NMR Tracing of Food Geographical Origin: The Impact of Seasonality, Cultivar and Production Year on Data Analysis
Abstract
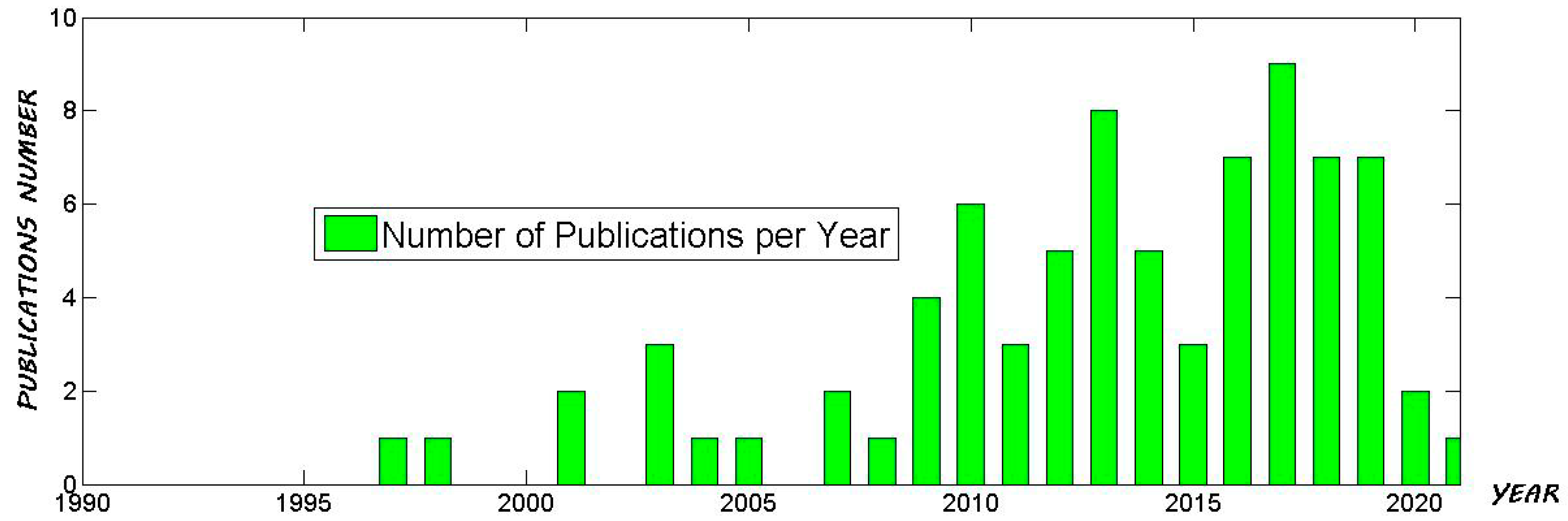
:1. Introduction
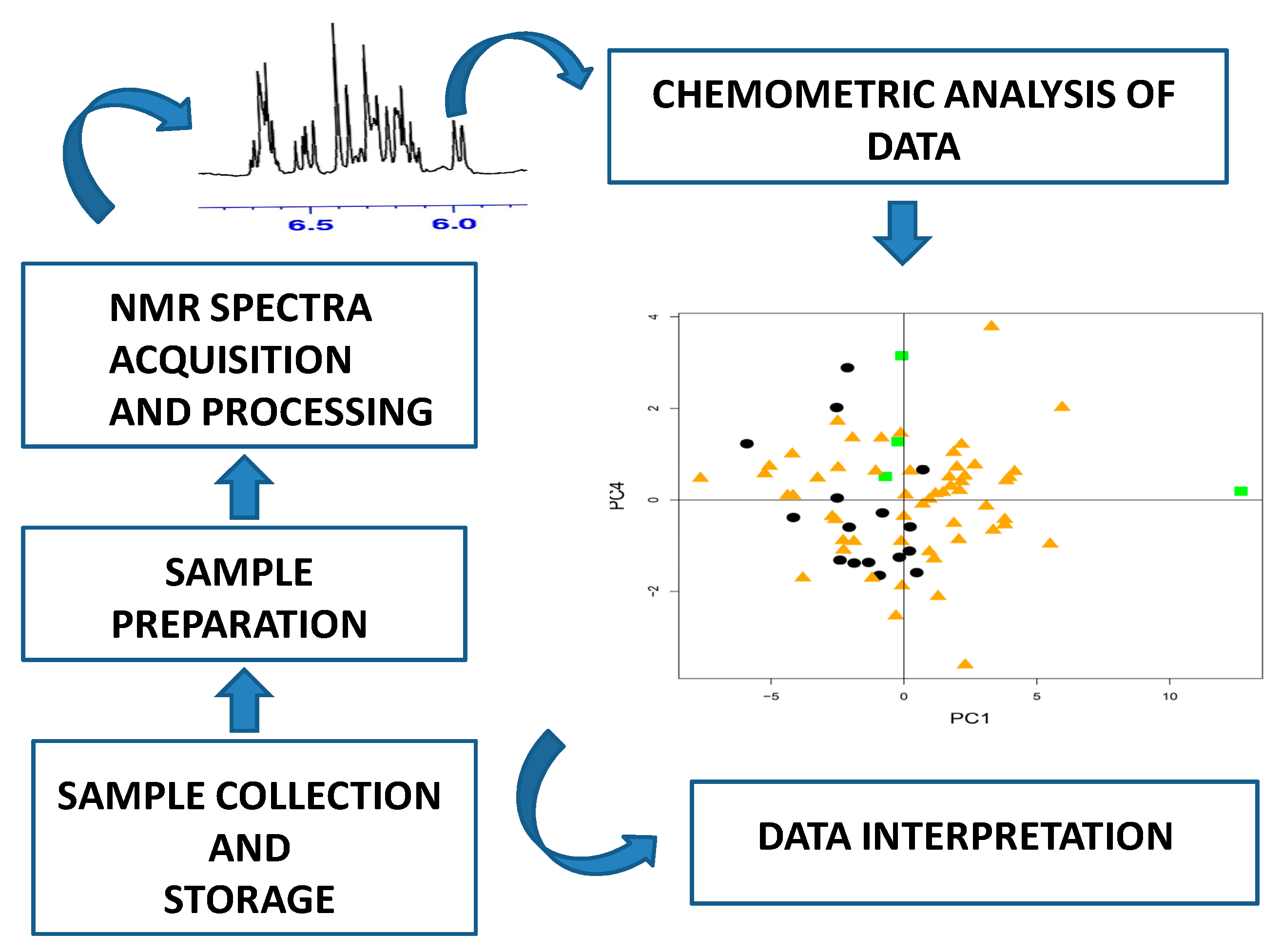
1.1. High-Field NMR Application in Food Analysis
1.2. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
2. Variety, Harvesting Yeas and Seasonality as Factors Influencing Geographical Origin Authentication
2.1. Variety
2.2. Harvesting Year
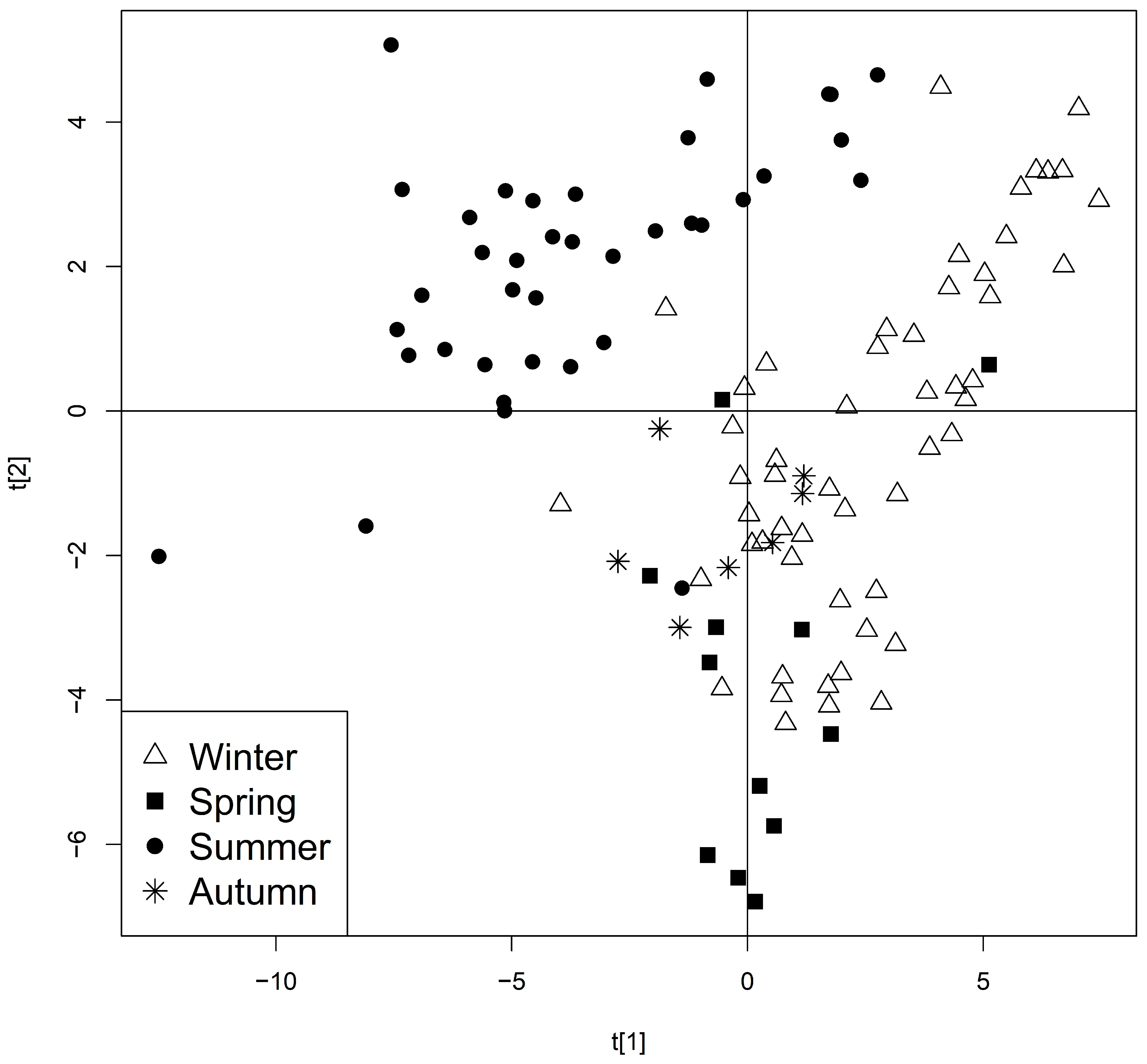
2.3. Seasonality
3. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mannina, L.; Sorbolev, A.P.; Viel, S. Liquid state 1H high field NMR in food analysis. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2012, 66, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Imperio, M.; Mannina, L.; Capitani, D.; Bidet, O.; Rossi, E.; Bucarelli, F.M.; Quaglia, G.B.; Segre, A.L. NMR and statistical study of olive oils from Lazio: A geographical, ecological and agronomic characterization. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Kamal, C.M.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Hu, Z.; Anwar, F.; Du, H. 1H NMR-based metabolomics for discrimination of rice from different geographical origins of China. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 76, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortesniemi, M.; Slupsky, C.M.; Ollikka, T.; Kauko, L.; Spevacek, A.R.; Sjövall, O.; Yang, B.; Kallio, H. 1H NMR profiling clarifies the characterization of Finnish honeys of different botanical origins. Food Res. Int. 2016, 86, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longobardi, F.; Ventrella, A.; Bianco, A.; Catucci, L.; Cafagna, I.; Gallo, V.; Mastrorilli, P.; Agostiano, A. Non-targeted 1HNMR fingerprinting and multivariate statistical analyses for the characterisation of the geographical origin of Italian sweet cherries. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3028–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Godelmann, R.; Kuballa, T.; Mushtakova, S.P.; Rutledge, D.H. Independent components analysis to increase efficiency of discriminant analysis methods (FDA and LDA): Application to NMR fingerprinting of wine. Talanta 2015, 141, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, R.; Klockmann, S.; Haerdter, J.; Fischer, M.; Hackl, T. 1H NMR spectroscopy for determination of the geographical origin of hazelnuts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11873–11879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caňo-Ochoa, S.; Ruiz-Aracama, A.; Guillén Lorén, M.D. Potential of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance for a discriminant characterization of PDOVOOs. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2019, 121, 1800137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, R.; Cagliani, R.L. The potentiality of NMR-based metabolomics in food science and food authentication assessment. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2019, 57, 558–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, M.; Christoph, N.; Wachter, H.; Holzrgrabe, U. 1H NMR profiling as an approach to differentiate conventionally and organically grown tomatoes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8530–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosir, J.; Kocjancic, M.; Kidric, J. Wine analysis by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy. Analusis 1998, 26, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuballa, T.; Brunner, T.S.; Thongpanchang, T.; Walch, S.G.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Application of NMR for authentication of honey, beer and spices. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 19, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, J.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Davis, A.L.; Collins, G.J.; Verhoeyen, M.E. Metabolite Profiling of tomato (Lycopersiconesculentum) using 1H NMR Spectroscopy as a tool to detect potential unintended effects following a genetical modification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 57, 2447–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, M.F.; Wang, S.; Albabish, W.; Nie, S.; Somnarain, D.; Hill, A. Diverse food-based application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 729–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dona, A.C.; Kyriakides, M.; Scott, F.; Shephard, E.A.; Varshavi, D.; Veselkov, K.; Everett, J.R. A guide to the identification of metabolites in NMR-based metabonomics/metabolomics experiments. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ackermann, S.M.; Dolsophon, K.; Monakhova, Y.B.; Kuballa, T.; Reusch, H.; Thongpanchang, T.; Bunzel, M.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Automated multicomponent analysis of soft drinks using 1D 1H and 2D 1H-1H J-resolved NMR spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmioli, A.; Alberici, D.; Ciaramelli, C.; Airoldi, C. Metabolomic profiling of beers: Combining 1H NMR spectroscopy and chemometric approaches to discriminate craft and industrial products. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, B.; Tomasini, M.; Mattei, M.; Parera, R.M.; Sommez, R.; Krefl, D.; Rueldi, R.; Bergmann, S. Automated analysis of large-scale NMR data generates metabolomics signatures and links them to candidate metabolites. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 3360–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perez, M. Autonomous driving in NMR. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2017, 55, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gresley, A.; Peron, J.M.R. A semi-automatic approach to the characterisation of dark chocolate by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Garcia, J.L.; Padro, D.; Villa, P.; Fadon, L. NMR based Metabolomics. Compr. Foodomics 2021, 2, 353–369. [Google Scholar]
- Sobolev, A.P.; Circi, S.; Capitani, D.; Ingallina, C.; Mannina, L. Molecular fingerprinting of food authenticity. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 16, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agiomyrgianaki, A.; Petrakis, P.V.; Dais, P. Influence of harvest year, cultivar and geographical origin on Greek extravirgin olive oils composition: A study by 1H NMR spectroscopy and biometric analysis. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2561–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiani, A.; Coisson, J.D.; Travaglia, F.; Acquotti, D.; Palla, G.; Palla, L.; Arlorio, M. Application of 1H NMR for the characterisation and authentication of “Tonda Gentile Trilobata” hazelnuts from Piedmont (Italy). Food Chem. 2014, 148, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiani, A.; Palla, L.; Acquotti, D.; Marseglia, A.; Palla, G. Application of 1H NMR for the characterisation of cocoa beans of different geographical origins and fermentation levels. Food Chem. 2014, 157, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Xiao, C.; Liu, H.; Hao, F.; Tang, H. Combined NMR and LC-DAD-MS analysis reveals comprehensive metabonomic variations for three phenotypic cultivars of Salvia Miltiorrhize Bunge. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 1565–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coco, L.; Perri, E.; Cesari, G.; Muzzalupo, I.; Zelasco, S.; Simeone, V.; Schena, F.P.; Fanizzi, F.P. NMR-based metabolomics approach for EVOO from secular olive trees of Apulia region. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2013, 115, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, C.R.; Accogli, R.; Del Coco, L.; Angilè, F.; De Bellis, L.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H-NMR-based metabolomics profiles of different sweet melon (Cucumis melo L.) Salento varieties: Analysis and comparison. Food Res. Int. 2018, 114, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, C.R.; Del Coco, L.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H NMR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis as possible tool to assess cultivars, from specific geographical areas, in EVOOs. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, C.R.; Del Cocco, L.; Fanizzi, F.P. Tunisian extravirgin olive oil traceability in the EEC market: Tunisian/Italian (Coratina) EVOOs blend as a case study. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girelli, C.R.; Del Cocco, L.; Zelasco, S.; Salimonti, A.; Conforti, F.L.; Biagianti, A.; Barbini, D.; Fanizzi, F.P. Traceability of “Tuscan PGI” extra virgin olive oils by 1H NMR metabolic profiles collection and analysis. Metabolites 2018, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girelli, C.R.; De Pascali, S.A.; Del Cocco, L.; Fanizzi, F.P. Metabolic profile comparison of fruit juice from certified sweet cherry trees (Prunus avium L.) of Ferrovia and Giorgia cultivars: A preliminary study. Food Res. Int. 2016, 90, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godelmann, R.; Fang, F.; Humpfer, E.; Schütz, B.; Bansbach, M.; Schäfer, H.; Spraul, M. Targeted and non-targeted wine analysis. Differentiation of important parameters: Grape variety, geographical origin, year of vintage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5610–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jung, Y.; Song, B.; Bong, Y.-S.; Ryu, D.H.; Lee, K.-S.; Hwang, G.S. Discrimination of cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis) cultivars grown in different geographical areas using 1H NMR-based metabolomics. Food Chem. 2013, 137, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magda, D.A.; Pirnau, A.; Feher, I.; Guyon, F.; Cozar, B.I. Alternative approach of applying 1H NMR in conjunction with chemometrics for wine classification. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 109, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, L.; Dugo, G.; Salvo, F.; Cicero, L.; Ansanelli, G.; Calcagni, C.; Segre, A.L. Study of the cultivar-composition relationship in Sicilian olive oils by GC, NMR, and statistical methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascellani, A.; Hoca, G.; Babisz, M.; Krska, P.; Kloucek, P.; Havlik, J. 1H NMR chemometric models for classification of Czech wine type and variety. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadia, P.; DelCoco, L.; Muzzalupo, I.; Rizzi, M.; Perri, E.; Cesari, G.; Simeone, V.; Mondelli, D.; Schena, F.P.; Fanizzi, F.P. Multivariate analysis of 1H NMR spectra of genetically characterized extra virgin olive oils and growth soil correlations. J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Furihata, K.; Koda, M.; Hu, F.; Kato, R.; Miyakawa, T.; Tanokura, M. 13C NMR-based metabolomics for classification of green coffee beans according to variety and origin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10118–10125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masetti, O.; Ciampa, A.; Nisini, L.; Sequi, P.; Dell’Abate, M.T. A multifactorial approach in characterizing geographical origin of Sicilian cherry tomatoes using 1H NMR profiling. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, C.R.; Calò, F.; Angilè, F.; Mazzi, L.; Barbini, D.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H NMR spectroscopy to characterize Italian Extra Virgin Olive Oils blends, using statistical models and databases based on monocultivar reference oils. Foods 2020, 9, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, M.; Galgano, F.; Castiglione Morelli, M.A.; Viggiani, L.; Lencioni, L.; Giussani, B.; Favati, F. Chemical profile of white wines produced from ‘Greco bianco’ grape variety indifferent Italian areas by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and conventional physico chemical analyses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, L.; Patumi, M.; Proietti, N.; Bassi, D.; Segre, A.L. Geographical characterization of Italian extra virgin olive oils using High Field 1-H NMR spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2687–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchak, N.; El Bacha, E.; Khouzam, R.B.; Rizk, T.; Akoka, S.; Bejjan, J. Geoclimatic, morphological, and temporal effects on Lebanese olive oils composition and classification: A 1H NMR metabolomic study. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, L.; Sorbolev, A.P. High resolution NMR characterization of olive oils in terms of quality, authenticity and geographical origin. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, S3–S511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binetti, G.; Del Coco, L.; Ragone, R.; Zelasco, S.; Perri, E.; Montemurro, C.; Valentini, R.; Naso, D.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Schena, F.P. Cultivar classification of Apulian olive oils: Use of artificial neural networks for comparing NMR, NIR and merceological data. Food Chem. 2017, 219, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinofta, R.I.; Theocharis, C.R. Chemometric Characterization of the Cypriot Spirit “Zivania”. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5067–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papotti, G.; Bertelli, D.; Graziosi, R.; Silvestri, M.; Bertacchini, L.; Durante, C.; Plessi, M. Application of One and two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy for the characterization of Protected Designation of Origin Lambrusco wines of Modena. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritota, M.; Casciani, L.; Valentini, M. PGI chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) traceability by means of HRMAS-NMR spectroscopy: A preliminary study. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, J.B.; Chung, J.O.; Kim, H.N.; Kim, E.H.; Jung, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.J.; Hong, Y.S. Metabolomic unveiling of a diverse range of green tea (Camellia sinensis) metabolites dependent on geography. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahov, G.; Schiavone, C.; Simone, N. Quantitative 13C NMR method using the DEPT pulse sequence for the determination of the geographical origin (DOP) of olive oils. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2001, 39, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Salces, R.M.; Moreno-Rojas, J.M.; Holland, M.V.; Reniero, F.; Guillou, C.; Héberger, K. Virgin Olive Oil authentication by multivariate analyses of 1H NMR fingerprints and δ13C and δ2H data. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5586–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arana, V.A.; Medina, J.; Alarcon, R.; Moreno, E.; Heintz, L.; Scháfer, H.; Wist, J. Coffee’s country of origin determined by NMR: The Colombian case. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffo, E.F.; Tavares, L.A.; Tobias, A.C.T.; Ferreira, M.M.C.; Ferreira, A.G. Identification of components of Brazilian honey by 1H NMR and classification of its botanical origin by chemometric methods. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filho, E.J.A.; Silva, L.M.A.; Ribeiro, P.R.V.; de Brito, E.S.; Zocolo, G.J.; Souza-Leǎo, P.C.; Marquez, A.T.B.; Quintela, A.L.; Larsen, F.H.; Canuto, K.M. 1HNMR and LC-MS-based metabolomic approach for evaluation for the seasonality and viticulturalpractices in wines from Sǎo Francisco River Valley, a Brazilian semi-arid region. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donarski, J.A.; Jones, S.A.; Charlton, A.J. Application of cryoprobe 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy and multivariate analysis for the verification of Corsican honey. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5451–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longobardi, F.; Innamorato, V.; Di Gioia, A. Geographical origin discrimination of lentils (Lens culinaris Medik.) using 1H NMR fingerprinting and multivariate statistical analyses. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievano, E.; Peggion, E.; Manni, S. 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectra of chloroform extracts of honey for chemometric determination of its Botanical Origin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciubba, L.; Capuani, G.; Di Cocco, M.E.; Avanzato, D.; Delfini, M. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance analysis of water soluble metabolites allows the geographic discrimination of pistachios (Pistacia vera). Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, S.; Nemoto, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Shoji, T.; Tanaka, F.; Nakagawa, H.; Ono, H.; Kikuchi, J.; Ohnishi-kameyama, M.; Sekiyama, Y. A NMR based, non-targeted multistep metabolic profiling revealed L-rhamnitol as a metabolite that characterised apples from geographical origins. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, P.S.; Delgadillo, I.; Gil, A.M.; Roma, P.; Casuscelli, F.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Dennis, M.J.; Spraul, M. High-Field proton NMR studies of apple juices. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1997, 35, S52–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, R.; Cagliani, R.L.; Stocchero, M.; Porretta, S. Evaluation of the production year in Italian and Chinese tomato paste for geographical determination using O2PLS models. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7520–7525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culeddu, N.; Chessa, M.; Bandino, G.; Sedda, P.; Zurru, R.; Anedda, R.; Motroni, A.; Molinu, M.G.; Dettori, S.; Santona, M. Classification of monovarietal Sardinian Extra Virgin Olive Oils by 1H NMR metabolomic approach. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1700035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, W.; Goodall, I.; Uhrín, D. Analysis of Scotch Whisky by 1H NMR and chemometrics yields insight into its complex chemistry. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rongai, D.; Sabatini, N.; Del Coco, L.; Perri, E.; Del Re, P.; Simone, N.; Marchegiani, D.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H NMR and multivariate analysis for geographical characterization of commercial extra virgin olive oil: A possible correlation with climate data. Foods 2017, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, H.; Dong, J.; Feng, J. Origin Identification and Quantitative Analysis of Honeys by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Chemometric Techniques. Food Anal. Metod. 2016, 9, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamanna, R.; Cattivelli, L.; Miglietta, M.L.; Troccoli, A. Geographical origin of durum wheat studied by 1H-NMR profiling. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahov, G.; Del Re, P.; Simone, N. Determination of geographical origin of olive oils using 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. I-Classification of olive oils of Puglia region with Denomination of Protected Origin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5612–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenori, L.; Santucci, C.; Meoni, G.; Morrocchi, V.; Matteucci, G.; Luchinat, C. NMR metabolomic fingerprinting distinguishes milk from different farms. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donarski, J.A.; Jones, S.A.; Harrison, M.; Driffield, M.; Charlton, A.J. Identification of botanical biomarkers found in Corsicanhoney. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masetti, O.; Nisini, L.; Ciampa, A.; Dell’Abate, M.T. 1H NMR spectroscopy coupled with multivariate analysis was applied to investigate Italian cherry tomatoes metabolic profile. J. Chemom. 2020, 34, e3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadi, M.; Zira, A.; Magiatis, P.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Mikros, E. 1H NMR-based metabonomics for the classification of Greek wines according to variety, region and vintage. Comparison with HPLC data. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 11067–11074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gougeon, L.; da Costa, G.; Le Mao, I.; Ma, W.; Teissedre, P.L.; Guyon, F.; Richard, T. Wine analysis and authenticity using 1H-NMR metabolomics data: Application to Chinese wines. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 3425–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savorani, F.; Capozzi, F.; Engelsen, S.B.; Dell’Abate, M.T.; Sequi, P. Pomodoro di Pachino: An authentication study using1H-NMR and chemiometrics–protecting its P.G.I. European certification. Magn. Reson. Food Sci. 2009, 158–166. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, J.B.; Chung, J.O.; Hwang, J.A.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, C.H.; Hong, Y.S. Geographical and climatic dependencies of green tea (Camellia sinensis) metabolites: A 1H NMR-based metabolomics study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10582–10589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masetti, O.; Ciampa, A.; Nisini, L.; Valentini, M.; Sequi, P.; Dell’Abate, M.T. Cherry tomatoes metabolic profile determined by1H-High Resolution-NMR spectroscopy as influenced by growing season. Food Chem. 2014, 162, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacchi, R.; Mannina, L.; Fiordiponti, P.; Barone, P.; Paolillo, L.; Patumi, M.; Segre, A.L. Characterization of Italian extra virgin olive oils Using 1H-NMR spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3947–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laincer, F.; Iaccarino, N.; Amato, J.; Pagano, B.; Pagano, A.; Tenore, G.; Tamendjari, A.; Rovellini, P.; Venturini, S.; Bellan, G.; et al. Characterization of monovarial extra virgin olive oils from the province of Béjaïa (Algeria). Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beteinakis, S.; Papachristodoulou, A.; Gogou, G.; Katsikis, S.; Mikros, E.; Halabalaki, M. NMR-based metabolic profiling of edible olives—Determination of quality parameters. Molecules 2020, 25, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coco, L.; Mondelli, D.; Mezzapesa, G.N.; Miano, T.; De Pascali, S.A.; Girelli, C.R.; Fanizzi, F.P. Protected designation of origin extra virgin olive oils assessment by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and multivariate statistical analysis: “Terra di Bari”, an Apulian (South east Italy) case study. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeGall, J.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Defernez, M. Metabolite profiling using1H NMR spectroscopy for quality assessment of green tea, Camellia sinensis (L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.K.; Kim, S.H. Discrimination of rice products by geographical origins and cultivars by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2016, 37, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Rutledged, D.N.; Roßmanne, A.; Waiblingerf, H.U.; Mahlera, M.; Ilsea, M.; Kuballa, T.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Determination of rice type by 1H NMR spectroscopy in combination with different chemometric tools. J. Chemom. 2014, 28, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, M.O.; Pisano, P.L.; Sierra, M.G.; Ricardo, L.E. NMR and multivariate data analysis to assess traceability of argentinecitrus. Microchem. J. 2018, 141, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viggiani, L.; Castiglione Morelli, M.A. Characterization of wines by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance: A work study on wines from the Basilicata region in Italy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8273–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougeon, L.; da Costa, G.; Guyon, F.; Richard, T. 1H NMR metabolomics applied to Bordeaux red wines. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, L.; Marini, F.; Gobbino, M.; Sobolev, A.P.; Capitani, D. NMR and chemometrics in tracing European olive oils: Thecase study of Ligurian samples. Talanta 2010, 80, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deborde, C.; Maucourt, M.; Baldet, P.; Bernillon, S.; Biais, B.; Talon, G.; Ferrand, C.; Jacob, D.; Ferry-Dumazet, H.; de Daruvar, A.; et al. Proton NMR quantitative profiling for quality assessment of greenhouse grown tomato fruit. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masetti, O.; Sorbo, A.; Nisini, L. NMR Tracing of Food Geographical Origin: The Impact of Seasonality, Cultivar and Production Year on Data Analysis. Separations 2021, 8, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8120230
Masetti O, Sorbo A, Nisini L. NMR Tracing of Food Geographical Origin: The Impact of Seasonality, Cultivar and Production Year on Data Analysis. Separations. 2021; 8(12):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8120230
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasetti, Olimpia, Angela Sorbo, and Luigi Nisini. 2021. "NMR Tracing of Food Geographical Origin: The Impact of Seasonality, Cultivar and Production Year on Data Analysis" Separations 8, no. 12: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8120230
APA StyleMasetti, O., Sorbo, A., & Nisini, L. (2021). NMR Tracing of Food Geographical Origin: The Impact of Seasonality, Cultivar and Production Year on Data Analysis. Separations, 8(12), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8120230