Separation and Identification of Non-Volatile Sour and Bitter Substances in Amomum villosum L. by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry and Electronic Tongue Analysis, as Well as Their In Vitro Anti-Tumor Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.3. Constructing Detection Methods for Sour and Bitter Substances
2.4. Separation, Collection, and Enrichment of Sour and Bitter Substances in Samples
2.5. Electronic Tongue Evaluations
2.6. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Sour and Bitter Substances
2.7. Cell Viability Detection Through a CCK-8 Experiment
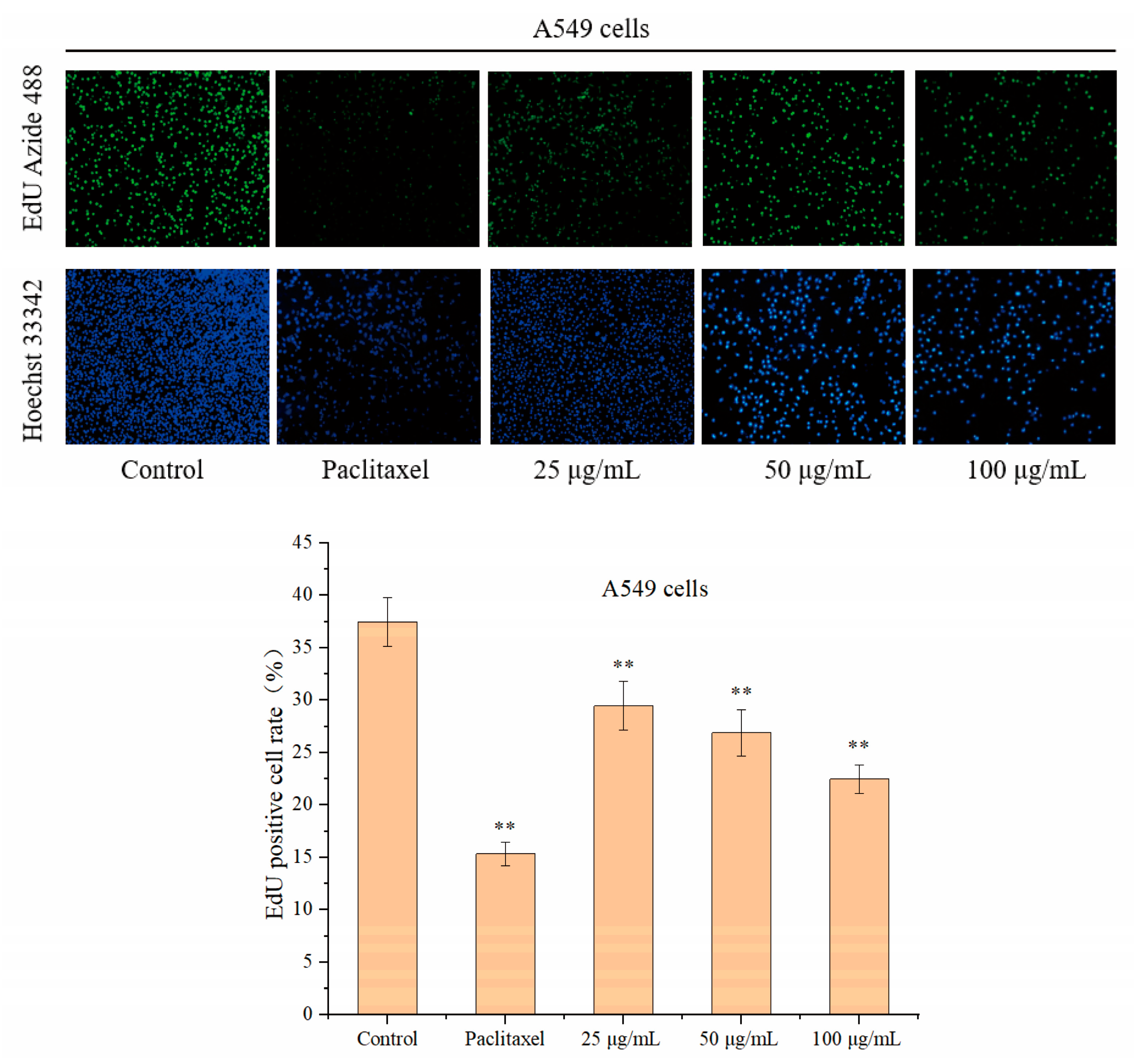
2.8. Cell Proliferation Rate Detection Through EdU Staining Experiment
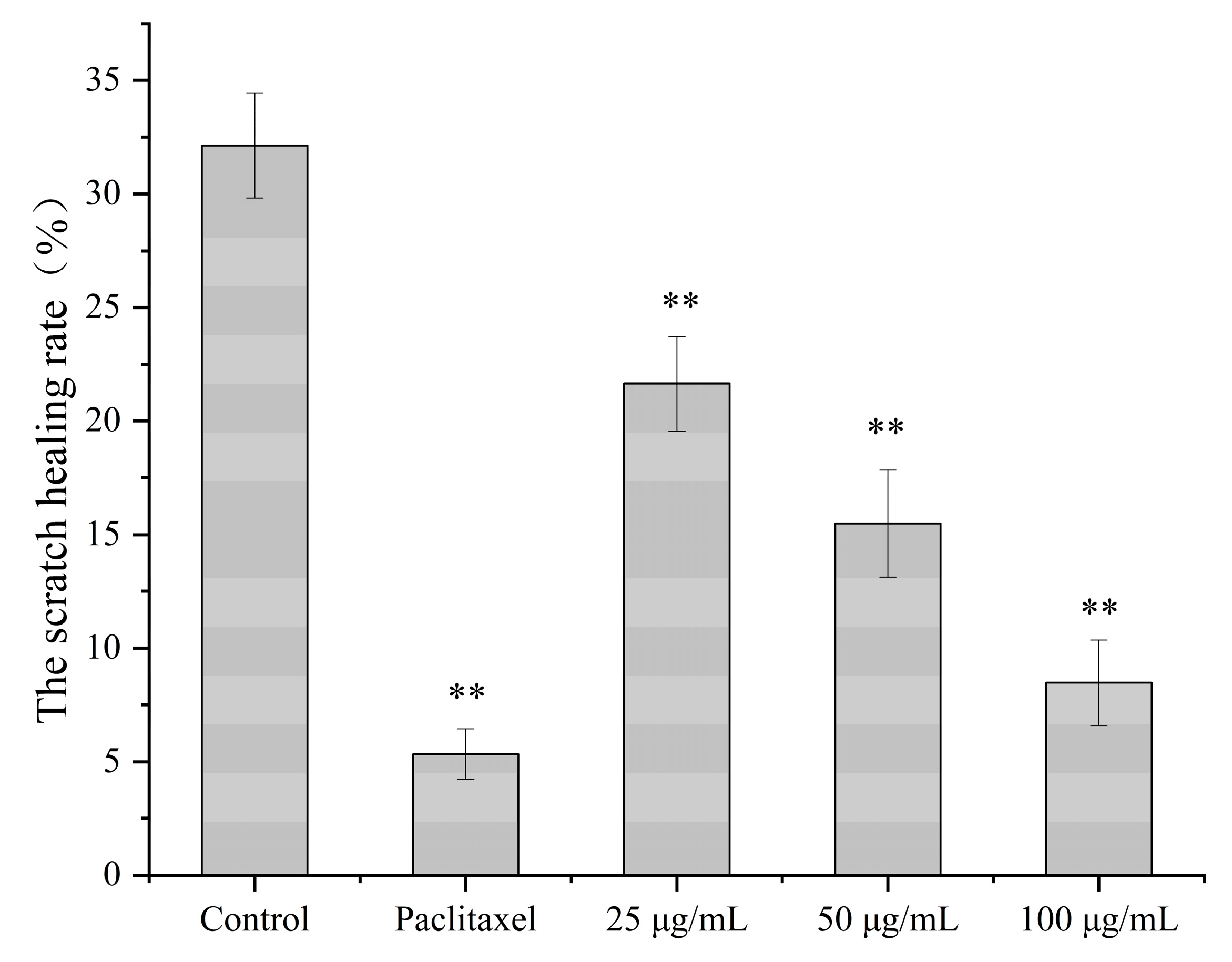
2.9. Cell Migration Ability Detection
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Separation and Identification of Sour and Bitter Substances from Amomum villosum L.
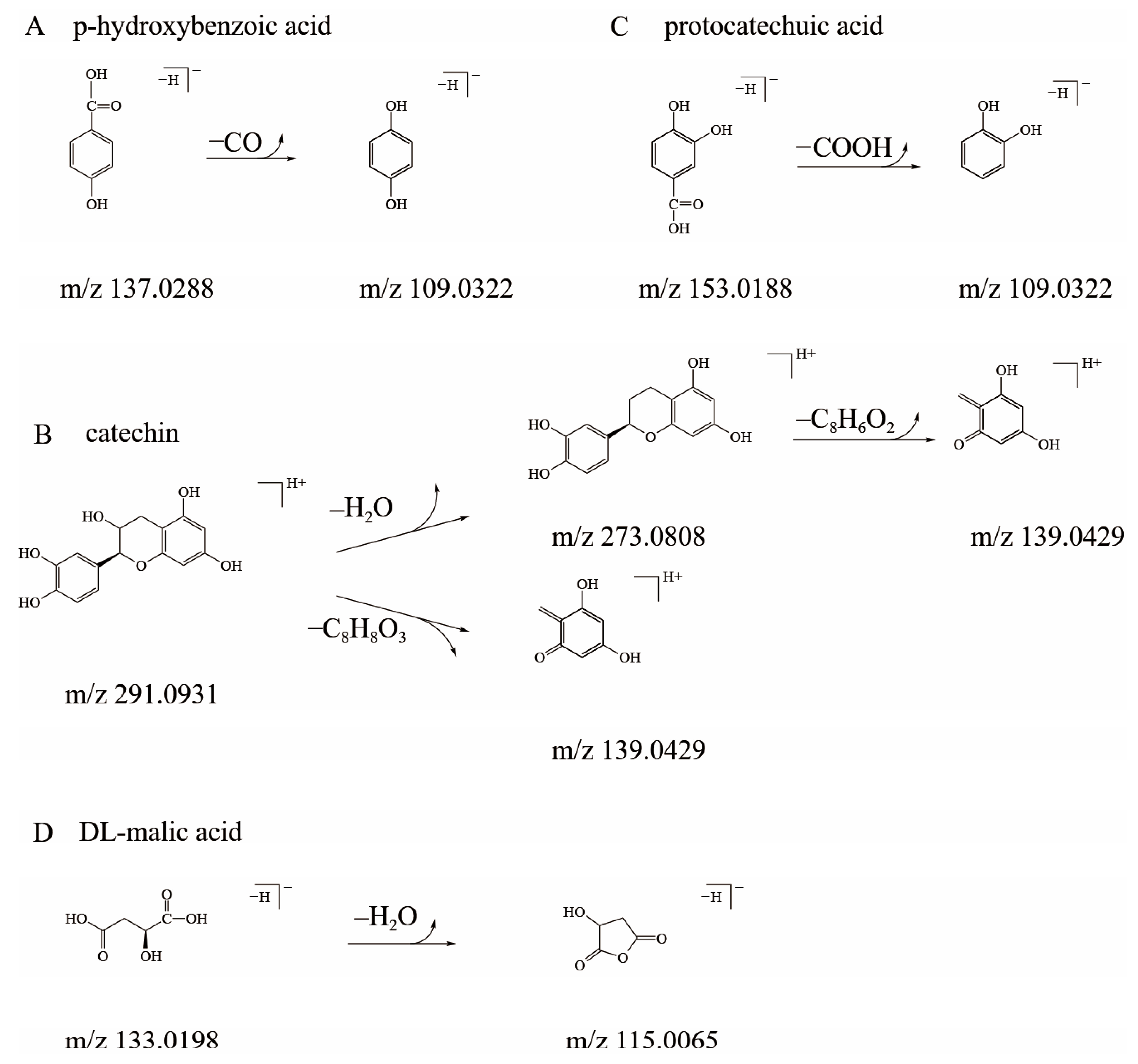
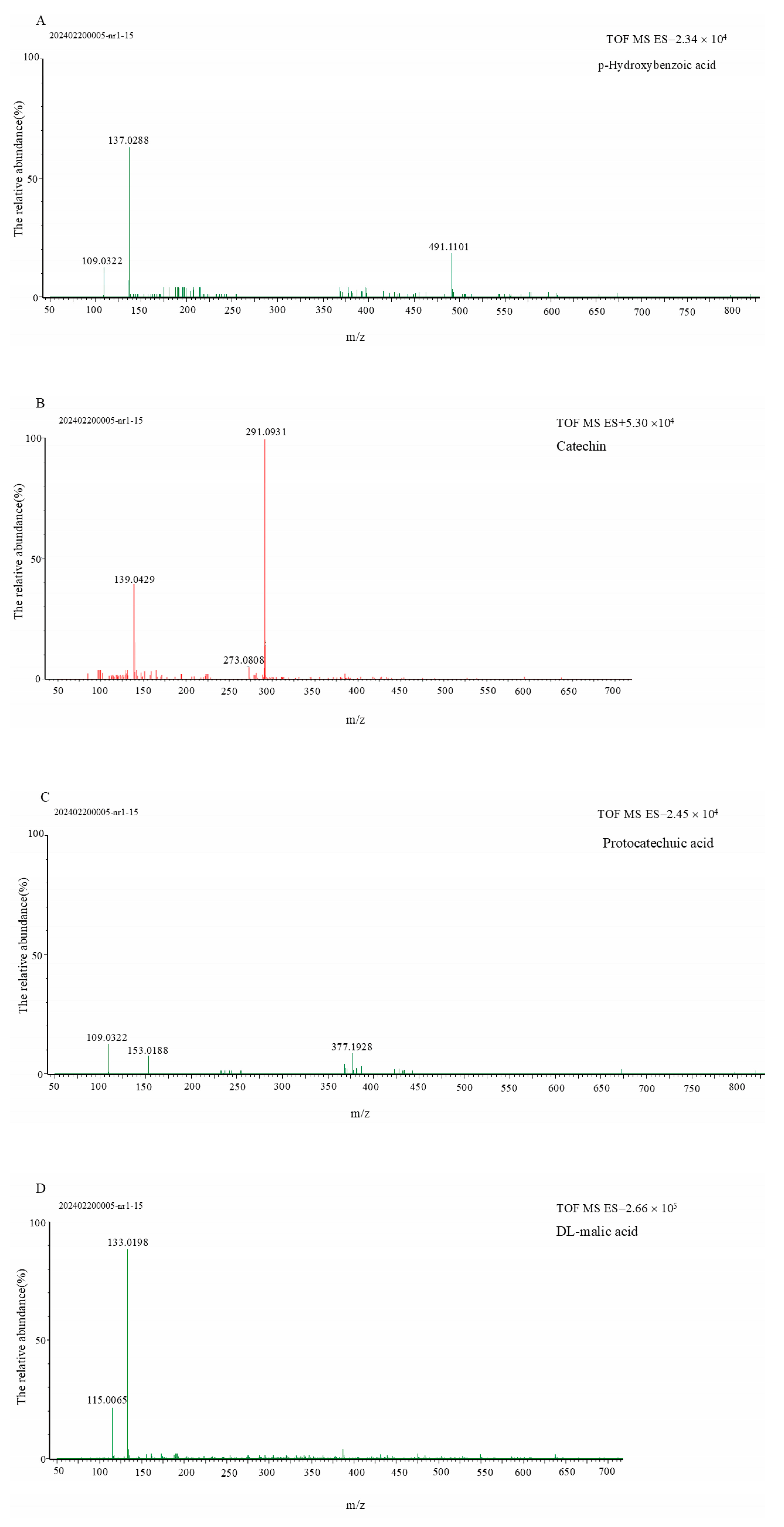
3.2. Qualitative Analysis of Sour and Bitter Fractions in Amomum villosum Extract
3.3. Quantitative Analysis of Sour and Bitter Fractions in Amomum villosum Extract
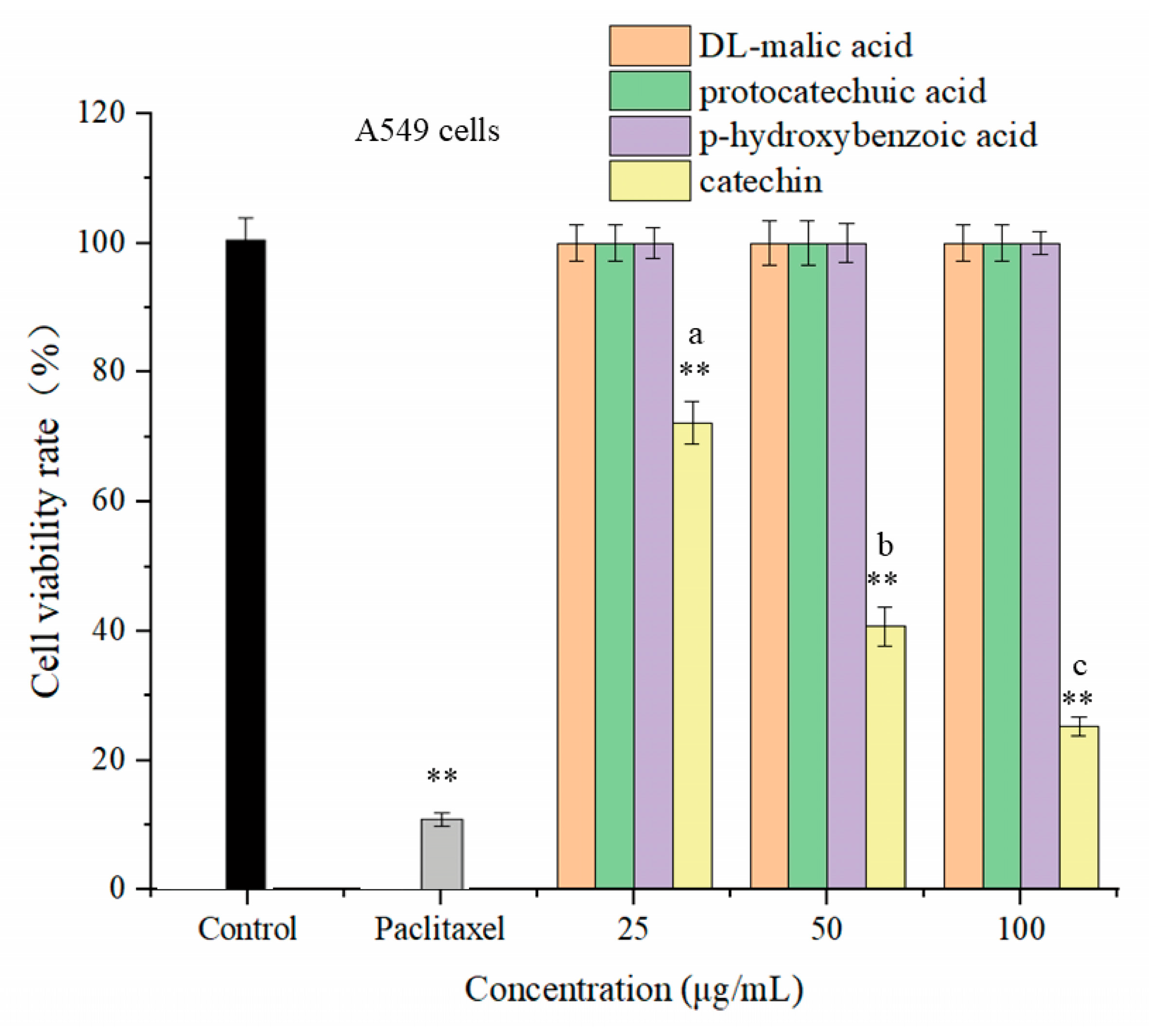
3.4. The In Vitro Anti-Tumor Activity of Sour and Bitter Substances
3.4.1. The Effects of Four Monomeric Substances on the Cell Viability of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer A549 Cells
3.4.2. The Effect of Catechin on the Proliferation of A549 Cells
3.4.3. The Effect of Catechin on the Migration Ability of A549 Cells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, L.; Wang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, B.; Sun, J.; Guo, D.; Wang, D.; Luan, F.; Zou, J.; et al. Amomum villosum Lour.: An insight into ethnopharmacological, phytochemical, and pharmacological overview. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 335, 118615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Liu, K.X.; Li, Y.X.; Sun, D.J.; Li, H.; Chen, L.X.J.C. Three New Labdane-Type Diterpenoids from the Fruits of Amomum villosum and Their Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202301014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Cao, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.J.P. Antibacterial Ingredients and Modes of the Methanol-Phase Extract from the Fruit of Amomum villosum Lour. Plants 2024, 13, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salto, L.; Muniyandi, K.; Porat, R.; Goldenberg, L.; Carmi, N.; Maoz, I. Bitterness and flavanone composition of ‘Redson’ fruit: A new red-fleshed pomelo×grapefruit hybrid. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 133, 106366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.W.; Cheng, H.L.; Hong, C.L.; Tao, L.; Lun, Z.Y.; Da, B.R.; Ying, G.; Shuo, W. Quantification of caffeine and catechins and evaluation of bitterness and astringency of Pu-erh ripen tea based on portable near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 125, 105793. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, S.L.; Yuan, Y.; Dong, D.L.; Ying, J.X.; Hui, G.; Qing, C.Y.; Jian, L.C.; Peng, X. Does saponin in quinoa really embody the source of its bitterness. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137872. [Google Scholar]
- Diána, K.; Attila, H.; Norbert, K.; Lajos, B.B.; Nikoletta, S.; Gabriella, S.; Dezső, C. Coumarins, furocoumarins and limonoids of Citrus trifoliata and their effects on human colon adenocarcinoma cell lines. Heliyon 2022, 8, 10453. [Google Scholar]
- Florian, Z.; Alexandra, S.; Antonella, D.P.; Maik, B. Physiological activation of human and mouse bitter taste receptors by bile acids. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 612. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Li, T.; Raza, A.; Wang, L.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Hua, Y. Sensory-guided identification of bitter compounds in Hangbaizhi (Angelica dahurica). Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, S.; Hopfer, H.; Moulinier, V.; Prescott, J.; Monteleone, E.; Hayes, J.E. Distinct sensory hedonic functions for sourness in adults. Food Qual Prefer. 2024, 116, 105152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santanatoglia, A.; Angeloni, S.; Caprioli, G.; Fioretti, L.; Ricciutelli, M.; Vittori, S.; Alessandroni, L. Comprehensive investigation of coffee acidity on eight different brewing methods through chemical analyses, sensory evaluation and statistical elaboration. Food Chem. 2024, 454, 139717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, J.W.; Yong, K.L.; Qin, W.L.; Qing, Y.H.; Ping, H.L.; Yao, W.Y.; Guo, D.L.; Hui, X.; Hui, R.T. Drying temperature affects essential oil yield and composition of black cardamom (Amomum tsao-ko). Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 168, 113580. [Google Scholar]
- Aknarin, P.; Surat, L. Volatile constituents of Amomum argyrophyllum Ridl. and Amomum dealbatum Roxb. and their antioxidant, tyrosinase inhibitory and cytotoxic activities. Arabian J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104148. [Google Scholar]
- HaeLim, K.; SungKwon, L.; DaEun, M.; BongKeun, C.; DongRyung, L. Anti-Obesity Effects of a Mixture of Atractylodes macrocephala and Amomum villosum Extracts on 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renata, B.; Rimantas, V.P.; Ona, R. Valorisation of Roman chamomile (Chamaemelum nobile L.) herb by comprehensive evaluation of hydrodistilled aroma and residual non-volatile fractions. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111715. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ji, H.; Li, X.; Julian, M.D.; Sang, S.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J.; Qiu, C. Co-encapsulation of curcumin and piperine in whey protein isolate fibrils improves their water dispersibility and antioxidant activity. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Shi, W.; Xu, J. Isolation and Identification of Bitter Compounds in Ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Mey.) Based on Preparative High Performance Liquid Chromatography, UPLC-Q-TOF/MS and Electronic Tongue. Separations 2024, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, L.G.; Tuo, F.; Ermeng, L.; Pei, S.; Zhan, K.Z.; Lan, L.; Haile, M. Ougan juice debittering using ultrasound-aided enzymatic hydrolysis: Impacts on aroma and taste. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128767. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Shan, H.Z.; Lina, C.; Jun, L.; Fu, H.Z.; Tie, M.L.; Jin, L.W.; Jia, Y.H.; Yuan, H.M.; Zheng, F.Q.; et al. In vivo anti-hyperuricemia and anti-gouty arthritis effects of the ethanol extract from Amomum villosum Lour. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114532. [Google Scholar]
- Ilhem, R.; Anouar, B.S.; Jazia, S.; Anouar, F.; Sana, N.; Salah, A.M.; Najla, H.; Sami, S. HPLC-DAD identification of polyphenols from ethyl acetate extract of Amaranthus spinosus leaves and determination of their antioxidant and antinociceptive effects. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 975–984. [Google Scholar]
- Violeta, I.P.; Dragana, P.; Sasa, M. Rapid and Simple Method for Determination of Target Organic Acids in Wine Using HPLC-DAD Analysis. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Bansode, V.; Jaddu, S.; Panda, T.C.; Dalbhagat, C.G.; Seth, D.; Roy, S.S.; Gosh, D.; Pradhan, R.C.; Dwivedi, M. Hurdle approach of plasma-activated water pretreatment with debittering treatment on naringin and limonin content of sweet orange peel powder. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104431. [Google Scholar]
- Kankılıç, N.A.; Küçükler, S.; Gür, C.; Akarsu, S.A.; Akaras, N.; Şimşek, H.; İleritürk, M.; Kandemir, F.M. Naringin protects against paclitaxel-induced toxicity in rat testicular tissues by regulating genes in pro-inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and JNK/MAPK signaling pathways. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2024, 38, 23751. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Jing, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, F.; Ge, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Guo, Y.; Cui, X. Naringin safeguards vertebral endplate chondrocytes from apoptosis and NLRP3 inflammasome activation through SIRT3-mediated mitophagy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 140, 112801. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sorachai, S.-l.; Lukana, N.; Kriengsak, L.; Thamrongjet, P.; Sutida, M.; Poomsith, T.; Withsakorn, S.; Jisnuson, S.; Pitak, C. Anthraquinones from the roots of Morinda scabrida Craib exhibit antiproliferative activity against A549 lung cancer cells and antitubulin polymerization. Fitoterapia 2024, 173, 105781. [Google Scholar]
- Kunte, M.; Desai, K. The Inhibitory Effect of C-phycocyanin Containing Protein Extract (C-PC Extract) on Human Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in Hepatocellular Cancer Cell Line (HepG2). Protein J. 2017, 36, 186–195. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Han, A.-R.; Kang, U.; Kim, J.-B.; Seo, E.K.; Jung, C.-H. Inhibitory Effects of Furanocoumarins From the Roots of Angelica dahurica on Ionizing Radiation-Induced Migration of A549 Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X20915036. [Google Scholar]
- Punnida, A.; Kamonwan, S.; Warathit, S.; Sonthaya, U.; Lapamas, R.; Aroonchai, S.; Methee, R.; Trinnakorn, K.; Songyot, A.; Pornngarm, D. Suppression of inflammation-induced lung cancer cells proliferation and metastasis by exiguaflavanone A and exiguaflavanone B from Sophora exigua root extract through NLRP3 inflammasome pathway inhibition. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1243727. [Google Scholar]
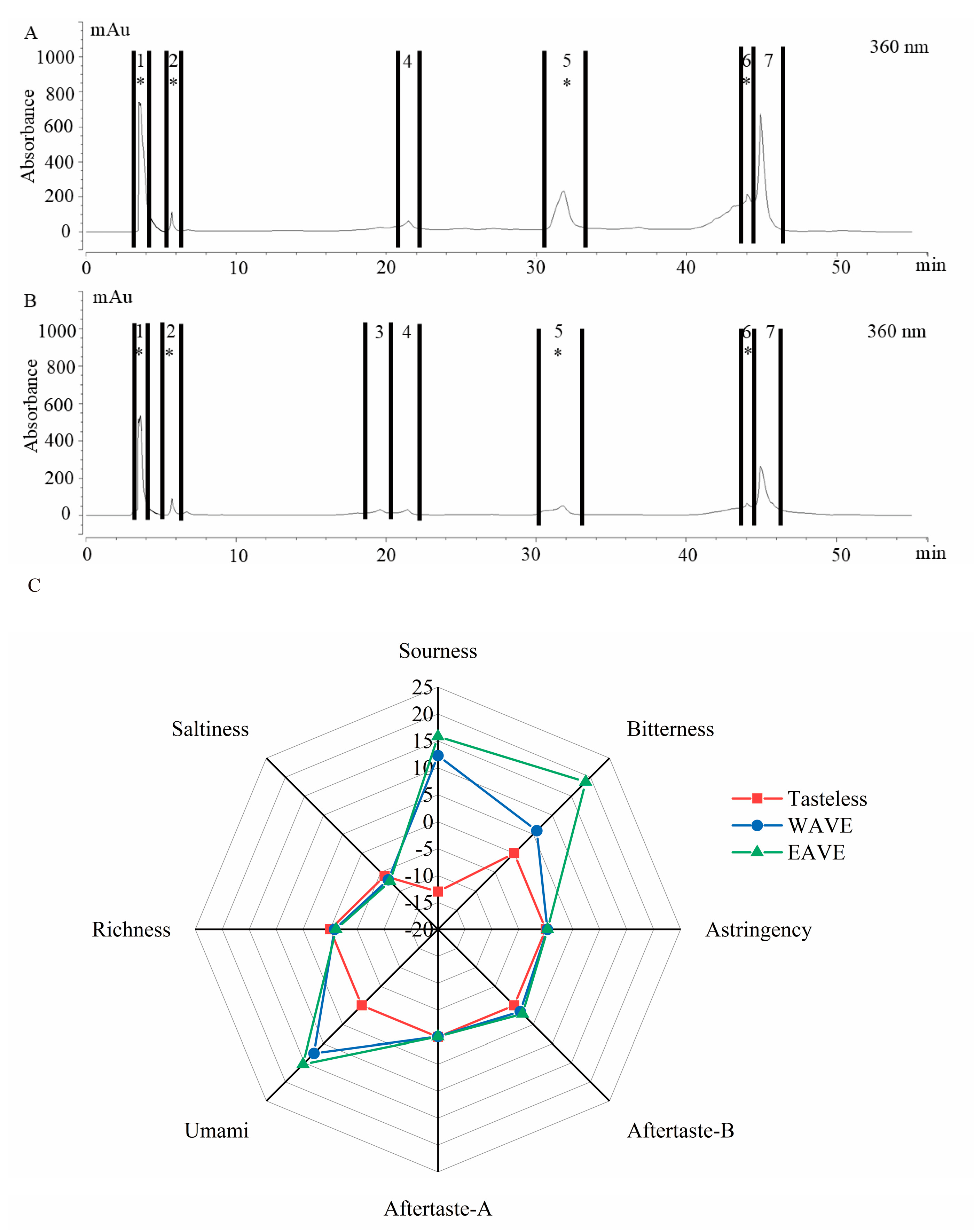
| Tasteless Point of Bitterness b | Tasteless Point of Sourness b | Code c | Bitterness | Sourness | Code d | Bitterness | Sourness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −13 | 1 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 10.74 ± 0.78 * | 1 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 10.21 ± 0.66 * |
| 0 | −13 | 2 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 14.67 ± 0.34 * | 2 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 14.38 ± 0.74 * |
| 0 | −13 | 3 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | −14.10 ± 0.44 | |||
| 0 | −13 | 4 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | −15.14 ± 1.04 | 4 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | −15.12 ± 0.83 |
| 0 | −13 | 5 | 12.97 ± 0.48 * | −14.84 ± 0.97 | 5 | 12.68 ± 0.55 * | −15.03 ± 0.74 |
| 0 | −13 | 6 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 5.78 ± 0.55 * | 6 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 5.69 ± 0.75 * |
| 0 | −13 | 7 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | −14.17 ± 1.02 | 7 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | −14.21 ± 1.14 |
| Code b | RT (min) | UV (nm) c | Parent Ion | Main Characteristic Fragments | Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.96 | 214 | [M−H]− 133.0198 | 115.0065 | DL-malic acid |
| 2 | 6.25 | 260; 294 | [M−H]− 153.0188 | 109.0322 | protocatechuic acid |
| 5 | 9.79 | 280 | [M+H]+ 291.0931 | 273.0808; 139.0429 | catechin |
| 6 | 8.54 | 254 | [M−H]− 137.0288 | 109.0322 | p-hydroxybenzoic acid |
| Category | Compounds | Linear Regression Equation | R2 | Linearity Range (mg/L) | LOD (μg/mL) | LOQ (μg/mL) | Quantitative Result of EAVE (mg/g) | Quantitative Result of WAVE (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL-malic acid | Y = 0.0090X + 0.0037 | 1.000 | 7.648~2447.5 | 2.2317 | 6.3827 | 356.67 ± 4.59 | 284.87 ± 3.78 | |
| Organic acids | protocatechuic acid | Y = 0.6115X + 0.1839 | 0.9999 | 5.698~91.162 | 0.4781 | 1.3913 | 9.37 ± 0.78 | 7.04 ± 0.05 |
| p-hydroxybenzoic acid | Y = 0.9070X + 0.5380 | 0.9999 | 7.821~125.125 | 1.1241 | 3.2149 | 5.25 ± 0.26 | 4.17 ± 0.34 | |
| Polyphenols | catechin | Y = 0.3336X + 0.0381 | 1.0000 | 5.968~95.480 | 1.0706 | 3.0940 | 63.79 ± 0.42 | 13.67 ± 3.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Liao, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Tang, W.; Yang, Q.; Xu, J. Separation and Identification of Non-Volatile Sour and Bitter Substances in Amomum villosum L. by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry and Electronic Tongue Analysis, as Well as Their In Vitro Anti-Tumor Activity. Separations 2025, 12, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12040077
Chen Y, Liao Z, Li W, Wang Z, Tang W, Yang Q, Xu J. Separation and Identification of Non-Volatile Sour and Bitter Substances in Amomum villosum L. by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry and Electronic Tongue Analysis, as Well as Their In Vitro Anti-Tumor Activity. Separations. 2025; 12(4):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12040077
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yang, Ziwei Liao, Weiqin Li, Zhe Wang, Wan Tang, Qiang Yang, and Jian Xu. 2025. "Separation and Identification of Non-Volatile Sour and Bitter Substances in Amomum villosum L. by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry and Electronic Tongue Analysis, as Well as Their In Vitro Anti-Tumor Activity" Separations 12, no. 4: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12040077
APA StyleChen, Y., Liao, Z., Li, W., Wang, Z., Tang, W., Yang, Q., & Xu, J. (2025). Separation and Identification of Non-Volatile Sour and Bitter Substances in Amomum villosum L. by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry and Electronic Tongue Analysis, as Well as Their In Vitro Anti-Tumor Activity. Separations, 12(4), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12040077





