Abstract
Schistosomiasis is a neglected tropical disease caused by parasitic worms of the genus Schistosoma. In Brazil, there are reports of infection by the Schistosoma mansoni species, which has the Biomphalaria glabrata snail as one of its intermediate hosts. The present work aimed to test the effects of different Abelmoschus esculentus seed extracts and fractions on adults and embryos of B. glabrata and S. mansoni cercariae. A total of four crude extracts and thirteen fractions with different organic solvents were used for the bioassays. The extracts were analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Molluscicidal activity was assessed in 24-well plates, after which the LC50 and LC90 were calculated. Assays with B. glabrata embryos and S. mansoni cercariae were also performed. These findings indicate the presence of flavanoids in the hexane, ethyl acetate, and ethanol crude extracts. For the molluscicidal activity assays, eight fractions had an LC90 value less than that recommended by the WHO. The methanol fraction of the dichloromethane extract (FrMeOH EDM) had the most promising results, with an LC90 of 37.15 mg/L and 100% mortality in embryos of B. glabrata and cercariae. FrMeOH, EDM, and other fractions are possible candidates for new drugs for the combat of schistosomiasis.
1. Introduction
Schistosomiasis is a neglected tropical disease caused by the parasitic worms of the genus Schistosoma [1,2]. It is the second most common infectious parasitic disease and has the most significant impact on socioeconomic factors, general morbidity, and public health [3]. The disease has been reported in 78 countries worldwide and is endemic in 52 countries [4]. In this sense, the present work proposed testing crude extracts and their fractions of Abelmoschus esculentus (okra) seeds on one mollusk species that acts as an intermediate host of Schistosoma mansoni, as well as on cercariae, in the second larval stage of the parasite.
The distribution of snails as intermediate hosts for schistosomes and socioeconomic issues, such as poor sanitation, are related to disease occurrence [5,6]. Thus, combatting snails is a necessary prophylactic measure [7]. In Brazil, the S. mansoni species is the only one with reports of infection to date [8], with three species of snails serving as intermediate hosts: Biomphalaria tenagophila, Biomphalaria straminea, and Biomphalaria glabrata [9]. The latter has a larger geographic distribution [10] and increased susceptibility to infection by the parasite [11] compared to the other species.
Niclosamide® (Baylucide, Bayer, Leverkusen, Germany) is currently the only molluscicide recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the control of schistosomiasis [12]. However, Niclosamide® has environmental toxicity [13,14,15] and has been used to treat mollusk infections [16,17]. Therefore, the discovery and development of new compounds to combat these snails without affecting other organisms are necessary [18]. To overcome the problem of environmental toxicity, several studies in the literature have sought to identify new compounds originating from natural products with molluscicidal activity. Therefore, we investigated the molluscicidal activity of A. esculentus.
Due to the existence of a large amount of biologically active molecules in plants, they have the potential to present therapeutic properties for the treatment of diseases [19]. These molecules can be observed in many manuscripts investigating the therapeutic activities of plants. The A. esculentus species is one of these studied plants and has several known biological activities [20,21,22,23,24].
Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the molluscicidal effect of crude A. esculentus seed extracts and fractions on embryos and adults of B. glabrata and S. mansoni cercariae.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Identification of Plant Material
The pods and seeds were collected from an A. esculentus plantation located at 50 Tupinambá Street, Paratí Neighborhood, in the municipality of Araruama, Rio de Janeiro state (RJ) (latitude: 22°51′42.72″, longitude: 42°17′40.57″).
Identification and classification were performed at the Botanical Garden, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, and were deposited in the Herbarium of Rio de Janeiro Botanical Garden under the number RB 762520.
2.2. Preparation and Fractionation of Extracts
Four extractions were performed using the solvents ethyl acetate, acetone, dichloromethane, ethanol, and hexane. The seeds were dried in an oven at 45 °C and then ground. After this, 20 g of seed was extracted in 250 mL of solvent until complete exhaustion in a Soxhlet extractor. After the extraction and subsequent evaporation of the entire solvent, each extract was diluted with 100 mL of pure dimethyl sulfoxide (100% DMSO), and a concentrated solution was obtained for future dilutions.
The extraction process described above was repeated separately in three solvents (acetone, hexane, and dichloromethane). Then, these three crude extracts were fractionated. The various extracts were mixed separately with 5 g of silica and placed on a rotary evaporator until they formed a pellet. In a vacuum filtration set, the pellet was placed over a layer of silica, after which another 5 g of silica was added to the pellet. The solvents were added in increasing order of polarity: hexane, dichloromethane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, acetone, ethanol, and methanol. Seven fractions were obtained in hexane, six in dichloromethane, and seven in acetone. No mass of the acetone fraction of the dichloromethane extract was obtained; therefore, it was not tested.
2.3. Analysis through Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry (LC-QTOF/MS) of Fractions of the Species Abelmoschus esculentus
The samples were prepared and analyzed using the liquid chromatography method coupled to a mass spectrometer at the Farmanguinhos Technological Platform (FIOCRUZ).
The samples were analyzed through liquid chromatography using a UFLC Shimadzu Nexera Chromatograph coupled to a Compact Q-TOF Bruker mass spectrometer. A Raptor Arc 18 column (100 m length × 2.1 µm internal diameter × 2.7 µm phase thickness) was used (CL-0254).
The sample was injected with a volume of 5 µL. These samples were diluted in 1.0 mL of methanol and filtered at 0.22 µm. Formic acid and acetonitrile were used in phase A. The flow rate was 0.5 mL/min. The total analysis time was 33.01 min. Chemical identification was performed using a Q-TOF orthogonal mass spectrometer (micrOTOF-QTM, Bruker Daltonics) equipped with an electrospray ionization source (ESI). The analysis parameters were provided for the positive mode, with a mass range of 100–1000 m/z, 4500 V capillary voltage, set end plate offset of −500 V, set charging voltage of 2000 V, drying gas temperature of 200 °C, drying gas flow of 10.0 mL/min, gas pressure of 4 bar, collision energy (MS/MS) of 35 eV, and collision gas N2. The mass data obtained were processed with Bruker Compass Data Analysis 4.2 software (Bruker Daltonics, Billerica, MA, USA, EUA). The spectrograms of the fractions were analyzed and compared to those of the Lipid Maps® website.
2.4. Molluscicidal Activity Assays of Biomphalaria glabrata
Snails originating from Sumidouro city, RJ, were kept in breeding tanks with unchlorinated water and fed lettuce leaves.
The trial was performed with some modifications to the methodology described by the WHO [25,26]. In 24-well plates, adult individuals of B. glabrata snails, 10–12 mm in diameter and free from S. mansoni infection, were placed individually in contact with 2 mL of aqueous solution (distilled water) from the extracts/fractions at concentrations ranging from 5 mg/L to 275 mg/L for 48 h at room temperature, using 3 snails per concentration. Mortality was verified through snail retraction into the shell and the release of hemolymph (circulating fluid similar to blood) every 24 h. The tests were performed in triplicate. Distilled water and 1% DMSO were used as negative controls, and 2 mg/L niclosamide® was used as a positive control. The LC50 and LC90 values were calculated at 48 h. These concentrations refer to the concentrations that cause the death of 50% or 90% of exposed mollusks, respectively. The LC50 and LC90 concentrations of the extracts/fractions were used in the other tests.
2.5. Molluscicidal Activity Assays of Physa acuta
Adult snails of the Physa acuta (Draparnaud, 1805) species, a freshwater snail, were collected in channels located at the Fundação Oswaldo Cruz, Campus Manguinhos, Rio de Janeiro, RJ. The plants were kept separately in plastic containers containing dechlorinated water and fed lettuce leaves, where they remained for at least 48 h before being used in the tests.
Snails were exposed to the LC50 and LC90 concentrations of crude extracts and fractions of A. esculentus to assess possible toxicity to nontarget species. The assay was conducted using the same methodology described previously for B. glabrata [26]. Niclosamide® (2 mg/L) was used as a positive control at its LC50 and LC90 concentrations, and distilled water and 1% DMSO were used as negative controls.
2.6. Ovicidal Activity Assays
Ovigerous capsules with embryos in an advanced stage of development were collected from the snail breeding tanks in styrofoam plates. The embryos were placed in contact with the crude extract/fraction solutions for 48 h at room temperature. Each ovigerous capsule was examined every 24 h through a stereomicroscope. The mortality criterion was the observation of disintegrated forms of the embryos inside the egg and the absence of movement of the embryos. The tests were performed in triplicate. Unchlorinated water and 1% DMSO were used as negative controls, and 2 mg/L niclosamide® at concentrations of LC50 and LC90 was used as a positive control.
2.7. Cercaricidal Activity Assays
The Malacology Laboratory, IOC/FIOCRUZ, supplied water containing S. mansoni cercariae. We used an estimated 1 mL of water containing approximately 80–100 cercariae. Additionally, we added 1 mL of the extract/fraction solutions, 1 mL of water containing the cercariae, and 20 µL of Trypan blue dye to a 24-well plate. The readings were taken from 1 h to 1 h through the stereomicroscope for a total period of 4 h. All tests were performed in triplicate. Unchlorinated water and 1% DMSO were used as negative controls, and 2 mg/L niclosamide® at the LC50 and LC90 concentrations was used as a positive control.
2.8. Acetylcholinesterase Assay in a 96-Well Microplate
We used the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE, E.C. 3.1.1.7 electric ell, code C3389), which was obtained from Sigma Aldrich (San Luis, MO, USA). A total of 30 mL of buffer A (Tris HCl pH 7.8 to 50 mM) was used to dilute the AChE enzyme to obtain a final concentration of 66.6 U/mL. We added 1% albumin for stabilization, after which the samples were stored at −2 °C. Additionally, we prepared buffer B, 0.067 M sodium phosphate, at pH 6.85. Acetonitrile was the solvent used to prepare the 1 mM para-nitrophenyl acetate substrate. The fractions were prepared in DMSO.
In the first step of the reaction, for the enzyme control (94 µL of Buffer B, 6 µL of enzyme with 1% albumin), for the enzyme control (94 µL of buffer B, 6 µL of Tris-HCl buffer with 1% albumin), and for the same enzyme conditions, 94 µL of buffer B containing the extract, 6 µL of Tris-HCl buffer with 1% albumin was added to the inhibitor blank, and 94 µL of buffer B containing the fraction and 6 µL of enzyme with 1% albumin at 2 U was added to the substance test/mL. Then, we conditioned in the presence of biological oxygen demand (B.O.D.) at 25 °C for 10 min to allow the inhibitor to interact with the enzyme. In the second step, we completed the reaction with 98 µL of Buffer B and 2 µL of 1 mM 4-nitrophenyl acetate (PNPA) substrate, which was added for 20 to 20 s. After completing the reaction with a volume of 200 µL, we waited for 2 min and 30 s to start the readings on the Elisa plate reader for 20 to 20 s within a period of 5 min at a wavelength of 405 nm.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad software (version 5). The proteins were analyzed through ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s test. The results are expressed as the mean ± SD, with a significance level of p < 0.05. The LC50 and LC90 values at 48 h were determined through dispersion analysis and mathematical calculation using the graph formula generated in the Microsoft Office Excel Program (2007 version) [27].
3. Results
3.1. Molluscicidal Activity Assays of Biomphalaria glabrata
The crude extracts in acetone caused 100% of the deaths at a concentration of 100 mg/L. The crude extracts in hexane, dichloromethane, and ethyl acetate showed 100% mortality at a concentration of 150 mg/L, with the crude extract in hexane presenting high mortality at 100 mg/L (Table 1).

Table 1.
Mortality (in percentage) of Biomphalaria glabrata treated with different crude extracts and fractions of Abelmoschus esculentus seeds after 48 h.
We evaluated a total of twenty fractions of A. esculentus seed extracts, and 100% mortality was detected for only seven of the mollusks at 50 mg/L; these were the chloroform fraction of the crude dichloromethane extract (FrCCl3 EDM); the ethanol fraction of the crude dichloromethane extract (FrETOH EDM); the hexane fraction of the crude dichloromethane extract (FrHex EDM); the methanol fraction of the crude dichloromethane extract (FrMeOH EDM); the ethyl acetate fraction of the crude hexane extract (FrAcO EHex); the chlorofom fraction of the crude hexane extract (FrCCl3 EHex); and the hexane fraction of the crude hexane extract (FrHex EHex). The acetone fraction of the acetone extract (FrAceto EAceto) showed 100% mortality at 55 mg/L. Two fractions presented 100% mortality at 100 mg/L: the dichloromethane fraction of the acetone extract (FrDM EAceto) and the methanol fraction of the acetone extract (FrMeOH EAceto).
The methanol fraction of the crude hexane extract (FrMeOH EHex) presented 100% mortality at 25 mg/L (Table 1). The fractions in ethyl acetate of the crude dichloromethane extract, dichloromethane of the crude dichloromethane extract, acetone of the crude hexane extract, dichloromethane of the crude hexane extract, ethanol from the crude hexane extract, hexane of the crude acetone extract, chloroform of the crude acetone extract, ethyl acetate of the crude acetone extract, and ethanol of the crude acetone extract presented mortality above 100 mg/L; therefore, the LC50 and LC90 values were not calculated.
3.2. Ovicidal Activity Assays
All embryos were killed at the LC90 concentration of the crude extract in ethanol. The crude extracts in acetone and hexane had mortality rates above 70% and 90%, respectively. The other crude extracts did not cause significant embryo mortality.
The FrCCl3 EDM, FrHex EDM, and FrMeOH EDM fractions showed 100% embryo death at the LC90. The FrAceto EAceto fraction showed almost 90% embryo mortality; the FrHex EHex and FrMeOH EAceto fractions presented almost 80% embryo mortality; and the FrETOH EDM fraction showed almost 70% embryo mortality at the LC90 concentration. The FrDM EAceto and FrCCl3 EHex fractions presented approximately 50% mortality. The FrAcO EHex and FrMeOH EHex fractions did not cause significant embryo mortality (Table 2).

Table 2.
Mortality (%) of Biomphalaria glabrata embryos in relation to the LC50 and LC90 concentrations of Abelmoschus esculentus crude seed extracts and fractions after 48 h of the experiment in triplicate on three distinct days.
3.3. Cercaricidal Activity Assays
The crude extract in dichloromethane showed the totality of dead cercariae at the LC90, whereas at the LC50, this crude extract presented almost the totality of mortality. The crude extract in acetone caused almost 100% death at the LC50 and LC90 concentrations. The crude extract in ethanol presented more than 50% dead cercariae at both concentrations. The other crude extracts did not cause significant cercaria mortality.
The FrDM EAceto and FrCCl3 EHex fractions showed 100% cercaria mortality at both the LC50 and LC90. The FrAcO EHex fraction also killed all cercariae at the LC90 and caused more than 65% mortality at the LC50. The FrMeOH EDM fraction presented more than 75% mortality at the LC50 and LC90 concentrations. The FrCCl3 EDM and FrETOH EDM fractions had more than 60% mortality according to the LC90, and the FrHex EDM, FrAceto EAceto, and FrHex EHex fractions had more than 50% mortality according to the LC90. FrMeOH EAceto and FrMeOH EHex did not cause significant cercaria mortality (Table 3).

Table 3.
Mortality (%) of Schistosoma mansoni cercariae in relation to the LC50 and LC90 of the crude Abelmoschus esculentus seed extracts and fractions after 4 h of the experiment in triplicate on three distinct days.
3.4. Molluscicidal Activity Assays of Physa acuta
In tests involving the snail P. acuta, the crude extracts were tested only at their LC50.
The crude hexane extract had the highest mortality, which was less than 60%. Crude extracts in ethyl acetate and ethanol resulted in less than 40% and 30% snail deaths, respectively. The crude extract in dichloromethane presented a mortality rate of approximately 5%, and for the crude extract in acetone, no snail deaths were observed.
The FrDM EAceto fraction had the lowest mortality rate for these snails, with less than 45% of deaths occurring at the LC90 concentration and approximately 10% of deaths occurring at the LC50 concentration. FrMeOH and EDM achieved more than 70% and 80% mortality, respectively, at the LC50 and LC90 concentrations. FrHex EDM and FrCCl3 EHex caused more than 70% of the deaths at the LC50 concentration and almost 80% at the LC90 concentration. Almost 70% of the FrAcO EHex and FrHex EHex died at the LC50, and almost 80% died at the LC90 (Table 4).

Table 4.
Mortality (%) of Physa acuta in relation to the LC50 and LC90 of the Abelmoschus esculentus crude seed extracts and fractions after 48 h of the experiment in triplicate on three distinct days.
3.5. Chemical Identification of the FrMeOH EDM Fraction through Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry (LC-QTOF/MS)
The major component of the FrMeOH EDM fraction was identified.
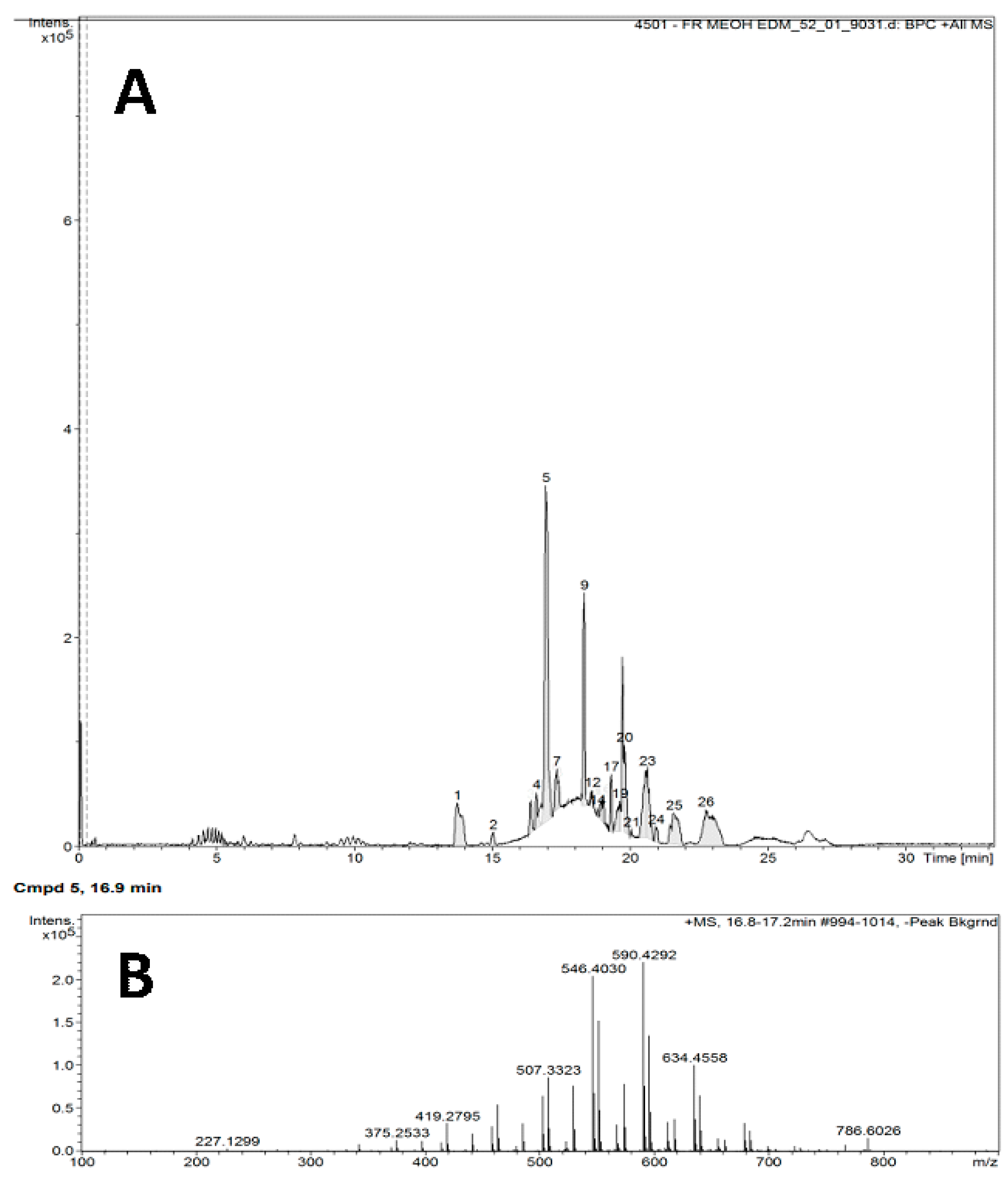
The chromatogram in Figure 1 shows the results for the FrMeOH EDM fraction (A), and the retention peak of the majority substance (B) was observed at 16.9 min. Chromatogram analysis of this fraction indicated the presence of glycerophosphocholine and 1-tridecenoyl-2-tricosenoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, also known as PC 36:2 (13:1/23:1) (Table 5).
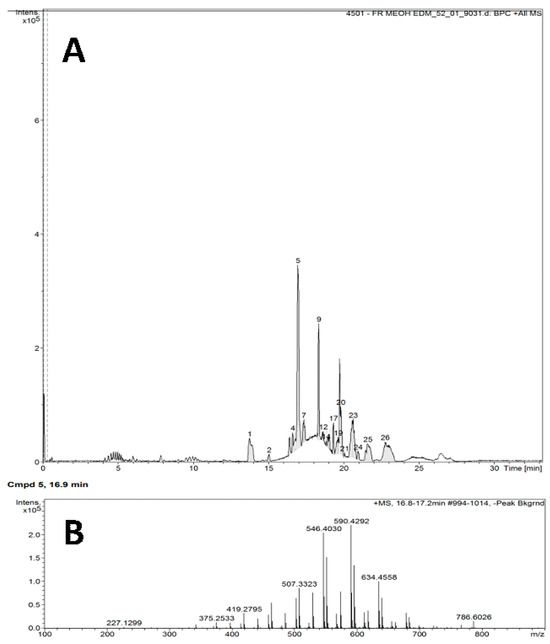
Figure 1.
Chromatogram (A) of the methanol fraction of the extract of Abelmoschus esculentus seeds in dichloromethane, analyzed through liquid chromatography coupled to a mass spectrometer; the peak retention of the majority substance is shown (B).

Table 5.
Chromatographic data of the FrMeOH EDM fraction and the major isolated substances.
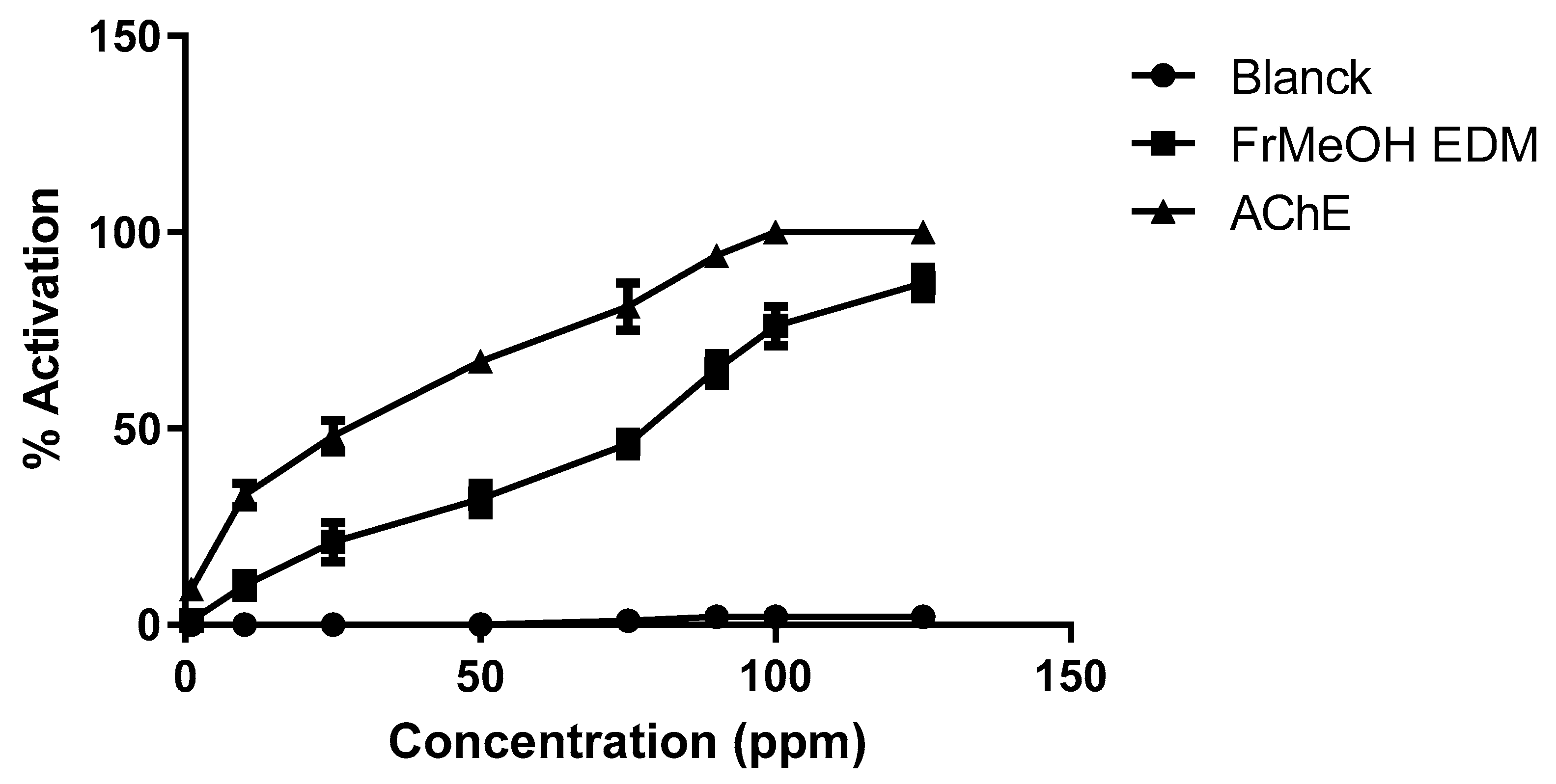
Additionally, we performed an assay evaluating the action of the most active fraction, which contains GCPs, against AChE activity (Figure 2).
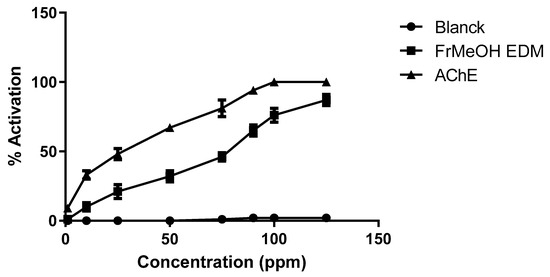
Figure 2.
Activity percentage of FrMeOH EDM against acetylcholinesterase activity. These experiments were performed in triplicate on at least three distinct days.
FrMeOH/EDM dose-dependently activated this enzyme (Figure 2), with a maximal activation of approximately 90% at a concentration of 125 ppm. In contrast, the blank (only with dichloromethane as the solvent at the final concentration used in the fermentation) did not exhibit an effect on this enzyme.
4. Discussion
GPs are the most common lipids found in the constitution of cell membranes [28]. A study indicated that the glycerophospholipid extract of marine sponges exhibited antibacterial activity [29]. Lipids with this type of activity have bacterial cell membranes as their main target, so they interact with cell membranes, leading to destabilization, which results in cell lysis [30]. In the present study, a glycerophospholipid was found in the FrMeOH EDM fraction. This substance may be associated with the molluscicidal activity of this fraction, and additional studies should be conducted to investigate whether this compound is linked to molluscicidal action and whether this cell lysis process may be linked to this action.
The molluscicidal potential of different plant species and their extraction products has been reported in several studies in the literature for B. glabrata species. In one of these studies, the LC90 values of ethanolic extracts were found to be 20.03 mg/L for Poincianella pyramidalis leaf, 91.57 mg/L for Chenopodium ambrosoides leaf, 62.05 mg/L for Mimosa tenuiflora stem, 75.66 mg/L for Hyptis pectinata leaf, and 56.26 mg/L for the stem of Jatropha mollissima [31]. In another study involving ethanolic extracts, promising results were also obtained, revealing molluscicidal potential for B. glabrata, with LC90 values of 51.8 mg/L for Adenocalymma comosum, 18.1 mg/L for Arrabidaea parviflora, 8.9 mg/L for Cuspidaria argentea, 26.5 mg/L for Clitostoma binatum, 25.8 mg/L for Melloa quadrivalvis, and 53.9 mg/L for Tabebuia aurea [32].
According to the WHO, a plant extract is considered active when at least 90% of dead mollusks are obtained from the total population tested at a concentration of 100.0 mg/L within 48 h (LC90) [12]. In this context, we follow this recommendation regarding the calculation of the LC90. The crude extracts in dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, and hexane presented LC90 values within 48 h similar to those recommended by the WHO, with values of 149.87 mg/L, 149.61 mg/L, and 130.47 mg/L, respectively. However, we performed fractionation of three of these crude extracts to achieve a reduction in the following parameters: the extracts were extracted in acetone, hexane, and dichloromethane, for a total of twenty fractions. The LC90 values of eleven fractions were within the recommended range.
Notably, both of the studies cited above used Becker’s assays as a methodology and obtained final volumes of the extract solutions of 125 mL [31] and 250 mL [32]. In the present study, we used a different methodology, in which we used 24-well plates [26]. This method yields similar results to those of Becker’s assays. However, with the 24-well plate assay, we used a smaller volume of 2 mL of solution as well as a smaller number of mollusks. In our study, 3 mollusks were used per concentration, whereas in Becker’s methodology, between 5 [31] and 10 [32] were used per concentration.
Another factor to be considered about the methodology is the size of the mollusks used in the assays. The studies mentioned above adopted snails with shell diameters ranging from 13 to 18 mm [31] and 8 to 12 mm [32]. We observed that both works used snails with considerable size variation. In the present study, we used a smaller variation in shell diameter, ranging from 10 to 12 mm.
Some studies aimed at evaluating molluscicidal activity against adult B. glabrata snails also consider methods that affect more than one part of the schistosomiasis cycle. Several of these methods seek to evaluate the action of extracts on less advanced stages of snail infection, such as embryos and cercariae, the infective form of the parasite in humans. In a study developed by Rapado and collaborators [33], Piper crassinervium inflorescence ethyl acetate extract at a concentration of 20 mg/L caused the death of 100% of B. glabrata embryos. Ethyl acetate extracts of the inflorescence and Piper tuberculatum leaves had 100% mortality in B. glabrata embryos at a concentration of 30 mg/L. In another study by the same author, the crude dichloromethane extract of P. crassinervium leaves had 100% mortality from B. glabrata embryos at a concentration of 50 mg/L, and the crude dichloromethane extracts of Piper cuyabanum and Piper hostmannianum leaves had 100% embryo mortality at a concentration of 20 mg/L [34].
In the literature, some studies indicate that a molluscicide may be effective against adult B. glabrata individuals but not as effective against embryos [34,35,36]. However, in our study, FrCCl3 EDM, FrHex EDM, FrMeOH EDM, FrAceto EAceto, FrMeOH EAceto, and FrHex EHex showed excellent efficacy for adult B. glabrata individuals and excellent efficacy for embryos. In addition, the crude hexane extract, which was similar to that recommended by the WHO for adult individuals, exhibited excellent efficacy against embryos, with a mortality rate close to 100%.
Identifying the mechanisms of action by which the fractions obtain molluscicidal activity is required [37]. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out biochemical tests to identify the mechanisms through which the fractions in this study affect B. glabrata. The biochemical parameters evaluated were aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) [38], alkaline phosphatase (ALP), acid phosphatase (ACP) [39], and total protein [40].
The cercariae, the larval stage of S. mansoni, infect their definitive hosts through skin penetration. Therefore, combating cercariae is also a prophylactic measure for schistosomiasis [41]. In a study by Martins and collaborators [42], the ethanol extract of the lichen Cladia aggregata and the barbatic acid found in this organism exhibited molluscicidal activity against B. glabrata, with an LC50 = 11.9 mg/L for both. Barbatic acid still resulted in 100% mortality of S. mansoni cercariae at a concentration of 1.0 mg/L after 1 h and 10 mg/L after 30 min. In another study, the penta-substituted pyridine alkaloid found in the Jatropha elliptica rhizome, at a concentration of 36.43 mg/L, resulted in 90% death of B. glabrata snails and 100% death of cercariae at 4.0 mg/L after 30 min [43]. Crude ethanol extracts from stem bark and the seeds of the species Rauwolfia vomitoria were analyzed for cercariae, which exhibited 100% mortality in 2 h at a concentration of 62.5 mg/L for the stem bark extract and 100% mortality at a concentration of 250 mg/L for the seed extract, indicating low efficacy [44].
In the present study, promising results were also obtained for four fractions that exhibited an LC90 within the WHO recommended range according to the cercariae test. After 4 h of the experiment, FrDM EAceto, FrMeOH EDM, FrAcO EHex, and FrCCl3 EHex died from all the cercariae at the concentration of LC90, whereas FrDM EAceto, FrMeOH EDM, and FrCCl3 EHex had 100% mortality at the LC50. In addition, the crude extract of dichloromethane, which has an LC90 close to that recommended by the WHO, also showed promising results, as mortality from almost all cercariae was already at the LC50 concentration, reaching the totality of deaths at the LC90 concentration. A relevant aspect when we analyze the results of the above works [42,43] is that, unlike in our study, where we tested crude extracts and fractions, we used isolated substances. Moreover, these works obtained better results than did studies that used crude extracts or fractions. Consequently, given our results with crude extracts and fractions, the prospect of mortality remains high after the isolation of the major substances from the fractions with the most significant effect. This expectation is higher if we take into consideration that, in the other study mentioned above [44] involving seed extract, only 100% of the deaths were observed at a concentration more than double that used in our study.
Several problems associated with the use of niclosamide®, a molluscicide used to combat schistosomiasis vector mollusks, have been reported [13,14,15,16,17], one of which is its high environmental toxicity [13,14,15]. Therefore, we believe that evaluating the environmental toxicity of plant extracts or fractions against other species is necessary. Other mollusks, fish, and microcrustaceans, among others, are commonly used in these types of tests. In the study by Silva and collaborators [38], cited above, tests were carried out with the microcrustacean Artemia salina to evaluate the environmental toxicity of the extracts tested on B. glabrata. In addition to the promising results on B. glabrata, the study also obtained excellent results against A. salina, with all the extracts showing LC50 values well above the values required to kill snails: A. comosum (LC50 = 485.5 mg/L), A. parviflora (LC50 = 590.8 mg/L), C. argentea (LC50 = 880.2 mg/L), C. binatum (LC50 = 801.6 mg/L), M. quadrivalvis (LC50 = 197.7 mg/L), and T. Aurea (LC50 = 815.4 mg/L). These results indicated the very selective molluscicidal activity of the extracts.
Toxicity assays on P. acuta species showed that FrDM EAceto presented low mortality. FrAco EHex, FrMeOH EAceto, FrCCl3 EHex, FrHex EHex, FrETOH EDM, FrHex EDM, FrCCl3 EDM, and FrMeOH EHex presented high mortality, above 70%.
Tests on other species must be carried out to verify the environmental toxicity of these fractions. To achieve this goal, tests using representative organisms of the habitat of the mollusk B. glabrata that represent different trophic levels of the food chain must be performed, such as acute toxicity tests with the fish Danio rerio [45] and the freshwater microcrustacean Daphnia similis [46]; growth inhibition tests of Chlorella vulgaris algae [47]; and analysis of bioluminescence inhibition of the bacterium Vibrio fischeri [48]. All of these are organisms commonly used for assessing environmental toxicity.
In this study, we observed that five crude extracts (dichloromethane, hexane, acetone, ethyl acetate, and ethanol) induced mortality in adult B. glabrata. The crude extract of acetone presented an LC90 within the recommended value by the WHO, and the other four extracts presented an LC90 close to the recommended value. The acetone extracts still showed great efficacy against S. mansoni cercariae and B. glabrata embryos. The crude extracts in hexane and ethanol still showed excellent efficacy against embryos, and the crude extract in dichloromethane showed excellent efficacy against cercariae. After the fractionation of the crude extracts, we observed that eleven fractions presented an LC90 value within that recommended by the WHO.
The lipid composition of the plasma membrane plays a key role in neurotransmitter storage and release from synaptic vesicles, transport from the synaptic cleft, synthesis, and degradation [49]. Additionally, lipids can affect the functioning of acetylcholinesterase [50,51]. Consequently, one of our hypotheses for the activity of the extracts would be through the direct action of lipids on acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Additionally, diverse fatty acids, such as omega-3, omega-6, fatty acid alpha-linolenic, arachidonic and linoleic acids [52], and others, such as (2E)α,β-unsaturated fatty acids [53], inhibit AChE in human erythrocytes. However, glycerophosphocholine (GPC) is a choline derivative and one of the two major forms of choline stored (along with phosphocholine) in the cytosol. The GPC functions as an osmolyte under normal physiological conditions and responds to hypertonic stress [54]. This choline, in presynaptic neurons, participates in the synthesis of acetylcholine (ACh) together with acetylcoenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) under the catalysis of choline acetyltransferase. The ACh produced is stored in vesicles and deposited until there is a stimulus that results in its release into the synaptic cleft. After the message is transmitted, the ACh molecule dissociates from the postsynaptic receptor and returns to the synaptic cleft, where it undergoes hydrolysis catalyzed by AChE, giving rise to acetic acid and choline [55]. From that point on, ACh binds to the postsynaptic receptor, propagating the information.
Therefore, we hypothesize that these lipids present in the extract may be used as a substrate for the exacerbated increase in ACh formation and overstimulation of AChE, which would not be able to degrade this excess ACh, resulting in the overstimulation of postsynaptic neurons and death. This mechanism is similar to that observed for neonicotinoid insecticides [56].
Monogalactosyl diglyceride (MGDG) is a minor galactolipid present in oligodendrocytes and myelin that is used as a marker for myelination and has also been shown to stimulate protein kinase C (PKC)α activity in oligodendrocytes [57]. PKC regulates innate defenses in mammals and snails by regulating nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) production, phagocytosis, and cell spreading by hemocytes [58,59,60,61]. Additionally, a receptor for activated protein kinase C (RACK) was characterized in B. glabrata [62], and this protein was found to bind to cytoskeletal factors. Based on this information, we can hypothesize that MGDGs may act on neurons, possibly increasing or reducing their conduction speed. In addition, an increase in oxidative stress and structural modulation of mollusk cells may contribute to the observed toxic effects. However, additional studies are needed to determine the relationship between MGDGs and the toxicity of mollusks.
FrMeOH EDM still presented an LC90 concentration, 100% mortality for embryos of B. glabrata, and great effectiveness against cercariae. This fraction showed high mortality for the snail P. acuta. Therefore, toxicity tests with other organisms are still necessary to assess the possible environmental toxicity of this fraction. Notably, FrDM EAceto and FrCCl3 EHex killed 100% of the cercariae. These fractions proved to be great candidates for new drugs to combat schistosomiasis, with emphasis on the FrMeOH EDM fraction.
Author Contributions
J.C.V.A.L. performed the experiments, analyzed and interpreted the data, and wrote the paper. L.d.S.R. performed the experiments. K.N.F.G. performed the experiments. Juliana Vieira Faria provided the bone marrow macrophages. R.D.D.G.d.A. performed the plant extract identification. J.A.A.d.S. provided plant extracts, supervised the study and approved the final version of the manuscript. R.X.F. interpreted the data, conceived and designed the study, supervised the study, and approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by CNPq (National Council of Research of Brazil) (RXF holds a grant with Fellowship Process Number 316568/2021-0), and CP holds a grant from the Brazilian agency CNPq. Research Support Foundation of the State of Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ) [JCNE] (Young Scientist from Our State) with fellowship process number [E-26/203.246/2017]; Emergent Group of Research from Rio de Janeiro [E-26/211.025/2019]; and Scientist from Our State (CNE) with fellowship process number E-26/200.982/2021 for financial support and Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) with support through scholarships. The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available upon request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Universidade Federal Fluminense and the Postgraduate Program in Science and Biotechnology; the team of the Laboratório de Avaliação e Promoção da Saúde Ambiental, Instituto Oswaldo Cruz; the Laboratório de Malacologia, Instituto Oswaldo Cruz; and the Farmanguinhos Technology Platform. We also thank CNPq (National Council of Research of Brazil), FAPERJ (Research Support Foundation of the State of Rio de Janeiro), and CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personel) for financial support. Financial and material support was obtained from the National Council of Research of Brazil (CNPq), the Research Support Foundation of the State of Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ) and the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Artal, F.J.C. Cerebral and Spinal Schistosomiasis. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2012, 12, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO—World Health Organization. Epidemiology and Control of Schistosomiasis; Technical Report Series 728; WHO—World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Secor, W.E. Water-based interventions for schistosomiasis control. Pathog. Glob. Health 2014, 108, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO—World Health Organization. Schistosomiasis. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schistosomiasis (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Abou-El-Naga, I.F. Demographic, socioeconomic and environmental changes affecting circulation of neglected tropical diseases in Egypt. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madinga, J.; Linsuke, S.; Mpabanzi, L.; Meurs, L.; Kanobana, K.; Speybroeck, N.; Lutumba, P.; Polman, K. Schistosomiasis in the Democratic Republic of Congo: A literature review. Parasit Vectors 2015, 8, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitorino, R.R.; Souza, F.P.C.; Costa, A.P.; Júnior, F.C.F.; Santana, L.A.; Gomes, A.P. Esquistossomose mansônica: Diagnóstico, tratamento, epidemiologia, profilaxia e controle. Rev. Bras. Clin. Med. 2012, 10, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ministério da Saúde. Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Coordenação-Geral de Desenvolvimento da Epidemiologia em Serviços. In Guia de Vigilância em Saúde 3, 1st ed.; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, D.P.; Melo, A.L.; Linardi, P.M.; Almeida, R.W.; Bezerra, F.S.M. Molusco transmissor do Schistosoma mansoni. In Parasitologia Humana, 12th ed.; Atheneu: São Paulo, Brazil, 2011; Volume 23, pp. 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, O.S.; Coelho, P.M.; Lenzi, H.L. Epidemiologia e controle da esquitossomose mansoni. In Schistosoma mansoni & Esquistossomose: Uma Visão Multidisciplinar; Fiocruz: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2008; pp. 965–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli, A.; Soares, M.S.; D’Andréa, P.S.; Gonçalves, M.M.L.; Rey, L. Abundância e infecção do molusco Biomphalaria glabrata pelo Schistosoma mansoni no Estado do Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. Rev. Saude Publica 2001, 35, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO—World Health Organization. Organization’s Guidelines on Screening for Plant Molluskicides; Technical Report Series 728; WHO—World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1983.
- Calumpang, S.M.F.; Medina, M.J.B.; Tejada, A.W.; Medina, J.R. Environmental impact of two molluscicides: Niclosamide and metaldehyde in a rice paddy ecosystem. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1995, 55, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diab, Y.; Ioannou, E.; Emam, A.; Vagias, C.; Roussis, V. Desmettianosides A and B, bisdesmosidic furostanol saponins with molluscicidal activity from Yucca desmettiana. Steroids 2012, 77, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H.K.; Omram, N.E.E.; Eissam, S.H.; Kandeil, M.A. Induction of teratogenesis of freshwater snail (Biomphalaria alexandrina) using the molluskicide niclosamide. Sci.-Afric. J. Scient. Issues Res. 2014, 2, 255–268. [Google Scholar]
- Mccllough, F.S.; Gayral, P.; Duncan, J.; Christie, J.D. Molluskicides in schistosomiasis control. B World Health Organ. 1980, 58, 681–689. [Google Scholar]
- Marston, A.; Hostettmann, K. Review article number 6: Plants moluscicides. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, P.M.Z.; Caldeira, R.L. Critical analysis of molluskicide application in schistosomiasis control programs in Brazil. BioMed Cent. 2016, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, C.M.O.; Schenkel, E.L.; Gosman, G. Farmacognosia: Da Planta ao Medicamento; Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 1999; p. 821. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Yu, W.; Li, Y.; Prasad, N.; Tang, Z. Antioxidant activity of extract and its major constituents from okra seed on rat hepatocytes injured by carbon tetrachloride. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 341291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, J.; Bhatt, P. Flavonoids derived from Abelmoschus esculentus attenuates UV-B induced cell damage in human dermal fibroblasts through Nrf2-AREpathway. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12 (Suppl. 2), S129–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrozadeh, M.; Heydari, N.; Abootalebi, M. The effect of Abelmoschus esculentus on blood levels of glucose in Diabetes Mellitus. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 41, S63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Mao, P.; Jin, J.; Huang, J.; Yang, M. Study on anti-fatigue effect of okra extracts. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2012, 29, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.N.; Seth, A.K.; Maheshwari, K.M.; Desai, R.V. Screening of Abelmoschus esculentus fruits for its analgesic activity. Pharmacol. Online 2010, 2, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- WHO—World Heatlh Organization. Molluskicide Screening and Evolution. Bull. World. Health.Org. 1965, 33, 567–581. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.A.A.; Cavalcante, V.P.; Rangel, L.S.; Leite, J.C.V.A.; Faria, R.X. A new technique using low volumes: A new technique to assess the molluscicidal activity using low volumes. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, J.T.; Wilcoxon, F.A.A. Simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiment. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 1949, 96, 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, T.M. Manual de Bioquímica com Correlações Químicas; Edgard Blucher: São Paulo, Brazil, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, W.R.; Lopesa, S.R.P.; Batista, D.; Nevesa, M.H.C.B.; Coutinhoa, R.; Lopesb, C.C.; Lopesb, R.S.C. Evaluating Antimicrobial Activity of Bioactive Glycerophospholipids Presents in Brazilian Marine Sponges Extracts. In The Battle against Microbial Pathogens: Basic Science, Technological Advances, and Educational Programs; Microbiology Book Series 5; Formatex Research Center S.L.: Badajoz, Spain, 2015; pp. 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, B.K.; Jackman, J.A.; Valle-González, E.R.; Cho, N.-J. Antibacterial free fatty acids and monoglycerides: Biological activities, experimental testing, and therapeutic applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, E.A.; de Carvalho, C.M.; Costa, A.L.S.; Conceição, A.S.; Moura, F.B.P.; Santana, A.E.G. Bioactivity Evaluation of plant extracts used in indigenous medicine against the snail, Biomphalaria glabrata, and the larvae of Aedes aegypti. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.M.; Da Silva, T.G.; Martins, R.M.; Maia, G.L.; Cabral, A.G.; Camara, C.A.; Agra, M.F.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M. Molluscicidal activities of six species of Bignoniaceae from northeastern Brazil, as measured against Biomphalaria glabrata under laboratory conditions. Ann. Trop Med. Parasitol. 2007, 101, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapado, L.N.; Pinheiro, A.S.; Lopes, P.O.; Fokoue, H.H.; Scotti, M.T.; Marques, J.V.; Ohlweiler, F.P.; Borrely, S.I.; Pereira, C.A.; Kato, M.J.; et al. Schistosomiasis control using piplartine against Biomphalaria glabrata at different developmental stages. PLoS Negl. Trop Dis. 2013, 7, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapado, L.N.; Nakano, E.; Ohlweiler, F.P.; Kato, M.J.; Yamaguchi, L.F.; Pereira, C.A.B.; Kawano, T. Molluscicidal and ovicidal activities of plant extracts of the Piperaceae on Biomphalaria glabrata (Say, 1818). J. Helminthol. 2011, 85, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasato, P.A.; Kawano, T.; Freitas, J.C.; Berlinck, R.G.; Nakano, E.; Tallarico, L.F. Molluscicidal activity of some marine substances against the snail Biomphalaria glabrata (Molluska, Planorbidae). Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 1873–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Filho, E.C.; Geraldino, B.R.; Coelho, D.R.; De-Carvalho, R.R.; Paumgartten, F.J. Comparative toxicity of Euphorbia milii latex and synthetic molluskicides to Biomphalaria glabrata embryos. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, D.K. Molluscicidal activity of Abrus precatorius Linn. and Argemone mexicana Linn. Chemosfere 1999, 38, 3319–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitman, S.; Frankel, S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxaloacetic and glutamic pyruvic trasaminases. Am. J. Clin. Path. 1957, 28, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kind, P.R.N.; King, E.J. Estimation of plasma phosphatase by determination of hydrolyzed phenol with amino-antipyrine. J. Clin. Pathol. 1954, 7, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Carvalho, R.R.; Maldonado Júnior, A.; Oliveira Filho, E.C.; Ribeiro, A.C.; Paumgartten, F.J.; Rey, L. Effects of Euphorbia milii latex on Schistosoma mansoni eggs, miracidia and cercariae. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 1998, 93 (Suppl. 1), 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.C.B.; Silva, M.C.; Silva, H.A.M.F.; Silva, L.R.S.; Albuquerque, M.C.P.A.; Aires, A.L.; Falcão, E.P.S.; Pereira, E.C.; Melo, A.M.M.A.; Silva, N.H. Barbatic acid offers a new possibility for control of Biomphalaria glabrata and schistosomiasis. Molecules 2017, 22, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.F.; Fonseca, S.A.; César, F.A.; Albuquerque, M.C.P.A.; Santana, J.V.; Santana, A. A penta-substituted pyridine alkaloid from the rhizome of Jatropha elliptica (Pohl) Muell. Arg. is active against Schistosoma mansoni and Biomphalaria glabrata. Parasitol. Res 2014, 113, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekwu, E.M.; Bosompem, K.M.; Anyan, W.K.; Appiah-Opong, R.; Owusu, K.B.A.; Tettey, M.D.; Kissi, F.A.; Appiah, A.A.; Beng, V.P.; Nyarko, A.K. In Vitro Assessment of Anthelmintic Activities of Rauwolfia vomitoria (Apocynaceae) Stem Bark and Roots against Parasitic Stages of Schistosoma mansoni and Cytotoxic Study. J. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 2017, 2583969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD—Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Test No. 203: Fish, Acute Toxicity Test; OECD iLibrary: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- NBR 12713; Ecotoxicologia Aquática—Toxicidade Aguda—Método de Ensaio com Daphnia spp. (Crustacea, Cladocera). ABNT—Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016; 23 p.
- OECD—Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Test No. 201: Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test. Guidel. Test. Chem. 2004, 201, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 11348-1; Water Quality—Determination of the Inhibitory Effect of Water Samples on the Light Emission of Vibrio fischeri (Luminecescentbacteria Test). ISO—International Organization for Standardization: Geneve, Switzerland, 1997.
- Postila, P.A.; Róg, T. A Perspective: Active Role of Lipids in Neurotransmitter Dynamics. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 910–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasiuk, M.; Janiszeweska, A.; Kozubek, A. Phenolic Lipids Affect the Activity and Conformation of Acetylcholinesterase from Electrophorus electricus (Electric eel). Nutrients 2014, 6, 1823–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiuk, M.; Bartosiewicz, D.; Kozubek, A. Inhibitory effect of some natural and semisynthetic phenolic lipids upon acetylcholinesterase activity. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akay, M.B.; Şener, K.; Sari, S.; Bodur, E. Inhibitory Action of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids Alpha-Linolenic, Arachidonic and Linoleic acid on Human Erythrocyte Acetylcholinesterase. Protein. J. 2023, 42, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loesche, A.; Wiemann, J.; Al Halabi, Z.; Karasch, J.; Sippl, W.; Csuk, R. Unexpected AChE inhibitory activity of (2E)α,β-unsaturated fatty acids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 3315–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blusztajn, J.K.; Lopez Gonzalez-Coviella, I.; Logue, M.; Growdon, J.H.; Wurtman, R.J. Levels of phospholipid catabolic intermediates, glycerophosphocholine and glycerophosphoethanolamine, are elevated in brains of Alzheimer’s disease but not of Down’s syndrome patients. Brain Res. 1990, 536, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fifer, E.K.; Lemke, T.L.; Williams, D.A. Em Foye’s Principles of Medicinal Chemistry, 7th ed.; Lemke, T.L., Williams, D.A., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; cap. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Vehovszky, Á.; Farkas, A.; Ács, A.; Stoliar, O.; Székács, A.; Mörtl, M.; Győri, J. Neonicotinoid insecticides inhibit cholinergic neurotransmission in a molluskan (Lymnaea stagnalis) nervous system. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 167, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Schultz, T.; Althaus, H.H. Monogalactosyl diglyceride, a marker for myelination, activates oligodendroglial protein kinase C. J. Neurochem. 1994, 62, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plows, L.D.; Cook, R.T.; Davies, A.J.; Walker, A.J. Activation of extracellular-signal regulated kinase is required for phagocytosis by Lymnaea stagnalis hemocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2004, 1692, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, B.; Lacchini, A.H.; Davies, A.J.; Walker, A.J. Regulation of nitric oxide production in snail (Lymnaea stagnalis) defense cells: A role for PKC and ERK signaling pathways. Biol. Cell 2006, 98, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, J.E.; Elizondo, L.; Yoshino, T.P. Protein kinase C regulation of cell spreading in the molluskan Biomphalaria glabrata embryonic (Bge) cell line. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2001, 1540, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacchini, A.H.; Davies, A.J.; Mackintosh, D.; Walker, A.J. β-1,3-glucan modulates PKC signaling in Lymnaea stagnalis defense cells: A role for PKC in H2O2 production and downstream ERK activation. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 4829–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardans, V.; Serra, E.; Capron, A.; Dissous, C. Characterization of an intracellular receptor for activated protein kinase C (RACK) from the mollusk Biomphalaria glabrata, the intermediate host for Schistosoma mansoni. Exp. Parasitol. 1998, 88, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).