Design of All-Optical Subtractors Utilized with Plasmonic Ring Resonators for Optical Computing
Abstract
1. Introduction
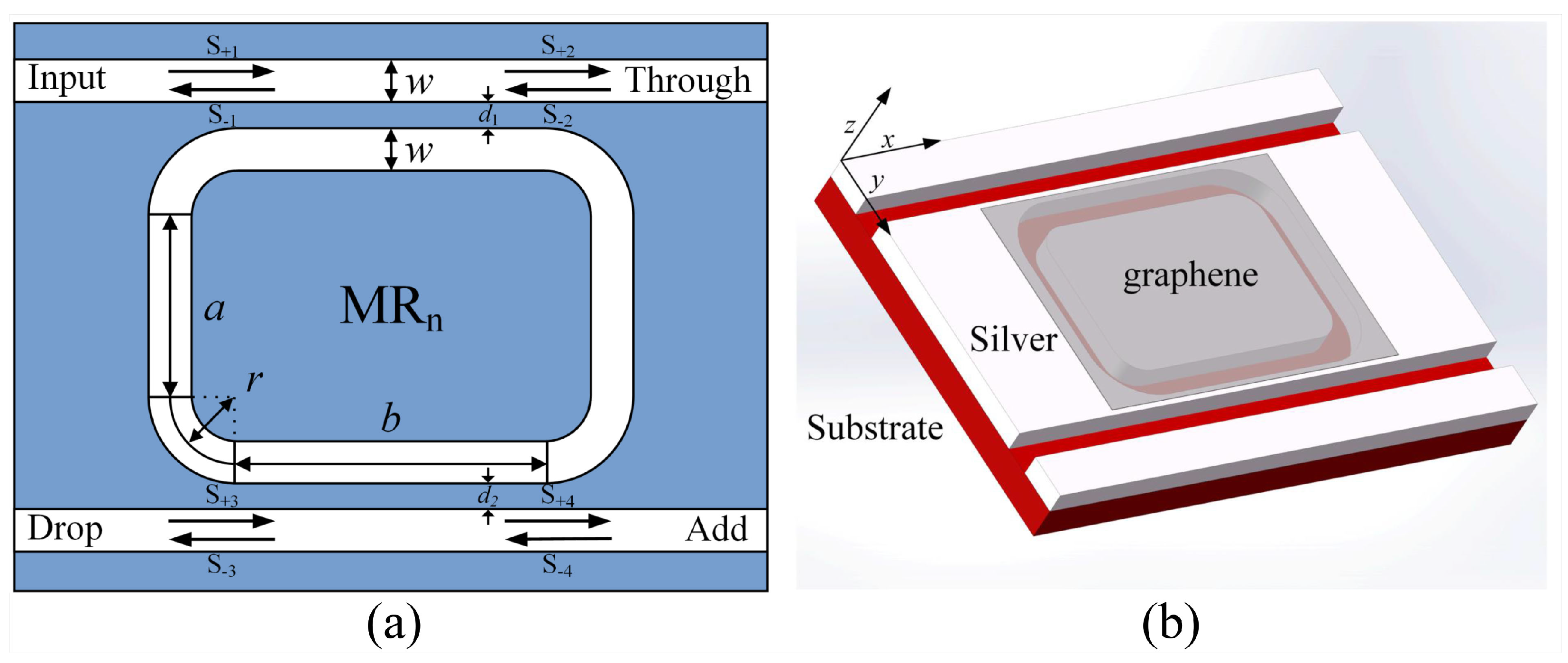
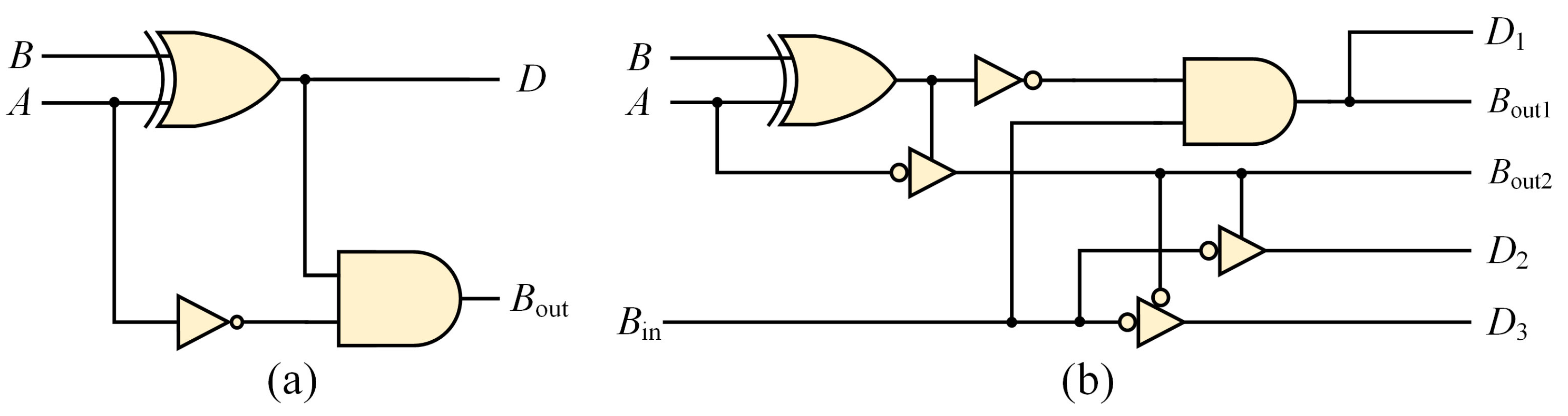
2. Architecture and Theory
2.1. All-Optical Switch
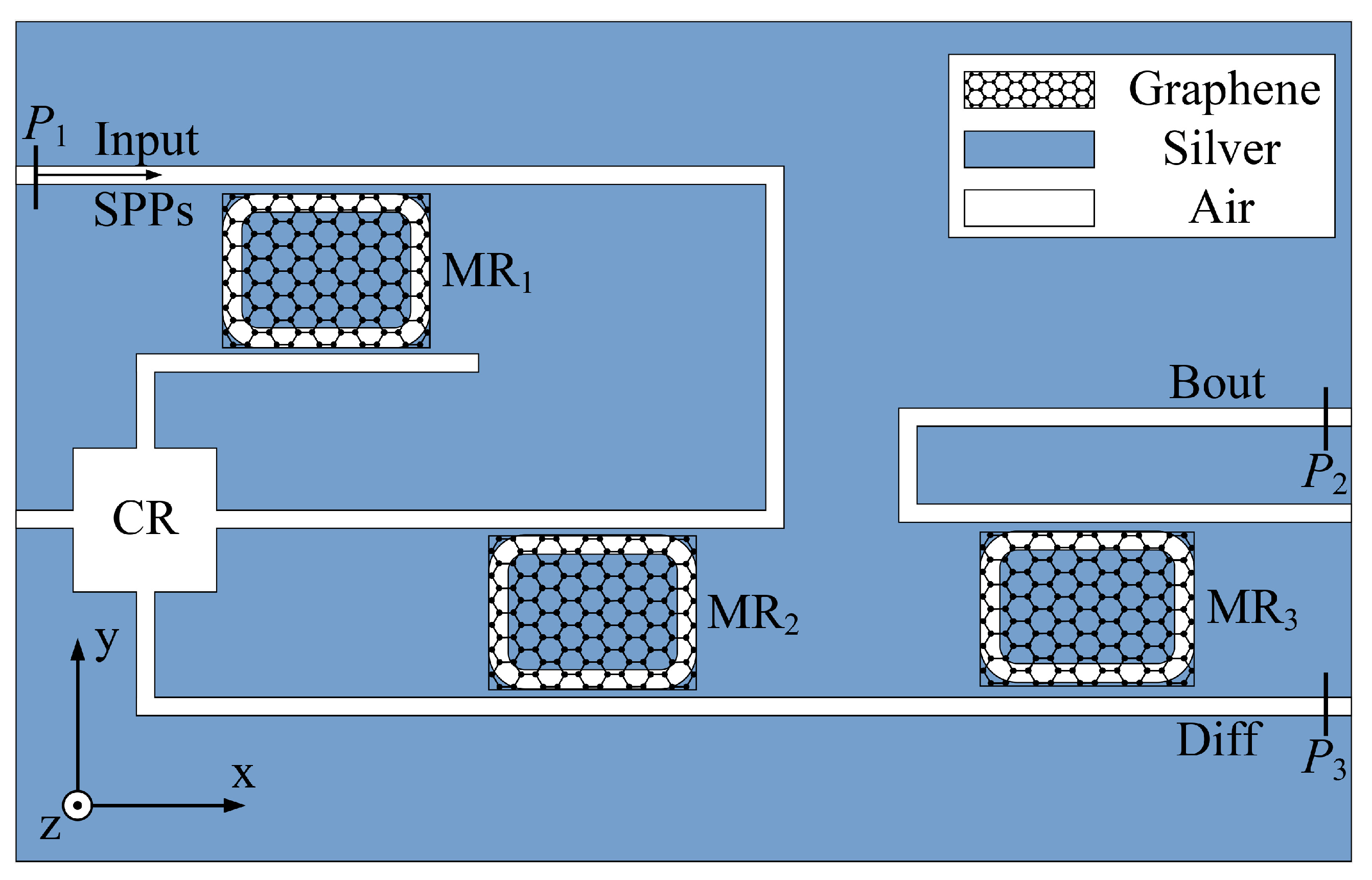
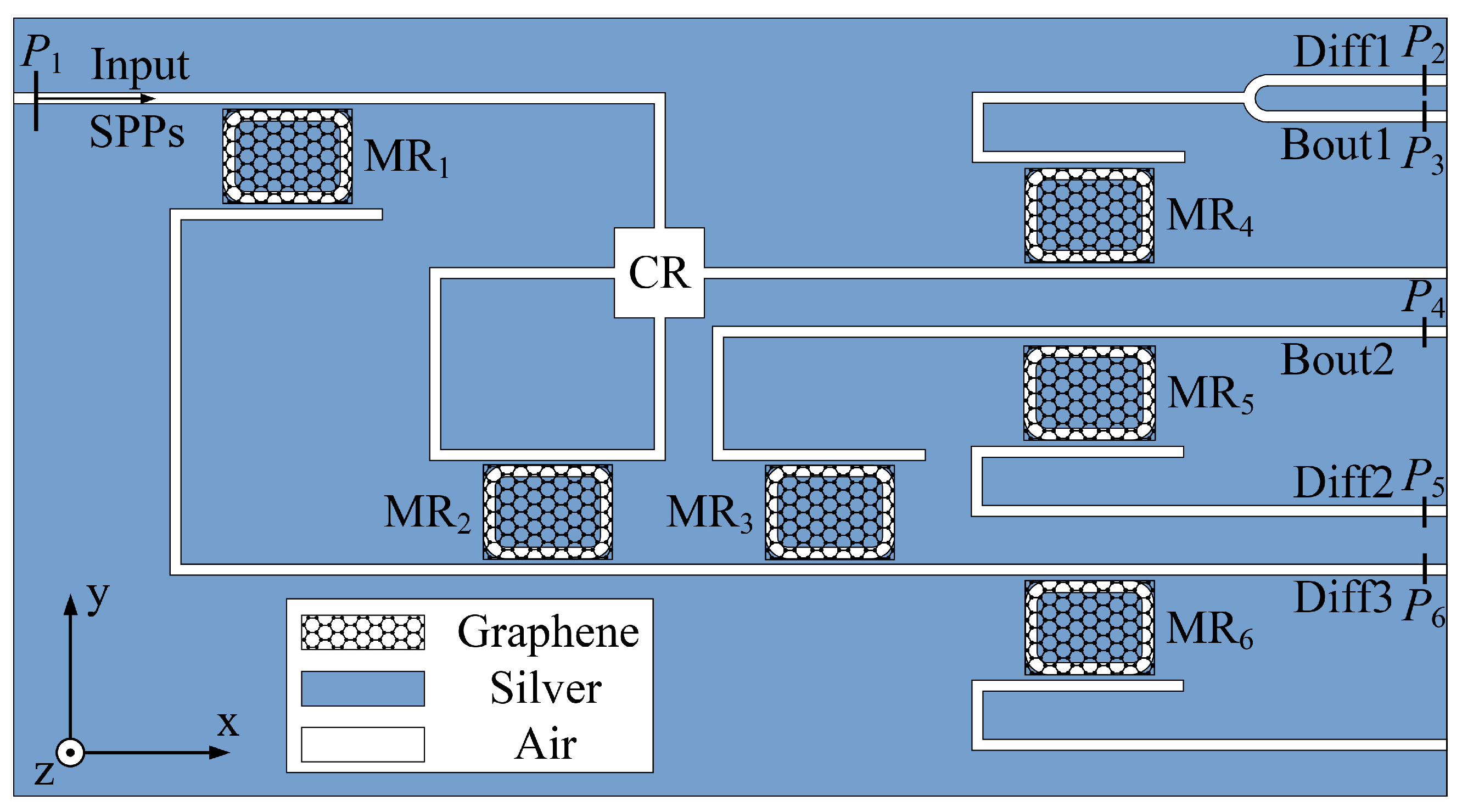
2.2. Plasmonic Subtractors
3. Results
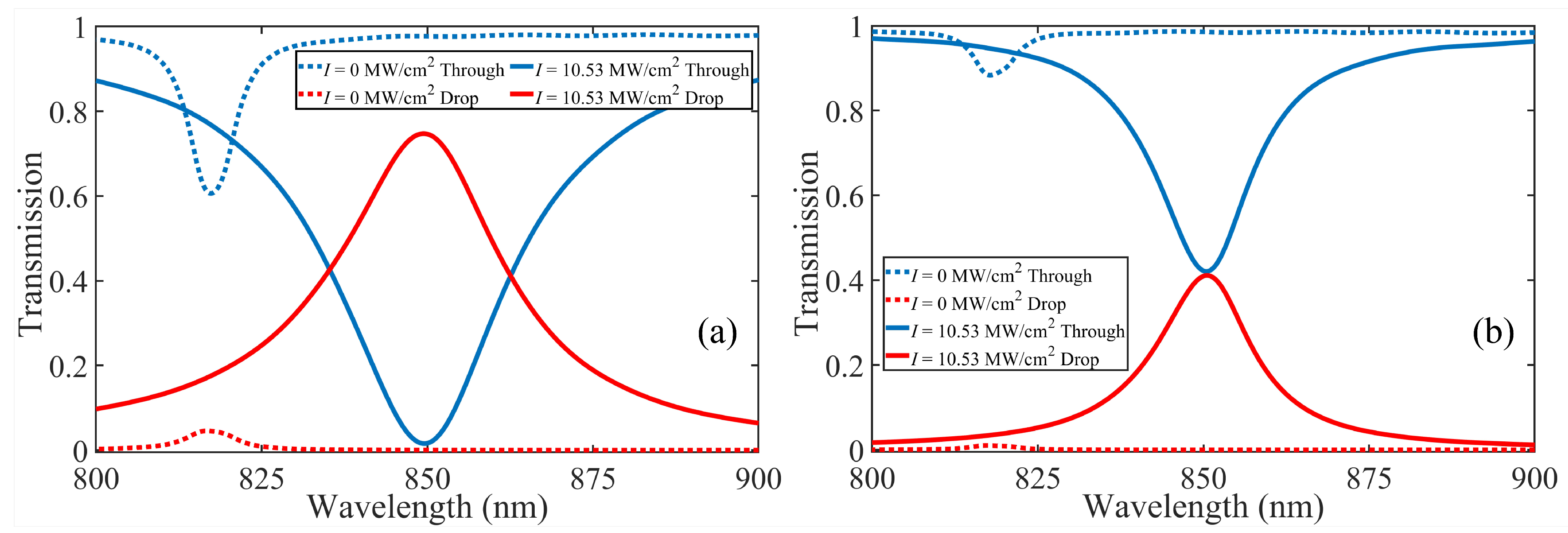
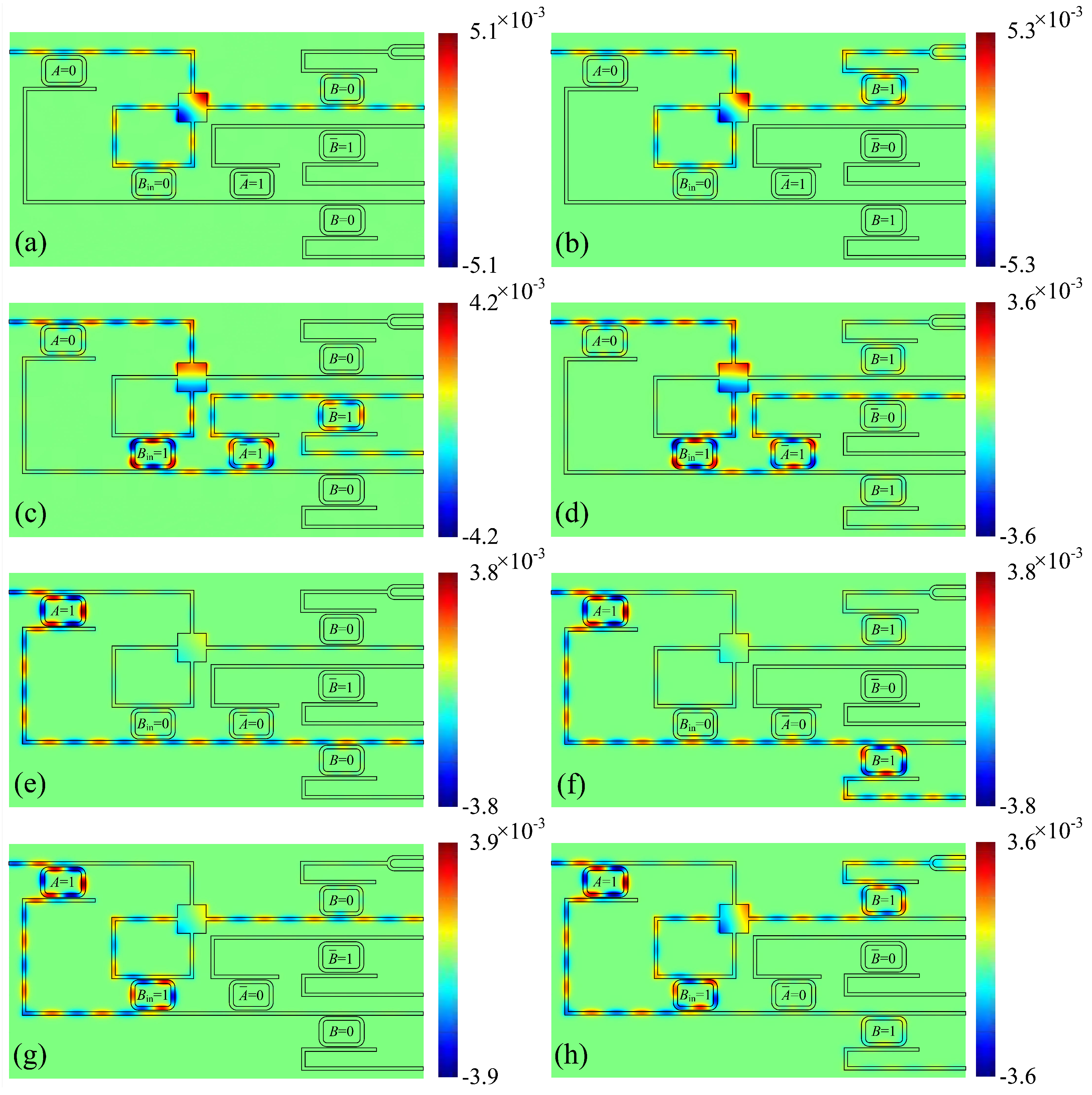
3.1. Simulated Results of the Plasmonic Half-Subtractor
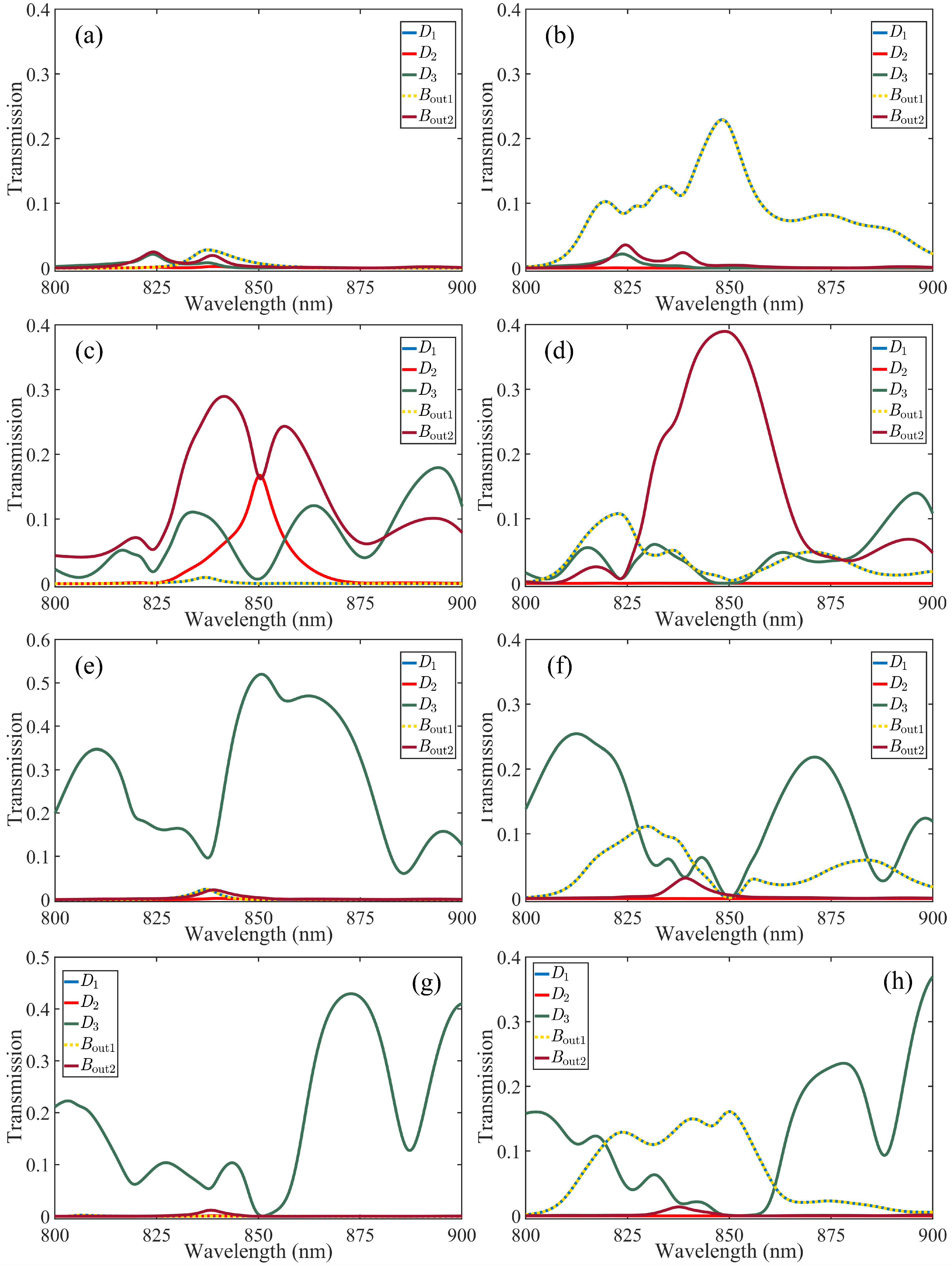
3.2. Simulated Results of Plasmonic Full-Subtractor
4. Comparisons
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Li, B.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, P.; Jo, G.-B.; Liu, J.; Du, S. All-optical neural network with nonlinear activation functions. Optica 2019, 6, 1132–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrop, M.M. The chips are down for Moore’s law. Nature 2016, 530, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Xiao, H.; Wang, L.; Tian, Y. Recent advances in integrated optical directed logic operations for high performance optical computing: A review. Front. Optoelectron. 2022, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Lei, L.; Chen, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X. All-optical 2 × 2-bit multiplier at 40 gb/s based on canonical logic units-based programmable logic array (clus-pla). J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 5586–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touch, J.; Badawy, A.-H.; Sorger, V.J. Optical computing. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Dhar, S.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, C.; Mital, R.; Chung, C.-J.; Pan, D.Z.; Soref, R.A.; Chen, R.T. Electro-optic ripple-carry adder in integrated silicon photonics for optical computing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2018, 24, 7600310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Lin, X.; Lin, X.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, E.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H. Performing optical logic operations by a diffractive neural network. Light Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, H.J.; Dolev, S. Why future supercomputing requires optics. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Ríos, C.; Youngblood, N.; Wright, C.D.; Pernice, W.H.P.; Bhaskaran, H. Device-Level photonic memories and logic applications using phase-change materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, C.; Peng, H.-T.; Bilodeau, S.; Jha, A.; Blow, E.; Lima, T.F.D.; Shastri, B.J.; Prucnal, P. Silicon microring synapses enable photonic deep learning beyond 9-bit precision. Optica 2018, 9, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, S.; Tang, R.; Toprasertpong, K.; Takagi, S.; Takenaka, M. Si microring resonator crossbar array for on-chip inference and training of the optical neural network. ACS Photonics 2022, 9, 2614–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Ma, T.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, J.-J. Parallelized and Cascadable Optical Logic Operations by Few-Layer Diffractive Optical Neural Network. Photonics 2023, 10, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.A.B. Are optical transistors the logical next step? Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Shamir, J. Optics inspired logic architecture. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L. Directed logic circuits based on silicon microring resonators. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2014, 51, 110004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Ye, X.; Soref, R.; Yang, L.; Xu, Q. Demonstration of reconfgurable electro-optical logic with silicon photonic integrated circuits. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 3942–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, C.; Mital, R.; Dhar, S.; Pan, D.Z.; Soref, R.; Chen, R.T. Automated logic synthesis for electro-optic logic-based integrated optical computing. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 28002–28012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Feng, C.; Zhao, Z.; Soref, R.; Pan, D.Z.; Chen, R.T. Integrated multi-operand electro-optic logic gates for optical computing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 171104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostimirovic, D.; Ye, W.N. Ultracompact CMOS-compatible optical logic using carrier depletion in microdisk resonators. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soref, R.; De Leonardis, F.; Ying, Z.; Passaro, V.M.N.; Chen, R.T. Silicon-based group-IV OEO devices for gain, logic, and wavelength conversion. ACS Photonics 2020, 7, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ji, R.; Yang, L.; Zhou, P.; Chen, H.; Ding, J.; Zhu, W.; Lu, Y.; Jia, L.; et al. Proof of concept of directed or/nor and and/nand logic circuit consisting of two parallel microring resonators. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 1650–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q.; Yang, L. Xor/Xnor directed logic circuit based on coupled-resonator-induced transparency. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Ying, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Mital, R.; Pan, D.Z.; Chen, R.T. Analysis of microresonator-based logic gate for high-speed optical computing in integrated photonics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2020, 26, 8302208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Dhar, S.; Pan, D.Z.; Soref, R.; Chen, R.T. Silicon microdisk-based full adders for optical computing. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, F.K.; Uddin, M.R.; Hashim, H.; Won, Y.H. Demonstration of photonic micro-ring resonator based digital bit magnitude comparator. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xiao, H.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Meng, Y.; Deng, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, G.; Yang, J. Experimental realization of an optical digital comparator using silicon microring resonators. Nanophotonics 2018, 7, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Zou, W. Optical Convolutional Neural Network with WDM-Based Optical Patching and Microring Weighting Banks. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2021, 33, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.Y.; Tait, A.N.; Lima, T.F.; Huang, C.; Shastri, B.J.; Prucnal, P.R. Photonic independent component analysis using an on-chip microring weight bank. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 1827–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramotnev, D.K.; Bozhevolnyi, S.I. Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Hu, X.; Yang, H.; Gong, Q. Ultracompact all-optical logic gates based on nonlinear plasmonic nanocavities. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Hu, X.; Lu, C.; Yue, S.; Yang, H.; Gong, Q. All-optical logic gates based on nanoscale plasmonic slot waveguides. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5784–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, S.L.; Maradudin, A.A.; Wallis, R.F. Effect of a charge layer on the surface-plasmon-polariton dispersion curve. Phys. Rev. B 1974, 10, 3342–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; He, X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, D.; Xu, S. All-optical multi-channel switching at telecommunication wavelengths based on tunable plasmon-induced transparency. Opt. Commun. 2018, 425, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Hata, M.; Tsunekawa, M.; Nozaki, K.; Sumikura, H.; Chiba, H.; Notomi, M. Ultrafast and energy-efficient all-optical switching with graphene-loaded deep-subwavelength plasmonic waveguides. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.M.; Darbari, S.; Moravvej-Farshi, M.K. Tunable plasmonic force switch based on graphene nano-ring resonator for nanomanipulation. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 26648–26660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Lu, P.; Chen, L.; Lv, C.; Liu, D. A subwavelength mim waveguide resonator with an outer portion smooth bend structure. Opt. Commun. 2011, 284, 4078–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. High transmission efciency wavelength division multiplexer based on metal–insulator–metal plasmonic waveguides. J. Light. Technol. 2014, 32, 4844–4848. [Google Scholar]
- Chou Chao, C.-T.; Chou Chau, Y.-F. Highly Sensitive Multichannel Fano Resonance-Based Plasmonic Sensor for Refractive Index and Temperature Sensing Application. Photonics 2023, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, P.T.; Lasson, J.R.; Heuck, M.; Gregersen, N.; Mørk, J. On the Theory of Coupled Modes in Optical Cavity-Waveguide Structures. J. Light. Technol. 2017, 35, 4247–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Hu, X.; Chai, Z.; Lu, C.; Yang, H.; Gong, Q. Tunable ultracompact chip-integrated multichannel flter based on plasmon-induced transparencies. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 221114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, T.; Liu, B.; He, Y.; Zhu, Y. Tunable triple plasmon-induced transparencies in dual t-shaped cavities side-coupled waveguide. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2016, 28, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendry, E.; Hale, P.; Moger, J.; Savchenko, A.; Mikhailov, S. Coherent nonlinear optical response of graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Virally, S.; Bao, Q.; Ping, L.K.; Massar, S.; Godbout, N.; Kockaert, P. Z-scan measurement of the nonlinear refractive index of graphene. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 1856–1858. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, S.; Shi, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Wen, S. Broadband ultrafast nonlinear optical response of few-layers graphene: Toward the mid-infrared regime. Photonics Res. 2015, 3, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, J.; Gerstenkorn, C.; Wang, R.; Chiu, H.; Smirl, A.L.; Zhao, H. Third harmonic generation in graphene and few-layer graphite films. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 121406(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, X.; Fu, F.; Yang, H.; Gong, Q. Ultralow-power and ultrafast all-optical tunable plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials at optical communication range. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckinger, N.; Vlad, A.; Melinte, S.; Colomer, J.-F.; Sarrazin, M. Graphene-coated holey metal flms: Tunable molecular sensing by surface plasmon resonance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 211108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Niu, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, F.; Chai, Z.; Yang, H.; Gong, Q. Ultracompact all-optical full-adder and half-adder based on nonlinear plasmonic nanocavities. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaenko, A.E.; Papasimakis, N.; Atmatzakis, E.; Luo, Z.; Shen, Z.X.; Angelis, F.; Boden, S.A.; Fabrizio, E.D.; Zheludev, N.I. Nonlinear graphene metamaterial. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 181109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wu, T.; Shao, Y.; Jia, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gao, Y. Ultrafast and low-power multichannel all-optical switcher based on multilayer graphene. Appl. Opt. 2023, 62, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, X.; Yang, H.; Gong, Q. On-chip plasmon-induced transparency based on plasmonic coupled nanocavities. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Dai, J.; Dai, Y.; Fan, Y.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Yin, F.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, K. Dynamically tunable plasmon induced absorption in graphene-assisted metal odielectric grating. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 26221–26233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, S.; Yang, H.; Gong, Q. Ultracompact chip-integrated electromagnetically induced transparency in a single plasmonic composite nanocavity. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2014, 2, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transmission—Script Command. Available online: https://optics.ansys.com/hc/en-us/articles/360034405354-transmission-Script-command (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Ye, Y.; Xie, Y.; Song, T.; Guan, N.; Lv, M.; Li, C. Integrated plasmonic full adder based on cascaded rectangular ring resonators for optical computing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 156, 108479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-W.; Lee, D.E.; Lee, Y.J.; Kwon, S.-H. Low cross-talk, deep subwavelength plasmonic metal/insulator/metal waveguide intersections with broadband tunability. Photonics Res. 2016, 4, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugger, H.; Jurich, M.; Swalen, J.D.; Sievers, A.J. Observation of an index-of-refraction-induced change in the Drude parameters of Ag films. Phys. Rev. B. 1986, 34, 1322–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.B.; Christy, R.W. Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. B. 1972, 6, 4370–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mode Source—Simulation Object. Available online: https://optics.ansys.com/hc/en-us/articles/360034902153-Mode-source-Simulation-object (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Dutta, S.; Zografos, O.; Gurunarayanan, S.; Radu, I.; Soree, B.; Catthoor, F.; Naeemi, A. Proposal for nanoscale cascaded plasmonic majority gates for non-Boolean computation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Hu, X.; Yang, H.; Gong, Q. Chip-integrated ultrawide-band all-optical logic comparator in plasmonic circuits. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birr, T.; Zywietz, U.; Chhantyal, P.; Chichkov, B.N.; Reinhardt, C. Ultrafast surface plasmon-polariton logic gates and half-adder. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 31755–31766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, L.; Raghuwanshi, S.K. Design of plasmonic half-adder and half-subtractor circuits employing nonlinear effect in Mach–Zehnder interferometer. J. Comput. Electron. 2017, 16, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarnakar, S.; Basha, S.C.A.; Azmathullah, S.; Prabhu, N.A.; Madhu, G.; Kumar, S. Improved design of all-optical half-adder and half-subtractor circuits using MIM plasmonic waveguides for optical networks. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2023, 55, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
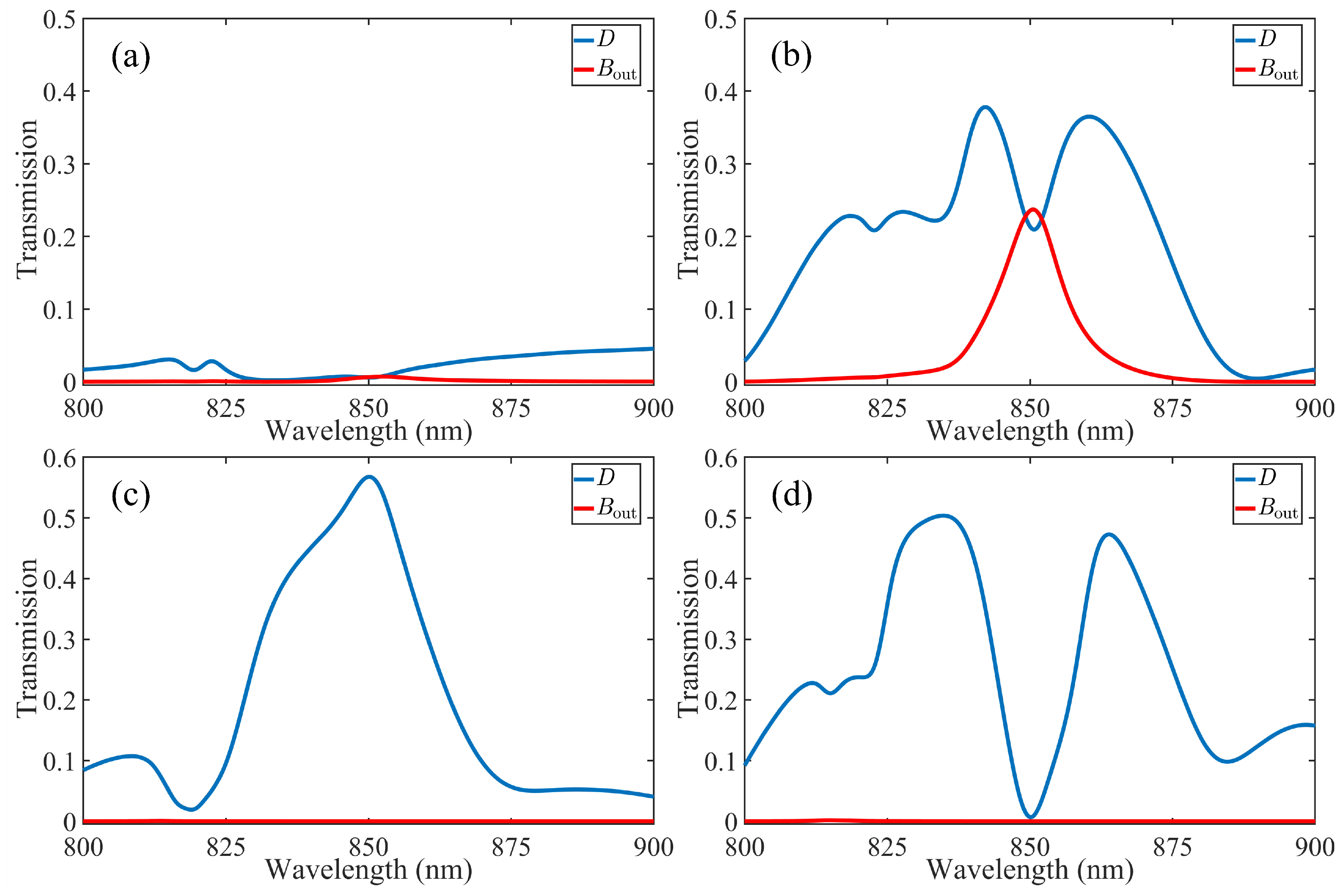

| Input State | Transmission at Port D | Transmission at Port | Difference | Output Borrow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.593% (0) | 0.652% (0) | 0 | 0 | |
| 20.96% (1) | 23.61% (1) | 1 | 1 | |
| 56.79% (1) | 0.002% (0) | 1 | 0 | |
| 0.692% (0) | 0.001% (0) | 0 | 0 |
| Input State | Transmission at Port D1 | Transmission at Port D2 | Transmission at Port D3 | Transmission at Port Bout1 | Transmission at Port Bout2 | Difference | Output Borrow |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.734% (0) | 0.069% (0) | 0.007% (0) | 0.734% (0) | 0.002% (0) | 0 | 0 | |
| 22.87% (1) | 0.000% (0) | 0.000% (0) | 22.87% (1) | 0.429% (0) | 1 | 1 | |
| 0.013% (0) | 16.75% (1) | 0.716% (0) | 0.013% (0) | 16.23% (1) | 1 | 1 | |
| 0.531% (0) | 0.011% (0) | 0.022% (0) | 0.531% (0) | 38.98% (1) | 0 | 1 | |
| 0.007% (0) | 0.139% (0) | 51.98% (1) | 0.007% (0) | 0.457% (0) | 1 | 0 | |
| 0.143% (0) | 0.000% (0) | 0.175% (0) | 0.143% (0) | 0.553% (0) | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.049% (0) | 0.006% (0) | 0.409% (0) | 0.049% (0) | 0.019% (0) | 0 | 0 | |
| 16.11% (1) | 0.000% (0) | 0.075% (0) | 16.11% (1) | 0.069% (0) | 1 | 1 |
| Works | Computing Functions | Simulation Method | Materials | Proposed Structure | Footprint | Operating Wavelength | Performance Measured |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. [50] | Half-adder Full-adder | FEM-2D | Gold | Nonlinear Plasmonic Nanocavities | Less than 15 m × 15 m | 750 nm | Transmission |
| Ref. [63] | Comparator One-Bit | FEM-2D | Gold | MZI Based on MIM Waveguides | Less than 10 m × 10 m | 1000 nm | Intensity and Contrast Ratio |
| Ref. [64] | Half-adder | FEM-2D | Gold | Dielectric Crossed Plasmonic Waveguides | 10 m × 28 m | 800 nm | Intensity |
| Ref. [65] | Half-adder Half-subtractor | Finite-difference Time-domain | Not given | MZI Based on Plasmonic MIM Waveguides | 75 m × 8 m | 1550 nm | Output Optical Power |
| Ref. [66] | Half-adder Half-subtractor | Finite-difference Time-domain | Silicon Oxynitride | Y-shaped Power Combiners Based on Plasmonic MIM Waveguides | 11 m × 6 m | 1550 nm | Intensity |
| This work | Half-subtractor | Finite-difference Time-domain | Silver | Cascaded Plasmonic Rectangular Ring Resonator | 3.2 m × 1.6 m | 850 nm | Transmission |
| This work | Full-subtractor | Finite-difference Time-domain | Silver | Cascaded Plasmonic Rectangular Ring Resonator | 3.2 m × 1.6 m | 850 nm | Transmission |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, Y.; Song, T.; Xie, Y.; Li, C. Design of All-Optical Subtractors Utilized with Plasmonic Ring Resonators for Optical Computing. Photonics 2023, 10, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10070724
Ye Y, Song T, Xie Y, Li C. Design of All-Optical Subtractors Utilized with Plasmonic Ring Resonators for Optical Computing. Photonics. 2023; 10(7):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10070724
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Yichen, Tingting Song, Yiyuan Xie, and Chuandong Li. 2023. "Design of All-Optical Subtractors Utilized with Plasmonic Ring Resonators for Optical Computing" Photonics 10, no. 7: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10070724
APA StyleYe, Y., Song, T., Xie, Y., & Li, C. (2023). Design of All-Optical Subtractors Utilized with Plasmonic Ring Resonators for Optical Computing. Photonics, 10(7), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10070724






