Isolation and Identification of Bitter Compounds in Ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Mey.) Based on Preparative High Performance Liquid Chromatography, UPLC-Q-TOF/MS and Electronic Tongue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. HPLC-DAD Analysis
2.4. Preparation and Collection of the Fractions
2.5. Distillate Collection and Treatment
2.6. Recognition of the Bitter Fraction
2.7. Qualitative Analysis of Bitter Compounds
2.8. Quantitation Analysis of Bitter Compounds
2.9. Bitter Taste Evaluation of Samples Using Electronic Tongue
2.10. Preparation of Debittered Samples
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
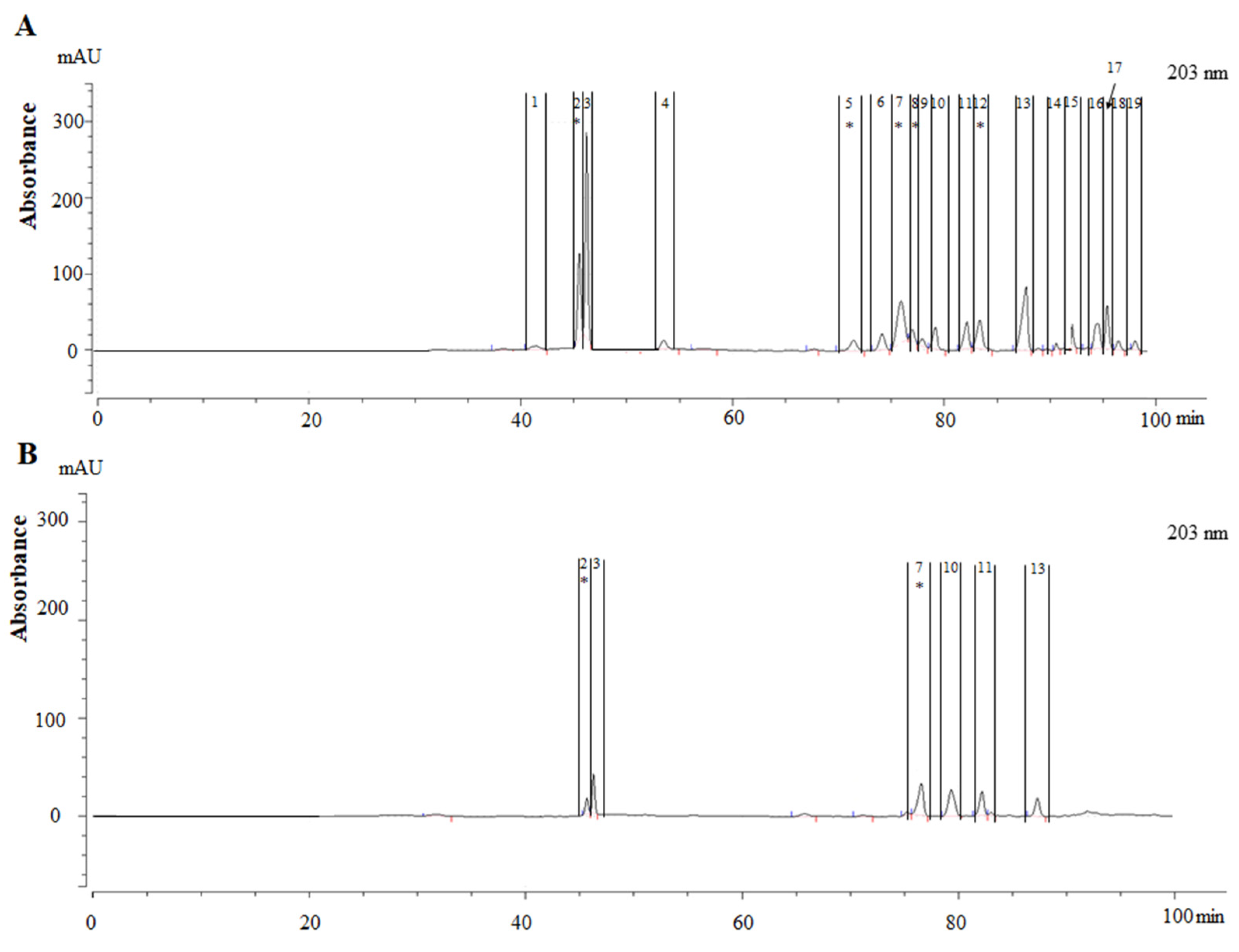
3.1. Separation of the Bitter Compounds from Ginseng
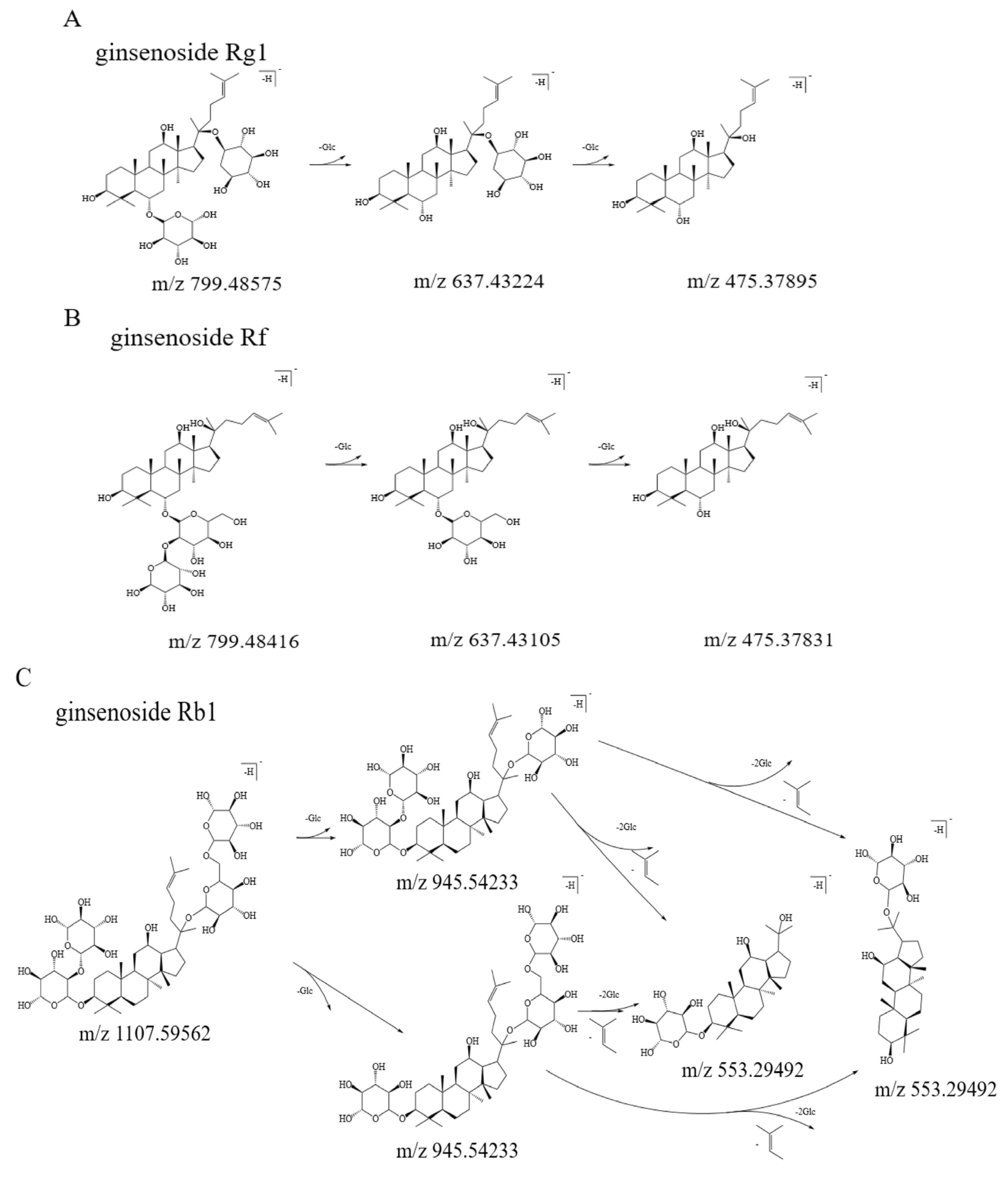
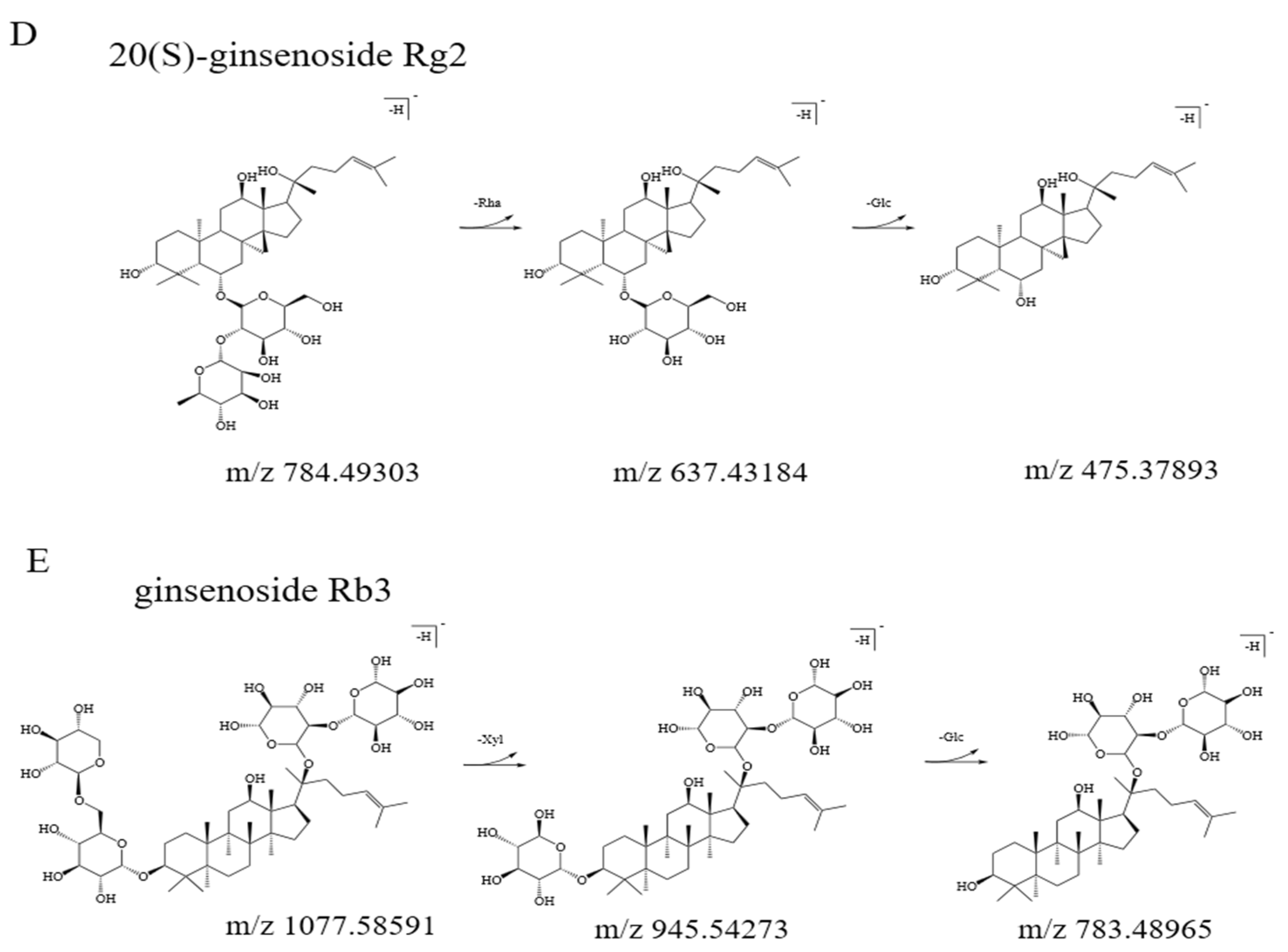
3.2. Qualitative Analysis of Bitter Fractions
3.3. Quantitation of the Bitter Fractions
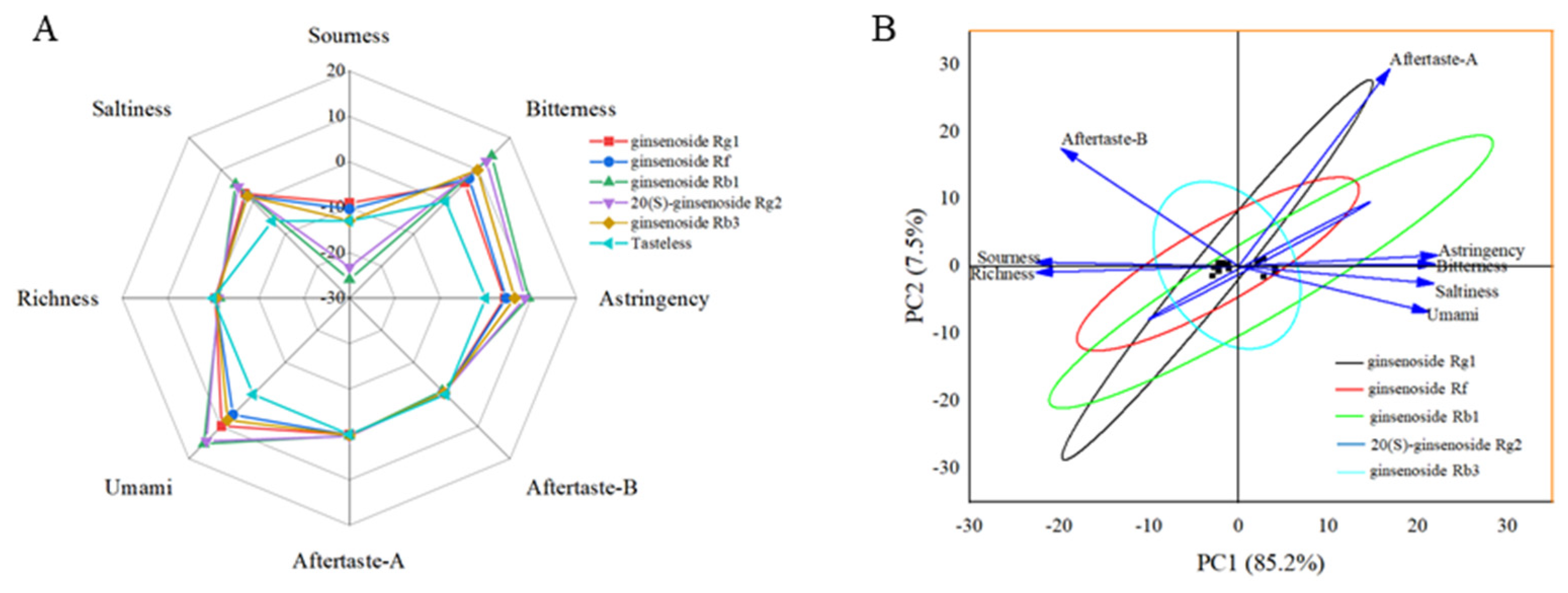
3.4. Bitterness Analysis of Ginsenoside Rg1, Ginsenoside Rf, Ginsenoside Rb1, 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg2 and Ginsenoside Rb3 by Electronic Tongue
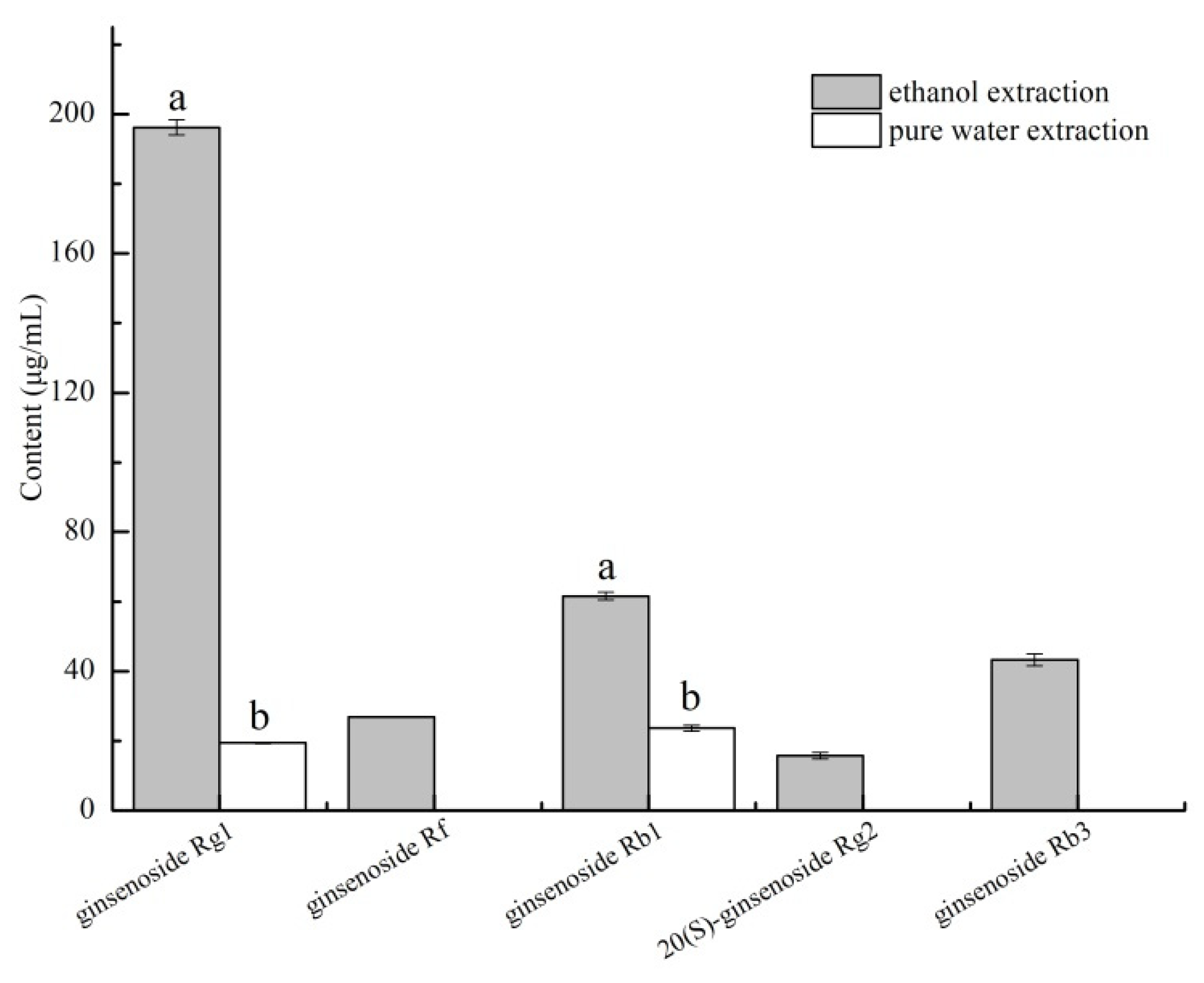
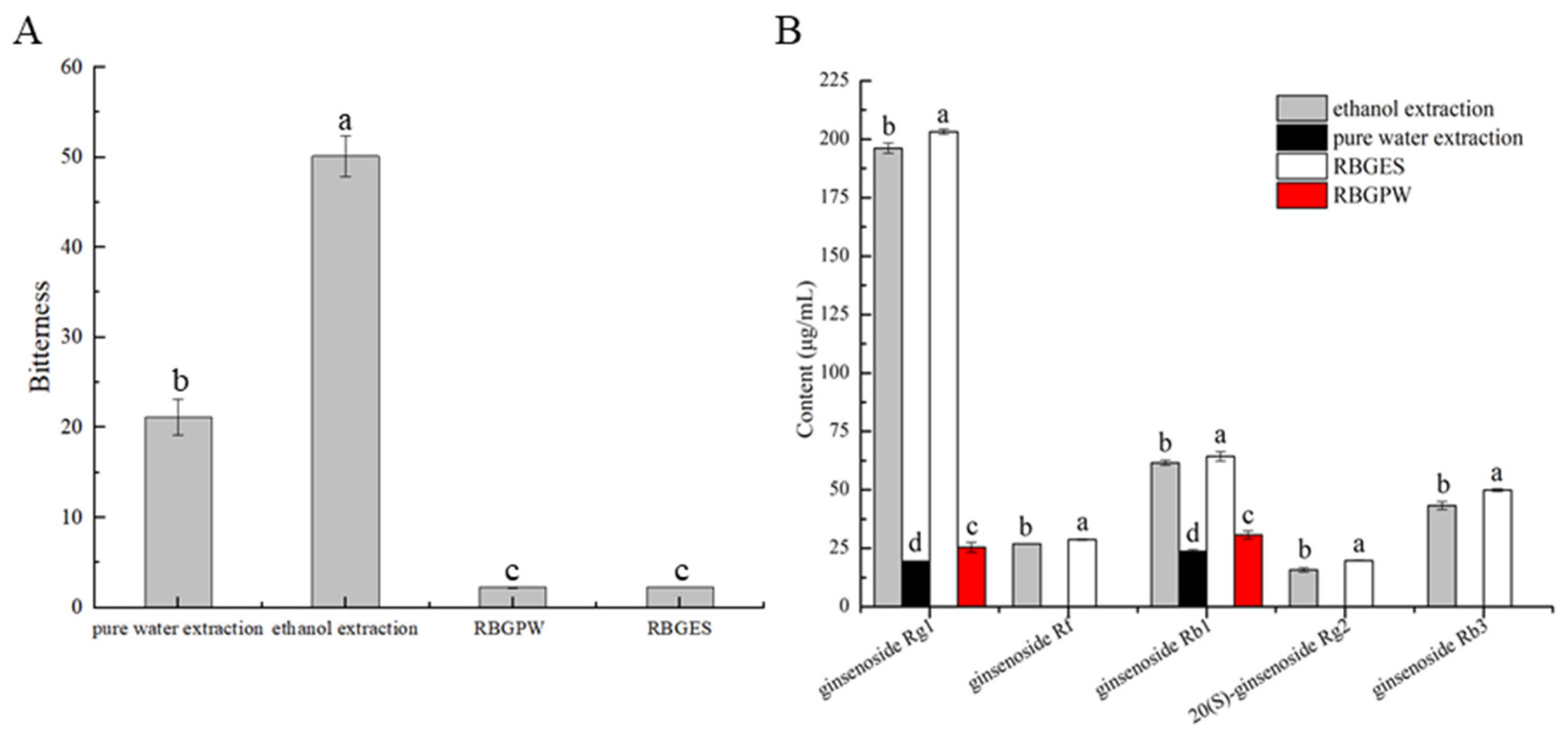
3.5. Analysis of Bitterness Elimination Effect
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Guo, M.; Li, H. Panax Ginseng in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. J. Ginseng Res. 2023, 47, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Abid, S.; Ahn, J.C.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Kim, Y.-J.; Yang, D.-C.; Wang, Y.; Cho, I.-H. Characteristics of Panax ginseng Cultivars in Korea and China. Molecules 2020, 25, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Xu, L.; Yu, H.; Feng, Q.; Yan, H.; Shahid, A.; Chen, Q.; Jibo, R.; Gao, X.; Wang, D. An efficient isolation and purification of broad partition coefficient range ginsenosides from roots of Panax quinquefolium L. by linear gradient counter-current chromatography coupled with preparative HPLC. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, 2300046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Chen, Q. Inhibition of the pyroptosis-associated inflammasome pathway: The important potential mechanism of ginsenosides in ameliorating diabetes and its complications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 253, 115336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Wu, C.; Ge, Q.; Zhou, J.; Long, F.; Mao, Q.; Li, S.; Shen, H. Structure-specific antitumor effects and potential gut microbiota-involved mechanisms of ginseng polysaccharides on B16F10 melanoma-bearing mice. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.J.; Bong, S.K.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y.; Jegal, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.N. Compound K improves skin barrier function by increasing SPINK5 expression. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhou, R.; Fan, H.; Sui, J. Amelioration of alcohol-induced liver injury in mice by ginsenosides in ginseng wine. J. Funct. Foods. 2019, 54, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Qualitative and quantitative analysis on aroma characteristics of ginseng at different ages using E-nose and GC–MS combined with chemometrics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 102, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sanjeevram, D.; Mi, X.; Hye-Ryung, P.; Yeon-Ju, K. Immune-enhancing efficacy of Curtobacterium proimmune K3 lysates isolated from Panax ginseng beverages in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice. J. Funct. Foods. 2022, 92, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, S.C.; Soo-Yeun, L. Modification of ginseng flavors by bitter compounds found in chocolate and coffee. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, S202–S210. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.K.; Dhua, S.; Kumar, V.; Naik, B.; Magwaza, L.S.; Ncama, K.; Opara, U.L.; McClements, D.J.; Mishra, P. Current and emerging applications in detection and removal of bitter compounds in citrus fruit juice: A critical review. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 102995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Ouyang, W.; Chen, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hua, J.; Yuan, H. Effects of electromagnetic roller-hot-air–steam triple-coupled fixation on reducing the bitterness and astringency and improving the flavor quality of green tea. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolkowski, A.; Meudec, E.; Bruguière, A.; Offer, A.C.M.; Bouzidi, E.; Levavasseur, L.; Sommerer, N.; Briand, L.; Salles, C. Faba Bean (Vicia faba L. minor) Bitterness: An Untargeted Metabolomic Approach to Highlight the Impact of the Non-Volatile Fraction. Metabolites. 2023, 13, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, G.; Oluwaseun, O.A.; Mo, Z.; Mao, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Ma, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H. Bitter and astringent substances in green tea: Composition, human perception mechanisms, evaluation methods and factors influencing their formation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Liu, G.; Tang, X.; Jia, X. Structure determination, bitterness evaluation and hepatic gluconeogenesis inhibitory activity of triterpenoids from the Momordica charantia fruit. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W.; Han, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ye, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. The Taste-Masking Mechanism of Chitosan at the Molecular Level on Bitter Drugs of Alkaloids and Flavonoid Glycosides from Traditional Chinese Medicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewnowski, A. The science and complexity of bitter taste. Nutr. Rev. 2001, 59, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Choi, B.-R.; Kim, Y.-C.; Choi, D.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, G.-S.; Baek, N.-I.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, D. Comprehensive Profiling and Quantification of Ginsenosides in the Root, Stem, Leaf, and Berry of Panax ginseng by UPLC-QTOF/MS. Molecules 2017, 22, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, M.; Gao, X.; LI, H.; et al. An off-line three-dimensional liquid chromatography/Q-Orbitrap mass spectrometry approach enabling the discovery of 1561 potentially unknown ginsenosides from the flower buds of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius and Panax notoginseng. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1675, 463177. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cong, X.; Hao, M. Effect of anti-skin disorders of ginsenosides—A Systematic Review. J. Ginseng Res. 2023, 47, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cao, D.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y. Anticancer therapeutic effect of ginsenosides through mediating reactive oxygen species. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1215020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Liang, X.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Hu, L.; Li, R. Total ginsenosides promotes intestinal epithelial proliferation via affecting polyamine-mediated HuR on post-transcriptional control. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 102970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, C.; Jin, Y.; Shen, W.; Pan, Y.; Shen, Y. Ginsenoside Rg1 improved learning and memory ability and reduces neuronal apoptosis in epileptic rats through ERK/CREB/BDNF signal pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 675, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; He, J.; Yu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Liao, X. In silico identification of novel small molecule umami peptide from ovotransferrin. Int. J. Food Sci Tech. 2022, 57, 2628–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sora, H.; Tatsuro, H.; Miho, K.; Kenlchi, K.; Hideyuki, O.; Satoru, T.; Satoshi, S.; Hideyuki, Y.; Kaoru, S.; Takayuki, M. Comparison of taste characteristics between koji mold-ripened cheese and Camembert cheese using an electronic tongue system. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 6701–6709. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, B.-Y.; Jen, C.-T.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.-H. A comparative study on analysis of ginsenosides in American ginseng root residue by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS and UPLC-HRMS-MS/MS. Molecules 2022, 27, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, L.; Huang, Y.; Xie, C.; Dou, D.; Xu, J. Correlations between ecological factors and the chemical compositions of mountainous forest cultivated ginseng. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Tao, L.; Wei, X.; Gao, L.; Gao, Y.; Suo, J.; Yu, W.; Hu, Y.; Yang, B. Ethylene treatment promotes umami taste-active amino acids accumulation of Torreya grandis nuts post-harvest by comparative chemical and transcript analyses. Food Chem. 2023, 408, 135214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iiyama, S.; Ezaki, S.; Toko, K. Analysis of saltiness and bitterness of inorganic salts using taste sensors. Sens. Mater. 2001, 13, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, C.G.; Clowers, B.H.; Moore, R.J.; Zink, E.M. Signature-discovery approach for sample matching of a nerve-agent precursor using liquid chromatography−mass spectrometry, XCMS, and chemometrics. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fávaro-Trindade, C.S.; Santana, A.d.S.; Monterrey-Quintero, E.S.; Trindade, M.A.; Netto, F.M. The use of spray drying technology to reduce bitter taste of casein hydrolysate. Food Hydrocolloids 2010, 24, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Huang, X.; Cheng, C.; McClements, D.J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Zou, L.; Wei, L. Encapsulation of bitter peptides in diphasic gel double emulsions: Bitterness masking, sustained release and digestion stability. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Tasteless | Code b | Bitterness | Code c | Bitterness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | −0.21 ± 0.02 | ||
| 0 | 2 | 1.62 ± 0.03 | 2 | 1.60 ± 0.03 |
| 0 | 3 | −0.27 ± 0.01 | 3 | −0.26 ± 0.02 |
| 0 | 4 | −0.31 ± 0.03 | ||
| 0 | 5 | 13.72 ± 0.37 | ||
| 0 | 6 | −0.34 ± 0.04 | ||
| 0 | 7 | 11.21 ± 0.32 | 7 | 11.24 ± 0.21 |
| 0 | 8 | 6.69 ± 0.51 | ||
| 0 | 9 | −0.32 ± 0.02 | ||
| 0 | 10 | −0.36 ± 0.03 | 10 | −0.38 ± 0.04 |
| 0 | 11 | −0.33 ± 0.04 | 11 | −0.35 ± 0.04 |
| 0 | 12 | 7.21 ± 0.45 | ||
| 0 | 13 | −0.41 ± 0.03 | 13 | −0.39 ± 0.04 |
| 0 | 14 | −0.29 ± 0.04 | ||
| 0 | 15 | −0.31 ± 0.02 | ||
| 0 | 16 | −0.36 ± 0.04 | ||
| 0 | 17 | −0.35 ± 0.02 | ||
| 0 | 18 | −0.29 ± 0.02 | ||
| 0 | 19 | −0.34 ± 0.03 |
| Code b | RT (min) c | TMUAW (nm) d | [M-H]− | Major Product Ions | Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 15.83 | 202.31 | 799.48575 | 637.43224; 475.37895 | ginsenoside Rg1 |
| 5 | 18.93 | 203.79; 234.68 | 799.48416 | 637.43105; 475.37831 | ginsenoside Rf |
| 7 | 20.01 | 201.76; 276.93 | 1107.59562 | 945.54233; 553.29492 | ginsenoside Rb1 |
| 8 | 19.79 | 205.53; 263.95; 385.40 | 784.49303 | 637.43184; 475.37893 | 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg2 |
| 12 | 21.03 | 198.10; 275.71; 365.45 | 1077.58591 | 945.54273; 783.48965 | ginsenoside Rb3 |
| Bitter Compound | Linear Regression Equation | R2 | Linearity Range (mg/L) | LOD (μg/mL) | LOQ (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ginsenoside Rg1 | Y = 0.0525X − 0.1264 | 1.000 | 6.72~537.57 | 1.0723 | 3.4532 |
| ginsenoside Rf | Y = 0.0516X + 0.0105 | 1.000 | 5.39~431.54 | 0.4565 | 1.6671 |
| ginsenoside Rb1 | Y = 0.0374X + 0.0089 | 1.000 | 7.32~585.61 | 1.0931 | 3.2864 |
| 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg2 | Y = 0.0544X + 0.4095 | 0.999 | 4.20~671.52 | 0.3504 | 1.0857 |
| ginsenoside Rb3 | Y = 0.0370X − 0.0051 | 1.000 | 12.97~518.79 | 2.7841 | 7.9123 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Liao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Shi, W.; Xu, J. Isolation and Identification of Bitter Compounds in Ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Mey.) Based on Preparative High Performance Liquid Chromatography, UPLC-Q-TOF/MS and Electronic Tongue. Separations 2024, 11, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11040114
Chen Y, Liao Z, Wang Z, Shi W, Xu J. Isolation and Identification of Bitter Compounds in Ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Mey.) Based on Preparative High Performance Liquid Chromatography, UPLC-Q-TOF/MS and Electronic Tongue. Separations. 2024; 11(4):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11040114
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yang, Ziwei Liao, Zhe Wang, Wanyin Shi, and Jian Xu. 2024. "Isolation and Identification of Bitter Compounds in Ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Mey.) Based on Preparative High Performance Liquid Chromatography, UPLC-Q-TOF/MS and Electronic Tongue" Separations 11, no. 4: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11040114
APA StyleChen, Y., Liao, Z., Wang, Z., Shi, W., & Xu, J. (2024). Isolation and Identification of Bitter Compounds in Ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Mey.) Based on Preparative High Performance Liquid Chromatography, UPLC-Q-TOF/MS and Electronic Tongue. Separations, 11(4), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11040114





