Programmable Low-Pressure Chromatographic Sub-90 s Assay of Parabens in Cosmetics with Post-Column Chemiluminescence Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
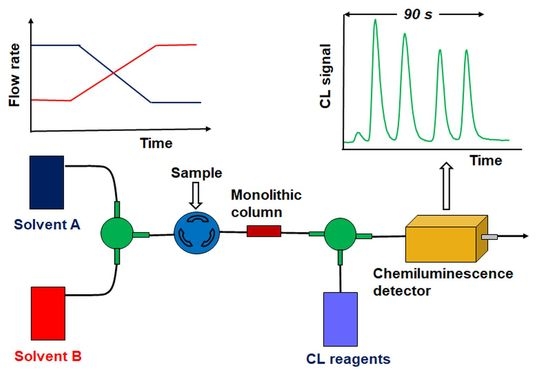
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.3.1. Preparation of Standard Solutions and Sample Extraction
2.3.2. Experimental Sequence
3. Results and Discussion
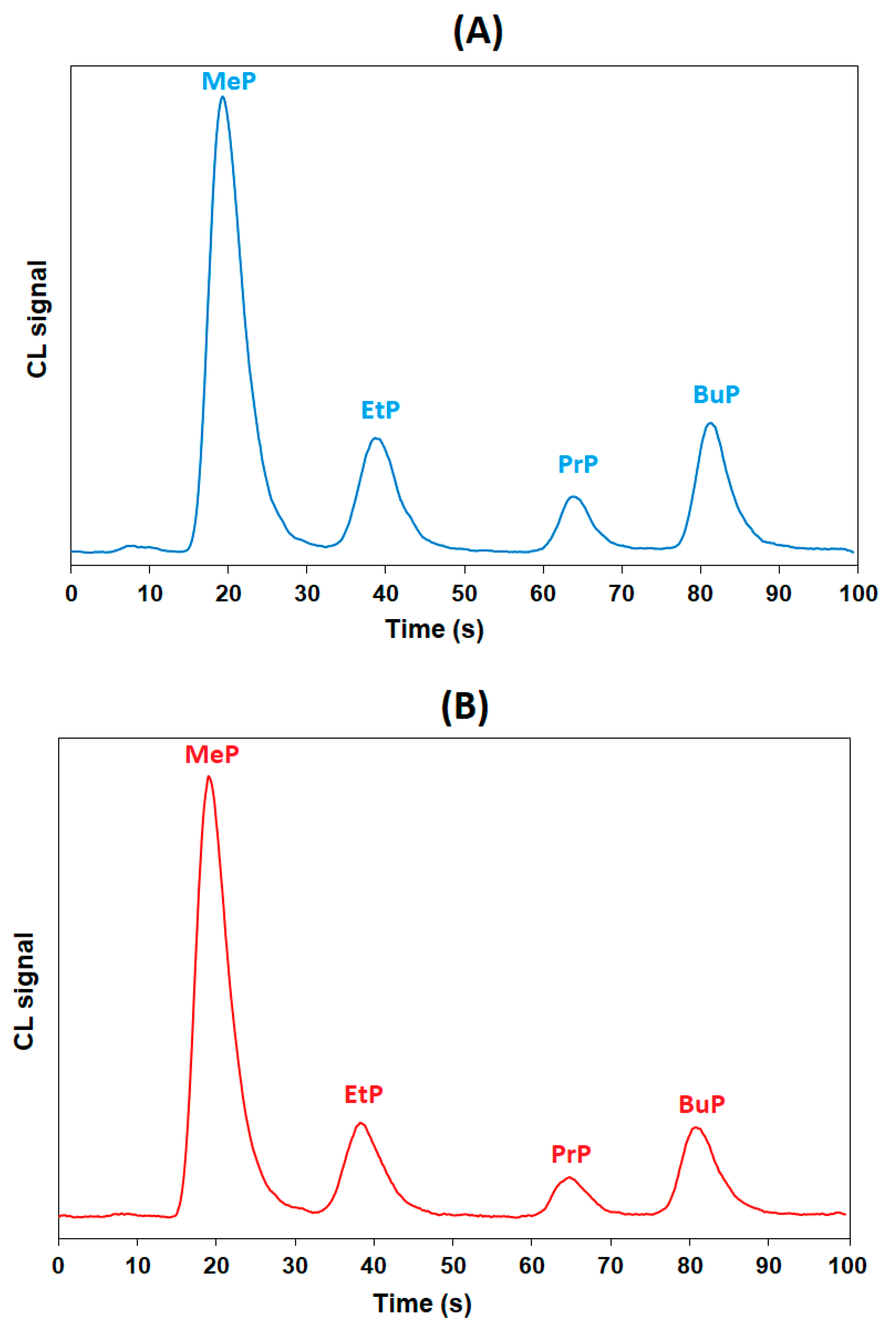
3.1. Selection of the Chromatographic Conditions
3.2. Selection of the Post-Colum CL Reaction Conditions
3.3. Method Validation
3.4. Application to Samples of Cosmetics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, F.; Mortimer, M.; Cheng, H.; Sang, N.; Guo, L.H. Parabens as chemicals of emerging concern in the environment and humans: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matwiejczuk, N.; Galicka, A.; Brzóska, M.M. Review of the safety of application of cosmetic products containing parabens Journal of Applied Toxicology. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2020, 40, 176–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Paul, N.; Ghosh, S.; Das, M. An Overview of Endocrine Disrupting Chemical Paraben and Search for An Alternative—A Review. Proc. Zool. Soc. 2021, 74, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Halaseh, L.K.; Al-Adaile, S.; Mbaideen, A.; Abu Hajleh, M.N.; Al-Samydai, A.; Zakaraya, Z.Z.; Dayyih, W.A. Implication of parabens in cosmetics and cosmeceuticals: Advantages and limitations. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 3265–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincho, J.; Martins, R.C.; Gomes, J. Paraben Compounds—Part I: An Overview of Their Characteristics, Detection, and Impacts. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas Resende, D.; da Silva Alves, G.C.; Oliveira do Couto, R.; Sanches, C.; Drumond Chequer, F.M. Can parabens be added to cosmetics without posing a risk to human health? A systematic review of its toxic effects, Rev. Ciênc. Farm. Básica Apl. 2021, 42, e706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 358/2014 of 9 April 2014 Amending Annexes II and V to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and on the Council on Cosmetic Products. EUR-Lex-32014R0358-EN-EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32014R0358 (accessed on 16 May 2023).
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 1004/2014 of 18 September 2014 Amending Annex V to Regulation /EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council on Cosmetic Products. EUR-Lex-32014R1004-EN-EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32014R1004 (accessed on 16 May 2023).
- Błędzka, D.; Gromadzińska, J. Wojciech Wąsowicz, Parabens. From environmental studies to human health. Environ. Int. 2014, 67, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, A.; Fonseca, A.P. Parabens paradoxes in cosmetic formulations: A review. Int. J. Med. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudi, F. Review of analytical methods for determination of parabens in cosmetic products. Def. ST Tech. Bull. 2020, 13, 217–226. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mohd-Faris-Mohd-Rudi/publication/344638102_REVIEW_OF_ANALYTICAL_METHODS_FOR_DETERMINATION_OF_PARABENS_IN_COSMETIC_PRODUCTS/links/5f864f55299bf1b53e262269/REVIEW-OF-ANALYTICAL-METHODS-FOR-DETERMINATION-OF-PARABENS-IN-COSMETIC-PRODUCTS.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2023).
- Piao, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. A review of the extraction and chromatographic determination methods for the analysis of parabens. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 969, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocaña-González, J.A.; Villar-Navarro, M.; Ramos-Payán, M.; Fernández-Torres, R.; Bello-López, M.A. New developments in the extraction and determination of parabens in cosmetics and environmental samples. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 858, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, M.; Forteza, R.; Cerdà, V. Monolithic columns in flow analysis: A review of SIC and MSC techniques. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2012, 40, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.M. The second five years of sequential injection chromatography: Significant developments in the technology and methodologies. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 44, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwell, S.K.; Kehling, A.; Lapanantnoppakhun, S.; Grudpan, K. Flow injection/sequential injection chromatography: A review of recent developments in low pressure with high performance chemical separation. Anal. Lett. 2013, 46, 1640–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economou, A. Advances in the Hyphenation of Flow Analysis Techniques with Liquid Separations for Pharmaceutical Analysis. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2012, 12, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, T.; Tanaka, N. Recent Progress in Monolithic Silica Columns for High-Speed and High-Selectivity Separations. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 9, 317–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svec, F.; Lv, Y. Advances and Recent Trends in the Field of Monolithic Columns for Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 250–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, J. Current trends in the development of porous polymer monoliths for the separation of small molecules. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.D.; Rocha, F.R.P. On-column preconcentration in sequential injection chromatography: Application to determination of parabens. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 4371–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondylis, P.; Barbatsi, M.; Economou, A. Automated Flow Injection Chromatography for the Rapid Assay of Parabens in Hygiene Wipes. Anal. Lett. 2015, 49, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Jiménez, J.F.; Carmen Valencia, M.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F. Parabens determination with a hybrid FIA/HPLC system with ultra-short monolithic column. J. Anal. Chem. 2010, 65, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Jiménez, J.F.; Valencia, M.C.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F. Simultaneous determination of antioxidants, preservatives and sweetener additives in food and cosmetics by flow injection analysis coupled to a monolithic column. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 594, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwell, K.S.; Kehling, A.; Lapanantnoppakhun, S. Low-Pressure Chromatographic Separation of p-Hydroxybenzoates Using Sequential Injection with Lab-on-Valve System and Miniature Monolithic Column. Chromatographia 2014, 77, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. Separations by gradient elution: Why are steep gradient profiles distorted and what is their impact on resolution in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1344, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbatsi, M.; Koupparis, M.; Economou, A. A new flow-injection chromatography method exploiting linear-gradient elution for fast quantitative screening of parabens in cosmetics. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 8337–8344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adcock, J.L.; Francis, P.S.; Agg, K.M.; Marshall, G.D.; Barnet, N.W. A hybrid FIA/HPLC system incorporating monolithic column chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2007, 600, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodas, M.; Portugal, L.A.; Avivar, J.; Estela, J.M.; Cerdà, V. Parabens determination in cosmetic and personal care products exploiting a multi-syringe chromatographic (MSC) system and chemiluminescent detection. Talanta 2015, 143, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesta Claver, J.; Valencia, M.C.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F. Analysis of parabens in cosmetics by low pressure liquid chromatography with monolithic column and chemiluminescent detection. Talanta 2009, 79, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heyden, Y.; Nijhuis, A.; Smeyers-Verbeke, J.; Vandeginste, B.G.M.; Massart, D.L. Guidance for robustness/ruggedness tests in method validation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 24, 723–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Separation of Paraben Preservatives by Reverse-Phase HPLC, Application Note, Agilent Technologies. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiT1ejN8K7_AhXLDd4KHVObAFEQFnoECAoQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.agilent.com%2FLibrary%2Fapplications%2F5989-3635EN.pdf&usg=AOvVaw3pLls0aOu9En1ZZDzWtAsi (accessed on 6 June 2023).

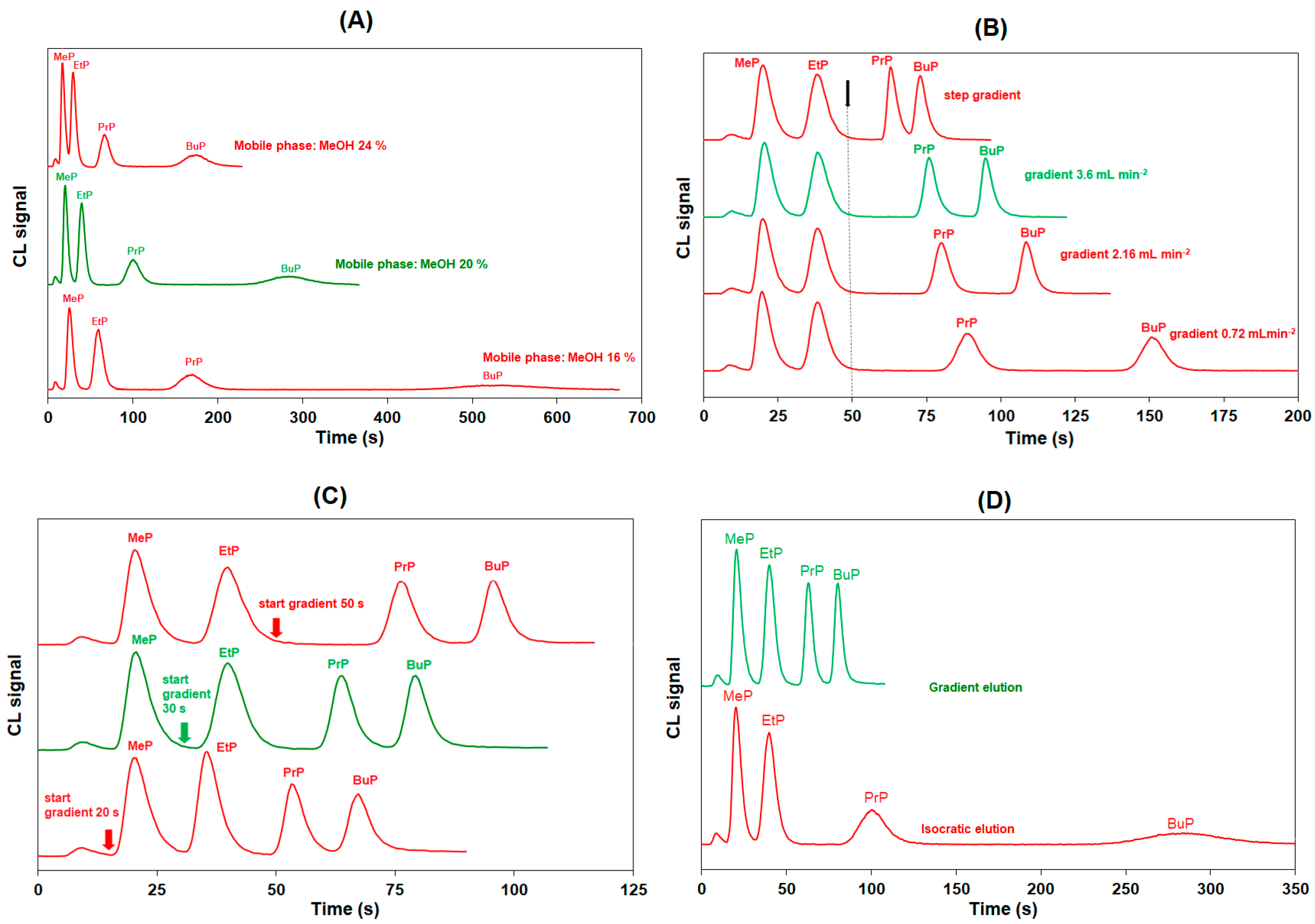
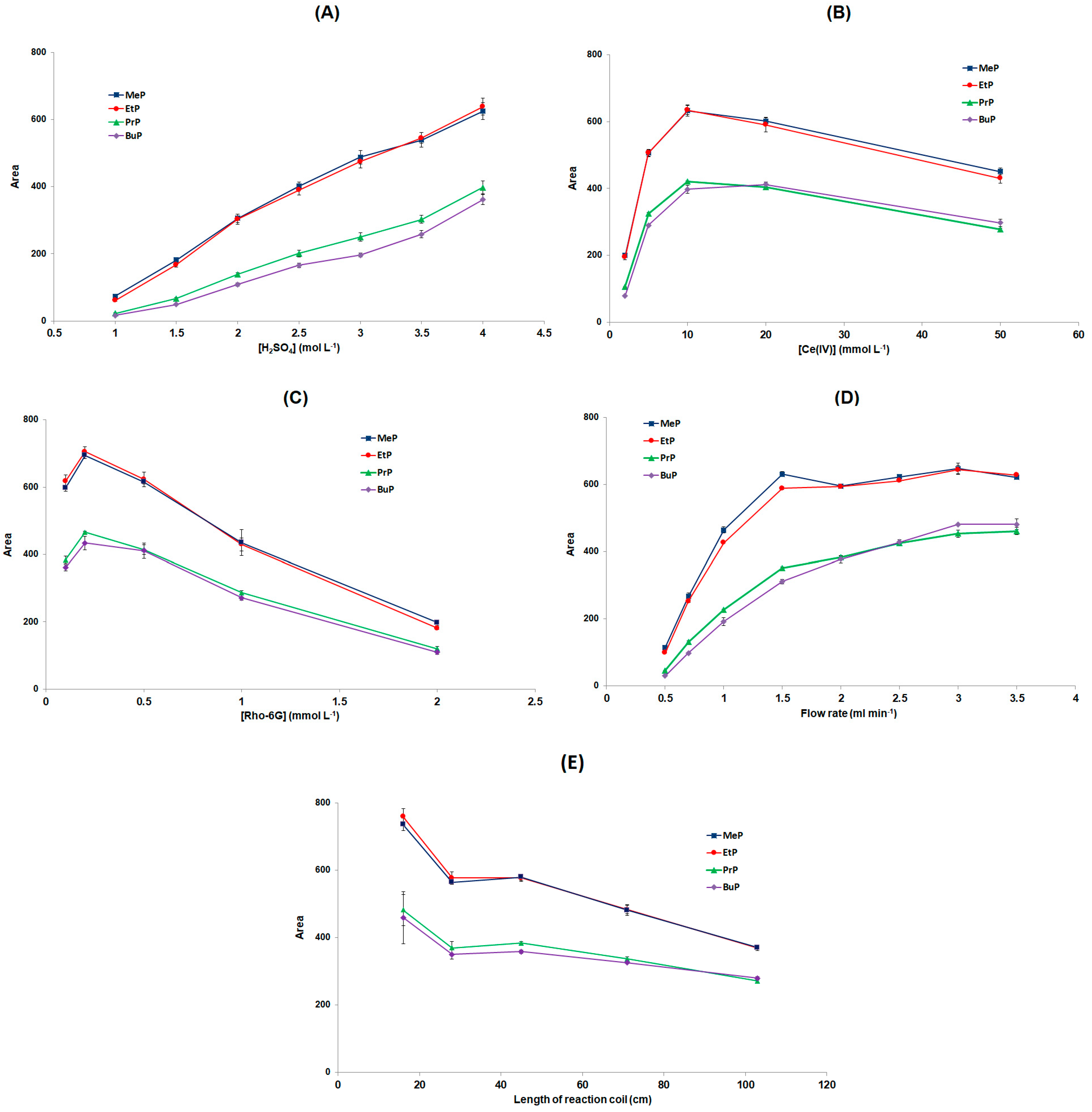
| Step | Operation | Total Time (s) | Separation Time (s) a | PP1 d | PP2 e | MG1 (mL min−1) | MG2 (mL min−1) | Solvent A/Solvent B f (% v/v) | Position of IV | Data Acquisition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Column equilibration in solvent A | 0–30 | - | Off | Off | 2.4 | 0 | 100:0 | Inject | Off |
| 2 | Sample loading | 31–35 | - | On | Off | 2.4 | 0 | 100:0 | Load | Off |
| 3 | Isocratic elution with solvent A | 36–55 | 0–30 | Off | On | 2.4 | 0 | 100:0 | Inject | On |
| 4 | Gradient elution | 56–129 | 31–95 | Off | On | 2.4 → 0 b | 0 → 2.4 c | 100:0 → 0:100 | Inject | On |
| 5 | Isocratic column cleaning in solvent B | 130–150 | - | Off | Off | 0 | 2.4 | 0:100 | Inject | Off |
| Parameter (Units) | Value |
|---|---|
| Chromatographic conditions | |
| Sample volume (μL) | 40 |
| Flow rate of the mobile phase (mL min−1) | 2.4 |
| Duration of the isocratic step (s) | 30 |
| Gradient rate (mL min−2) | 3.6 |
| Solvent A | MeOH 20% (v/v) |
| Solvent B | MeOH 36% (v/v) |
| CL detection conditions | |
| Flow rate of the CL reagents (mL min−1) | 2 |
| [Ce(IV)] (mmol L−1) | 20 |
| [Rho 6G] (mmol L−1) | 0.5 |
| [H2SO4] (mol L−1) | 4 |
| Parameter (Units) | MeP | EtP | PrP | BuP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retention time, tR (s) | 20.7 | 38.4 | 65.7 | 81.3 |
| Asymmetry factor, As | 1.32 | 1.56 | 1.42 | 1.68 |
| Resolution, Rs | 1.8 | 2.0 | ||
| Number of theoretical plates, Ν | 85 | 211 | 1150 | 2094 |
| Theoretical plates per column length (N/m) | 17,000 | 42,200 | 230,000 | 418,800 |
| MeP | EtP | PrP | BuP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear range (μmol L−1) | 0.2–20 | 0.2–20 | 0.2–20 | 0.2–20 |
| Slope (±SD) | 60.9 ± 0.10 | 66.4 ± 0.09 | 46.7 ± 0.08 | 42.0 ± 0.07 |
| Intercept (±SD) | 10.5 ± 8.5 | 6.0 ± 7.8 | 3.5 ± 6.6 | 4.0 ± 6.4 |
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 |
| LOD (μmol L−1) | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| LOQ (μmol L−1) | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Concentration | RSDr (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeP | EtP | PrP | BuP | |
| 1 μmol L−1 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.7 |
| 10 μmol L−1 | 1.1 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 2.7 |
| MeP | EtP | PrP | BuP | |
| Paraben-free wet tissues | ||||
| R% | 101 | 102 | 95 | 93 |
| RSDR % | 8.5 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 8.1 |
| Paraben-free liquid soap | ||||
| R% | 94 | 92 | 88 | 90 |
| RSDR % | 5.5 | 5.5 | 6.2 | 6.4 |
| Paraben-free face lotion | ||||
| R | 96 | 97 | 93 | 94 |
| RSDR % | 7.8 | 5.5 | 6.7 | 8.7 |
| Interval | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeP | EtP | PrP | BuP | |
| Gradient rate (mL min−2) | [3.8, 3.4] | [3.8, 3.4] | [3.7, 3.5] | [3.7, 3.5] |
| MeOH (% v/v) in solvent A | [19, 21] | [19, 21] | [18,22] | [18, 22] |
| MeOH (% v/v) in solvent B | [33, 39] | [33, 39] | [33, 39] | [34, 38] |
| Isocratic elution time (s) | [28, 32] | [28, 32] | [28, 32] | [28, 32] |
| [Ce(IV)] (mmol L−1) | [18, 22] | [18, 22] | [18, 22] | [18, 22] |
| [Rho 6G] (mmol L−1) | [0.45, 0.55] | [0.45, 0.55] | [0.45, 0.55] | [0.45, 0.55] |
| H2SO4 (mol L−1) | [3.8–4.2] | [3.8–4.2] | [3.8–4.2] | [3.8–4.2] |
| MeP | EtP | PrP | BuP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet tissues (% (w/w) | ||||
| Low pressure chromatography | 0.080 | 0.016 | 0.011 | 0.026 |
| HPLC | 0.088 | 0.017 | 0.010 | 0.024 |
| % bias | −9.1 | 5.9 | 10 | −8.3 |
| Liquid soap (% (w/w) ± SD) | ||||
| Low pressure chromatography | 0.11 | 0.020 | 0.014 | 0.025 |
| HPLC | 0.12 | 0.021 | 0.015 | 0.023 |
| % bias | 8.3 | 8.5 | 6.7 | −8.7 |
| Face lotion (% (w/w) ± SD) | ||||
| Low pressure chromatography | 0.092 | 0.023 | 0.0092 | 0.023 |
| HPLC | 0.086 | 0.021 | 0.0088 | 0.025 |
| % bias | −7.0 | −9.5 | −4.5 | 8.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbatsi, M.; Economou, A. Programmable Low-Pressure Chromatographic Sub-90 s Assay of Parabens in Cosmetics with Post-Column Chemiluminescence Detection. Separations 2023, 10, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060350
Barbatsi M, Economou A. Programmable Low-Pressure Chromatographic Sub-90 s Assay of Parabens in Cosmetics with Post-Column Chemiluminescence Detection. Separations. 2023; 10(6):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060350
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbatsi, Margarita, and Anastasios Economou. 2023. "Programmable Low-Pressure Chromatographic Sub-90 s Assay of Parabens in Cosmetics with Post-Column Chemiluminescence Detection" Separations 10, no. 6: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060350
APA StyleBarbatsi, M., & Economou, A. (2023). Programmable Low-Pressure Chromatographic Sub-90 s Assay of Parabens in Cosmetics with Post-Column Chemiluminescence Detection. Separations, 10(6), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060350