Modified Model of Polarized Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function Used for Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modified pBRDF Model
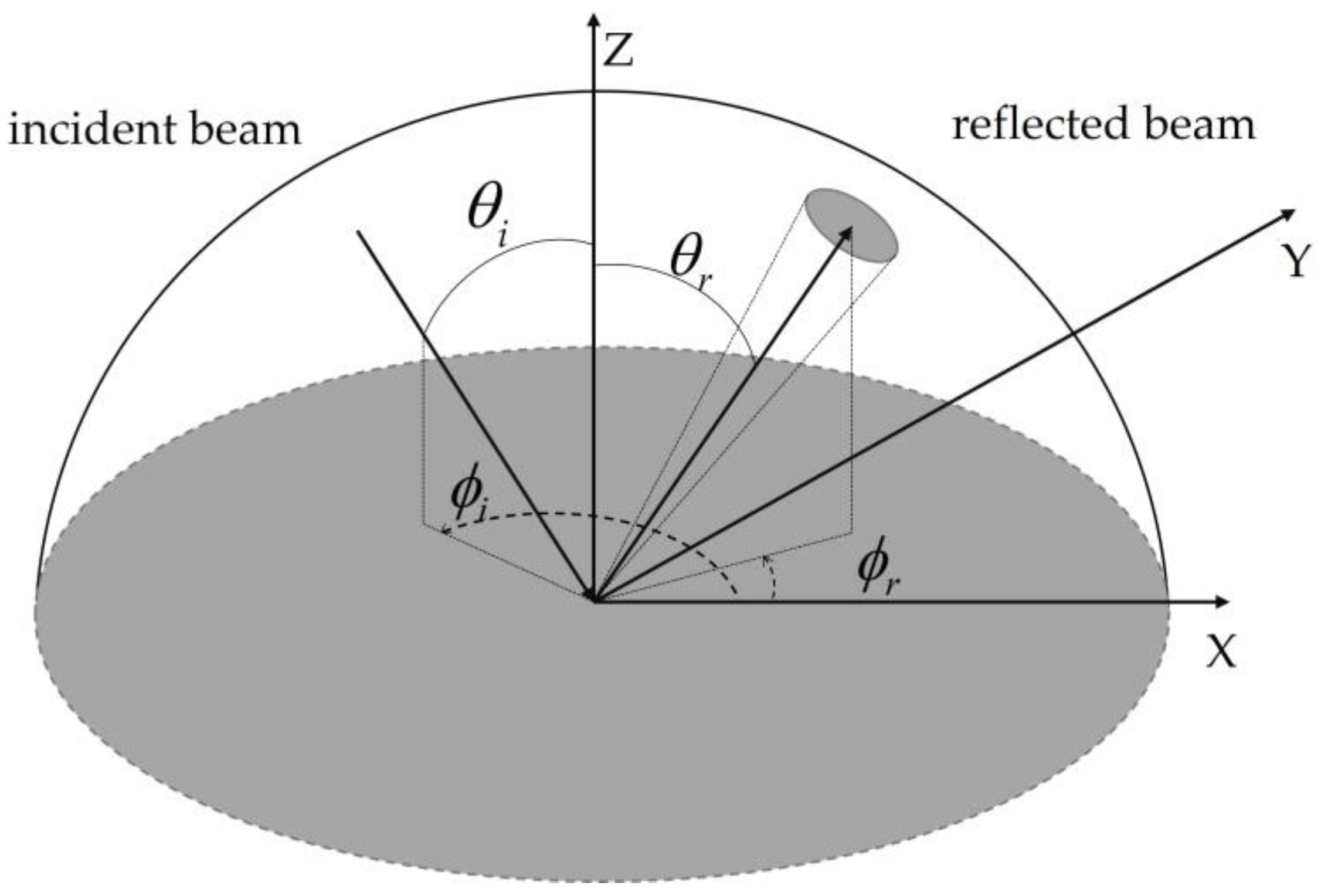
2.1. BRDF Model
2.2. Classical pBRDF Model
2.3. Modified pBRDF Model
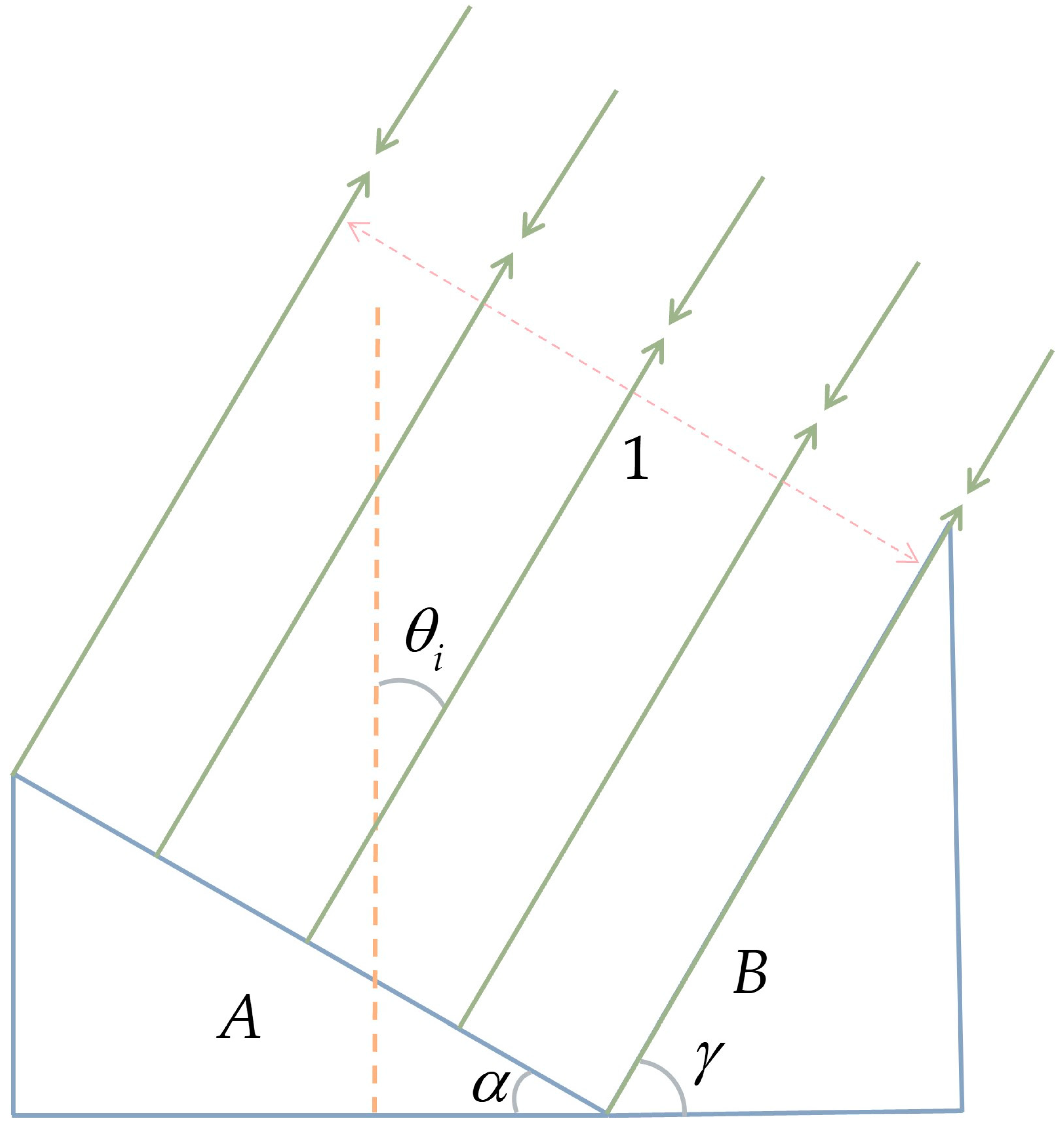
2.3.1. Modified Geometric Attenuation Factor
- Each microfacet is independent of each other, and its tilt angle obeys a Gaussian distribution.
- Because the attenuation factor is only used to correct the specular reflection component, the relationship between the light and the microfacet can be considered to comply with Fresnel’s law.
- In the derivation process, the area of all microfacets is taken as 1 to facilitate the calculation.
2.3.2. Subsurface Scattering Component
2.3.3. Surface Scattering Component
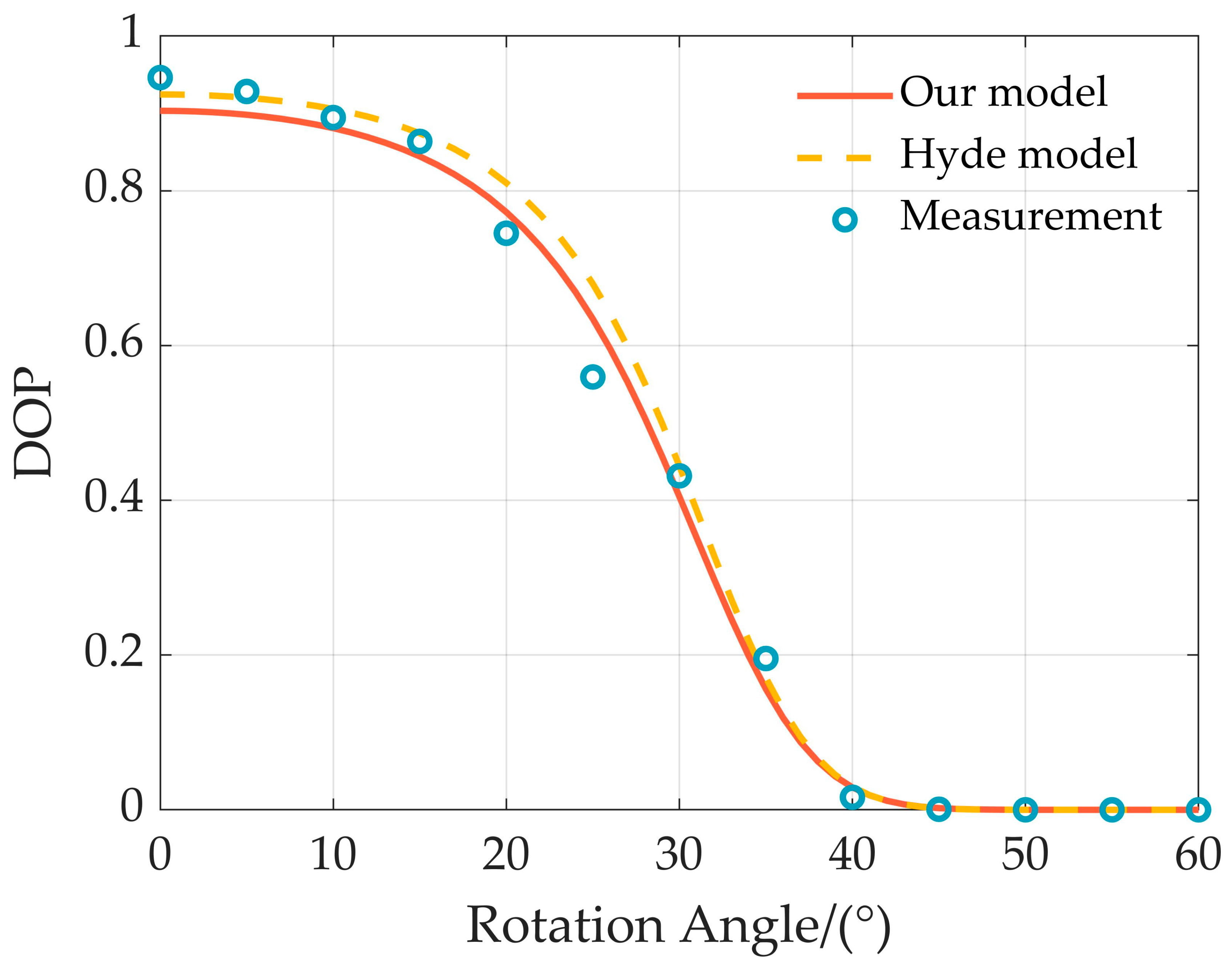
3. Measurement and the Determination of Parameters
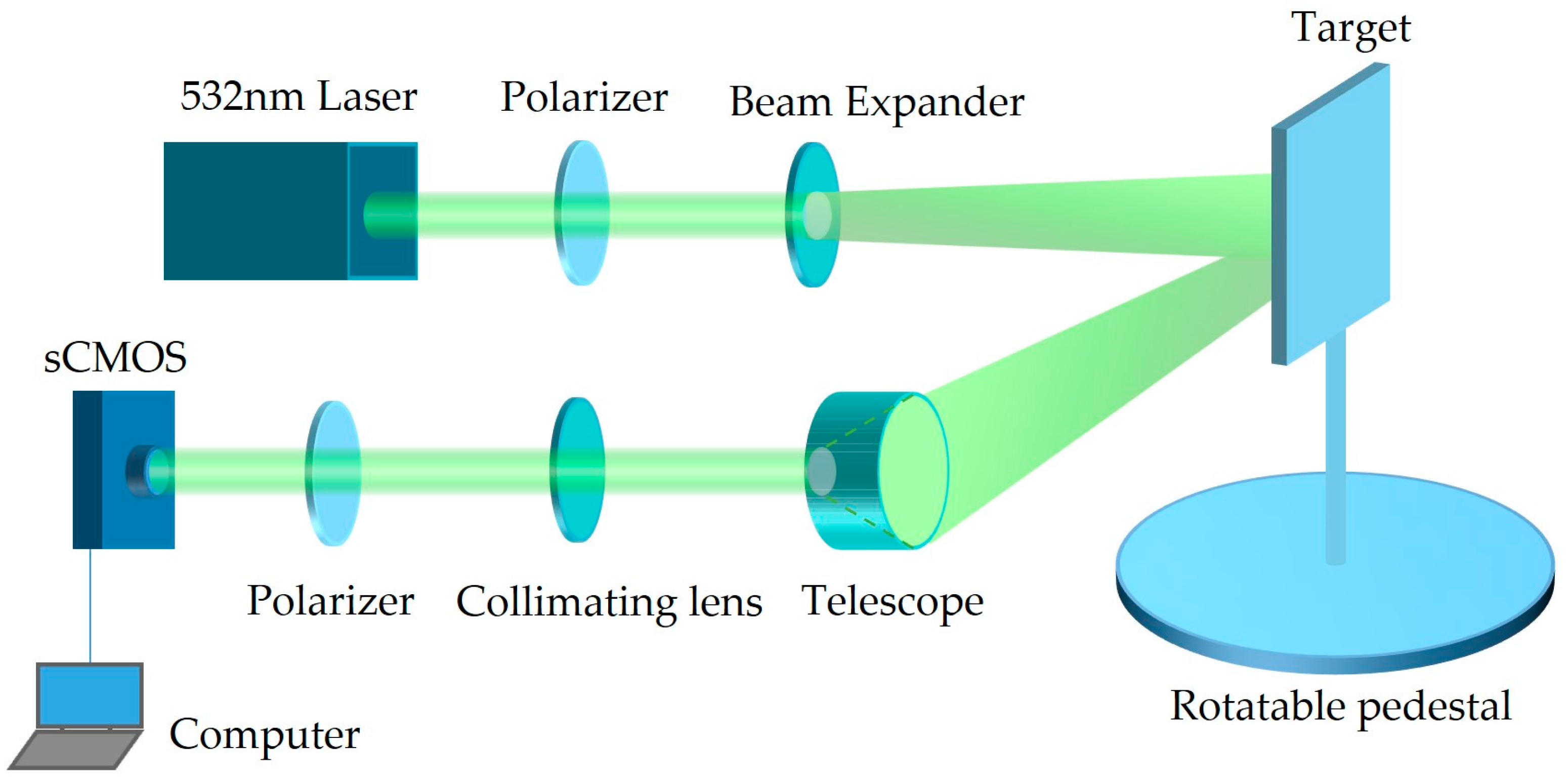
3.1. Measurement
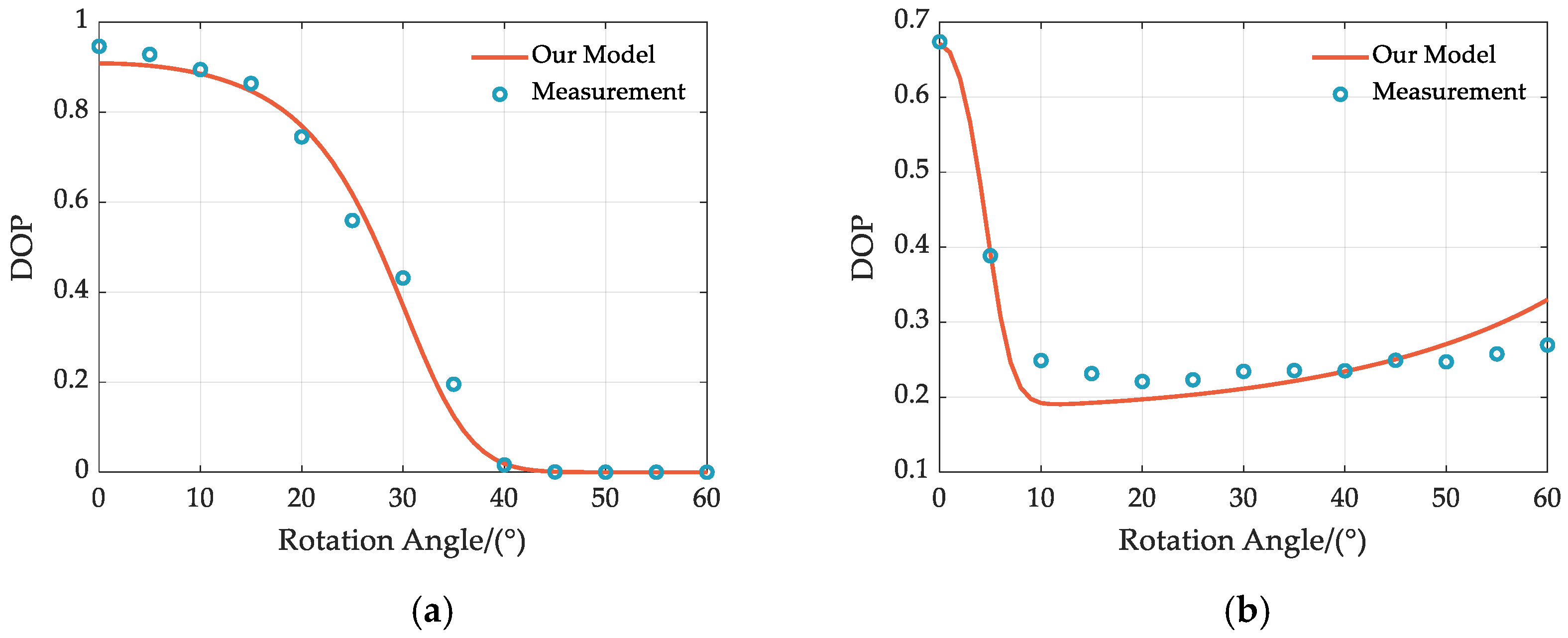
3.2. Determination of Parameters
4. Simulation
4.1. Simulation and Analysis of the Modified Geometric Attenuation Factor
4.2. Analysis of the Influence of Specular Reflection Coefficient on the Model
4.3. Analysis of the Influence of Subsurface Scattering Coefficient on the Model
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jo, S.; Hong, J.K.; Bang, H.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, S. High resolution three-dimensional flash LIDAR system using a polarization modulating Pockels cell and a micro-polarizer CCD camera. Opt. Express 2016, 24, A1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Du, X.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y.; Chen, H. High resolution flash three-dimensional LIDAR systems based on polarization modulation. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 3889–3894. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Lv, X.; Zhang, J. The potassium tantalate niobate (KTN) crystal-based polarization-modulated 3D ladar with a large field of view. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 5319–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Luan, C.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, H. Electro-optic modulation aberration correction algorithm based on phase difference compensation. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 8982–8987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Sun, H. Range-Gated LIDAR Utilizing a LiNbO3 (LN) Crystal as an Optical Switch. Photonics 2023, 10, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. Research on Three-Dimensional Active Imaging with Polarization-Modulated Method. Doctor’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.; Jiang, Z.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, L.; Hu, Y. Reflective Tomography LiDAR Image Reconstruction for Long Distance Non-Cooperative Target. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Yin, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Mei, L. Modeling and Evaluation of the Systematic Errors for the Polarization-Sensitive Imaging LiDAR Technique. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, D.S. Polarized surface scattering expressed in terms of a bidirectional reflectance distribution function matrix. Opt. Eng. 1995, 34, 1646–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Priest, R.G.; Meier, S.R. Polarimetric microfacet scattering theory with applications to absorptive and reflective surfaces. Opt. Eng. 2002, 41, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrance, K.E.; Sparrow, E.M. Theory for off-specular reflection from roughened surfaces. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1967, 57, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetrow, M.P.; Wellems, D.; Sposato, S.H.; Bishop, K.P.; Caudill, T.R.; Davis, M.L.; Simrell, E.R. Results of a new polarization simulation. Proc. SPIE 2002, 4481, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wellems, D.; Ortega, S.; Bowers, D.; Boger, J.; Fetrow, M. Long wave infrared polarimetric model: Theory, measurements and parameters. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2006, 10, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinn, J.F. Models of light reflection for computer synthesized pictures. ACM SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 1977, 11, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, M.W.; Schmidt, J.D.; Havrilla, M.J. A geometrical optics polarimetric bidirectional reflectance distribution function for dielectric and metallic surfaces. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 22138–22153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, K.; Rong, X. Polarized BRDF for coatings based on three-component assumption. Opt. Commun. 2017, 384, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.; Du, B.; Guo, F. Modified model of polarized bidirectional reflectance distribution function for metallic surfaces. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 99, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Xu, R. Three-Component Model for Bidirectional Reflection Distribution Function of Thermal Coating Surfaces. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2016, 33, 064204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y. Analysis of Near-Infrared Polarization Characteristics of Typical Satellite Surface Materials. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2021, 58, 1929001. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Fang, J.; Hu, Y. Degree of Polarization Calculation for Laser Backscattering from Typical Geometric Rough Surfaces at Long Distance. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hors, L.L.; Hartemann, P.; Dolfi, D.; Breugnot, S. Phenomenological model of paints for multispectral polarimetric imaging. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2001, 4370, 94–105. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Xu, W.; Sun, Z.; Jia, A.; Xiu, P.; Chen, W.; Li, T.; Zheng, C.; Li, J. Degree of polarization modeling based on modified microfacet pBRDF model for material surface. Opt. Commun. 2019, 453, 124390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghatte, H.F. A Hybrid of Firefly and Biogergraphy-Based Optimization Algorithms for Optimal Design of Steel Frames. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 4703–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Guo, H.; Fan, Y.; Wang, S. Analysis of BRDF character in active laser imaging. Infrared Laser Eng. 2017, 46, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z. Optical Polarization Characteristics of Low-Earth-Orbit Space Targets. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2020, 76, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, W.; Lu, G. Analysis and Improvement on Integral Geometrical Attenuation Factor of Bidirectional Reflection Distribution Functio. Acta Opt. Sin. 2022, 42, 1029001. [Google Scholar]
- Heitz, E. Understanding the Masking-Shadowing Function in Microfacet-Based BRDFs. J. Comput. Graph. Tech. 2014, 2, 32–91. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, S. Biogeography-Based Optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2009, 12, 702–713. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.S. Firefly Algorithm, Stochastic Test Functions and Design Optimisation. Int. J. Bio-Inspired Comput. 2010, 2, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Sample | n | k | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum plate | 4.32 | 0.65 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 5.76 | 1.0 |
| White painted coating | 0.92 | 0.54 | 0.052 | 0.93 | 0.63 | 0.021 |
| RMSE/R2 | RMSE | R2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | L0 | L1 | L2 | L0 | L1 | L2 |
| Aluminum plate | 0.0225 | 0.0288 | 0.0204 | 0.9918 | 0.9931 | −0.2279 |
| White painted coating | 0.0215 | 0.0473 | 0.0408 | 0.9865 | 0.9176 | −4.3576 |
| Model | n | k | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our model with | 4.32 | 0.65 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 5.76 | 1.0 |
| Our model without | 4.82 | 0.63 | 0.22 | 0.27 | 1 | 0.31 |
| Model | n | k | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyde model | 5.83 | 1.35 | 0.22 | - | 1 | 0 |
| Our model | 4.32 | 0.65 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 5.76 | 1.0 |
| RMSE/R2 | RMSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Models | ||
| Hyde model | 0.0332 | 0.9898 |
| Our model | 0.0306 | 0.9939 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luan, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, X. Modified Model of Polarized Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function Used for Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR). Photonics 2023, 10, 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10101119
Luan C, Li Y, Guo H, Sun H, Zhang L, Zheng H, Zhang X. Modified Model of Polarized Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function Used for Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR). Photonics. 2023; 10(10):1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10101119
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuan, Chenglong, Yingchun Li, Huichao Guo, Houpeng Sun, Laixian Zhang, Haijing Zheng, and Xiaoyu Zhang. 2023. "Modified Model of Polarized Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function Used for Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR)" Photonics 10, no. 10: 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10101119
APA StyleLuan, C., Li, Y., Guo, H., Sun, H., Zhang, L., Zheng, H., & Zhang, X. (2023). Modified Model of Polarized Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function Used for Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR). Photonics, 10(10), 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10101119




