Fundamental Properties of Packing Materials for Liquid Chromatography
Abstract
1. Introduction
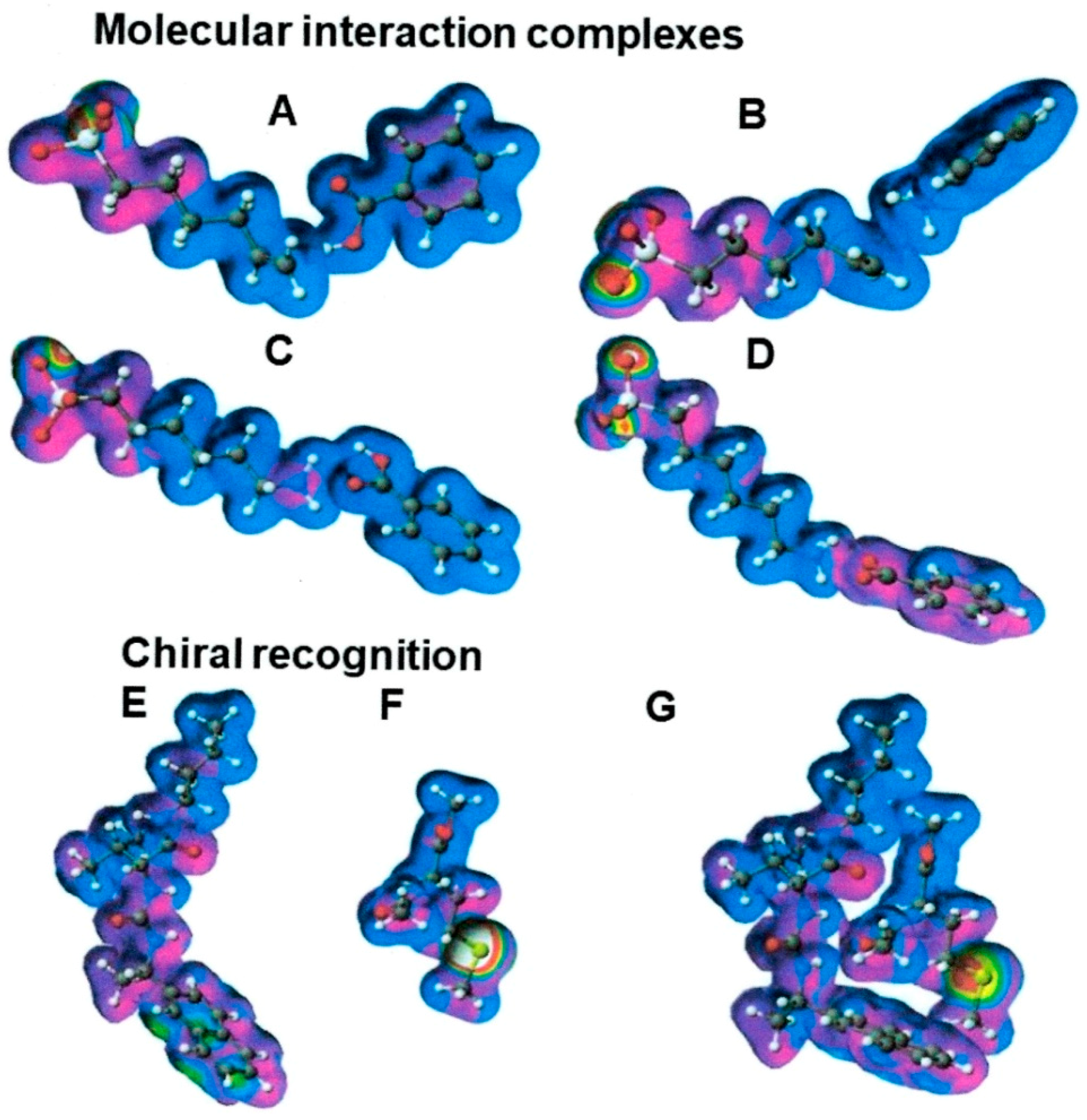
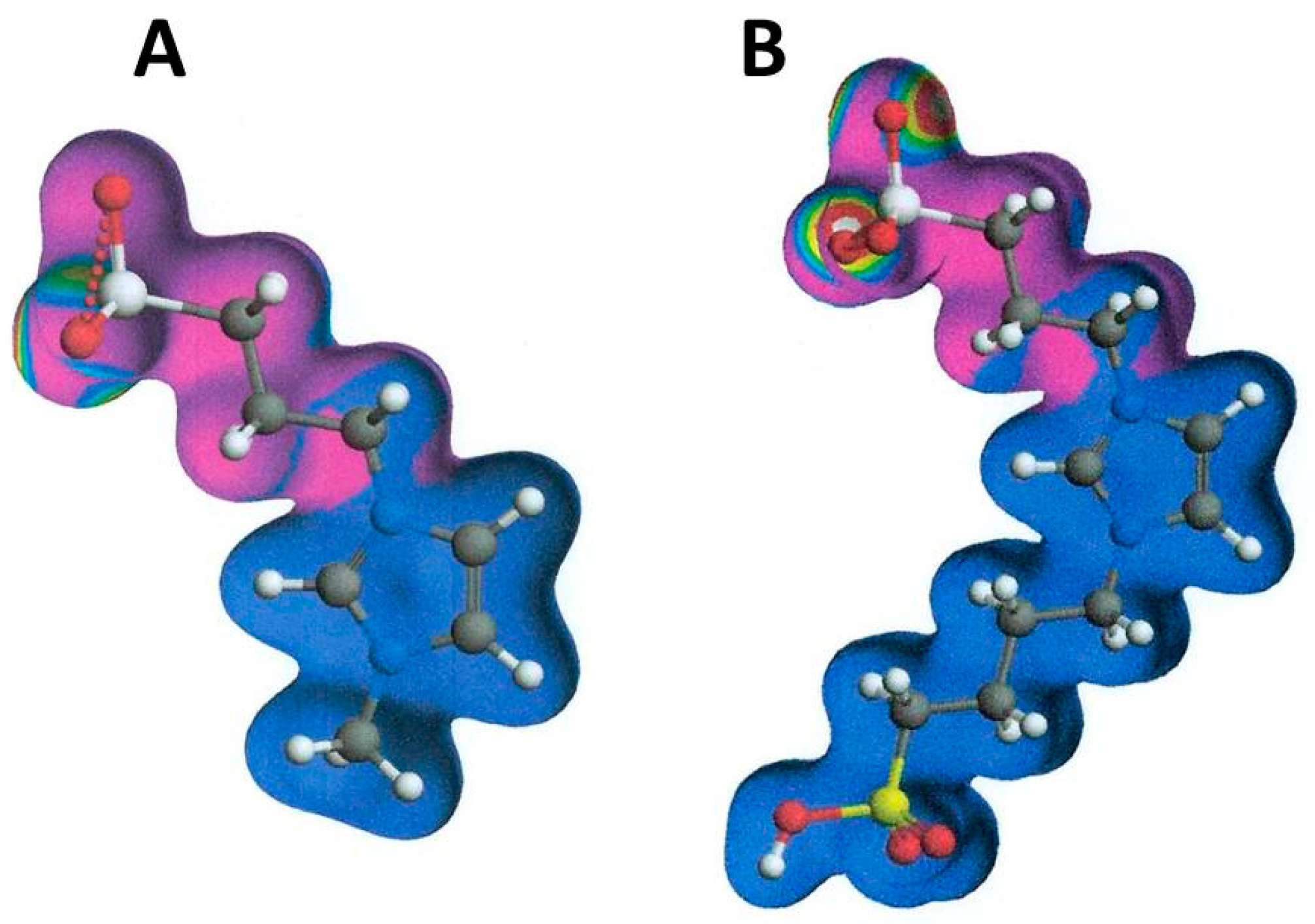
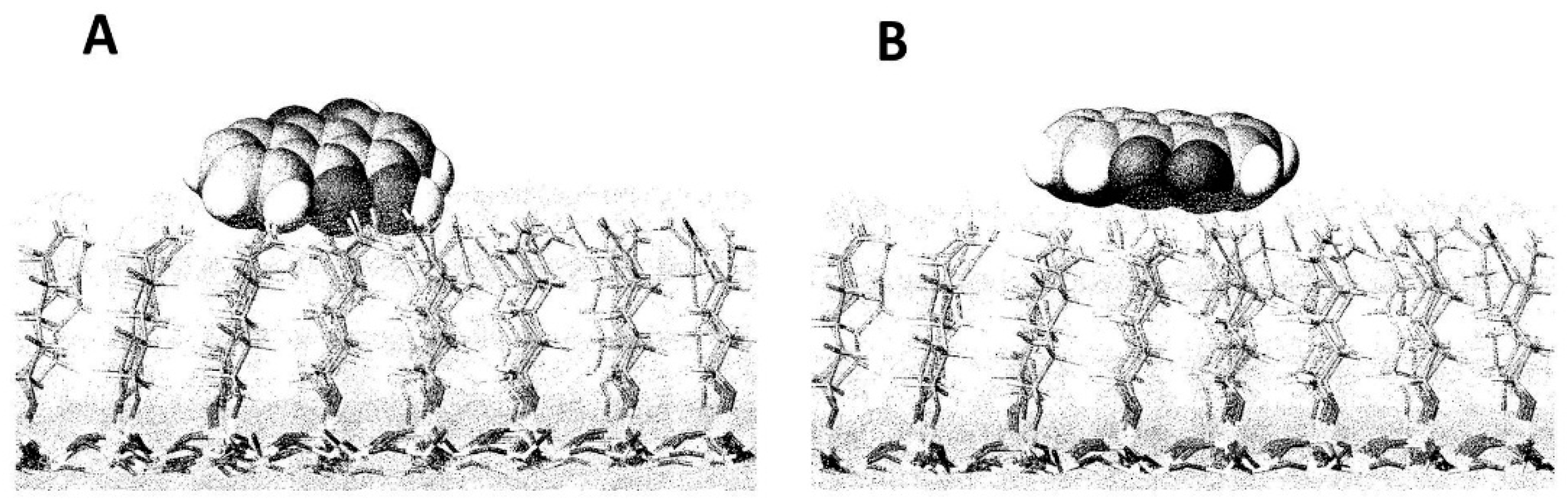
- MIHB = HB (molecule A) + HB (molecule B) – HB (molecule A and molecule B complex),
- MIES = ES (molecule A) + ES (molecule B) – ES (molecule A and molecule B complex), and
- MIVW = VW (molecule A) + VW (molecule B) – VW (molecule A and molecule B complex).
2. Definition in Liquid Chromatography
3. New Developments in Bonded-Phases
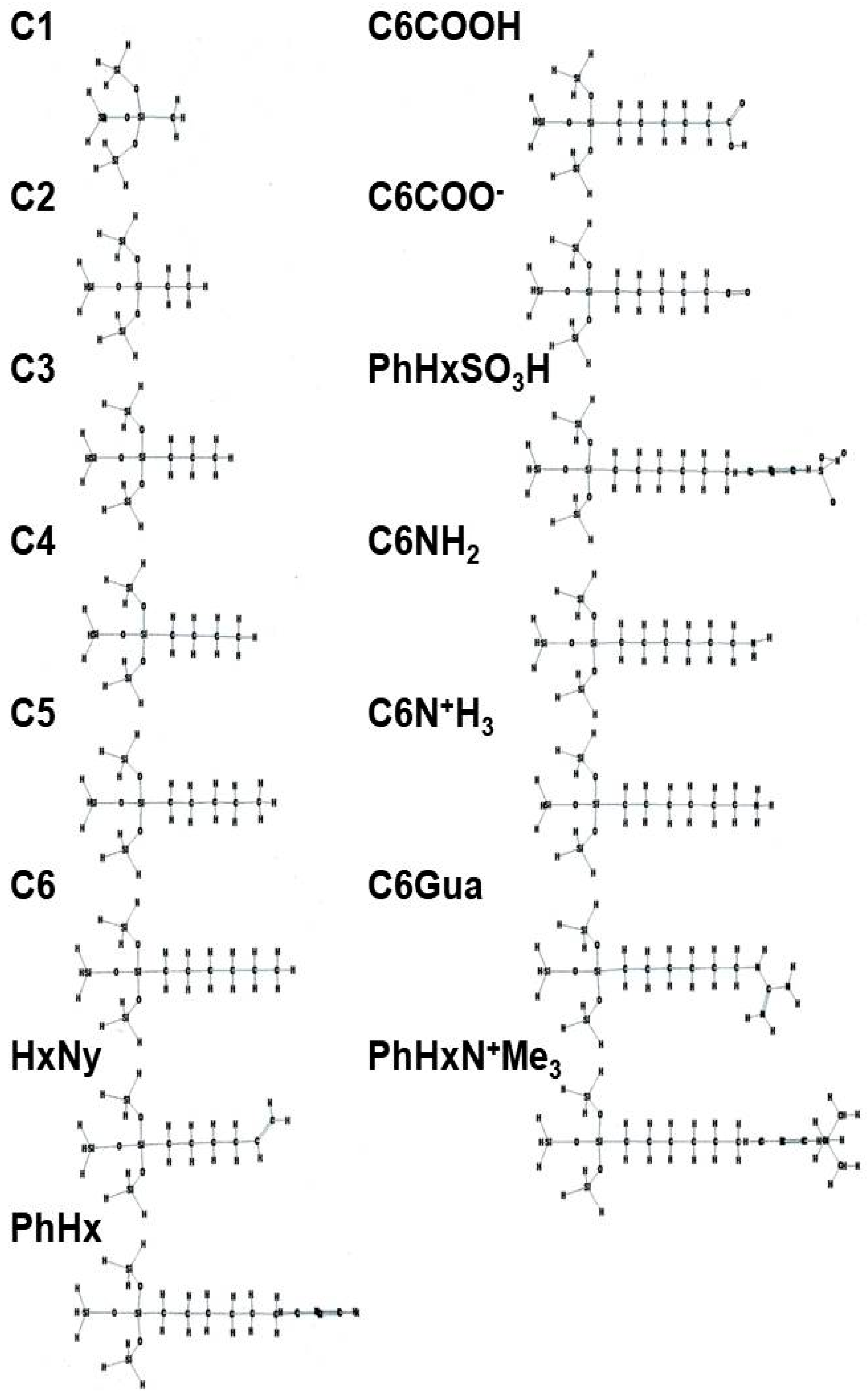
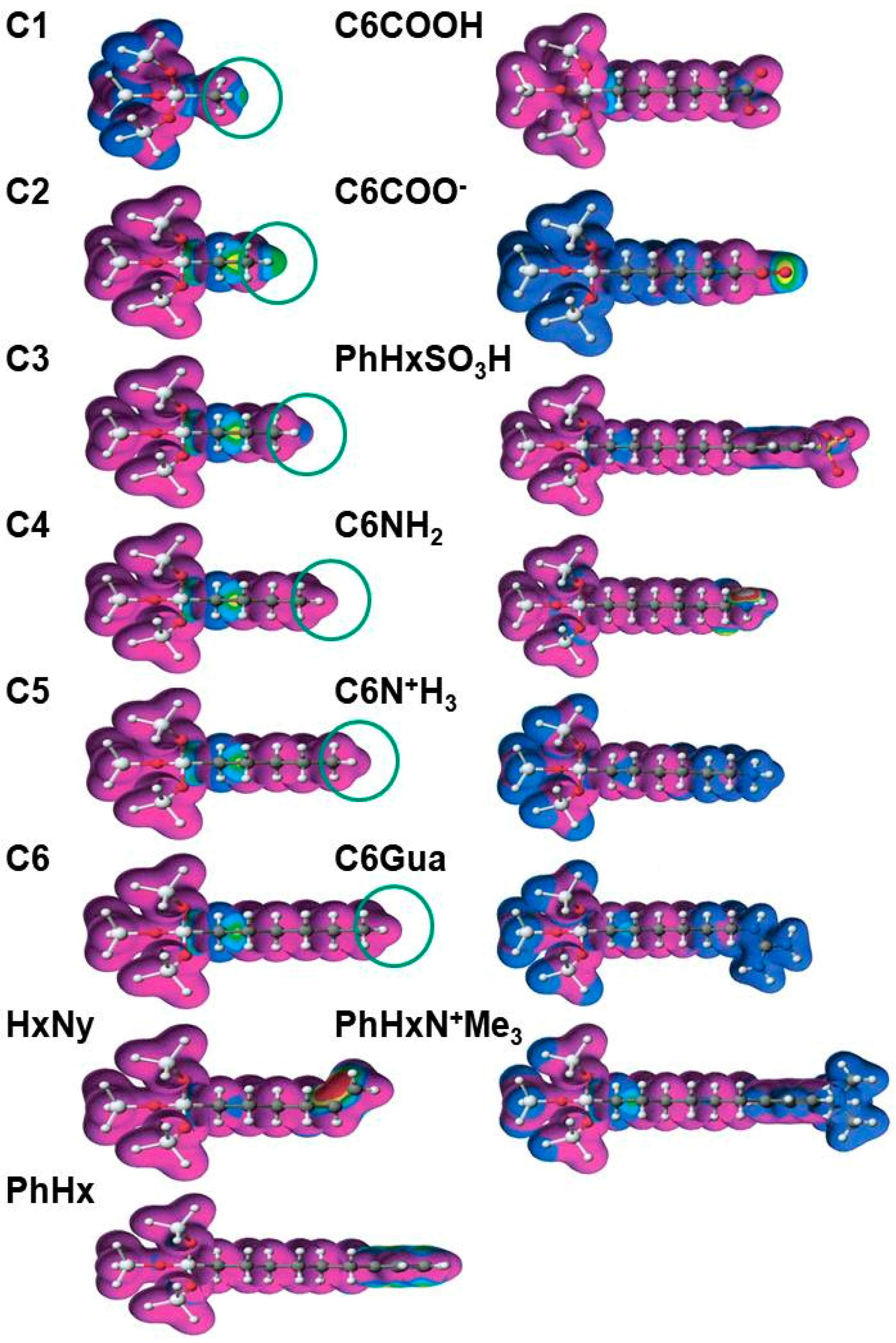
Typical Structures of Bonded-Phase for HILIC
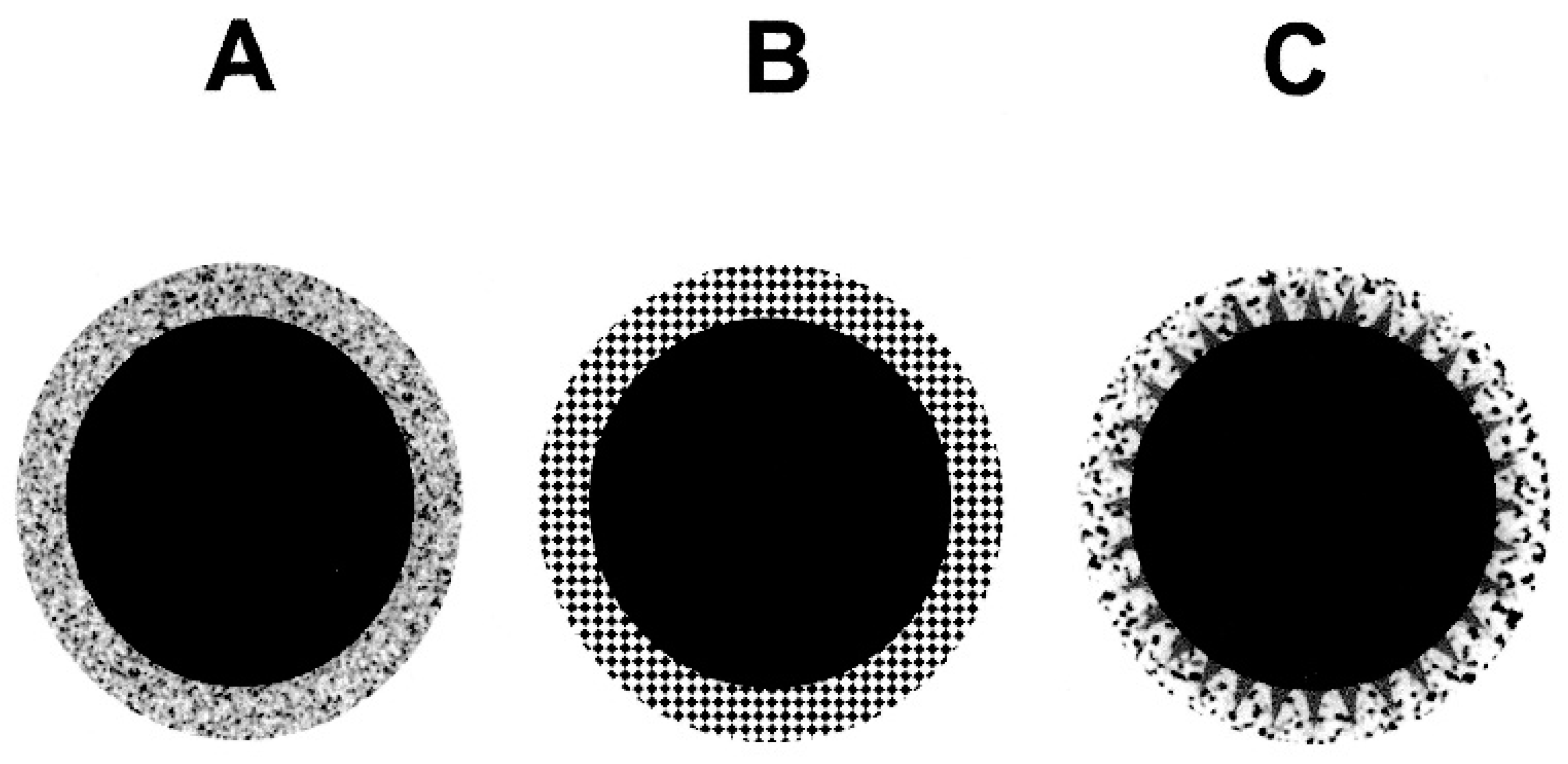
4. Superficially Porous (Core-Shell and Fused-Core) Packing Materials
4.1. Synthesis of Superficially Porous Silica Gels
- Attaching small nonporous particles on the surface of nonporous core silica gels [104,106]: Nanoparticles in solution are fused to the surface of the nonporous silica core using urea-formaldehyde, and the remaining organics are removed by high temperature treatment [104]. A SPP of 1.1 μm was synthesized by depositing colloidal silica [106]. Nanodiamond SPP was also developed. The chemical (pH 1–13) and thermal (<100 °C) stability may make them especially opportunity to use for special separations [107].
- Growing porous silica gels or whiskers on the surface of nonporous core silica gels [108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121]: Many synthesis methods are focused on growing porous silica gels or silica whiskers on the surface of nonporous core silica gels. However, the reaction methods used to do this are similar and based on polymerizing organic silicones such as tetraethoxysilicone and tetramethoxysilicone in solutions containing cationic surfactants. The selection of additives and different physical conditions produced a variety of SPPs [108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119].
- Further etching the surface of SPPs [111,116,122]: SPPs were synthesized, and the pore size was enlarged via acid-refluxing [116]. The SPP was synthesized using a pseudomorphic transformation. The outer-layer of solid silica was dissolved and reprecipitated to form a porous layer during this process [122], thus growing a porous silica layer from organic silicones onto the surface of a nonporous silica gel. Further washing using an acidic or basic solution can be used to increase pore size [111].
4.2. Performance of Superficially Porous Packing Materials based on the van Deemter Equation
4.3. Applications of Superficially Porous Packing Materials
5. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanai, T. New developments in liquid-chromatographic stationary phases. Adv. Chromatogr. 2000, 40, 315–357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Skinley, K.; Herodotou, S.; Zhang, H. Core-shell microspheres with porous nanostructured shells for liquid chromatography. Sep. Sci. 2017, 41, 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, D.S. Current state of superficially porous particle technology in liquid chromatography. LC&GC 2015, 33, 386–395. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, G.K.; Gragg, M.A. Scaling LC methods using superficially porous particle stationary phases. LC&GC 2018, 36, 184–193. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, D.S.; Wiest, L.; Liang, S.-H.; Li, D. When do we need sub-2 m superficially porous particles for liquid chromatography. LC&GC 2018, 36, 436–439. [Google Scholar]
- Fekete, S.; Oláh, E.; Fekete, J. Fast liquid chromatography: The domination of core-shell and very fine particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1228, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Barber, W.E.; Lon, W.J. Applications of superficially porous particles: High speed, high efficiency or both? J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1228, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesterenko, E.P.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Connolly, D.; He, X.; Floris, P.; Duffy, E.; Paull, B. Nano-particle modified stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography. Analyst 2013, 138, 4229–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, T.H.; Andrews, R.W. Recent innovations in UHPLC columns and instrumentation. TrAC 2014, 63, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, R.; Ahmed, A.; Edge, T.; Zhang, H. Core-shell particles: Preparation, fundamentals and applications in high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1357, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Ruiz, V.; Olives, A.I.; Martín, M.A. Core-shell particles lead the way to renewing high-performance liquid chromatography. TrAC 2015, 64, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderheyden, Y.; Broeckhoven, K.; Desmet, G. Peak deconvolution to correctly assess the band broadening of chromatographic columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1465, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanai, T. Basic selection method of stationary and mobile phases in liquid chromatography. In Separation System in Chromatography, APPROACH and Selection Methods; Hara, S., Mori, S., Hanai, T., Eds.; Maruzen: Tokyo, Japan, 1981; pp. 121–156. ISBN 4-621-02586-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hanai, T. HPLC, A Practical Guide; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 1999; pp. 1–134. ISBN 0-85404-515-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hanai, T. Quantitative in Silico Chromatography: Computational Modeling of Molecular Interactions; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1–338. ISBN 978-1-84973-991-7. [Google Scholar]
- Arwidi, B.; Samuelson, O. Partition chromatography of sugars on ion-exchange resins. Svensk Kemish Tidskift 1965, 77, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, L.-I.; Samuelson, O. An automated procedure for separation of monosaccharides on ion exchange resins. Acta Chem. Scand. 1965, 19, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funasaka, W.; Hanai, T. The relationship between molecular structure and chromatographic behavior, and the application of high-speed liquid chromatography. In High-speed Liquid Chromatography; Hatano, H., Ed.; Nankodo: Tokyo, Japan, 1973; pp. 153–167. [Google Scholar]
- Funasaka, W.; Hanai, T.; Fujimura, K. High speed liquid chromatographic separations of phthalic esters, carbohydrates, TCA organic acids, and organic mercury compounds. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1974, 12, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funusaka, W.; Hanai, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Fujimura, K.; Ando, T. Nonaqueous solvent chromatography. IV. Effects of solvents and ion-exchange resins on adsorption mechanisms and their application in high-speed liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1974, 88, 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- Hanai, T.; Fujimura, K. Non-aqueous solvent chromatography. V: The comparison of organic and inorganic adsorbents. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1976, 14, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T.; Hatano, H. Experimental High Speed Liquid Chromatography; Kagakudojin: Kyoto, Japan, 1977; pp. 1–265. [Google Scholar]
- Hanai, T.; Hatano, H. New Experimental High Speed Liquid Chromatography; Kagakudojin: Kyoto, Japan, 1988; pp. 1–338. [Google Scholar]
- Alpert, A.J. Hydrophilic-interaction chromatography for the separation of peptides, nucleic acids and other polar compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 1990, 499, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesek, J.; Matyska, M.T. A comparison of two separation modes: HILIC and aqueous normal phase chromatography. LCGC N. Am. 2007, 25, 480–490. [Google Scholar]
- Horvath, C.; Melander, W.; Molnar, I. Solvophobic interactions in liquid chromatography with non-polar stationary phases. J. Chromatogr. A 1976, 125, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. Definition of HILIC system and quantitative analysis of retention mechanisms. Cur. Chromatogr. 2018, 5, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. Introduction of in silico chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sep. Tech. 2016, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. Quantitative explanation of retention mechanisms of hydrophobic and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-Inductive effect of alkyl-chain. Separations 2017, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography for LC-MS. Mass Spectrom. Purif. Tech. 2017, 4, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. Simple model bonded-phases to design a homogeneous support for in silico chromatography. Int. J. Anal. Tech. 2018, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. Quantitative in silico analysis of the specificity of graphitized (graphitic) carbons. Adv. Chromatogr. 2011, 49, 257–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanai, T.; Hatano, H.; Nimura, N.; Kinoshita, T. Computer-aided analysis of molecular recognition in chromatography. Analyst 1993, 118, 1371–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T.; Koizumi, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Arora, R.; Ahmed, F. Prediction of pKa values of phenolic and nitrogen-containing compounds by computational chemical analysis compared to those measured by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 762, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. Chromatography in silico, quantitative analysis of retention mechanisms of benzoic acid derivatives. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1087, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. Molecular modeling for quantitative analysis of molecular interaction. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2005, 2, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T.; Homma, H. Chromatography in silico: Retention of acidic drugs on a guanidino ion-exchanger. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2007, 30, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T.; Masuda, Y.; Homma, H. Chromatography in silico; Retention of basic compounds on a carboxyl ion exchanger. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2005, 28, 3087–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. Simulation chromatography of phenolic compounds using a computational chemical method. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1027, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T.; Mizutani, C.; Homma, H. Computational chemical simulation of chromatographic retention of phenolic compounds. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2003, 26, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. In silico modeling study on molecular interactions in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 53, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanai, T.; Miyazaki, R.; Koseki, A.; Kinoshita, T. Computational chemical analysis of the retention of acidic drugs on a pentyl-bonded silica gel in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2004, 42, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. Chromatography in silico for basic drugs. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2005, 28, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. Quantitative in silico analysis of retention in normal-phase liquid chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2010, 33, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. In silico chromatography: Modeling a new support for alkyl-bonded phases and a solvent phase. J. Anal. Bioanal. Sep. Tech. 2017, 2, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Lu, Z.; Li, X.; Sarker, A.K.; Hu, L.; Choi, P.; Li, X.; Hakobyan, N.; Serpe, M.J. Responsive polymers for analytical applications: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 789, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenca, N.; Poole, C.F. Liquid chromatography with room temperature ionic liquids. J. Plan. Chromatogr. Modern TLC 2017, 30, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.D.; Emaus, M.; Varona, M.N.; Bowers, A.N.; Anderson, J.L. Ionic liquids; solvents and solbents in sample preparation. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.N.; Roy, K. Advances in QSPR/QSTR models of ionic liquids for the design of greener solvents of the future. Mol. Div. 2013, 17, 151–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Namiesnik, J. Greener organic solvents in analytical chemistry. Cur. Opinion Green Subst. Chem. 2017, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, B.; Passos, H.; Freire, C.S.R.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, M.G. Ionic liquids in chromatographic techniques: Toward additional improvements in the separation of natural compounds. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 4582–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berton, P.; Lana, N.B.; Rios, J.M.; Garcia-Reyes, J.F.; Altamirano, J.C. State of the art of environmentally friendly sample preparation approaches for determination of PBDEs and metabolites in environmental and biological samples: A critical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 905, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabre, M.; Ferey, L.; Some, I.T.; Gaudin, K. Greening reversed-phase liquid chromatography methods using alternative solvents for pharmaceutical analysis. Molecules 2018, 23, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Qiao, L.; Xu, G. Recent development of ionic liquid stationary phases for liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1420, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, L.; Riekkola, M.-L.; Canals, A. Ionic liquid-modified materials for solid-phase extraction and separation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 715, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowski, L.; Pereira, F.; Kloskowski, A.; Namiesnik, J. Opportunities and shortcomings of ionic liquids in single-drop microextraction. TrAC 2015, 72, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spietelun, A.; Marcinkowski, L.; De la Guardia, M.; Mamiesnik, J. Green aspects, developments and perspectives of liquid phases microextraction techniques. Talanta 2014, 119, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, E.M.; Grijalba, A.C.; Perez, M.B.; Llaver, M.; Wuilloud, R.G. Synergistic analytical preconcentration with ionic liquid-nanomaterial hybrids. TrAC 2017, 97, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawata, J.; Dawidziuk, B.; Dziedzic, D.; Gordon, D.; Popiel, S. Applictions of ionic liquids in analytical chemistry with a particular emphasis on their use in solid-phase microextraction. TrAC 2018, 105, 18–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, C.A.; Momen, M.A.; Dietz, M.L. Application of ionic liquids in the preparation of extraction chromatographic materials for metal ion separations: Progress and prospects. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1820–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Liu, J.-F. Development of a solid-phase microextraction fiber by chemical binding of polymeric ionic liquid on a silica coated stainless steel wire. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1230, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, L.; Parshintsev, J.; Hartonen, K.; Canals, A.; Riekkola, M.-L. Ionic liquid-functionalized silica for selective solid-phase extraction of organic acids, amines and aldehydes. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1226, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Jiang, Q.; Wei, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S. Preparation and evaluation of a silica-based 1-alkyl-3-(propyl-3-sulfonate) imidazolium zwitter ionic stationary phase for high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1163, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Haddad, P.R.; Hasebe, K.; Tanaka, K. Electrostatic ion chromatography using hydroxide solution as mobile phase with suppressed conductivity detection. Anal. Commun. 1999, 36, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhadze, M.; Lominadze, N.; Akhalkatsi, L.; Gvaramia, M. Study of chromatographic characteristics of inorganic analytes in biopartitioning miceller cdhromatography with ion-pair additives. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2010, 24, 1338–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysling, S.; Palmisano, G.; Hojrup, P.; Thaysen-Andersen, M. Utilizing ion-pairing hydrophilic interaction chromatography solid phase extraction for efficient glycopeptide enrichment in glycoproteomics. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5598–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Alvarez-Coque, M.C.; Ruiz-Angel, M.J.; Berthod, A.; Carda-Broch, S. On the use of ionic liquids as mobile phase additives in high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 883, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartsova, L.A.; Bessonova, E.A.; Kolobova, E.A. Ionic liquids as modifiers of chromatographic and electrophoretic systems. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 71, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewska-Forajta, M.; Markuszewski, M.L.; Kaliszan, R. Free silanols and ionic liquids as heir suppressors in liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1559, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Mallik, A.K.; Takafuji, M.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Ihara, H. Enhancement of molecular shape selectivity by in situ anion-exchange in poly(octadecylimidazolium)silica column. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1232, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, V.; Afonso, A.M. Surface-bonded ionic liquid stationary phases in high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 714, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, W.; Zhou, J.; Row, K.-H. Preparation and application of ionic liquid-modified stationary phases in high performance liquid chromatography. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Dou, A.; Shi, X.; Li, H.; Shan, Y.; Lu, X.; Xu, G. Development and evaluation of new imidazolium-based zwitterionic stationary phases for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liang, X.; Jiang, S.; Qiu, H. Preparation and applications of surface-confined ionic-liquid stationary phases for liquid chromatography. TrAC 2014, 53, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, P.A.; Cesar, I.C. Chiral method development strategies for HPLC using macrocyclic glysopeptide-based stationary phases. Chromatographia 2018, 81, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Mallik, A.K.; Takafuji, M.; Ihara, H.; Qiu, H. Versatile ligands for high-performance liquid chromatography: An overview of ionic liquid-functionalized stationary phases. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 887, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, C.A.; Rud, A.; Guthrie, M.L.; Dietz, M.L. Rapid quantification of imidazolium-based ionic liquids by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography: Methodology and an investigation of the retention mechanisms. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1400, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xu, H.; Yu, J.; Li, D.; Li, M.; Qiao, X.; Qin, X.; Yan, H. Novel imidazolium-embedded N,N-dimethylaminopropyl-functionalized silico-based stationary phase for hydrophilic/reversed-phase mixed-mode chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8989–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Shi, X.; Xu, G. Recent advances in development and characterization of stationary phases for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. TrAC 2016, 81, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, M.R.; Harrison, M.W.; Hutt, A.J. Use of chiral zwitterionic surfactants for enantiomeric resolutions by capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 2508–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapnissi-Christodoulou, C.P.; Stavrou, I.J.; Mavroudi, M.C. Chiral ionic liquids in chromatographic and electrophoretic separations. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Chopra, H.K. Chiral ionic liquids: Design, synthesis and applications in asymmetric organocatalysis. Curr. Org. Syn. 2017, 14, 488–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, B.Y.; Raoov, M.; Zain, N.N.M.; Mohamad, S.; Osman, H. Combination of cyclodextrin and ionic liquid in analytical chemistry: Current and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 47, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, J.C.; Svec, F. Porous monoliths for on-line smple preparation: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 964, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Qiao, L.; Shi, X.; Xu, G. Preparation and evaluation of a novel hybrid monolithic column based on pentafluorobenzyl imidazolium bormide ionic liquid. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1375, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamichatani, W.; Inoue, Y.; Saito, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yamamoto, A. Counter-ionic effect on the separation of water-soluble compounds applying hydrophilic stationary phase onded with a zwitter-ionic polymer. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, M.A.; Bylund, D. Liquid Chromatography with electrospray ionization and tandem mass cpectrometry applied in the quantitative analysis of chitin-derived glucosamine for a rapid estimation of fungal biomass in soil. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 2016, 9269367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Bi, W.; Tian, M.; Row, K.H. Application of ionic liquid for extraction and separation of bioactive compounds from plants. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 904, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kailasa, S.K.; Rawat, K.A.; Wu, H.-F. Ionic liquids in bioanalysis. Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 2251–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, R.P.; Srinivas, N.R.; Rais, R. A review of bioanalytical quantitative methods for selected sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulators. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 32, e4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.A.; Rasheed, A.S. Retention characteristic of ranitidine hydrochloride on new polymer-based in zwitter ion chromatography-hydrophilic interaction chromatography stationary phases. J. Chem. Soc. Pakistan 2018, 40, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, A.; Hoffler, S.; Fischer, K. Anion-exchange chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry method development for the environmental analysis of aliphatic polyhydroxy carboxylic acids. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1170, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Yao, S.; Song, H. Aplication of ionic liquids in liquid chromatography and electrodriven separation. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2013, 51, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Khoshmaram, L.; Sheykhizadeh, S. A review on application of microextraction techniques for analysis of chemical compounds and metal ions in foodstuffs. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res. 2014, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Feng, J.; Chen, W.; Li, L.; Duan, H.; Luo, C. Improvement of the chromatographic separation performance of an imidazolium ionic liquid functionalized silica column by in situ anion-exchange with dodecyl sulfonate and dodecylbenzene sulfonate anions. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzeskowiak, T.; Czarczynska-Goslinska, B.; Zgota-Grezeskowiak, A. Current approaches in sample preparation for trace analysis of selected endocrine-disrupting compounds: Focus on polychlorinated biphenyls, alkylphenols, and parabens. TrAC 2016, 75, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitkare, S.S.; Lakhane, K.G.; Kokulwar, P.U. Ionic liquids: Novel applications in drug delivery. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2013, 6, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Liu, G.; Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Ito, Y. Organic-high ionic strength aqueous solvent systems for spriral counter-current chromatography: Graphic optimization of partition coefficient. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Rel. Technol. 2013, 36, 504–512. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Liu, G.; Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Ito, Y. Organic high ionic strength aqueous two phase solvent system series for separation of ultra-polar compounds spiral high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 8715–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkland, J.J. Modern Practice of Liquid Chromatography; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1971; p. 454. ISBN O-471-48878-X. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, L.R.; Kirkland, J.J. Introduction to Modern Liquid Chromatography; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979; p. 863. ISBN O-471-03822-9. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, L.R. Principles of Adsorption Chromatography; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1968; p. 174. [Google Scholar]
- Small, H.; Stevens, T.S.; Bauman, W.C. Novel ion-exchange chromatographic method using conductmetric detection. Anal. Chem. 1975, 47, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, J.J.; Langlois, T.J. Process for preparing substrates with porous surface. U.S. Patent 2009/0297853 A1, 23 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wyndham, K.D.; Muriithi, B.W.; Morris, M.T.; Lawrence, N.L. Superficially porous materials comprising a substantially non porous core having narrow particle size distribution; Process for the preparation thereof; and use thereof for chromatographic separations. WO 2012/018598, 26 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Blue, L.E.; Jorgenson, J.W. 1.1 μm superficially porous particles for liquid chromatography. Part I: Synthesis and particle structure characterization. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 7989–7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond Analytics. Available online: http://diamond-analytics.com/app-notes/flare-small-molecules/ (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Nakamura, T.; Mizutani, M.; Nozaki, H.; Suzuki, N.; Yano, K. Formation mechanism for mono-dispersed meso-porous silica spheres and its applications to the synthesis of core/shell particles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glennon, J.D.; Omamogho, J. A process for preparing silica micro particles. WO 2010/061367 A2, 26 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, C.; Unger, K.K. Porous monodispersed SiO2 particles. WO 97/007056, A1, 16 August 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Coakley, J.M.; Hanrahan, J.P.; Hogan, J.J.; Spalding, T.R.; Tobin, J.M. Silica core-shell microparticles. WO 2012/110995 A1, 16 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Omamogho, J.O.; Hanrahan, J.P.; Tobin, J.; Glennon, J.D. Porous shell of 1.7 μm core-shell silica particles on chromatographic performance: Narrow bore columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Brennan, J.D. One-pot synthesis of silica core-shell particles with double shells and different pore orientations from their nonporous counterparts. J. Mat. Chem. 2012, 22, 13197–13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Ritchie, H.; Myers, P.; Zhang, H. One-pot synthesis of spheres-on-sphere silica particles from a single precursor for fast HPLC with low back pressure. Adv. Mat. 2012, 24, 6042–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Abdelmagid, W.; Ritchie, H.; Myers, P.; Zhang, H. Investigation on synthesis of spheres-on-sphere silica particles and their assessment for high performance liquid chromatography applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1270, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Jiang, B.; Wu, C.; Xia, S.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. 1.9μm superficially porous packing material with radially oriented pores and tailored pore size for ultra-fast separation of small molecules and biomolecules. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1356, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langsi, V.K.; Ashu-Arrah, B.A.; Glennon, J.D. Sub-2-μm seeded growth mesoporous thin shell particles for high-performance liquid chromatography: Synthesis, functionalization and characterization. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1402, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Q.; Min, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q.; Yin, Y. Silica microspheres with fibrous shells: Synthesis and application in HPLC. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9631–9638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.-C.; Mack, A.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Dittmann, M.; Wang, X.; Barber, W.E. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of a superficially porous particle with unique, elongated pore channels normal to the surface. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1440, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enke, D.; Glaser, R.; Tallarek, U. Sol-gel and porous glass-based silica monoliths with hierarchiral pore structure for solid-liquid catalysis. Chemie-Ingenieur-Technik 2016, 88, 1561–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Chen, X.; Alghamdi, A.; Abdullah, A.M.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, D. Synthesis of ordered miso-porous silica with tunable morphologies and pore sizes via a non-polar solvent-assisted Stober method. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 2356–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.-C.; Chen, W.; Barber, W.E. Superficially porous metal oxide particles, methods for making them, and separation devices using them. US 8,685,283, B2, 29 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Daneyko, A.; Höltzel, A.; Khirevich, S.; Tallarek, U. Influence of the particle size distribution on hydraulic permeability and eddy dispersion in bulk packings. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, S.; Stoeckel, D.; Smarsly, B.M.; Tallarek, U. Influence of particle properties on the wall region in packed capillaries. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1268, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. Theoretical investigation of diffusion along columns packed with fully and superficially porous particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 3476–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. Diffusion models in chromatographic columns packed with fully and superficially porous particles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 3773–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, S.; Fekete, J. The impact of extra-column band broadening on the chromatographic efficiency of 5cm long narrow-bore very efficient columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 5286–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. Mass transfer kinetics, band broadening and column efficiency. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1221, 2–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. Measurement of the eddy dispersion term in chromatographic columns. II. Application to new prototypes of 2.3 and 3.2mm I.D. monolithic silica columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1227, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritti, F.; Shiner, S.; Fairchild, J.N.; Guiochon, G. Characterization and kinetic performance of 2.1 × 100 mm production columns packed with new 1.6 μm superficially porous particles. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 3418–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritti, F.; Shiner, S.J.; Fairchild, J.N.; Guiochon, G. Evaluation of the kinetic performance of new prototype 2.1 mm × 100 mm narrow-bore columns packed with 1.6 μm superficially porous particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1334, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. The quantitative impact of the mesopore size on the mass transfer mechanism of the new 1.9μm fully porous Titan-C18 particles.1: Analysis of small molecules. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1384, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillicuddy, N.; Nesterenko, E.P.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Stack, E.M.; Omamogho, J.O.; Glennon, J.D.; Paull, B. A new N-hydroxyethyliminodiacetic acid modified core-shell silica phase for chelation ion chromatography of alkaline earth, transition and rare earth elements. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1321, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignot, M.; De Saint Jores, C.; Tchapla, A.; Boyer, F.; Cardinae, P.; Peulon-Agasse, V. New anthracenyl polar embedded stationary phases with enhanced aromatic selectivity, a combined experimental and theoretical study: Part 1-experimental study. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1512, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.C.; Breitbach, Z.S.; Wahab, M.F.; Barhate, C.L.; Armstrong, D.W. Gone in seconds: Praxis, performance, and peculiarities of ultrafast chiral liquid chromatography with superficially porous particles. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9137–9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spudeit, D.A.; Breitbach, Z.S.; Dolzan, M.D.; Micke, G.A.; Armstrong, D.W. Superficially porous particle based hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin stationary phase for high-efficiency enantiomeric separations. Chirality 2015, 27, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.C.; Breitbach, Z.S.; Yu, J.; Nguyen, K.A.; Armstrong, D.W. Quinine bonded to superficially porous particles for high-efficiency and ultrafast liquid and supercritical fluid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 963, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catani, M.; Felletti, S.; Ismail, O.H.; Gasparrini, F.; Pasti, L.; Marchetti, N.; De Luca, C.; Costa, V.; Cavazzini, A. New frontiers and cutting edge applications in ultra high performance liquid chromatography through latest generation superficially porous particles with particular emphasis to the field of chiral separations. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 2457–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeStefano, J.J.; Schuster, S.A.; Lawhorn, J.M.; Kirkland, J.J. Performance characteristics of new superficially porous particles. J. Chromatogr. A 1258, 1258, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, S.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Guillarme, D. New trends in reversed-phase liquid chromatographic separations of therapeutic peptides and proteins: Theory and applications. J. Pharm. Biom. Anal. 2012, 69, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.A.; Wagner, B.M.; Boyes, B.E.; Kirkland, J.J. Optimized superficially porous particles for protein separations. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1315, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preti, R. Core-shell columns in high-performance liquid chromatography: Food analysis applications. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 2016, 3189724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanai, T. Fundamental Properties of Packing Materials for Liquid Chromatography. Separations 2019, 6, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations6010002
Hanai T. Fundamental Properties of Packing Materials for Liquid Chromatography. Separations. 2019; 6(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations6010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanai, Toshihiko. 2019. "Fundamental Properties of Packing Materials for Liquid Chromatography" Separations 6, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations6010002
APA StyleHanai, T. (2019). Fundamental Properties of Packing Materials for Liquid Chromatography. Separations, 6(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations6010002




