Abstract
With the continuous expansion of rare earth resource development, the large-scale accumulation of ionic rare earth tailings (IRETs) has exerted pressure on both environmental and resource management. Due to their inherent low reactivity, unstable composition, and potential environmental risks, their widespread engineering application faces many challenges. To achieve the resource utilization of this solid waste, scholars in recent years have conducted extensive research on their application in silicate materials. This study systematically reviews the existing research. Given that the trace rare earth oxides in IRETs exhibit excellent mineralization effects and that IRETs contain a significant amount of clay minerals, IRETs can be feasibly applied in the production of silicate materials, including clinker, tiles, ceramics, glass-ceramics, and geopolymers. The research findings aim to provide technical support and practical guidance for the large-scale resource utilization of IRETs, promoting their application in silicate material production. This study identifies the common issues found in the research and provides recommendations for the high-value and large-scale resource utilization of IRETs in the future.
1. Introduction
Over the past few decades, the global mining industry has rapidly developed to meet the growing demand for metals and mineral resources. The processes of mining and mineral extraction consume vast amounts of natural mineral resources while generating large quantities of tailings [1]. Tailings refer to the crushed rocks and mineral fragments discarded after the separation of target minerals from gangue minerals [2]. The extensive exploitation of primary mineral resources has led to the depletion of high-grade deposits, shifting the mining focus toward lower-grade ores. Meanwhile, the increased amount of mining waste has compelled the industry to address escalating environmental challenges [3].
China possesses some of the world’s richest rare earth resources [4]. The Bayan Obo Mine stands as the global leader in light rare earth element (REE) production, while southern China—particularly Jiangxi Province, where ionic REE deposits were first discovered in the late 1960s [5]—holds abundant reserves of these unique minerals. Traditionally used in metallurgy, petroleum refining, glass manufacturing, and defense, ion adsorption-type rare earth materials now also play a vital role in advanced applications such as glass ceramics and cutting-edge materials. Their importance has grown significantly with the rapid development of high-tech industries, particularly in functional advanced materials [6,7,8,9,10].
At present, ionic rare earth deposits have been found in many countries, including Vietnam, China, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, the Philippines, the United States, and Madagascar. The distribution of global weathering crust, ionic rare earth deposits, and related projects is shown in Figure 1 [11].
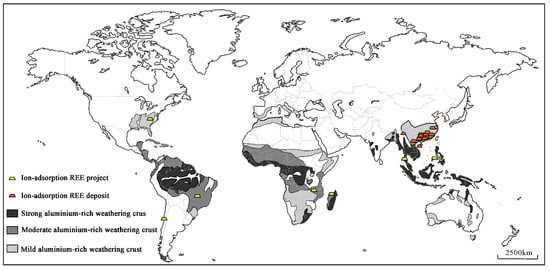
Figure 1.
Distribution of the global weathering crust, ionic rare earth deposits, and related projects [11].
The major processed/refined pure REE producers in terms of quantity are China (69%), the USA (12%), Burma (11%), and Australia (5%) (U.S. Geological Survey, 2023) [12]. Since the late 1980s, China has dominated the REE market in the supply of both raw ores and processed/purified products. Over the past decade, China alone has accounted for around 70–90% of global production [13,14,15,16]. Currently, China produces about 80% of the world’s REEs, particularly through the mining of ion adsorption clay deposits. These are also referred to as regolith-hosted clay or weathered-crust elution deposits, which supply over 95% of the heavy REEs [17,18,19,20]. The large REE production results in a significant amount of ionic rare earth tailings (RETs). Therefore, we investigated the treatment of the large volume of IRETs in China.
Rare earth tailings (RETs) represent a major byproduct of rare earth mining operations. Their long-term stockpiling not only consumes valuable land but also creates ecological risks. With the growing emphasis on resource circularity and sustainable mining practices, finding productive uses for RETs has become an important research focus. Recent studies highlight their promising applications in silicate materials, particularly as substitutes or functional additives. Given their inherent mineral reactivity and fine particle size, as well as their high contents of SiO2, Al2O3, etc., these tailings can comprise silicate materials such as clinker, geopolymer, ceramic, and glass.
In this paper, Section 2 introduces the types and origins of RETs, including the types of rare earth ore, production of RETs, and their characteristics and hazards. Section 3 includes the application of IRETs, such as in clinker, bricks, geopolymer, ceramics, glass-ceramics, and so on. Further investigations are proposed in Section 4.
This review mainly focuses on utilizing a large volume of RETs in preparing silicate materials, such as building materials, and primarily cites research publications published from 2000 to 2025. The authors searched numerous electronic databases, including Google Scholar, Elsevier, Science Direct, Research Gate, Scopus, and CKNI. A total of 988 published papers on RET applications were initially identified using the following search terms: rare earth elements, ion adsorption-type rare earth tailings, ionic rare earth tailings, ionic rare earth ore, construction materials, cementitious materials, silicate materials, and chemical composites. Article selection was based on the titles and abstracts of the most relevant literature available, including review papers and research articles [12].
2. Introduction to IRETs
2.1. Ionic Rare Earth Ore
Ion adsorption deposits are a unique type of REE deposit in which the REEs are adsorbed onto clay mineral surfaces within the weathering profiles of certain rocks [21,22]. Most known deposits of this type are located in southern China, particularly within the weathered profiles of REE-enriched granites in provinces such as Hunan, Jiangxi, Fujian, and Guangdong [23]. Unlike conventional rare earth deposits, these ores contain REEs adsorbed as ions onto clay minerals—a unique characteristic that offers several distinct advantages. Research has shown that these ionic rare earth ores require simpler extraction processes and feature lower radioactivity levels compared to other rare earth sources, making them particularly valuable as critical materials in high-tech applications [21,24]. Recognizing both the strategic importance and limited supply of ionic rare earth materials, China has classified them as protected mineral resources. These ionic rare earth ores primarily consist of quartz, kaolinite, and other clay minerals, and their characteristic chemical compositions are detailed in Table 1 [25,26,27,28,29,30].

Table 1.
Main chemical compositions of ionic rare earth raw ore/wt.%.
Ion adsorption clay deposits also have global potential. In 2020, a significant new clay-hosted ionic REE deposit was discovered at Mt. Clere in Australia, and additional occurrences have been identified in Southeast Asia and Japan [31]. The clay minerals in these deposits are primarily composed of kaolinite, along with varying proportions of illite, halloysite, montmorillonite, vermiculite, and chlorite. Additionally, Fe–Mn oxides can play a crucial role in REE enrichment, particularly for cerium (Ce). In relatively oxidized environments, Ce3+ is converted to Ce4+, forming insoluble precipitates within the Fe–Mn oxides or Ce-bearing minerals. This process leads to the accumulation of Ce in the upper weathered layers [13]. These REE-rich deposits form through the weathering of granitic bedrock under subtropical conditions. While currently mined only in China, similar deposits have been identified in other subtropical regions, including Southeast Asia, Madagascar, the Sierra Nevada (USA), Brazil, and Myanmar [17,20,32,33,34,35,36,37,38].
2.2. Production of IRETs
Since the 1970s, ion adsorption-type rare earth extraction has progressed through three generations: barrel leaching, heap leaching, and in situ leaching [39]. Heap leaching improved upon barrel methods with a higher throughput, simpler operation, and reduced labor costs. However, unregulated early-stage mining generated substantial RET accumulations [40,41,42,43]. To mitigate the ecological damage from the earth-moving practices of earlier methods, the 1980s introduced in situ leaching—now the dominant approach. By preserving topsoil and vegetation, it remains the most sustainable extraction technique [42]. RET chemistry varies regionally due to ore types, processing methods, and disposal practices (Table 2). For comparison, in Table 2, Tailings A represent Bayan Obo’s tailings [44], while B [45] and C [46] are characteristic IRETs.

Table 2.
The main chemical composition of RETs/wt.%.
In 2023, global demand for REEs reached approximately 271,000 tons, reflecting an annual growth rate of 6%. This upward trend is expected to continue, with demand projected to rise to 305,000 tons by 2025 [12]. However, REE extraction generates significant waste; depending on ore grade and processing methods, producing 1 ton of REE product can yield 2000–20,000 tons of leaching waste (Gregoir and van Acker, 2022) [12,47]. The Bayan Obo Mine, currently the world’s largest REE producer, has accumulated roughly 200 million tons of REE-bearing tailings across a 12 km2 area since the 1960s. Similarly, Sweden’s Kiruna (LKAB) iron mine—another site with substantial REE content—has historically produced ~700 million tons of tailings, with 8 million tons added annually [48,49]. Extracting 1 ton of rare earth oxides from China’s ion adsorption-type rare earth deposits in Ganzhou adds 2000 tons of RETs [50]. Compounding the problem, frequent rainfall and acid rain in these areas intensify the environmental risks posed by heavy metals leaching from the tailings [51].
2.3. Mineralogical Composition and Particle Size Distribution of IRETs
IRETs are primarily composed of quartz and clay minerals, offering the dual potential for recovering residual rare earth ions and repurposing the clay content. Figure 2 is a comparison of the XRD patterns of raw IRETs, and Figure 3 and Figure 4 characterize the IRETs’ microstructure and particle size distribution, respectively. It can be seen that the main mineral components of IRETs are quartz (SiO2) and kaolinite (Al4[Si4O10](OH)8).
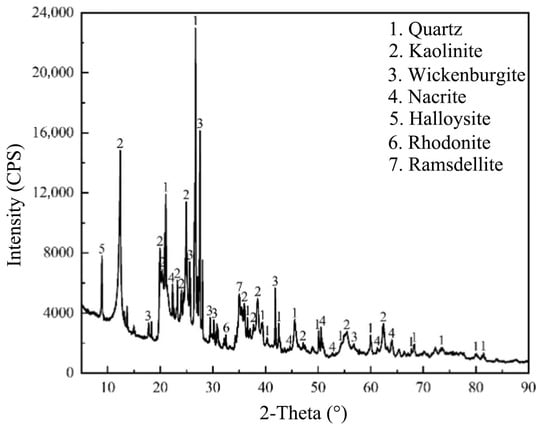
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of IRETs from Ganzhou City, Jiangxi Province, China [51].
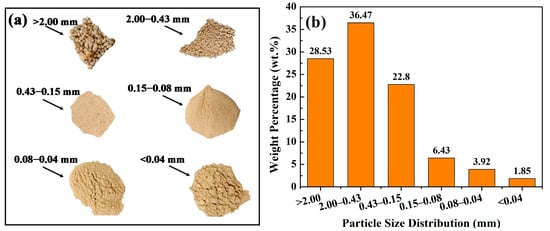
Figure 3.
Images of IRETs with different particle size ranges (a) and particle size distribution of IRETs (b) from Hunan Province, China [52].

Figure 4.
(a) Photograph and (b) SEM image of IRETs; (c,d) SEM images of IRETs at 750 °C [43].
2.4. Hazards of IRETs
In production, a considerable amount of RETs are deposited behind dams or in dry stacks. RETs pose significant environmental risks owing to their high concentrations of leachable metals, which can contaminate surrounding ecosystems [53]. Additionally, REEs are often associated with radioactive elements like thorium (Th) and uranium (U), which can accumulate in tailing dams over time [54]. Another concern is the generation of dust from uncovered tailing sites—fine particles can travel kilometers away, spreading contaminants [12]. Since tailings are already finely ground, they present a much greater leaching risk compared to unprocessed ore. The reduced particle size increases the surface area and suspension, accelerating the metal release into the environment. For example, studies have shown that decreasing the particle size from 1.14 to 0.25 mm can enhance cerium (Ce) leaching efficiency by 30% in red mud [12,55].
Untreated tailing accumulations pose significant landslide and mudslide risks to mining regions and adjacent areas [56]. The extraction process leaves residual sodium chloride and ammonium sulfate reagents in the tailings, contaminating groundwater and rivers [57]. Additionally, leachates from these ores contain Al3+, Fe2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Mn2+, and Cu2+ [58]—a problem exacerbated by southern China’s acid rain, which accelerates heavy metal leaching under acidic conditions [51]. Addressing RETs has thus become an urgent environmental priority.
2.5. Significance of Utilizing IRETs
In recent years, IRETs have gained recognition as significant emerging pollutants due to their environmental persistence and ecological risks [59,60]. In subtropical regions, IRETs pose particular environmental challenges such as leaching and erosion. Millions of tons of such tailings in South China have caused significant ecological damage to the surrounding areas [17]. Heavy metals migrate from IRETs via two natural pathways: atmospheric deposition (air) and rainfall leaching (water). Key factors controlling the heavy metal release from these tailings include chemical speciation, rainfall pH, ammonia nitrogen content, and mineral properties. Rainfall as the primary driver was related to four key mechanisms: (1) The large water volume from rainfall exerts stronger leaching and transport effects than atmospheric deposition. (2) Acid rain lowers the tailings’ pH, increasing heavy metal solubility. Even weakly acidic precipitation can mobilize bioavailable metal fractions, with acid rain elevating Cd, Zn, Cu, and Pb leaching by >70% [51]. (3) Rainfall’s physical force rapidly transports metals from tailing surfaces into runoff. (4) Metals migrate not only to surface water via runoff but also infiltrate groundwater, where their mobility and dispersion intensify. During these processes, water-mediated desorption, dissolution, and mineral weathering (including redox reactions) further promote heavy metal release [51]. Because IRETs threaten the environment during the production of REEs, the consumption of IRETs is crucial to achieving the sustainability of the rare earth industry.
3. Application of IRETs in Silicate Materials
IRETs exhibit fine particle size; stable mineral structure; low radioactivity; and abundant active components such as silicon, aluminum, and iron [61]. Aligned with green mining initiatives, researchers have increasingly utilized these tailings in silicate materials to achieve both resource recovery and environmental benefits [62]. Their applications span cement clinker production, supplementary admixtures, and geopolymer precursors.
3.1. Preparation of Clinker
IRETs are rich in reactive components such as SiO2 and Al2O3, which can form hydration products under alkali activation, thus exhibiting certain cementitious properties. When properly activated, IRETs participate in silicate hydration or form secondary cementitious phases, with studies demonstrating their ability to enhance volumetric stability while reducing the carbon footprint of cement products [63]. Experiments have demonstrated that the tailings enhanced the formation of early-strength and durable mineral phases in clinker (Figure 5), and the newly produced cement exhibited high strength (Figure 6) [64]. Some studies found that the tailings containing residual REEs and metal oxides exhibit chemical reactivity after the appropriate thermal treatment and alkali activation and perform well as binders in geopolymer systems. By co-activating the ion-adsorbed type with coal gangue and fly ash, synergistic activity can be achieved, improving overall utilization efficiency. IRETs exhibit favorable mineralizing effects during clinker burning, especially in promoting the formation of C3S and lowering the sintering temperature. Thermogravimetric analysis showed that trace elements such as Ce and La in the tailings react with lime and silicates at high temperatures to form stable minerals, enhancing the density and strength potential of clinker minerals [65,66,67,68,69]. IRETs can be applied in the production of limestone calcined clay cement, acting as clay, and high temperature treatment enhances the pozzolanic activity of RETs owing to the transformation of clay minerals and the formation of reactive silica-alumina phases [45].
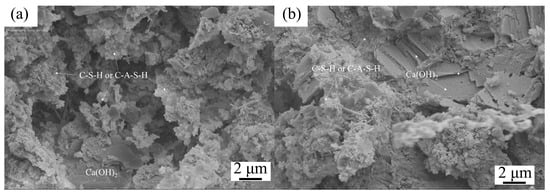
Figure 5.
SEM images of cement mortar with 0% (a) and 12% (b) IRETs after 28 d curing [64].
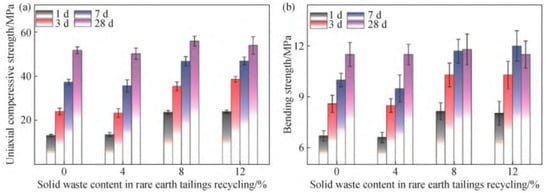
Figure 6.
Uniaxial conpressive strength (a) and bending strength (b) of cement mortar with IRETs (0~12%) [64].
3.2. Preparation of Bricks and Tiles
Since tailings are primarily composed of SiO2, Al2O3, and CaO, various types—such as iron ore tailings and IRETs—have been utilized in the production of bricks, tiles, and other prefabricated components [70,71]. This method not only enables large-scale consumption of solid waste, reducing the risks associated with tailing dams, but also generates economic benefits. Previous studies have shown that two types of IRETs can be used to produce ceramic vitrified tiles through dry pressing and sintering, with bending strength and sintering shrinkage being regulated by the types and amounts of fluxing agents added [72]. Furthermore, by adjusting the proportions of black clay, sand, talc, wollastonite, and bauxite, the performance of ceramic vitrified tiles—including bending strength and shrinkage—can be further enhanced [73,74].
IRETs are a silicate-rich mineral with high SiO2 and Al2O3 content, with quartz as the primary mineral (40–50% content). Kaolinite is the next most abundant mineral. Theoretically, IRETs can be used as a ceramic raw material in the production of building ceramics, but due to the high content of alkali metal oxides such as potassium and sodium, as well as a significant amount of iron–titanium compounds in the tailings, using them in large quantities in vitrified brick bodies can reduce the brick’s resistance to high-temperature creep, narrow the firing range, and cause defects such as bubbles and deformation. Therefore, there has been limited research in China on the application of rare earth tailings in the ceramic industry, and no reports have been published on the large-scale production of building ceramics using tailings [73].
3.3. Preparation of Geopolymer
Geopolymers are three-dimensional inorganic polymers synthesized from aluminum and silica-rich materials through alkali activation. A wide range of solid wastes—including tailings, red mud, fly ash, and blast furnace slag—can be used to produce geopolymers, which have proven effective in immobilizing municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWIFA), heavy metals, and other pollutants [75,76,77]. The mechanical properties of RET-based geopolymers are highly dependent on the alkaline activator concentration, curing temperature, and liquid-to-solid ratio.
As illustrated in Figure 7, RET-based geopolymers form a dense structure, with tailing particles encapsulated within the solid gel phase. Given that RETs are a specific type of tailing with a high heavy metal content, their stabilization via geopolymerization offers a viable solution for safe storage in tailing dams [78]. Previous studies have demonstrated that grinding and calcination enhance the reactivity of RETs, enabling the synthesis of geopolymers with improved strength. The addition of sodium silicate provides SiO32−, which readily reacts with [AlO4]− to form gel structures, thereby enhancing the mechanical performance [79,80]. To further optimize RET-based geopolymers, a response surface methodology has been employed to study the effects of the Si/Al ratio, alkaline activator type and concentration, and RET content [81,82]. The optimal sample was prepared using the “KOH + silica gel powder” as an alkaline activator [81].
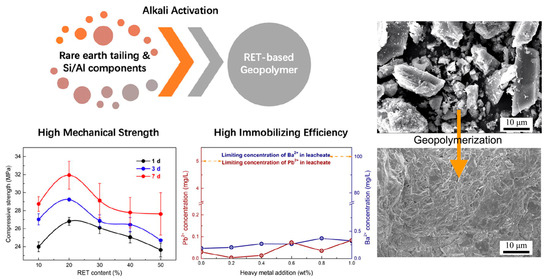
Figure 7.
Production of rare earth tailing-based geopolymers: methods, properties, and microstructure [78].
Another study has shown that these produced geopolymers effectively immobilize heavy metals such as Pb2+ and Cd2+ [43]. Figure 8 shows that heavy metals predominantly reside in the silicate glass phase or exist in an atomically dispersed state within the glass network, rather than in crystalline form. As revealed by the TEM elemental mapping of the geopolymers (Figure 8a), Pb and Cd exhibit homogeneous distribution throughout the geopolymer matrix alongside Si and Al. This confirms the uniform incorporation of heavy metals into the entire geopolymer matrix, aligning with findings by Hu et al., who reported that RET-optimized geopolymers exhibit exceptional heavy metal immobilization performance. The immobilization mechanisms involve the participation of Pb2+/Ba2+ in the polycondensation of the Si/Al gel phase. These ions bond with either Si/Al or oxygen atoms within the -[T-O-T]- structural units (where T = Si or Al), forming PbO/BaSiO3 compounds fixed within the framework, thereby achieving heavy metal stabilization (Figure 9).
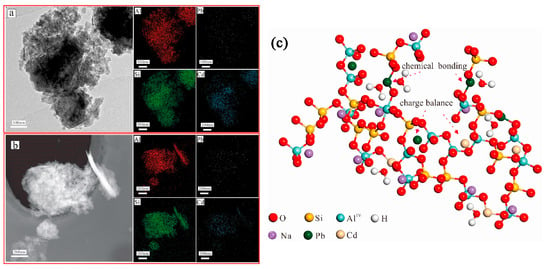
Figure 8.
Transmission electron microscopy images showing the elemental mapping of RET-based geopolymers (a,b) and the immobilization mechanism of heavy metals in RET-based geopolymers (c) [43].
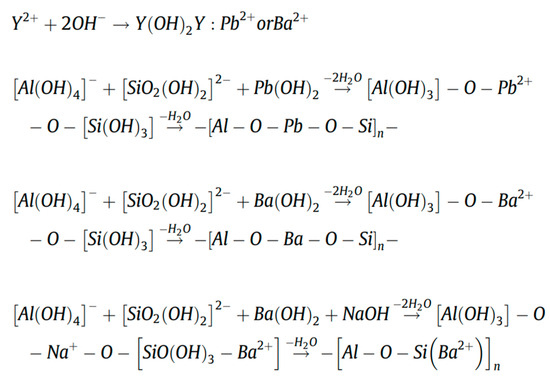
Figure 9.
Immobilization of Pb2+ and Ba2+ in RET-based geopolymer [78].
3.4. Preparation of Ceramics
Solid wastes such as iron tailings can be utilized in ceramic production [83,84]. Given the significant role of REEs in ceramic modification, RETs also show promise for incorporation into functional ceramics. Previous studies have systematically reviewed the properties and applications of rare earth–mineral composites in functional ceramics, demonstrating that optimal rare earth doping can substantially enhance material performance. Specifically, rare earths can either introduce lattice defects by substituting cations in the ceramic matrix or form distinct phases at the grain boundaries [85,86].
For instance, a novel far-infrared radiating ceramic material was synthesized using iron ore tailings, where the addition of Ce significantly improved the far-infrared emission properties of the tailing-based ceramic system [87]. Given the abundance of RETs in southern China, researchers have proposed using IRETs for ceramic production as a sustainable disposal method [88]. Additionally, they have been successfully employed in celadon production, with formulations containing up to 75% IRETs [89]. Other researchers [90] used rare earth tailings with a large amount of La2O3 (16.54%) to replace limestone for production of the calcium-based matte glaze surface. The study indicates that as the replacement content of rare earth tailings increases, the whiteness of the glaze surface becomes higher while the glossiness decreases. Moreover, the glaze surface becomes increasingly rough as the content of rare earth tailings increases [90]. A high-quality matte glaze—achieving 68.5% whiteness and 18.0% gloss—has also been developed using RETs combined with potash feldspar, quartz, calcite, kaolinite, and other raw materials [90].
RET-based ceramsite represents another important application of IRETs. Experimental results indicate that sintering temperature and steam curing conditions critically influence the performance of these ceramsites [91,92]. Furthermore, porous ceramics, such as foamed ceramic thermal insulation panels, can be fabricated from IRETs, meeting industry performance standards [93,94], as illustrated in Figure 10.
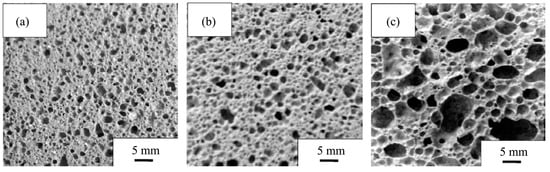
Figure 10.
Images of sample cross-sections at different temperatures ((a): 1125 °C; (b): 1150 °C; (c): 1200 °C) [93].
3.5. Preparation of Glass-Ceramics
The rapid expansion of the mining and power industries has led to significant environmental concerns about the accumulation and discharge of solid wastes. In this context, the conversion of solid wastes into high-value glass-ceramics has emerged as a promising solution, gaining recognition in academic circles for its potential to address both environmental and ecological challenges. Glass-ceramics, characterized by their exceptional mechanical strength, toughness, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance, offer a wide range of applications in mechanical manufacturing, chemical production, and power generation [95,96].
Previous studies on Bayan Obo RETs have revealed that REEs play a crucial role in determining glass-ceramic properties. Notably, Ce4+ exhibits high electric field characteristics that enhance the stability of glass network structures. Increasing the CeO2 content facilitates the rearrangement of metal ions within the glass system, promoting aggregate formation that effectively limits crack propagation. Furthermore, Ce4+ contributes to glass phase densification, significantly improving the material’s acid corrosion resistance (Figure 11). The microstructural alterations triggered by Ce4+ doping are illustrated in Figure 12 [97]. The experimental data reveal an inverse correlation between CeO2 concentration and the crystallinity of glass-ceramics. Progressive incorporation of CeO2 leads to the nucleation of particulate aggregates, whose population density exhibits dose-dependent augmentation. Notably, these aggregates serve as effective obstacles for crack propagation, causing discernible path deflection and termination phenomena. While rare earth incorporation maintains invariant effects on both crystalline phase composition and morphological characteristics, the observed aggregate formation is presumably attributable to the mechanisms of rare earth-mediated metallic ion accumulation.
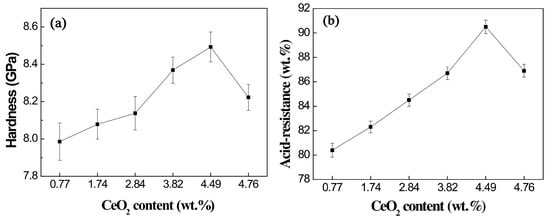
Figure 11.
Hardness (a) and acid-resistance (b) of glass-ceramics with different ratios of CeO2 [97].
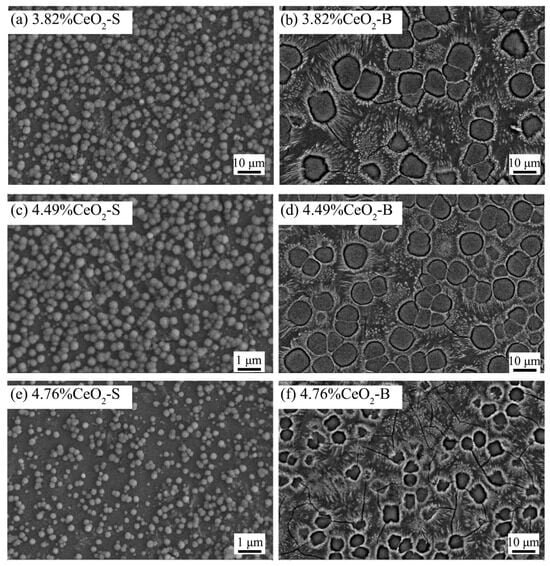
Figure 12.
Surface topography of glass-ceramics with increasing total CeO2 contents (secondary electron images for (a,c,e), and backscattered electron images for (b,d,f)) [97].
Bayan Obo RETs have been successfully incorporated into conventional glass formulations to develop novel glass-ceramic materials [98]. Researchers have also employed microwave heating—an eco-friendly, low-carbon approach—to produce nanocrystalline glass-ceramics from these tailings (Figure 13). This method not only enhances flexural strength and thermal stability but also enables the rapid production of high-performance tailing-based nanocrystalline glass-ceramics [99]. While IRETs have been used in glass-ceramic production through sintering processes (with tailing proportions reaching 20% [100]), their applications are limited compared to the Bayan Obo RETs, indicating a need for further research to expand their utilization in this field.
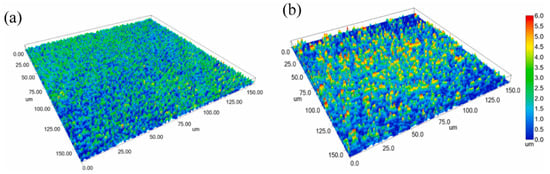
Figure 13.
Nanocrystalline glass-ceramic microstructure after microwave (a) and conventional (b) heating [98].
3.6. Other IRET Applications
Beyond their applications in ceramics, glass-ceramics, and geopolymers, IRETs show potential for other uses, including as novel functional pigments with excellent near-infrared reflectance, acid/alkali resistance, and thermal stability [101]. Since these tailings still contain significant amounts of REEs, their recovery has become a current research priority, offering both environmental protection and resource security benefits.
While traditional hydrometallurgical methods (leaching/solvent extraction) for REE recovery have primarily emphasized energy efficiency and scalability, more research is needed to address wastewater treatment, solid waste management, and comprehensive environmental impact assessments [102]. Recent advancements include an innovative supergravity-assisted green recovery technology that can produce high-purity REEs without additives, hazardous waste, or secondary pollution [103]. Additionally, researchers have developed an efficient bioleaching method that achieves remarkable leaching efficiencies exceeding 80% for La, Ce, Pr, Nd, and Sm, while maintaining environmental sustainability [104].
3.7. Summary and Outlook
In summary, IRETs have significant practical value and can be used to prepare typical silicate materials such as cement, ceramics, and glass, yielding products that meet industry standards. Table 3 summarizes the RETs and their applications in previous studies. It is evident that RETs are extensively utilized primarily in China. No research or applications were identified in other countries on Google Scholar. This may be attributed to China’s substantial reserves of ionic rare earths and its status as one of the most technologically advanced nations in rare earth extraction. Another possible reason is that other countries process relatively small volumes of rare earth ore, not yet requiring the large-scale utilization of rare earth tailings. Furthermore, Jiangxi, China, has the largest IRET reserves, and the utilization of RETs in Jiangxi is also the most extensive.

Table 3.
List of RETs and their applications in previous studies.
In terms of chemical composition, as shown in Table 3, the distinctive feature of the IRETs produced in Jiangxi is their high SiO2 content, which can reach 60% to 80%, while the Al2O3 content can reach approximately 14% to 30%. This provides a valuable material basis for the production of silicate materials. Regarding mineral composition, IRETs are primarily quartz, kaolinite, feldspar, etc. Therefore, RETs can replace kaolinite and other clay materials in the production of clinker, ceramics, and other silicate materials. In addition, some research institutes use RETs with relatively high total rare earth oxide (TREO) content [97,98,99,100]. Given the high value of rare earth elements, more research should be conducted on the recovery and extraction of REEs from tailings [105,106,107,108] before using them to produce silicate materials.
From both environmental and economic perspectives, utilizing RETs to produce cement clinker, ceramics, glass-ceramics, and other products can stabilize the harmful elements within them through high-temperature melting and other methods, thereby avoiding the risk of leaching in natural environments and enabling high-value production. This approach fully leverages the value of RETs. However, this method requires high-temperature melting, resulting in high energy consumption. Therefore, before industrial-scale production, economic feasibility studies must be conducted for specific application scenarios, and improvements must be made to produce aesthetically pleasing, high-value products under low-energy conditions, ensuring the economic viability of the technology. Additionally, this utilization method can fully leverage the coloring properties of residual REEs in RETs, as well as the fluxing properties of other components in RETs, thereby reducing production costs and enhancing product quality. Among several application methods, the production of geopolymers is considered the most energy-efficient, as curing conditions only require 50–85 °C, rather than the over 1000 °C of other methods. However, due to the low activity of RETs, pre-treatment typically involving grinding and calcination at 750 °C is necessary to enhance their activity, which also consumes significant energy.
As shown in Table 3, the RETs used for producing glass-ceramics primarily originate from Bayan Obo. Compared to the IRETs from Jiangxi, this type of RET has a higher CaO content but lower SiO2 and Al2O3 contents. Therefore, the appropriate glass system is typically selected based on the RET’s compositional characteristics, and pure chemical components are introduced to adjust the raw material composition, thereby achieving the preparation of microcrystalline glass. It is worth noting that the residual Ce4+ in Bayan Obo RETs was beneficial to performance improvement.
It is worth noting that silicate materials prepared using RETs must comply with national environmental risk standards for solid waste and silicate products, such as GB/T 30760 [109], GB/T 35605 [110], GB/T 30810 [111], and HJ 557 [112], etc.
In general, it is necessary to thoroughly research the chemical and mineral composition of specific types of RETs before determining their appropriate application. IRETs can typically be used as substitutes for clay minerals such as kaolinite, and they can also leverage the unique properties of residual REEs, such as coloring and reducing firing temperatures, to achieve a high-value utilization of their quality. RETs with lower Si and Al content are more suitable for the preparation of clinker, glass-ceramics, and geopolymers, etc.
4. Conclusions
IRETs contain a wide variety of valuable components, representing a secondary resource with significant utilization potential. While existing research has made considerable progress in the recovery and extraction of REEs, effective management of the massive accumulation of IRETs remains limited. To promote large-scale tailing utilization, this study reviewed the applications of IRETs in silicate materials, including clinker, ceramics, glass-ceramics, bricks and tiles, and geopolymers.
In traditional silicate materials such as cement clinker and bricks, IRETs can reduce sintering temperatures and improve the phase composition of clinker. Given the unique properties of RETs, particularly their enrichment in readily activated clay minerals, they are also suitable for geopolymer synthesis. In addition to meeting mechanical performance requirements, these geopolymers exhibit excellent heavy metal immobilization capabilities.
Furthermore, IRETs have broad applications in high-value-added products such as ceramic pellets, functional ceramics, and functional pigments, owing to their inherent content of REEs. REEs, including lanthanum (La), cerium (Ce), and neodymium (Nd), play a distinctive role in enhancing the performance of glass-ceramics and improving the aesthetic and functional properties of ceramics. However, the application of IRETs in glass-ceramics remains underexplored.
There remain limitations in RET-related research. Firstly, the research is still in its infancy, with a limited scope that has not yet attracted global attention. This is related to the scarcity and uneven distribution of rare earth deposits. Global cooperation should be strengthened to conduct systematic research and planning. Secondly, current research primarily focuses on the direct industrial utilization of RETs in silicate material production, whereas studies on the activation mechanisms, reaction kinetics, long-term durability, and heavy metal leaching behavior of IRETs in such materials remain scarce. These aspects are critical for the future large-scale application and promotion of RET-based silicate materials. Additionally, future research should emphasize the co-utilization of IRETs with other industrial solid wastes, such as steel slag, blast furnace slag, and refining slag, to further advance the sustainable management of RETs. Lastly, to make the best use of REEs, their further recovery and extraction from tailings is encouraged before using them to produce silicate materials.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, X.W.; investigation, X.W.; writing—review and editing, X.W., W.N. and J.L.; Conceptualization, W.N.; supervision, W.N. and S.Z.; formal analysis, W.N.; funding acquisition, J.L. and S.Z.; data curation, J.L. and S.Z.; project administration, S.Z.; validation, S.Z.; resources, S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Jing-Jin-Ji Regional Integrated Environmental Improvement-National Science and Technology Major Project (2024ZD12004), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (FRF-TP-25-002), Central Leading Local Science and Technology Development Fund (YDZJSX2025D092), and Key Laboratory of Investigation, Monitoring and Protection of Natural Resources in Mining Cities, Ministry of Natural Resources (No.2024-B01).
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| RET | Rare earth tailing |
| IRET | Ionic rare earth tailing |
| REE | Rare earth element |
| TREO | Total rare earth oxide content |
| MK | Metakaolin |
| LS | Limestone |
| OPC | Ordinary Portland cement |
| MSWIFA | Municipal solid waste incineration fly ash |
References
- Mäkinen, J.; Pietek, G.; Miettinen, V.; Khoshkhoo, M.; Sundkvist, J.E.; Kinnunen, P. Removal of Pyrrhotite from High-Sulphur Tailings Utilising Non-Oxidative H2SO4 Leaching. Minerals 2022, 12, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gao, Y.T.; Jin, A.B.; Wang, X. Influence of Water Loss on Mechanical Properties of Superfine Tailing–Blast-Furnace Slag Backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.B.; Liu, B.; Gao, Y.T.; Sun, H. Evaluation of Safety and Deformation Characteristics of the Secondary Stope Sandwiched between Backfills in Underground Iron Mines. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoulnia, P.; Barthen, R.; Lakaniemi, A.M. A Critical Review of Bioleaching of Rare Earth Elements: The Mechanisms and Effect of Process Parameters. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 378–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Kang, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Wan, Y. Enhancing Leaching Efficiency of Ion Adsorption Rare Earths by Ameliorating Mass Transfer Effect of Rare Earth Ions by Applying an Electric Field. J. Rare Earths 2024, 42, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, H.; Tong, L.; Sand, W. Some Aspects of Industrial Heap Bioleaching Technology: From Basics to Practice. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2022, 43, 510–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Ding, L.; Li, Y.; He, R.; Li, J. Changing the Calcination Temperature to Tune the Microstructure and Polishing Properties of Ceria Octahedrons. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 16554–16560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Fordjour, E.Y.; Yang, X. Bioleaching of Rare Earth Elements Challenges and Opportunities: A Critical Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, T. Review of Rare Earth Oxide (Nano and Micro Sized Crystalline) Materials: Preparation from Rare Earth Chlorides, Characterisation and Applications. Hydrometallurgy 2025, 234, 106464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, A. A Systematic Review on Leaching of Rare Earth Metals from Primary and Secondary Sources. Miner. Eng. 2022, 184, 107632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; He, K.; Luo, C.; Liu, Z.; Tang, X. Review on the Development and Utilization of Ionic Rare Earth Ore. Minerals 2022, 12, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdu-Rahkama, R.; Kinnunen, P. Tailings Valorisation: Opportunities to Secure Rare Earth Supply and Make Mining Environmentally More Sustainable. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 520, 146147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Ilton, E.S.; Wang, Z.; Rosso, K.M.; Zhang, X. Global Rare Earth Element Resources: A Concise Review. Appl. Geochem. 2024, 175, 106158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Geng, Y.; Ye, X.; Ma, S.; Hao, X.; Xin, W.; Chai, Y. A Review of the Main Rare Earth Ore Smelting Processes in the World: From Traditional Methods to New Technologies. J. Rare Earths, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancheri, N.A. Chinese Monopoly in Rare Earth Elements: Supply-Demand and Industrial Applications. China Rep. 2012, 48, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.B.; Paetzel, V.; Struis, R.P.W.J.; Ludwig, C. Separation and Recycling Potential of Rare Earth Elements from Energy Systems: Feed and Economic Viability Review. Separations 2022, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janot, N.; Huot, H.; Rivard, C.; Perrin, M.; Noirault, A.; Tang, Y.T.; Watteau, F.; Montargès-Pelletier, E. Localization and Speciation of Rare Earth Elements in Mine Tailings from Ion-Adsorption Clay Deposits, Southern China: Insights from Microfocused X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 17, 100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, S.A.; Balaram, V.; Roy, P.; Mir, A.R.; Javed, M.; Teja, M.S. Phosphorite Deposits: A Promising Unconventional Resource for Rare Earth Elements. Geosci. Front. 2025, 16, 102044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesgo García, M.V.; Krzemień, A.; Manzanedo del Campo, M.Á.; Menéndez Álvarez, M.; Gent, M.R. Rare Earth Elements Mining Investment: It Is Not All about China. Resour. Policy 2017, 53, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanematsu, K.; Watanabe, Y. Characteristics and Genesis of Ion Adsorption-Type Rare Earth Element Deposits. Rare Earth Crit. Elem. Ore Depos. 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, G.A.; Papangelakis, V.G. An Overview of Rare-Earth Recovery by Ion-Exchange Leaching from Ion-Adsorption Clays of Various Origins. Mineral. Mag. 2016, 80, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrade, G.; Marquis, E.; Smith, M.; Goodenough, K.; Nason, P. REE Concentration Processes in Ion Adsorption Deposits: Evidence from the Ambohimirahavavy Alkaline Complex in Madagascar. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 112, 103027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, Y.; Kamitani, M. Rare Earth Minerals and Resources in the World. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 408–412, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.K.; Gupta, A.; Ramteke, P.; Sahoo, H.; Sengupta, A. Biosorption-a Green Method for the Preconcentration of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) from Waste Solutions: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 274, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.; Li, Z.; Zheng, X.; Liu, D.; Zhao, L.; Feng, Z.; Huang, X. Readsorption of Rare Earths and Aluminum during Column Leaching of Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Ore Using Magnesium Sulfate in the Presence of Lean Ore Layer. J. Rare Earths, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Feng, Z.; Chen, J. Occurrence and Vertical Distribution of Aluminum and Rare Earths in Weathered Crust Elution-Deposited Rare Earth Ore: Effect of Soil Solution PH and Clay Minerals. J. Rare Earths 2024, 42, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanematsu, K.; Kon, Y.; Imai, A.; Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, Y. Geochemical and Mineralogical Characteristics of Ion-Adsorption Type REE Mineralization in Phuket, Thailand. Miner. Depos. 2013, 48, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohar, S.Z.; Yunus, M.Y.M. Mineralogy and BCR Sequential Leaching of Ion-Adsorption Type REE: A Novelty Study at Johor, Malaysia. Phys. Chem. Earth 2020, 120, 102947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zhou, J.; Du, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, H.; Hu, Q.; Wang, W.; Tian, M.; Chen, B.; et al. The Characteristics and Enrichment Process of Dabu Ion-Adsorption Heavy Rare-Earth Element (HREE) Deposits in Jiangxi Province, South China. Minerals 2024, 14, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.X.; Wang, X.G.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhang, Y.W.; Gong, L.X.; Zhong, W. Petrogenesis and REE Mineralogical Characteristics of Shitouping Granites in Southern Jiangxi Province: Implication for HREE Mineralization in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 168, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Honda, T.; Tanaka, M.; Tanaka, K.; Takahashi, Y. Discovery of Ion-Adsorption Type Deposits of Rare Earth Elements (REE) in Southwest Japan with Speciation of REE by Extended X-Ray Absorption Fine Structure Spectroscopy. Geochem. J. 2018, 52, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobri, N.A.M.; Harun, N.; Yunus, M.Y.M. A Review of the Ion Exchange Leaching Method for Extracting Rare Earth Elements from Ion Adsorption Clay. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 208, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, A.M.; Smith, M.P.; Finch, A.A.; Estrade, G.; Villanova-de-Benavent, C.; Nason, P.; Marquis, E.; Horsburgh, N.J.; Goodenough, K.M.; Xu, C.; et al. Adsorption of Rare Earth Elements in Regolith-Hosted Clay Deposits. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Ren, T.; Chen, H.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; et al. Redistribution and Chemical Speciation of Rare Earth Elements in an Ion–Adsorption Rare Earth Tailing, Southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, R.; Becker, M.; Brugger, J.; Etschmann, B.; Burcher-Jones, C.; Howard, D.; Kooyman, P.J.; Petersen, J. Characterisation of a Rare Earth Element- and Zirconium-Bearing Ion-Adsorption Clay Deposit in Madagascar. Chem. Geol. 2019, 522, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanematsu, K.; Murakami, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Duangsurigna, S.; Siphandone, V. Enrichment of Rare Earth Elements (REE) in Granitic Rocks and Their Weathered Crusts in Central and Southern Laos. Bull. Geol. Surv. Japan 2009, 60, 527–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zheng, X.; Ji, B.; Xu, Z.; Bao, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Mei, J.; Li, Z. Green Recovery of Rare Earth Elements under Sustainability and Low Carbon: A Review of Current Challenges and Opportunities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, H.; Kon, Y.; Sanematsu, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Ito, M. Microscopic Analyses of Weathered Granite in Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Deposit of Jianxi Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Qiu, J.; Chen, J.; Zan, M.; Xiao, Y. Progress in Green and Efficient Enrichment of Rare Earth from Leaching Liquor of Ion Adsorption Type Rare Earth Ores. J. Rare Earths 2022, 40, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, Z.; Yu, J.; Xu, Z.; Chi, R. Novel Solution Injection Technology for In-Situ Leaching of Weathered Crust Elu-tion-Deposited Rare Earth Ores. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, N.; Kraslawski, A.; Cisternas, L.A. Towards Mine Tailings Valorization: Recovery of Critical Materials from Chilean Mine Tailings. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xiao, Y.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, Z.; Yao, R.; Zhai, Y.; Tian, L. Leaching of Ion Adsorption Rare Earths and the Role of Bioleaching in the Process: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 468, 143067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yu, T.; Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, L.; Peng, Y. Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Tailings for Preparation of Alkali-Based Geopolymer with Capacity for Heavy Metals Immobilization. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 134, 104768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Jiang, M. A Novel Approach for Recovery of Rare Earths and Niobium from Bayan Obo Tailings. Miner. Eng. 2014, 65, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Peng, Z.; Fahimizadeh, M.; Yu, T.; Faheem, M.; Belaroui, L.S.; Hamada, B.; Yuan, P. Recycling of an Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Tailing in a Low-Carbon Construction Material: Performance Modulation and Life Cycle Assessment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 475, 141167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Hua, X.; Zhang, G.; Yu, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; et al. Synthesis of High-Crystallinity Zeolite A from Rare Earth Tailings: Investigating Adsorption Performance on Typical Pollutants in Rare Earth Mines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 468, 133730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapp, P.; Schreiber, A.; Marx, J.; Kuckshinrichs, W. Environmental Impacts of Rare Earth Production. MRS Bull. 2022, 47, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunsu, C.; Menard, Y.; Eriksen, D.Ø.; Ekberg, C.; Petranikova, M. Recovery of Critical Materials from Mine Tailings: A Comparative Study of the Solvent Extraction of Rare Earths Using Acidic, Solvating and Mixed Extractant Systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peelman, S.; Kooijman, D.; Sietsma, J.; Yang, Y. Hydrometallurgical Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Mine Tailings and WEEE. J. Sustain. Metall. 2018, 4, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packey, D.J.; Kingsnorth, D. The Impact of Unregulated Ionic Clay Rare Earth Mining in China. Resour. Policy 2016, 48, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Liu, Z.; Mao, Q.; Ye, H.; Tian, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L. Leaching Characteristics and Environmental Impact of Heavy Metals in Tailings under Rainfall Conditions: A Case Study of an Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Mining Area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 281, 116642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, R.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, G. Efficient Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Tailings: Based on the Addition of Pyrite Calcination Modification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 356, 129767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.K.; Haque, N.; Bhuiyan, M.; Bruckard, W.; Pramanik, B.K. Recovery of Strategically Important Critical Minerals from Mine Tailings. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levett, A.; van der Ent, A.; Ray Jones, T.; Bolouri, K.; Kelly, K.; Vaughan, J.; Edraki, M.; Erskine, P.; Southam, G. Water-Soluble Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Recovered from Uranium Tailings. Miner. Eng. 2024, 210, 108675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, S.S.; Shekar, K.R.; Viswanathan, V.; Surendran, G. Dissolution Kinetics of Cerium from Red Mud. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gao, Y.T.; Jin, A.B.; Wang, X. Dynamic Characteristics of Superfine Tailings-Blast Furnace Slag Backfill Featuring Filling Surface. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 242, 118173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbadi, A.; Mucsi, G. A Review on Complex Utilization of Mine Tailings: Recovery of Rare Earth Elements and Residue Valorization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, T.; Sun, Z.; Bo, Y.; Zou, C.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, C. Solidification Treatment of Rare Earth Tailings by a Re-newable Biological Cementation Method. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 179, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Faz, A.; Zornoza, R.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Shahrokh, V.; Acosta, J.A. Environmental Pollution and Depth Distribution of Metal(Loid)s and Rare Earth Elements in Mine Tailing. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uugwanga, M.N.; Kgabi, N.A. Assessment of Metals Pollution in Sediments and Tailings of Klein Aub and Oamites Mine Sites, Namibia. Environ. Adv. 2020, 2, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Chen, Z.; Hong, B.; Wang, H.; Feng, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Chen, Z. Transport and Distribution of Residual Nitrogen in Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Tailings. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyemi, B.A.; Alaba, P.A.; Rashedi, A. Selected Performance of Alkali-Activated Mine Tailings as Cementitious Compo-sites: A Review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 50, 104154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diosdado-Aragón, A.J.; Valenzuela-Díaz, M.J.; Dávila, J.M.; Becerra-Herrera, M.; Caraballo, M.A. Influence of Mine Tailings Mineralogy and Curing Conditions in the Cementation of Pastes for Mine Galleries Backfilling. Miner. Eng. 2025, 232, 109524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, A.; Tang, J.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Jiang, J. Preparation and Properties of Portland Cement from Secondary Recycle Waste of Rare Earth Tailing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 406, 133337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q. The Effects of La series Trace Elements on Cement Clinker Formation. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1998, 4, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y. Effects of Rare Earth on Formation of Cement Clinkers. Rare Earths 2000, 21, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wu, B.; Xu, Y. Study on the sintering of Portland cement clinker by substitution of rare earth tailing for clay in batch mixing. China Mining Magazine 2006, 2, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, H. Experimental Study on Calcination of Portland Cement Clinker with Rare Earth Tailings. Multipurp. Util. Miner. Resour. 2021, 5, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Zhou, H.; Luo, Y. The effect of rare earth tailings on carbonate decomposition of cement raw materials. China Cement 2013, 12, 55–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Tang, B.; Liu, X. Cementitious Activity of Iron Ore Tailing and Its Utilization in Cementitious Materials, Bricks and Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 288, 123022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M. Study on Preparation of Red Floor Tiles Using Rare Earth Tail Somewhere in Southern. Ceram. Eng. 1999, 33, 4–6+12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Feng, X.; Zeng, Z. Preparation of building ceramic vitrified tiles with South Jiangxi rare-earth tailings. China Ceram. 2014, 50, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zha, Y.; Yang, K. Study on Factors of Influencing Sinter-ability of Ceramic Vitrified Tiles Derived from South Jiangxi Rare Earth Tailings Preparation. China Ceram. 2015, 51, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y. Research of Preparation of Polished Tiles Derived from South Jiangxi Rare Earth Tailings. Master’s Thesis, Jingdezhen Ceramic Institute, Jingdezhen, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Deng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Tian, C.; Ma, J.; Shao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Y. Utilization of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash with Different Pretreatments with Gold Tailings and Coal Fly Ash for Environmentally Friendly Geopolymers. Waste Manag. 2025, 194, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, Q.; Mao, Y.; Yang, A. Geopolymers Prepared from Industrial Solid Waste: Compre-hensive Properties and Application Prospects. Environ. Res. 2025, 278, 121518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, C. Solidification/Stabilization of Gold Ore Tailings Powder Using Sustainable Waste-Based Composite Geopolymer. Eng. Geol. 2022, 309, 106793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhong, L.; Yang, X.; Bai, H.; Ren, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ju, X.; Wen, H.; Mao, S.; et al. Synthesis of Rare Earth Tailing-Based Geopolymer for Efficiently Immobilizing Heavy Metals. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y. Preparation of Ionic Rare Earth Based Geopolymer Porous Material and its Properties Research. Master’s Thesis, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Yan, Q.; Luo, X.; Jiao, X.; Wang, J. Research on utilizing ionic rare earth tailings for preparing geopolymer. Non-Met. Mines 2015, 38, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, X.; Cao, Z.; Li, T.; Luo, X.; Yan, Q.; Chen, Q.; Huang, Z. Compressive strength and efflorescence extent of rare earth tailings-based geopolymer with different alkaline activators. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 35, 3819–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, L.; Bai, H. Modeling and optimization of rare earth tailing based geopolymer by response surface methodology. Metal Mine 2020, 49, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sun, Q.; Sun, W.; Han, X.; Zhang, K. Preparation and Sintering Mechanism of Foamed Ceramics from Iron Tailings and Feldspar Powder. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 24123–24135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Kou, Y.; Wang, D.; Bai, R.; Luo, Q.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, Z. Preparation and Characterization of Iron Ore Tailings-Based Sound Absorbing Ceramics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2025, 344, 131189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, G.; Meng, J.; Ding, Y. Far Infrared Radiation Property of Rare Earth Mineral Composite Materials. J. Rare Earths 2006, 24, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazhugasalamoorthy, S.; Jegatheesan, P.; Mohandoss, R.; Giridharan, N.V.; Karthikeyan, B.; Joseyphus, R.J.; Dhanuskodi, S. Investigations on the Properties of Pure and Rare Earth Modified Bismuth Ferrite Ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 493, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Meng, J.; Liang, J.; Duan, X.; Huo, X.; Tang, Q. Effect of Rare Earth Ce on the Far Infrared Radiation Property of Iron Ore Tailings Ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 66, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Lu, J. Experiments on the application of tailings in ceramic materials. Multipurp. Util. Miner. Resour. 1996, 3, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D. The Application of Rare Earth Tailings in Ceramic Bases and Glazes. Ceram. Res. 1991, 3, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, X. Study on the application of rare earth tailing in matle glaze. Foshan Ceram. 2022, 32, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Yan, Y.; Yan, Q.; Jiao, X.; Luo, X. Effect of calcination temperature and Al/Si ratio on performance of the rare earth tailings based ceramsite. J. Ceram. 2014, 35, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Yan, Q.; Luo, X.; Jiao, X.; Xu, J. Effect of steam curing system on compressive strength of ceramsite from rare earth tailings and its application to waste water treatment. J. Ceram. 2016, 37, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cheng, K.; Liu, X. Study on Preparation of the Foamed Ceramics with the Rare Earth Tailings and the Wastes of Polished Tile. China Ceram. 2014, 50, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Ding, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Long, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, W. Preparation and properties of porous ceramics from rare earth tailings. Non-Met. Mines 2021, 44, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, J.; Zhang, T.; Srinivasakannan, C.; Wei, X.; Duan, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, F.; Liang, J. Phase Evolution, Microstructure and Properties of Glass-Ceramics Derived from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Bottom Ash and Molybdenum Tailings. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 45353–45361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Li, D. Study on Low-Cost Preparation of Glass–Ceramic from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Fly Ash and Lead–Zinc Tailings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 356, 129231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Du, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M.; Chen, H.; Ouyang, S.; Li, B. Influence of Rare Earth Ions on Metal Ions Distribution and Corrosion Behavior of Tailing-Derived Glass-Ceramics. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2018, 482, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lai, H.; Zhang, K. Heat Transfer, Crystallization and Properties of Bayan Obo Tailings-Based Nanocrystalline Glass-Ceramics Processed with Microwave Radiation. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Li, B.W.; Gao, Z.Y.; Chang, D.Q. The Utilization of Rare Earth Tailing for the Production of Glass-Ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2010, 170, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Ji, S. A study on sintered glass-ceramic decorative material made from rare-earth tailings. Glass Enamel 2008, 4, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Feng, L.; Huang, B.; Zhai, R.; Sun, X. Sustainable Reutilization of Ion-Adsorbed Rare Earth Tailings: Preparation of Low-Cost Functionalized Pigments. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 11575–11587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.R.; Mishra, S. Hydro Metallurgical Technique as Better Option for the Recovery of Rare Earths from Mine Tailings and Industrial Wastes. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 36, 101311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z. A Green Method of Respectively Recovering Rare Earths (Ce, La, Pr, Nd) from Rare-Earth Tailings under Super-Gravity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 367, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Gao, P.; Zhao, X.; Dong, Z. Potential and Characteristics of Rare-Earth Metals Acid Bioleaching from the Ra-re-Earth-Rich Tailings with the Enriched Functional Bacterial Consortium: Comparison between One-Step and Two-Step Processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famobuwa, V.; Talan, D.; Sanyal, O.; Grushecky, S.; Amini, H. A Review of Biomass-Based Adsorption for Rare Earth Elements Recovery. J. Rare Earths, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, P.; Han, Y. Rare Earth Elements Resources and Beneficiation: A Review. Miner. Eng. 2024, 218, 109011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, M.; Sanematsu, K.; Watanabe, Y. REE Mineralogy and Resources. In Handbook on the Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths; Jean-Claude, B., Vitalij, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 49, pp. 129–291. ISBN 0168-1273. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, E.; Sherman, A.M.; Wallington, T.J.; Everson, M.P.; Field, F.R.; Roth, R.; Kirchain, R.E. Evaluating Rare Earth Element Availability: A Case with Revolutionary Demand from Clean Technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3406–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 30760-2024; Technical Specification for Co-Processing of Solid Waste in Cement Kiln. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2024.
- GB/T 35605-2024; Green Product Assessment—Wall Material. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2024.
- GB/T 30810-2014; Test methods for leachable ions of heavy metals in cement mortar. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- HJ 557-2010; Solid Waste-Extraction Procedure for Leaching Toxicity-Horizontal Vibration Method. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).