Abstract
Mogroside V crude extract from Siraitia grosvenorii has many pharmacological effects, such as anti-diabetes, antioxidant, etc. It is being used as a kind of natural sweetener in more and more countries. The improvement of Mogroside V purity can greatly promote the utilization value of Siraitia grosvenorii and the quality of related products. For this paper, a boronic acid-functionalized silica gel adsorbent (SiO2-GP-APBA) was synthesized and applied for the first time in the purification of mogroside V from the crude extract of Siraitia grosvenorii. It was demonstrated that it was 30–100 μm with 163.1 μmol/g of boronic acid groups on the surface of silica gel and stable at below 380.20 °C. Its maximum adsorption capacity to mogroside V was up to 206.74 mg/g at room temperature. After the saturated absorption from the crude extract of Siraitia grosvenorii in a pH 3 solution, 96.36% mogroside V could be released from SiO2-GP-APBA using a pH 7 aqueous solution, which was better than ethanol. The purity of mogroside V was significantly increased from 35.67% to 76.34%. Semi-preparative HPLC could further improve the purity of mogroside V to 99.60%. Additionally, the direct inhibition effect of the mogroside V on α-glucosidase was determined for the first time. Its inhibitory constant was 46.11 μM, indicating mogroside V was beneficial for the treatment of diabetes.
1. Introduction
According to data from the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the global prevalence of diabetes in people aged 20–79 years was 10.5% (536.6 million people) in 2021, rising to 12.2% (783.2 million people) by 2045 [1]. Diabetes mellitus (DM) can lead to a range of complications, including amputation, blindness, kidney failure, cardiovascular disease, etc. In 2021, global health spending related to diabetes was estimated to be USD 966 billion and was predicted to rise to USD 1054 billion by 2045. Diabetes-related deaths account for 11.3% of total deaths worldwide [2,3]. China has the highest prevalence of diabetes globally, accounting for nearly a one-quarter of all cases, and this trend will continue until 2045 [4]. There are some ways to treat diabetes, such as traditional oral hypoglycemic drugs, insulin injection, or islet transplantation. However, the progression of diabetes mellitus cannot be effectively controlled [5], and there are some other problems, such as an increased risk of hypoglycemia, a patient’s decreasing quality of life [6], the risk of autoimmune rejection [7], and various side effects (gastrointestinal discomfort) [8]. Thus, the most effective way to prevent diabetes is through lifestyle changes, dietary control, psychological regulation, etc. [9]. Among them, dietary control methods include controlling glucose intake. To maintain the sweet taste of some foods, sweeteners are used to replace sucrose, fructose, glucose, maltose, and lactose [10]. Since artificial sweeteners such as saccharin, aspartame, and sucralose cause certain health problems [11], people are switching their attention to natural sweeteners such as sugar alcohols, steviol glycosides, mogrosides, and sweetener proteins [12,13].
Siraitia grosvenorii as homology substance of medicine and food [14] that belongs to the family of Cucurbitaceae [15] and mainly grows in Guangxi, China [16]. Cucurbitane-type triterpene glycosides are its most important active ingredients [17]. Mogrosides are a subclass of glycosides with cucurbitane triterpene mogrol as the glycoside element [18]; it has pharmacological effects such as hypoglycemic [19,20,21,22], antioxidant [23,24,25], anticancer, cough suppressant, antibacterial, immunity-enhancing, and gastrointestinal motility effects [17]. For obese and diabetic patients, they are substitutes for sugar [26,27,28,29] because of their high sweetness, few calories, pure taste, and no toxic side effects. After the isolation of 18 mogrosides [30], it was found that mogrosides V is the most abundant and is considered as a quality indicator. It is about 0.3% to 0.5% present in the ripe, fresh fruit and about 1.0% present in the dried fruit of Siraitia grosvenorii [16]. Most importantly, its sweetness is equivalent to 350 times that of sucrose, but it has only one-fiftieth of the calories [17,29,30,31]. Thus, mogrosides V is being widely accepted. For example, mogrosides V was approved as a high-intensity sweetener in Japan. It also was generally recognized as a safe non-nutritive sweetener and flavor enhancer in United States, where it showed a significant upsurge in consumption pattern [18,32] due to the antioxidant potential, promotion of insulin secretion, and anti-diabetic effect of mogroside V crude extract [33,34,35]. Thus, improving the purity of mogroside V could greatly enhance the utilization value of Siraitia grosvenorii and the quality of related products. Currently, the widely used method to purify mogroside V is preparative chromatography based on materials such as C18 and macroporous resins [36,37,38]. However, it cannot be purified well in a cycle that has strict requirements for loading the amount of the sample, flow rate, type and volume of elution, and time [38]. Even the use of fraction collection in a cycle is also imperfect. To obtain a high-purity product, multiple iterations of separation or combination with other methods are required, which makes the whole process complex and expensive. Therefore, the development of new materials and methods for the efficient and simple isolation and purification of mogroside V is a hot topic.
Boronic acids can be reversibly covalently bound to diol groups of molecules [39]. Thus, silica, agarose, cellulose, and polyacrylamide polymer with boronic acid ligand are widely used as affinity ligands for capturing diols’ substances, like sugars, ribonucleosides and ribonucleotides, nucleic acids, glycosylated polymers, etc. [40,41]. As far as we known, there is little in the literature regarding the purification of mogroside V by a boronic acid-modified absorbent. Mogroside V is a triterpene glucoside. It contains five glycosyl ligands and a large number of diols [27], which can combine with boronic acid functional groups in theory. Thus, we utilized the affinity of boronic acid for diols to prepare a phenylboronic acid-functionalized silica gel adsorbent (SiO2-GP-APBA). The synthesis route was investigated and SiO2-GP-APBA was used to purify mogroside V from the crude extract of Siraitia grosvenorii for the first time. The adsorption performance, separation, and purification ability of a boronic acid-functionalized affinity silica gel to improve the purity of mogroside V were investigated, which could provide the theoretical basis for the industrial preparation of high-purity mogroside V. In addition, the inhibitory effect of the mogroside V on α-glucosidase was analyzed for the first time.
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Silica gel (SiO2, 200–300 mesh) was from Yantai Xinnuo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. (Shandong, China). The 3-glycidyloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (GPTES) was from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The 3-aminophenylboronic acid monohydrate (3-APBA) was from Shanghai Bid Pharmatech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Sodium dihydrogen phosphate (NaH2PO4, 99%) was from Tianjin Kawin Technology Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China). Disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4, 99%) was from Tianjin Jieerzheng Chemical Trade Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China). Chloroform was purchased from Shanghai Saen Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The standard mogroside V was purchased from Beijing Soleibao Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Toluene, acetone, sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 99%), methanol, ethanol, hydrochloric acid (HCl, 36~38%), potassium bromide (KCl, spectrography), dichloromethane, diethyl ether, and other chemicals were from Tianjin Jiangtian Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China). The Siraitia grosvenorii crude extract containing mogroside V was a gift from Professor Zhang Zesheng, Tianjin University of Science & Technology. The α-glucosidase (78.08 U/mg) was from Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The p-nitrobenzene-α-glucoside (98%) and p-nitrophenol (99.5%) were from Bide Pharmatech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Unless otherwise stated, all chemicals were of analytical grade and used without further purification. Deionized water was from Tianjin Yongyuan Distilled Water Manufacturing Center (Tianjin, China).
2.2. Instruments
SiO2-GP-APBA and its intermediates were characterized by a TENSOR 27 Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR, Bruker, Karlsruhe, Germany), Nanosem 430 scanning electron microscope (SEM, FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA), JEM100CXII transmission electron microscope (TEM, JEOL, Japan), PHI-1600 ESCA X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS, Thermo Scientific, USA), and Optima2100DV inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer (ICP-OES, Perkin Elmer, Norwalk, CT, USA). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) based on a TA 550 analyzer (Discovery, New Castle, DE, USA) was carried out to determine weight loss of SiO2-GP-APBA as temperature under N2 flow at a heating rate of 10 °C/min ranging from 30–800 °C. The purified mogroside V was identified by a Bruker Advance 600 MHz nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer (NMR, Bruker, Germany). The model of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) used in this experiment was LC3000 from Chuangxintongheng (Beijing, China). Activity analysis of α-glucosidase was performed in a capillary electrophoresis. It was composed of a Spectra 100 full wavelength UV detector (Spectra-Physics, Santa Clara, CA, USA), a HB-Z153-3AC DC power supply from Zhejiang Hengbo Electrical Appliance Manufacturing Co., Ltd. (Zhejiang, China), and a N-2000 chromatographic workstation from Institute of Intelligent Information (Zhejiang, China).
2.3. Preparation of Boronic Acid-Functionalized Affinity Silica Gel
The synthetic route of SiO2-GP-APBA is shown in Figure 1. It consisted of two steps. The detailed procedures were as follows:
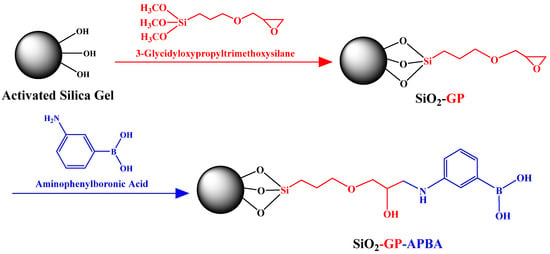
Figure 1.
The synthetic route of SiO2-GP-APBA.
2.3.1. Preparation of Epoxy Groups-Functionalized Silica Gel (SiO2-GP)
Silica gel of 50 g was dispersed in 6 mol/L HCl of 200 mL. After 6 h of heating and stirring at 60 °C, the solid was washed with deionized water to a neutral pH and dried in a vacuum oven to obtain acidified silica gel. The acidified silica gel was placed in a vacuum oven at 130 °C for 3 h to obtain the activated silica gel. Then, 3 g of the activated silica gel was dispersed in 60 mL of distilled toluene. After addition of 5 mL GPTES, the mixture was continually stirred for 24 h at 110 °C under nitrogen protection [42]. The product was washed three times by toluene and acetone in turns. After drying, SiO2-GP was obtained.
2.3.2. Preparation of Phenylboronic Acid-Functionalized Silica Gel
Then, 400 mg of 3-aminophenylboronic acid monohydrate was added to 60 mL of deionized water and sonicated for 20 min to dissolve it fully. The pH of the solution was adjusted by NaOH to 7.5. Then, 1.5 g of SiO2-GP was dispersed in the above solution, and the mixture was stirred for 24 h at 90 °C under nitrogen protection. The product was washed three times by dichloromethane, acetone, and diethyl ether in turns. After drying, SiO2-GP-APBA was obtained.
2.4. Determination of Mogroside V
The analysis of mogroside V was performed by HPLC. The chromatographic conditions were as follows. The separation column was a 1Ailtma-C18 column (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm). The column temperature was 32 °C. The mobile phase was the mixture of acetonitrile and H2O (22:78, v/v). The flow rate was 1.0 mL/min. The detection wavelength was at 203 nm, and the injection volume was 10 μL.
2.5. Adsorption of SiO2-GP-APBA to Mogroside V
The 10 mg/mL stock solution of mogroside V was prepared by dissolving 200 mg of mogroside V in 20 mL deionized water. All testing of the mogroside V solutions at different concentrations (1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 mg/mL) was performed by diluting the stock solution with deionized water. NaOH of 1.0 mol/L or HCl of 1.0 mol/L was used to adjust the pH to 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9. SiO2-GP-APBA of 20 mg was incubated with 5 mL of the mogroside V solution for 150 min at 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, or 80 °C. After incubation, the supernatant was separated through centrifugation at 4000 rpm for 10 min. The concentration of mogroside V was measured by HPLC. All experiments were repeated at least three times. The optimal procedure was performed in the isolation of mogroside V from the crude extract of Siraitia grosvenorii.
The adsorption capacity of the mogroside V (mg/g) was determined by the following Equation (1):
where C0 and Ce are the initial and equilibrium mogroside V concentrations (mg/mL), respectively, V is the volume (mL) of mogroside V solution, and m is the mass (mg) of adsorbent.
2.6. Desorption of Mogroside V from SiO2-GP-APBA
Mogroside V solution of 4 mg/mL was loaded to the SPE column with 20 mg SiO2-GP-APBA. Each 5 mL effluent was collected for analysis until adsorption saturation. Then, ethanol aqueous solutions at pH 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10 adjusted by NaOH were selected as the elution solvent, respectively. All experiments were repeated at least three times. The best desorption conditions were in the release of mogroside V from the crude extract of Siraitia grosvenorii.
The desorption rate of mogroside V from SiO2-GP-APBA was determined by the following Equation (2):
where Cd is the concentration of mogroside V in desorption solution and Vd is the volume (mL) of desorption solution.
2.7. Semi-Preparation and Further Purification of Mogroside V
After the initial purification of the mogroside V crude extract by SiO2-GP-APBA, it was further prepared and purified by LC-6AD semi-preparative liquid chromatography (China Shimadzu Enterprise Management Co., Ltd.) to obtain the highly purified mogroside V. Chromatographic separation was carried out on a C18 column (30 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm). The mobile phase was the mixture of acetonitrile and H2O (22:78, v/v). The flow rate was 15 mL/min. The detection wavelength was at 203 nm. The purified mogroside V was checked by HPLC and NMR.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Absorbent with Boronic Acid Group
Although mogroside V was never purified by the absorbent with the boronic acid group, in theory it could specifically be absorbed due to its five glycosyl ligands and a large number of diols. Furthermore, the size of the boronic acid group in the absorbent may affect the absorption capacity. Thus, the synthetic route of the absorbent was investigated, and its absorption capacity to mogroside V was used as the evaluation criterion. As far as we know, the separation of the target from the other components is a precondition for an accurate analysis. Thus, the chromatographic separation conditions of mogroside V in HPLC were optimized by investigating the mobile phase, flow rate, injection volume, and column temperature. The HPLC analysis was performed according to the optimized chromatographic conditions. The retention time of mogroside V was about 28 min. The linear range of standard mogroside V was obtained from 0.18 to 4.4 μg with an average recovery of 99.05% (RSD = 0.78%, n = 8). It was seen that the results of the analysis of mogroside V by this method were stable with good recoveries and could be used for the determination of mogroside V in a solution before and after adsorption.
After this, three different synthetic routes of boronic acid-bonded silica gel were investigated (see Figure 1 and Figure S1). The first route was to prepare chloropropyl-bonded silica gel and then APBA reacted with chloropropyl to obtain a boronic acid-modified silica gel. The maximum absorption capacity to mogroside V was only 133.19 mg/g. After testing the B content using ICP-OES, it was verified that the low absorption ability was due to the low content in the boronic acid group (99.4 μmol/g). The second route was to graft 3-glycidyloxypropyl to the surface of an irregular silica gel; then, the amino group in APBA reacted with the epoxy. It could absorb 206.74 mg/g of mogroside V, indicating this route was better than the first one. The third route included three steps. First, aminopropyl was bonded to the surface of the silica gel. Then, glutaraldehyde was employed as the middle linker to obtain a glutaraldehyde-substituted silica gel by reacting with an amino group under a pH 7.4 phosphate buffer. Subsequently, the free aldehyde group reacted with the amino group in APBA to obtain a boronic acid-modified silica gel. This type of absorbent could absorb 205.42 mg/g of mogroside V, which was similar to the second one. Considering the additional steps and the residual aldehyde groups, which have reducing properties [43] that might affect the structure of the target, the second route was adopted.
3.2. Characterization of SiO2-GP-APBA
SiO2-GP-APBA and its intermediates were characterized by FT-IR, SEM, TEM, XPS, ICP-OES, and TGA.
The FT-IR spectra of SiO2-GP-APBA as well as its intermediates are plotted in Figure 2a. The peak at 3449 cm−1 was the stretching vibrational peak of -OH, and the peak at 1627 cm−1 was the vibrational absorption of the adsorbed water. In the intermediate SiO2-GP and final absorbent SiO2-GP-APBA, the absorption peaks at 2938 cm−1 and 2862 cm−1 were typical peaks of methylene, indicating the successful bonding of the epoxy ring to the silica gel. Comparing SiO2-GP with SiO2-GP-APBA, most of the peaks were covered by Si-O-Si at 1097 cm−1. The characteristic absorption of the benzene ring at 1424 cm−1 and the vibrational absorption peak of B-O at 1357 cm−1 were easily found, fully indicating the successful obtaining of boronic acid-functionalized silica [44].
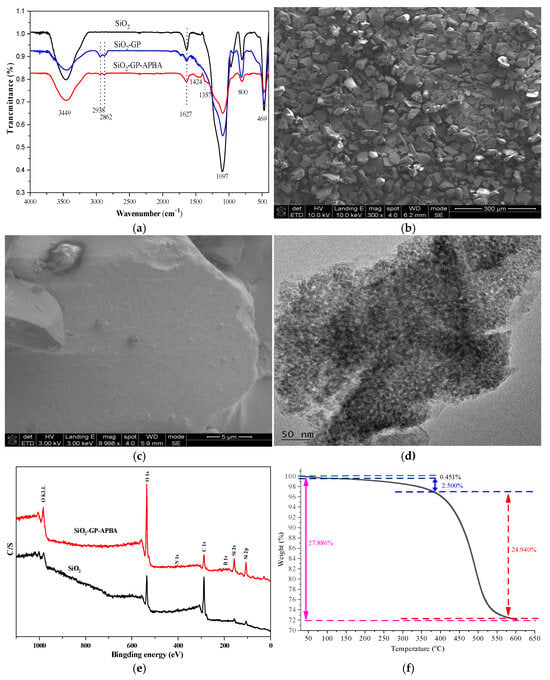
Figure 2.
The FT-IR spectra of SiO2-GP-APBA and its intermediates (a); the SEM images of SiO2-GP-APBA (b,c); the TEM image of SiO2-GP-APBA (d); XPS spectra of SiO2-GP-APBA and SiO2 (e); and TGA curve of SiO2-GP-APBA (f).
The surface morphology of the prepared SiO2-GP-APBA was observed by SEM; results are shown in Figure 2b,c. It can be seen that SiO2-GP-APBA was irregularly shaped and its particle size was in the range of 30–100 μm. When it was decreased to 5 μm, it was found that the surface was rough, uneven, porous, and had concavities, which effectively provided a large number of adsorption sites and facilitated adsorption [45]. The pores and concavities structure of SiO2-GP-APBA were further verified by TEM, as shown in Figure 2d.
XPS was used to analyze the elemental information in the silica gel and boronic acid-modified silica gel. Their XPS spectra are shown in Figure 2e. It can be seen that there were C, O, and Si peaks. By comparing the two spectra, we see the peaks at 189 eV and 400 eV showing the signals of element B and element N, demonstrating the successful grafting of the functionalized group 3-aminophenylboronic acid to the surface of the silica. The composition of the B and N elements was 0.18% and 0.21%, respectively. The content of the B element in SiO2-GP-APBA was exactly determined by ICP-OES. It was 163.1 μmol/g, which indicated the boronic acid functional groups attached to the silica matrix.
The thermostability of SiO2-GP-APBA was investigated by TGA. On the TGA curve in Figure 2f, when the temperature rose from 30 °C to 130.11 °C, the weight of the SiO2-GP-APBA only decreased by 0.451%. It indicated there was a little intermolecular water through physical absorption. With the increase in temperature to 380.20 °C, a sustained weight loss (2.500%) was observed, which was due to intramolecular dehydration (like Si-OH and -OH). When the temperature further increased to 595.86 °C, the weight of the SiO2-GP-APBA significantly decreased by 24.940%. The rapidly dropping curve in the range of 380.20–595.86 °C indicated the decomposition of organic matter bound to the silica surface. These data showed SiO2-GP-APBA was stable below 380.20 °C.
3.3. The Adsorption of SiO2-GP-APBA to Mogroside V
3.3.1. Effect of Time on Adsorption to Mogroside V
The study on adsorption kinetics was significant, providing the information on adsorption efficiency. Thus, a different time was investigated. Then, 20 mg of SiO2-GP-APBA was added to 5 mL of the mogroside V solution; the supernatant was sampled at 10, 30, 60, 90, 120, and 150 min and measured.
The kinetic curve for the SiO2-GP-APBA is shown in Figure 3a. Data showed the adsorption amount of mogroside V increased significantly with time, and the adsorption equilibrium (205.0 mg/g) was reached when the adsorption time was 120 min. As the time continued to increase to 150 min, the adsorption amount (204.8 mg/g) did not further increase. Therefore, to ensure the adsorption equilibrium, 120 min or more was selected as the best.
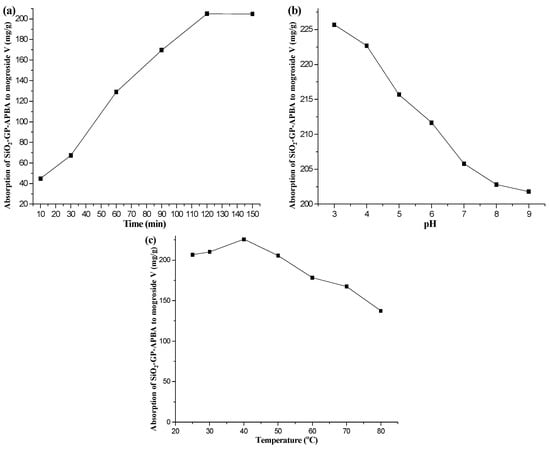
Figure 3.
Effect of time (a), pH (b), and temperature (c) on the absorption capacity of SiO2-GP-APBA to mogroside V.
3.3.2. Effect of pH on Adsorption to Mogroside V
The pH of a solution not only affects the absorbent but also the analyte. Thus, the effect of different pH values on the adsorption of mogroside V to SiO2-GP-APBA was investigated. Twenty mg of SiO2-GP-APBA was added to 4 mg/mL of the mogroside V solution with a pH from 3 to 9, which was adjusted by 1 mol/L HCl or NaOH. After shaking for 150 min, the mixture was centrifuged at 4000 rpm and the supernatant was measured. The results are shown in Figure 3b. It was found that, although the adsorption capacities were all in the range of 200–230 mg/g in the pH range of 3–9, pH affected the adsorption performance of mogroside V to SiO2-GP-APBA. The best adsorption performance was found at pH 3. The adsorption performance gradually decreased with an increasing pH. It may have been because of the diol reversible covalent reaction of the boronic acid group, which was most likely to occur in the opposite direction under neutral and basic conditions, reducing its adsorption performance [46]. The pKa value of 3-APBA in aqueous solution was 8.9; when the pH was close to or reached the pKa of the 3-APBA, the boronic acid group dissociated more easily after covalently binding to the diol of mogroside V. Therefore, its adsorption effect was significantly reduced when the pH reached 9.
3.3.3. Effect of Temperature on Adsorption to Mogroside V
Temperature can greatly affect the analyte and the functional groups on an absorbent. Thus, the effect of temperature on the adsorption of mogroside V to SiO2-GP-APBA was investigated. Twenty mg of SiO2-GP-APBA was added to 4 mg/mL of the mogroside V solution with temperature settings at 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, and 80 °C. After shaking for 150 min, the mixture was centrifuged at 4000 rpm and the supernatant was measured. The results are shown in Figure 3c. At a low temperature (25–40 °C), the absorption to mogroside V slightly increased. The adsorption performance decreased with the increase in temperature above 40 °C due to the decreased activity of boronic acid with the increasing temperature. On the one hand, the concentration of mogroside V decomposed easily under high temperature. In addition, because of the cost, the adsorption process was performed at room temperature.
3.3.4. Adsorption Isotherm
As far as we know, the initial concentration of the substance to be adsorbed can also have an effect on the adsorption. Thus, the effect of the mogroside V concentration on the adsorption of the boronic acid-functionalized silica was investigated at room temperature. The mogroside V concentrations were sequentially prepared as 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 mg/mL, respectively. Twenty mg of SiO2-GP-APBA was added to 5 mL of the mogroside V solutions. After shaking for 150 min, the mixture was centrifuged and the supernatant was measured. The results are shown in Figure 4a. The adsorption amount increased when the initial concentration increased from 1 mg/mL to 3 mg/mL. This is because the adsorption sites were not fully involved in the adsorption, so that the adsorption did not reach saturation. When the initial concentration was 4 mg/mL, the adsorption amount reached the maximum. When the initial concentration was increased to 5 mg/mL, the adsorption amount did not change significantly, indicating that all adsorption sites were involved in adsorption at this time and the adsorption reached saturation.
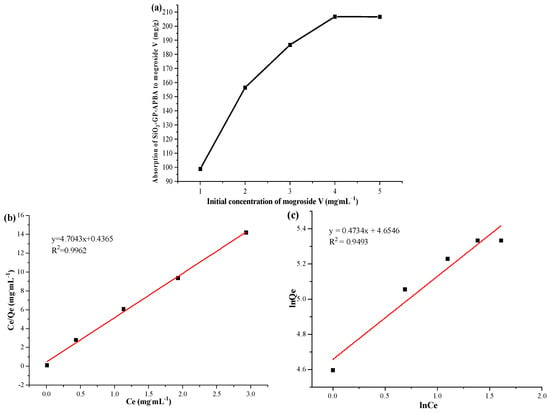
Figure 4.
Effect of initial concentration (a) on the absorption of SiO2-GP-APBA to mogroside V, Langmuir isotherm (b), and Freundlich isotherm (c).
The results of the adsorption measurements at equilibrium were analyzed using two different adsorption models, the Langmuir and Freundlich models. The Langmuir model assumed a monolayer adsorption, which means adsorption molecules adsorbed on the surface of the adsorbent had the same adsorption activation energy. The Freundlich model assumed a multilayer adsorption, which means there were many adsorption sites on the adsorbent. The adsorption sites had different levels of free energy, which could adsorb multiple molecules. These two models can be expressed using Equations (3) and (4).
where Qe is the adsorption capacity at equilibrium (mg/g), Ce is the concentration of the solution at equilibrium (mg/mL), Q0 is the saturation adsorption capacity (mg/g), b represents the equilibrium adsorption constant and the adsorption affinity, and n is the Freundlich constant. When n > 1, the adsorption process occurs easily; it is difficult to adsorb when n < 0.5 and Kf is the binding constant.
The fitting curves of mogroside V adsorption are shown in Figure 4b,c. It can be seen that the R2 of the Langmuir model (0.9962) was larger than that of the Freundlich model (0.9493). The adsorption behavior was consistent with the Langmuir adsorption model. This verified that this adsorption mode of the SiO2-GP-APBA to mogroside V was monolayer adsorption. The specific values are shown in Table 1. According to the slope and intercept of the Langmuir equation, it could be concluded that the maximum adsorption capacity of the SiO2-GP-APBA for mogroside V was around 212.57 mg/g, which was similar to the measured value, 206.74 mg/g at room temperature.

Table 1.
Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm parameters.
3.4. Desorption of Mogroside V from SiO2-GP-APBA
To select a suitable solution for the rapid desorption of mogroside V from the SiO2-GP-APBA, after saturation adsorption of the mogroside V, six parts of the SiO2-GP-APBA were eluted by 20 mL of ethanol at pH 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10 aqueous solutions adjusted by NaOH, respectively. As shown in Figure 5, the results showed ethanol only eluted 43.27% of mogroside V. The mogroside V was easily covalently broken in an alkaline solution, and the desorption rate was as high as 98.31% when the pH was 9. However, mogroside V is commonly used in the food industry, so elution with water at pH 7 is the most safe and reliable method. When a solution at pH 7 was used, the recovery could reach 96.36%, which enabled the effective desorption of mogroside V and reuse of the borated silica gel. After analyzing the released solution by HPLC, it showed the purity of mogroside V dramatically increased from 35.67% to 76.34% (see Figure 6), which proved the preliminary isolation was effective. There are many hydroxyl groups, -C=C-, diol, and steroid mother nucleus structures in a mogroside V molecule. The diol structure could produce a specific boronate affinity with the boric acid group in the SiO2-GP-APBA, which formed five- or six-membered cyclic ester. The SiO2-GP-APBA also could absorb mogroside V through electrostatic means, hydrogen bond, hydrophobic interactions, etc. These co-contributed the high isolation efficiency of the SiO2-GP-APBA to the mogroside V.
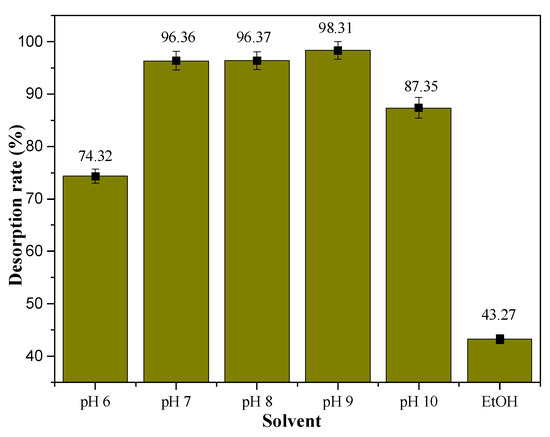
Figure 5.
Desorption of mogroside V from SiO2-GP-APBA.
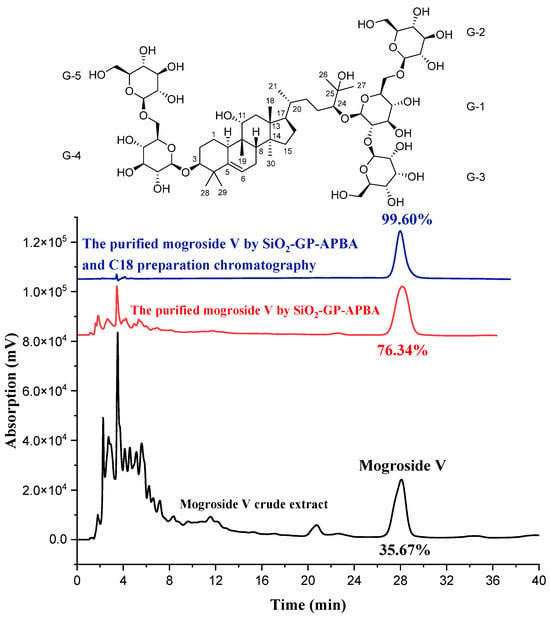
Figure 6.
Typical chromatograms of mogroside V.
3.5. Further Purification of Mogroside V
A high purity of mogroside V is beneficial to the pharmacological application of mogroside V. In order to obtain a purer mogroside V product, the desorption of mogroside V from SiO2-GP-APBA was combined with semi-preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. The purity of mogroside V could be further improved to 99.60% (see Figure 6). The obtained product was dried to a white powder, and its structure was verified using NMR. The 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6), 13C NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6), two-dimensional spectra, and data are shown in Figures S2–S6 and Table 2. From the NMR data, it is known that its chemical formula is C60H102O29.

Table 2.
1H and 13C NMR data of mogroside V.
The 1H NMR spectrum exhibited the presence of eight methyls, eight methylenes, and seven methines, with the majority of proton signals concentrated in the range of 0–3.5 ppm. A proton signal at δH 5.34 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 1H, H-6), in conjunction with the carbon signals at δC 143.6 (C-5) and 117.2 (C-6), indicated the presence of a double bond. In addition, five anomeric protons at δH 4.36 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H, G-1), 4.16 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H, G-2), 4.32 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, G-3), 4.14 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, G-4), and 4.53 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H, G-5), in combination with thirty carbon signals, revealed that five β-D-glucopyranosyl units were present in mogroside V. The 1 → 6 linked β-D-glucobiosyl substituent at C-3 and 2,6-branched β-D-glucotriosyl moiety at C-24 were identified on the basis of the HMBC spectrum. The 1H and 13C NMR spectral data in Table 2 were assigned based on the COSY, HSQC, and HMBC spectra and verified mogroside V. These results also were consistent with those reported in the literature [47] for mogroside V, further confirming its structure. Therefore, the tandem method of SiO2-GP-APBA and semi-preparative HPLC has potential for rapid and simple purification to obtain a high-purity mogroside V.
3.6. Inhibition of Mogroside V on α-Glucosidase
It was reported that mogroside crude extracts exhibited hypoglycemic activity [34,35]. As far as we know, there is no direct determination about hypoglycemic activity of mogroside V. Thus, the activity of the characteristic diabetes enzyme, α-glucosidase, was analyzed using capillary electrophoresis. The p-nitrobenzene-α-glucoside was hydrolyzed by α-glucosidase to p-nitrophenol. A phosphate buffer of 40 mM (pH7.0) containing 5 mM Mg2+ was used as a running buffer. Under 8000 V, 40 cm/30 cm of total length/effective capillary length, 75 μm inner diameter, and 214 nm, the kinetic constant Km of α-glucosidase activity was calculated by the double reciprocal method. Based on these, the inhibitory effect of the mogroside V on α-glucosidase was tested for the first time. With mogroside V, the activity kinetic constant Km,app also was obtained by the double reciprocal method. The inhibitor constant KI of mogroside V on α-glucosidase was calculated according to the following Equation (5).
where [I] is the concentration of mogroside V.
Results are shown in Figure 7. Without mogroside V, the double reciprocal linear regression equation is y = 0.0572x + 0.1209 (R2 = 0.998) and the kinetic constant of α-glucosidase is 0.473 mM. With mogroside V, the double reciprocal linear regression equation changed to y = 0.3320x + 0.1315 (R2 = 0.995), corresponding to Km,app = 2.525 mM. The inhibitory constant KI value of mogroside V on α-glucosidase was 46.11 μM. This indicates that mogroside V was effective for α-glucosidase.
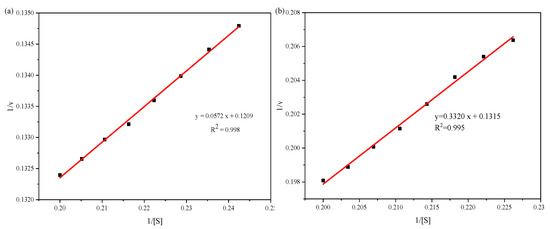
Figure 7.
The regression line using double reciprocal method to determine the α-glucosidase kinetic constant (a) and inhibitory constant of mogroside V (b).
3.7. The Advantages of SiO2-GP-APBA
The SiO2-GP-APBA showed significant advantages over macroporous resins in the purification of mogroside V. In terms of adsorption efficiency, the SiO2-GP-APBA could dramatically increase the purity of mogroside V to 76.34% at room temperature after a simple absorption and desorption cycle, which was superior to 71.1% of the macroporous resin-type LX-100B and 63.3% of D101 [48]. In terms of process economy, the isolation process did not require a high-temperature or high-concentration ethanol elution. Operating at room temperature significantly reduced energy consumption and solvent costs. Its analytical recovery rate under the pH7 condition was as high as 96.36%, which was superior to the elution mode of macroporous resins that relied on these complex parameters (such as flow rate and ethanol gradient) [49]. In terms of specificity, the boric acid-functionalized silica gel precisely targeted glycoside components through a chemical bond based on the specific boronate affinity, selectively adsorbing to reduce impurity interference, while macroporous resins relied on physical adsorption mechanisms and were easily affected by coexisting substances. Although macroporous resins (such as LX-T28) have the convenience of parameter regulation in large-scale production, the SiO2-GP-APBA was more comprehensively competitive in terms of purity, efficiency, and cost effectiveness, providing a better choice for the preparation of high-purity mogroside V from natural products.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the specific effect of boronic acid on diol was utilized to study the application of adsorption and desorption of SiO2-GP-APBA on mogroside V. A series of adsorption conditions were optimized and the best conditions were 4 mg/mL of mogroside V in 20 mg of SiO2-GP-APBA, pH 3, at room temperature for more than 120 min. At room temperature, the maximum adsorption capacity was 206.74 mg/g, which was more consistent with the Langmuir model. Furthermore, 96.36% of mogroside V could be released using an aqueous solution at pH 7. SiO2-GP-APBA could rapidly increase the purity of mogroside V in the Siraitia grosvenorii crude extract from 35.67% to 76.34%. Semi-preparative HPLC could further improve the purity of mogroside V to 99.60%, which would be beneficial to its pharmacodynamic application. The inhibitory constant KI value of mogroside V on α-glucosidase was 46.11 μM, which showed potential research significance for the treatment of diabetes. SiO2-GP-APBA is a huge potential absorbent for the effective and low-cost isolation of mogroside V from natural products and supplies a reference for the purification of other substances from a complex matrix.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/separations12060135/s1, Figure S1: The synthetic routes of SiO2-CP-APBA (up) and SiO2-AP-GA-APBA (down); Figure S2: 1H NMR (600 MHz) spectrum of mogroside V recorded in DMSO-d6 at 298 K; Figure S3: 13C NMR (150 MHz) spectrum of mogroside V recorded in DMSO-d6 at 298 K; Figure S4: 1H-1H COSY spectrum of mogroside V recorded in DMSO-d6 at 298 K; Figure S5: 1H-13C HSQC spectrum of mogroside V recorded in DMSO-d6 at 298 K; Figure S6: 1H-13C HMBC spectrum of mogroside V recorded in DMSO-d6 at 298 K.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L. and J.J.B.; methodology, Y.L.; validation, Y.X., L.L. and P.Z.; formal analysis, Y.X. and Y.S.; investigation, Y.X. and L.L.; resources, Y.X.; data curation, Y.X. and L. L.; writing—original draft preparation, P.Z., R.Z. and M.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.L.; supervision, Y.L.; project administration, Y.L.; funding acquisition, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China grant number [No. 21605112].
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this paper are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, X. Advances in oral peptide drug nanoparticles for diabetes mellitus treatment. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 15, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Yang, F.Q.; Tang, P.; Gao, T.H.; Yang, C.X.; Tan, L.; Yue, P.; Hua, Y.N.; Liu, S.J.; Guo, J.L. Regulation of the intestinal flora: A potential mechanism of natural medicines in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113091–113105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF diabetes atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119–109132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Woo, S.L. Hepatic insulin production for type 1 diabetes. Trends Inendocrinology Metab. 2001, 12, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heise, T.; Meneghini, L.F. Insulin stacking versus therapeutic accumulation: Understanding the differences. Endocr. Pract. 2014, 20, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.M.; Lakey, J.R.; Ryan, E.A.; Korbutt, G.S.; Toth, E.; Warnock, G.L.; Kneteman, N.M.; Rajotte, R.V. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, F. Advances in anti-type 2 diabetes drug research. Chin. Remedies Clin. 2017, 17, 833–834. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Saldivar, G.; Millan-Alanis, J.M.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, J.G.; Sanchez-Gomez, R.A.; Obeso-Fernandez, J.; McCoy, R.G.; Maraka, S.; Brito, J.P.; Ospina, N.S.; Oyervides-Fuentes, S.; et al. Treatment burden and perceptions of glucose-lowering therapy among people living with diabetes. Prim. Care Diabetes 2022, 16, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Yang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, G. Characteristics of sugar substitutes and evaluation of their advantages and disadvantages to human health. Sugarcane Canesugar 2022, 51, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Munoz, R.; Correa-Delgado, M.; Cordova-Almeida, R.; Castro-Munoz, R.; Correa-Delgado, M.; Córdova-Almeida, R.; Lara-Nava, D.; Chávez-Muñoz, M.; Velásquez-Chávez, V.F.; Hernández-Torres, C.E.; et al. Natural sweeteners: Sources, extraction and current uses in foods and food industries. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 130991–131008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J.A.; Akkermans, S.; Nimmegeers, P.; Van Impe, J.F. Bioproduction of the recombinant sweet protein thaumatin: Current state of the art and perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 695–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, C.R.; Boullata, J.; Mccauley, L.A. The potential toxicity of artificial sweeteners. Aaohn J. 2008, 56, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Wang, J.X.; Hu, J.J.; Feng, M.; Jiang, H.M.; Li, M.Q.; Lu, K.H.; Yang, X.G.; Liang, X.W. Mogroside V attenuates constant light exposure-induced accumulation of body fat mass in mice. J. South. Agric. 2022, 53, 2624–2633. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Lin, S.; Han, C.; Zhu, Z.; Hou, X.; Long, Z.; Xu, K. Rapid identification and quantification of five major mogrosides in Siraitia grosvenorii (Luo-Han-Guo) by high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole linear ion trap tandem mass spectrometry combined with microwave-assisted extraction. Microchem. J. 2014, 116, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.Z.; Liao, N.; Zhang, B.; Fan, B. Research on development and application of natural sweeteners. China Food Addit. 2022, 33, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Li, L.; Qin, J.; Lan, J.Y.; Jiang, S.Y.; Li, F. Research advances on Siraitia grosvenorii. J. South. Argiculture 2011, 42, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Shi, H.; Zhang, K.; Qin, X.; Guo, Y.; Ma, X. Liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of multiple sweet mogrosides in the fruits of Siraitia grosvenorii and its marketed sweeteners. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 4124–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.A.; Tomoda, M.; Murata, Y.; Inui, H.; Sugiura, M.; Nakano, Y. Antidiabetic effect of long-term supplementation with Siraitia grosvenori on the spontaneously diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rat. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Z. Mogroside derivatives exert hypoglycemics effects by decreasing blood glucose level in HepG2 cells and alleviates insulin resistance in T2DM rats. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 63, 103566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Chen, W.; Song, Y.; Xie, B.J. Efficacy study on Siraitia Grosvenori powder and its extracts on reducing blood glucose in diabetic rabbits. Food Sci. 2003, 24, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, X. The metabolism of a natural product mogroside V, in healthy and type 2 diabetic rats. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1079, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Wang, J.; Qi, X.Y.; Xie, B.J. The antioxidant activities of natural sweeteners, mogrosides, from fruits of Siraitia grosvenori. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 58, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, W.; Zhiren, Z.H.U.; Yingming, P.A.N.; Wang, H.; Meizhen, H.O.U.; Lei, Y. Study on antioxidant activity of different solvents extracts of the stem of Siraitia grosvenori. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2008, 29, 57–58,62. [Google Scholar]
- Liqin, Z.; Qi, X.; Chen, W.; Song, Y. Study on in vitro antioxidant activity of extracts from Siraitia grosvenori. Fruits. Food Sci. 2006, 27, 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.; Song, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, N.; Yang, F.; Guan, W.; Liu, J.; Huang, H.; Ho, C.-T.; et al. Effects of Siraitia grosvenorii extracts on high fat diet-induced obese mice: A comparison with artificial sweetener aspartame. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, C.; Wang, W.C.; Sun, S.Y. Research progress of extraction and active of mogroside. Food Res. Dev. 2017, 38, 220–224. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.-Y.; Chen, W.J.; Zhang, L.Q.; Xie, B.-J. Mogrosides extract from Siraitia grosvenori scavenges free radicals in vitro and lowers oxidative stress, serum glucose, and lipid levels in alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, G. Metabolic profiling analysis of Siraitia grosvenorii revealed different characteristics of green fruit and saccharified yellow fruit. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Refinement study of mogroside (V). Ion Exch. Adsorpt. 1999, 4, 364–368. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, D.; Liang, X.; Fang, H.; Yao, C.H. Preparation of mogroside Ⅴ from the fruits of Siraitia grosvenorii by semi-preparative HPLC. Food Sci. 2010, 31, 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Cicek, S.S.; Esposito, T.; Girreser, U. Prediction of the sweetening effect of Siraitia grosvenorii (luo han guo) fruits by two-dimensional quantitative NMR. Food Chem. 2021, 335, 127622–127629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, G.; Li, X. The pharmacokinetic profiles of mogrosides in T2DM rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 282, 114639–114647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Chen, W.; Liu, L.; Yao, P.; Xie, B. Effect of a Siraitia grosvenori extract contalning mogrosides on the cellular immune system of type 1 diabetes mellitus mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 732–738. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Qi, X.; Yu, K.; Lu, A.; Lin, K.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Z. AMPK activation is involved in hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities of mogroside-rich extract from Siraitia grosvenorii (Swingle) fruits on high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, P. Development of a process for separation of mogroside V from Siraitia grosvenorii by macroporous resins. Molecules 2011, 16, 7288–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.H.; Wang, R.; Zhuang, S.; Lin, P.Y.; Lo, Y.C.; Lu, T.J. Biotransformation of mogrosides from Siraitia grosvenorii by Ganoderma lucidum mycelium and the purification of mogroside III E by macroporous resins. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 28, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; He, A.; Huang, H.; Hung, J.; Xiong, Y. Process optimization study on the purification of sweeteners of mogroside (V) based on macroporous adsorbent resin. Sci-Tech Dev. Enterp. 2021, 6, 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Song, H.; Suo, Z.; Li, F.; Jin, Q.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Q. A molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on surface imprinted polymerization and boric acid affinity for selective and sensitive detection of P-glycoproteins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1207, 339797–339805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Yang, R.; Hua, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, W.; Jin, Z. Adsorption characteristics of stevioside and rebaudioside A from aqueous solutions on 3-aminophenylboronic acid-modified poly(divinylbenzene-co-acrylic acid). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Bao, J.J. Preparation and evaluation of a novel and high efficient boronic acid-substituted silica supported Pt catalyst. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 570, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, R.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. Fe3O4@SiO2-Protein A-oHSV/CD63 Ab for capturing virus and exosomes. J. Anal. Test. 2024, 8, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Cheng, M.; Liu, H.; Jia, H.; Nan, Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, Y.; Bao, J.J. Preparation of phenylboronic acid and aldehyde bi-functional groups modified silica absorbent and applications in removing Cr(VI) and reducing to Cr(III). RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 15554–15565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Sun, L.; Yu, B.; Cao, M.; Zhong, S. One-step synthesis of boronic acid group modified silica particles bythe aid of epoxy silanes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 351, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Xu, Q.; Qu, R.; Zhao, G. Removal of transition metal ions from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto a novel silica gel matrix composite adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Springsteen, G.; Deeter, S.; Wang, B. The relationship among pKa, pH, and binding constants in the interactions between boronic acids and diols it is not as simple as it appears. Tetrahedron 2014, 60, 11205–11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedula, V.S.P.; Prakash, I. Cucurbitane glycosides from Siraitia grosvenorii. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2011, 30, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; He, A.; Huang, H.; Huang, J.; Xong, Y. Study on process optimization of purification of mogroside V from Siraitia grosvenorii using macroporous adsorption resin. Enterp. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2021, 42, 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- He, A.; Xiong, Y. Study on competitive adsorption behavior of macroporous adsorption resin on Siraitia grosvenorii mogroside V and purification process optimization. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 48, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).