Nanotubes in Chitin Mode Locker for Passive Mode−Locked Fibre Laser in 2.0 µm Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
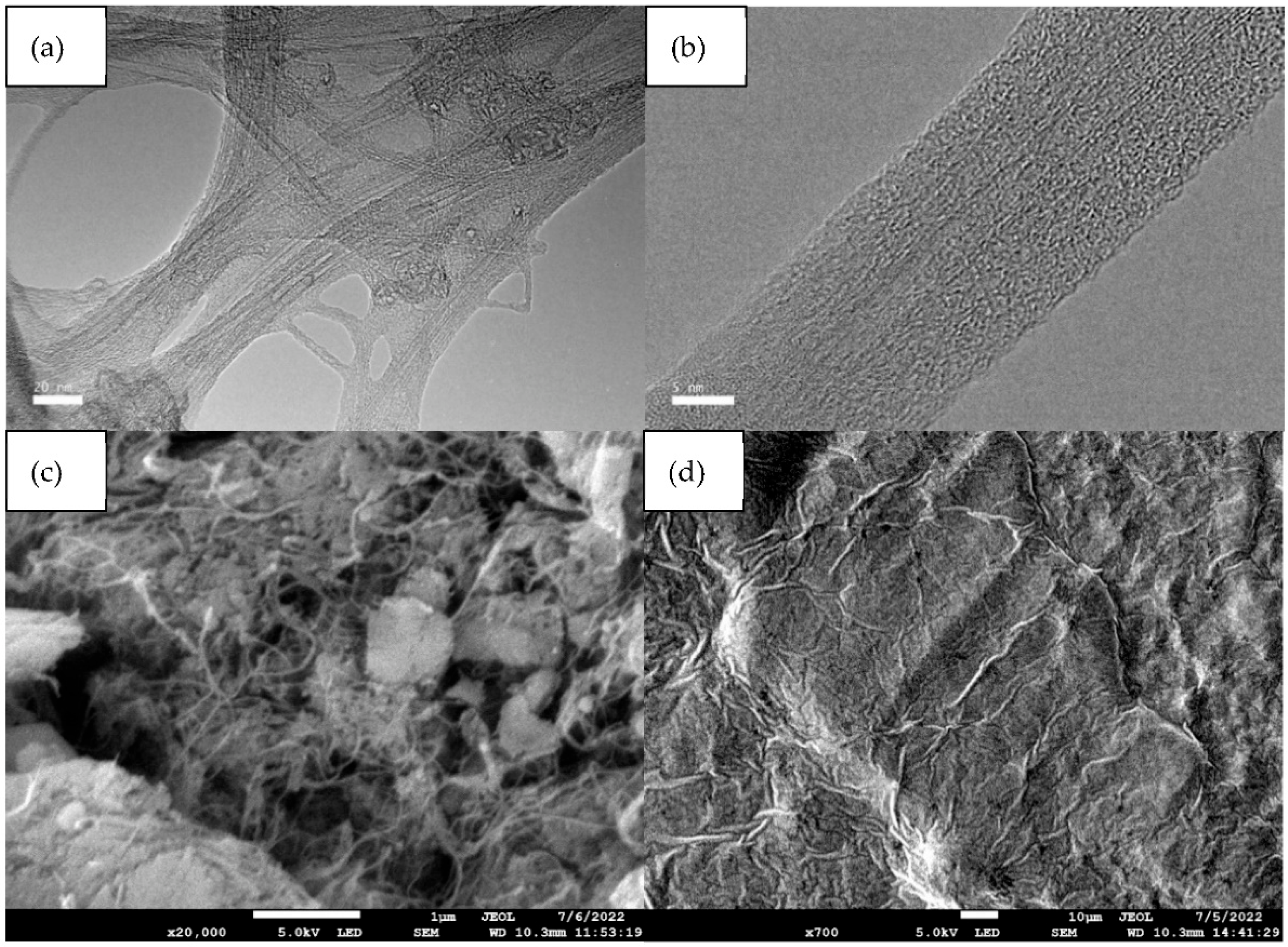
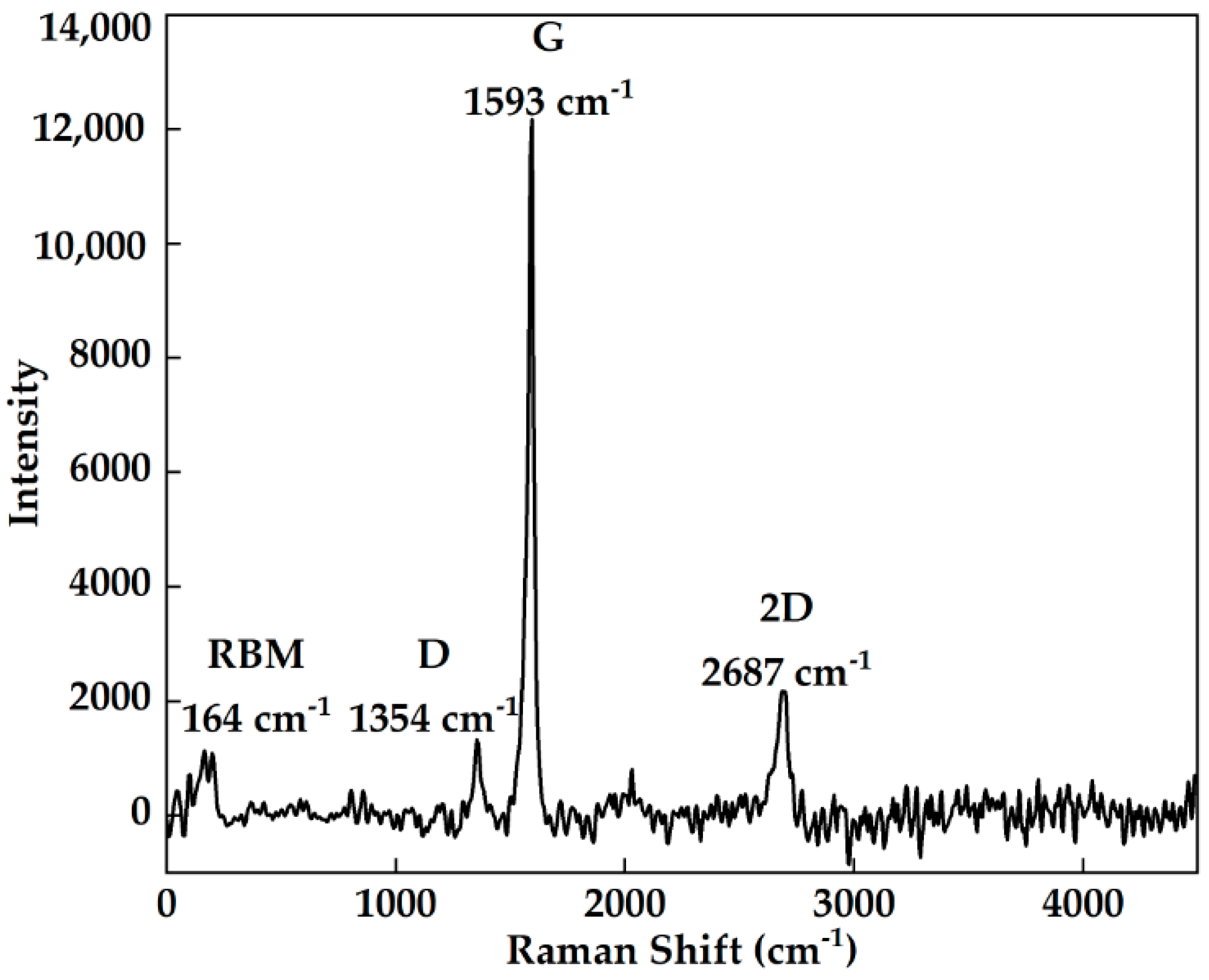
2.1. Preparation and Characterisation of CNT–Chitin
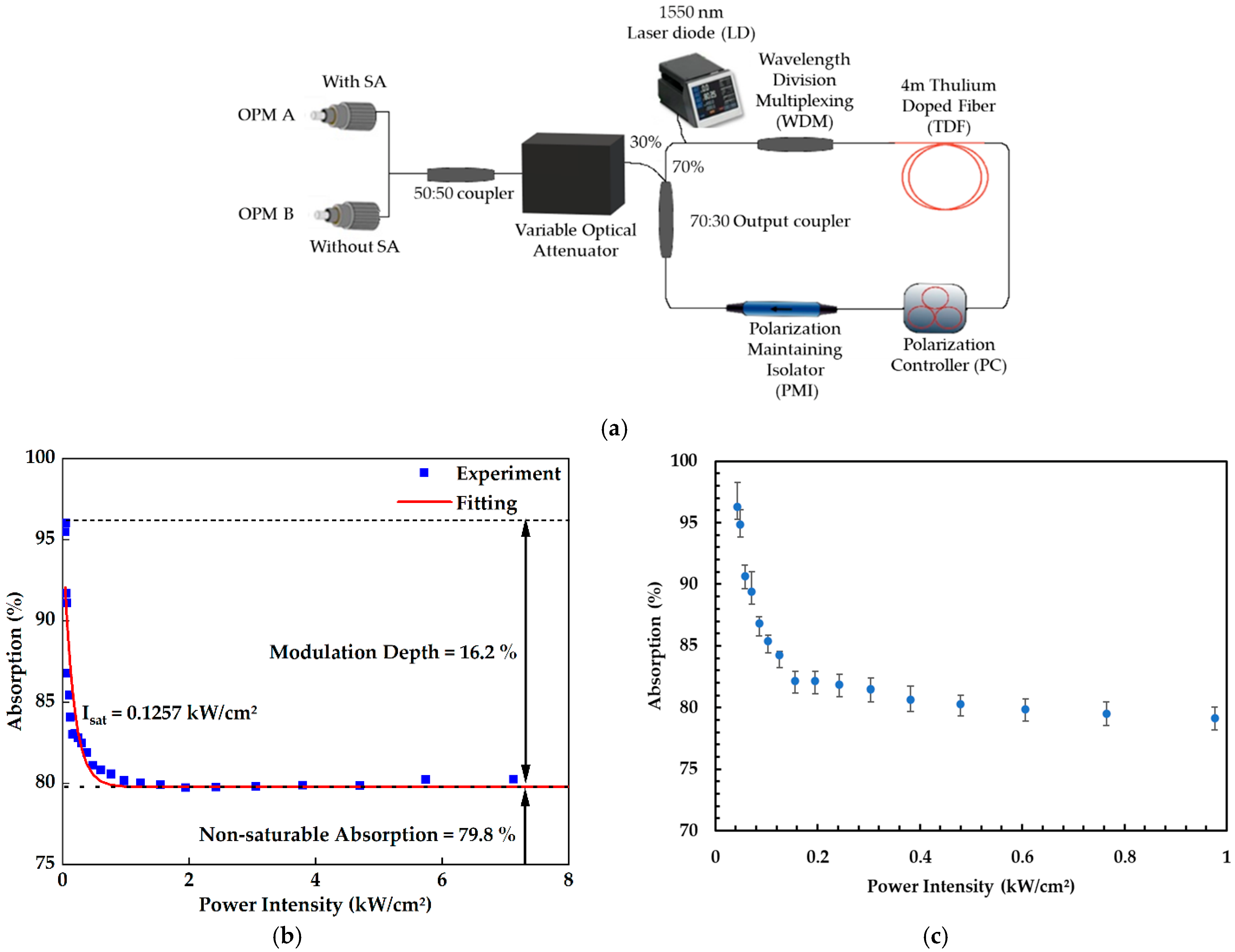
2.2. Determination of Linear and Non-Linear Optical Properties of CNT–Chitin Saturable Absorber
2.3. Fiber Laser Setup
3. Results and Discussion
| Material | Diameter of Material (nm) | Center Wavelength (nm) | Threshold Pump Power (mW) | Pulse Width (ps) | Repetition Rate (MHz) | SNR (dB) | TBP | Modulation Depth (%) | Average Output Power (mW) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWCNT-PVA | - | 2003.1 | - | 9300 | 1.718 | 63 | ~904 | 23.7 | 46 | [17] |
| SWCNT (Polymer free) | 1.4 | 1928.5 | 410 | 0.501 | 56.37 | ~70 | 0.343 | 13 | 28.5 | [50] |
| CNT-SA with a diffraction grating mirror | ~1.3–1.6 | 1960 | 240 | 2.43 | 18.4 | >60 | 0.567 | 42.3 | ~1 | [55] |
| SWCNT microfiber | - | 1967.79 | 500 | 0.896 | 17.2 | >57 | 0.318 | 16.5 | 6.54 | [68] |
| SWCNT-Polyimide film | 1.6 | 2000 | - | 0.211 | 21.4 | 66 | - | 10 | 36.1 | [70] |
| Graphene-Chitin | - | 1982.7 | 76.2 | 1.88 | 11.35 | 43 | 0.416 | 18.56 | 3.43 | [28] |
| Graphene-PMMA | - | 2060 | 1000 | 0.19 | 20.98 | 65 | 0.72 | 12 | 54 | [69] |
| CNT–chitin | 1–2 | 1908.53 | 203 | 1.1 | 16 | 69 | 0.325 | 16.7 | 0.4 | This work |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; Tian, J.; Song, Y. A 66 fs highly stable single wall carbon nanotube mode locked fiber laser. Laser Phys. 2013, 24, 015105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernysheva, M.; Rozhin, A.; Fedotov, Y.; Mou, C.; Arif, R.; Kobtsev, S.M.; Dianov, E.M.; Turitsyn, S.K. Carbon nanotubes for ultrafast fibre lasers. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Rozhin, A.G.; Scardaci, V.; Sun, Z.; Hennrich, F.; White, I.H.; Milne, W.I.; Ferrari, A.C. Wideband-tuneable, nanotube mode-locked, fibre laser. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, S.; Thomsen, C.; Maultzsch, J. Carbon Nanotubes: Basic Concepts and Physical Properties; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Set, S.Y.; Yaguchi, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Jablonski, M.; Sakakibara, Y.; Rozhin, A.; Tokumoto, M.; Kataura, H.; Achiba, Y.; Kikuchi, K. Mode-locked fiber lasers based on a saturable absorber incorporating carbon nanotubes. In Proceedings of the Conference on Optical Fiber Communication, Atlanta, GA, USA, 28 March 2003; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.; Yan, F.; Feng, T.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Hou, Y. Single weakly tilted FBG in 2-μm band capable of measuring temperature, axial strain, and surrounding refractive index. Opt. Eng. 2018, 57, 096107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Wang, Q.; Lee, Y.; Jiang, S. Development of Eye-Safe Fiber Lasers Near 2 μm. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2014, 20, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholle, K.; Lamrini, S.; Koopmann, P.; Fuhrberg, P. 2 µm Laser Sources and Their Possible Applications. In Frontiers in Guided Wave Optics and Optoelectronics; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.; Lu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Huang, F.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J. Spectroscopy of thulium and holmium co-doped silicate glasses. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 2252–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieu, K.; Wise, F.W. Soliton thulium-doped fiber laser with carbon nanotube saturable absorber. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2009, 21, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivistö, S.; Hakulinen, T.; Kaskela, A.; Aitchison, B.; Brown, D.P.; Nasibulin, A.G.; Kauppinen, E.I.; Härkönen, A.; Okhotnikov, O.G. Carbon nanotube films for ultrafast broadband technology. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 2358–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B. Carbon nanotubes and their polymeric composites: The applications in tissue engineering. Biomanuf. Rev. 2020, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurazzi, N.M.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Khalina, A.; Abdullah, N.; Sabaruddin, F.A.; Kamarudin, S.H.; Ahmad, S.; Mahat, A.M.; Lee, C.L.; Aisyah, H.A.; et al. Fabrication, Functionalization, and Application of Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced Polymer Composite: An Overview. Polymers 2021, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Sharbirin, A.S.; Ismail, M.F. 1.8 µm passively Q-switched thulium-doped fiber laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 120, 105757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, S.W.; Saidin, N.; Zen, D.I.M.; Ali, N.M.; Ahmad, H.; Ahmad, F.; Dimyati, K. Self-starting harmonic mode-locked thulium-doped fiber laser with carbon nanotubes saturable absorber. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2013, 30, 094204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, J. 463-MHz fundamental mode-locked fiber laser based on few-layer MoS2 saturable absorber. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1374–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Song, Z.; Wei, J.; Pei, J.; Ruan, S. Two-micron all-fiberized passively mode-locked fiber lasers with high-energy nanosecond pulse. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Samion, M.Z.; Sharbirin, A.S.; Norizan, S.F.; Aidit, S.N.; Ismail, M.F. Graphene-PVA saturable absorber for generation of a wavelength-tunable passively Q-switched thulium-doped fiber laser in 2.0 μm. Laser Phys. 2018, 28, 055105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Yang, W.; Zhang, H. Nonlinear saturable absorption properties of indium selenide and its application for demonstrating a Yb-doped mode-locked fiber laser. Opt. Mater. Express 2018, 8, 3092–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Nofal, M.M.; Brza, M.A.; Hussein, S.A.; Mahmoud, K.H.; El-Bahy, Z.M.; Dannoun, E.M.A.; Kareem, W.O.; Hussein, A.M. Characteristics of PEO Incorporated with CaTiO3 Nanoparticles: Structural and Optical Properties. Polymers 2021, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrazek, E.M.; Abdelghany, A.M.; Badr, S.I.; Morsi, M.A. Structural, optical, morphological and thermal properties of PEO/PVP blend containing different concentrations of biosynthesized Au nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, K.S.; Ramesh, S.; Ramesh, K.; Juan, J.C. A review of polymer electrolytes: Fundamental, approaches and applications. Ionics 2016, 22, 1259–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, D.S.; Brza, M.A.; Nofal, M.M.; Aziz, S.B.; Hussen, S.A.; Abdulwahid, R.T. Optical Dielectric Loss as a Novel Approach to Specify the Types of Electron Transition: XRD and UV-vis as a Non-Destructive Techniques for Structural and Optical Characterization of PEO Based Nanocomposites. Materials 2020, 13, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhong, M.; Huang, Y.; Wan, X.; Peng, J.; Weng, J. Nonlinear optical absorption of few-layer molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2) for passively mode-locked soliton fiber laser. Photonics Res. 2015, 3, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Rani, V.D.; Shalumon, K.T.; Kumar, P.T.; Nair, S.V.; Furuike, T.; Tamura, H. Bioactive and osteoblast cell attachment studies of novel α-and β-chitin membranes for tissue-engineering applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 45, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elieh-Ali-Komi, D.; Hamblin, M.R. Chitin and Chitosan: Production and Application of Versatile Biomedical Nanomaterials. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 4, 411–427. [Google Scholar]
- Shervani, Z. Chitin-gold nanocomposite film and electro-optical properties. Front. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 3, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuikafly, S.N.F.; Ahmad, H.; Nawawi, W.M.F.W.; Yahaya, H.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Latif, A.A.; Ahmad, F. Graphene-chitin bio-composite polymer based mode locker at 2 micron region. Optik 2021, 245, 167710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, S.X.L.; Goh, E.X.Y.; Lee, H.K. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-multi-walled carbon nanotubes-coated-membrane solid phase extraction of glucocorticoids in aqueous matrices. Talanta 2021, 221, 121624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisman, L.; Wagner, H.D.; Marom, G. The role of surfactants in dispersion of carbon nanotubes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 21, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Grossiord, N.; Koning, C.E.; Loos, J. Controlling the dispersion of multi-wall carbon nanotubes in aqueous surfactant solution. Carbon 2007, 45, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strano, M.S.; Moore, V.C.; Miller, M.K.; Allen, M.J.; Haroz, E.H.; Kittrell, C.; Hauge, R.H.; Smalley, R.E. The role of surfactant adsorption during ultrasonication in the dispersion of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2003, 3, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazli Wan Nawawi, W.M.; Lee, K.Y.; Kontturi, E.; Murphy, R.J.; Bismarck, A. Chitin Nanopaper from Mushroom Extract: Natural Composite of Nanofibers and Glucan from a Single Biobased Source. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6492–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorio, A.; Pimenta, M.A.; Souza Filho, A.G.; Saito, R.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Characterizing carbon nanotube samples with resonance Raman scattering. New J. Phys. 2003, 5, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalpando-Paez, F.; Son, H.; Nezich, D.; Hsieh, Y.P.; Kong, J.; Kim, Y.A.; Shimamoto, D.; Muramatsu, H.; Hayashi, T.; Endo, M.; et al. Raman spectroscopy study of isolated double-walled carbon nanotubes with different metallic and semiconducting configurations. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3879–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, M.J.; Wall, M.H. Representative raman measurements of carbon nanotubes. Spectrosc. Eur. 2012, 24, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, A.; Sun, Z. Nanotube and graphene saturable absorbers for fibre lasers. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Harun, S.W.; Nor, R.M.; Zulkepely, N.R.; Ahmad, H.; Shum, P. A passively mode-locked erbium-doped fiber laser based on a single-wall carbon nanotube polymer. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2013, 30, 054210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarka, J.; Sobon, G.; Boguslawski, J.; Sotor, J.; Jagiello, J.; Aksienionek, M.; Lipinska, L.; Zdrojek, M.; Judek, J.; Abramski, K.M. 168 fs pulse generation from graphene-chitosan mode-locked fiber laser. Opt. Mater. Express 2014, 4, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hu, G.; Hu, G.; Howe, R.C.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Z.; Hasan, T. Yb- and Er-doped fiber laser Q-switched with an optically uniform, broadband WS2 saturable absorber. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.Y.; Liu, X.; Qiu, J. Comparison for Saturable Absorbers: Carbon Nanotube Versus Graphene. Adv. Photonics Res. 2022, 3, 2200023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.H.; Chow, K.K.; Yamashita, S.; Set, S.Y. Carbon-nanotube-based passively Q-switched fiber laser for high energy pulse generation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2013, 45, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.N.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, G.R. Single- and double-walled carbon nanotube based saturable absorbers for passive mode-locking of an erbium-doped fiber laser. Laser Phys. 2013, 23, 045105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Deslippe, J.; Xiao, F.; Capaz, R.B.; Hong, X.; Aloni, S.; Zettl, A.; Wang, W.; Bai, X.; Louie, S.G.; et al. An atlas of carbon nanotube optical transitions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, T.; Sun, Z.; Tan, P.; Popa, D.; Flahaut, E.; Kelleher, E.J.; Bonaccorso, F.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Torrisi, F.; et al. Double-wall carbon nanotubes for wide-band, ultrafast pulse generation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4836–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, S.N.M.; Ahmad, F.; Lokman, M.Q.; Sapingi, H.H.J.; Taib, M.F.M.; Nawawi, W.M.F.W.; Yahaya, H.; Rahman, M.A.A.; Shafie, S.; Harun, S.W. First Principles Study and Experimental Investigation of Graphene-Molybdenum Disulphide Nanocomposites Based Passive Saturable Absorber. Photonics 2022, 9, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.Z.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, K.K.; Han, G.H.; Park, H.K.; Lee, Y.H. Absorption spectroscopy of surfactant-dispersed carbon nanotube film: Modulation of electronic structures. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2008, 455, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apandi, N.M.; Ahmad, H.; Lokman, M.Q.; Zuikafly, S.N.F.; Yahaya, H.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Rosnan, R.M.; Ahmad, F. Observation of soliton and bound soliton in erbium-doped fiber lasers using single-walled carbon nanotubes mode-lockers under gamma irradiation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 157, 108775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Rozhin, A.; Sergeyev, S.; Al Araimi, M.; Mou, C. Carbon nanotube mode-locked fiber lasers: Recent progress and perspectives. Nanophotonics 2021, 10, 749–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobon, G.; Duzynska, A.; Świniarski, M.; Judek, J.; Sotor, J.; Zdrojek, M. CNT-based saturable absorbers with scalable modulation depth for Thulium-doped fiber lasers operating at 1.9 μm. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, D.; Sun, Z.; Hasan, T.; Cho, W.; Wang, F.; Torrisi, F.; Ferrari, A.C. 74-fs nanotube-mode-locked fiber laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 153107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, S.; Martinez, A.; Xu, B. Short pulse fiber lasers mode-locked by carbon nanotubes and graphene. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2014, 20, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.H. Numerical study on the minimum modulation depth of a saturable absorber for stable fiber laser mode locking. JOSA B 2015, 32, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liang, X.; Hu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, S.; Ouyang, D.; Wu, X.; Yan, P.; Ruan, S.; Sun, Z.; et al. 152 fs nanotube-mode-locked thulium-doped all-fiber laser. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F. Carbon Nanotube Mode-Locked Thulium Fiber Laser With 200 nm Tuning Range. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Huang, W.; Gao, C.; Liu, M.; Zhu, T. All-fiber mode-locked laser via short single-wall carbon nanotubes interacting with evanescent wave in photonic crystal fiber. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 23450–23458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Lin, G.R. Kelly sideband variation and self four-wave-mixing in femtosecond fiber soliton laser mode-locked by multiple exfoliated graphite nano-particles. Laser Phys. Lett. 2013, 10, 045109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.Y.; Zulkifli, M.Z. 1.56 µm and 1.93 µm synchronized mode-locked fiber laser with graphene saturable absorber. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 112, 103606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Zhang, J.H.; Peng, X.L.; Mao, X.F. Generation and evolution of multiple operation states in passively mode-locked thulium-doped fiber laser by using a graphene-covered-microfiber. Chin. Phys. B 2018, 27, 084215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Meng, Y.; Li, Y.; Qin, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, F. Nanotube mode-locked, wavelength and pulsewidth tunable thulium fiber laser. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 3518–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jussila, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, G.; Albrow-Owen, T.C.T.; Howe, R.; Ren, Z.; Bai, J.; Hasan, T.; Sun, Z. Wavelength and pulse duration tunable ultrafast fiber laser mode-locked with carbon nanotubes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawliszewska, M.; Dużyńska, A.; Zdrojek, M.; Sotor, J. Metallic carbon nanotube-based saturable absorbers for holmium-doped fiber lasers. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 11361–11369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Sharbirin, A.S.; Muhamad, A.; Samion, M.Z.; Ismail, M.F. 2 μm mode-locked thulium-doped fiber laser using Mach-Zehnder interferometer tuning capability. Laser Phys. 2017, 27, 065104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, K.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, X.; Jiang, T. All-Fiber Bidirectional Mode-Locked Ultrafast Fiber Laser at 2 μm. IEEE Photonics J. 2019, 11, 7105708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhai, J.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Ruan, S.; Tang, Z. Mode-locked thulium-doped fiber laser based on 0.3 nm diameter single-walled carbon nanotubes at 1.95 μm. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2017, 15, 041403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Wu, Z.; Fu, S.; Song, J.; Li, H.; Tang, M.; Shum, P.; Liu, D. Switchable dual-wavelength mode-locking of thulium-doped fiber laser based on SWNTs. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2016, 28, 2019–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; El-Damak, A.R.; Feng, Y.; Gu, X. Experimental and numerical studies of mode-locked fiber laser with large normal and anomalous dispersion. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 12014–12021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, L.; Li, X.; Tao, Z.; Ma, W.; Wang, T.; Lou, Y.; Jiang, H. Noise-Like Pulse Generated by All-Fiber Ultrafast Thulium-Doped Fiber Laser Based on Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes. IEEE Photonics J. 2022, 14, 7122905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawliszewska, M.; Martynkien, T.; Przewłoka, A.; Sotor, J. Dispersion-managed Ho-doped fiber laser mode-locked with a graphene saturable absorber. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Zhou, Y.; Saitoh, A.; Sakakibara, Y.; Nishizawa, N. Dispersion Managed, High Power TM-Doped Ultrashort Pulse Fiber Laser at 1.9 UM Using Single Wall Carbon Nanotube Polyimide Film. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, CLEO, San Jose, CA, USA, 5–10 May 2019. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamad Rashid, N.N.; Ahmad, H.; Ismail, M.F.; Lokman, M.Q.; Zuikafly, S.N.F.; Yahaya, H.; Nordin, N.A.; Wan Nawawi, W.M.F.; Ahmad, F. Nanotubes in Chitin Mode Locker for Passive Mode−Locked Fibre Laser in 2.0 µm Region. Photonics 2023, 10, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030257
Mohamad Rashid NN, Ahmad H, Ismail MF, Lokman MQ, Zuikafly SNF, Yahaya H, Nordin NA, Wan Nawawi WMF, Ahmad F. Nanotubes in Chitin Mode Locker for Passive Mode−Locked Fibre Laser in 2.0 µm Region. Photonics. 2023; 10(3):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030257
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamad Rashid, Nur Nadhirah, Harith Ahmad, Mohammad Faizal Ismail, Muhammad Quisar Lokman, Siti Nur Fatin Zuikafly, Hafizal Yahaya, Nur Azmah Nordin, Wan Mohd Fazli Wan Nawawi, and Fauzan Ahmad. 2023. "Nanotubes in Chitin Mode Locker for Passive Mode−Locked Fibre Laser in 2.0 µm Region" Photonics 10, no. 3: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030257
APA StyleMohamad Rashid, N. N., Ahmad, H., Ismail, M. F., Lokman, M. Q., Zuikafly, S. N. F., Yahaya, H., Nordin, N. A., Wan Nawawi, W. M. F., & Ahmad, F. (2023). Nanotubes in Chitin Mode Locker for Passive Mode−Locked Fibre Laser in 2.0 µm Region. Photonics, 10(3), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030257




