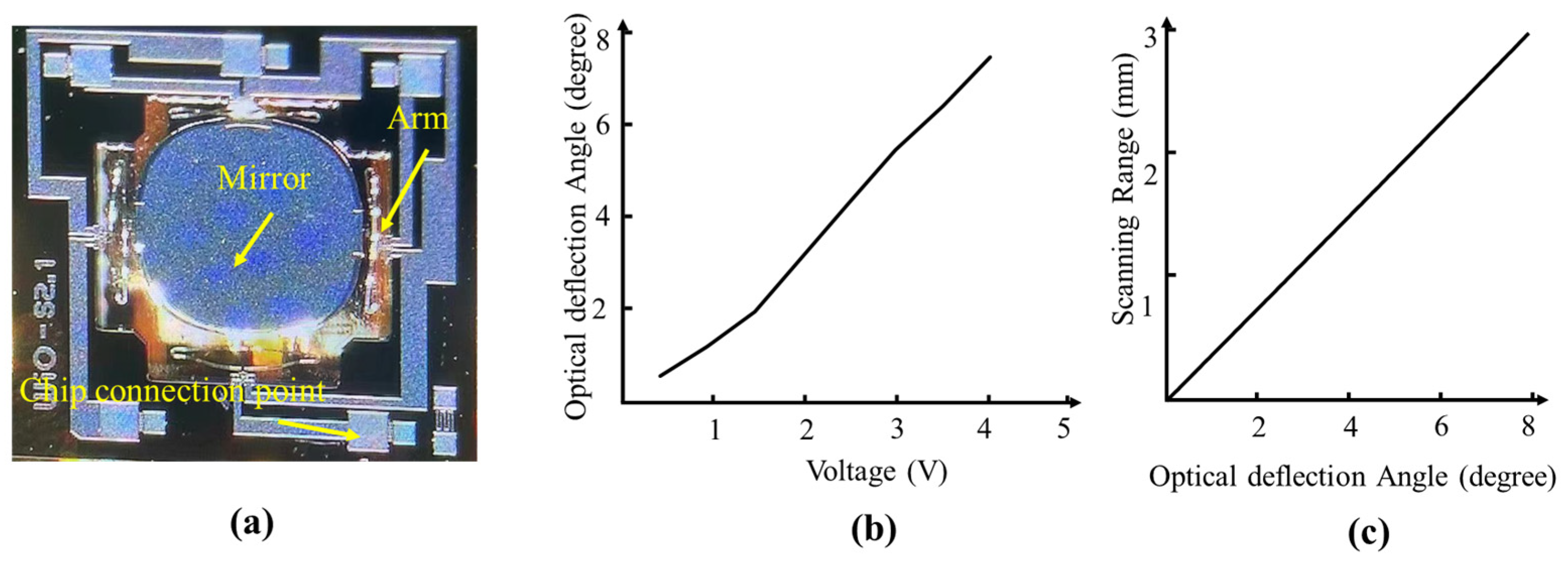
3.1. Parameter Testing of the MEMS and MEMS-Based Handheld Probe
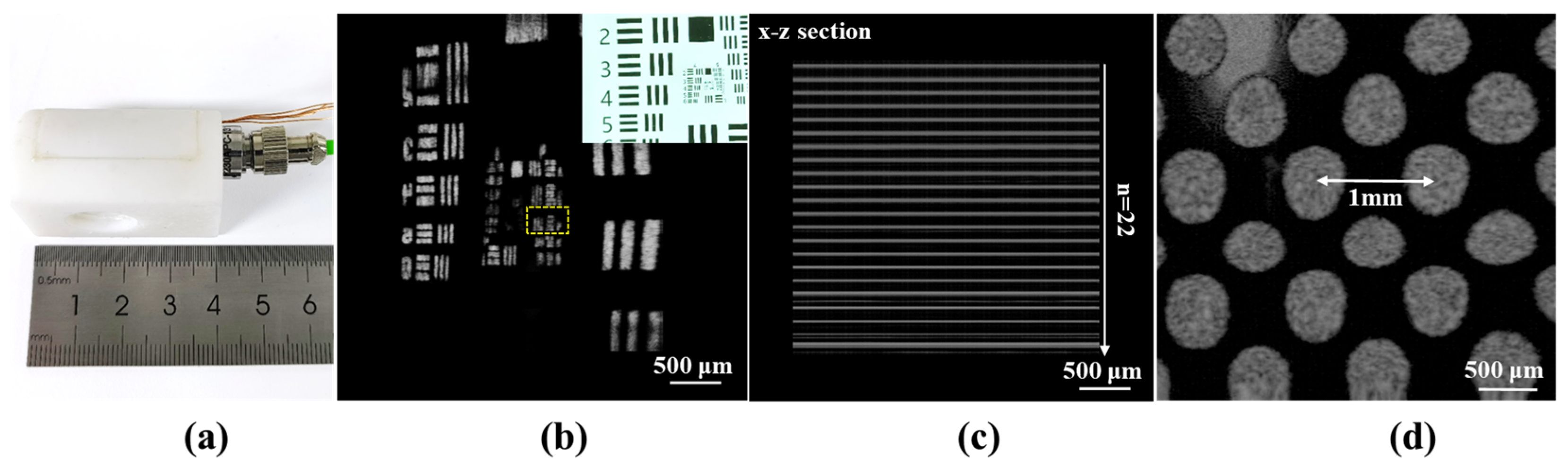
3.2. The Ex Vivo Biological Sample and In Vivo Human Skin Imaging Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.; Luo, Y.; Wang, T.; Wan, C.; Pan, L.; Pan, S.; He, K.; Neo, A.; Chen, X. Artificial Skin Perception. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2003014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douzinas, E.E. Biochemical structural and physical changes in aging human skin, and their relationship. Biogerontology 2022, 23, 275–288. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.; Zhang, H.L.; Guo, B.L. The cerebral microcirculation is protected during experimental hemorrhagic shock. Nanomicro. Lett. 2022, 14, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Waszczuk, L.; Ogien, J.; Perrot, J.L.; Dubois, A. Co-localized line-field confocal optical coherence tomography and confocal Raman microspectroscopy for three-dimensional high-resolution morphological and molecular characterization of skin tissues ex vivo. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 2467–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polańska, A.; Bowszyc-Dmochowska, M.; Olek-Hrab, K.; Adamski, Z.; Żaba, R.; Dańczak-Pazdrowska, A. High-frequency ultrasonography a new quantitative method in evaluation of skin lymphomas—First comparative study in relation to histopathology. Ski. Res. Technol. 2019, 25, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, K.; Mccarthy, W.H.; Menzies, S.W. Increase in the sensitivity for melanoma diagnosis by primary care physicians using skin surface microscopy. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 143, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridis, A.; Triantafyllou, A.; Dipla, K.; Dolgyras, P.; Koletsos, N.; Anyfanti, P.; Aslanidis, S.; Douma, S.; Gkaliagkousi, E. Skin microvascular function, as assessed with laser speckle contrast imaging, is impaired in untreated essential and masked hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2022, 45, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Asao, Y.; Yoshikawa, A.; Sekiguchi, H.; Takada, M.; Furu, M.; Saito, S.; Kataoka, M.; Abe, H.; Yagi, T.; et al. Label-free photoacoustic imaging of human palmar vessels: A structural morphological analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.L.; Xia, Q.; Yu, T.T.; Zhu, J.T.; Zhu, D. Transmissive-detected laser speckle contrast imaging for blood flow monitoring in thick tissue: From Monte Carlo simulation to experimental demonstration. Light. Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 241. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Ma, H.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, K.; Shen, T.; Yang, S. Bifocal 532/1064 nm alternately illuminated photoacoustic microscopy for capturing deep vascular morphology in human skin. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.G.; Cheng, Z.W.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S. Switchable optical and acoustic resolution photoacoustic dermoscope dedicated into in vivo biopsy-like of human skin. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 073703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Ma, H.G.; Cheng, Z.W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, S. Miniaturized photoacoustic probe for in vivo imaging of subcutaneous microvessels within human skin. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chizari, A.; Schaap, M.J.; Knop, T.; Boink, Y.E.; Seyger, M.M.; Steenbergen, W. V Handheld versus mounted laser speckle contrast perfusion imaging demonstrated in psoriasis lesions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Rank, E.; Meiburger, K.M.; Sinz, C.; Hodul, A.; Zhang, E.; Hoover, E.; Minneman, M.; Ensher, J.; Beard, P.C.; et al. Non-invasive multimodal optical coherence and photoacoustic tomography for human skin imaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, W.; Kim, C. High-resolution functional photoacoustic monitoring of vascular dynamics in human fingers. Photoacoustics 2021, 23, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welzel, J.; Schuh, S. Optical coherence tomography for skin pathologies. Ophthalmologe 2018, 115, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Puliafito, C.A.; et al. Optical coherence tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtkowski, M.; Leitgeb, R.; Kowalczyk, A.; Bajraszewski, T.; Fercher, A.F. In vivo human retinal imaging by Fourier domain optical coherence tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2002, 7, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deegan, A.J.; Lu, J.; Sharma, R.; Mandell, S.P.; Wang, R.K. Imaging human skin autograft integration with optical coherence tomography. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adabi, S.S.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Noei, S.; Conforto, S.; Daveluy, S.; Clayton, A.; Mehregan, D.; Nasiriavanaki, M. Universal in vivo Textural Model for Human Skin based on Optical Coherence Tomograms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Mandal, M.; Mitra, P.; Chatterjee, J. Attenuation corrected-optical coherence tomography for quantitative assessment of skin wound healing and scar morphology. J. Biophotonics 2020, 14, e202000357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Y.; Lee, S.; Ju, M.; Heisler, M.; Ding, W.; Zawadzki, R.J.; Bonora, S.; Sarunic, M.V. Lens-based wavefront sensorless adaptive optics swept source OCT. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britten, A.; Matten, P.; Weiss, J.; Niederleithner, M.; Roodaki, H.; Sorg, B.; Hecker-Denschlag, N.; Drexler, W.; Leitgeb, R.A.; Schmoll, T. Surgical microscope integrated MHz SS-OCT with live volumetric visualization. Biomed. Opt. Express 2023, 14, 846–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.K.; Tsai, M.T.; Chang, F.Y.; Yang, C.-H.; Shen, S.-C.; Yuan, O.; Yang, C.-H. Evaluation of Moisture-Related Attenuation Coefficient and Water Diffusion Velocity in Human Skin Using Optical Coherence Tomography. Sensors 2013, 13, 4041–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.H.; Liu, T.; Wang, R.K. Handheld swept-source optical coherence tomography guided by smartphone-enabled wide-field autofluorescence photography for imaging facial sebaceous glands. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 5704–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.D.; Kraus, M.F.; Potsaid, B.; Liu, J.J.; Choi, W.; Jayaraman, V.; Cable, A.E.; Hornegger, J.; Duker, J.S.; Fujimoto, J.G. Handheld ultrahigh speed swept source optical coherence tomography instrument using a MEMS scanning mirror. Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 5, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho-Durá, J.; Zinoviev, K.; Lloret-Soler, J.; Rubio-Guviernau, J.L.; Margallo-Balbás, E.; Drexler, W. Handheld multi-modal imaging for point-of-care skin diagnosis based on akinetic integrated optics optical coherence tomography. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201800193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Guo, H.; Jin, T.; Qi, W.; Xie, H.; Xi, L. Ultracompact high-resolution photoacoustic microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 1615–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Chen, Q.; Xi, L. A handheld microscope integrating photoacoustic microscopy and optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorecki, C.; Bargie, S. MEMS scanning mirrors for optical coherence tomography. Photonics 2020, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.M.; Pal, S.; Xie, H.K. An Electrothermal Tip–Tilt–Piston Micromirror Based on Folded Dual S-Shaped Bimorphs. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2009, 18, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y. Robust Electrothermally Actuated Scanners for Fiberoptic Endoscopic Imaging and Wide-Angle Optics; ProQuest LLC: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2018; p. 10987163. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; You, J.; Gu, X.; Du, C.; Pan, Y. High-speed swept source optical coherence Doppler tomography for deep brain microvascular imaging. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.O.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, N.; Tang, S.; Chen, L.J.; Cheung, C.Y.; Yam, J.C. Comparison of choroidal thickness measurements between spectral domain optical coherence tomography and swept source optical coherence tomography in children. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, U.; Qin, W.; Qi, X.; Kalkan, G.; Wang, R.K. OCT-based label-free in vivo lymphangiography within human skin and areola. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Burrow, M.F.; Araki, K.; Zhou, Y.; Hosaka, K.; Sadr, A.; Yoshiyama, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Sumi, Y.; Tagami, J. 3D imaging of proximal caries in posterior teeth using optical coherence tomography. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.T.; Chen, Y.; Lee, C.Y.; Huang, B.-H.; Trung, N.H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Wang, Y.-L. Noninvasive structural and microvascular anatomy of oral mucosae using handheld optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 5001–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.C.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, L.; Xie, H.; Li, X. Ultralow-voltage electrothermal MEMS based fiber-optic scanning probe for forward-viewing endoscopic OCT. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 2232–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Qi, T.; Wang, H.; Xie, H. A Miniaturized Electrothermal-MEMS-Based Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Handheld Microscope. Photonics 2024, 11, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11010017
Chen Q, Zhao H, Qi T, Wang H, Xie H. A Miniaturized Electrothermal-MEMS-Based Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Handheld Microscope. Photonics. 2024; 11(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qian, Hui Zhao, Tingxiang Qi, Hua Wang, and Huikai Xie. 2024. "A Miniaturized Electrothermal-MEMS-Based Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Handheld Microscope" Photonics 11, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11010017
APA StyleChen, Q., Zhao, H., Qi, T., Wang, H., & Xie, H. (2024). A Miniaturized Electrothermal-MEMS-Based Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Handheld Microscope. Photonics, 11(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11010017





