Abstract
In dual-wavelength free-space optical communication systems, the wavefront distortion differences caused by the wavelength difference of the signal and beacon lights cannot be completely corrected. In this study, according to the method of geometric optics, the relationship between the wavefront phases of the signal and beacon lights is analyzed by establishing a mathematical model of the cross-correlation ratio of the arrival-angle fluctuation and phase relationship of different Gaussian-beam wavelengths under weak turbulence near the surface. The numerical results show that after Gaussian beams of different wavelengths propagate through the same atmospheric channel, the cross-correlation number of the arrival-angle fluctuation decreases with an increase in the wavelength difference, waist radius, and turbulence intensity, and increases with an increase in propagation distance. The beam-wavefront phase difference increases with an increasing wavelength difference. Finally, a wavefront distortion correction experiment of a dual-wavelength adaptive optical system verified the correctness of the wavefront phase-difference relationship between the signal light and beacon light established in this study.
1. Introduction
In a free-space optical (FSO) communication system, when influenced by random fluctuations of the atmospheric refractive index after being transmitted through a free channel, a signal beam will experience optical turbulence effects, such as phase distortion, light-intensity fluctuation, beam drift, and arrival-angle fluctuation [1,2,3]. Adaptive optics (AO) technology can effectively suppress the influence of atmospheric turbulence on a signal light based on real-time detection and correction [4,5,6].
When the selected signal-light wavelength has poor penetrability or serious attenuation in the atmospheric channel, the system transmits a beacon light along the same optical path as the signal light [7,8]. Wavefront distortion data are obtained through beacon light detection, and the wavefront distortion of the signal light is corrected accordingly [9,10]. In dual-wavelength FSO communication systems, the signal light and beacon light have different wavelengths; hence, the refraction angle and optical path difference caused by turbulence differ when Gaussian beams are transmitted through an atmospheric channel. This causes a dispersion effect, which results in an incomplete correction of the signal light when correcting it according to the beacon light distortion data. A correction residual exists in AO caused by the signal light and the beacon light [11,12].
In recent years, considerable research has been carried out on wavefront aberrations between the signal light and beacon light in dual-wavelength FSO communication systems. From the beam propagation perspective, the Gaussian beam is modulated by atmospheric turbulence in the atmospheric channel, and the propagation direction of the local wave vector changes, resulting in random fluctuations in the phase plane of the beam and its angle of arrival (AOA) [13,14].
Toselli et al. established an arrival angle scintillation model under a non-Kolmogorov turbulence spectrum [15]. David et al. analyzed the arrival angles of beams of different wavelengths in strong and weak turbulent regions using ray tracing and wave optics [16]. Conan and Borgnino analyzed the AOA of a beam on the receiving plane with a theoretical derivation and numerical calculation, and explained the space–time correlation of the variance of the AOA fluctuation and the difference under the influence of different wavelengths [17]. The correlation between beams of different wavelengths in the weak turbulence region was described by Akira using the cross-correlation power spectrum. Ben-Yosef et al. experimentally measured the intensity flicker correlation coefficients of beams with different wavelengths [18].
Based on a study of the fluctuation of the beam AOA, and to correct the correction residual in a dual-wavelength FSO communication system, Gorelava et al. measured the wavefront distortion variables of two beams with 530 nm and 1060 nm wavelengths through a Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor. By comparing the measurement results, they found a certain correlation between the wavefront distortion of two beams with different wavelengths. The degree of distortion increased with an increase in the transmission path distance [19].
Li et al. proposed an adaptive optics technique to correct the AOA fluctuation of beams of different wavelengths [20] and analyzed in detail the influence of the beam wavelength on the AOA fluctuation. Kibblewhite et al. designed deformable mirrors in an adaptive optics system according to the power spectrum of the AOA fluctuation with different beam wavelengths [21]. Lukin calculated the correction accuracy and efficiency of an adaptive optical system when the beacon light and signal light wavelengths were inconsistent [22].
Jolissaint used a Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor to measure the wavefront distortion results of a two-color laser after transmission in an atmospheric path and revealed the correlation between different wavelength distortions [23]. Ke et al. analyzed the correction residuals of the wavefront fluctuation of an adaptive optical system with different wavelengths and determined the correction coefficients of the correction residuals between the beacon wavefront and target wavefront fluctuation [24].
The key to correcting signal wavefront distortions in dual-wavelength FSO communication systems is to determine the wavefront phase relationship between the signal light and beacon light. In view of the residual error in the correction of signal wavefront distortions in weak turbulent regions, this study analyzes the correlation function between the AOA fluctuation of different Gaussian beam wavelengths. Wavefronts of different wavelengths have a specific phase relationship, and the expression of the distortion phase of Gaussian beams with different wavelengths is provided. Finally, the relationship obtained in this study is verified experimentally.
2. Theory
2.1. Correlation Function of the AOA Fluctuation at Different Wavelengths
After Gaussian beams with wavelengths of λ1 and λ2 are transmitted through the same atmospheric channel, the AOA fluctuations of the beams at the receiving plane are and , respectively. The correlation between the two can be described by a cross-correlation function [25]:
where F = z/(1 + (z/f))2 is the curvature radius of the beam wavefront, z is the beam transmission distance, f is the beam parameter, and are wave numbers of beams with different wavelengths, is the beam waist radius, and D is the pupil diameter of the receiving optical system. represents the distance between and on the wavefront; when , the two points coincide. In Equation (1), represents the ensemble average; its specific expression is [26]:
where
where is a dual-frequency phase-structure function, , , , is a logarithmic amplitude structure function, and is the phase-structure function. Equations (2)–(4) are substituted into Equation (1) and solved for the correlation function of the arrival angle fluctuation of Gaussian beams with different wavelengths:
where , , is a Gaussian hypergeometric function, R is the equivalent curvature radius of the wavefront, and is the atmospheric refractive index structure constant.
2.2. Phase Relationship between Gaussian Beams of Different Wavelengths
The essence of arrival angle scintillation is the change of wave vector propagation direction caused by wavefront phase distortion, so calculating the relationship between different phases is essential.
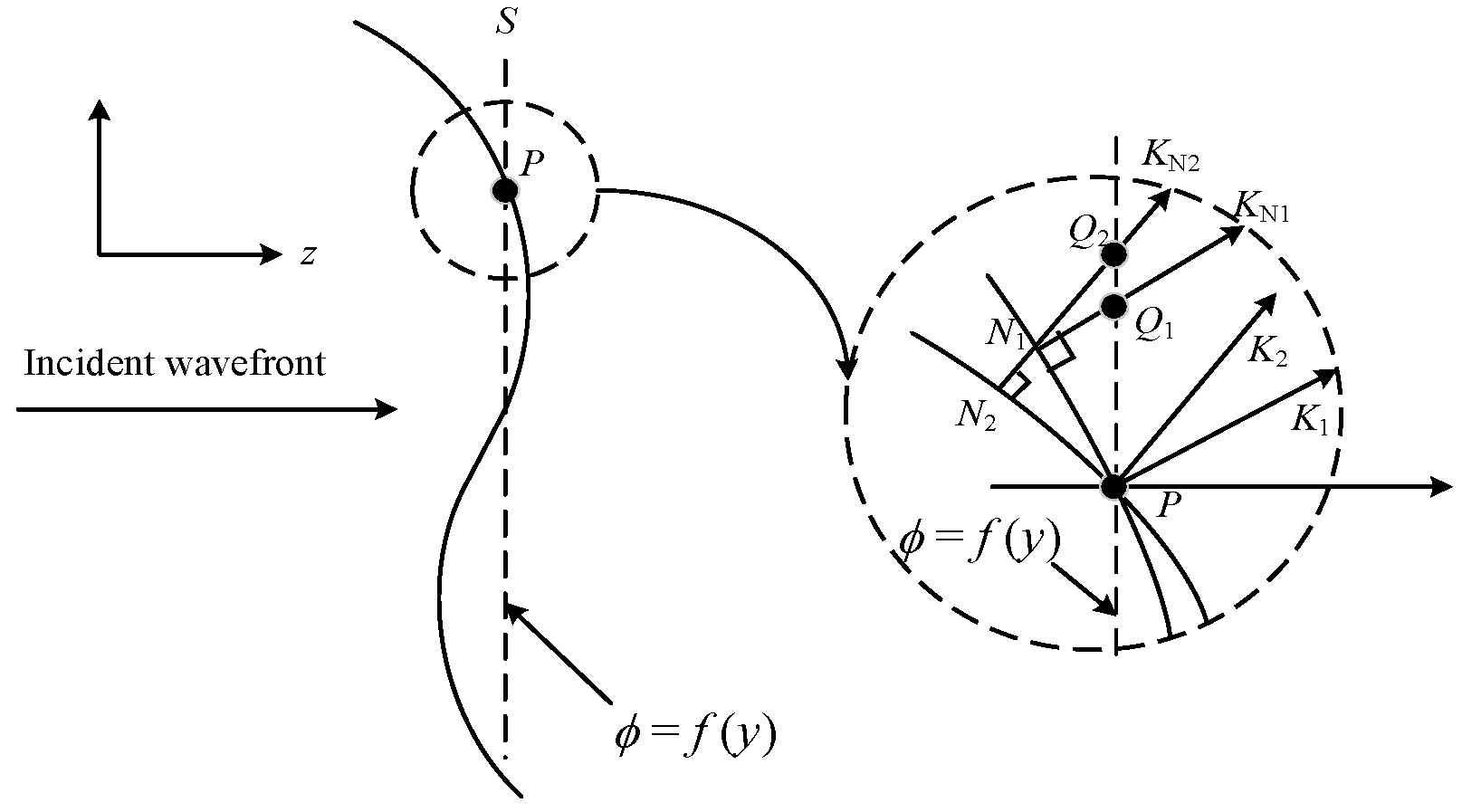
As shown in Figure 1, the incident light is incident along the z-axis in the normal direction, and the entire wave surface is distributed in the XOY plane. The wavefront measuring plane S is perpendicular to the z-axis, and the phase-distribution function of the incident light at the measuring line position is . Owing to the phase distortion of the wavefront, there is a phase difference between point P on the wave surface and the surrounding adjacent position.
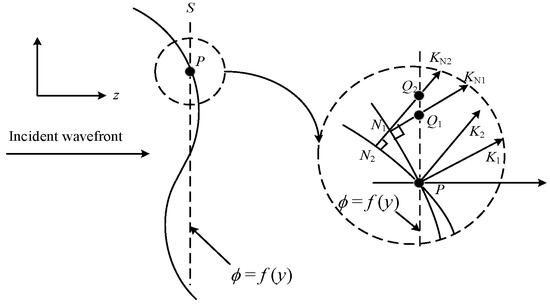
Figure 1.
Diagram of incident wavefront section.
Assuming that the signal wavelength is and the beacon wavelength is , we selected points N1 and N2 along the equal phase plane of the front of the two light beams near point P. The distance between the two points PN1 and PN2 is the optical path difference, and the beam-transmission distance is L.
Perpendicular lines of two wavelength beam equal-phase planes are made at points N1 and N2; that is, the propagation directions of the wave surface at points N1 and N2 are KN1 and KN2, respectively, and the two propagation vectors intersect the measuring surface S at points Q1 and Q2, respectively. When is very small and close to 0, triangles N1Q1P and N2Q2P can be considered as right triangles. The phase difference between points Q1P and Q2P is the wavefront phase difference corresponding to the beacon and signal lights. The corresponding signal light wavefront phase difference is , the beacon light wavefront phase difference is , and the signal light and beacon light wavefront distortion phases under the above conditions can be expressed as:
Because the signal light and beacon light are transmitted along the same path, the air refractive index variation between the corresponding point positions is the same:
When the signal light and beacon light are transmitted in the same atmospheric channel, the random changes of the refractive index in atmospheric turbulence have different modulation effects on different wavelengths of Gaussian beams. There are also certain differences in the wavefront fluctuation and distortion, the phase difference between PQ2 and PQ1 is different, and the corresponding wavefront distortion phase difference is:
Furthermore, the relationship between the signal wavefront phase and beacon wavefront phase at point P is:
After substituting Equations (8) and (9) into Equation (10), the relationship between the distortion phases of the Gaussian beams with different wavelengths is obtained as follows:
According to this relationship, the phase difference of the wavefront distortion of beams with different wavelengths can be calculated, based on the known wavelengths of the signal light and beacon light, beam transmission distance L, and refractive index change. The wavefront distortion measurement value of the signal light can also be calculated, based on the wavefront distortion measurement value of the beacon light.
3. Simulation
3.1. Propagation Characteristics of Gaussian Beams with Different Wavelengths in the Same Atmospheric Channel
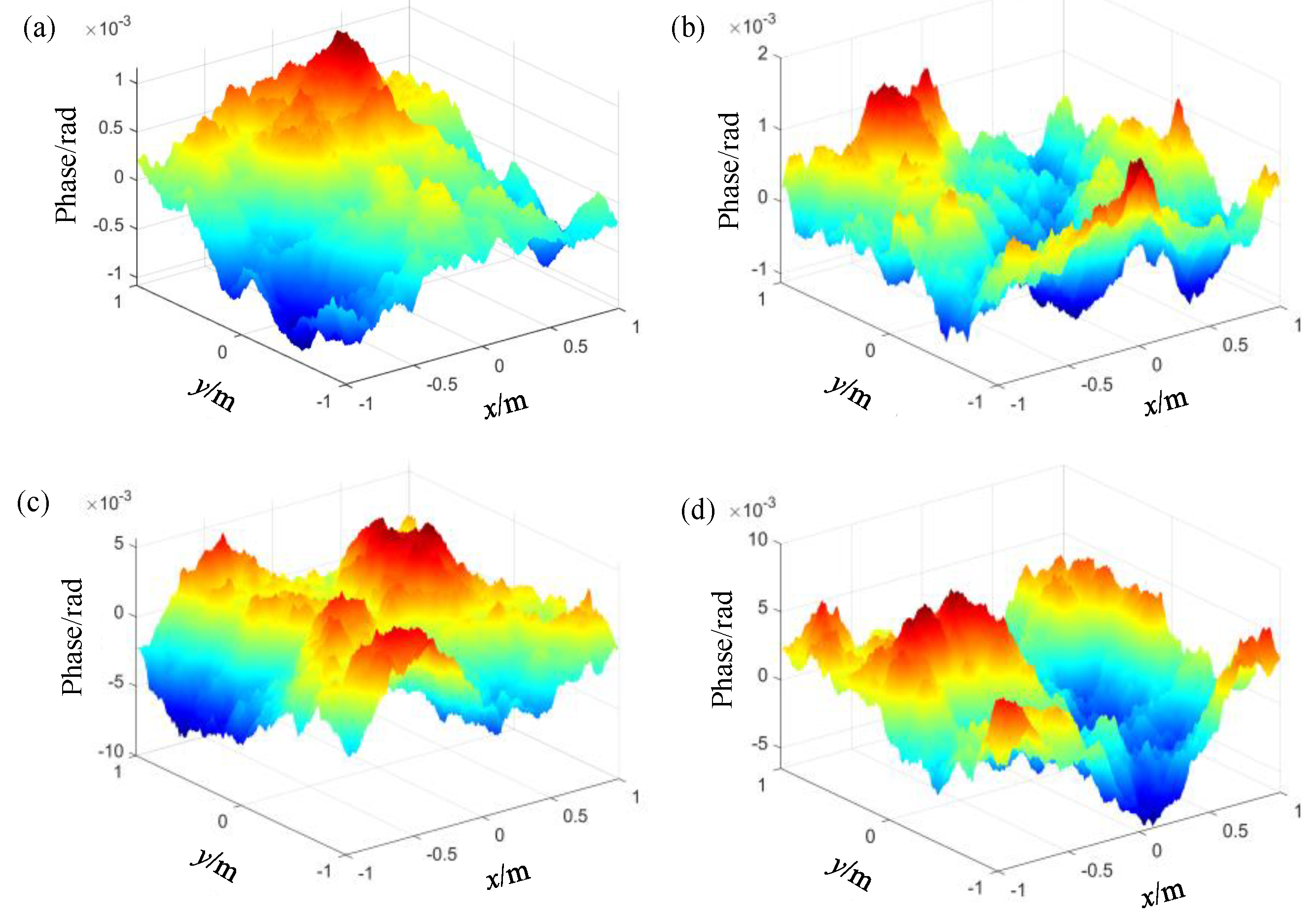
The outer turbulence scale L0 = 5 m, inner turbulence scale l0 = 0.1 m, waist radius = 5 mm, and atmospheric refractive index structure constant = 1 × 10−18 m−2/3. Figure 2 shows the simulation results of the wavefront phase distortion of Gaussian beams with 1550 nm, 850 nm, 632.8 nm, and 530 nm wavelengths after transmission in the same atmospheric channel, with transmission distance L = 10 km.
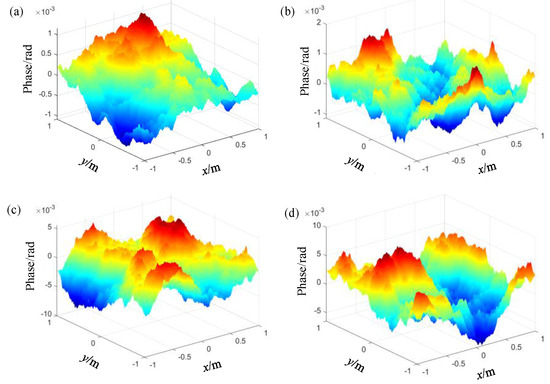
Figure 2.
Wavefront phase distortion of Gaussian beams with different wavelengths in the same atmospheric turbulence. (a) 1550 nm; (b) 850 nm; (c) 632.8 nm; (d) 530 nm.
It can be seen from the figure that under the same transmission conditions, the degree of the phase distortion of the Gaussian beam varies significantly with the wavelength. This indicates that the atmospheric turbulence differently modulates Gaussian beams of different wavelengths.
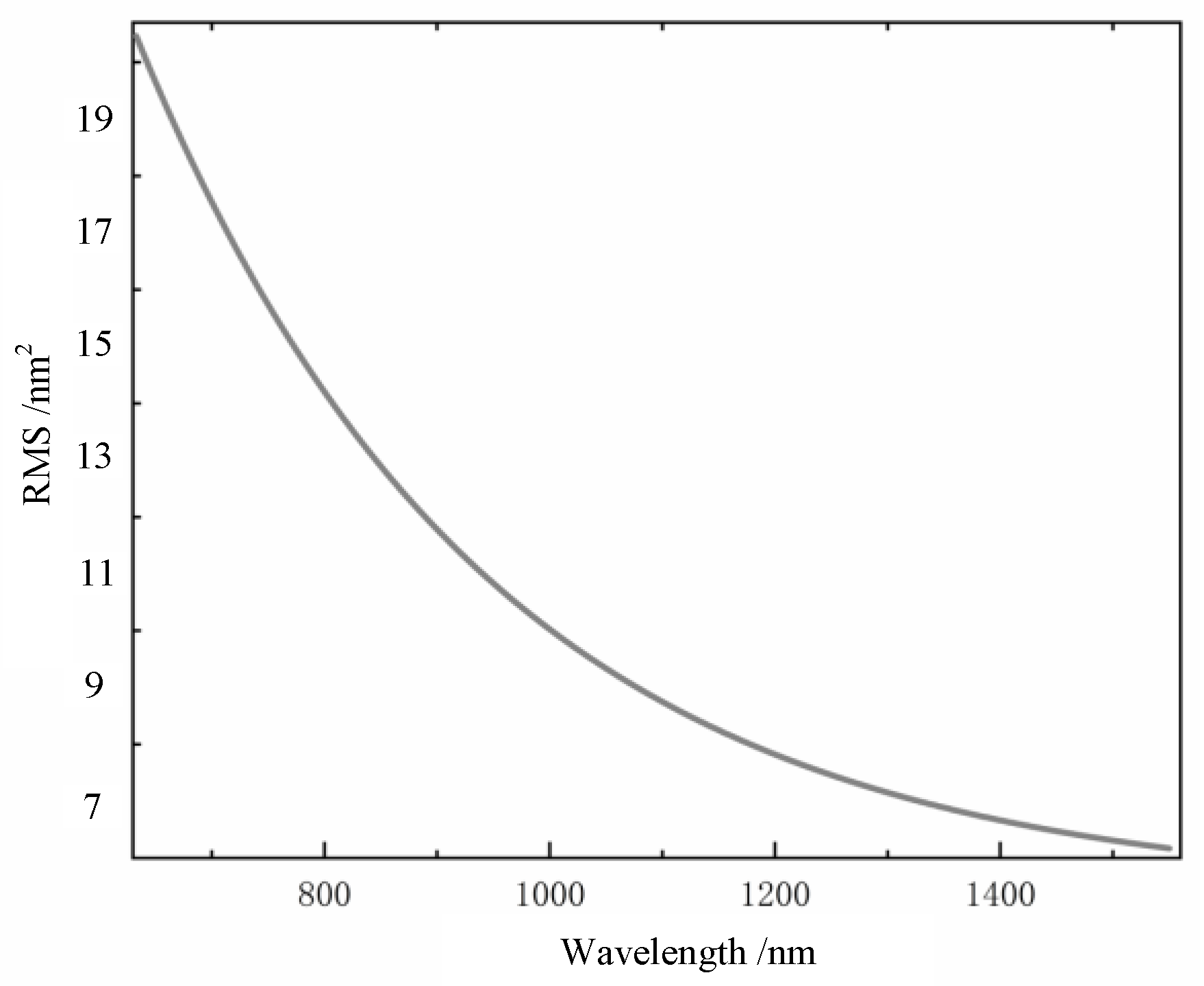
Red represents the fluctuation of the phase to the transmission direction, and blue represents the phase fluctuation of the reverse transmission direction. The darker the color is, the more intense the fluctuation is. Figure 3 shows the relationship between the fluctuation variance of the wavefront phase distortion of the Gaussian beam and wavelength, under the simulation conditions in Figure 2. It can be seen from Figure 3 that the variance of the wavefront phase fluctuation gradually decreases with the increase in wavelength. This indicates that the atmospheric turbulence disturbs long waves less than it does short waves; that is, the phase-fluctuation degree of short waves is higher than that of long waves.
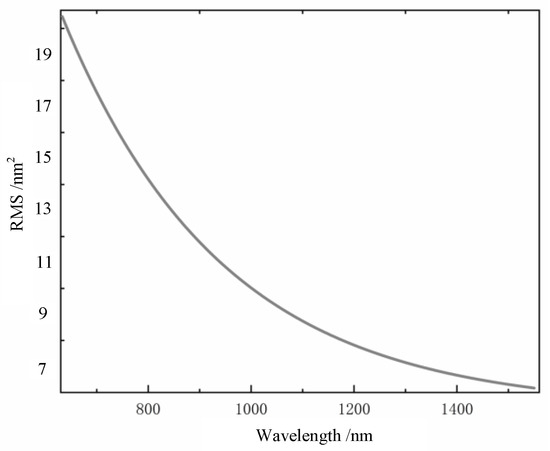
Figure 3.
Relationship between the root mean square value of the distorted wavefront and wavelength.
If a long-wave beacon light is used to correct a short-wave signal light, the correction will be insufficient, and the correction residual will increase with the increase in the wavelength difference between the two, until finally the compensation effect tends to disappear. If a short-wave beacon light is used to correct a long-wave signal light, the correction amount is greater than the actual phase-distortion variable, and the correction residual increases rapidly with the increase in wavelength. Finally, when the wavelength difference reaches a certain value, the correction residual will reach the phase distortion error without correction.
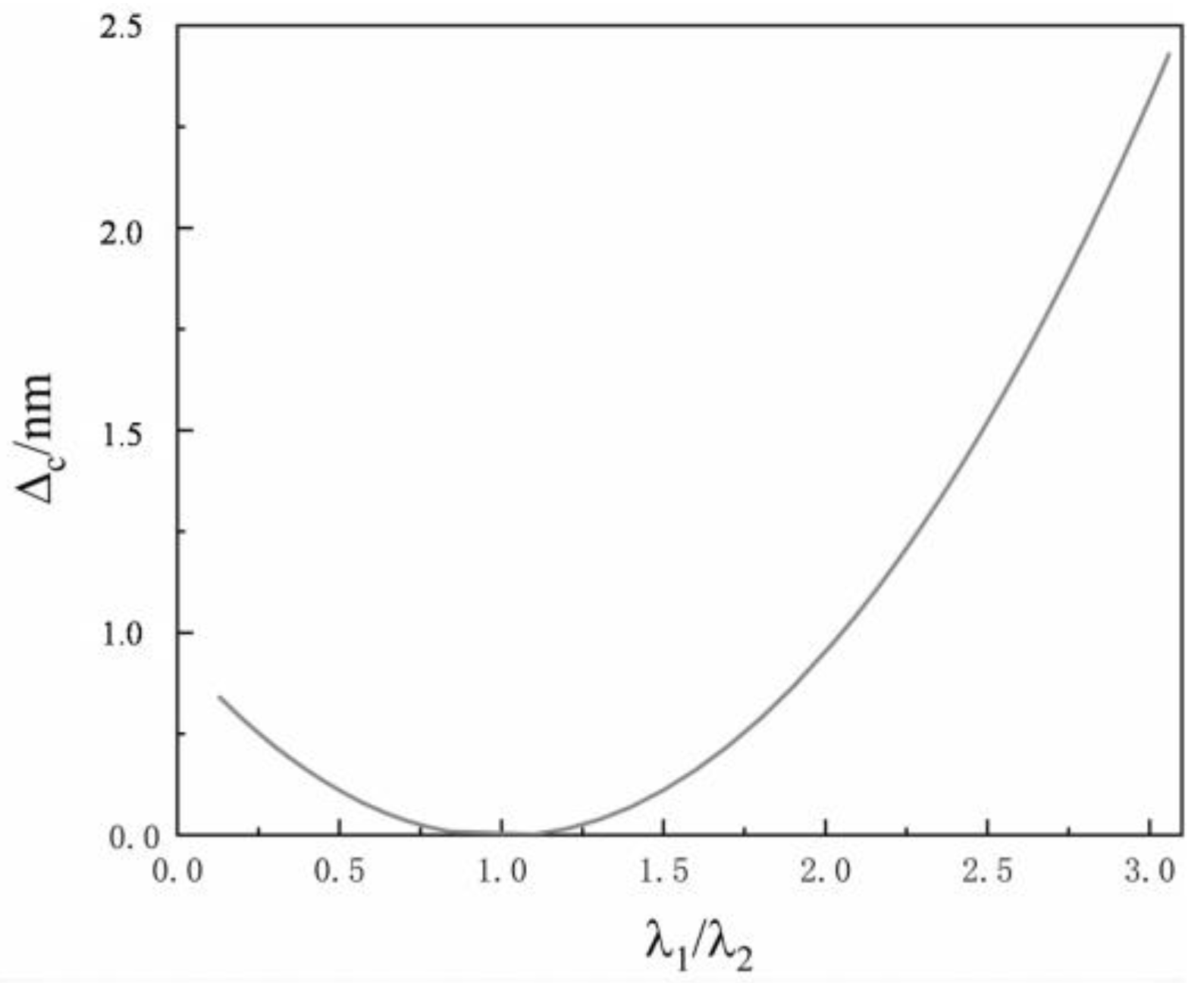
Figure 4 shows the relationship between the wavefront phase distortion difference and the wavelength difference of different Gaussian beams, in which the beacon light wavelength is . It can be seen from the figure that the smaller the wavelength difference between the signal and beacon lights, the smaller the distortion phase difference. This indicates that the beacon light wavefront distortion variable can be approximated to the signal light wavefront distortion variable only when the signal and beacon light wavelengths are very close.
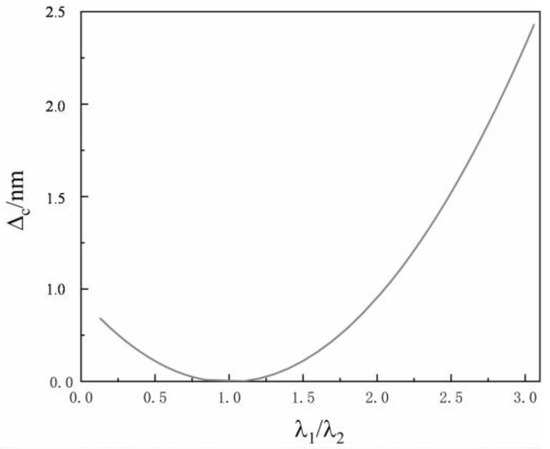
Figure 4.
Change in the distortion phase difference of different wavelength beams with the wavelength difference.
In addition, it can also be concluded that when the signal light wavelength is larger than that of the beacon light, the minus sign should be considered in the phase relationship between the two wavelength beams. When the signal light wavelength is smaller than the beacon light wavelength, the plus sign should be considered in the relationship.
3.2. Correlation of Variance of the Arrival Angle Fluctuation of Gaussian Beams with Different Wavelengths
The correlation of the AOA fluctuation is related to multiple factors, such as the transmission distance, atmospheric refractive index structure constant, waist radius, and wavelength. This section analyzes the influence of the transmission distance, beam wavelength difference, and turbulence intensity on the correlation. Unless otherwise specified, the simulation parameters are as follows: transmission distance, L = 10 km; signal optical wavelength, 1550 nm; beacon optical wavelengths, 632.8 nm, 750 nm, 950 nm, and 1280 nm; and the atmospheric refractive index structure constant ranges from 1 × 10−17 m−2/3–1 × 10−19 m−2/3.
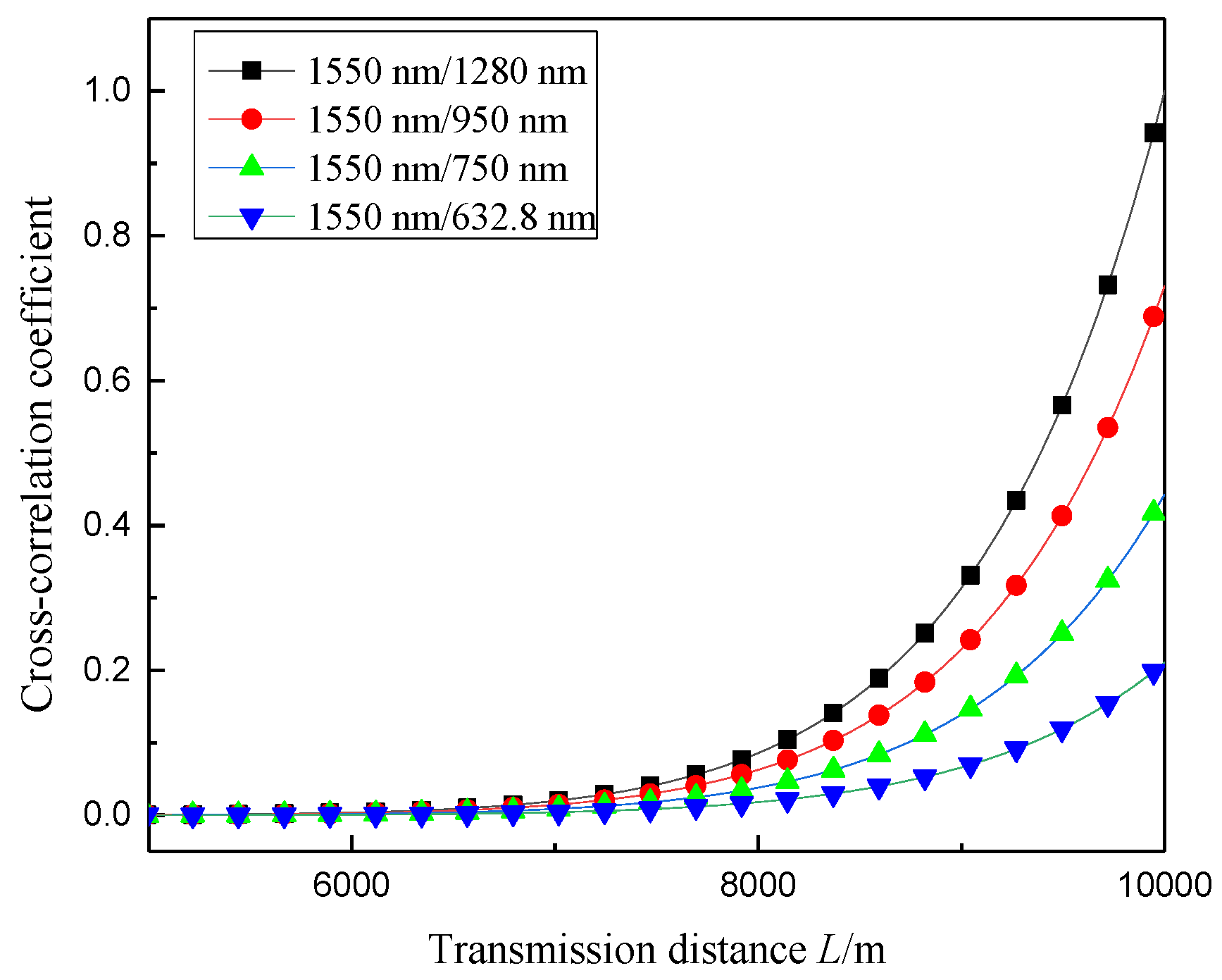
When the beam waist radius is 6.2 × 10−5 m and the atmospheric refractive index structure constant is 1 × 10−19 m−2/3, Figure 5 shows the change in correlation number between the arrival angle fluctuations of different wavelengths with the transmission distance. As shown in the figure, as the transmission distance increases, the correlation between the arrival angle fluctuations of the different wavelengths gradually increases. The reason for this phenomenon is a statistical correlation between the wavefront distortions of different wavelengths in the same turbulence disturbance [26]. With the same distance, the smaller the wavelength difference between the two beams, the greater the cross-correlation coefficient between the corresponding AOA fluctuations.
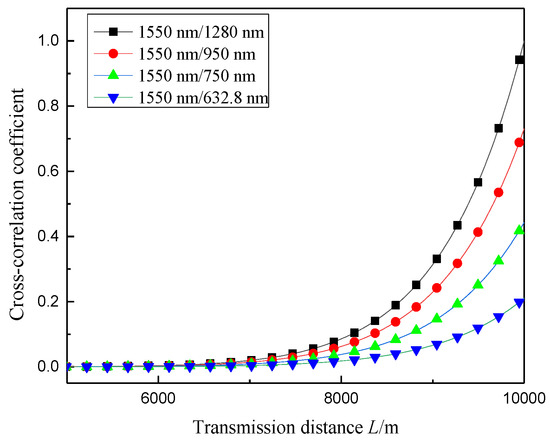
Figure 5.
Variation of correlation coefficient between angle-of-arrival fluctuations of different wavelengths and transmission distances.
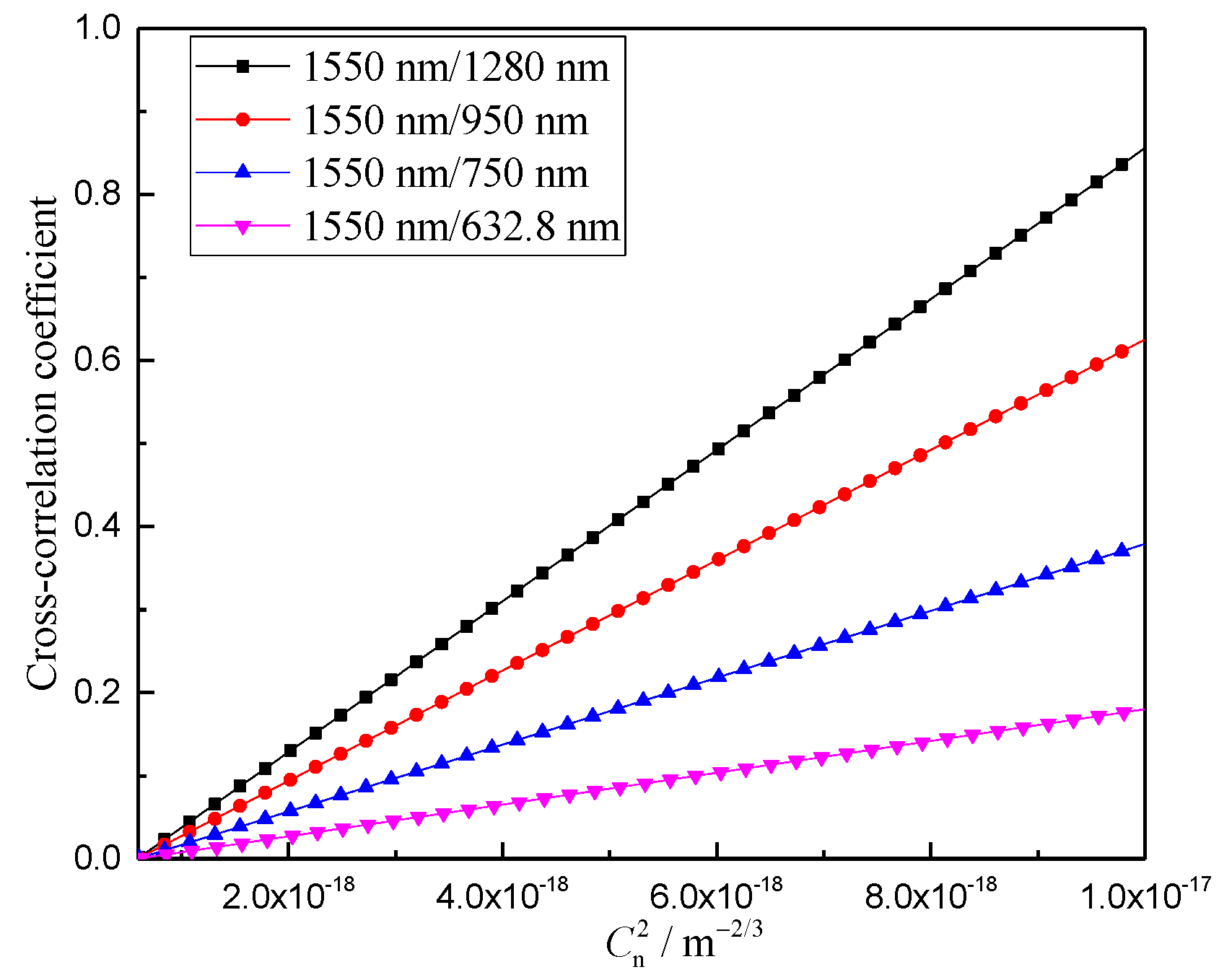
Figure 6 shows the variation curve of the correlation number of the arrival angle fluctuations of Gaussian beams of different wavelengths with the atmospheric turbulence intensity. It can be seen from Figure 6 that the correlation number between the arrival angle fluctuations of the Gaussian beams of different wavelengths gradually increases with the decrease in the atmospheric refractive index structure constant. The smaller the wavelength difference between the beacon and signal lights, the larger the cross-correlation coefficient between the corresponding arrival angle fluctuations of beams of different wavelengths. This indicates that the distortion information between the arrival angle fluctuations of different wavelengths has a higher consistency.
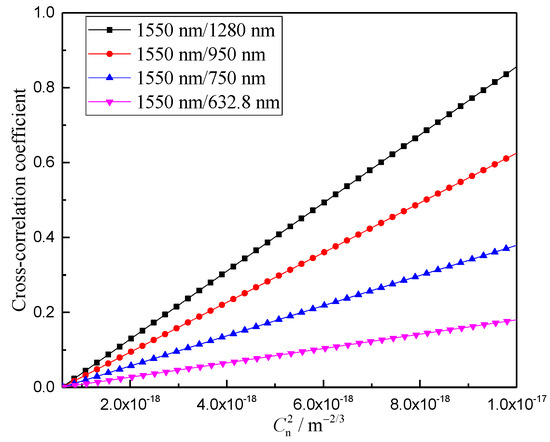
Figure 6.
Variation of the correlation coefficient between angle-of-arrival fluctuations of different wavelengths and the refractive-index structure constant.
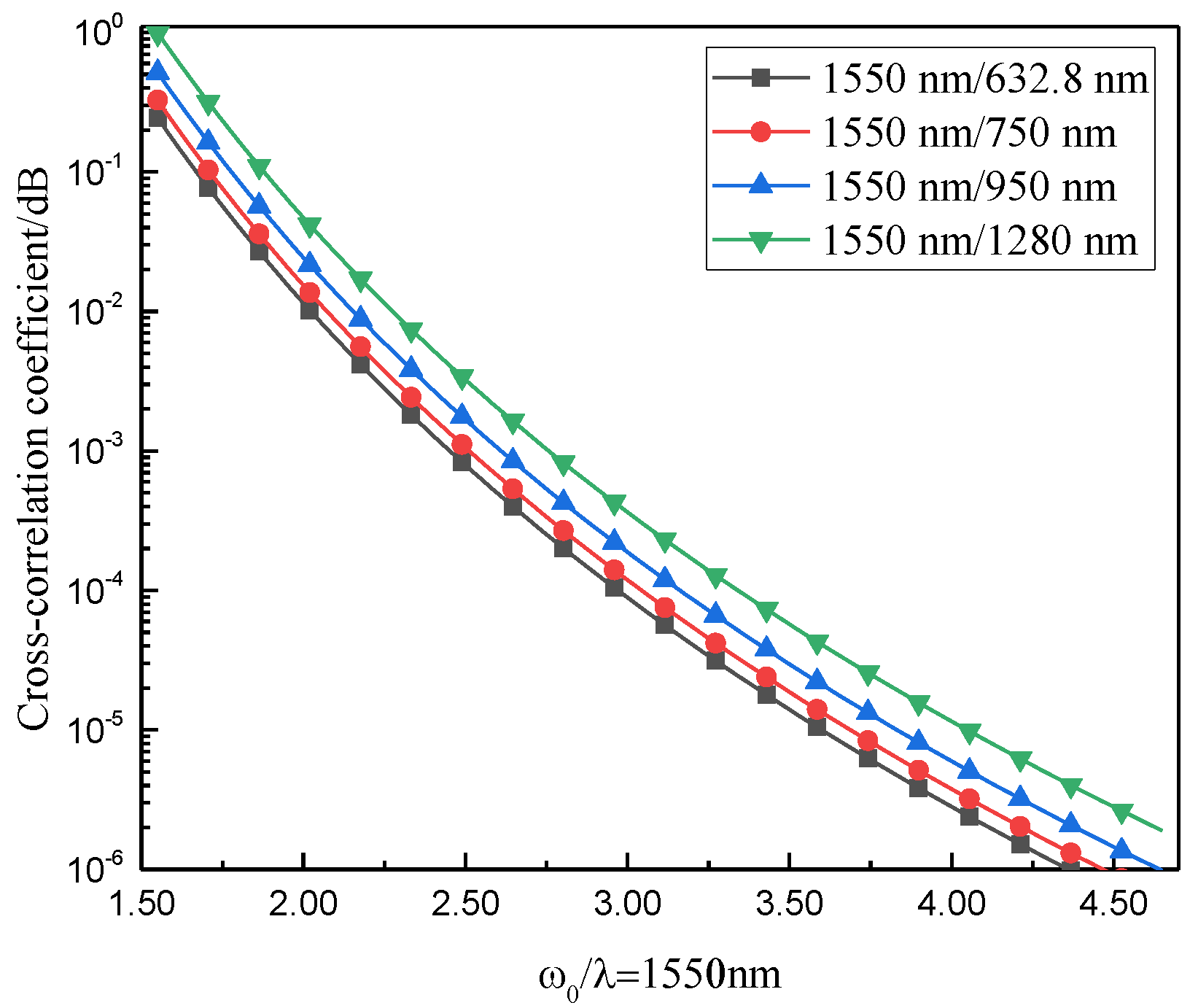
Figure 7 shows the influence of the waist radius on the correlation between the arrival angle fluctuations of Gaussian beams of different wavelengths. The vertical axis represents the cross-correlation coefficient after translation into logarithm 10. It can be seen from the figure that the number of mutual relations between the angle-of-arrival fluctuations of Gaussian beams of different wavelengths decreases gradually with an increase in the waist radius. In addition, the smaller the wavelength difference between the two beams, the higher the number of mutual relations.
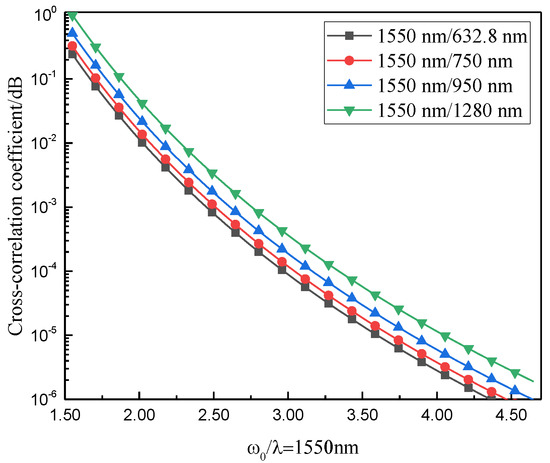
Figure 7.
Variation of the correlation coefficient between angle-of-arrival fluctuations of different wavelengths and the refractive index structure constant.
From the above analysis, it can be observed that the correlation between the arrival angle fluctuations of Gaussian beams of different wavelengths decreases with an increase in the atmospheric refractive index structure constant. For the same transmission distance and atmospheric refractive index structure constant, the arrival angle fluctuation of a short wave is higher than that of a long wave. In addition, for the same wavelength, the sensitivity of the AOA fluctuation to the transmission distance is much higher than that to the atmospheric refractive index structure constant.
4. Experiment
4.1. Wavefront Distortion Correction Compensation for a Dual-Wavelength FSO Communication System
The dual-wavelength FSO communication system uses a Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor to measure the wavefront distortion phase of the beacon light, generate a wavefront reconstruction matrix, and correct the signal optical distortion wavefront, according to the reconstruction matrix. The correction matrix is calculated according to the quantitative relationship between the wavefront distortion phases of Gaussian beams of different wavelengths, as described in Section 2.2. The measured beacon light wavefront-reconstruction matrix is corrected to obtain the wavefront reconstruction matrix of the signal light to compensate for the chromatic difference between the signal and beacon lights and reduce the correction residual.
The distorted wavefront can be expressed as follows:
where is a Zernike polynomial, is the coefficient of the Zernike polynomial, and j is the order of the Zernike polynomial, is the measurement wavefront, is the reference-plane wavefront, and the distorted wavefront is obtained from the difference between the two. A Gaussian beam with wavelength is transmitted as a beacon light along with a signal light with wavelength in the same optical path. The Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor measures the beacon light wavefront to obtain the beacon light gradient matrix, including the distortion:
where and . According to Equation (11), the following relationship can be obtained by calculating the offset gradient of the distortion of two Gaussian beams with different wavelengths on the measuring surface of the sensor:
where . According to this relationship, a coefficient correction matrix can be obtained:
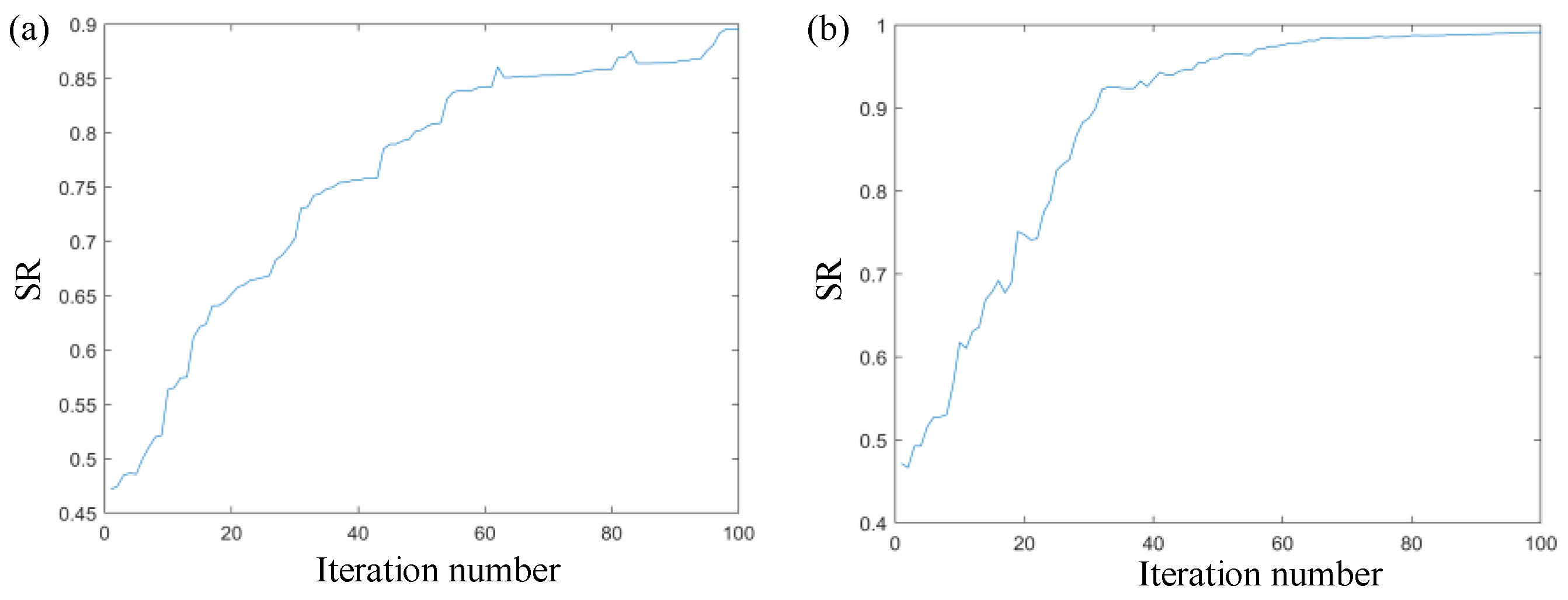
The wavefront reconstruction matrix of the beacon light was obtained by multiplying the wavefront reconstruction matrix of the signal light by the coefficient correction matrix. In the adaptive optics control system, the beacon optical wavefront reconstruction matrices before and after correction are used to correct the signal optical wavefront distortion. The signal optical Strehl ratio (SR) is obtained, as shown in Figure 8.
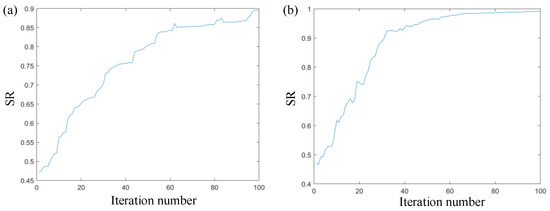
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of the corrected signal lights by beacon. (a) Beacon without the wavefront correction coefficient and (b) beacon with the wavefront correction coefficient.
Figure 8 shows the change curve of the system SR value during the correction process; (a) is the SR curve when the beacon wavefront distortion variable is directly used as the signal wavefront distortion variable for correction, and (b) is the SR curve when the beacon wavefront distortion variable is corrected using the wavefront phase matrix corrected by Equation (11) as the signal wavefront distortion variable.
It can be observed from the figure that the corrected SR ratio of the wavefront reconstruction matrix converges to 1. Compared to the situation in which the wavefront reconstruction matrix converges to 0.9 before the correction, the overall SR ratio increases by 10%. When the beacon wavefront distortion matrix and signal light are corrected, the system SR converges quickly. The SR tends to stabilize when the number of iterations is 80 and the SR jitter is significantly reduced. This verifies the correctness of the wavefront phase relationship between the signal light and the beacon light derived by Equation (10), and also explains the importance and practical significance of compensating the aberration color difference between the signal light and the beacon light.
4.2. Experimental Device
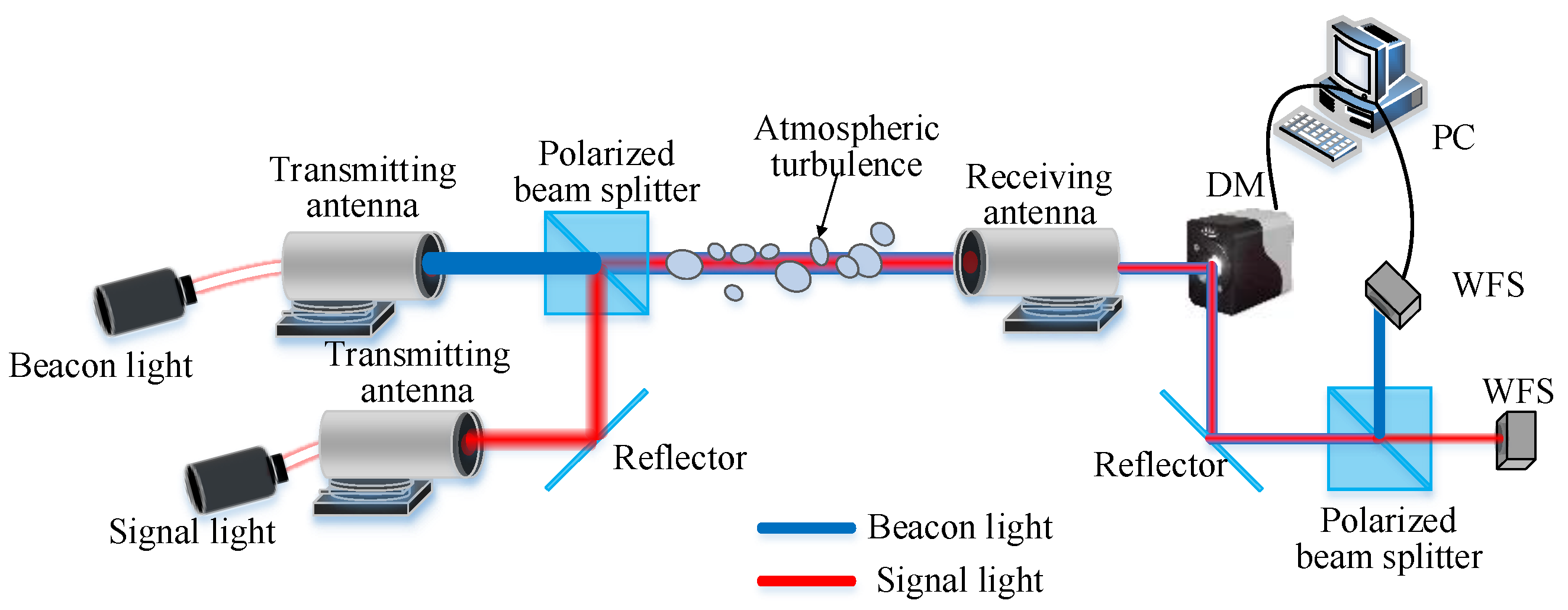
To verify the correctness of the theoretical analysis, the research team built a 1.2 km experimental optical path between the seventh floor of the North Discipline Building and the seventh floor of the Fifth Teaching Building of Xi’an University of Technology. A schematic diagram of the experimental setup is shown in Figure 9. The signal light and beacon light were transmitted by a beam combiner through the same atmospheric channel to the optical end on the seventh floor of the North Discipline Building and then transmitted to the receiving antenna on the seventh floor of the Fifth Teaching Building after being reflected by the plane reflector. The combined beam was reflected by the deformable mirror and the reflector, and then incident to the beam splitter.
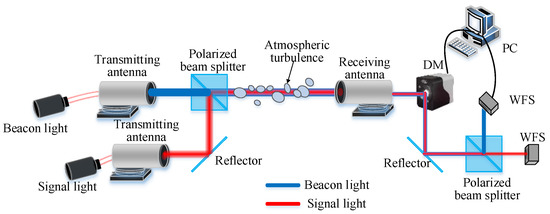
Figure 9.
Diagram of experimental structure.
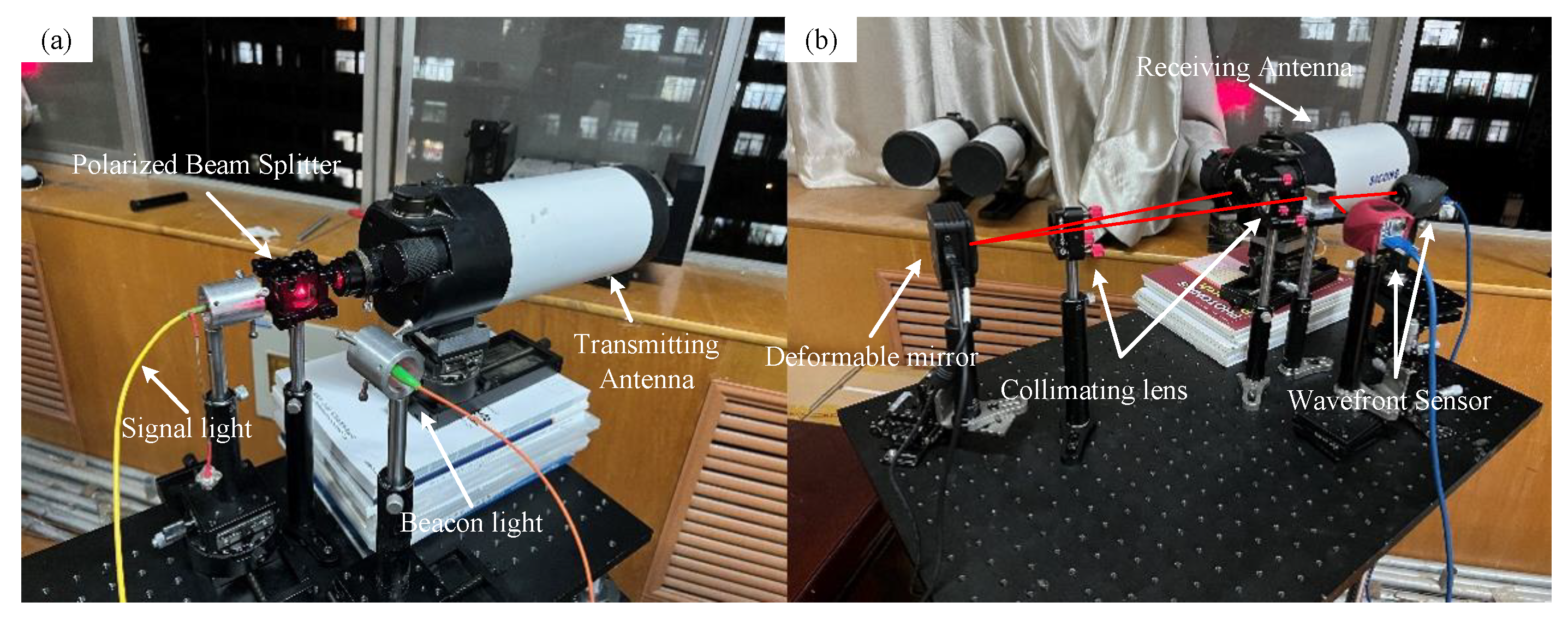
The beam splitter separates the signal light from the beacon light. The wavefront sensor detects the wavefront distortions of the beacon and signal lights. Using an adaptive PID algorithm control, the wavefront distortion of the signal light is corrected [27]. In the experiment, the signal light wavelength was 1550 nm, and the beacon light wavelength was 650 nm. Figure 10 shows a physical image of the experiment, and Table 1 shows the corresponding experimental instrument parameters.
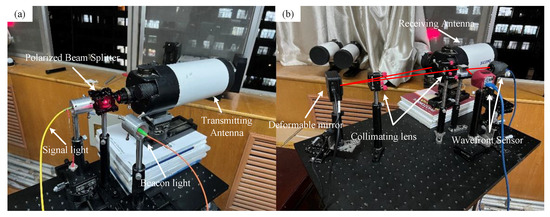
Figure 10.
Experimental optical path. (a) Transmitting end. (b) Receiving end.

Table 1.
Parameters of experimental equipment.
5. Results and Discussion
The beacon light wavefront slope matrix size was 32 × 40, the partial matrix (size is 5 × 9) of the wavefront slope was selected for convenience, and the beacon light wavefront Wb(x,y) was:
The wavelengths of signal light and beacon light were 650 nm and 1550 nm; according to Equation (16), the modified beacon light wavefront Wm_b(x,y) is:
the cross-correlation coefficient between signal light wavefront W(x,y) and beacon light wavefront Wb(x,y) was 0.82, and the cross correlation coefficient between signal light wavefront Wx(x,y) and modified beacon light wavefront Wm_b(x,y) was 0.89, indicating that the similarity between the signal light and modified beacon light wavefronts increased. In this case, the wavefront distortion of the signal light could be corrected by measuring the wavefront distortion of the beacon light.
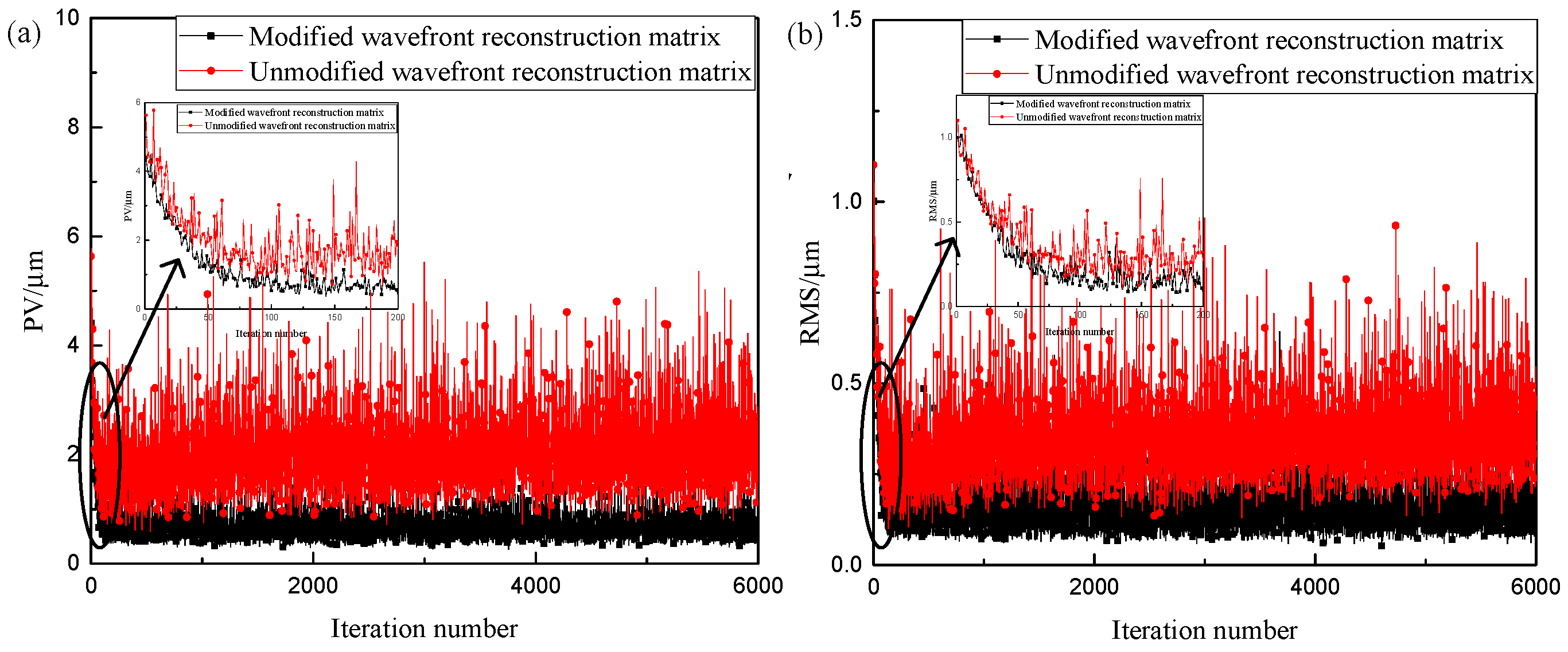
Figure 11 shows the variation curves of the signal wavefront peak-to-valley (PV) and wavefront root mean square (RMS) during the experiment. Table 2 lists the PV and RMS values of the signal wavefront before and after the experiment. Considering Figure 11 and Table 2, when the beacon optical wavefront reconstruction matrix was directly used as the signal optical wavefront reconstruction matrix to correct the signal optical wavefront distortion, the signal optical wavefront PV and RMS values converged slowly during the correction process and fluctuated significantly after convergence.
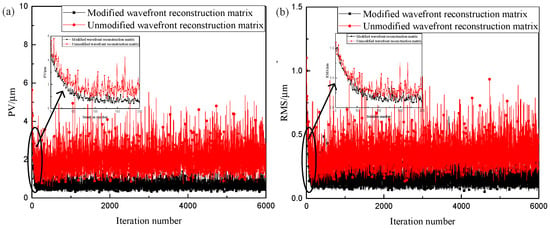
Figure 11.
Wavefront variation curve of the signal light in the experiment. (a) PV of wavefront; (b) RMS of wavefront.

Table 2.
PV and RMS of signal beam wavefronts.
When the correction matrix of the beacon optical wavefront reconstruction matrix was used as the signal optical wavefront reconstruction matrix to correct the signal wavefront distortion, the PV and RMS values of the signal wavefront converged faster and fluctuated less after convergence. The accuracy of the wavefront phase relationship of beams with different wavelengths derived in this study was further verified.
In the existing research on the distortion difference between beams of different wavelengths, plane waves are mainly used to describe the distortion difference; at the same time, the results of the distortion difference have not been applied to actual work.
In this paper, a description model of wavefront distortion difference is established for the Gaussian beam commonly used in optical signal transmission; and in the dual-wavelength adaptive optics system, an accurate calculation formula is given, and a method for compensating and correcting the distortion difference is proposed according to the working principle of the adaptive optics system, further reducing the correction residual, improving the correction accuracy, and applying the theoretical research results to practice.
6. Conclusions
The wavefront distortion correction residual of an adaptive optical system is a systematic error caused by the differences between the wavefront of the system signal and beacon lights. In this study, the correlation between the angle-of-arrival fluctuations at different wavelengths was analyzed. The expression of the cross-correlation function between the AOA fluctuations of different Gaussian-beam wavelengths and the relationship between the wavefront distortion phase of different Gaussian-beam wavelengths were derived.
On this basis, the effects of the propagation distance, atmospheric refractive index structure constant, Gaussian-beam waist radius, and wavelength difference on the angle-of-arrival fluctuation cross-correlation coefficient were analyzed. The wavefront distortion phase relations of beams with different wavelengths obtained in this study were verified experimentally.
The difference in wavefront distortion between beams of different wavelengths is caused by atmospheric dispersion. On the basis that there is no common optical path error, the correction of the wavefront distortion difference can improve the overall quality of the beam by 5%–10%.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.K.; methodology, X.K., J.W., and W.K.; software, W.K.; validation, W.K., and J.L.; formal analysis, C.K.; investigation, J.W.; resources, J.W. and W.K.; data curation, J.W. and W.K.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W. and W.K.; writing—review and editing, J.W. and J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Key Industrial Innovation Chain Project of Shaanxi Province [grant number 2017ZDCXLGY-06-01]; the Xi’an Science and Technology Planning Project [grant number 2020KJRC0083, 22GXFW0115]; and the Scientific Research Plan Projects of Shaanxi Education Department [grant number 18JK0341].
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
The study did not involve humans.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, J.; Wei, D.; Wroblowski, O.; Chen, Q.; Mantel, K.; Olschewski, F.; Kaufmann, M.; Riese, M. Analysis and correction of distortions in a spatial heterodyne spectrometer system. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 2190–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ke, X. Development of adaptive optical correction and polarization control modules for 10-km free-space coherent optical communications. J. Mod. Opt. 2019, 67, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Masouros, C. Beam drift in millimeter wave links: Beamwidth tradeoffs and learning based optimization. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 6661–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykal, Y. Adaptive optics corrections of scintillations of Hermite–Gaussian modes in an oceanic medium. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 4826–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cvijetic, M. Coherent free space optics communications over the maritime atmosphere with use of adaptive optics for beam wavefront correction. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, W.; Cvijetic, M. Slant-path coherent free space optical communications over the maritime and terrestrial atmospheres with the use of adaptive optics for beam wavefront correction. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.E.; Kong, Y.J. Performance prediction of a laser-guide star adaptive optics system for a 1.6 m telescope. Curr. Opt. Photonics 2018, 2, 269–279. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Ke, X.; Wu, J.; Ding, D. Dual-mirror adaptive-optics fiber coupling for free-space coherent optical communication. Opt. Eng. 2021, 60, 076109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, S.; Tan, L.; Ma, J. Approach for recognizing and tracking beacon in inter-satellite optical communication based on optical flow method. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 28080–28090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.; Kai, W.; Kai, J.; Gongchang, W.; Min, L.; Yudong, Z. Study on spot size and photo return of a sodium laser guide star. Infrared Laser Eng. 2019, 48, 0106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Jiang, W.H. Modal decomposition of anisoplanatic error of atmospheric turbulence for a laser guide star. Acta Opt. Sin. 2003, 23, 348–355. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Li, X.Y. Investigation of anisoplanatic effect in atmospheric turbulence probing with beaconⅠ: Numerical modeling. Chin. J. Lasers 2014, 41, 232–241. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Yang, C.P. Study on geometric method for angle-of-arrival distribution according to phase fluctuation. Laser Technol. 2008, 32, 534–535. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Tan, L.Y.; Ma, J. Experimental research of angle-of-arrival fluctuations in free-space optical communications. High Power Laser Part. Beams 2007, 19, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Toselli, I.; Andrews, L.C.; Phillips, R.L.; Ferrero, V. Angle of arrival fluctuations for free space laser beam propagation through non kolmogorov turbulence. In Proceedings of the SPIE 6551, Atmospheric Propagation IV, Orlando, FL, USA, 11–12 July 2007; pp. 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Voelz, D.; Wijerathna, E.; Muschinski, A.; Xiao, X. Computer simulations of optical turbulence in the weak- and strong-scattering regime: Angle-of-arrival fluctuations obtained from ray optics and wave optics. Opt. Eng. 2018, 57, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conan, R.; Borgnino, J.; Ziad, A.; Martin, F. Analytical solution for the covariance and for the decorrelation time of the angle of arrival of a wave front corrugated by atmospheric turbulence. JOSA A 2000, 17, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Yosef, N.N.; Goldner, E.; Weitz, A. Two-color correlation of scintillations. Appl. Opt. 1986, 25, 3486–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelaya, A.V.; Shubenkova, E.V.; Dmitriev, D.I.; Dmitrieva, A.D.; Kudryashov, A.V.; Lovchiy, I.L.; Shalymov, E.V.; Sheldakova, Y.V.; Tsvetkov, A.D.; Venediktov, D.V.; et al. Investigation of dual-wavelength laser beam propagation along the in-door atmospheric path. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9641, Optics in Atmospheric Propagation and Adaptive Systems XVIII, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 22 September 2014; p. 96410C. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Rong, J.; Zhong, X.-C.; Ding, X.-K. Study on correcting angle-of-arrival fluctuations of space optical communication with AO. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Space Information Technology, Wuhan, China, 10 November 2007; pp. 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kibblewhite, E.J.; Chun, M.R. Design of tip-tilt and adaptive optics servos using measured angle-of-arrival and phase power spectra. Adapt. Opt. Syst. Technol. SPIE 1998, 33, 522–530. [Google Scholar]
- Lukin, V.P. Efficiency of some correction systems. Opt. Lett. 1979, 4, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolissaint, L.; Kendrew, S. Modeling the Chromatic Correction Error in Adaptive Optics: Application to the Case of Mid-Infrared Observations in Dry to Wet Atmospheric Conditions. In Proceedings of the 1st AO4ELT Conference—Adaptive Optics for Extremely Large Telescopes, Paris, France, 22–26 June 2009; p. 05021. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, X.Z.; Chen, X.Z. Correcting wavefront distortion of dual-wavelength beams due to atmospheric turbulence with a correction coefficient. Opt. Photonics J. 2020, 10, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X. Arrival Angle of Beam Wave Propagation in Turbulent Atmosphere. Chin. J. Quantum Electron. 1987, 12, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, J.W.; Qin, K.C. Statistical Optics, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1992; pp. 132–134. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.-W.; Li, Z.-D.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; Yuan, X.-W. Adaptive optics correction technique based onfuzzy control. Acta Phys. Sin. 2016, 65, 014206. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).